713a8edc2432a324b5dd09676c1c3af0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78

Database Use & Abuse Shoo K. Lee, MBBS, FRCPC, Ph. D Director, Canadian Neonatal Network Director, Centre for Healthcare Innovation & Improvement University of British Columbia Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Growth of Vermont-Oxford Network Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Neonatal Networks • • Australia-New Zealand Neonatal Network Canadian Neonatal Network European Neonatal Network International Neonatal Network Israel Neonatal Network South American Neonatal Network Vermont-Oxford Neonatal Network Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
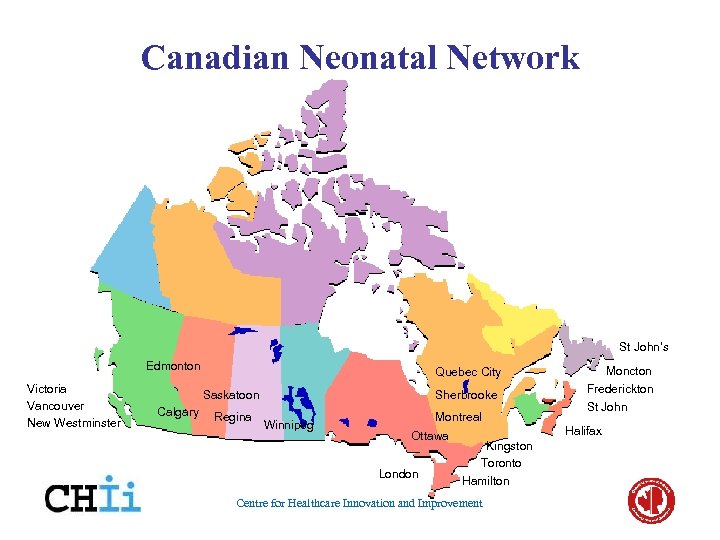
Canadian Neonatal Network St John’s Edmonton Victoria Vancouver New Westminster Quebec City Saskatoon Calgary Regina Sherbrooke Winnipeg Montreal Ottawa London Moncton Frederickton St John Halifax Kingston Toronto Hamilton Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
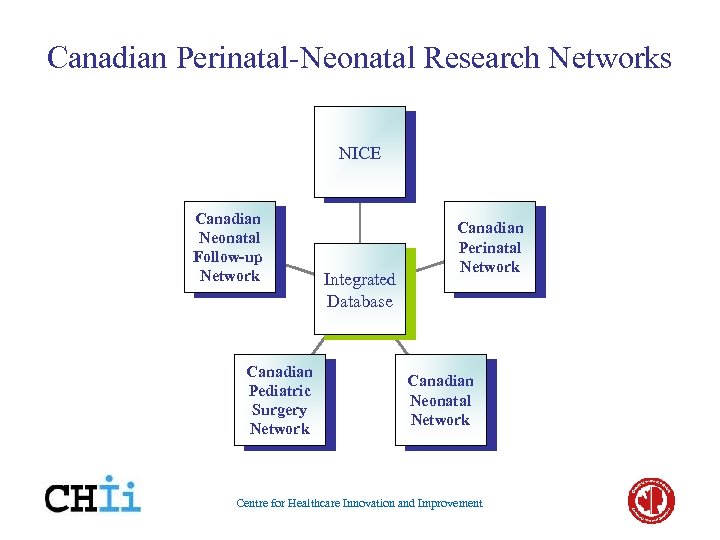
Canadian Perinatal-Neonatal Research Networks NICE Canadian Neonatal Follow-up Network Canadian Pediatric Surgery Network Integrated Database Canadian Perinatal Network Canadian Neonatal Network Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
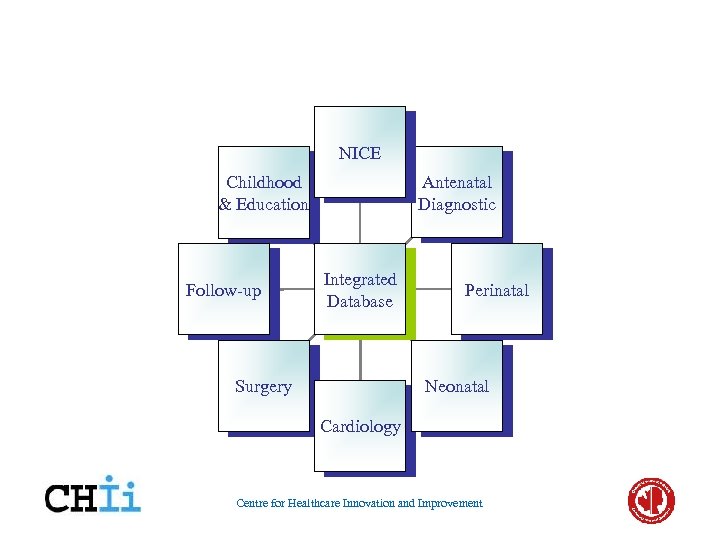
