52cf5ac8c89fe6f5c2cae9a87f6a9376.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 DDo. S
DDo. S
 Recent Trends in Do. S Attacks • Network-based flood attacks – vulnerable software is being patched, it is harder to find susceptible hosts • Local Subnet spoofing – ingress / egress filtering becoming more popular • Infrastructure attacks – targeting upstream routers and links • Hit-and-run – pulsing / short-lived floods – Cyclic use of multiple zombie armies • Internet-scale – widely-distributed, large-scale zombie “armies”
Recent Trends in Do. S Attacks • Network-based flood attacks – vulnerable software is being patched, it is harder to find susceptible hosts • Local Subnet spoofing – ingress / egress filtering becoming more popular • Infrastructure attacks – targeting upstream routers and links • Hit-and-run – pulsing / short-lived floods – Cyclic use of multiple zombie armies • Internet-scale – widely-distributed, large-scale zombie “armies”
 Emerging Do. S Threats • Obfuscation of network audit trail – redirection features of certain application protocols – recursive DNS queries, gnutella, etc. • Mutation of attack signatures – address, protocol, port randomization • Routing infrastructure attacks – BGP route hijacking for attack launch • Automated conscription of zombie armies – recent Internet worms and viruses – Microsoft Outlook, IE, IIS, SMB
Emerging Do. S Threats • Obfuscation of network audit trail – redirection features of certain application protocols – recursive DNS queries, gnutella, etc. • Mutation of attack signatures – address, protocol, port randomization • Routing infrastructure attacks – BGP route hijacking for attack launch • Automated conscription of zombie armies – recent Internet worms and viruses – Microsoft Outlook, IE, IIS, SMB
 Sequence of a DDo. S attack A. B. C. D. E. A large set of machines are compromised Attacker identifies exploitable hosts with scanners, or other techniques Attacker accesses the system with automated remote exploits, sniffers, password cracking, worms, trojans Attacker installs attack tools Attacker remotely instructs compromised machines to attack target
