6e37f64b57ff7e99326754b42a45b30a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Date: 6 June 2016 Dispenser printed actively controlled thermochromic colour changing device on fabric for smart fabric applications Y Wei, Z Ahmed, R Torah and J Tudor University of Southampton CIMTEC 2016, Perugia, Italy FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Date: 6 June 2016 Dispenser printed actively controlled thermochromic colour changing device on fabric for smart fabric applications Y Wei, Z Ahmed, R Torah and J Tudor University of Southampton CIMTEC 2016, Perugia, Italy FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
 Overview o EU CREATIF project o Chromism o Materials o Dispenser printing o Results o Conclusions FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Overview o EU CREATIF project o Chromism o Materials o Dispenser printing o Results o Conclusions FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
 CREATIF project o This research is funded within an EU project: CREATIF (www. creatif. ecs. soton. ac. uk) of which the target is to offer the creative and cultural industries state of the art printed smart fabrics and collaborative design software. o Smart fabric creative applications are: proximity sensing, electroluminescence, colour change and sound emission. o Demonstrating the fundamentals of a dispenser printing process to achieve thermochromic devices on fabric substrates. FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
CREATIF project o This research is funded within an EU project: CREATIF (www. creatif. ecs. soton. ac. uk) of which the target is to offer the creative and cultural industries state of the art printed smart fabrics and collaborative design software. o Smart fabric creative applications are: proximity sensing, electroluminescence, colour change and sound emission. o Demonstrating the fundamentals of a dispenser printing process to achieve thermochromic devices on fabric substrates. FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
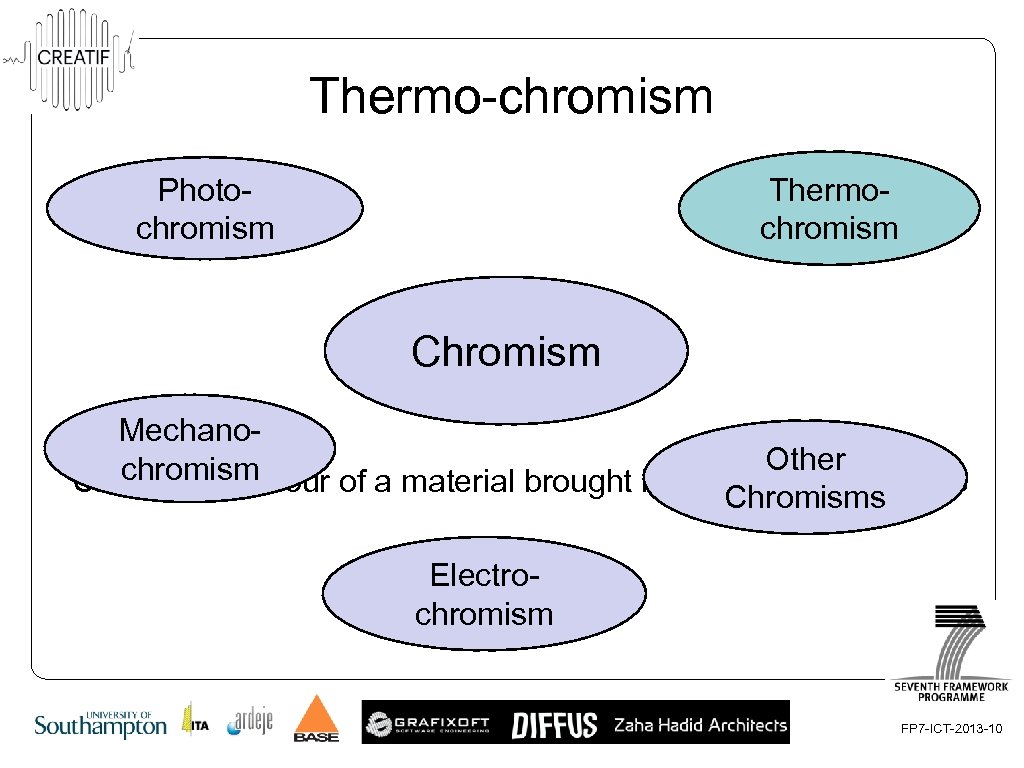 Thermo-chromism Thermochromism Photochromism Chromism Mechano. Other chromism Changes in colour of a material brought by an Chromisms external stimulus