Lecture_10.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Decision-Making Principles Managing Technical People
Decision-Making Principles Managing Technical People
 Topics and Agenda l Why is Decision Making Important? l How Do We Make Decisions? l Exercise 09: Decision Making l Decision-Making Techniques and Styles l Group Decision Making l Factors Influencing Decision Making 2
Topics and Agenda l Why is Decision Making Important? l How Do We Make Decisions? l Exercise 09: Decision Making l Decision-Making Techniques and Styles l Group Decision Making l Factors Influencing Decision Making 2
 Course Progress l Module 0: Factors Influencing Human Interaction l Module 01: Communication Ø Module 02: Decision Making Ø Class 09: Decision-Making Principles l Module 03: Negotiation l Module 04: Conflict Management l Module 05: Relationship Management l Module 06: Leadership 3
Course Progress l Module 0: Factors Influencing Human Interaction l Module 01: Communication Ø Module 02: Decision Making Ø Class 09: Decision-Making Principles l Module 03: Negotiation l Module 04: Conflict Management l Module 05: Relationship Management l Module 06: Leadership 3
 Why is Decision Making Important? Decision making is an integral part of the job • For you as a manager • For the technical people you manage http: //www. flickr. com/photos/theilr/345056969/ 4
Why is Decision Making Important? Decision making is an integral part of the job • For you as a manager • For the technical people you manage http: //www. flickr. com/photos/theilr/345056969/ 4
 Thought Experiment #1 • Two coins are in front of you. They are both skewed • Coin 1 has 55% chance of landing on heads • Coin 2 has 45% chance of landing on heads • If you call a coin and it lands on heads you get $10, 000. If it lands on tails you win $0 • Which coin do you choose? 5
Thought Experiment #1 • Two coins are in front of you. They are both skewed • Coin 1 has 55% chance of landing on heads • Coin 2 has 45% chance of landing on heads • If you call a coin and it lands on heads you get $10, 000. If it lands on tails you win $0 • Which coin do you choose? 5
 Thought Experiment #2 • You are the CEO of a company and you have the option of promoting one of two products • Product 1 has 55% chance of being a success • Product 2 has 45% chance of being a success • If you choose a product and it is successful, your company will get a $10, 000 pre=tax benefit. If it is unsuccessful you get $0 • Which product do you promote? 6
Thought Experiment #2 • You are the CEO of a company and you have the option of promoting one of two products • Product 1 has 55% chance of being a success • Product 2 has 45% chance of being a success • If you choose a product and it is successful, your company will get a $10, 000 pre=tax benefit. If it is unsuccessful you get $0 • Which product do you promote? 6
