2e1a8692589e662d3d19587532c47eb6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Date DRILL 1. Why are the + and – symbols unnecessary when drawing the DC power source in an electric schematic? 1. The length of the lines tell you which is positive and which is negative. U 3 e-L 3
Date DRILL 1. Why are the + and – symbols unnecessary when drawing the DC power source in an electric schematic? 1. The length of the lines tell you which is positive and which is negative. U 3 e-L 3
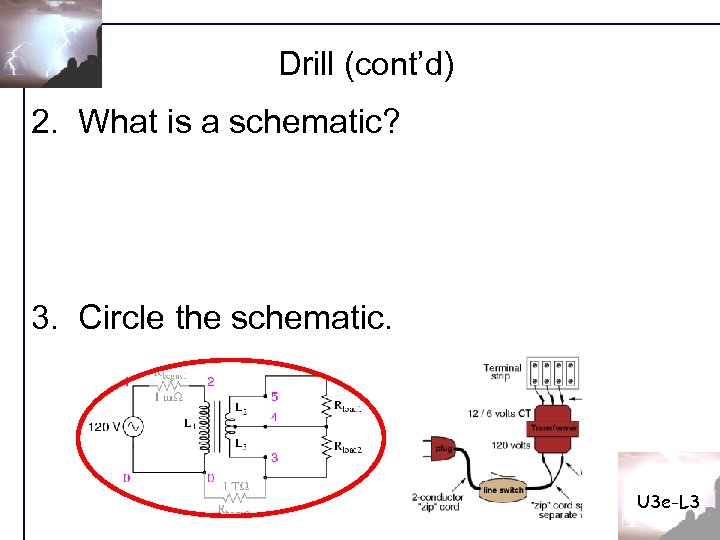 Drill (cont’d) 2. What is a schematic? 3. Circle the schematic. U 3 e-L 3
Drill (cont’d) 2. What is a schematic? 3. Circle the schematic. U 3 e-L 3
 Drill (cont’d) Joule’s Law & Ohm’s Law P=VI & V=IR 4. An electric fan has a power of 600 W. The voltage is 120 v AC. What is the current in this circuit? What is the resistance? (1 Schematic, 1 Table, 2 formulae, 2 calculations, 2 answers) U 3 e-L 3
Drill (cont’d) Joule’s Law & Ohm’s Law P=VI & V=IR 4. An electric fan has a power of 600 W. The voltage is 120 v AC. What is the current in this circuit? What is the resistance? (1 Schematic, 1 Table, 2 formulae, 2 calculations, 2 answers) U 3 e-L 3
