b71367197ab3b256e00059e5c7c05636.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Dave Cavena HPA Tech Retreat February 16, 2012 ARCHIVING CONTENT DIGITALLY

15 min = 3 Points Longevity Accuracy - Readability Cost

Longevity Film has proved an excellent media on which to archive images The archive is the only part of the workflow that has not been digitized We archiving exactly not what we create and watch

Longevity “the data is the master record” – Leon Silverman, Opening Remarks, JTS 2004 “All polymers are subject to decay. ” – W. Mark Ritchie, KINEMA, 1995 “Traditional analog methods of archiving cannot keep up with … the loss of analog process expertise. ” – Dan Rosen, VP, WB, May 2007

Longevity In a “perfect” archive, the archive would retain the content … forever Nothing in the physical world could cause its deterioration This cannot happen if content is attached to a physical carrier. Only digital technology provides disintermediation

Accuracy - Readability Digital technology – HW and SW – change often YCM 3 -strip lasts a long time … recombination issues … generational loss

Accuracy Content integrity over extended time durations requires a managed archive A Digital Archive without an automated management SYSTEM is not an archive – it’s sheet metal, plastic & media

Model Overview Automated, rules-based software archive system Automated computer tape libraries Servers & front-end disk Why tape? Holo is too slow, disk too expensive When tape is replaced the robots & price point will survive

Model Overview Location 1 Location 2 Movie Copy 1 Movie Copy 3 Movie Copy 2 Movie Copy 4

Accuracy Irreplaceable content Multiple copies Multiple libraries Automated audit, copy Algorithmic assurance of bit integrity Error Correction Codes (ECC) Bit Error Detection Bit Error Correction

Accuracy ECC Standard on tape drives COTS technology Bit Error Rates (BER) differ by manufacturer ECC undetected BER = 10 -33 Four copies = 10 -132 ECC uncorrected BER = 10 -19 Four copies = 10 -76

Accuracy How big is the archive object? DCDM + Trims & Outs … 20 TB? 2 x 1013 Bytes 2 x 1014 bits OCN … 100 TB? 1014 Bytes 1015 bits

Accuracy ECC BER 10 -76 20 TB archive object 2 x 1014 bits = one bit lost in 2 x 1062 DCDM 100 TB archive object 1015 bits = one bit lost in 1061 objects Generational loss? Minimum 20 generations of migration

Accuracy For this application it doesn’t matter how many times the data is accessed; how many generations of rewrite ECC undetected = 1 -10 -19 … on one copy of four in the archive Failure probability one or more times during N accesses is = 1 -(1 -10 -19)N For N less than 1019, this is approximated by N*10 -19

Accuracy Example – one archived copy Assume a movie accessed 103 times The chance of an uncorrectable bit error per read is 10 -19 103 * 10 -19 = 10 -16 Model has four copies 103 * (2 * 10 -62) = 2 * 10 -59… one bit lost in 2 * 1059 (10 TB) 103 * 10 -61 = 10 -58 … one bit lost in 1058 (100 TB)
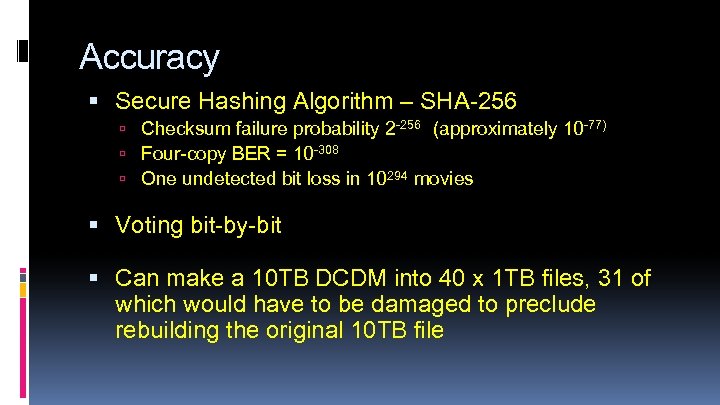
Accuracy Secure Hashing Algorithm – SHA-256 Checksum failure probability 2 -256 (approximately 10 -77) Four-copy BER = 10 -308 One undetected bit loss in 10294 movies Voting bit-by-bit Can make a 10 TB DCDM into 40 x 1 TB files, 31 of which would have to be damaged to preclude rebuilding the original 10 TB file

Accuracy Software Reliability A digital archive is a managed archive Audit every bit every 6 months Read in old format, rewrite in new format Image data is not changed, only the file wrapper, application accessing the file, or operating system running the app.