Sequence of a DDo. S attack A. B. C. D. E. A large set of machines are compromised Attacker identifies exploitable hosts with scanners, or other techniques Attacker accesses the system with automated remote exploits, sniffers, password cracking, worms, trojans Attacker installs attack tools Attacker remotely instructs compromised machines to attack target
 Mitigation Options Customer Portal or Operator
Mitigation Options Customer Portal or Operator
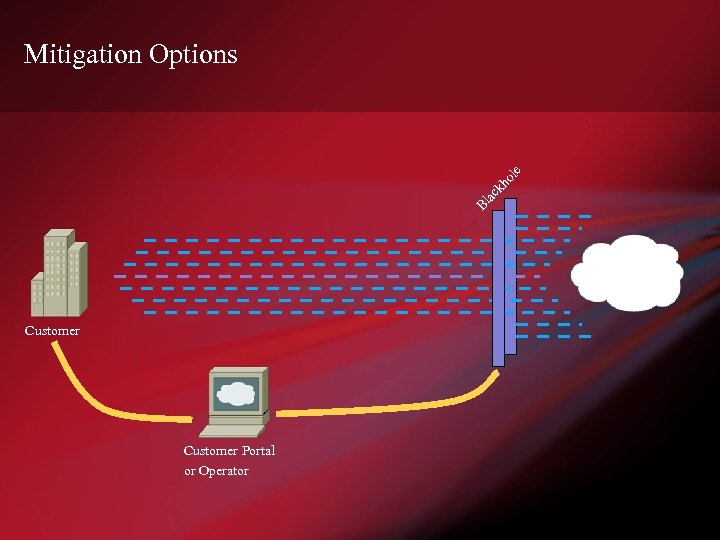 Bl ac kh ol e Mitigation Options Customer Portal or Operator
Bl ac kh ol e Mitigation Options Customer Portal or Operator
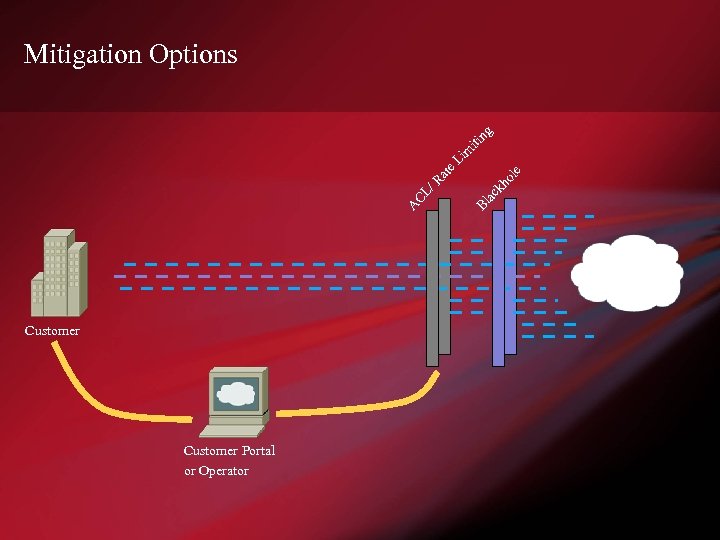 Customer Portal or Operator e ol kh Bl ac A CL /R at e. L im iti n g Mitigation Options
Customer Portal or Operator e ol kh Bl ac A CL /R at e. L im iti n g Mitigation Options
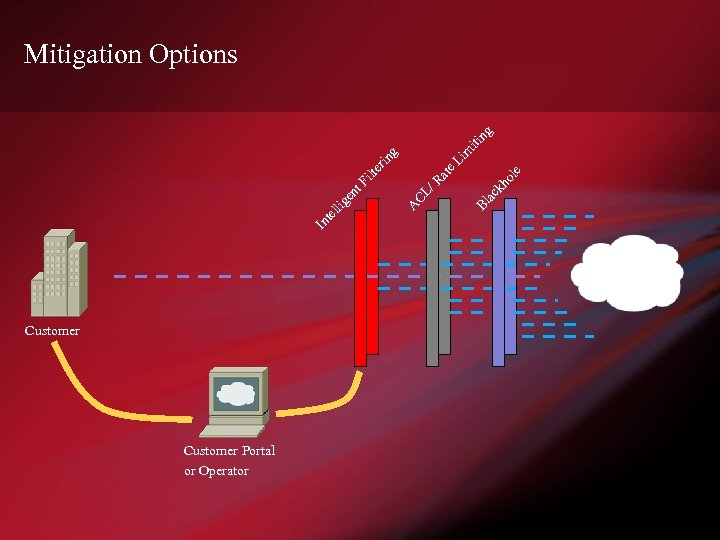 In te l Customer Portal or Operator e ol kh Bl ac /R CL A lig en t. F ilt at er in g e. L im iti ng Mitigation Options
In te l Customer Portal or Operator e ol kh Bl ac /R CL A lig en t. F ilt at er in g e. L im iti ng Mitigation Options
 Version 5 - Flow Format • Packet Count • Byte Count • Source IP Address • Destination IP Address • Start sys. Up. Time • End sys. Up. Time • Source TCP/UDP Port • Destination TCP/UDP Port Utilization • Input if. Index • Output if. Index Qo. S • Type of Service • TCP Flags • Protocol • Next Hop Address • Source AS Number • Dest. AS Number • Source Prefix Mask • Dest. Prefix Mask Usage Time of Day From/To Application Routing and Peering
Version 5 - Flow Format • Packet Count • Byte Count • Source IP Address • Destination IP Address • Start sys. Up. Time • End sys. Up. Time • Source TCP/UDP Port • Destination TCP/UDP Port Utilization • Input if. Index • Output if. Index Qo. S • Type of Service • TCP Flags • Protocol • Next Hop Address • Source AS Number • Dest. AS Number • Source Prefix Mask • Dest. Prefix Mask Usage Time of Day From/To Application Routing and Peering
 Misuse Anomalies § Detected against /32 hosts § Misuse anomalies cover the following types of traffic: § ICMP Anomaly § TCP NULL Flag Anomaly § TCP SYN Flag Anomaly § TCP RST Flag Anomaly § IP NULL (Proto 0) Anomaly § IP Fragmentation Anomaly § IP Private Address Space Anomaly § Total Traffic bps § Total traffic pps § Deployed against common attacks targeted at individual network hosts.