NICE Antenatal Diagnostic Childhood & Education Follow-up Integrated Database Surgery Perinatal Neonatal Cardiology Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Relationship between Networks Canadian Perinatal Network (CPN) Canadian Neonatal Network (CNN) Data Project NICE-Team Integrated Database System Project NICE-Team is CIHR-funded to provide: - Database support and management - Network coordination - Data analysis services - Training awards - Resource of experienced multidisciplinary researchers who can assist investigators Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement Project

Why join Databases and Networks? • Audit – outcomes and resource use • Research – clinical trials, health services, population health, translational research • Quality improvement • Professional guidelines • Education and Training • Policy and resource allocation decisions • Advocacy • International collaborations Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Database Use – A Looking Glass Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Database Abuse – Distortions and Illusions Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Descriptive Data - Uses • Tells the Simple Facts • Reader does all the interpretation Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
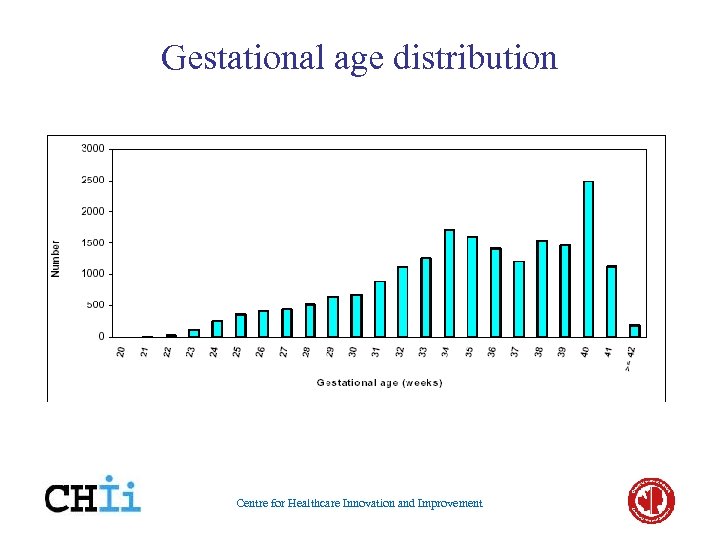