Digital Archive Longevity Accuracy Cost

Digital Cost Conservative pricing model List price, no depreciation or salvage HW, SW, Maintenance, Media 150% uplift (Avg $728 K/yr 20 TB; $826 K/yr 100 TB) Labor Floor space Electricity

What are the Film costs? Conformed OCN (6* x 2, 000’ cans of color film – stored) = $15, 000 12, 000’ color film, processed: $7, 800 -- $1. 00 / can / mo. storage fees 6 cans X 1200 months X $1. 00 / can / mo. = $7, 200 Color Match Print (6* x 2, 000’ cans of color film – stored) = $15, 000 Entire OCN (5* pallets of the OCN – color film – stored) = $70, 000 Color Separations (18* x 2, 000’ cans of film YCMs archived) = $29, 600 36, 000’ B&W film, processed = $8, 000 -- 18 cans X 1200 months X $1. 00 / can / mo. = $21, 600 $130, 000 * *approximately
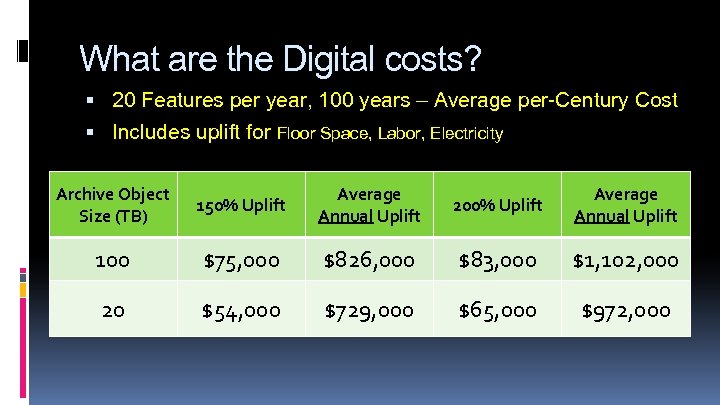
What are the Digital costs? 20 Features per year, 100 years – Average per-Century Cost Includes uplift for Floor Space, Labor, Electricity Archive Object Size (TB) 150% Uplift Average Annual Uplift 200% Uplift Average Annual Uplift 100 $75, 000 $826, 000 $83, 000 $1, 102, 000 20 $54, 000 $729, 000 $65, 000 $972, 000
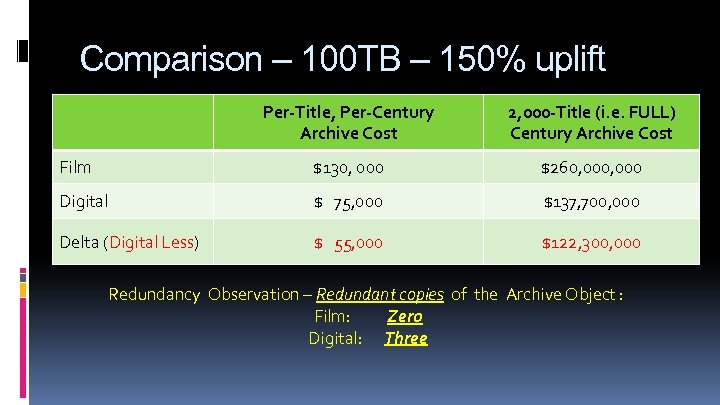