 Good use of electricity
Good use of electricity
 Bad use of electricity
Bad use of electricity
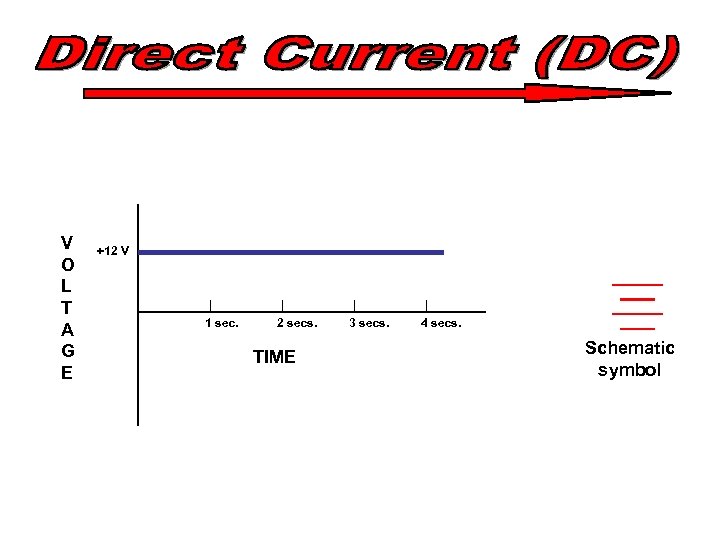 V O L T A G E +12 V 1 sec. 2 secs. TIME 3 secs. 4 secs. Schematic symbol
V O L T A G E +12 V 1 sec. 2 secs. TIME 3 secs. 4 secs. Schematic symbol
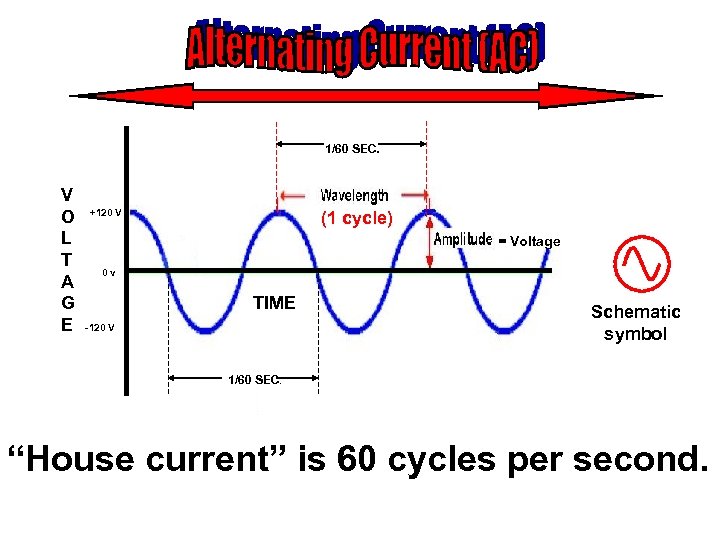 1/60 SEC. V O L T A G E +120 V (1 cycle) = Voltage 0 v TIME -120 V Schematic symbol 1/60 SEC. “House current” is 60 cycles per second.
1/60 SEC. V O L T A G E +120 V (1 cycle) = Voltage 0 v TIME -120 V Schematic symbol 1/60 SEC. “House current” is 60 cycles per second.
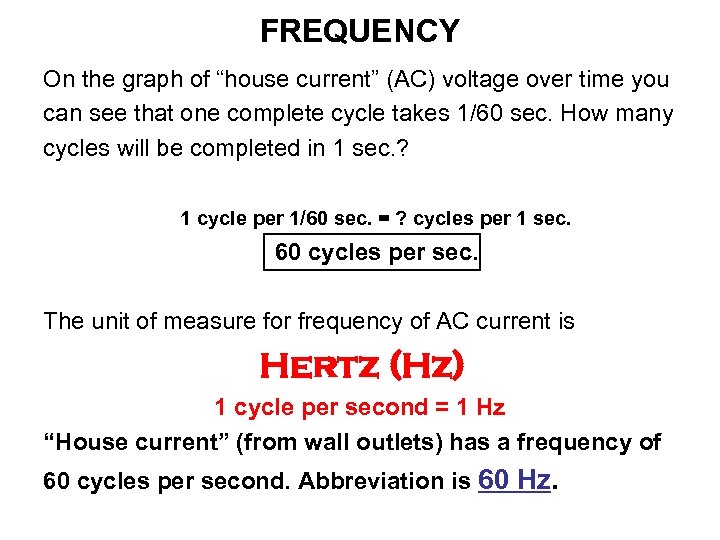 FREQUENCY On the graph of “house current” (AC) voltage over time you can see that one complete cycle takes 1/60 sec. How many cycles will be completed in 1 sec. ? 1 cycle per 1/60 sec. = ? cycles per 1 sec. 60 cycles per sec. The unit of measure for frequency of AC current is Hertz (Hz) 1 cycle per second = 1 Hz “House current” (from wall outlets) has a frequency of 60 cycles per second. Abbreviation is 60 Hz.