 How Do You Make Decisions? • Are you following a general process? • Are you using intuition? • Are you consistent? 7
How Do You Make Decisions? • Are you following a general process? • Are you using intuition? • Are you consistent? 7
 What Types of Decisions Will You Need to Make? • Operational • Everyday decisions, often made with little thought or structure • Tactical • Normally support strategic decisions and direction • Strategic • Relate to general direction, long term goals, philosophies and values 8
What Types of Decisions Will You Need to Make? • Operational • Everyday decisions, often made with little thought or structure • Tactical • Normally support strategic decisions and direction • Strategic • Relate to general direction, long term goals, philosophies and values 8
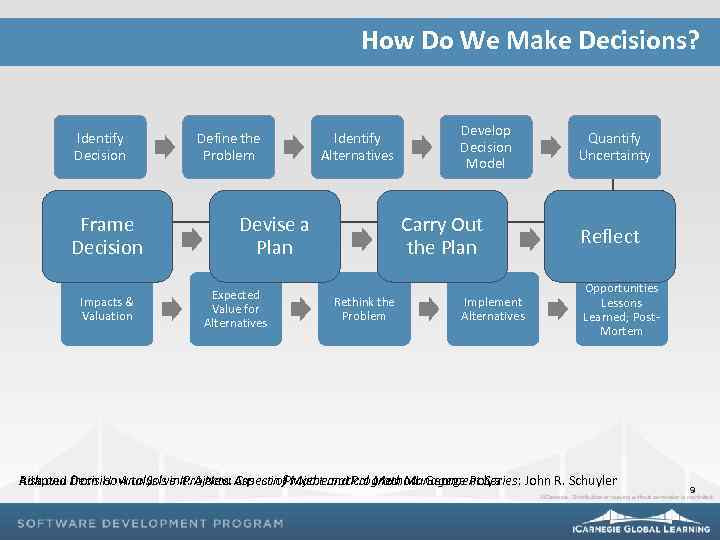 How Do We Make Decisions? Identify Decision Frame Decision Impacts & Valuation Define the Problem Identify Alternatives Devise a Plan Expected Value for Alternatives Develop Decision Model Carry Out the Plan Rethink the Problem Implement Alternatives Quantify Uncertainty Reflect Opportunities Lessons Learned; Post. Mortem Adapted from How to Solve It: A New Aspectin Project and Program Management Series: John R. Schuyler Risk and Decision Analysis in Projects: Cases of Mathematical Method: George Polya 9
How Do We Make Decisions? Identify Decision Frame Decision Impacts & Valuation Define the Problem Identify Alternatives Devise a Plan Expected Value for Alternatives Develop Decision Model Carry Out the Plan Rethink the Problem Implement Alternatives Quantify Uncertainty Reflect Opportunities Lessons Learned; Post. Mortem Adapted from How to Solve It: A New Aspectin Project and Program Management Series: John R. Schuyler Risk and Decision Analysis in Projects: Cases of Mathematical Method: George Polya 9
 How Do We Make Decisions? Frame the Decision • What is the unknown? • What are the data? • What are the conditions? • Root cause or symptom? 10
How Do We Make Decisions? Frame the Decision • What is the unknown? • What are the data? • What are the conditions? • Root cause or symptom? 10
 How Do We Make Decisions? Devise a Plan • Draw a picture • Look for similar decisions/problems • Break up the decision/problem • Work backwards 11
How Do We Make Decisions? Devise a Plan • Draw a picture • Look for similar decisions/problems • Break up the decision/problem • Work backwards 11
 How Do We Make Decisions? Carry Out the Plan • Check each step • Can you derive the solution another way? 12
How Do We Make Decisions? Carry Out the Plan • Check each step • Can you derive the solution another way? 12
 How Do We Make Decisions? Reflect • Was your solution successful? • If not, how can you modify it? • If so, can it be used on other decisions or problems? 13
