
Decisions 1

Subjective 2

=> Objective 3

Decision-making process: ü To determine the content of the problem and to set a goal ü To reveal, relevant factors, constraints and dependencies ü To collect data ü To analyze this data ü To identify alternative solutions and evaluate them in terms of costs and benefits ü To choose the optimal solution 4
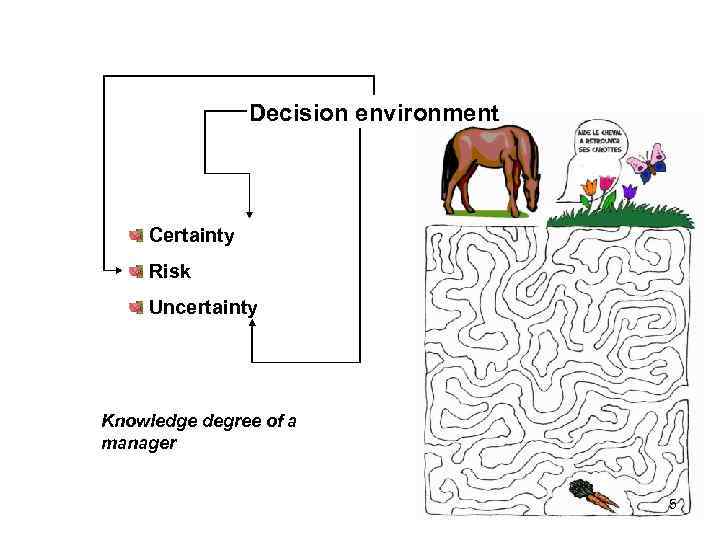
Decision environment Certainty Risk Uncertainty Knowledge degree of a manager 5

Certainty conception Manager knows the outcome of each alternative in advance The conception is real for shortterm period 6

Risk conception Manager is aware of one or several outcomes for each alternative. Also probability of each outcome realization is known. Some objective knowledge is presented 7

Uncertaity conception Alternatives have variety of probable outcomes with no known chances 8

How managers can make a decision in certainty environment? 9
About the conditions of certainty once again : we know everything and just choose a project that will bring the greatest return That is, we either maximize benefit or minimize costs 10

Search for options with the maximum benefit or minimum costs is called the optimization analysis 3 optimization methods: marginal analysis linear programming Incremental profit analysis 11

Marginal analysis We are aware of incomes and expenses for any level of production and sales Our task is to find an optimal ratio of known data to maximize profits Use the concepts of marginal costs and marginal revenue 12
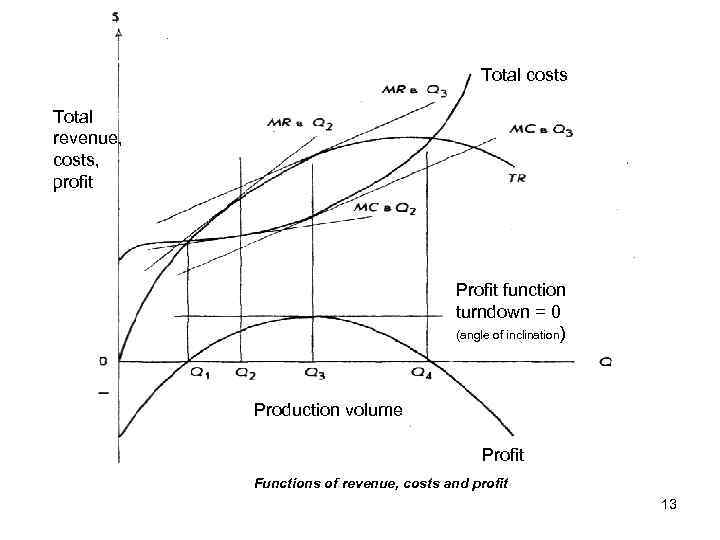
Total costs Total revenue, costs, profit Profit function turndown = 0 (angle of inclination) Production volume Profit Functions of revenue, costs and profit 13

14

Linear programming Helps to find the optimal variant of allocating scarce resources between competing works The Manager limits himself to the statement of the problem and hand it over to the technicians who use special computer programs (linear programming) 15

16
Incremental profit analysis In the real world demand, revenue, production and costs functions are unknown precisely, and are exposed to changes The development of the concept of marginal analysis Refers to the change of costs and revenues associated with a specific solution The basic rule of the decision: to accept the offer, increasing profits and reject - reducing 17
Only the variables exposed to change are considered. Revenues and costs that are fixed point in the interval, are not considered. Short-term conception Many managers do not use the incremental terms, and make decisions based on the average values of the total cost Incorrect short-term solutions 18

19