FREQUENCY On the graph of “house current” (AC) voltage over time you can see that one complete cycle takes 1/60 sec. How many cycles will be completed in 1 sec. ? 1 cycle per 1/60 sec. = ? cycles per 1 sec. 60 cycles per sec. The unit of measure for frequency of AC current is Hertz (Hz) 1 cycle per second = 1 Hz “House current” (from wall outlets) has a frequency of 60 cycles per second. Abbreviation is 60 Hz.
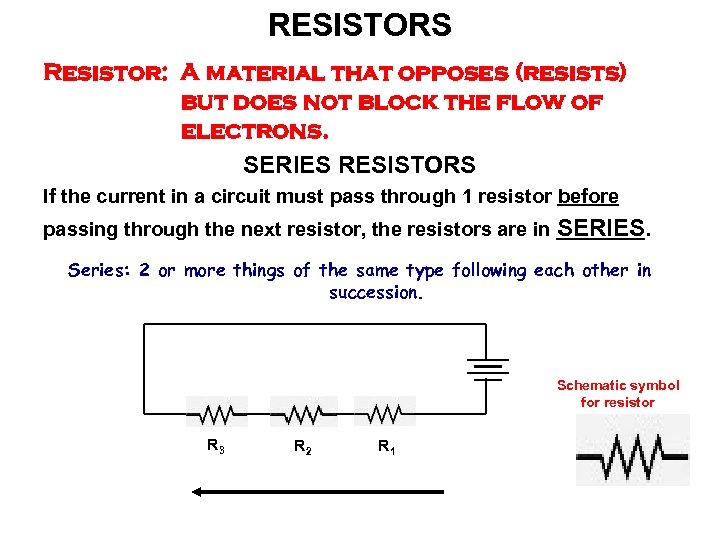 RESISTORS Resistor: A material that opposes (resists) but does not block the flow of electrons. SERIES RESISTORS If the current in a circuit must pass through 1 resistor before passing through the next resistor, the resistors are in SERIES. Series: 2 or more things of the same type following each other in succession. Schematic symbol for resistor R 3 R 2 R 1
RESISTORS Resistor: A material that opposes (resists) but does not block the flow of electrons. SERIES RESISTORS If the current in a circuit must pass through 1 resistor before passing through the next resistor, the resistors are in SERIES. Series: 2 or more things of the same type following each other in succession. Schematic symbol for resistor R 3 R 2 R 1