Electrochromism FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Thermo-chromism Thermochromism Photochromism Chromism Mechano. Other chromism Changes in colour of a material brought by an Chromisms external stimulus Electrochromism FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
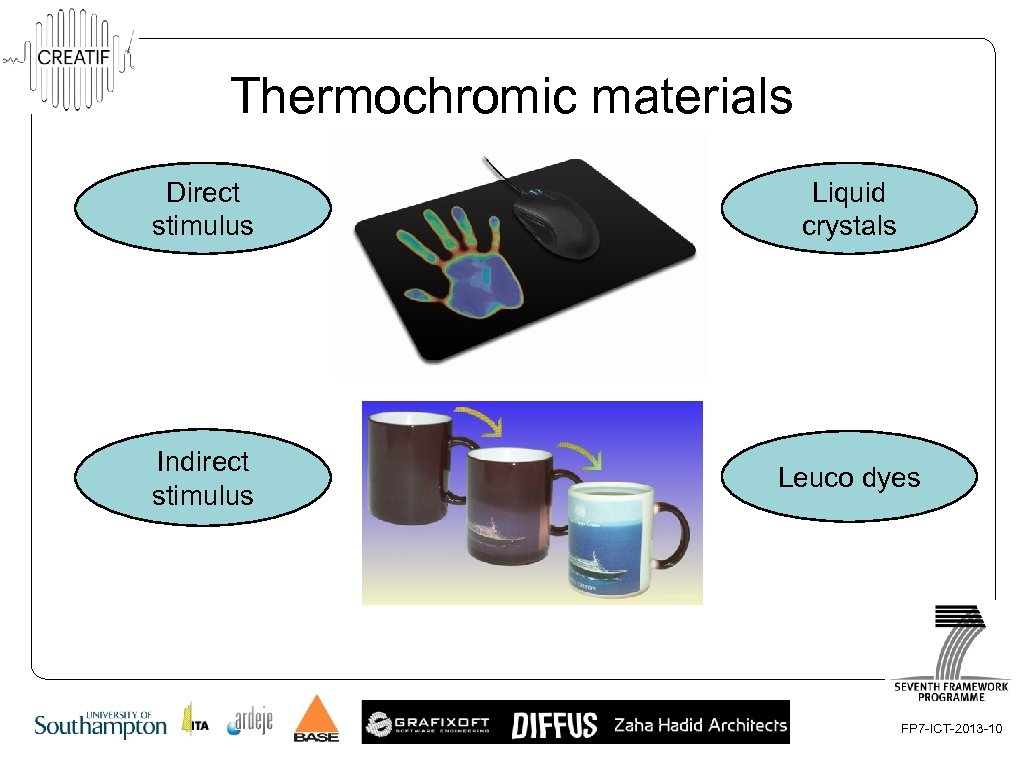 Thermochromic materials Direct stimulus Structural properties (Physical) Liquid crystals Indirect stimulus Chromophore (Chemical) Leuco dyes FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Thermochromic materials Direct stimulus Structural properties (Physical) Liquid crystals Indirect stimulus Chromophore (Chemical) Leuco dyes FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
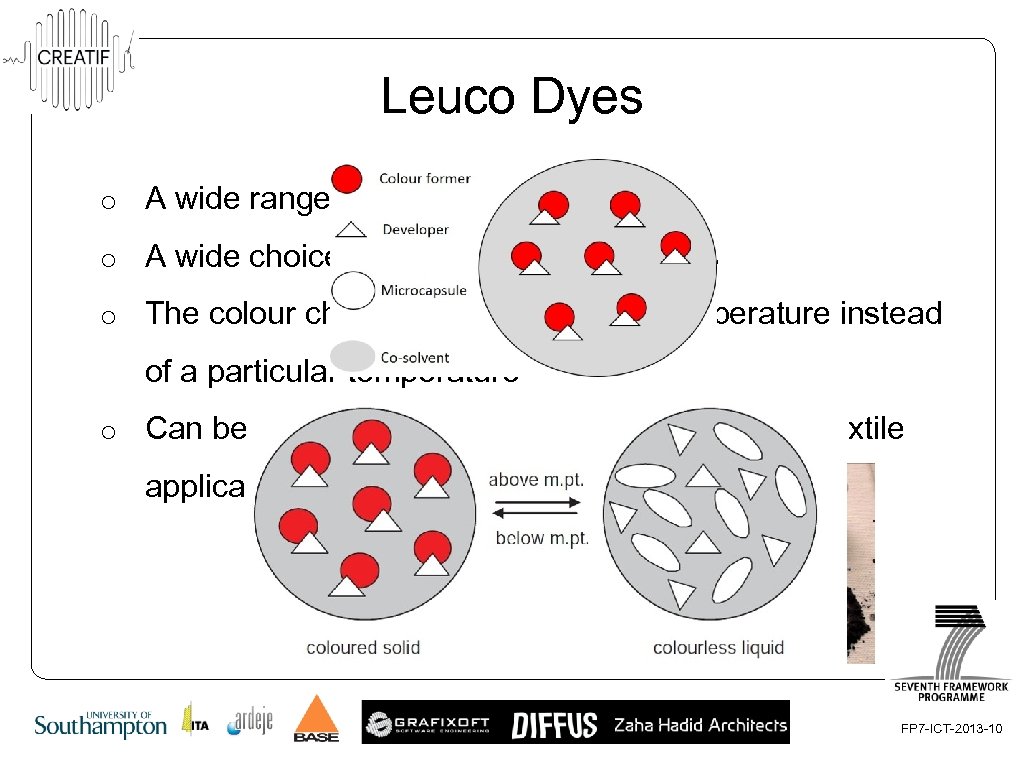 Leuco Dyes o A wide range of colours available o A wide choice of activation temperatures o The colour changes over a range of temperature instead of a particular temperature o Can be easily formulated into a printable ink for textile applications FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Leuco Dyes o A wide range of colours available o A wide