f9b08b0b5c08bb5c6b3f4060b924988b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Decentralized Surface Water Irrigation in the mega-delta of Southern Bangladesh: An ex-ante assessment of land area and intensification potential Timothy J. Krupnik Urs Schulthess Samina Yasmin M. E. Baksh Zia Uddin Ahmed Andy J. Mc. Donald
Decentralized Surface Water Irrigation in the mega-delta of Southern Bangladesh: An ex-ante assessment of land area and intensification potential Timothy J. Krupnik Urs Schulthess Samina Yasmin M. E. Baksh Zia Uddin Ahmed Andy J. Mc. Donald
 Sustainable intensification (SI) in Southern Bangladesh • Bangladesh: losing agricultural land (-10% in the last decade) (Hassan et al. 2013) • SI: ‘. . . producing more output from the same area of land while reducing negative environmental impacts and … increasing contributions to … the flow of environmental services’ (Pretty et al. 2011) Two practical approaches to SI: • ‘Crop’ intensification: Boosting yield, while sparing resources and harnessing ecological services (e. g. , yield focused) • ‘Systems’ intensification: Moving from one to two crops, while sparing resources and harnessing ecological services (e. g. , double cropping focused)
Sustainable intensification (SI) in Southern Bangladesh • Bangladesh: losing agricultural land (-10% in the last decade) (Hassan et al. 2013) • SI: ‘. . . producing more output from the same area of land while reducing negative environmental impacts and … increasing contributions to … the flow of environmental services’ (Pretty et al. 2011) Two practical approaches to SI: • ‘Crop’ intensification: Boosting yield, while sparing resources and harnessing ecological services (e. g. , yield focused) • ‘Systems’ intensification: Moving from one to two crops, while sparing resources and harnessing ecological services (e. g. , double cropping focused)
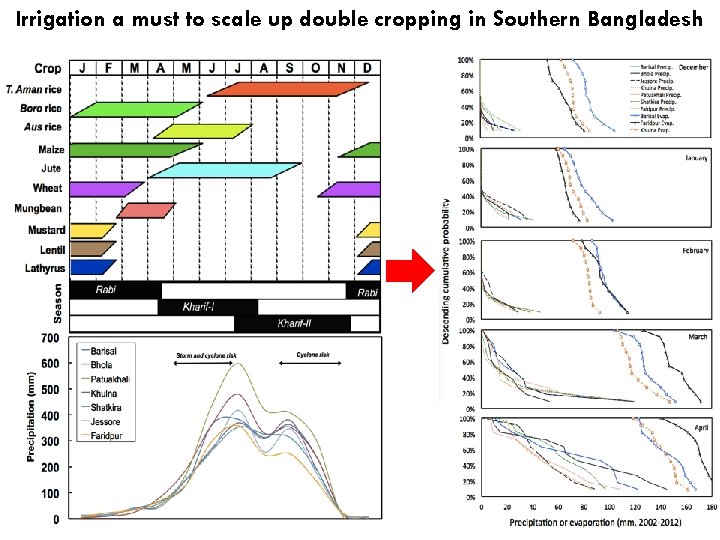 Irrigation a must to scale up double cropping in Southern Bangladesh