Comparison – 100 TB – 150% uplift Per-Title, Per-Century Archive Cost 2, 000 -Title (i. e. FULL) Century Archive Cost Film $130, 000 $260, 000 Digital $ 75, 000 $137, 700, 000 Delta (Digital Less) $ 55, 000 $122, 300, 000 Redundancy Observation – Redundant copies of the Archive Object : Film: Zero Digital: Three
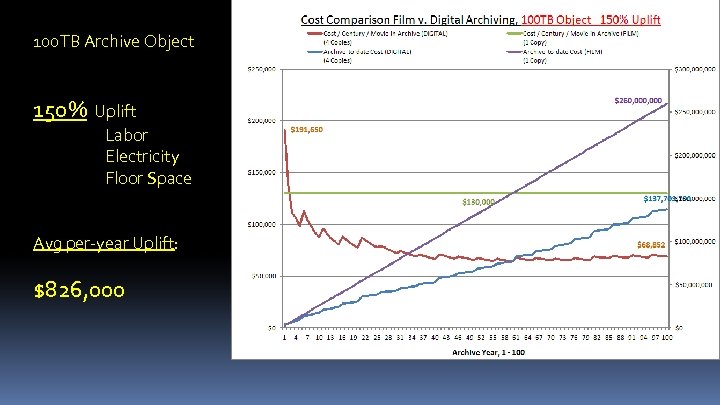
100 TB Archive Object 150% Uplift Labor Electricity Floor Space Avg per-year Uplift: $826, 000
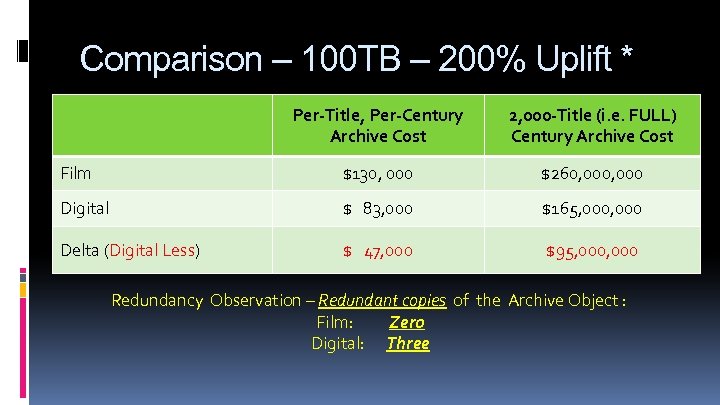
Comparison – 100 TB – 200% Uplift * Per-Title, Per-Century Archive Cost 2, 000 -Title (i. e. FULL) Century Archive Cost Film $130, 000 $260, 000 Digital $ 83, 000 $165, 000 Delta (Digital Less) $ 47, 000 $95, 000 Redundancy Observation – Redundant copies of the Archive Object : Film: Zero Digital: Three
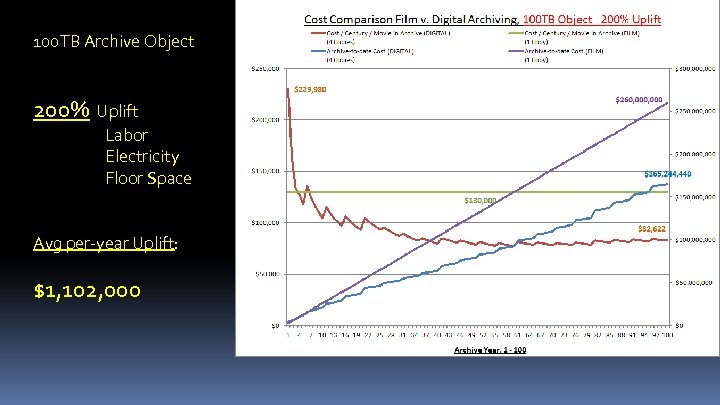
100 TB Archive Object 200% Uplift Labor Electricity Floor Space Avg per-year Uplift: $1, 102, 000
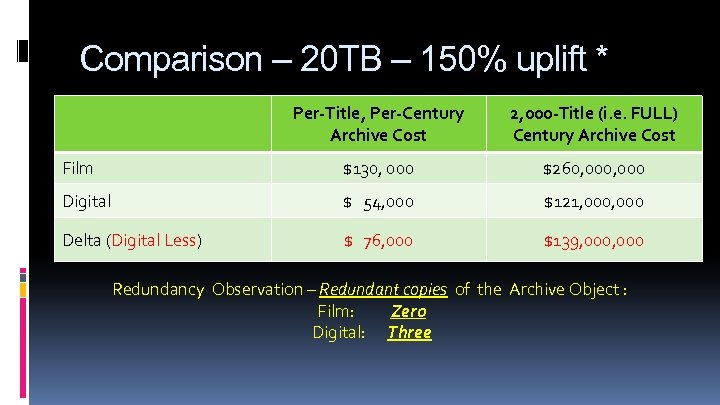
Comparison – 20 TB – 150% uplift * Per-Title, Per-Century Archive Cost 2, 000 -Title (i. e. FULL) Century Archive Cost Film $130, 000 $260, 000 Digital $ 54, 000 $121, 000 Delta (Digital Less) $ 76, 000 $139, 000 Redundancy Observation – Redundant copies of the Archive Object : Film: Zero Digital: Three
