dc925a94ef5eda13e266055e69492018.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

Decentralization & Sub-national Regional Economics Ongoing Activities & Engagement in the MNA Regional Team Decentralization and Sub-national Regional Economics Thematic Group Informal Open House March 8, 2007 1
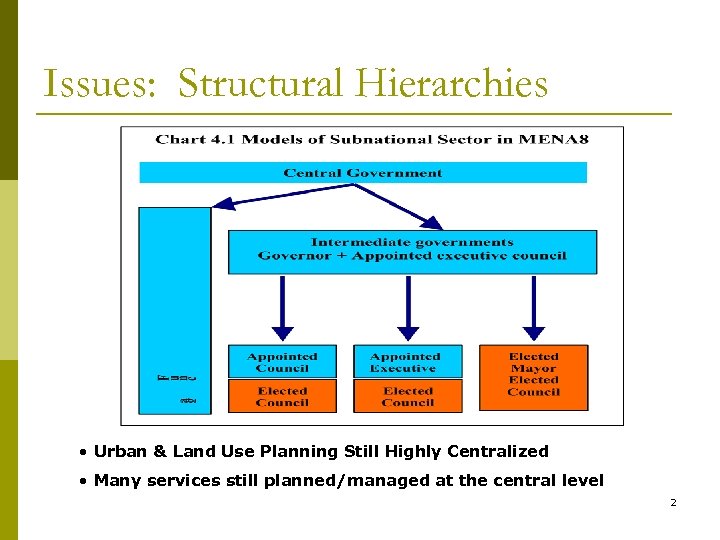
Issues: Structural Hierarchies • Urban & Land Use Planning Still Highly Centralized • Many services still planned/managed at the central level 2
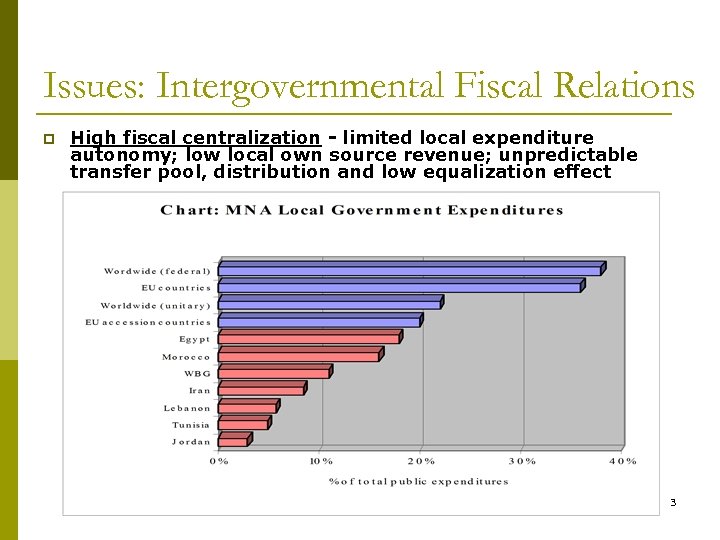
Issues: Intergovernmental Fiscal Relations p High fiscal centralization - limited local expenditure autonomy; low local own source revenue; unpredictable transfer pool, distribution and low equalization effect 3
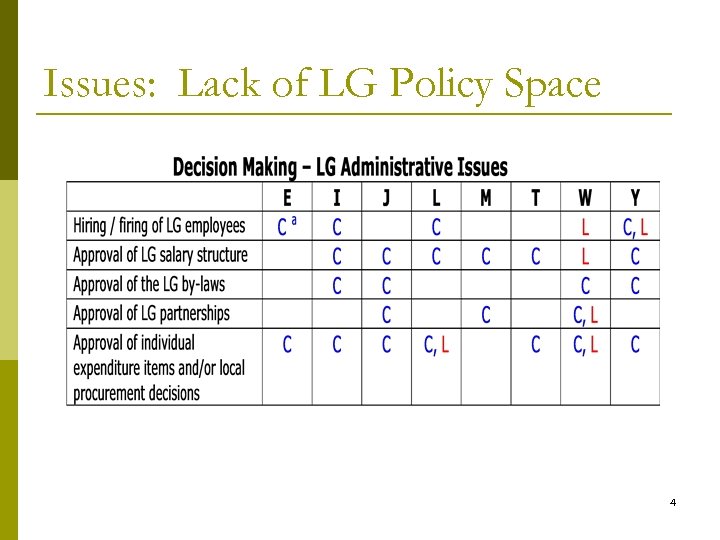
Issues: Lack of LG Policy Space 4
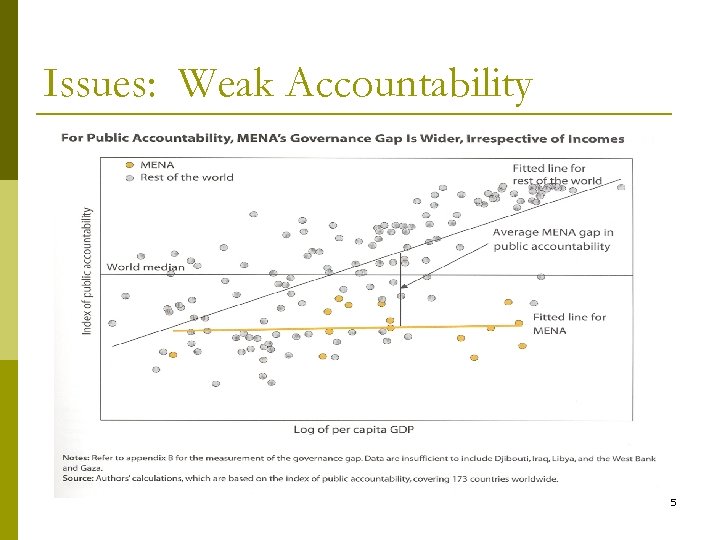
Issues: Weak Accountability 5

Government Responses p p p A “managed” process of decentralization with incremental improvements Responding to political pressures from wellorganized and financed socio-religious groups Increasing political decentralization: local elections in Lebanon (1998), Yemen (2000), WBG (2004 -5), Jordan (forthcoming) Rethinking