Irrigation a must to scale up double cropping in Southern Bangladesh
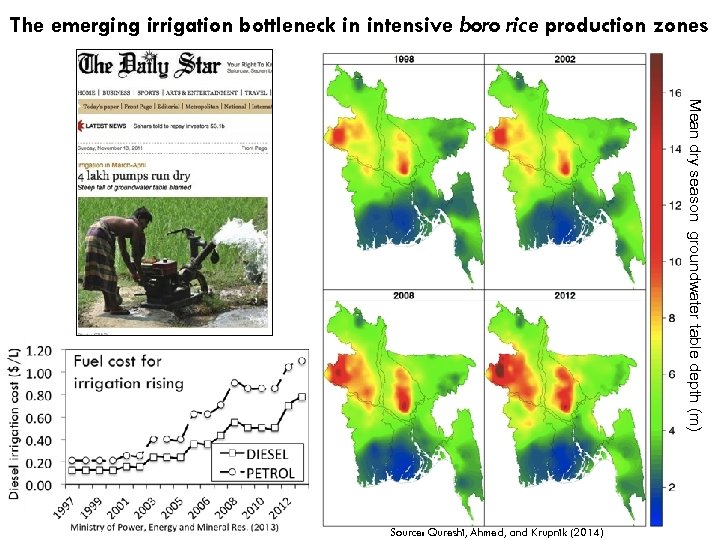 The emerging irrigation bottleneck in intensive boro rice production zones Mean dry season groundwater table depth (m) Source: Qureshi, Ahmed, and Krupnik (2014)
The emerging irrigation bottleneck in intensive boro rice production zones Mean dry season groundwater table depth (m) Source: Qureshi, Ahmed, and Krupnik (2014)
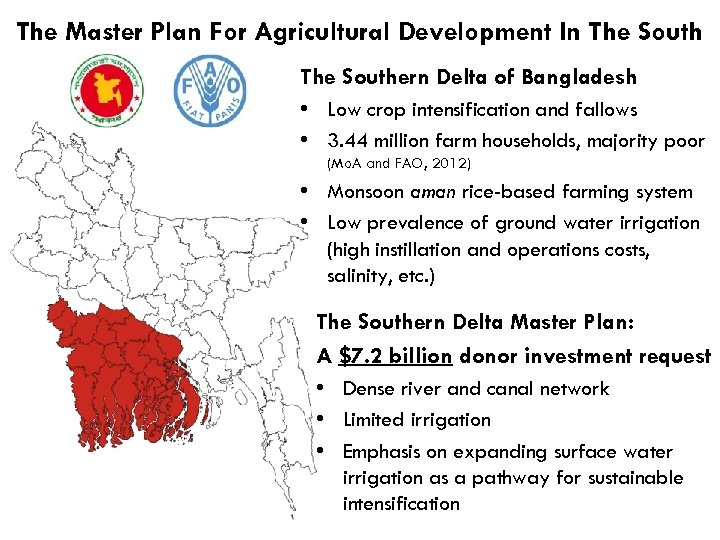 The Master Plan For Agricultural Development In The Southern Delta of Bangladesh • Low crop intensification and fallows • 3. 44 million farm households, majority poor (Mo. A and FAO, 2012) • Monsoon aman rice-based farming system • Low prevalence of ground water irrigation (high instillation and operations costs, salinity, etc. ) The Southern Delta Master Plan: A $7. 2 billion donor investment request • Dense river and canal network • Limited irrigation • Emphasis on expanding surface water irrigation as a pathway for sustainable intensification
The Master Plan For Agricultural Development In The Southern Delta of Bangladesh • Low crop intensification and fallows • 3. 44 million farm households, majority poor (Mo. A and FAO, 2012) • Monsoon aman rice-based farming system • Low prevalence of ground water irrigation (high instillation and operations costs, salinity, etc. ) The Southern Delta Master Plan: A $7. 2 billion donor investment request • Dense river and canal network • Limited irrigation • Emphasis on expanding surface water irrigation as a pathway for sustainable intensification
 How can dry season irrigation be encouraged? Large-scale, centralized irrigation schemes? • • • Costly and challenging to maintain Ganges-Kabadak (1955): Siltation, bank instability, etc. (Brammer, 2002) Barisal Irrigation Project (1980). Low land area achievement (cf. Gumma et al. , 2014). • Farmers unwilling to rent pumps from parastatals (Brammer, 