 Day 10 LAN
Day 10 LAN
 Why? • Allow more than one machine to share – Resources – Internet connectivity – Information
Why? • Allow more than one machine to share – Resources – Internet connectivity – Information
 Good • LANs are abstract from the hardware – HP printer will work with an IBM PC or a MAC or Linux – You usually don’t know what type of machine you are connecting to, it’s irrelevant since you both talk the same protocols. • More web servers run on Linux (apache) than windows (IIS), but you can access them all from windows.
Good • LANs are abstract from the hardware – HP printer will work with an IBM PC or a MAC or Linux – You usually don’t know what type of machine you are connecting to, it’s irrelevant since you both talk the same protocols. • More web servers run on Linux (apache) than windows (IIS), but you can access them all from windows.
 Shared Bus • Anytime we see a network where everyone shares a single wire (either physically or logically) – Traffic from any host to any host goes to all hosts – Everyone is supposed to ignore it unless it is addressed to them Computer
Shared Bus • Anytime we see a network where everyone shares a single wire (either physically or logically) – Traffic from any host to any host goes to all hosts – Everyone is supposed to ignore it unless it is addressed to them Computer
 Topologies • Tree – Cable TV – Single wire, bidirectional, can be broadband – Need Taps (jaws) – One break it all goes down – Shared Bus Computer Computer
Topologies • Tree – Cable TV – Single wire, bidirectional, can be broadband – Need Taps (jaws) – One break it all goes down – Shared Bus Computer Computer
 Star Wired Bus • Works like a bus (single wire) • Looks like a star (each workstation connects to central point) • Most networks use this today – Ethernet – Token Ring • Shared bus Computer
Star Wired Bus • Works like a bus (single wire) • Looks like a star (each workstation connects to central point) • Most networks use this today – Ethernet – Token Ring • Shared bus Computer
 Hubs • Workstations connect to hubs – Dumb repeaters – Take data in one port, broadcast it to all ports • Can be connected to other hubs via a crossover cable • Mostly obsolete Computer 1 Computer 2 HUB A Computer 3 Computer 4 Computer 5 HUB B
Hubs • Workstations connect to hubs – Dumb repeaters – Take data in one port, broadcast it to all ports • Can be connected to other hubs via a crossover cable • Mostly obsolete Computer 1 Computer 2 HUB A Computer 3 Computer 4 Computer 5 HUB B
 Media Access Control Protocol • Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) • Collision Detection (CD) – CSMA/CD – E. g. Ethernet • Listen for Carrier • Transmit and listen for collision • Wait and retransmit • 100 Mbps Ethernet has max speed of 40 Mbps because of collisions
Media Access Control Protocol • Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) • Collision Detection (CD) – CSMA/CD – E. g. Ethernet • Listen for Carrier • Transmit and listen for collision • Wait and retransmit • 100 Mbps Ethernet has max speed of 40 Mbps because of collisions
 CSMA/CA • Collision Avoidance: – a station that intends to transmit sends a jam signal – after waiting a sufficient time for all stations to receive the jam signal, the data station transmits a frame – while transmitting, if the data station detects a jam signal from another station, it stops transmitting for a random time and then tries again. ,
CSMA/CA • Collision Avoidance: – a station that intends to transmit sends a jam signal – after waiting a sufficient time for all stations to receive the jam signal, the data station transmits a frame – while transmitting, if the data station detects a jam signal from another station, it stops transmitting for a random time and then tries again. ,
 Star-Wired Ring • Token ring is the most common example – Every workstation connects to a Hub like device (MAU). – MAU creates a circle between workstations • Empty ports are shorted – Workstation adds data to ring, and removes it when it gets back. – Token decides who can talk Computer 1 Computer 2
Star-Wired Ring • Token ring is the most common example – Every workstation connects to a Hub like device (MAU). – MAU creates a circle between workstations • Empty ports are shorted – Workstation adds data to ring, and removes it when it gets back. – Token decides who can talk Computer 1 Computer 2
 Token Ring 802. 5 • Round Robin Protocol – – – Single token No collisions More efficient More expensive Slower speeds Basically dead
Token Ring 802. 5 • Round Robin Protocol – – – Single token No collisions More efficient More expensive Slower speeds Basically dead
 Wireless • Access point – Converts from wireless to wired – Can be more than one used to blanket a larger area Computer
Wireless • Access point – Converts from wireless to wired – Can be more than one used to blanket a larger area Computer
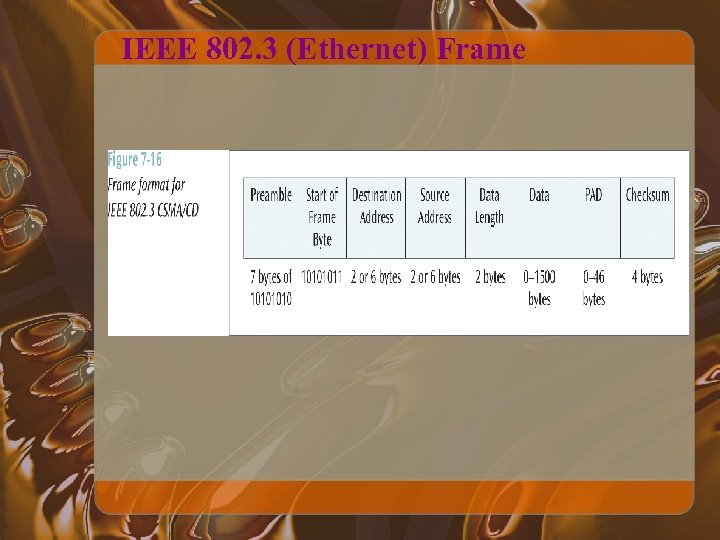 IEEE 802. 3 (Ethernet) Frame
IEEE 802. 3 (Ethernet) Frame
![Ethernet – [speed][base/broad][distance (in 100 meters) • 10 Base 2 – 10 Mbps baseband Ethernet – [speed][base/broad][distance (in 100 meters) • 10 Base 2 – 10 Mbps baseband](https://present5.com/presentation/309b320078a9493279a8ad96a128391e/image-14.jpg) Ethernet – [speed][base/broad][distance (in 100 meters) • 10 Base 2 – 10 Mbps baseband signal for 200 meters • 10 Base. T – 10 Mbps baseband signal for 100 meters • 100 base. T – 100 Mbps baseband for 100 meters • 1000 base. T • 1000 Base. Fx – 1000 m, SX/LX – 100 m, LX • 10 Gbase-fiber/T
Ethernet – [speed][base/broad][distance (in 100 meters) • 10 Base 2 – 10 Mbps baseband signal for 200 meters • 10 Base. T – 10 Mbps baseband signal for 100 meters • 100 base. T – 100 Mbps baseband for 100 meters • 1000 base. T • 1000 Base. Fx – 1000 m, SX/LX – 100 m, LX • 10 Gbase-fiber/T