choice of activation temperatures o The colour changes over a range of temperature instead of a particular temperature o Can be easily formulated into a printable ink for textile applications FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
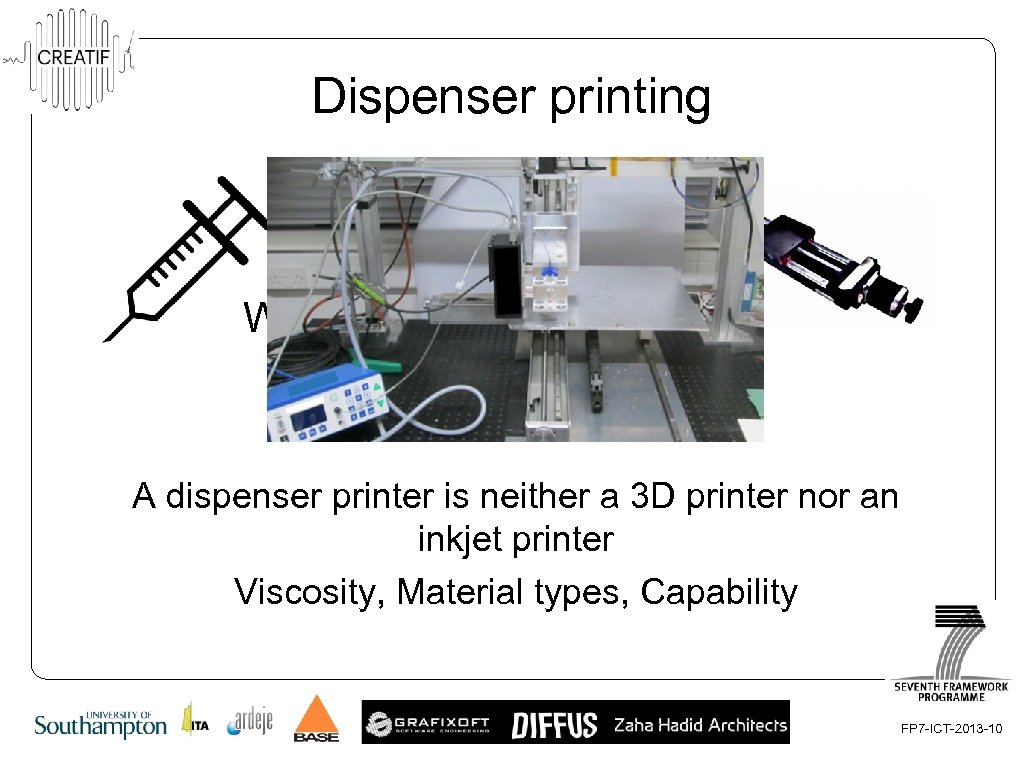 Dispenser printing What is a dispenser printer? A dispenser printer is neither a 3 D printer nor an inkjet printer Viscosity, Material types, Capability FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Dispenser printing What is a dispenser printer? A dispenser printer is neither a 3 D printer nor an inkjet printer Viscosity, Material types, Capability FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
 Active control thermochromic materials o The colour changing of a thermochromic material can be triggered passively or actively (electronically). o A printed resistive heater controls the colour changing process of thermochromic device. o The temperature generated from the heater must match the activation temperature of thermochromic material. o The thermochromic device can interact with other external