Misuse Anomalies § Detected against /32 hosts § Misuse anomalies cover the following types of traffic: § ICMP Anomaly § TCP NULL Flag Anomaly § TCP SYN Flag Anomaly § TCP RST Flag Anomaly § IP NULL (Proto 0) Anomaly § IP Fragmentation Anomaly § IP Private Address Space Anomaly § Total Traffic bps § Total traffic pps § Deployed against common attacks targeted at individual network hosts.
 How Peakflow SP IS works Three types of anomalies are reported by Peakflow SP IS: • Profiled Anomalies – deviations from normal traffic levels on the network • Misuse Anomalies – Traffic towards specific hosts that should not normally be seen on a network • Fingerprint Anomalies – Traffic that fits a user specified signature
How Peakflow SP IS works Three types of anomalies are reported by Peakflow SP IS: • Profiled Anomalies – deviations from normal traffic levels on the network • Misuse Anomalies – Traffic towards specific hosts that should not normally be seen on a network • Fingerprint Anomalies – Traffic that fits a user specified signature
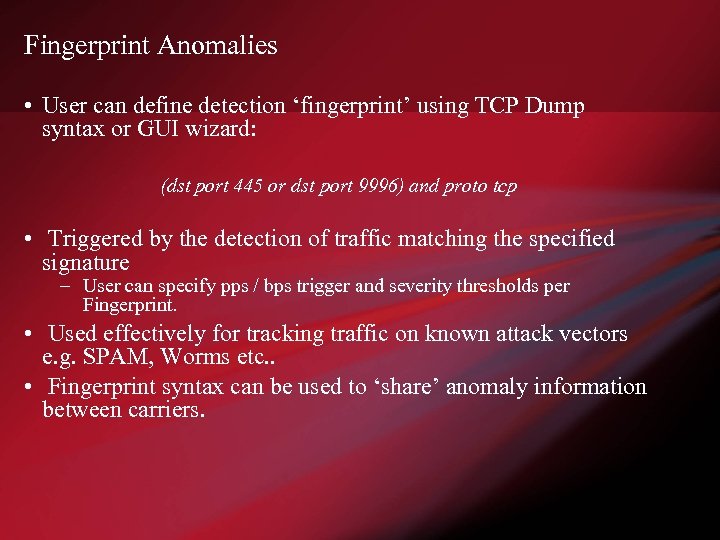 Fingerprint Anomalies • User can define detection ‘fingerprint’ using TCP Dump syntax or GUI wizard: (dst port 445 or dst port 9996) and proto tcp • Triggered by the detection of traffic matching the specified signature – User can specify pps / bps trigger and severity thresholds per Fingerprint. • Used effectively for tracking traffic on known attack vectors e. g. SPAM, Worms etc. . • Fingerprint syntax can be used to ‘share’ anomaly information between carriers.
Fingerprint Anomalies • User can define detection ‘fingerprint’ using TCP Dump syntax or GUI wizard: (dst port 445 or dst port 9996) and proto tcp • Triggered by the detection of traffic matching the specified signature – User can specify pps / bps trigger and severity thresholds per Fingerprint. • Used effectively for tracking traffic on known attack vectors e. g. SPAM, Worms etc. . • Fingerprint syntax can be used to ‘share’ anomaly information between carriers.
