c3f4957ba706da7f5820ee48aecc7641.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Decision Support and Business Intelligence Systems T. Nourah AL-Aseem n. alaseem@psau. edu. sa

Schedule of Assessment Tasks for Students During the Semester Assessment task (eg. essay, test, Week due group project, examination etc. ) 1 Midterm Exam (1) 6 20% 2 Midterm Exam (2) 12 20% 3 Assignment Commitment and perseverance Not Specified 15% 5% 4 1 -2 Proportion of Final Assessment Final Exam Period 40% Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Chapter 1: n Decision Support Systems and Business Intelligence 1 -3 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Course Syllabus n n n 1 -4 Introduction to Decision Support Systems and Business Intelligence Decision Making, Systems, Modeling, and Support Decision Support Systems Concepts, Methodologies, and Technologies: Modeling and Analysis Collaborative Computer-Supported Technologies and Group Support Systems Decision Support Systems development Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

n n Companies are moving aggressively to computerized support of their operations => Business Intelligence Business Pressures–Responses–Support Model Business pressures result of today's competitive business climate n Responses to counter the pressures n Computerized Support to better facilitate the process Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall n 1 -5
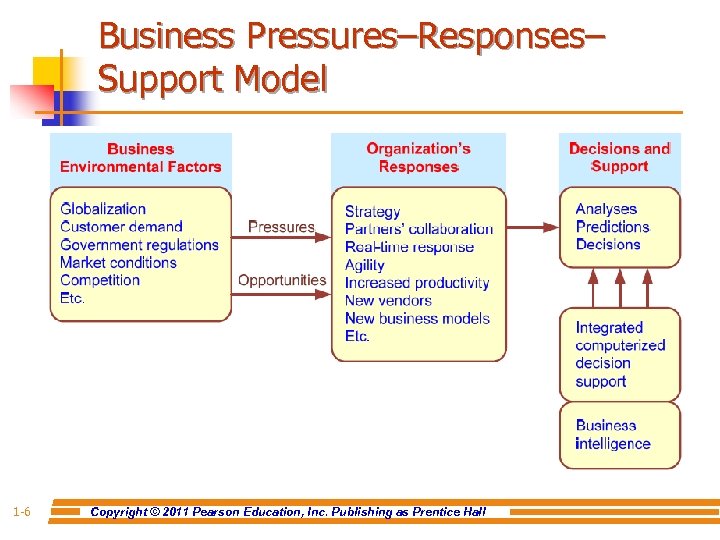
Business Pressures–Responses– Support Model 1 -6 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

The Business Environment n The environment in which organizations operate today is becoming more and more complex, creating: n n n Business environment factors: n 1 -7 opportunities, and problems Example: globalization markets, consumer demands, technology, and societal… Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Business Environment Factors FACTOR Markets Consumer demand Technology Societal 1 -8 DESCRIPTION Strong competition Expanding global markets Blooming electronic markets on the Internet Innovative marketing methods Opportunities for outsourcing with IT support Need for real-time, on-demand transactions Desire for customization Desire for quality, diversity of products, and speed of delivery Customers getting powerful and less loyal More innovations, new products, and new services Increasing obsolescence rate Increasing information overload Social networking, Web 2. 0 and beyond Growing government regulations and deregulation Workforce more diversified, older, and composed of more women Prime concerns of homeland security and terrorist attacks Necessity of Sarbanes-Oxley Act and other reporting-related legislation Increasing social responsibility of companies Copyright © 2011 Greater emphasis on sustainability Prentice Hall Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as