How Do We Make Decisions? Reflect • Was your solution successful? • If not, how can you modify it? • If so, can it be used on other decisions or problems? 13
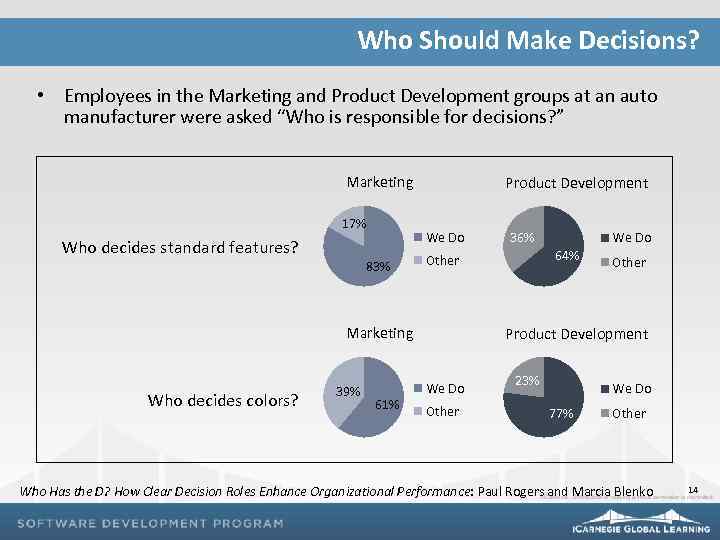 Who Should Make Decisions? • Employees in the Marketing and Product Development groups at an auto manufacturer were asked “Who is responsible for decisions? ” Marketing 17% Who decides standard features? Product Development We Do 83% Who decides colors? 61% We Do 64% Other Marketing 39% 36% Other Product Development We Do Other 23% We Do 77% Other Who Has the D? How Clear Decision Roles Enhance Organizational Performance: Paul Rogers and Marcia Blenko 14
Who Should Make Decisions? • Employees in the Marketing and Product Development groups at an auto manufacturer were asked “Who is responsible for decisions? ” Marketing 17% Who decides standard features? Product Development We Do 83% Who decides colors? 61% We Do 64% Other Marketing 39% 36% Other Product Development We Do Other 23% We Do 77% Other Who Has the D? How Clear Decision Roles Enhance Organizational Performance: Paul Rogers and Marcia Blenko 14
 Who Should Make Decisions? • RAPID Decision Making Roles • Recommend: This role gathers the input and information necessary to make a proposal. Individuals in this role must be analytical and organized. • Agree: An individual in the “agree” role has the ability to say yes or no to a recommendation. • Perform: This is the individual or group responsible for implementing a decision. • Input: These individuals provide input and advice on the decision. • Decide: This is the individual responsible for making the final decision. Who Has the D? How Clear Decision Roles Enhance Organizational Performance: Paul Rogers and Marcia Blenko 15
Who Should Make Decisions? • RAPID Decision Making Roles • Recommend: This role gathers the input and information necessary to make a proposal. Individuals in this role must be analytical and organized. • Agree: An individual in the “agree” role has the ability to say yes or no to a recommendation. • Perform: This is the individual or group responsible for implementing a decision. • Input: These individuals provide input and advice on the decision. • Decide: This is the individual responsible for making the final decision. Who Has the D? How Clear Decision Roles Enhance Organizational Performance: Paul Rogers and Marcia Blenko 15
 Decision-Making Techniques • T-Charts • SWOT • Pareto Analysis • Pairwise Comparison • Cost/Benefit Analysis 16
Decision-Making Techniques • T-Charts • SWOT • Pareto Analysis • Pairwise Comparison • Cost/Benefit Analysis 16
 Decision-Making Techniques: T-Charts Should I go to Carol’s party tonight? Pros Cons 1. She makes the most delicious canapes 1. I have to get up early tomorrow 2. I might see Susie 2. I might run into Lester 3. Etc. 17