Institutional Arrangements: The Role of Intermediate-Level Governorates Increasing central transfers for approved investments (off budget) But the institutions for fiscal/admin decentralization remain weak 6
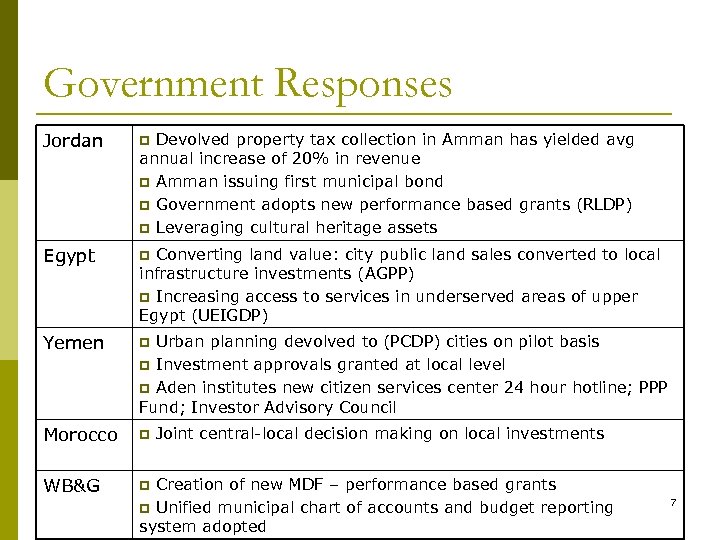
Government Responses Jordan p Egypt p Yemen p Morocco p WB&G p Devolved property tax collection in Amman has yielded avg annual increase of 20% in revenue p Amman issuing first municipal bond p Government adopts new performance based grants (RLDP) p Leveraging cultural heritage assets Converting land value: city public land sales converted to local infrastructure investments (AGPP) p Increasing access to services in underserved areas of upper Egypt (UEIGDP) Urban planning devolved to (PCDP) cities on pilot basis p Investment approvals granted at local level p Aden institutes new citizen services center 24 hour hotline; PPP Fund; Investor Advisory Council Joint central-local decision making on local investments Creation of new MDF – performance based grants p Unified municipal chart of accounts and budget reporting system adopted 7