 Mitigation Strategies • Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (u. RPF) • Rate Limiting • ACL – Filter traffic targeted at a destination • Blackhole / Sinkhole / Shunt – Off-ramping for filtering, scrubbing and forensics • Integrated Filtering – Uses a combination of BGP sinkhole and network ‘cleaning’ appliances. • Fingerprint Sharing – Mitigation closer to the source
Mitigation Strategies • Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (u. RPF) • Rate Limiting • ACL – Filter traffic targeted at a destination • Blackhole / Sinkhole / Shunt – Off-ramping for filtering, scrubbing and forensics • Integrated Filtering – Uses a combination of BGP sinkhole and network ‘cleaning’ appliances. • Fingerprint Sharing – Mitigation closer to the source
 IF Filtering Levels: Standard & Integrated • Standard integration – Peakflow has recommended filtering options » ACLs, rate limiting, BGP blackholing, off-ramping/sinkholing and flexible scripting – Peakflow can detect and then initiate scrubbing • Integrated Filtering API – Tightly coupled API, remain mitigation agnostic (dedicated or shared mitigation) » Cisco/Riverhead Guard
IF Filtering Levels: Standard & Integrated • Standard integration – Peakflow has recommended filtering options » ACLs, rate limiting, BGP blackholing, off-ramping/sinkholing and flexible scripting – Peakflow can detect and then initiate scrubbing • Integrated Filtering API – Tightly coupled API, remain mitigation agnostic (dedicated or shared mitigation) » Cisco/Riverhead Guard
 Intelligent Filtering • Integration with dedicated mitigation devices – Cisco Guard • Peakflow triggers devices to use BGP to off-ramp attack traffic through themselves • Process data at gigabit per second speeds and do deep packet inspection • Apply advanced heuristics to traffic to filter bad while preserving good – TCP SYN authentication – Zombie army detection – Enforce traffic baselines • Provide Feedback to Peakflow system on what is filtered/passed
Intelligent Filtering • Integration with dedicated mitigation devices – Cisco Guard • Peakflow triggers devices to use BGP to off-ramp attack traffic through themselves • Process data at gigabit per second speeds and do deep packet inspection • Apply advanced heuristics to traffic to filter bad while preserving good – TCP SYN authentication – Zombie army detection – Enforce traffic baselines • Provide Feedback to Peakflow system on what is filtered/passed
 Dealing with DDo. S attacks: Remediation • Three key steps: – Detection » Determine attack methodology and what resources are affected – Traceback » Determine the source and transit path – Mitigation » Determine what traffic to block, and where best to block it