Gestational age distribution Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
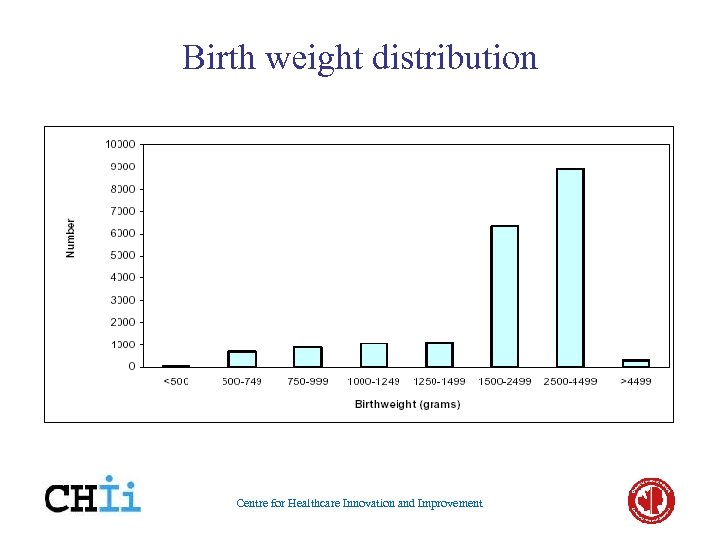
Birth weight distribution Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Descriptive Data - Abuses • Are the Data complete, accurate and unbiased? • Reader may interpret incorrectly • Often does not provide answers to address specific policy questions Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Garbage In - Garbage Out Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Crude Outcome Incidences - Uses • • Answers specific questions Permit longitudinal and trend analysis Surveillance and monitoring tool Early warning - emerging events and trends Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
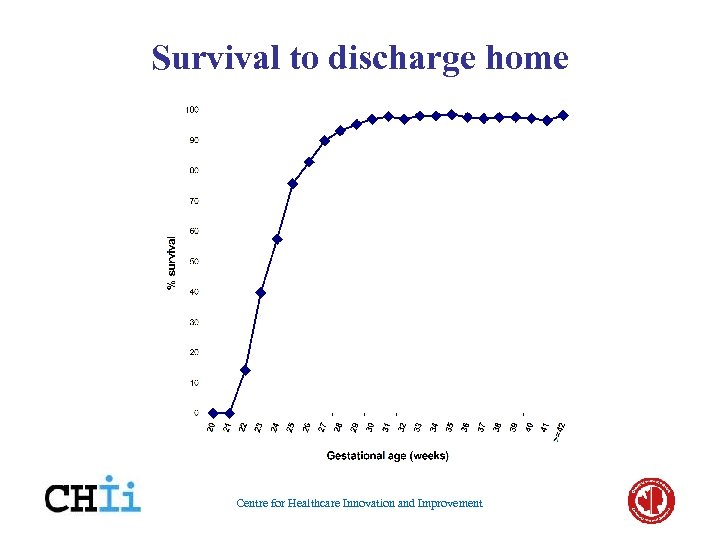
Survival to discharge home Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
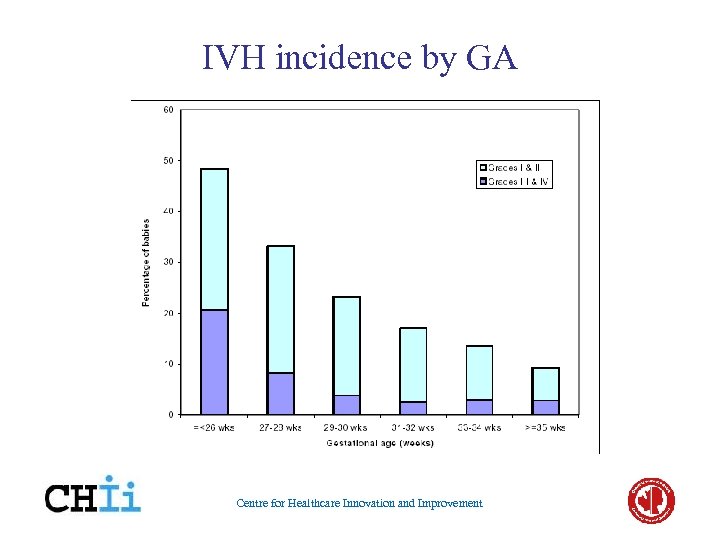
IVH incidence by GA Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Crude Outcome Incidences - Abuses • Similar to descriptive data Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
Outcome Comparisons - Uses • • • Increased level of complexity Benchmark against industry standards Sentinel for monitoring patient safety Potential for improving quality and efficiency Provides management tool – measure performance, use carrot and stick • Competitive advantage Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