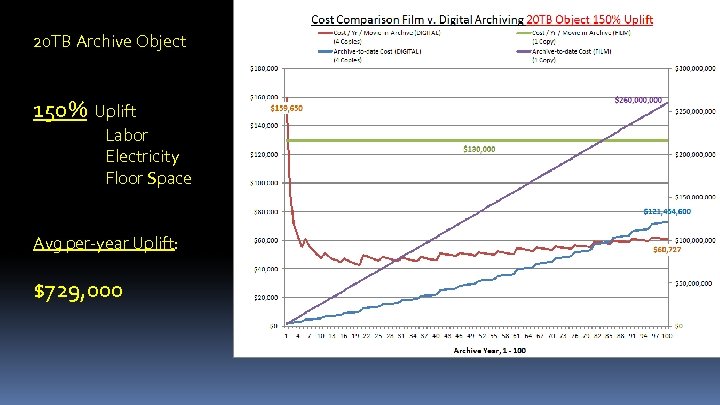
20 TB Archive Object 150% Uplift Labor Electricity Floor Space Avg per-year Uplift: $729, 000
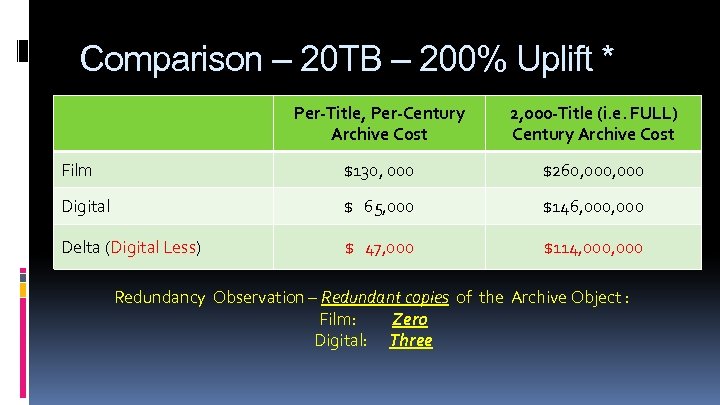
Comparison – 20 TB – 200% Uplift * Per-Title, Per-Century Archive Cost 2, 000 -Title (i. e. FULL) Century Archive Cost Film $130, 000 $260, 000 Digital $ 65, 000 $146, 000 Delta (Digital Less) $ 47, 000 $114, 000 Redundancy Observation – Redundant copies of the Archive Object : Film: Zero Digital: Three
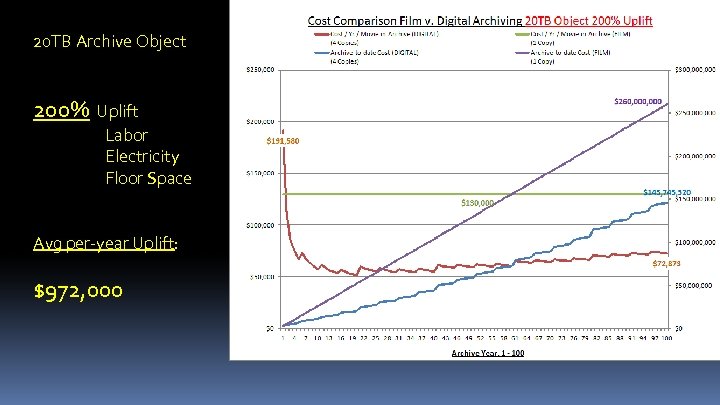
20 TB Archive Object 200% Uplift Labor Electricity Floor Space Avg per-year Uplift: $972, 000
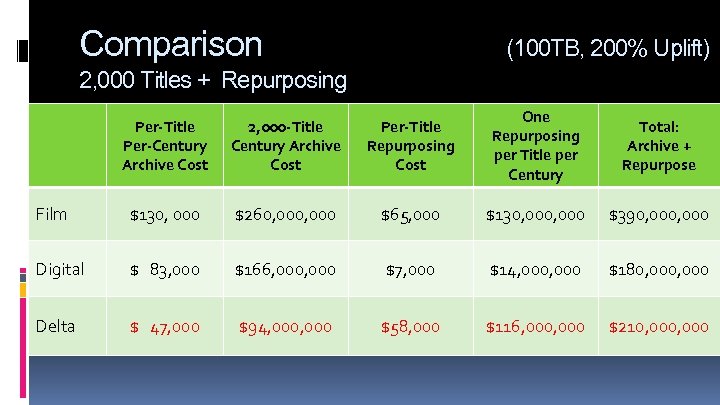
Comparison (100 TB, 200% Uplift) 2, 000 Titles + Repurposing Per-Title Per-Century Archive Cost 2, 000 -Title Century Archive Cost Per-Title Repurposing Cost One Repurposing per Title per Century Total: Archive + Repurpose Film $130, 000 $260, 000 $65, 000 $130, 000 $390, 000 Digital $ 83, 000 $166, 000 $7, 000 $14, 000 $180, 000 Delta $ 47, 000 $94, 000 $58, 000 $116, 000 $210, 000

