b3c266efdeefd241ca91c65c53739059.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Dec. 16, 2013 Visualization with 3 D CG Digital 2 D Image Basic Masaki Hayashi
Dec. 16, 2013 Visualization with 3 D CG Digital 2 D Image Basic Masaki Hayashi
 2 D Image Digitization
2 D Image Digitization
 2 D coordinate in image processing
2 D coordinate in image processing
 Scanning
Scanning
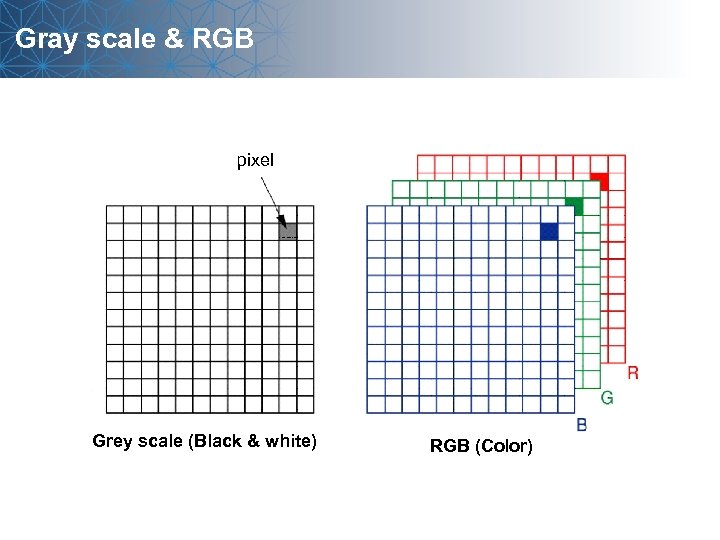 Gray scale & RGB pixel Grey scale (Black & white) RGB (Color)
Gray scale & RGB pixel Grey scale (Black & white) RGB (Color)
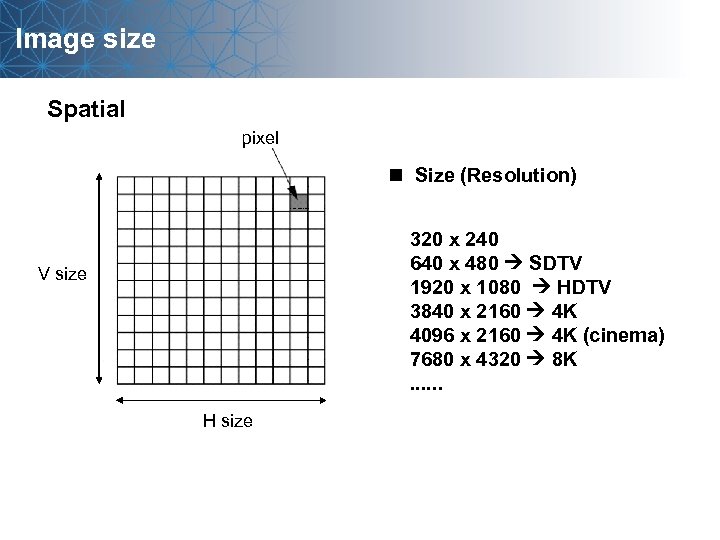 Image size Spatial pixel n Size (Resolution) 320 x 240 640 x 480 SDTV 1920 x 1080 HDTV 3840 x 2160 4 K 4096 x 2160 4 K (cinema) 7680 x 4320 8 K. . . V size H size
Image size Spatial pixel n Size (Resolution) 320 x 240 640 x 480 SDTV 1920 x 1080 HDTV 3840 x 2160 4 K 4096 x 2160 4 K (cinema) 7680 x 4320 8 K. . . V size H size
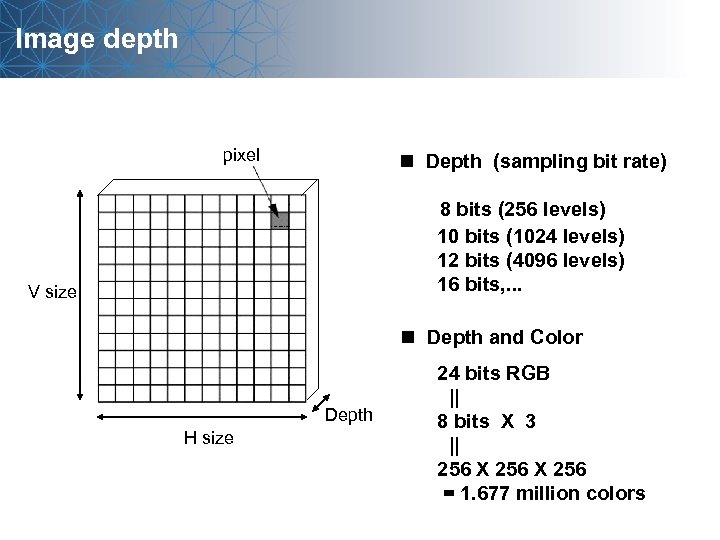 Image depth pixel n Depth (sampling bit rate) 8 bits (256 levels) 10 bits (1024 levels) 12 bits (4096 levels) 16 bits, . . . V size n Depth and Color Depth H size 24 bits RGB || 8 bits X 3 || 256 X 256 = 1. 677 million colors
Image depth pixel n Depth (sampling bit rate) 8 bits (256 levels) 10 bits (1024 levels) 12 bits (4096 levels) 16 bits, . . . V size n Depth and Color Depth H size 24 bits RGB || 8 bits X 3 || 256 X 256 = 1. 677 million colors
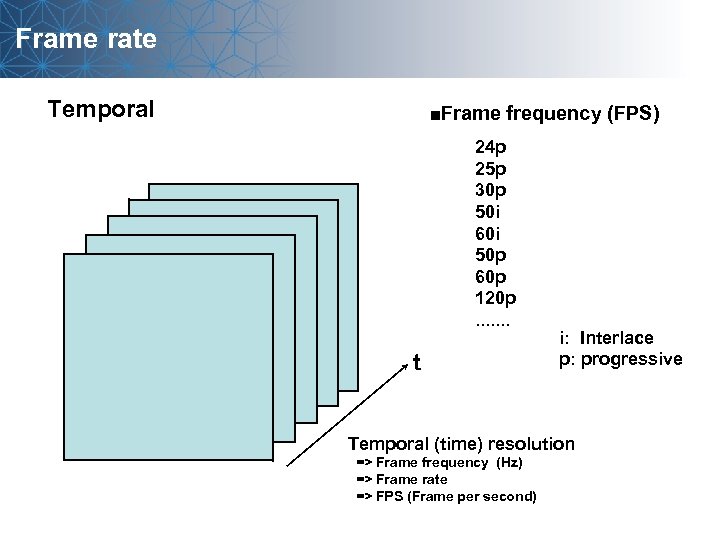 Frame rate Temporal ■Frame frequency (FPS) 24 p 25 p 30 p 50 i 60 i 50 p 60 p 120 p. . . . t i: Interlace p: progressive Temporal (time) resolution => Frame frequency (Hz) => Frame rate => FPS (Frame per second)