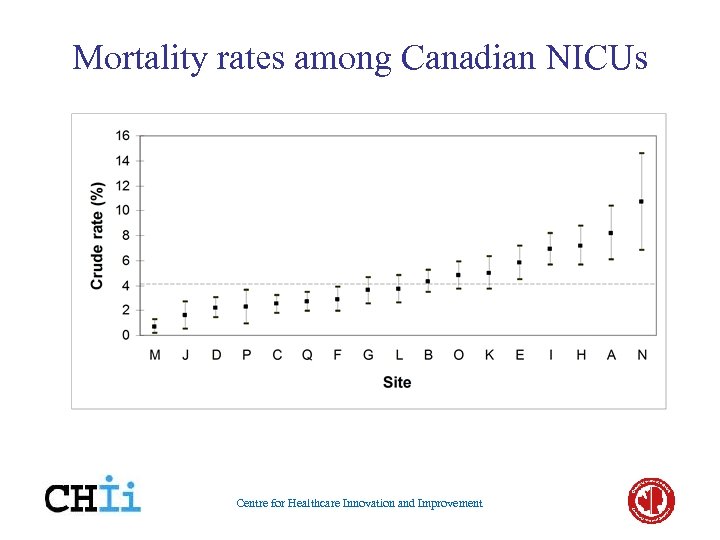
Mortality rates among Canadian NICUs Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Comparison of Outcomes - Abuses • Lack of appropriate risk-adjustment • Why do comparisons at all? - wrong interpretation - inappropriate change in practice patterns - competitive advantage/disadvantage - “gaming” system • Fear-mongering • Potential for inappropriate shifts in patterns of patient use Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Benchmarking & Risk Adjustment • Promise of overcoming problems associated with comparison of crude outcomes • Permit population based data analysis and interpretation, and design of system to provide optimal quality and efficiency of care Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Risk Adjustment • • • Epidemiologic baseline population risks Diagnostic groups Therapeutic intensity (NTISS) Physiologic illness severity (CRIB, SNAP) True measure of illness severity at admission (TRIPS? ) • Where is the state of the art/science? Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
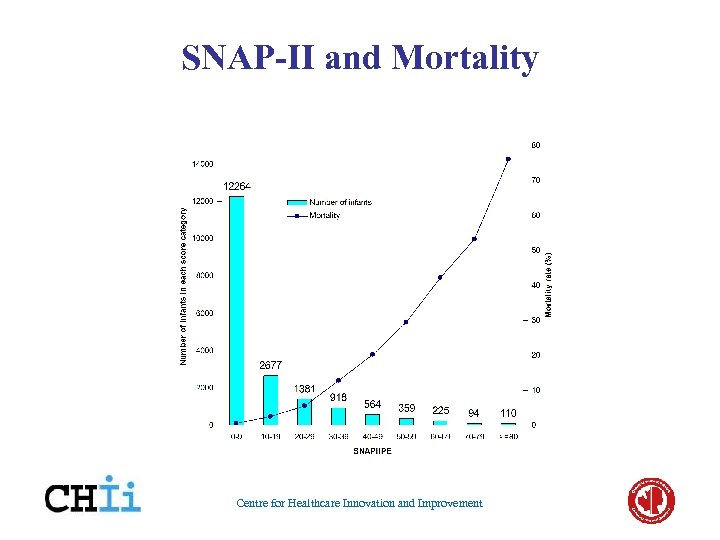
SNAP-II and Mortality Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