Organizational Responses n n Be Reactive, Anticipative, Adaptive, and Proactive Managers may take actions, such as n n n n 1 -9 Employ strategic planning Use new and innovative business models Restructure business processes Participate in business alliances Improve corporate information systems Improve partnership relationships Encourage innovation and creativity …cont…> Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Managers actions, continued n n n n 1 -10 Improve customer service and relationships Move to electronic commerce (e-commerce) Move to make-to-order production and on-demand manufacturing and services Use new IT to improve communication, data access (discovery of information), and collaboration Respond quickly to competitors' actions (e. g. , in pricing, promotions, new products and services) Automate many tasks of white-collar employees Automate certain decision processes Improve decision making by employing analytics Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Closing the Strategy Gap n 1 -11 One of the major objectives of computerized decision support is to facilitate closing the gap between the current performance of an organization and its desired performance, as expressed in its mission, objectives, and goals, and the strategy to achieve them Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Managerial Decision Making n Management is a process by which organizational goals are achieved by using resources n n n 1 -12 Inputs: resources Output: attainment of goals Measure of success: outputs / inputs Management Decision Making Decision making: selecting the best solution from two or more alternatives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Decision Making Process n Managers usually make decisions by following a four-step process (a. k. a. the scientific approach) 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 -13 Define the problem (or opportunity) Construct a model that describes the realworld problem Identify possible solutions to the modeled problem and evaluate the solutions Compare, choose, and recommend a potential solution to the problem Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Decision making is difficult, because n n n 1 -14 Technology, information systems, advanced search engines, and globalization result in more and more alternatives from which to choose Government regulations and the need for compliance, political instability and terrorism, competition, and changing consumer demands produce more uncertainty, making it more difficult to predict consequences and the future Other factors are the need to make rapid decisions, the frequent and unpredictable changes that make trialand-error learning difficult, and the potential costs of making mistakes Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Why Use Computerized DSS n Computerized DSS can facilitate decision via: n n n n 1 -15 Speedy computations Improved communication and collaboration Increased productivity of group members Improved data management Overcoming cognitive limits Quality support; agility support Using Web; anywhere, anytime support Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Management Science Approach n n Also referred to as Operation Research In solving problems, managers should follow the five-step MS approach 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1 -16 Define the problem Classify the problem into a standard category (*) Construct a model that describes the real-world problem Identify possible solutions to the modeled problem and evaluate the solutions Compare, choose, and recommend a potential solution to the problem Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Automated Decision Making n n A new approach to supporting decision making Applies to highly structures decisions Automated decision systems (ADS) (or decision automation systems) An ADS is a rule-based system that provides a solution to a repetitive managerial problem in a specific area n 1 -17 e. g. , simple-loan approval system Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Computer Support for Unstructured Decisions n 1 -18 Unstructured problems can be only partially supported by standard computerized quantitative methods Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Computer Support for Semi-structured Problems n 1 -19 Solving semi-structured problems may involve a combination of standard solution procedures and human judgment Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Concept of Decision Support Systems Classical Definitions of DSS n n 1 -20 Interactive computer-based systems, which help decision makers utilize data and models to solve unstructured problems" - Gorry and Scott-Morton, 1971 Decision support systems couple the intellectual resources of individuals with the capabilities of the computer to improve the quality of decisions. It is a computer-based support system for management decision makers who deal with semistructured problems - Keen and Scott-Morton, 1978 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

DSS as an Umbrella Term n 1 -21 The term DSS can be used as an umbrella term to describe any computerized system that supports decision making in an organization Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

DSS as a Specific Application n n In a narrow sense DSS refers to a process for building customized applications for unstructured or semistructured problems Components of the DSS Architecture n n 1 -22 Data, Model, Knowledge/Intelligence, User, Interface. DSS often is created by putting together of these components Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

High-Level Architecture of a DSS 1 -23 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

Types of DSS n Two major types: n n 1 -24 Model-oriented DSS Data-oriented DSS Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
Business Intelligence (BI) n n n 1 -25 BI is an umbrella term that combines architectures, tools, databases, analytical tools, applications, and methodologies BI's major objective is to enable easy access to data (and models) to provide business managers with the ability to conduct analysis BI helps transform data, to information (and knowledge), to decisions and finally to action Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
The Architecture of BI n A BI system has four major components n n 1 -26 a data warehouse, with its source data business analytics, a collection of tools for manipulating, mining, and analyzing the data in the data warehouse; business performance management (BPM) for monitoring and analyzing performance a user interface (e. g. , dashboard) Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
Components in a BI Architecture n n 1 -27 The data warehouse is a large repository of well-organized historical data Business analytics are the tools that allow transformation of data into information and knowledge Business performance management (BPM) allows monitoring, measuring, and comparing key performance indicators User interface (e. g. , dashboards) allows access and easy manipulation of other BI components Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall

End of the Chapter n 1 -28 Questions / Comments… Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
c3f4957ba706da7f5820ee48aecc7641.ppt