Frame rate Temporal ■Frame frequency (FPS) 24 p 25 p 30 p 50 i 60 i 50 p 60 p 120 p. . . . t i: Interlace p: progressive Temporal (time) resolution => Frame frequency (Hz) => Frame rate => FPS (Frame per second)
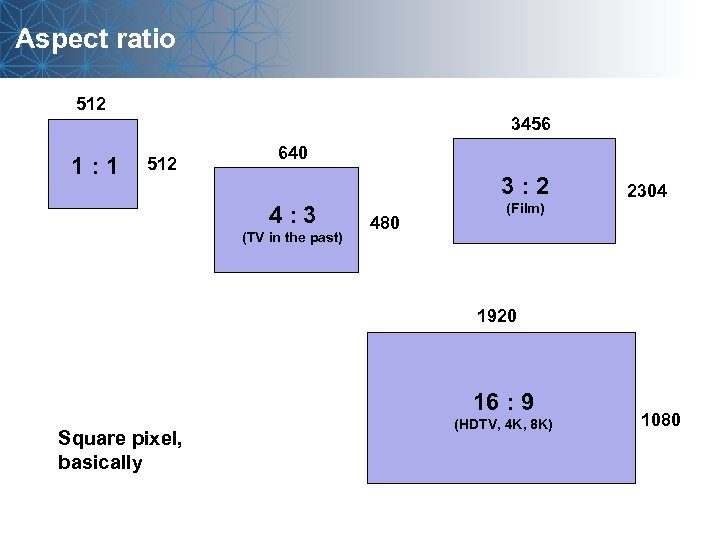 Aspect ratio 512 1: 1 3456 512 640 3: 2 4: 3 (TV in the past) 480 (Film) 2304 1920 16 : 9 Square pixel, basically (HDTV, 4 K, 8 K) 1080
Aspect ratio 512 1: 1 3456 512 640 3: 2 4: 3 (TV in the past) 480 (Film) 2304 1920 16 : 9 Square pixel, basically (HDTV, 4 K, 8 K) 1080
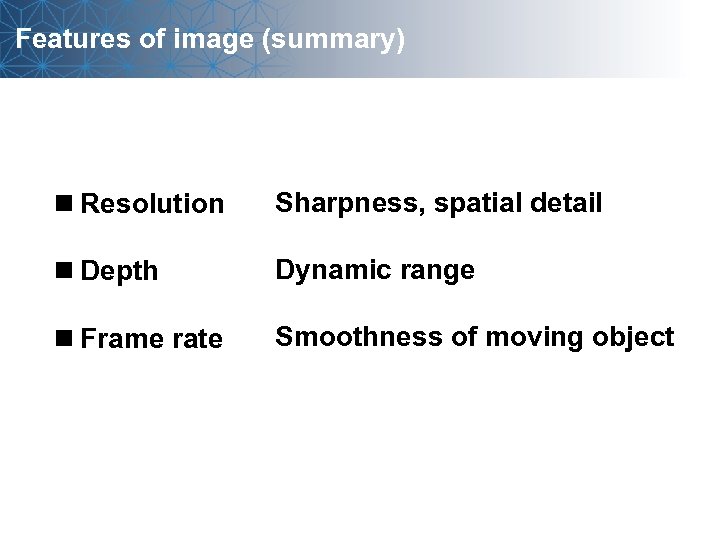 Features of image (summary) n Resolution Sharpness, spatial detail n Depth Dynamic range n Frame rate Smoothness of moving object
Features of image (summary) n Resolution Sharpness, spatial detail n Depth Dynamic range n Frame rate Smoothness of moving object
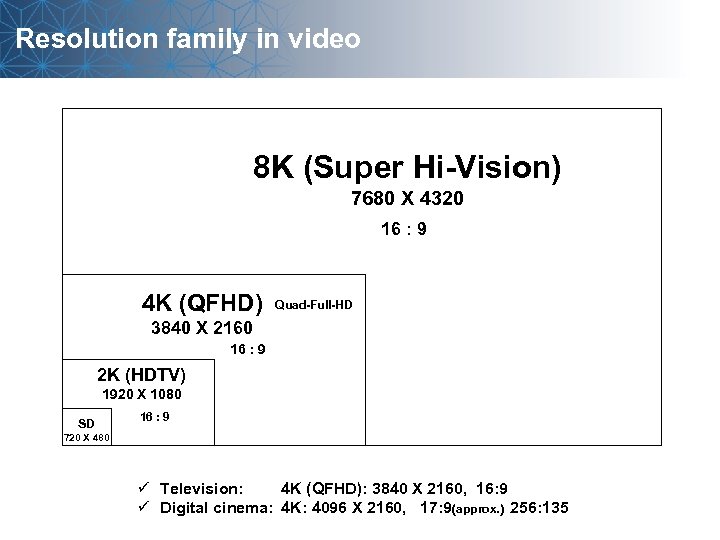 Resolution family in video 8 K (Super Hi-Vision) 7680 X 4320 16 : 9 4 K (QFHD) Quad-Full-HD 3840 X 2160 16 : 9 2 K (HDTV) 1920 X 1080 SD 16 : 9 720 X 480 ü Television: 4 K (QFHD): 3840 X 2160, 16: 9 ü Digital cinema: 4 K: 4096 X 2160, 17: 9(approx. ) 256: 135
Resolution family in video 8 K (Super Hi-Vision) 7680 X 4320 16 : 9 4 K (QFHD) Quad-Full-HD 3840 X 2160 16 : 9 2 K (HDTV) 1920 X 1080 SD 16 : 9 720 X 480 ü Television: 4 K (QFHD): 3840 X 2160, 16: 9 ü Digital cinema: 4 K: 4096 X 2160, 17: 9(approx. ) 256: 135
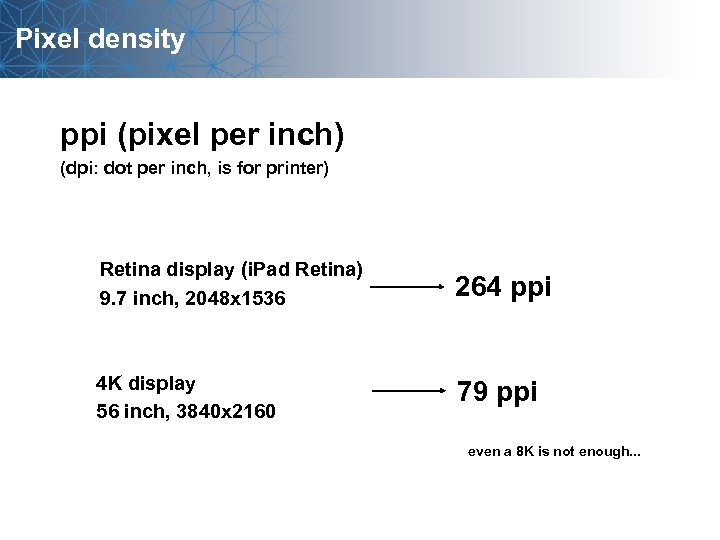 Pixel density ppi (pixel per inch) (dpi: dot per inch, is for printer) Retina display (i. Pad Retina) 9. 7 inch, 2048 x 1536 264 ppi 4 K display 56 inch, 3840 x 2160 79 ppi even a 8 K is not enough. . .
Pixel density ppi (pixel per inch) (dpi: dot per inch, is for printer) Retina display (i. Pad Retina) 9. 7 inch, 2048 x 1536 264 ppi 4 K display 56 inch, 3840 x 2160 79 ppi even a 8 K is not enough. . .
