PBL (May, 11-16).pptx
- Количество слайдов: 7
 Dear Students! Please, do the following exercises to be ready for the next week (11. 05 – 16. 05). Use explanation below. In this module, we are going to study TWO units: Unit-9 and Unit-4. You are going to pass your module control starting from May, 25 (25. 05 – 30. 05). Unit-9 is devoted to Project-based learning (PBL). You need first two tasks to learn more about PBL. We are going to discuss it in class. Please, fix your answers in written form (with key words, briefly). You will get one mark for first two tasks. Task-3 (PAIR WORK) is estimated separately (second mark). Please, observe slide-3 (“Sun” scheme) before doing Task-3 (p. 87 t. 2).
Dear Students! Please, do the following exercises to be ready for the next week (11. 05 – 16. 05). Use explanation below. In this module, we are going to study TWO units: Unit-9 and Unit-4. You are going to pass your module control starting from May, 25 (25. 05 – 30. 05). Unit-9 is devoted to Project-based learning (PBL). You need first two tasks to learn more about PBL. We are going to discuss it in class. Please, fix your answers in written form (with key words, briefly). You will get one mark for first two tasks. Task-3 (PAIR WORK) is estimated separately (second mark). Please, observe slide-3 (“Sun” scheme) before doing Task-3 (p. 87 t. 2).
 Project Based Learning is a teaching method in which students gain knowledge and skills by working for an extended period of time to investigate and respond to a complex question, problem, or challenge. Essential Elements of PBL include: Significant Content - At its core, the project is focused on teaching students important knowledge and skills, derived from standards and key concepts at the heart of academic subjects. 21 st century competencies - Students build competencies valuable for today’s world, such as problem solving, critical thinking, collaboration, communication, and creativity/innovation, which are explicitly taught and assessed. In-Depth Inquiry - Students are engaged in an extended, rigorous process of asking questions, using resources, and developing answers. Driving Question - Project work is focused by an open-ended question that students understand find intriguing, which captures their task or frames their exploration. Need to Know - Students see the need to gain knowledge, understand concepts, and apply skills in order to answer the Driving Question and create project products, beginning with an Entry Event that generates interest and curiosity. Voice and Choice - Students are allowed to make some choices about the products to be created, how they work, and how they use their time, guided by the teacher and depending on age level and PBL experience. Critique and Revision - The project includes processes for students to give and receive feedback on the quality of their work, leading them to make revisions or conduct further inquiry. Public Audience - Students present their work to other people, beyond their classmates and teacher. Please, visit http: //bie. org/about/what_pbl for more information.
Project Based Learning is a teaching method in which students gain knowledge and skills by working for an extended period of time to investigate and respond to a complex question, problem, or challenge. Essential Elements of PBL include: Significant Content - At its core, the project is focused on teaching students important knowledge and skills, derived from standards and key concepts at the heart of academic subjects. 21 st century competencies - Students build competencies valuable for today’s world, such as problem solving, critical thinking, collaboration, communication, and creativity/innovation, which are explicitly taught and assessed. In-Depth Inquiry - Students are engaged in an extended, rigorous process of asking questions, using resources, and developing answers. Driving Question - Project work is focused by an open-ended question that students understand find intriguing, which captures their task or frames their exploration. Need to Know - Students see the need to gain knowledge, understand concepts, and apply skills in order to answer the Driving Question and create project products, beginning with an Entry Event that generates interest and curiosity. Voice and Choice - Students are allowed to make some choices about the products to be created, how they work, and how they use their time, guided by the teacher and depending on age level and PBL experience. Critique and Revision - The project includes processes for students to give and receive feedback on the quality of their work, leading them to make revisions or conduct further inquiry. Public Audience - Students present their work to other people, beyond their classmates and teacher. Please, visit http: //bie. org/about/what_pbl for more information.