 RESISTANCE Resistance: A measure of the degree to which a material opposes (resists) electron FLOW. The total Resistance (RT) of resistors in is the sum of their values. RT = R 1 + R 2 + R 3…… series
RESISTANCE Resistance: A measure of the degree to which a material opposes (resists) electron FLOW. The total Resistance (RT) of resistors in is the sum of their values. RT = R 1 + R 2 + R 3…… series
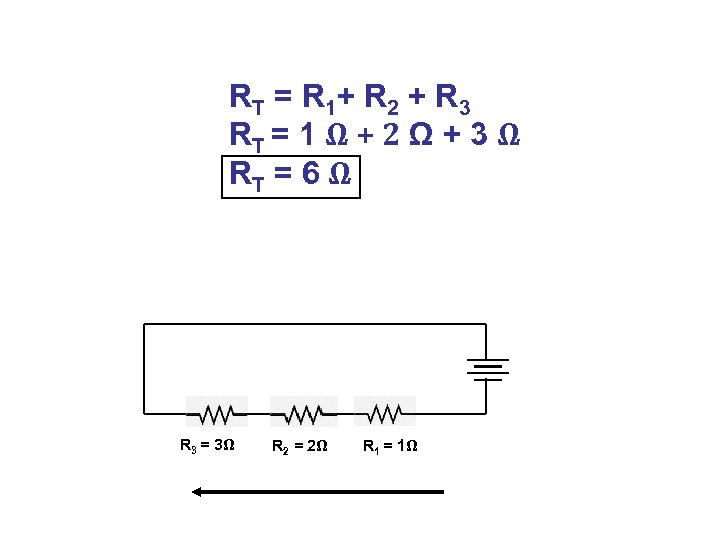 R T = R 1+ R 2 + R 3 RT = 1 Ω + 2 Ω + 3 Ω RT = 6 Ω R 3 = 3Ω R 2 = 2Ω R 1 = 1Ω
R T = R 1+ R 2 + R 3 RT = 1 Ω + 2 Ω + 3 Ω RT = 6 Ω R 3 = 3Ω R 2 = 2Ω R 1 = 1Ω
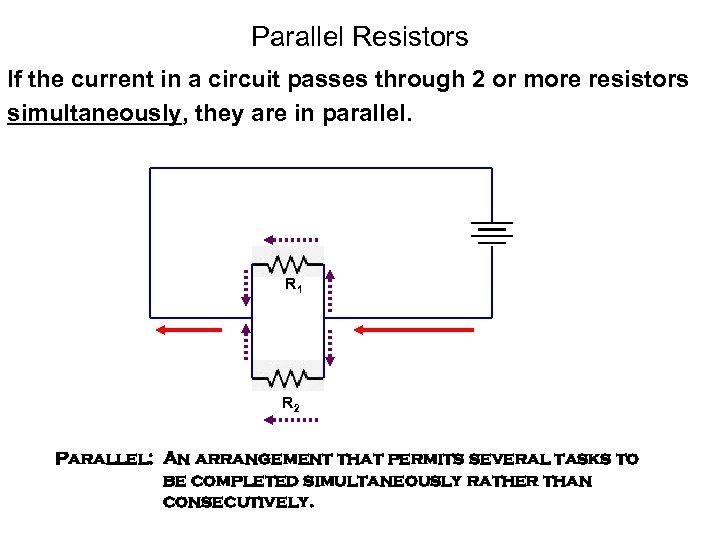 Parallel Resistors If the current in a circuit passes through 2 or more resistors simultaneously, they are in parallel. R 1 R 2 Parallel: An arrangement that permits several tasks to be completed simultaneously rather than consecutively.