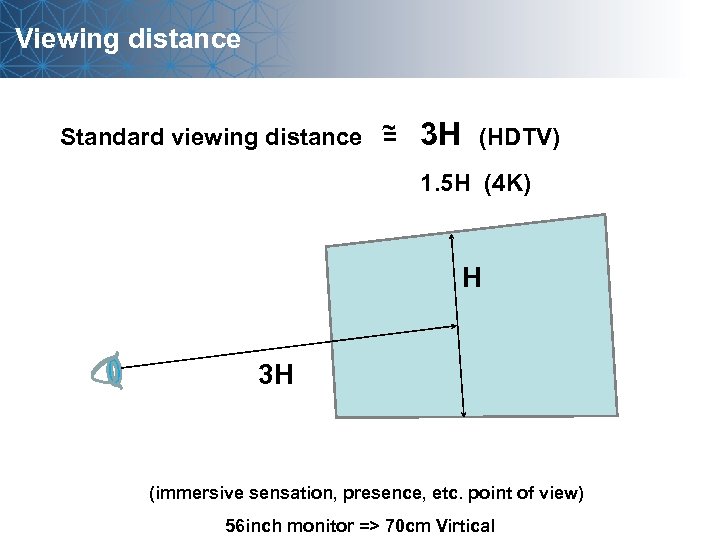 Viewing distance Standard viewing distance ~ = 3 H (HDTV) 1. 5 H (4 K) H 3 H (immersive sensation, presence, etc. point of view) 56 inch monitor => 70 cm Virtical
Viewing distance Standard viewing distance ~ = 3 H (HDTV) 1. 5 H (4 K) H 3 H (immersive sensation, presence, etc. point of view) 56 inch monitor => 70 cm Virtical
 Image compression
Image compression
 Image format JPEG l Most popular l Mosquito noise, Blocky noise l Not suitable for Logo, text, cartoon… GIF l Popular in the past. Motion-GIF l Only 256 colors PNG l Improved version of GIF, Most used on the Internet l Un-limited color. OK for both natural image and logo stuff BMP l Bitmap. Uncompressed, Microsoft
Image format JPEG l Most popular l Mosquito noise, Blocky noise l Not suitable for Logo, text, cartoon… GIF l Popular in the past. Motion-GIF l Only 256 colors PNG l Improved version of GIF, Most used on the Internet l Un-limited color. OK for both natural image and logo stuff BMP l Bitmap. Uncompressed, Microsoft
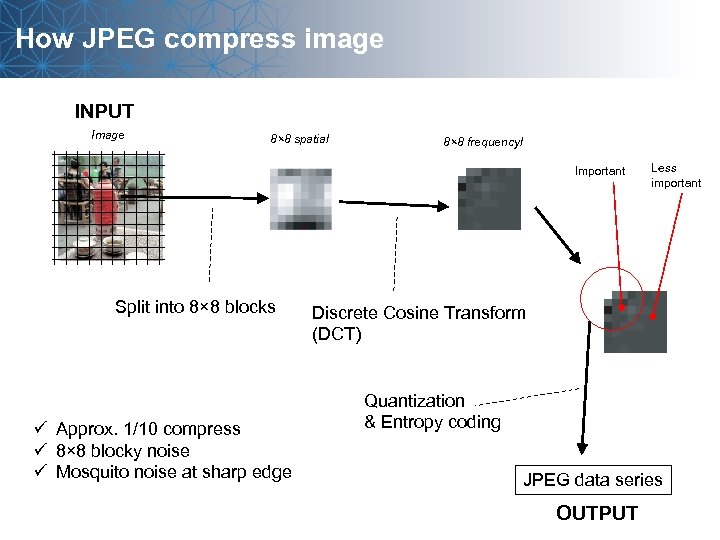 How JPEG compress image INPUT Image 8× 8 spatial 8× 8 frequencyl Important Split into 8× 8 blocks ü Approx. 1/10 compress ü 8× 8 blocky noise ü Mosquito noise at sharp edge Less important Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) Quantization & Entropy coding JPEG data series OUTPUT
How JPEG compress image INPUT Image 8× 8 spatial 8× 8 frequencyl Important Split into 8× 8 blocks ü Approx. 1/10 compress ü 8× 8 blocky noise ü Mosquito noise at sharp edge Less important Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) Quantization & Entropy coding JPEG data series OUTPUT