Decision-Making Techniques: T-Charts Should I go to Carol’s party tonight? Pros Cons 1. She makes the most delicious canapes 1. I have to get up early tomorrow 2. I might see Susie 2. I might run into Lester 3. Etc. 17
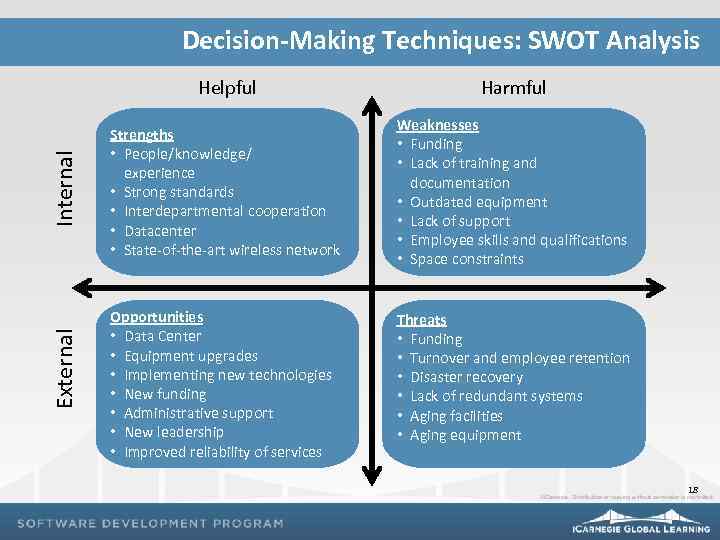 Decision-Making Techniques: SWOT Analysis External Internal Helpful Harmful Strengths • People/knowledge/ experience • Strong standards • Interdepartmental cooperation • Datacenter • State-of-the-art wireless network Weaknesses • Funding • Lack of training and documentation • Outdated equipment • Lack of support • Employee skills and qualifications • Space constraints Opportunities • Data Center • Equipment upgrades • Implementing new technologies • New funding • Administrative support • New leadership • Improved reliability of services Threats • Funding • Turnover and employee retention • Disaster recovery • Lack of redundant systems • Aging facilities • Aging equipment 18
Decision-Making Techniques: SWOT Analysis External Internal Helpful Harmful Strengths • People/knowledge/ experience • Strong standards • Interdepartmental cooperation • Datacenter • State-of-the-art wireless network Weaknesses • Funding • Lack of training and documentation • Outdated equipment • Lack of support • Employee skills and qualifications • Space constraints Opportunities • Data Center • Equipment upgrades • Implementing new technologies • New funding • Administrative support • New leadership • Improved reliability of services Threats • Funding • Turnover and employee retention • Disaster recovery • Lack of redundant systems • Aging facilities • Aging equipment 18
 Decision-Making Techniques: Pareto Analysis • 80/20 Rule: • 80% of sales come from 20% of customers • 80% of employees take 20% of sick time • Microsoft discovered that they could eliminate 80% of the errors and crashes by fixing the top 20% most reported bugs 19
Decision-Making Techniques: Pareto Analysis • 80/20 Rule: • 80% of sales come from 20% of customers • 80% of employees take 20% of sick time • Microsoft discovered that they could eliminate 80% of the errors and crashes by fixing the top 20% most reported bugs 19
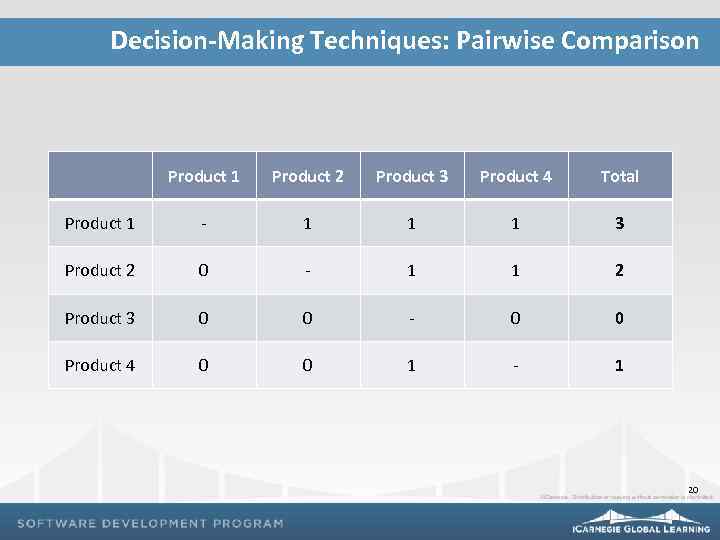 Decision-Making Techniques: Pairwise Comparison Product 1 Product 2 Product 3 Product 4 Total Product 1 - 1 1 1 3 Product 2 0 - 1 1 2 Product 3 0 0 - 0 0 Product 4 0 0 1 - 1 20
Decision-Making Techniques: Pairwise Comparison Product 1 Product 2 Product 3 Product 4 Total Product 1 - 1 1 1 3 Product 2 0 - 1 1 2 Product 3 0 0 - 0 0 Product 4 0 0 1 - 1 20
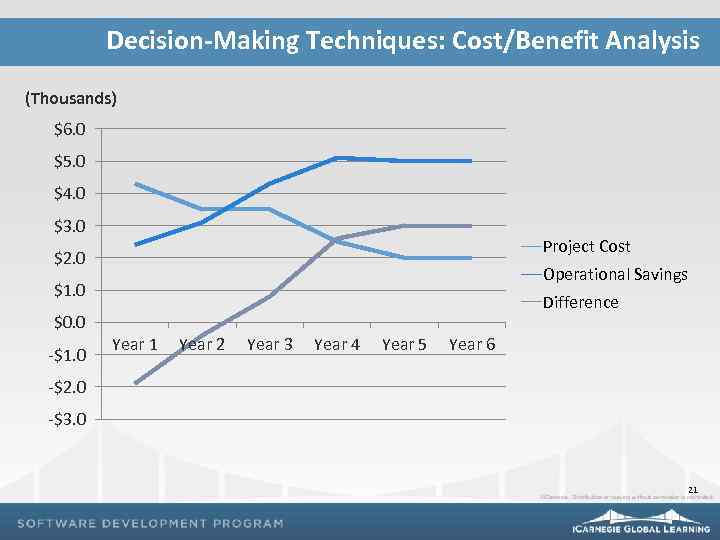 Decision-Making Techniques: Cost/Benefit Analysis (Thousands) $6. 0 $5. 0 $4. 0 $3. 0 Project Cost $2. 0 Operational Savings $1. 0 $0. 0 -$1. 0 Difference Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 -$2. 0 -$3. 0 21