Parallel Resistors If the current in a circuit passes through 2 or more resistors simultaneously, they are in parallel. R 1 R 2 Parallel: An arrangement that permits several tasks to be completed simultaneously rather than consecutively.
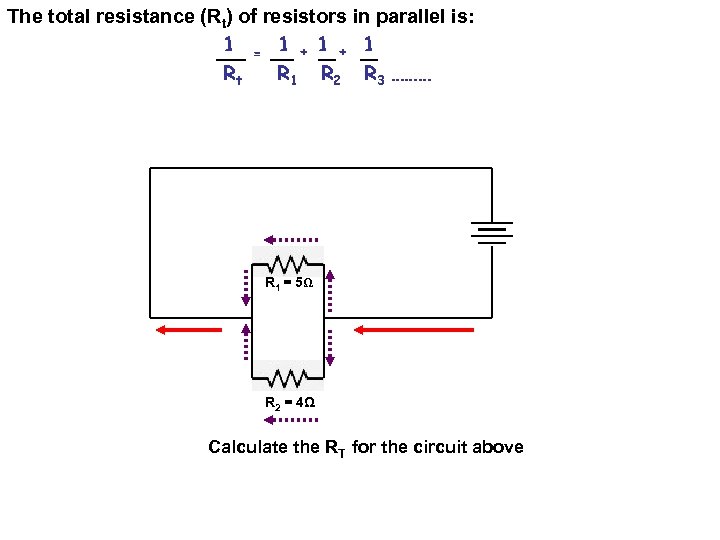 The total resistance (Rt) of resistors in parallel is: 1 = 1 + 1 Rt R 1 R 2 R 3 ……… R 1 = 5Ω R 2 = 4Ω Calculate the RT for the circuit above
The total resistance (Rt) of resistors in parallel is: 1 = 1 + 1 Rt R 1 R 2 R 3 ……… R 1 = 5Ω R 2 = 4Ω Calculate the RT for the circuit above
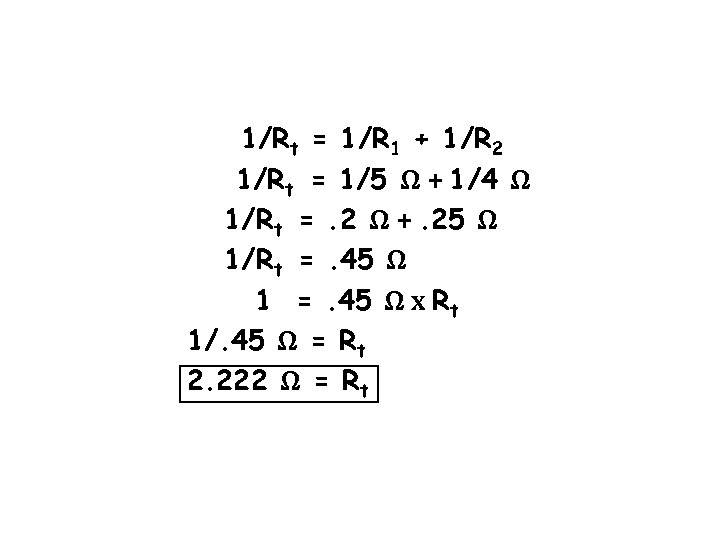 1/Rt = 1/R 1 + 1/R 2 1/Rt = 1/5 Ω + 1/4 Ω 1/Rt =. 2 Ω +. 25 Ω 1/Rt =. 45 Ω 1 =. 45 Ω x Rt 1/. 45 Ω = Rt 2. 222 Ω = Rt
1/Rt = 1/R 1 + 1/R 2 1/Rt = 1/5 Ω + 1/4 Ω 1/Rt =. 2 Ω +. 25 Ω 1/Rt =. 45 Ω 1 =. 45 Ω x Rt 1/. 45 Ω = Rt 2. 222 Ω = Rt
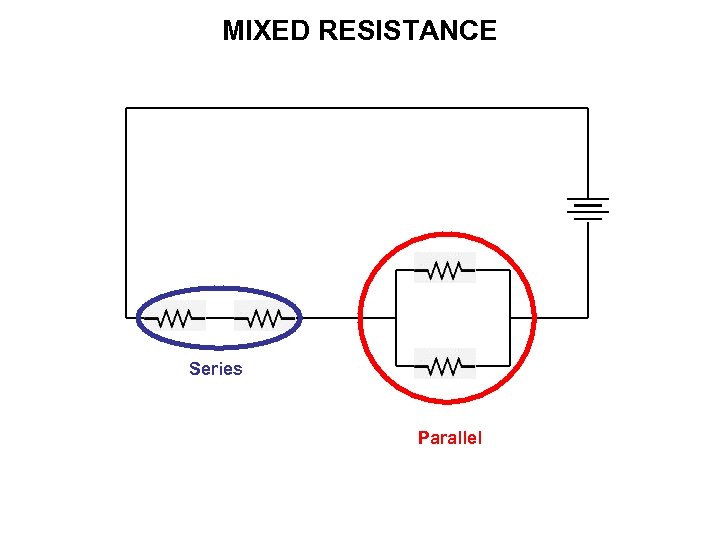 MIXED RESISTANCE Series Parallel
MIXED RESISTANCE Series Parallel
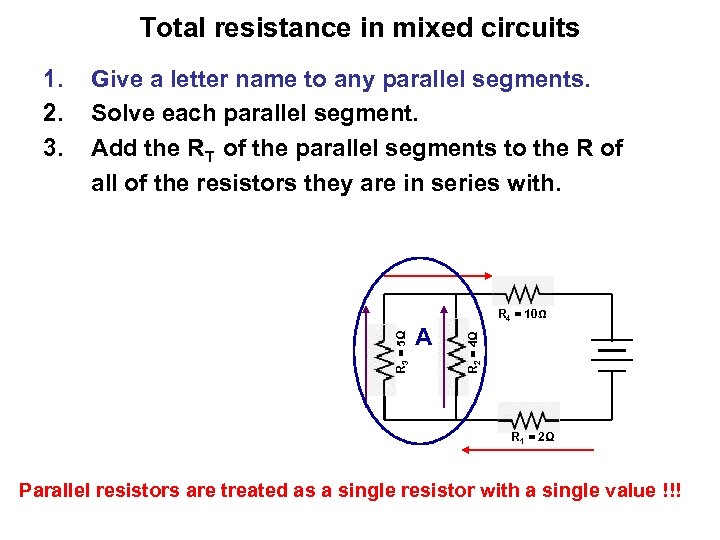 Total resistance in mixed circuits 1. 2. 