Dealing with DDo. S attacks: Remediation • Three key steps: – Detection » Determine attack methodology and what resources are affected – Traceback » Determine the source and transit path – Mitigation » Determine what traffic to block, and where best to block it
 What is a Do. S Attack ? • Malicious attempt by a group of people to cripple an online service • Flood the victim (server) with packets – Overload packet processing capacity – Saturate network bandwidth • Two Types of Do. S Attacks – Resource Exhaustion Attacks – Bandwidth Consumption Attacks
What is a Do. S Attack ? • Malicious attempt by a group of people to cripple an online service • Flood the victim (server) with packets – Overload packet processing capacity – Saturate network bandwidth • Two Types of Do. S Attacks – Resource Exhaustion Attacks – Bandwidth Consumption Attacks
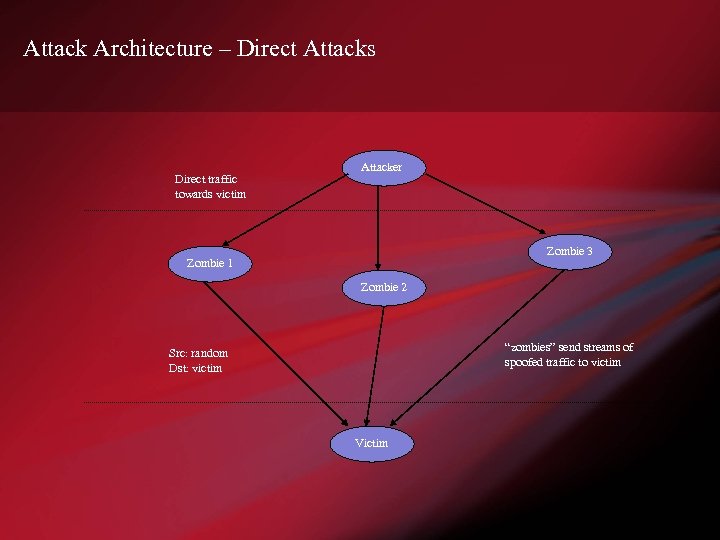 Attack Architecture – Direct Attacks Direct traffic towards victim Attacker Zombie 3 Zombie 1 Zombie 2 “zombies” send streams of spoofed traffic to victim Src: random Dst: victim Victim
Attack Architecture – Direct Attacks Direct traffic towards victim Attacker Zombie 3 Zombie 1 Zombie 2 “zombies” send streams of spoofed traffic to victim Src: random Dst: victim Victim
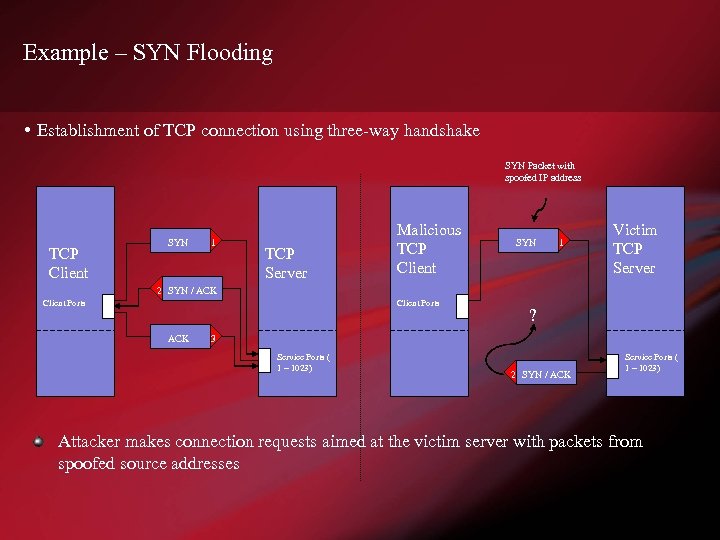 Example – SYN Flooding • Establishment of TCP connection using three-way handshake SYN Packet with spoofed IP address TCP Client SYN 1 TCP Server Malicious TCP Client SYN 1 Victim TCP Server 2 SYN / ACK Client Ports ACK ? 3 80 Service Ports ( 1 – 1023) Service Ports ( 2 SYN / ACK 80 1 – 1023) Attacker makes connection requests aimed at the victim server with packets from spoofed source addresses
Example – SYN Flooding • Establishment of TCP connection using three-way handshake SYN Packet with spoofed IP address TCP Client SYN 1 TCP Server Malicious TCP Client SYN 1 Victim TCP Server 2 SYN / ACK Client Ports ACK ? 3 80 Service Ports ( 1 – 1023) Service Ports ( 2 SYN / ACK 80 1 – 1023) Attacker makes connection requests aimed at the victim server with packets from spoofed source addresses
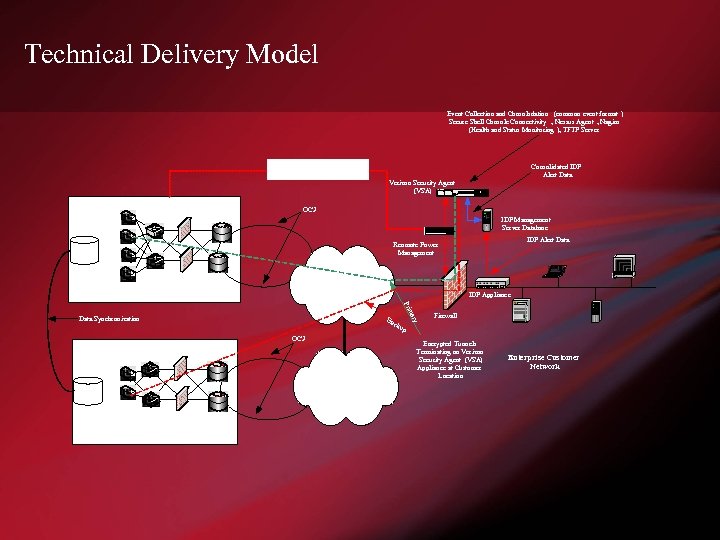 Technical Delivery Model Event Collection and Consolodation (common event format ) Secure Shell Console Connectivity , Nessus Agent , Nagios (Health and Status Monitoring ), TFTP Server Consolidated IDP Alert Data Out of Band PSTN Connectivity Verizon Security Agent (VSA) Bay Netwo rks OC 3 IDP Management Server Database Remedy 1 Storage Area Network Remedy 2 Arcsight 2 Public Internet Primary Security Operations Center (Irving, TX) IDP Appliance Remedy 1 Arcsight 1 Hot Site Security Operations Center (Baltimore, MD) ku p ry OC 3 ma P ri Ba c Data Synchronization Storage Area Network IDP Alert Data Reomote Power Management Arcsight 1 Firewall Encrypted Tunnels Terminating on Verizon Security Agent (VSA) Appliance at Customer Location Public Internet Enterprise Customer Network