TRIPS (higher score is worse) TRIPS Variable Temperature (o. C) TRIPS Score Points 8 1 0 <36. 1 or >37. 6 36. 1 – 36. 5 or 37. 2 -37. 6 36. 6 – 37. 1 Respiratory status Severe (apnoea, gasping, intubated) Moderate (RR >60/min or Sp. O 2 <85) None (RR <60/min & Sp. O 2 >85) Systolic BP (mm Hg) <20 20 -40 >40 Response to noxious stimuli None, seizure, muscle relaxant Lethargic response, no cry Withdraws vigorously, cries Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement 14 5 0 26 16 0 17 6 0
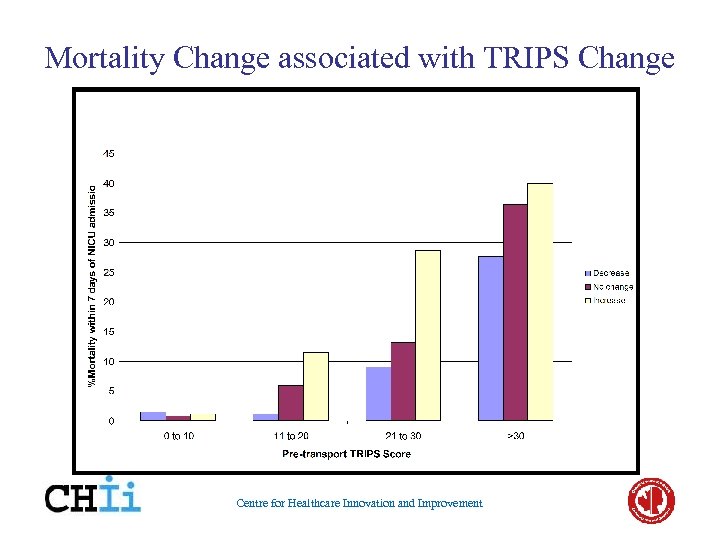
Mortality Change associated with TRIPS Change Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
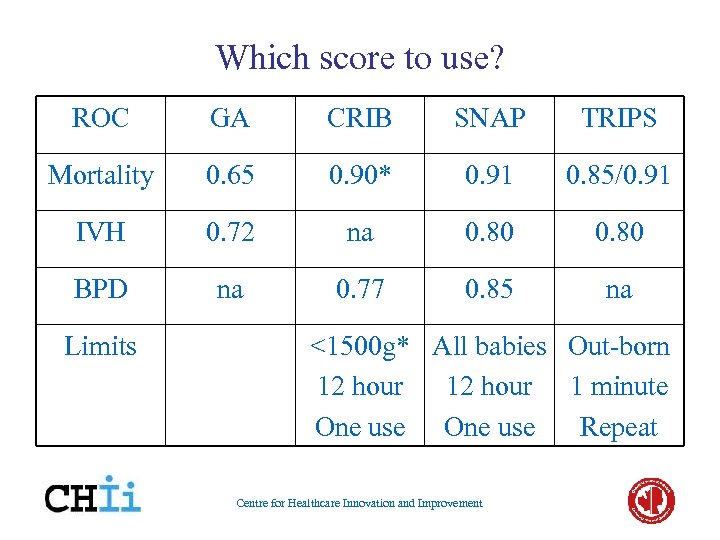
Which score to use? ROC GA CRIB SNAP TRIPS Mortality 0. 65 0. 90* 0. 91 0. 85/0. 91 IVH 0. 72 na 0. 80 BPD na 0. 77 0. 85 na Limits <1500 g* All babies Out-born 12 hour 1 minute One use Repeat Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Risk-adjusted Outcome Comparisons - Uses • “True” comparison of outcomes • Separate outcome differences due to patient differences from those due to practice differences • Permits study and design of practice change to improve outcomes • New tool that may overcome some of the disadvantages of randomized clinical trials Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