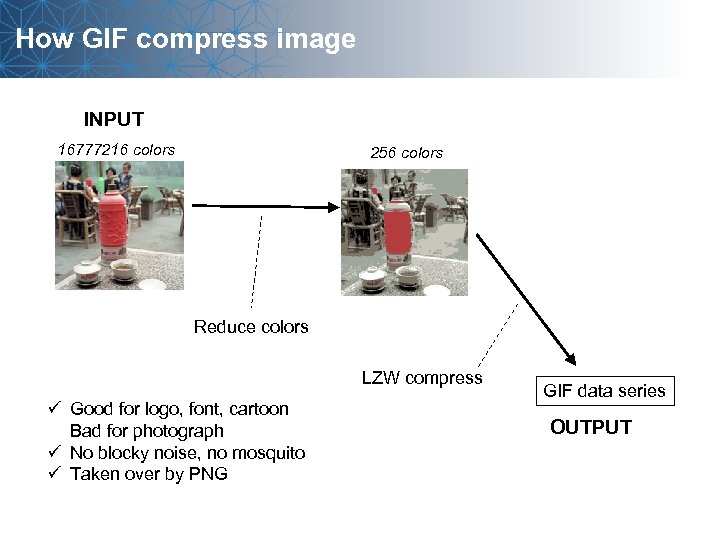 How GIF compress image INPUT 16777216 colors 256 colors Reduce colors LZW compress ü Good for logo, font, cartoon Bad for photograph ü No blocky noise, no mosquito ü Taken over by PNG GIF data series OUTPUT
How GIF compress image INPUT 16777216 colors 256 colors Reduce colors LZW compress ü Good for logo, font, cartoon Bad for photograph ü No blocky noise, no mosquito ü Taken over by PNG GIF data series OUTPUT
 Image processing
Image processing
 Image and array RGB Luminance and Chroma Luminance Y = 0. 3 R + 0. 59 G + 0. 11 B Chroma (Hue and Saturation) CR = R - Y CB = B - Y
Image and array RGB Luminance and Chroma Luminance Y = 0. 3 R + 0. 59 G + 0. 11 B Chroma (Hue and Saturation) CR = R - Y CB = B - Y
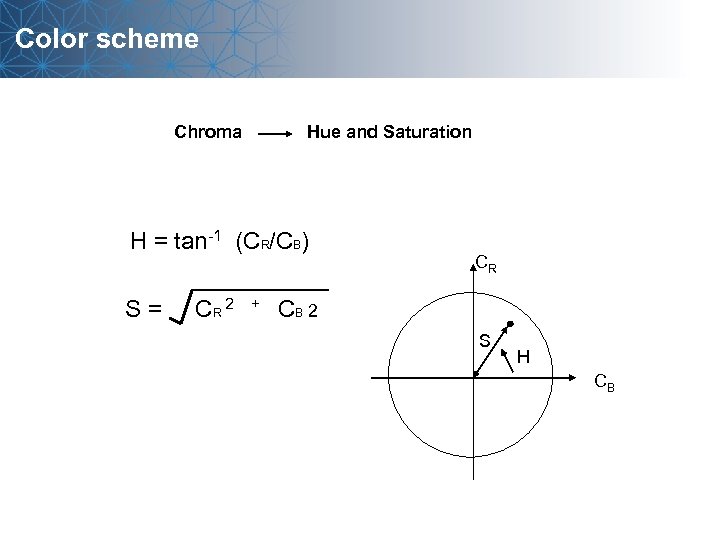 Color scheme Chroma Hue and Saturation H = tan-1 (CR/CB) CR S = CR 2 + CB 2 S H CB
Color scheme Chroma Hue and Saturation H = tan-1 (CR/CB) CR S = CR 2 + CB 2 S H CB
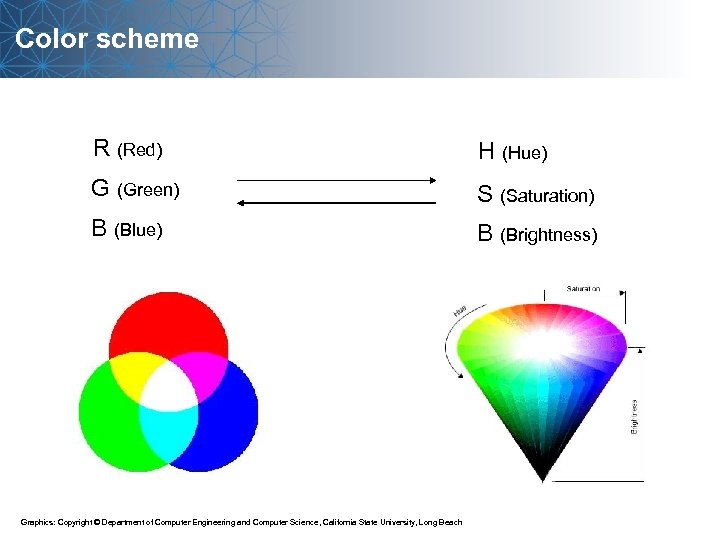 Color scheme R (Red) H (Hue) G (Green) S (Saturation) B (Blue) B (Brightness) Graphics: Copyright © Department of Computer Engineering and Computer Science, California State University, Long Beach
Color scheme R (Red) H (Hue) G (Green) S (Saturation) B (Blue) B (Brightness) Graphics: Copyright © Department of Computer Engineering and Computer Science, California State University, Long Beach
 Color bar White Yellow Cyan Magenta Green Blue Red
Color bar White Yellow Cyan Magenta Green Blue Red