Technical Delivery Model Event Collection and Consolodation (common event format ) Secure Shell Console Connectivity , Nessus Agent , Nagios (Health and Status Monitoring ), TFTP Server Consolidated IDP Alert Data Out of Band PSTN Connectivity Verizon Security Agent (VSA) Bay Netwo rks OC 3 IDP Management Server Database Remedy 1 Storage Area Network Remedy 2 Arcsight 2 Public Internet Primary Security Operations Center (Irving, TX) IDP Appliance Remedy 1 Arcsight 1 Hot Site Security Operations Center (Baltimore, MD) ku p ry OC 3 ma P ri Ba c Data Synchronization Storage Area Network IDP Alert Data Reomote Power Management Arcsight 1 Firewall Encrypted Tunnels Terminating on Verizon Security Agent (VSA) Appliance at Customer Location Public Internet Enterprise Customer Network
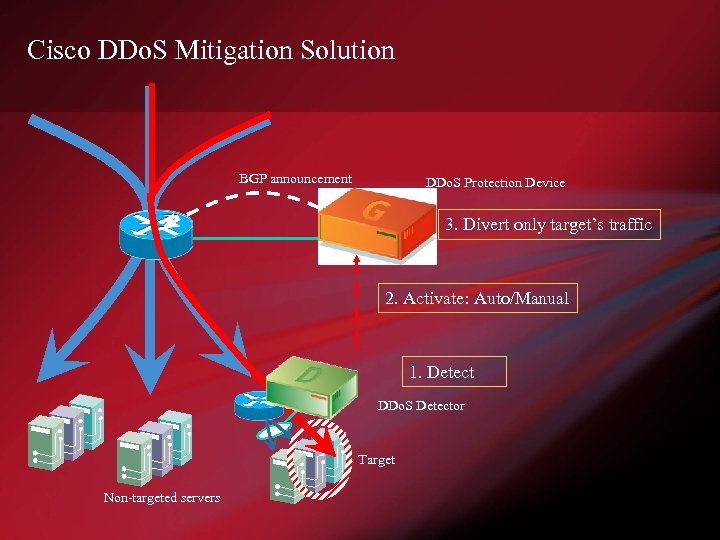 Cisco DDo. S Mitigation Solution BGP announcement DDo. S Protection Device 3. Divert only target’s traffic 2. Activate: Auto/Manual 1. Detect DDo. S Detector Target Non-targeted servers
Cisco DDo. S Mitigation Solution BGP announcement DDo. S Protection Device 3. Divert only target’s traffic 2. Activate: Auto/Manual 1. Detect DDo. S Detector Target Non-targeted servers
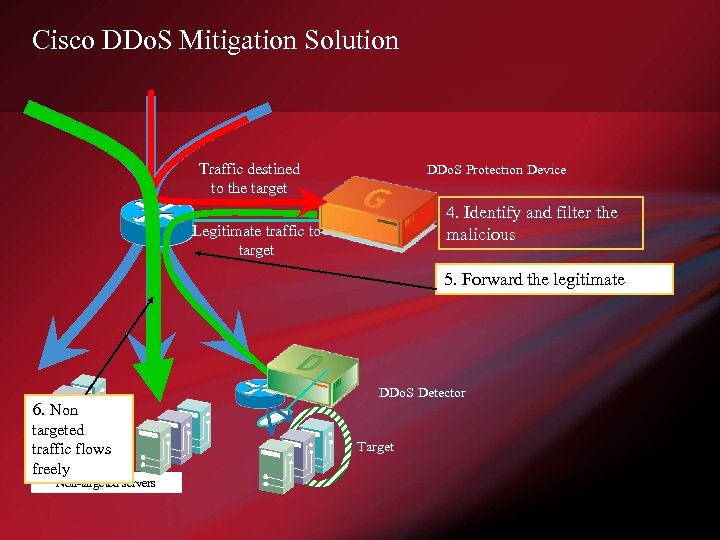 Cisco DDo. S Mitigation Solution Traffic destined to the target DDo. S Protection Device 4. Identify and filter the malicious Legitimate traffic to target 5. Forward the legitimate 6. Non targeted traffic flows freely Non-targeted servers DDo. S Detector Target
Cisco DDo. S Mitigation Solution Traffic destined to the target DDo. S Protection Device 4. Identify and filter the malicious Legitimate traffic to target 5. Forward the legitimate 6. Non targeted traffic flows freely Non-targeted servers DDo. S Detector Target
 Peakflow SP Anomaly Reporting • Profiled Anomalies – deviations from normal traffic levels on the network • Misuse Anomalies – Traffic towards specific hosts that exceed what should normally be seen on a network • Fingerprint/Worm Anomalies – Traffic that fits a user specified signature
Peakflow SP Anomaly Reporting • Profiled Anomalies – deviations from normal traffic levels on the network • Misuse Anomalies – Traffic towards specific hosts that exceed what should normally be seen on a network • Fingerprint/Worm Anomalies – Traffic that fits a user specified signature
 Detect Attack - Profiled Anomalies • Detects network-wide anomalies such as DDo. S attacks and worm outbreaks in non-intrusive data collection methods. • A baseline of normal behavior leveraging flow data available from the routers deployed on the network would be built. • In real-time, the system compares traffic against the baseline.