NICU Mortality Comparisons Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Risk adjusted outcome comparisons - abuses • Definitions - do we mean the same thing? • Measurement criteria – were they the same? • Consistency - were criteria applied consistently? • Was the treatment the same? • Was risk-adjustment appropriate? Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
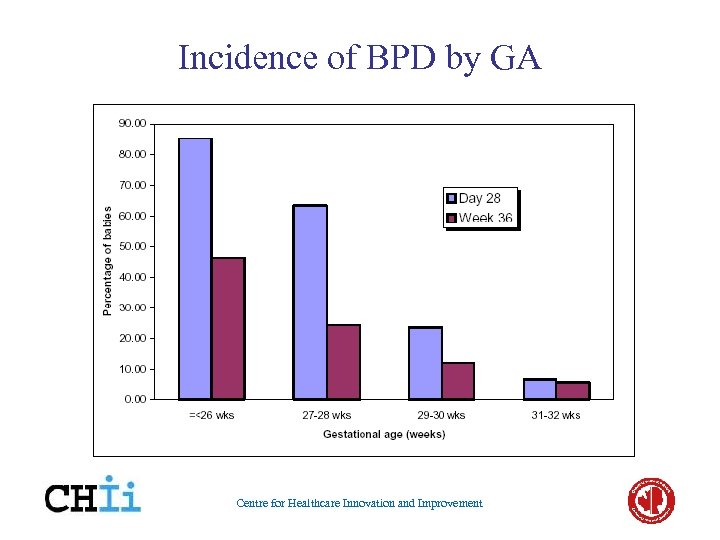
Incidence of BPD by GA Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
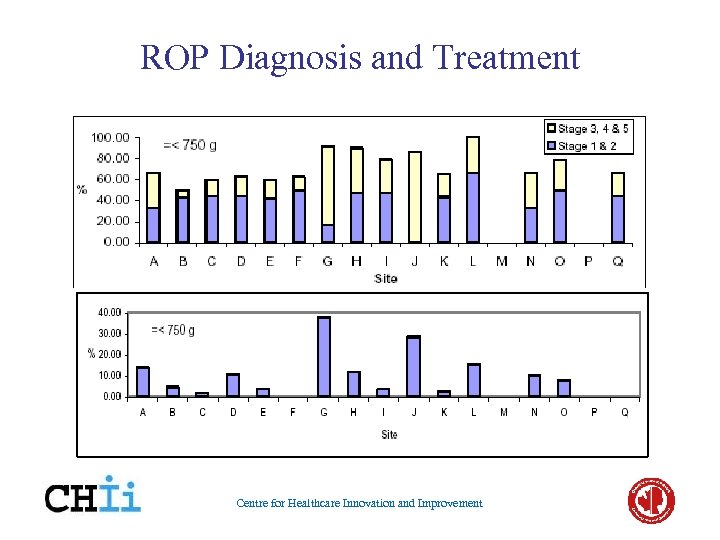
ROP Diagnosis and Treatment Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

How do we use data for quality improvement? Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
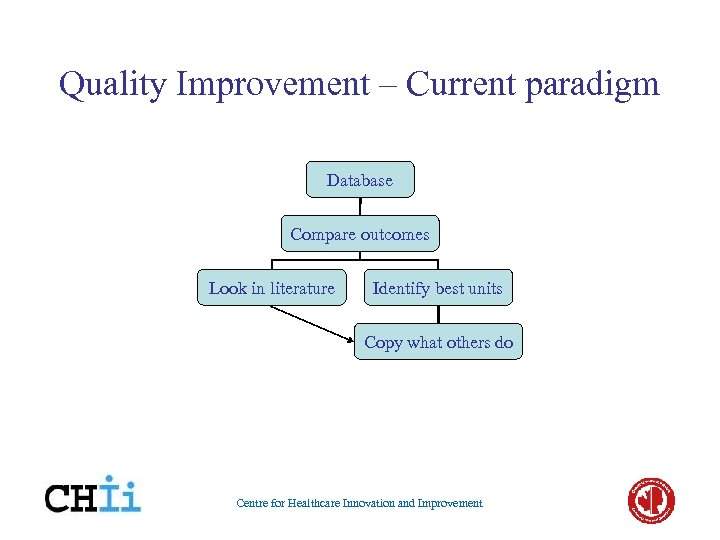
Quality Improvement – Current paradigm Database Compare outcomes Look in literature Identify best units Copy what others do Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Is this good enough? • • • Why do some units have better results? Are all their practices “best”? Are their practices applicable to you? Might you copy something that is harmful? Is this shot-gun approach efficient? At best, this is a subjective and unscientific approach • Is there another way? Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