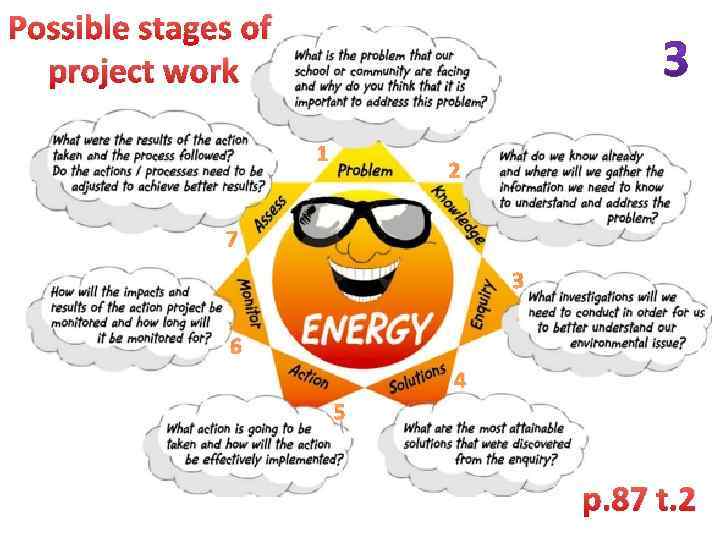 Possible stages of project work 1 2 7 3 6 4 5 p. 87 t. 2
Possible stages of project work 1 2 7 3 6 4 5 p. 87 t. 2


 Example (English language project – “Fashion”): 1. I choose the book “Opportunities”, level Intermediate, topic “Fashion. ” 2. I look through the unit studying its content and thinking: “ What problematic issues can I list from this unit? ” (I list a number of problems: fashion addiction, various clothes styles, fashion as a marketing trick, designing clothes, futuristic clothes, etc. ). 3. I choose one subtopic to offer my learners: designing clothes. But it is not enough. Now, I need to design a problematic question/task to specify WHAT problem/task in particular my students need to solve. For example: “Design a multifunctional futuristic clothes model that is transformable and can be used in any conditions. ” As we see, this question needs investigation of different clothes design and creativity to invent possible models. If your question/task can be solved immediately, such a question/task is NOT project-oriented. It should be oriented to new ideas generation. The last stage of Bloom’s Taxonomy “Create” (pp. 33 -34) helps to construct problem question/task with key words. 4. I use stages of project that I have in the “ Sun” and stages of project that I’ve seen in the “ Video” (p. 85) in order to work out my own stages. I can take some stages from sun, some from video and invent my own stages, too, depending on my task, topic and content of the unit. For example, my project will be held in 6 stages: 1) Brainstorming: Offering my students a fragment of sci-fi movie where people wear futuristic clothes and discussing its functionality; 2) Imagination: Discussing what the world will be like in 500 years and what clothes people will need to be protected; 3) Enquiry: Visiting websites where it is shown how to model “transformative” clothes; 4) Pair modeling: Working together (in pair/group) to design several possible models of futuristic clothes; 5) Draft presentation: Presenting models to audience and getting reflection/criticism from peers and teacher; 6) Final show: Choosing a final model and advertising it the audience. Please, make sure you mention BOTH students’ and teacher's roles. See the table (Slide 6) for that. 5. Still, I understand that my learners may have some problems in the process of fulfilling the project. I need to think about how to prevent these problems and how to solve them if they still occur in the process of project fulfillment ( example below): Possible problems (that my learners may have) Preventive measures (What can I do to prevent this problem? ) Troubleshooting techniques (What can I do if the problem still occurred? ) 1. Difficulties in sorting information necessary for solving the task Teacher can give out list of certain sources (books, sites, etc. ) to specify necessary information Teacher can work with some groups checking information that they’ve collected and helping them to sort information by asking: “What will your group use this information for? ” 2. 3.
Example (English language project – “Fashion”): 1. I choose the book “Opportunities”, level Intermediate, topic “Fashion. ” 2. I look through the unit studying its content and thinking: “ What problematic issues can I list from this unit? ” (I list a number of problems: fashion addiction, various clothes styles, fashion as a marketing trick, designing clothes, futuristic clothes, etc. ). 3. I choose one subtopic to offer my learners: designing clothes. But it is not enough. Now, I need to design a problematic question/task to specify WHAT problem/task in particular my students need to solve. For example: “Design a multifunctional futuristic clothes model that is transformable and can be used in any conditions. ” As we see, this question needs investigation of different clothes design and creativity to invent possible models. If your question/task can be solved immediately, such a question/task is NOT project-oriented. It should be oriented to new ideas generation. The last stage of Bloom’s Taxonomy “Create” (pp. 33 -34) helps to construct problem question/task with key words. 4. I use stages of project that I have in the “ Sun” and stages of project that I’ve seen in the “ Video” (p. 85) in order to work out my own stages. I can take some stages from sun, some from video and invent my own stages, too, depending on my task, topic and content of the unit. For example, my project will be held in 6 stages: 1) Brainstorming: Offering my students a fragment of sci-fi movie where people wear futuristic clothes and discussing its functionality; 2) Imagination: Discussing what the world will be like in 500 years and what clothes people will need to be protected; 3) Enquiry: Visiting websites where it is shown how to model “transformative” clothes; 4) Pair modeling: Working together (in pair/group) to design several possible models of futuristic clothes; 5) Draft presentation: Presenting models to audience and getting reflection/criticism from peers and teacher; 6) Final show: Choosing a final model and advertising it the audience. Please, make sure you mention BOTH students’ and teacher's roles. See the table (Slide 6) for that. 5. Still, I understand that my learners may have some problems in the process of fulfilling the project. I need to think about how to prevent these problems and how to solve them if they still occur in the process of project fulfillment ( example below): Possible problems (that my learners may have) Preventive measures (What can I do to prevent this problem? ) Troubleshooting techniques (What can I do if the problem still occurred? ) 1. Difficulties in sorting information necessary for solving the task Teacher can give out list of certain sources (books, sites, etc. ) to specify necessary information Teacher can work with some groups checking information that they’ve collected and helping them to sort information by asking: “What will your group use this information for? ” 2. 3.