Decision-Making Techniques: Cost/Benefit Analysis (Thousands) $6. 0 $5. 0 $4. 0 $3. 0 Project Cost $2. 0 Operational Savings $1. 0 $0. 0 -$1. 0 Difference Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 -$2. 0 -$3. 0 21
 What Is Intuitive Decision Making? • Developed from research by Gary Klein • Fire Fighters • Police forces • Other First Responders • A “translation of experience into action” • Making decisions without a comprehensive formal analysis • Intuition can be built, applied and safeguarded The Power of Intuition: How to Use Your Gut Feelings to Make Better Decisions at Work: Gary Klein 22
What Is Intuitive Decision Making? • Developed from research by Gary Klein • Fire Fighters • Police forces • Other First Responders • A “translation of experience into action” • Making decisions without a comprehensive formal analysis • Intuition can be built, applied and safeguarded The Power of Intuition: How to Use Your Gut Feelings to Make Better Decisions at Work: Gary Klein 22
 Thin-Slicing Rapid decisions made with minimal information: • John Gottman’s Love Lab • Morse Code/British Interceptors • Doctors and Malpractice Blink: The Power of Thinking without Thinking: Malcolm Gladwell 23
Thin-Slicing Rapid decisions made with minimal information: • John Gottman’s Love Lab • Morse Code/British Interceptors • Doctors and Malpractice Blink: The Power of Thinking without Thinking: Malcolm Gladwell 23
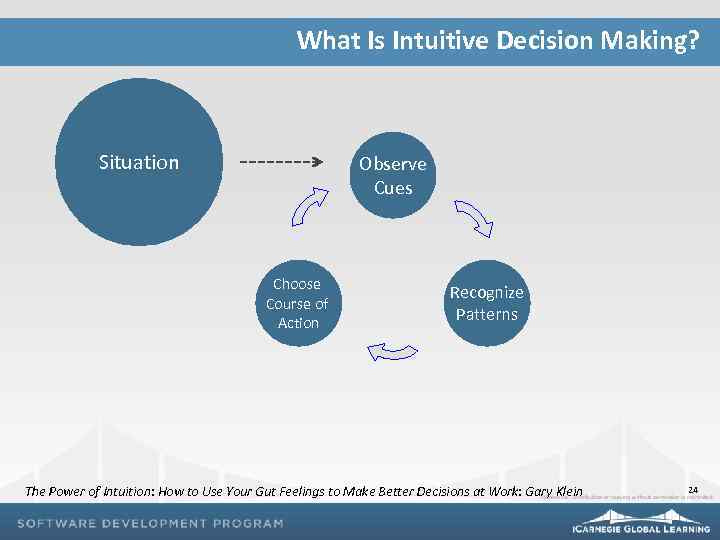 What Is Intuitive Decision Making? Situation Observe Cues Choose Course of Action Recognize Patterns The Power of Intuition: How to Use Your Gut Feelings to Make Better Decisions at Work: Gary Klein 24
What Is Intuitive Decision Making? Situation Observe Cues Choose Course of Action Recognize Patterns The Power of Intuition: How to Use Your Gut Feelings to Make Better Decisions at Work: Gary Klein 24
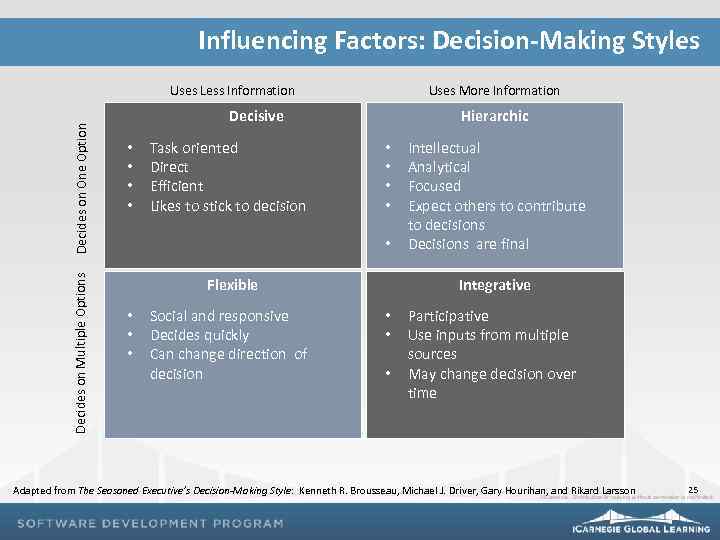 Influencing Factors: Decision-Making Styles Decides on Multiple Options Decides on One Option Uses Less Information Uses More Information Decisive • • Task oriented Direct Efficient Likes to stick to decision Hierarchic • • • Flexible • • • Social and responsive Decides quickly Can change direction of decision Intellectual Analytical Focused Expect others to contribute to decisions Decisions are final Integrative • • • Participative Use inputs from multiple sources May change decision over time Adapted from The Seasoned Executive’s Decision-Making Style: Kenneth R. Brousseau, Michael J. Driver, Gary Hourihan, and Rikard Larsson 25