3. Give a letter name to any parallel segments. Solve each parallel segment. Add the RT of the parallel segments to the R of all of the resistors they are in series with. A R 2 = 4Ω R 3 = 5Ω R 4 = 10Ω R 1 = 2Ω Parallel resistors are treated as a single resistor with a single value !!!
Total resistance in mixed circuits 1. 2. 3. Give a letter name to any parallel segments. Solve each parallel segment. Add the RT of the parallel segments to the R of all of the resistors they are in series with. A R 2 = 4Ω R 3 = 5Ω R 4 = 10Ω R 1 = 2Ω Parallel resistors are treated as a single resistor with a single value !!!
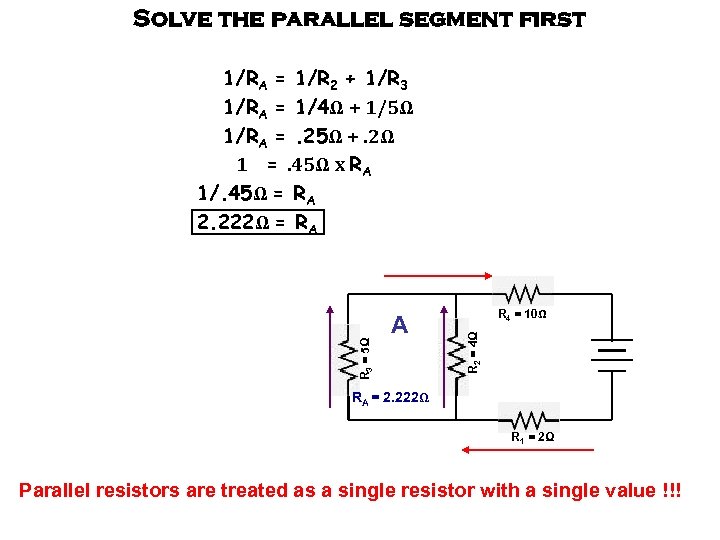 Solve the parallel segment first A R 4 = 10Ω R 2 = 4Ω R 3 = 5Ω 1/RA = 1/R 2 + 1/R 3 1/RA = 1/4Ω + 1/5Ω 1/RA =. 25Ω +. 2Ω 1 =. 45Ω x RA 1/. 45Ω = RA 2. 222Ω = RA RA = 2. 222Ω R 1 = 2Ω Parallel resistors are treated as a single resistor with a single value !!!
Solve the parallel segment first A R 4 = 10Ω R 2 = 4Ω R 3 = 5Ω 1/RA = 1/R 2 + 1/R 3 1/RA = 1/4Ω + 1/5Ω 1/RA =. 25Ω +. 2Ω 1 =. 45Ω x RA 1/. 45Ω = RA 2. 222Ω = RA RA = 2. 222Ω R 1 = 2Ω Parallel resistors are treated as a single resistor with a single value !!!