2002) Bangladesh’s historical irrigation boom relied on decentralized service provision: • Decentralized irrigation supplies 90% of Bangladesh’s agricultural water, largely from tube wells in the north (Chowdhury, 2010) • Technological options exist to address energy and cost problems for surface water in the south Eric Lam: Design Axial - Mixed flow pump
How can dry season irrigation be encouraged? Large-scale, centralized irrigation schemes? • • • Costly and challenging to maintain Ganges-Kabadak (1955): Siltation, bank instability, etc. (Brammer, 2002) Barisal Irrigation Project (1980). Low land area achievement (cf. Gumma et al. , 2014). • Farmers unwilling to rent pumps from parastatals (Brammer, 2002) Bangladesh’s historical irrigation boom relied on decentralized service provision: • Decentralized irrigation supplies 90% of Bangladesh’s agricultural water, largely from tube wells in the north (Chowdhury, 2010) • Technological options exist to address energy and cost problems for surface water in the south Eric Lam: Design Axial - Mixed flow pump
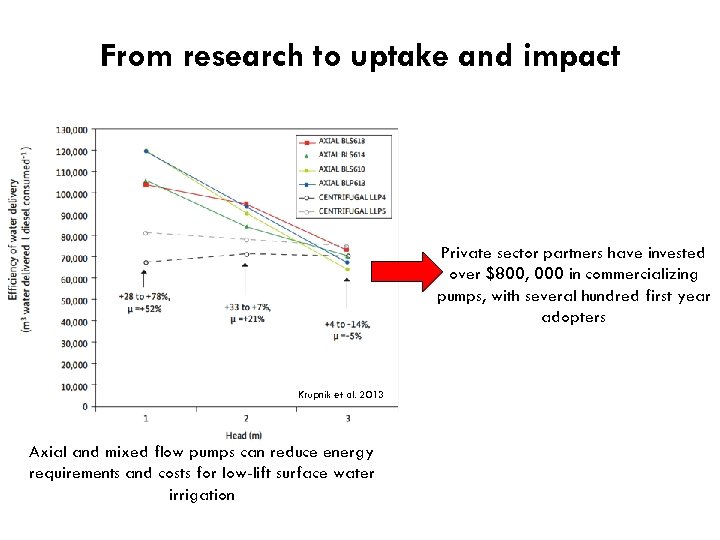 From research to uptake and impact Private sector partners have invested over $800, 000 in commercializing pumps, with several hundred first year adopters Krupnik et al. 2013 Axial and mixed flow pumps can reduce energy requirements and costs for low-lift surface water irrigation
From research to uptake and impact Private sector partners have invested over $800, 000 in commercializing pumps, with several hundred first year adopters Krupnik et al. 2013 Axial and mixed flow pumps can reduce energy requirements and costs for low-lift surface water irrigation
 Forgoing the fallow and establishing dry season rabi cropping • Location and estimates of fallow land vary by year, method, and definition: • 800, 000 ha (Poulton and Dalgliesh, 2008) • 634, 000 ha (BADC 2010) • 136, 000 ha (Mo. A and FAO, 2012) • 240, 000 ha (BBS, 2011) • No estimates are related to targeting fallows for surface water irrigation and intensification • Analytical challenges: Fallow identification, soil and water salinity, water availability, timely land availability • More questions than answers at this point in time