sensors. FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Active control thermochromic materials o The colour changing of a thermochromic material can be triggered passively or actively (electronically). o A printed resistive heater controls the colour changing process of thermochromic device. o The temperature generated from the heater must match the activation temperature of thermochromic material. o The thermochromic device can interact with other external sensors. FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
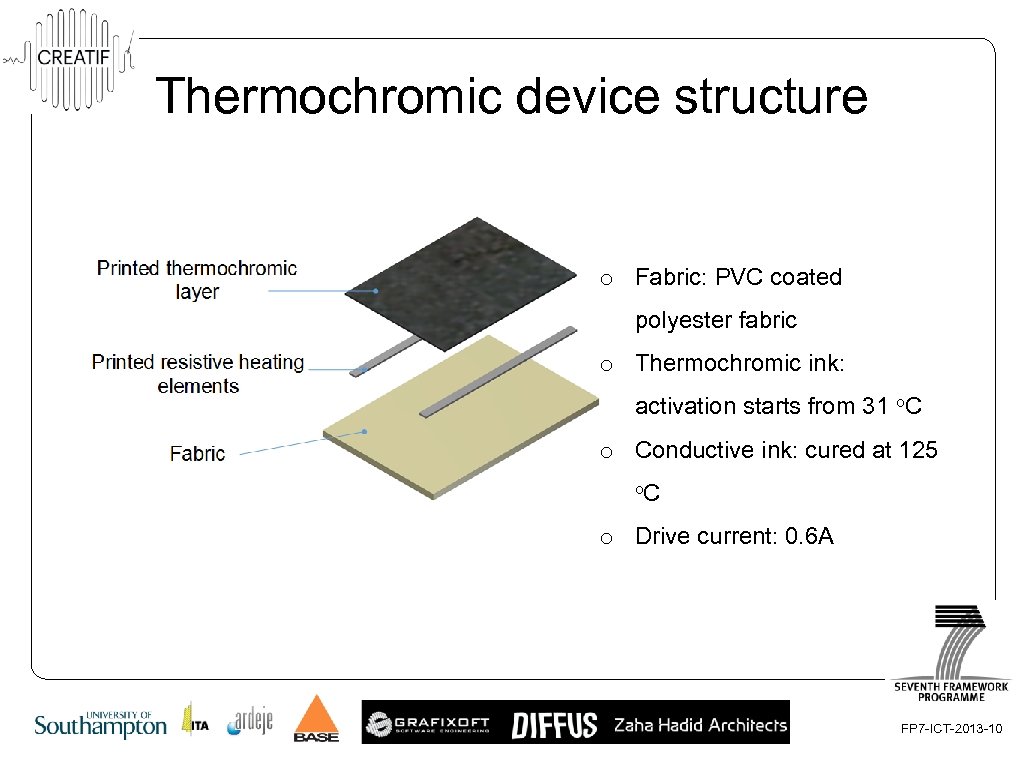 Thermochromic device structure o Fabric: PVC coated polyester fabric o Thermochromic ink: activation starts from 31 o. C o Conductive ink: cured at 125 o. C o Drive current: 0. 6 A FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Thermochromic device structure o Fabric: PVC coated polyester fabric o Thermochromic ink: activation starts from 31 o. C o Conductive ink: cured at 125 o. C o Drive current: 0. 6 A FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