Detect Attack - Profiled Anomalies • Detects network-wide anomalies such as DDo. S attacks and worm outbreaks in non-intrusive data collection methods. • A baseline of normal behavior leveraging flow data available from the routers deployed on the network would be built. • In real-time, the system compares traffic against the baseline.
 Detection Classes: Misuse • Detected independently from the established baselines, on a set of known attack signatures. • Traffic of specific types exceeding what should be normal for a network. • Misuse anomalies cover the following types of traffic: – ICMP Anomaly – – – TCP NULL Flag Anomaly TCP SYN Flag Anomaly TCP RST Flag Anomaly IP NULL (Proto 0) Anomaly IP Fragmentation Anomaly IP Private Address Space Anomaly
Detection Classes: Misuse • Detected independently from the established baselines, on a set of known attack signatures. • Traffic of specific types exceeding what should be normal for a network. • Misuse anomalies cover the following types of traffic: – ICMP Anomaly – – – TCP NULL Flag Anomaly TCP SYN Flag Anomaly TCP RST Flag Anomaly IP NULL (Proto 0) Anomaly IP Fragmentation Anomaly IP Private Address Space Anomaly
 Misuse Anomalies - Dark IP Fingerprint/Worm Anomalies(1) Tracing Anomalies • Automatically trace the source and destination IP/Port, TCP Flag of abnormal traffic. • Distribution of attack traffic by source and destination IP/Port. • Trace the network device that the abnormal traffic pass through.
Misuse Anomalies - Dark IP Fingerprint/Worm Anomalies(1) Tracing Anomalies • Automatically trace the source and destination IP/Port, TCP Flag of abnormal traffic. • Distribution of attack traffic by source and destination IP/Port. • Trace the network device that the abnormal traffic pass through.
 Prevent/Mitigate Network-wide Anomalies • System can recommend appropriate mitigation measures to mitigate anomalies such as Do. S attack and worm outbreaks. – Generate recommended ACLs or rate limit commands. – Blackhole routing – Sinkhole routing
Prevent/Mitigate Network-wide Anomalies • System can recommend appropriate mitigation measures to mitigate anomalies such as Do. S attack and worm outbreaks. – Generate recommended ACLs or rate limit commands. – Blackhole routing – Sinkhole routing
 Alert • BGP – BGP Instability – BGP Route Hijacking • Data Source – BGP Down – Flow Down – SNMP Down • Do. S Alert • Interface Usage: traffic exceeded configured baseline Use E-mail, SNMP Traps, Syslog etc to notify network administrators.
Alert • BGP – BGP Instability – BGP Route Hijacking • Data Source – BGP Down – Flow Down – SNMP Down • Do. S Alert • Interface Usage: traffic exceeded configured baseline Use E-mail, SNMP Traps, Syslog etc to notify network administrators.