![Lookup table (LUT) Output pixel value 256 0 256 Input pixel value out[0][i][j] = Lookup table (LUT) Output pixel value 256 0 256 Input pixel value out[0][i][j] =](https://present5.com/presentation/b3c266efdeefd241ca91c65c53739059/image-23.jpg) Lookup table (LUT) Output pixel value 256 0 256 Input pixel value out[0][i][j] = LUT[ in[0][i][j] ] ; LUT[ 0 ] = 0; LUT[ 1 ] = 1; LUT[ 2 ] = 2; LUT[ 3 ] = 3; LUT[ 4 ] = 4; LUT[ 5 ] = 5; LUT[ 6 ] = 6; LUT[ 7 ] = 7; ……. LUT[ 255 ] = 255;
Lookup table (LUT) Output pixel value 256 0 256 Input pixel value out[0][i][j] = LUT[ in[0][i][j] ] ; LUT[ 0 ] = 0; LUT[ 1 ] = 1; LUT[ 2 ] = 2; LUT[ 3 ] = 3; LUT[ 4 ] = 4; LUT[ 5 ] = 5; LUT[ 6 ] = 6; LUT[ 7 ] = 7; ……. LUT[ 255 ] = 255;
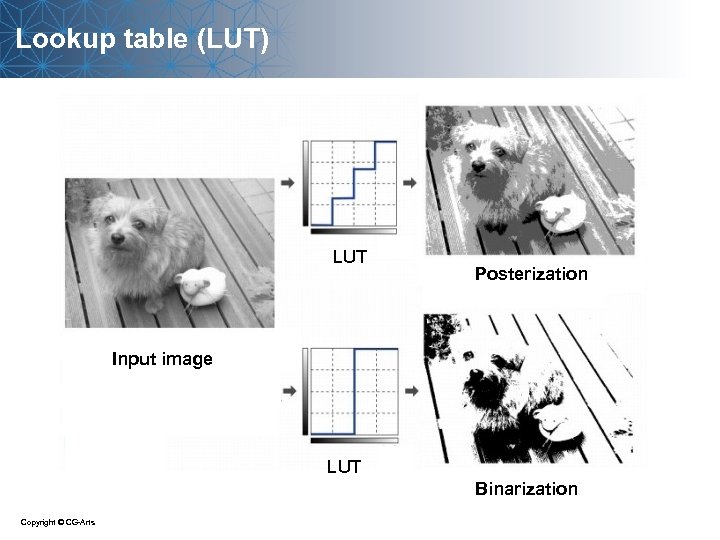 Lookup table (LUT) LUT Posterization Input image LUT Binarization Copyright © CG-Arts
Lookup table (LUT) LUT Posterization Input image LUT Binarization Copyright © CG-Arts
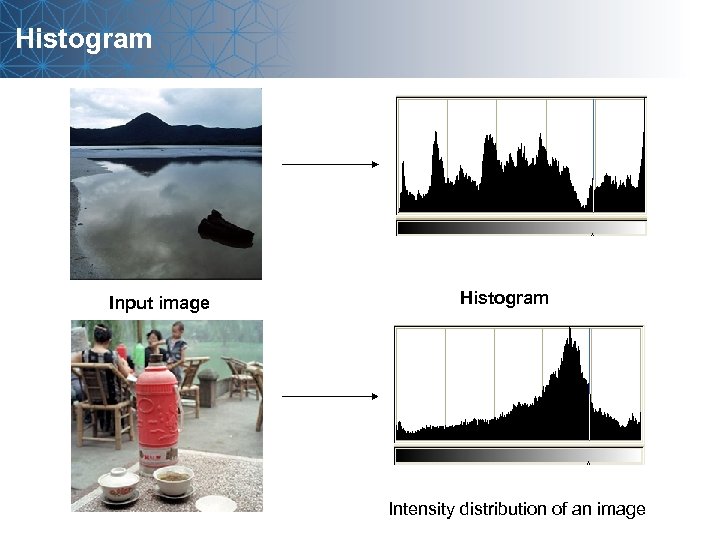 Histogram Input image Histogram Intensity distribution of an image
Histogram Input image Histogram Intensity distribution of an image
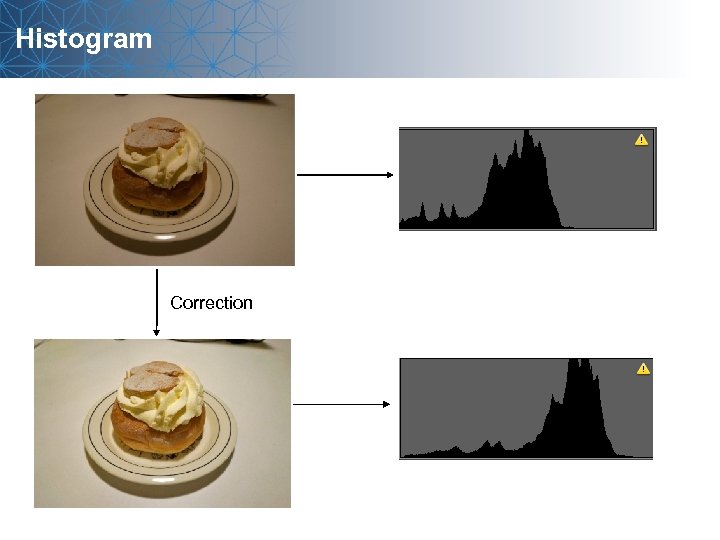 Histogram Correction
Histogram Correction
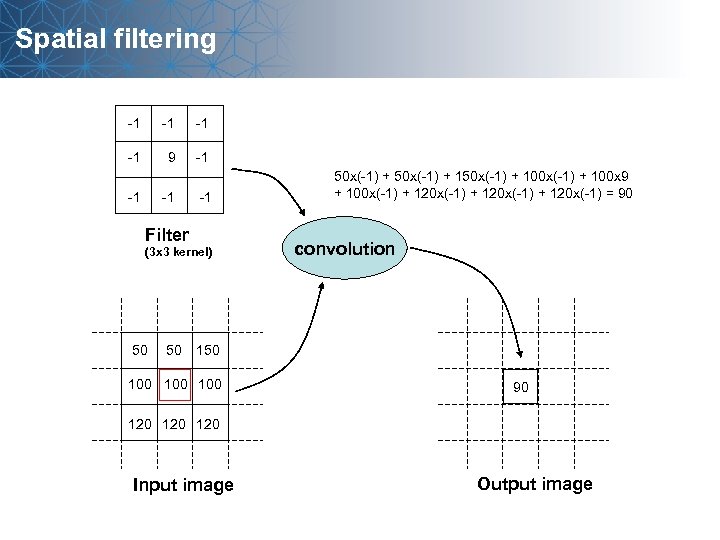 Spatial filtering -1 -1 9 -1 -1 Filter (3 x 3 kernel) 50 50 50 x(-1) + 150 x(-1) + 100 x 9 + 100 x(-1) + 120 x(-1) = 90 convolution 150 100 100 90 120 120 Input image Output image
Spatial filtering -1 -1 9 -1 -1 Filter (3 x 3 kernel) 50 50 50 x(-1) + 150 x(-1) + 100 x 9 + 100 x(-1) + 120 x(-1) = 90 convolution 150 100 100 90 120 120 Input image Output image
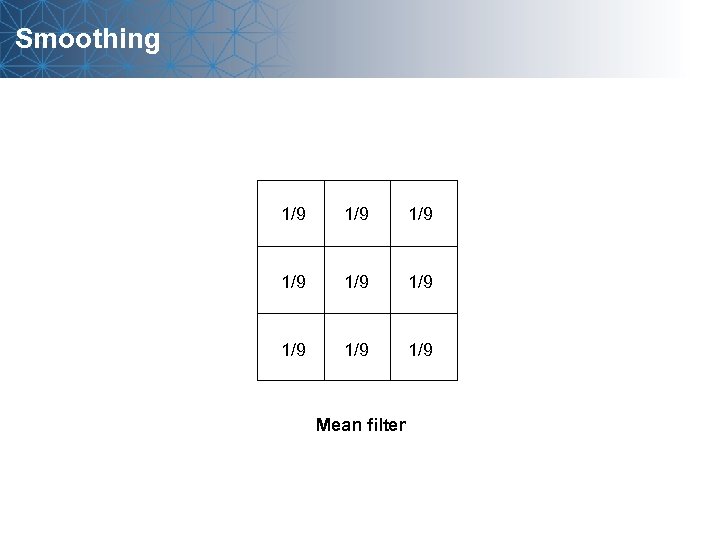 Smoothing 1/9 1/9 1/9 Mean filter
Smoothing 1/9 1/9 1/9 Mean filter