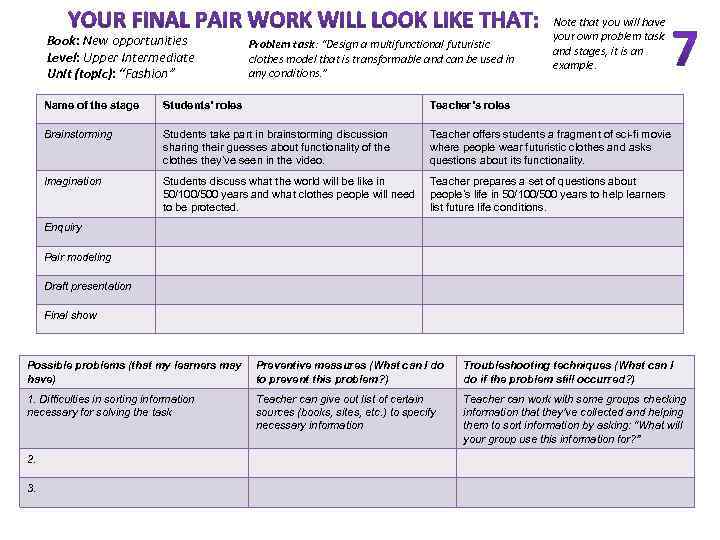 Book: New opportunities Level: Upper Intermediate Unit (topic): “Fashion” Problem task: “Design a multifunctional futuristic clothes model that is transformable and can be used in any conditions. ” Note that you will have your own problem task and stages, it is an example. Name of the stage Students’ roles Teacher’s roles Brainstorming Students take part in brainstorming discussion sharing their guesses about functionality of the clothes they’ve seen in the video. Teacher offers students a fragment of sci-fi movie where people wear futuristic clothes and asks questions about its functionality. Imagination Students discuss what the world will be like in 50/100/500 years and what clothes people will need to be protected. Teacher prepares a set of questions about people’s life in 50/100/500 years to help learners list future life conditions. Enquiry Pair modeling Draft presentation Final show Possible problems (that my learners may have) Preventive measures (What can I do to prevent this problem? ) Troubleshooting techniques (What can I do if the problem still occurred? ) 1. Difficulties in sorting information necessary for solving the task Teacher can give out list of certain sources (books, sites, etc. ) to specify necessary information Teacher can work with some groups checking information that they’ve collected and helping them to sort information by asking: “What will your group use this information for? ” 2. 3.
Book: New opportunities Level: Upper Intermediate Unit (topic): “Fashion” Problem task: “Design a multifunctional futuristic clothes model that is transformable and can be used in any conditions. ” Note that you will have your own problem task and stages, it is an example. Name of the stage Students’ roles Teacher’s roles Brainstorming Students take part in brainstorming discussion sharing their guesses about functionality of the clothes they’ve seen in the video. Teacher offers students a fragment of sci-fi movie where people wear futuristic clothes and asks questions about its functionality. Imagination Students discuss what the world will be like in 50/100/500 years and what clothes people will need to be protected. Teacher prepares a set of questions about people’s life in 50/100/500 years to help learners list future life conditions. Enquiry Pair modeling Draft presentation Final show Possible problems (that my learners may have) Preventive measures (What can I do to prevent this problem? ) Troubleshooting techniques (What can I do if the problem still occurred? ) 1. Difficulties in sorting information necessary for solving the task Teacher can give out list of certain sources (books, sites, etc. ) to specify necessary information Teacher can work with some groups checking information that they’ve collected and helping them to sort information by asking: “What will your group use this information for? ” 2. 3.