Digital Archive Longevity Accuracy Cost
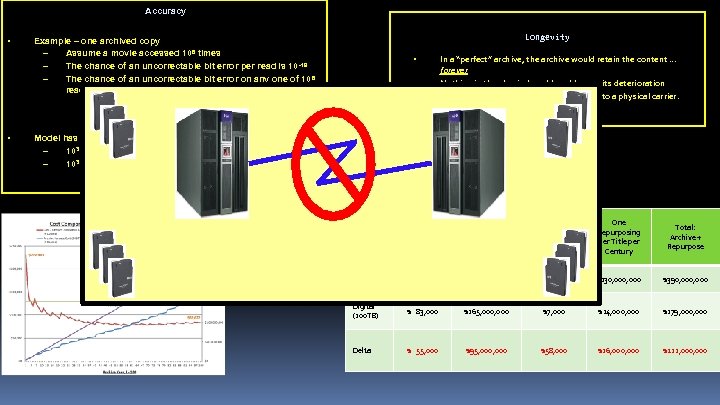
Accuracy • Longevity Example – one archived copy – Assume a movie accessed 106 times – The chance of an uncorrectable bit error per read is 10 -19 – The chance of an uncorrectable bit error on any one of 106 reads is • • 103 * 10 -19 = 10 -16 • In a “perfect” archive, the archive would retain the content … forever Nothing in the physical world could cause its deterioration This cannot happen if content is attached to a physical carrier. Disintermediation Model has four copies – 103 * (2 * 10 -63) = 2 * 10 -59… one bit lost in 2 * 1059 (10 TB) – 103 * 10 -62 = 10 -58 … one bit lost in 1058 (100 TB) Per-Title Per-Century Archive Cost 2, 000 -Title Century Archive Cost Per-Title Repurposing Cost One Repurposing per Title per Century Total: Archive + Repurpose Film $130, 000 $260, 000 $65, 000 $130, 000 $390, 000 Digital (100 TB) $ 83, 000 $165, 000 $7, 000 $14, 000 $179, 000 Delta $ 55, 000 $95, 000 $58, 000 $16, 000 $211, 000

If you remember only ONE thing… “Traditional analog methods of archiving cannot keep up with … the loss of analog process expertise. ” – Dan Rosen, VP, WB, May 2007

Model Overview Location 1 Location 2 Movie Copy 1 Movie Copy 3 Movie Copy 2 Movie Copy 4

ARCHIVING CONTENT DIGITALLY Thank You For further discussion: • Google: “Archiving Movies in a Digital World” (2008) • Grab me in the hall • Breakfast Roundtable tomorrow • Office: 626 -812 -0930, cell: 626 -488 -3100 • Dave. Cavena@Image. Trends. Inc. com
b71367197ab3b256e00059e5c7c05636.ppt