Forgoing the fallow and establishing dry season rabi cropping • Location and estimates of fallow land vary by year, method, and definition: • 800, 000 ha (Poulton and Dalgliesh, 2008) • 634, 000 ha (BADC 2010) • 136, 000 ha (Mo. A and FAO, 2012) • 240, 000 ha (BBS, 2011) • No estimates are related to targeting fallows for surface water irrigation and intensification • Analytical challenges: Fallow identification, soil and water salinity, water availability, timely land availability • More questions than answers at this point in time
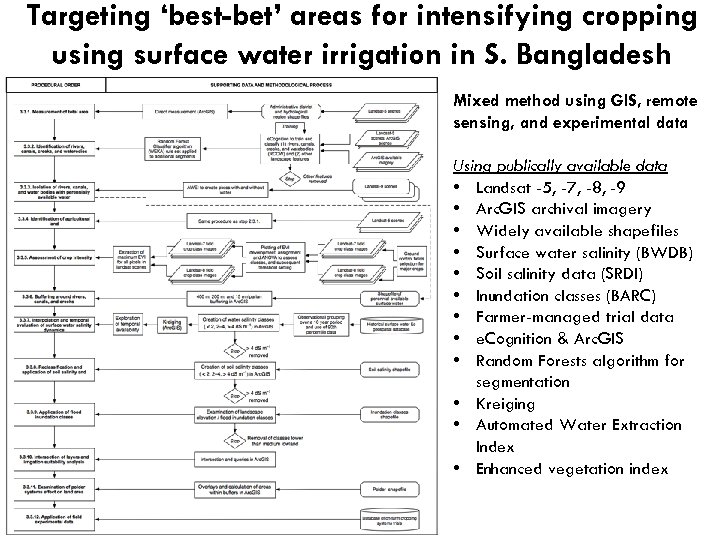 Targeting ‘best-bet’ areas for intensifying cropping using surface water irrigation in S. Bangladesh Mixed method using GIS, remote sensing, and experimental data Using publically available data • Landsat -5, -7, -8, -9 • Arc. GIS archival imagery • Widely available shapefiles • Surface water salinity (BWDB) • Soil salinity data (SRDI) • Inundation classes (BARC) • Farmer-managed trial data • e. Cognition & Arc. GIS • Random Forests algorithm for segmentation • Kreiging • Automated Water Extraction Index • Enhanced vegetation index
Targeting ‘best-bet’ areas for intensifying cropping using surface water irrigation in S. Bangladesh Mixed method using GIS, remote sensing, and experimental data Using publically available data • Landsat -5, -7, -8, -9 • Arc. GIS archival imagery • Widely available shapefiles • Surface water salinity (BWDB) • Soil salinity data (SRDI) • Inundation classes (BARC) • Farmer-managed trial data • e. Cognition & Arc. GIS • Random Forests algorithm for segmentation • Kreiging • Automated Water Extraction Index • Enhanced vegetation index