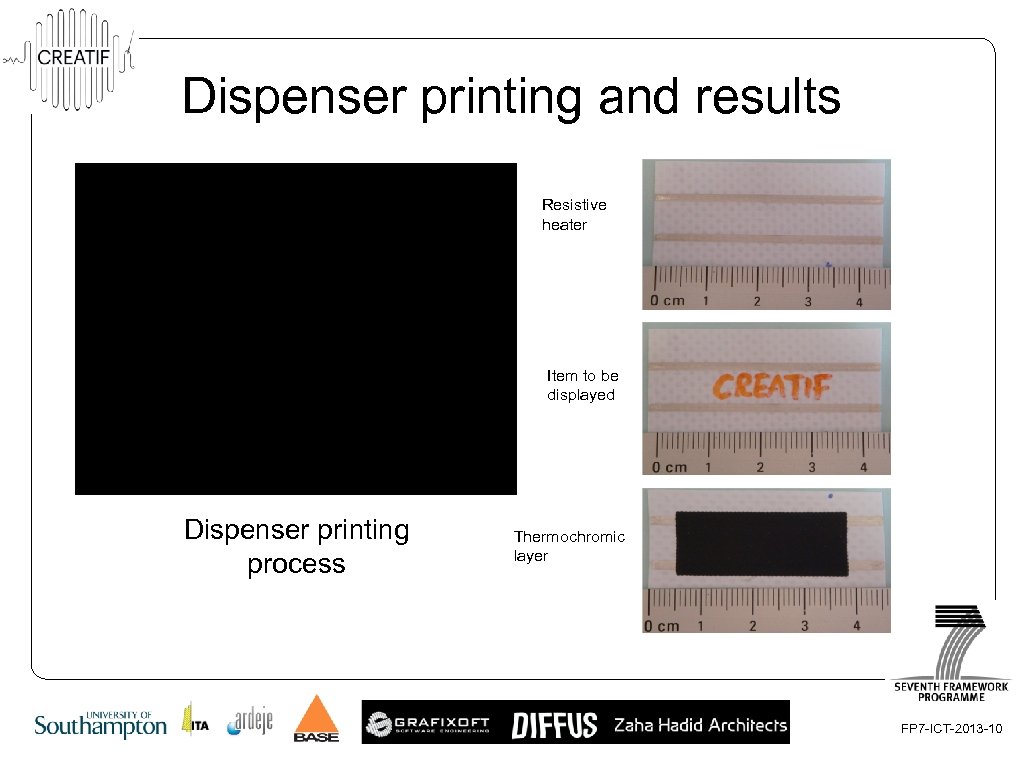 Dispenser printing and results Resistive heater Item to be displayed Dispenser printing process Thermochromic layer FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Dispenser printing and results Resistive heater Item to be displayed Dispenser printing process Thermochromic layer FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
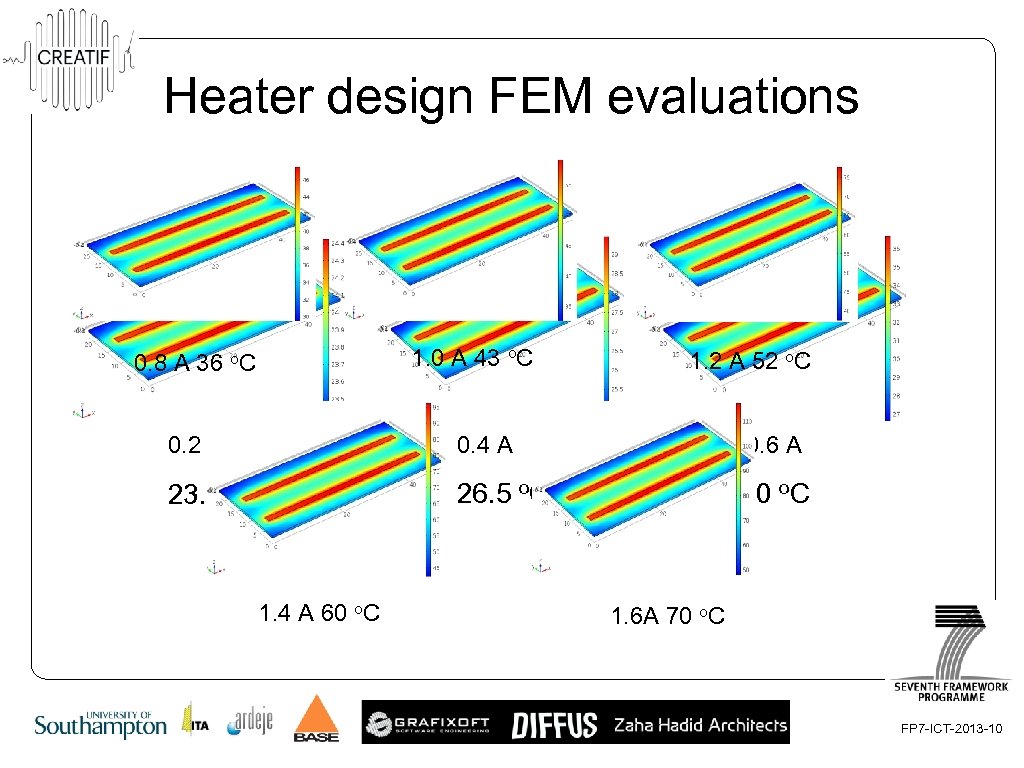 Heater design FEM evaluations 1. 0 A 43 o. C 0. 8 A 36 o. C 1. 2 A 52 o. C 0. 2 A 0. 4 A 0. 6 A 23. 7 o. C 26. 5 o. C 30 o. C 1. 4 A 60 o. C 1. 6 A 70 o. C FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Heater design FEM evaluations 1. 0 A 43 o. C 0. 8 A 36 o. C 1. 2 A 52 o. C 0. 2 A 0. 4 A 0. 6 A 23. 7 o. C 26. 5 o. C 30 o. C 1. 4 A 60 o. C 1. 6 A 70 o. C FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
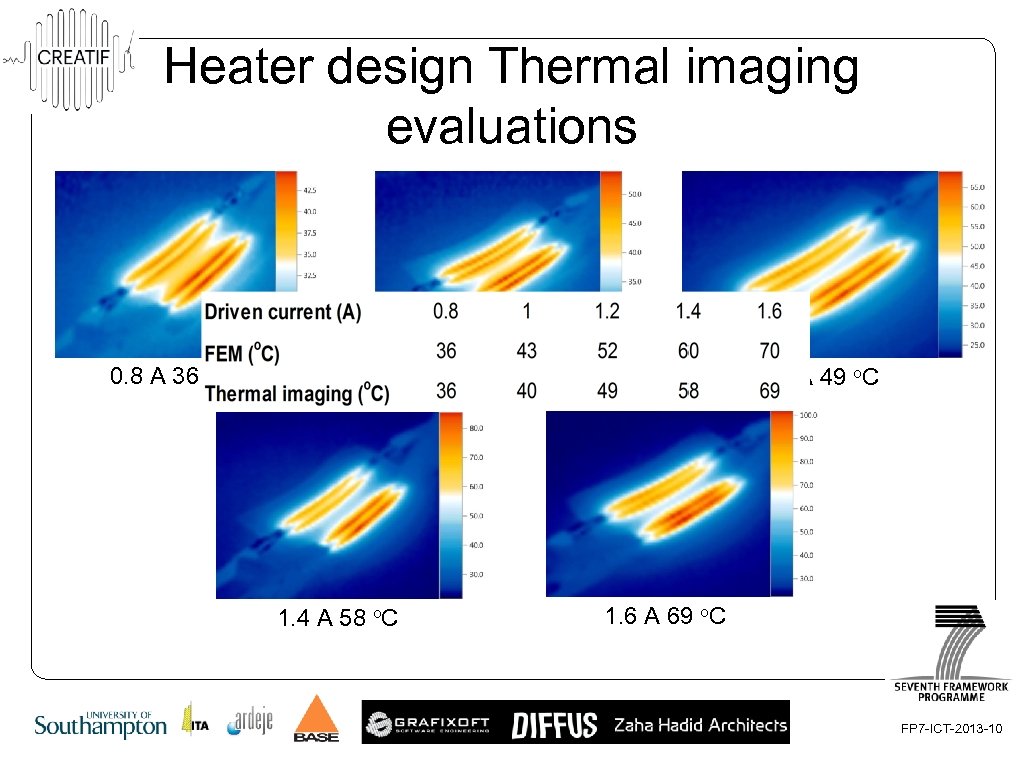 Heater design Thermal imaging evaluations 1. 0 A 40 o. C 0. 8 A 36 o. C 1. 4 A 58 o. C 1. 2 A 49 o. C 1. 6 A 69 o. C FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Heater design Thermal imaging evaluations 1. 0 A 40 o. C 0. 8 A 36 o. C 1. 4 A 58 o. C 1. 2 A 49 o. C 1. 6 A 69 o. C FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