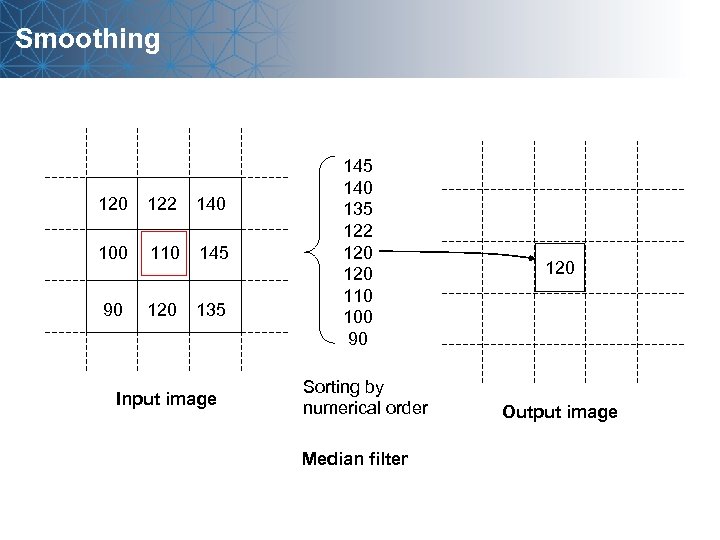 Smoothing 120 122 140 100 110 145 90 120 135 Input image 145 140 135 122 120 110 100 90 Sorting by numerical order Median filter 120 Output image
Smoothing 120 122 140 100 110 145 90 120 135 Input image 145 140 135 122 120 110 100 90 Sorting by numerical order Median filter 120 Output image
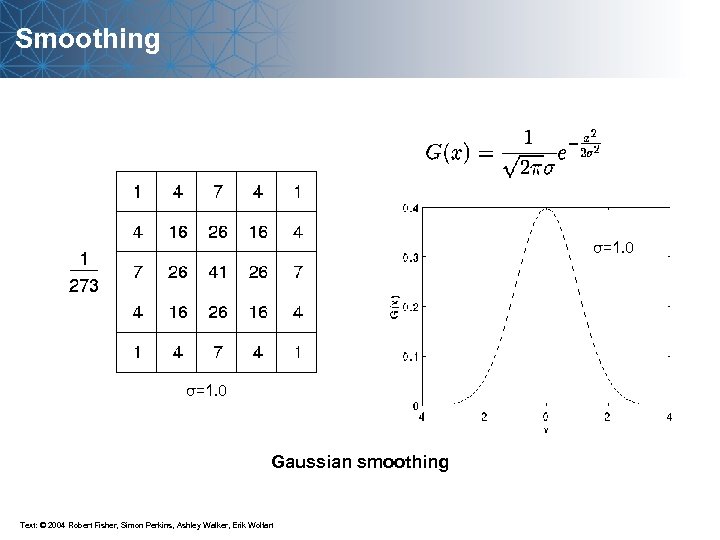 Smoothing σ=1. 0 Gaussian smoothing Text: © 2004 Robert Fisher, Simon Perkins, Ashley Walker, Erik Wolfart
Smoothing σ=1. 0 Gaussian smoothing Text: © 2004 Robert Fisher, Simon Perkins, Ashley Walker, Erik Wolfart
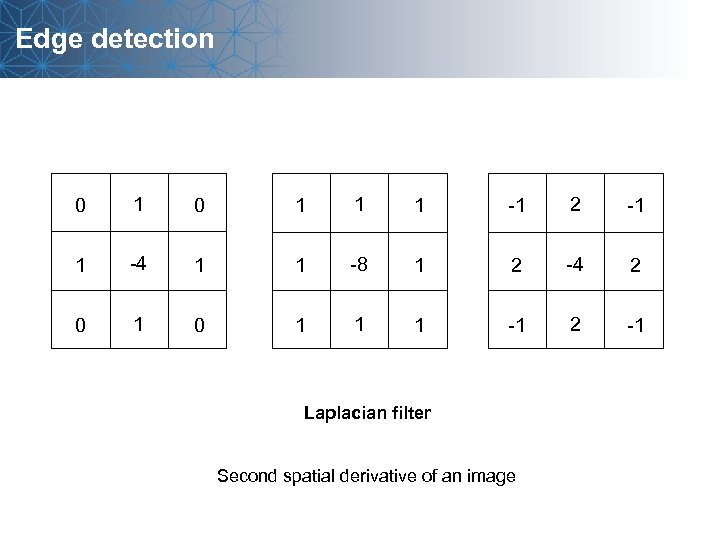 Edge detection 0 1 1 1 -1 2 -1 1 -4 1 1 -8 1 2 -4 2 0 1 1 1 -1 2 -1 Laplacian filter Second spatial derivative of an image
Edge detection 0 1 1 1 -1 2 -1 1 -4 1 1 -8 1 2 -4 2 0 1 1 1 -1 2 -1 Laplacian filter Second spatial derivative of an image
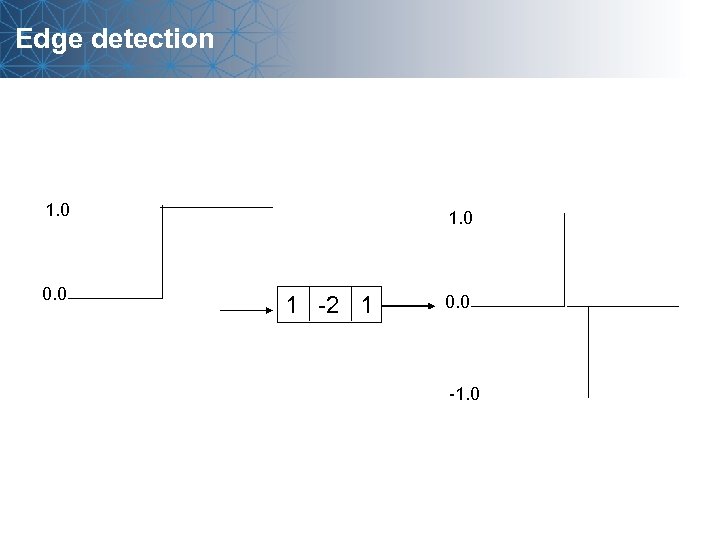 Edge detection 1. 0 0. 0 1 -2 1 0. 0 -1. 0
Edge detection 1. 0 0. 0 1 -2 1 0. 0 -1. 0
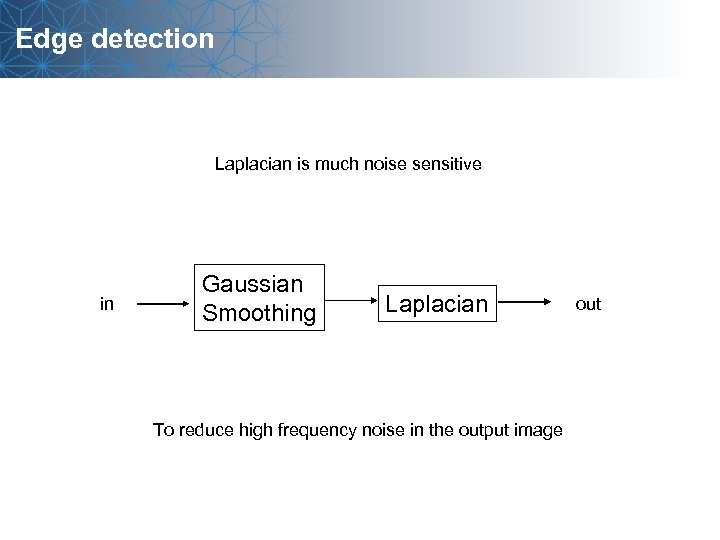 Edge detection Laplacian is much noise sensitive in Gaussian Smoothing Laplacian To reduce high frequency noise in the output image out
Edge detection Laplacian is much noise sensitive in Gaussian Smoothing Laplacian To reduce high frequency noise in the output image out
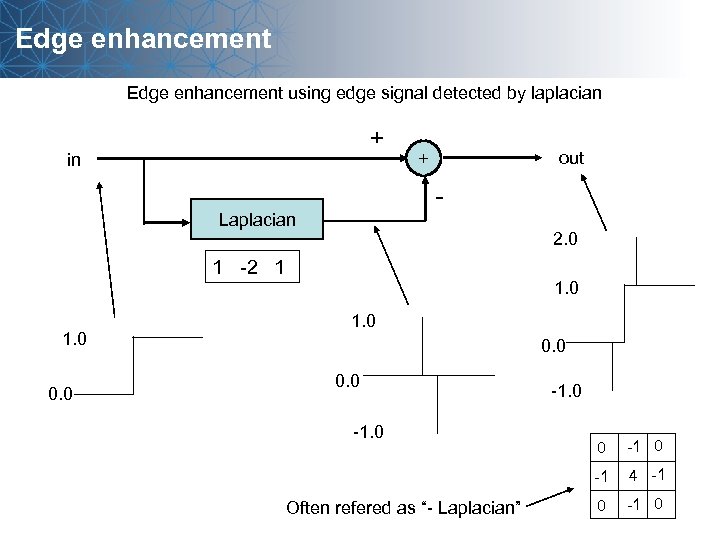 Edge enhancement using edge signal detected by laplacian + in out + - Laplacian 2. 0 1 -2 1 1. 0 0. 0 -1 Often refered as “- Laplacian” 0 4 -1 0
Edge enhancement using edge signal detected by laplacian + in out + - Laplacian 2. 0 1 -2 1 1. 0 0. 0 -1 Often refered as “- Laplacian” 0 4 -1 0