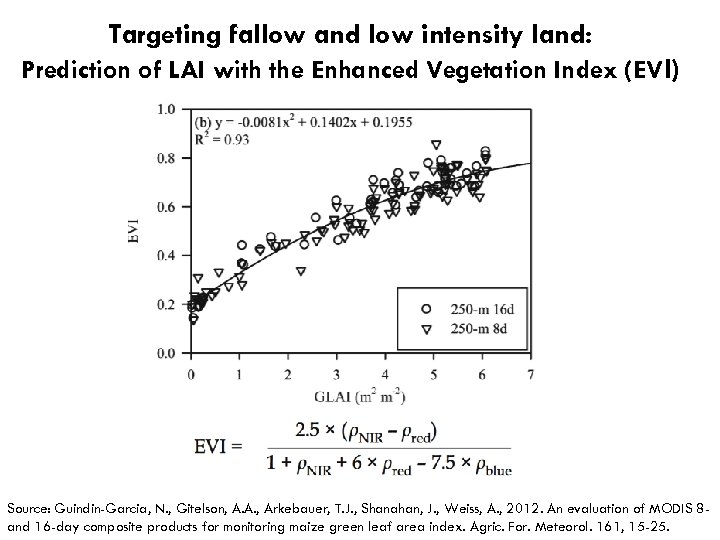 Targeting fallow and low intensity land: Prediction of LAI with the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EV I) Source: Guindin-Garcia, N. , Gitelson, A. A. , Arkebauer, T. J. , Shanahan, J. , Weiss, A. , 2012. An evaluation of MODIS 8 and 16 -day composite products for monitoring maize green leaf area index. Agric. For. Meteorol. 161, 15 -25.
Targeting fallow and low intensity land: Prediction of LAI with the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EV I) Source: Guindin-Garcia, N. , Gitelson, A. A. , Arkebauer, T. J. , Shanahan, J. , Weiss, A. , 2012. An evaluation of MODIS 8 and 16 -day composite products for monitoring maize green leaf area index. Agric. For. Meteorol. 161, 15 -25.
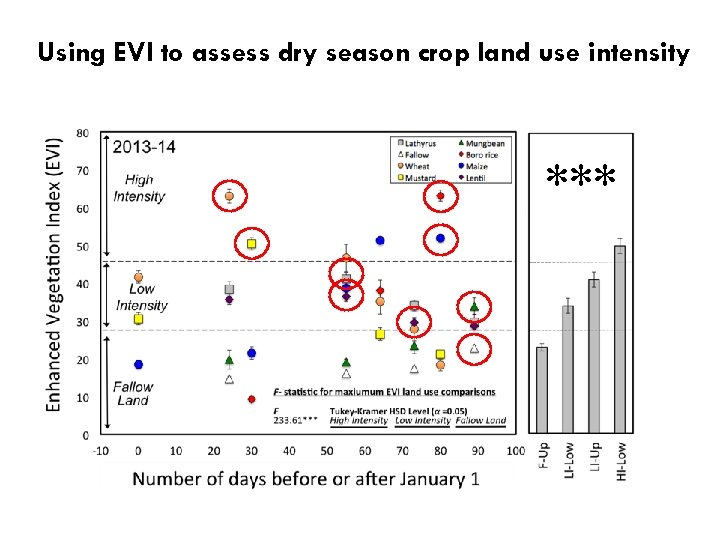 Using EVI to assess dry season crop land use intensity ***
Using EVI to assess dry season crop land use intensity ***
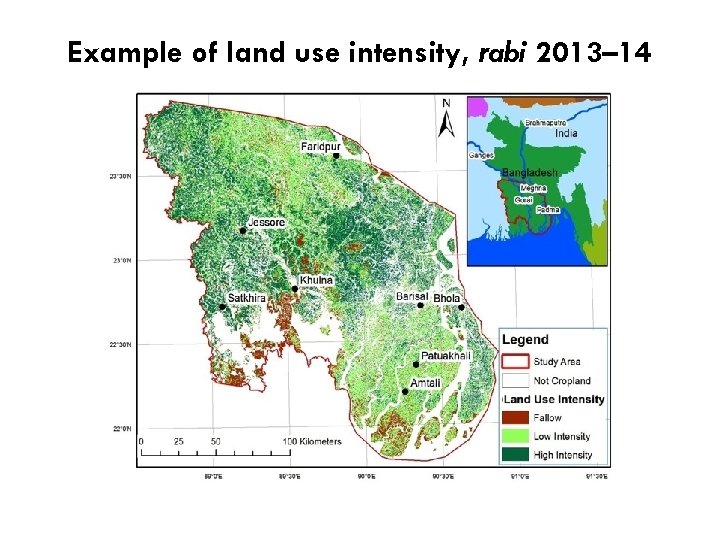 Example of land use intensity, rabi 2013– 14
Example of land use intensity, rabi 2013– 14
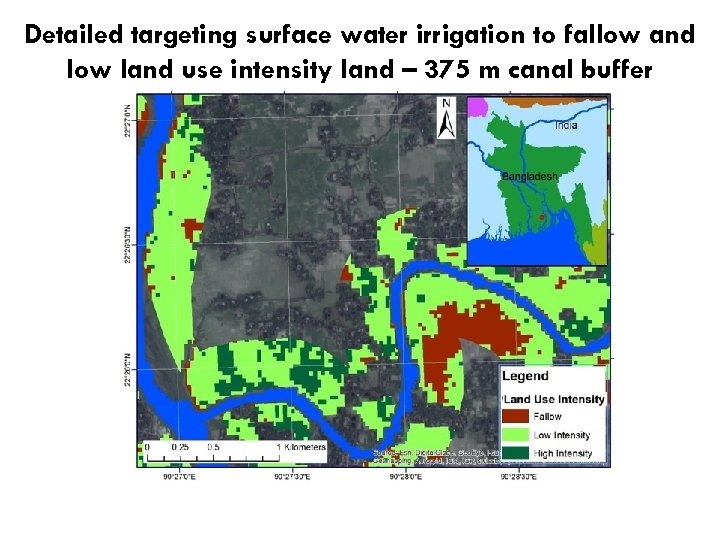 Detailed targeting surface water irrigation to fallow and low land use intensity land – 375 m canal buffer
Detailed targeting surface water irrigation to fallow and low land use intensity land – 375 m canal buffer
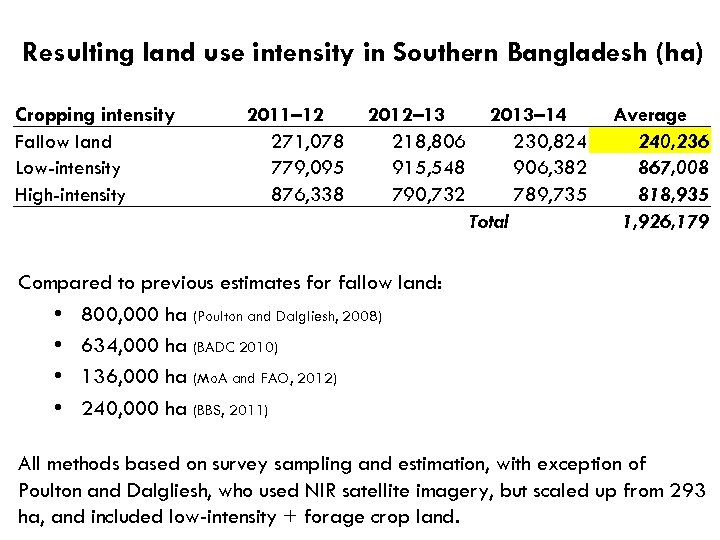 Resulting land use intensity in Southern Bangladesh (ha) Cropping intensity Fallow land Low-intensity High-intensity 2011– 12 271, 078 779, 095 876, 338 2012– 13 218, 806 915, 548 790, 732 2013– 14 230, 824 906, 382 789, 735 Total Average 240, 236 867, 008 818, 935 1, 926, 179 Compared to previous estimates for fallow land: • 800, 000 ha (Poulton and Dalgliesh, 2008) • 634, 000 ha (BADC 2010) • 136, 000 ha (Mo. A and FAO, 2012) • 240, 000 ha (BBS, 2011) All methods based on survey sampling and estimation, with exception of Poulton and Dalgliesh, who used NIR satellite imagery, but scaled up from 293 ha, and included low-intensity + forage crop land.