Influencing Factors: Decision-Making Styles Decides on Multiple Options Decides on One Option Uses Less Information Uses More Information Decisive • • Task oriented Direct Efficient Likes to stick to decision Hierarchic • • • Flexible • • • Social and responsive Decides quickly Can change direction of decision Intellectual Analytical Focused Expect others to contribute to decisions Decisions are final Integrative • • • Participative Use inputs from multiple sources May change decision over time Adapted from The Seasoned Executive’s Decision-Making Style: Kenneth R. Brousseau, Michael J. Driver, Gary Hourihan, and Rikard Larsson 25
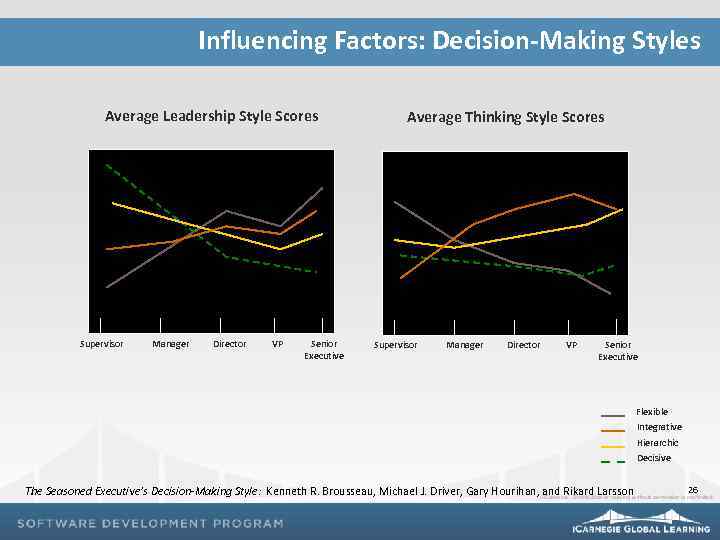 Influencing Factors: Decision-Making Styles Average Leadership Style Scores Supervisor Manager Director VP Senior Executive Average Thinking Style Scores Supervisor Manager Director VP Senior Executive Flexible Integrative Hierarchic Decisive The Seasoned Executive’s Decision-Making Style: Kenneth R. Brousseau, Michael J. Driver, Gary Hourihan, and Rikard Larsson 26
Influencing Factors: Decision-Making Styles Average Leadership Style Scores Supervisor Manager Director VP Senior Executive Average Thinking Style Scores Supervisor Manager Director VP Senior Executive Flexible Integrative Hierarchic Decisive The Seasoned Executive’s Decision-Making Style: Kenneth R. Brousseau, Michael J. Driver, Gary Hourihan, and Rikard Larsson 26
 Influencing Factors: Group Decision Making • What typically happens in a group, committee, board? • No decision • Self-Appointed Decision Maker • Minority Rule • Majority Rule • Consensus Decision-Making Styles and Techniques: Marlene K. Rebori 27
Influencing Factors: Group Decision Making • What typically happens in a group, committee, board? • No decision • Self-Appointed Decision Maker • Minority Rule • Majority Rule • Consensus Decision-Making Styles and Techniques: Marlene K. Rebori 27
 Influencing Factors: Group Decision Making • When making decisions in a group, consider: • Timeliness • Appropriateness • Relationships Decision-Making Styles and Techniques: Marlene K. Rebori 28
Influencing Factors: Group Decision Making • When making decisions in a group, consider: • Timeliness • Appropriateness • Relationships Decision-Making Styles and Techniques: Marlene K. Rebori 28
 Influencing Factors: Time How do time pressures affect decision making? Blink: The Power of Thinking without Thinking: Malcolm Gladwell 29
Influencing Factors: Time How do time pressures affect decision making? Blink: The Power of Thinking without Thinking: Malcolm Gladwell 29
 Influencing Factors: Personality Types Relater Thinker Socializer Director 30
Influencing Factors: Personality Types Relater Thinker Socializer Director 30
 Remember… l Case Study 01: Due by Next Class l l Video Analysis 02: Due by Class 11 l l Due by 8 p. m. Role Play 02 Scenario Planning Questionnaire: Due by Class 12 l Due by 8 p. m. 31
Remember… l Case Study 01: Due by Next Class l l Video Analysis 02: Due by Class 11 l l Due by 8 p. m. Role Play 02 Scenario Planning Questionnaire: Due by Class 12 l Due by 8 p. m. 31