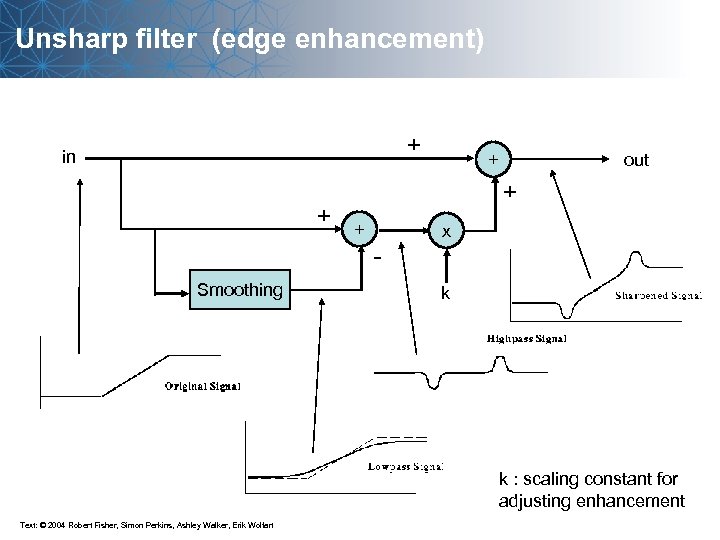 Unsharp filter (edge enhancement) + in + Smoothing out + + + - x k k : scaling constant for adjusting enhancement Text: © 2004 Robert Fisher, Simon Perkins, Ashley Walker, Erik Wolfart
Unsharp filter (edge enhancement) + in + Smoothing out + + + - x k k : scaling constant for adjusting enhancement Text: © 2004 Robert Fisher, Simon Perkins, Ashley Walker, Erik Wolfart
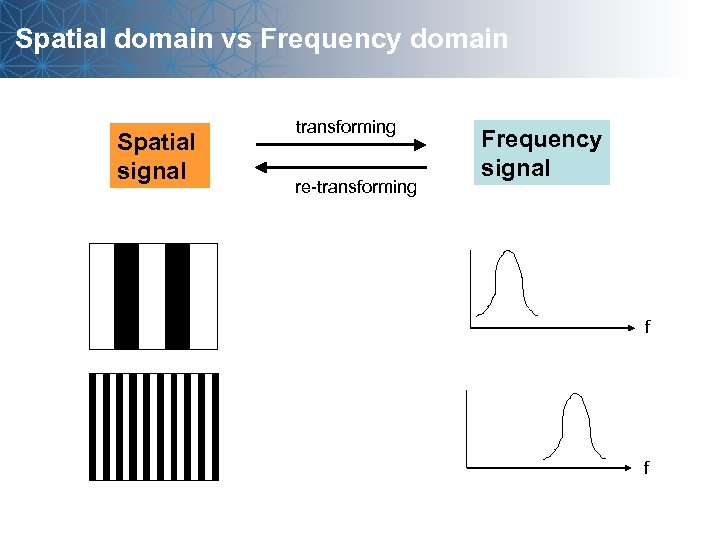 Spatial domain vs Frequency domain Spatial signal transforming re-transforming Frequency signal f f
Spatial domain vs Frequency domain Spatial signal transforming re-transforming Frequency signal f f
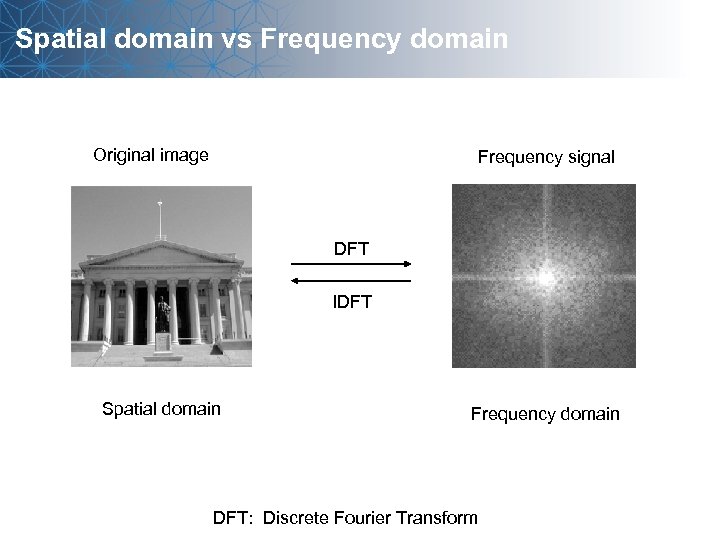 Spatial domain vs Frequency domain Original image Frequency signal DFT IDFT Spatial domain Frequency domain DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform
Spatial domain vs Frequency domain Original image Frequency signal DFT IDFT Spatial domain Frequency domain DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform
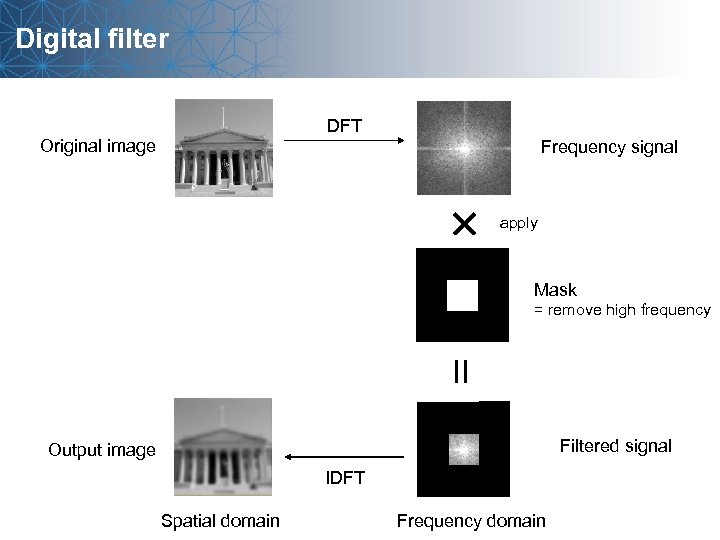 Digital filter DFT Original image Frequency signal apply Mask = remove high frequency Filtered signal Output image IDFT Spatial domain Frequency domain
Digital filter DFT Original image Frequency signal apply Mask = remove high frequency Filtered signal Output image IDFT Spatial domain Frequency domain
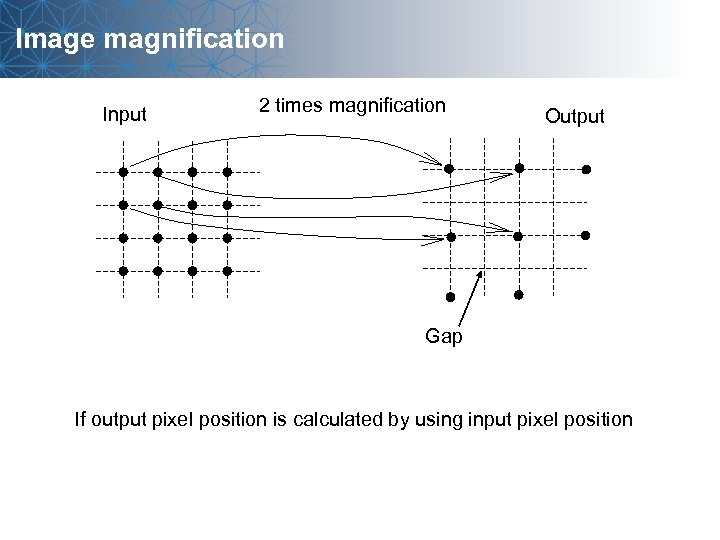 Image magnification Input 2 times magnification Output Gap If output pixel position is calculated by using input pixel position