Resulting land use intensity in Southern Bangladesh (ha) Cropping intensity Fallow land Low-intensity High-intensity 2011– 12 271, 078 779, 095 876, 338 2012– 13 218, 806 915, 548 790, 732 2013– 14 230, 824 906, 382 789, 735 Total Average 240, 236 867, 008 818, 935 1, 926, 179 Compared to previous estimates for fallow land: • 800, 000 ha (Poulton and Dalgliesh, 2008) • 634, 000 ha (BADC 2010) • 136, 000 ha (Mo. A and FAO, 2012) • 240, 000 ha (BBS, 2011) All methods based on survey sampling and estimation, with exception of Poulton and Dalgliesh, who used NIR satellite imagery, but scaled up from 293 ha, and included low-intensity + forage crop land.
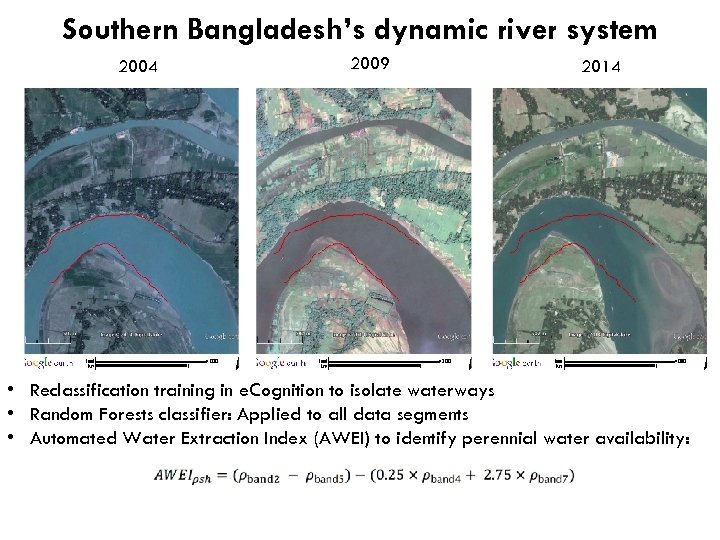 Southern Bangladesh’s dynamic river system 2004 2009 2014 • Reclassification training in e. Cognition to isolate waterways • Random Forests classifier: Applied to all data segments • Automated Water Extraction Index (AWEI) to identify perennial water availability:
Southern Bangladesh’s dynamic river system 2004 2009 2014 • Reclassification training in e. Cognition to isolate waterways • Random Forests classifier: Applied to all data segments • Automated Water Extraction Index (AWEI) to identify perennial water availability:
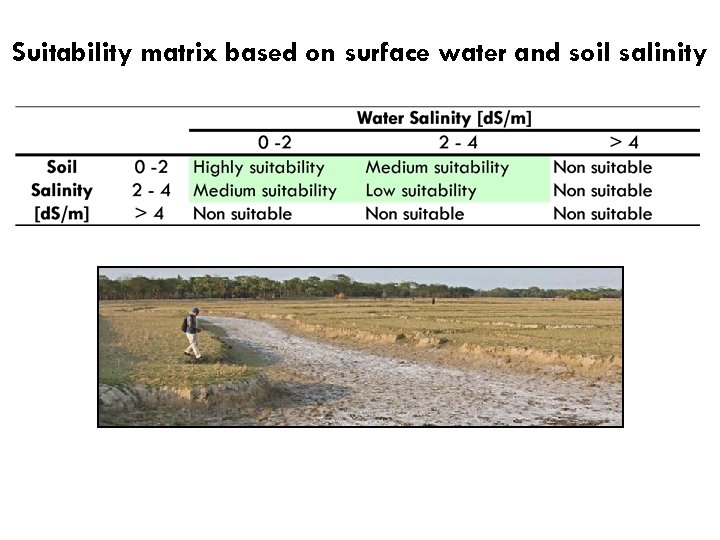 Suitability matrix based on surface water and soil salinity
Suitability matrix based on surface water and soil salinity
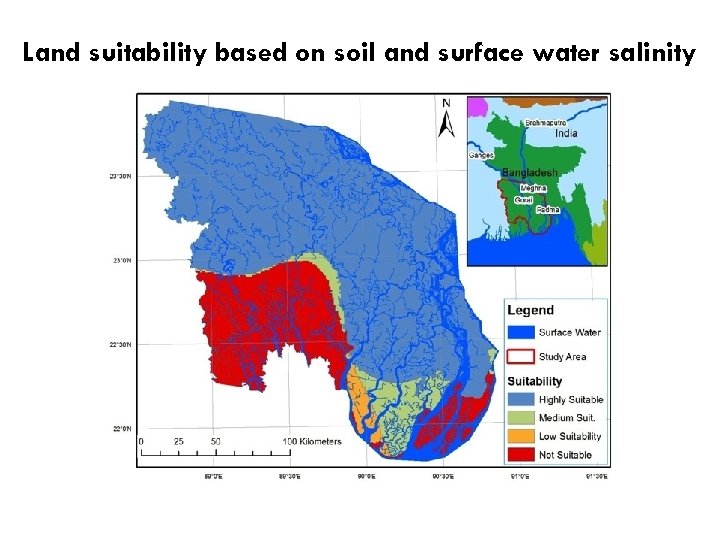 Land suitability based on soil and surface water salinity
Land suitability based on soil and surface water salinity
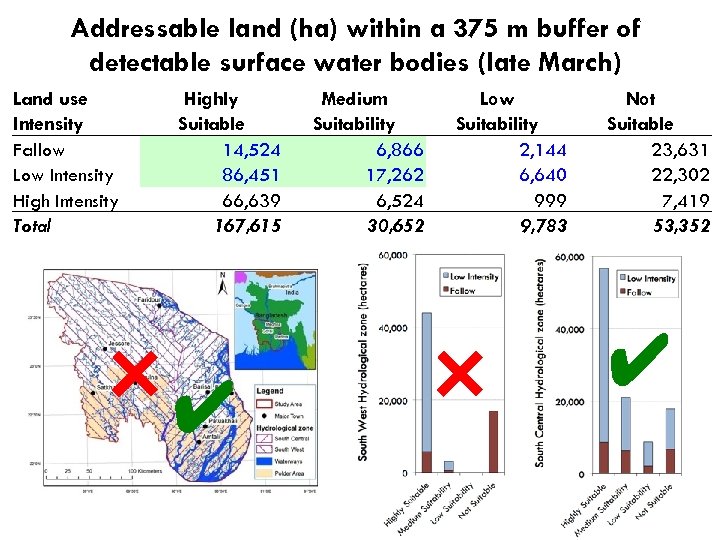 Addressable land (ha) within a 375 m buffer of detectable surface water bodies (late March) Land use Intensity Fallow Low Intensity High Intensity Total Highly Suitable 14, 524 86, 451 66, 639 167, 615 ×✔ Medium Suitability 6, 866 17, 262 6, 524 30, 652 Low Suitability 2, 144 6, 640 999 9, 783 × Not Suitable 23, 631 22, 302 7, 419 53, 352 ✔