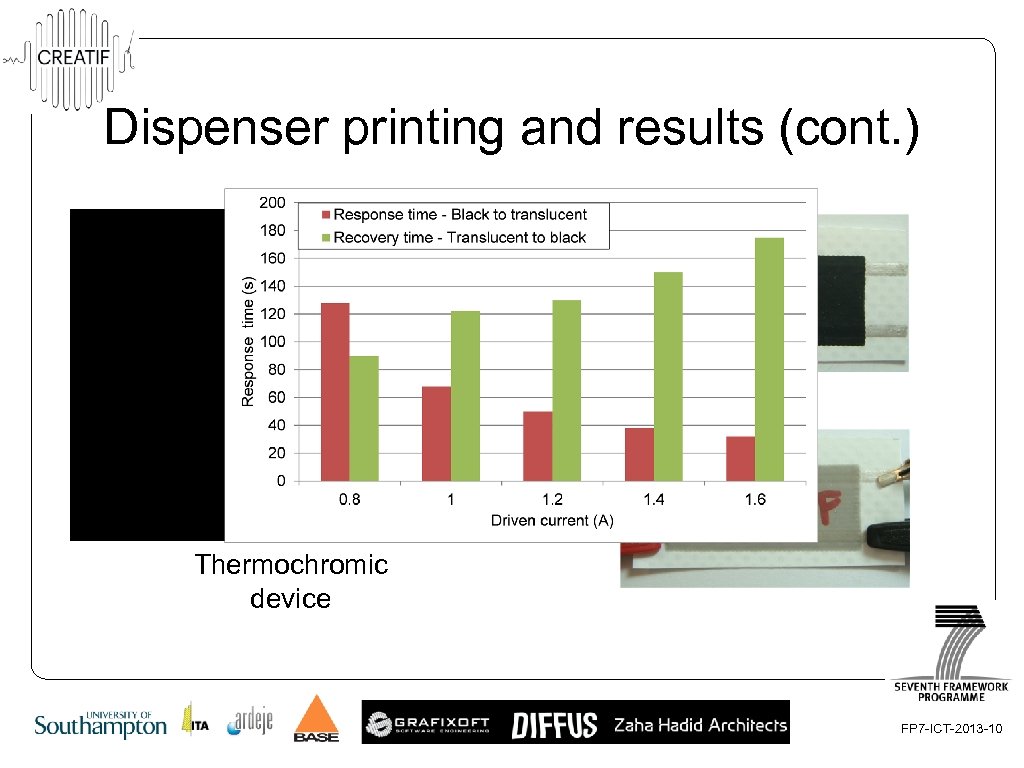 Dispenser printing and results (cont. ) OFF ON Thermochromic device FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Dispenser printing and results (cont. ) OFF ON Thermochromic device FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
 Conclusions o A printable thermochromic ink has been achieved with an activation temperature around 31 o. C. o The printed thermochromic layer changes its colour from opaque black to translucent to review anything underneath. o The cured thermochromic and conductive layers are flexible. FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Conclusions o A printable thermochromic ink has been achieved with an activation temperature around 31 o. C. o The printed thermochromic layer changes its colour from opaque black to translucent to review anything underneath. o The cured thermochromic and conductive layers are flexible. FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
 Thank you. FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10
Thank you. FP 7 -ICT-2013 -10