Image magnification Input 2 times magnification Output Gap If output pixel position is calculated by using input pixel position
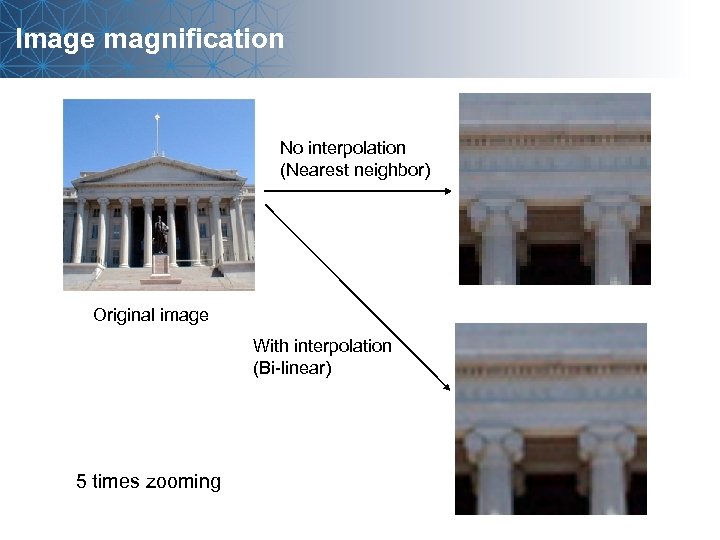 Image magnification No interpolation (Nearest neighbor) Original image With interpolation (Bi-linear) 5 times zooming
Image magnification No interpolation (Nearest neighbor) Original image With interpolation (Bi-linear) 5 times zooming
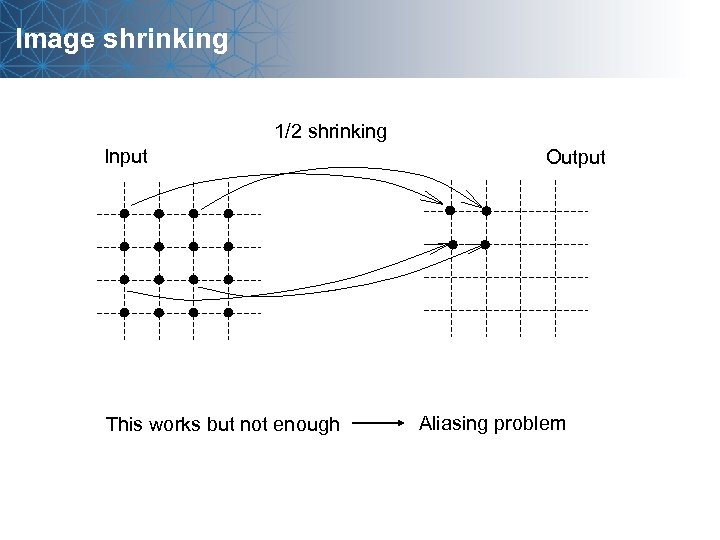 Image shrinking 1/2 shrinking Input This works but not enough Output Aliasing problem
Image shrinking 1/2 shrinking Input This works but not enough Output Aliasing problem
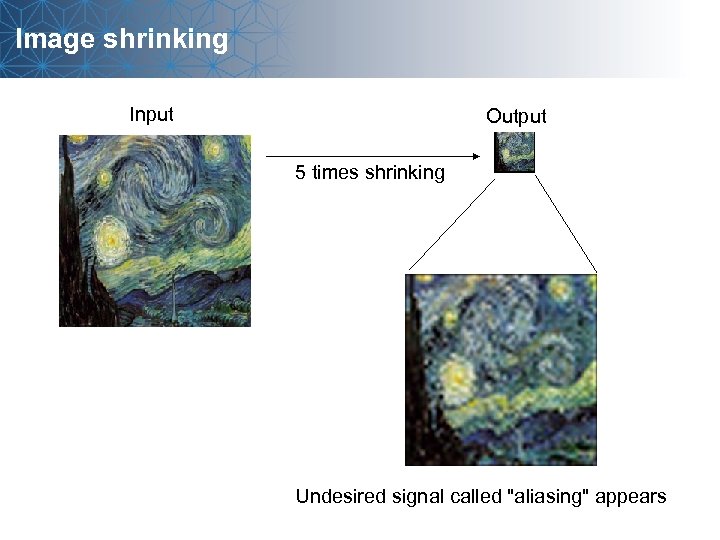 Image shrinking Input Output 5 times shrinking Undesired signal called "aliasing" appears
Image shrinking Input Output 5 times shrinking Undesired signal called "aliasing" appears
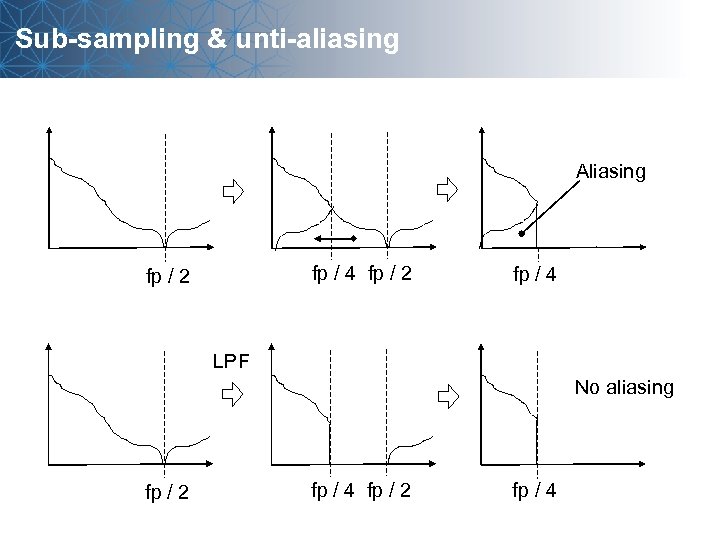 Sub-sampling & unti-aliasing Aliasing fp / 4 fp / 2 fp / 4 LPF No aliasing fp / 2 fp / 4
Sub-sampling & unti-aliasing Aliasing fp / 4 fp / 2 fp / 4 LPF No aliasing fp / 2 fp / 4
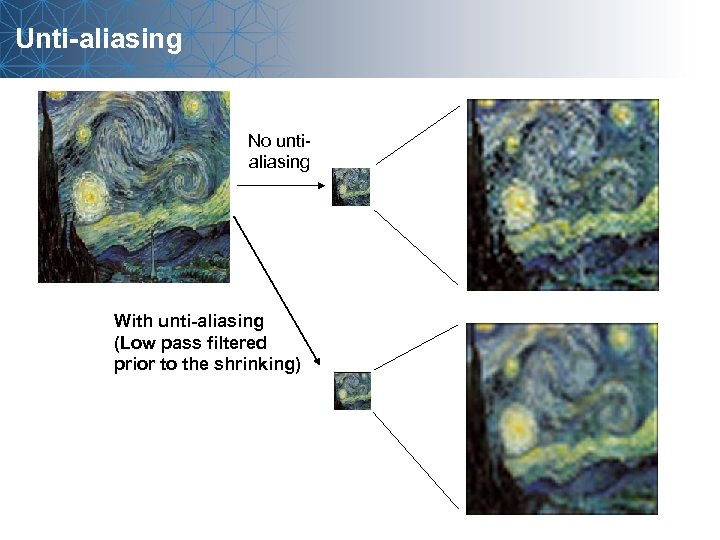 Unti-aliasing No untialiasing With unti-aliasing (Low pass filtered prior to the shrinking)
Unti-aliasing No untialiasing With unti-aliasing (Low pass filtered prior to the shrinking)
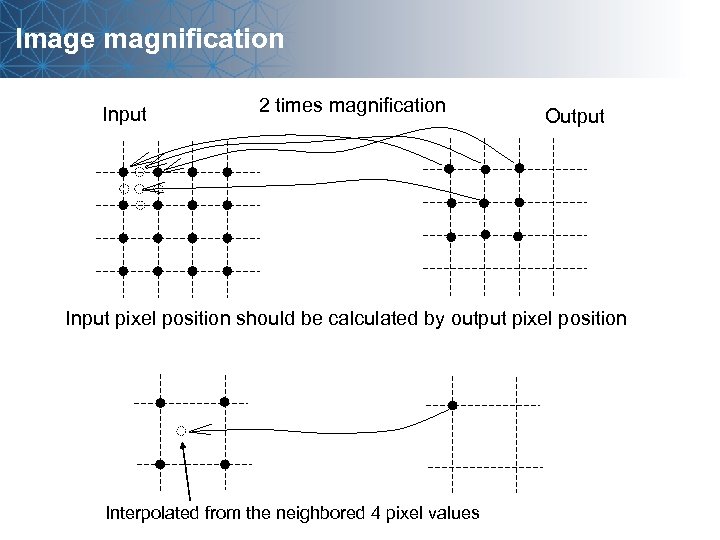 Image magnification Input 2 times magnification Output Input pixel position should be calculated by output pixel position Interpolated from the neighbored 4 pixel values
Image magnification Input 2 times magnification Output Input pixel position should be calculated by output pixel position Interpolated from the neighbored 4 pixel values