Addressable land (ha) within a 375 m buffer of detectable surface water bodies (late March) Land use Intensity Fallow Low Intensity High Intensity Total Highly Suitable 14, 524 86, 451 66, 639 167, 615 ×✔ Medium Suitability 6, 866 17, 262 6, 524 30, 652 Low Suitability 2, 144 6, 640 999 9, 783 × Not Suitable 23, 631 22, 302 7, 419 53, 352 ✔
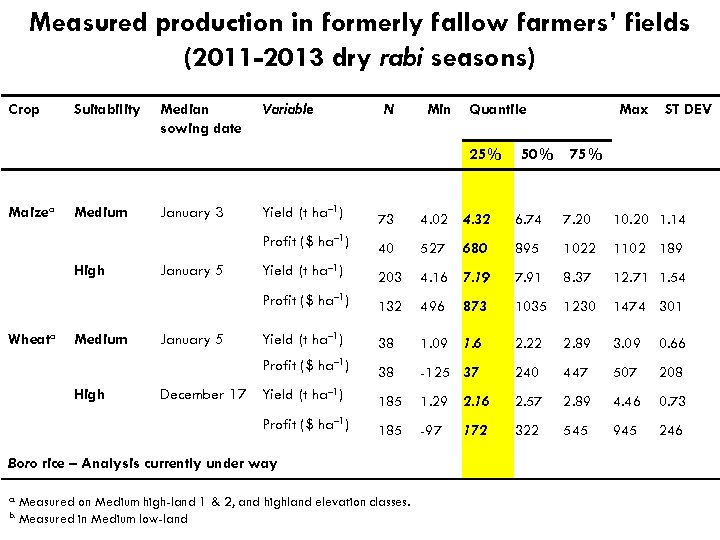 Measured production in formerly fallow farmers’ fields (2011 -2013 dry rabi seasons) Crop Suitability Median sowing date Variable N Min Quantile 25% Maizea 50% Max ST DEV 75% Medium High January 5 4. 02 4. 32 6. 74 7. 20 10. 20 1. 14 40 527 680 895 1022 1102 189 Yield (t ha– 1) 203 4. 16 7. 19 7. 91 8. 37 12. 71 1. 54 132 496 1035 1230 1474 301 Yield (t ha– 1) 38 1. 09 1. 6 2. 22 2. 89 3. 09 0. 66 Profit ($ ha– 1) Wheata January 5 73 Profit ($ ha– 1) High January 3 Yield (t ha– 1) Profit ($ ha– 1) Medium 38 -125 37 240 447 507 208 185 1. 29 2. 16 2. 57 2. 89 4. 46 0. 73 185 -97 322 545 945 246 December 17 Yield (t ha– 1) Profit ($ ha– 1) Boro rice – Analysis currently under way a. Measured b. Measured on Medium high-land 1 & 2, and highland elevation classes. in Medium low-land 873 172
Measured production in formerly fallow farmers’ fields (2011 -2013 dry rabi seasons) Crop Suitability Median sowing date Variable N Min Quantile 25% Maizea 50% Max ST DEV 75% Medium High January 5 4. 02 4. 32 6. 74 7. 20 10. 20 1. 14 40 527 680 895 1022 1102 189 Yield (t ha– 1) 203 4. 16 7. 19 7. 91 8. 37 12. 71 1. 54 132 496 1035 1230 1474 301 Yield (t ha– 1) 38 1. 09 1. 6 2. 22 2. 89 3. 09 0. 66 Profit ($ ha– 1) Wheata January 5 73 Profit ($ ha– 1) High January 3 Yield (t ha– 1) Profit ($ ha– 1) Medium 38 -125 37 240 447 507 208 185 1. 29 2. 16 2. 57 2. 89 4. 46 0. 73 185 -97 322 545 945 246 December 17 Yield (t ha– 1) Profit ($ ha– 1) Boro rice – Analysis currently under way a. Measured b. Measured on Medium high-land 1 & 2, and highland elevation classes. in Medium low-land 873 172