MNA Regional Strategies/Interventions p p p p Financial Systems Approach: Municipal Development Funds (performance-based grant incentives introduced) -- Tunisia, WBG, Jordan *Working with IFC Subnatl Finance Dept Lagging Regions: Analytical & Operational – Iran, Egypt and Jordan (poverty driven) CDD/Participatory Approaches: Focusing on access to services -- Morocco, WBG (poverty driven) Competitive Cities: Egypt (Alex), Yemen Ports (PCDP) (growth driven) * Working with IFC-PEPMNA & Cities Alliance Land & Municipal Asset Management: Yemen & Egypt Cultural Heritage Assets: Jordan, Morocco (growth driven) Fiscal Decentralization & Governance Issues: Joint work with Urban/PREM on MNA Governance website and joint efforts on PERs Regional Stocktaking & Knowledge Dissemination: Data collection and analysis & Service Delivery Surveys (costeffective tools to gauge end-user perception of services) 8
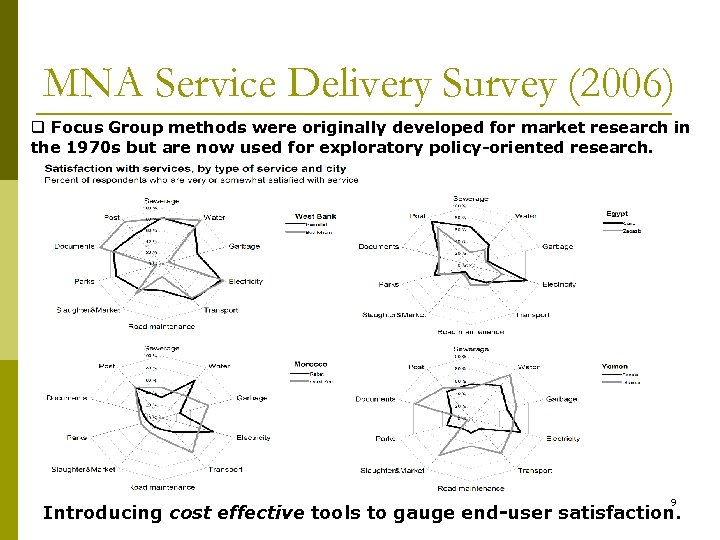
MNA Service Delivery Survey (2006) q Focus Group methods were originally developed for market research in the 1970 s but are now used for exploratory policy-oriented research. 9 Introducing cost effective tools to gauge end-user satisfaction.
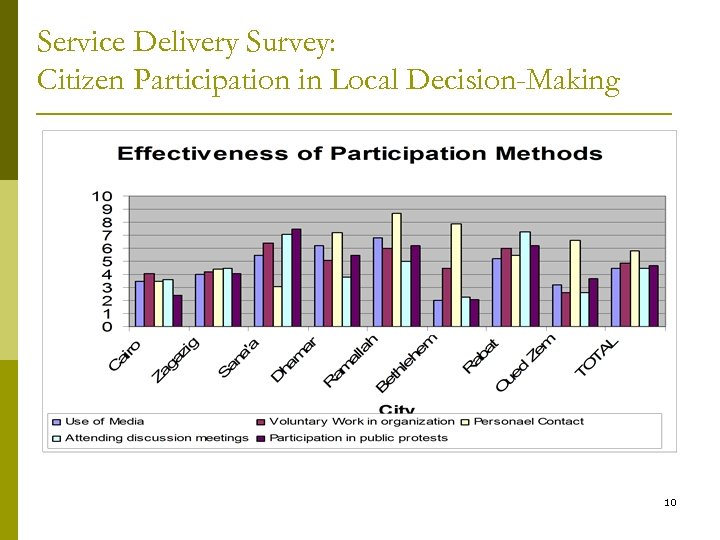
Service Delivery Survey: Citizen Participation in Local Decision-Making 10
dc925a94ef5eda13e266055e69492018.ppt