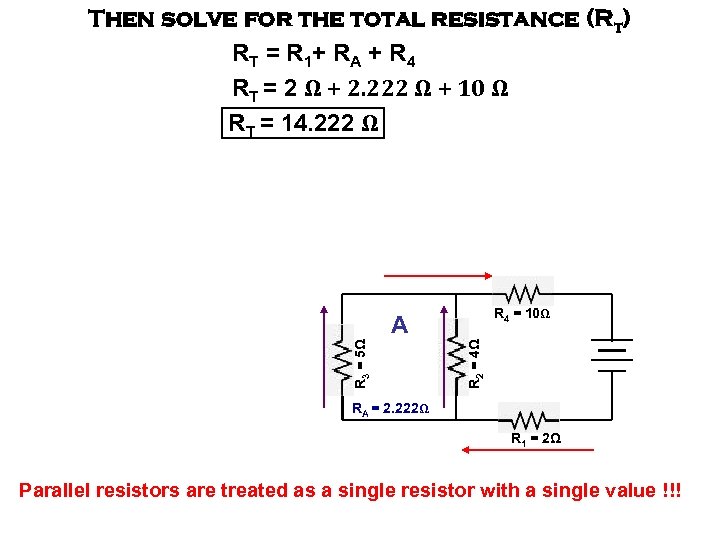 Then solve for the total resistance (Rt) R T = R 1+ R A + R 4 RT = 2 Ω + 2. 222 Ω + 10 Ω RT = 14. 222 Ω R 4 = 10Ω R 2 = 4Ω R 3 = 5Ω A RA = 2. 222Ω R 1 = 2Ω Parallel resistors are treated as a single resistor with a single value !!!
Then solve for the total resistance (Rt) R T = R 1+ R A + R 4 RT = 2 Ω + 2. 222 Ω + 10 Ω RT = 14. 222 Ω R 4 = 10Ω R 2 = 4Ω R 3 = 5Ω A RA = 2. 222Ω R 1 = 2Ω Parallel resistors are treated as a single resistor with a single value !!!
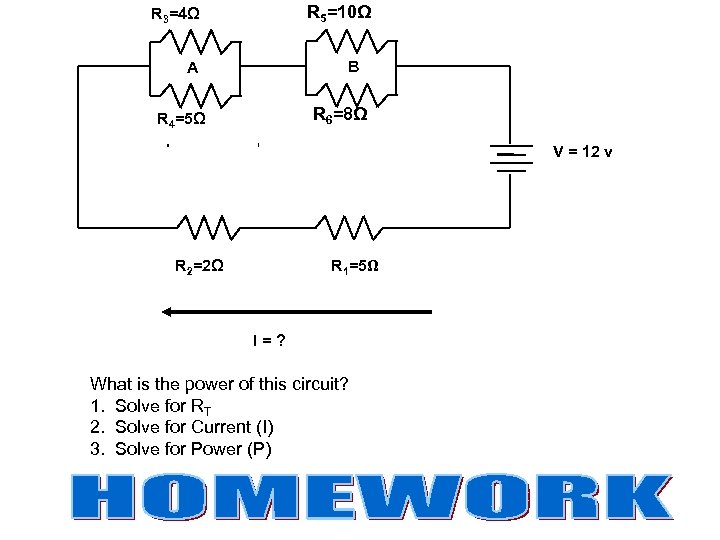 R 5=10Ω R 3=4Ω B A R 6=8Ω R 4=5Ω V = 12 v R 2=2Ω R 1=5Ω I=? What is the power of this circuit? 1. Solve for RT 2. Solve for Current (I) 3. Solve for Power (P)
R 5=10Ω R 3=4Ω B A R 6=8Ω R 4=5Ω V = 12 v R 2=2Ω R 1=5Ω I=? What is the power of this circuit? 1. Solve for RT 2. Solve for Current (I) 3. Solve for Power (P)
 Do homework here
Do homework here