 A conservative estimate of intensification potential in the south central hydrological zone • Assuming a 50 -50% mix of wheat and maize on 50% of suitable medium-highland area and above (to maintain legumes): • New maize year– 1: 144, 000 mt (+11% national production) • New wheat year– 1: 30, 366 (+8% national production) • +$120 million income increase to farmers year– 1 • Analysis for Boro dry season rice (Medium low-land elevation) underway. Compared to National production statistics: BBS 2012.
A conservative estimate of intensification potential in the south central hydrological zone • Assuming a 50 -50% mix of wheat and maize on 50% of suitable medium-highland area and above (to maintain legumes): • New maize year– 1: 144, 000 mt (+11% national production) • New wheat year– 1: 30, 366 (+8% national production) • +$120 million income increase to farmers year– 1 • Analysis for Boro dry season rice (Medium low-land elevation) underway. Compared to National production statistics: BBS 2012.
 Conclusions and caveats • The potential for decentralized surface water irrigation to intensify cropping in the south of Bangladesh is high. • Our estimate is conservative: Maps indicate we detected just ~25% of rivers and canals in the irrigable zone • Methods are needed to rapidly assess water volume • Cooperation is key: Good water governance and canal rehabilitation will be crucial.
Conclusions and caveats • The potential for decentralized surface water irrigation to intensify cropping in the south of Bangladesh is high. • Our estimate is conservative: Maps indicate we detected just ~25% of rivers and canals in the irrigable zone • Methods are needed to rapidly assess water volume • Cooperation is key: Good water governance and canal rehabilitation will be crucial.