Factors affecting IVH variations • Synnes et al - 4 NICU practices accounted for IVH variation: (a) Antenatal steroids (b) C-section vs Vaginal delivery (c) Treatment for hypotension (d) Treatment for acidosis • Implication – change in clinical practice may reduce IVH rates in some hospitals • Mac. Nab et al – developed Bayesian statistical methods using Markov Chain Monte Carlo hierarchical modeling to identify risk factors specific to each hospital Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Log odds plot for risk factor small for gestational age, two-level hierarchical model C, Canadian NICU data 1996 -97. Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
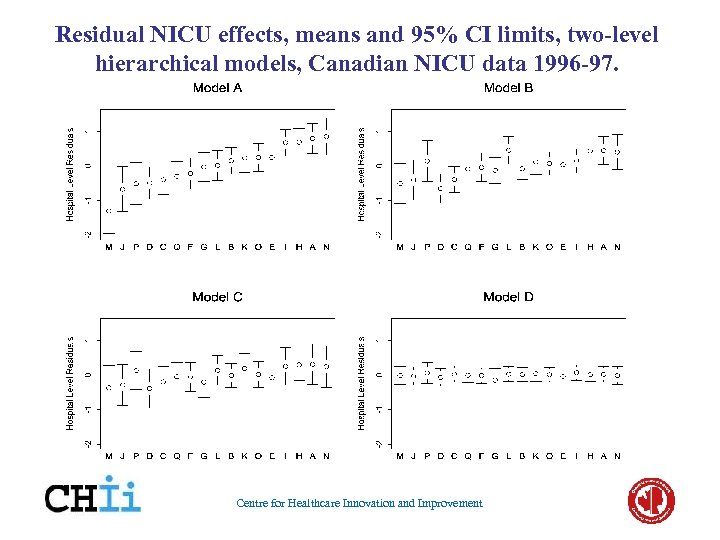
Residual NICU effects, means and 95% CI limits, two-level hierarchical models, Canadian NICU data 1996 -97. Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Probability of being NI free Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
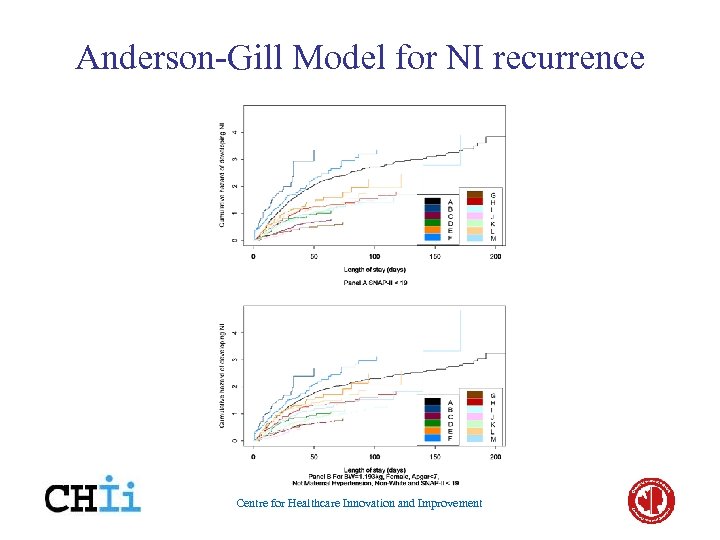
Anderson-Gill Model for NI recurrence Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
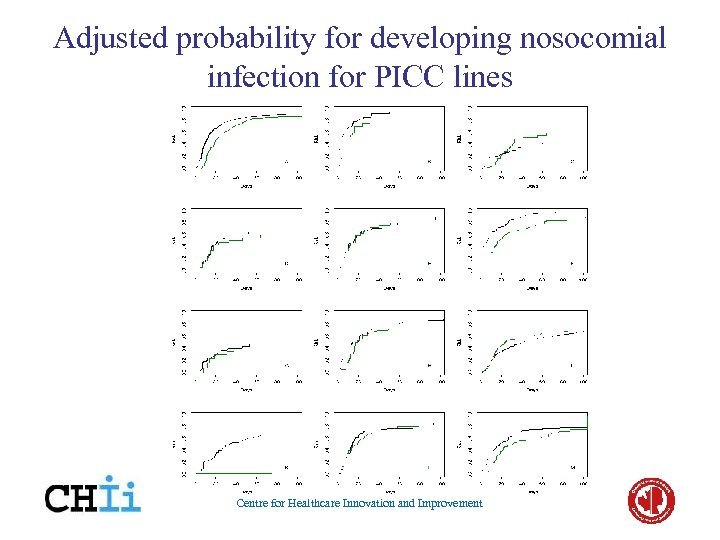
Adjusted probability for developing nosocomial infection for PICC lines Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

The EPIC paradigm Database Compare outcomes Look in literature Identify your problems and strengths Targeted intervention Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement Identify best practices among units

New Method for Quality Improvement Clinical Trials CQI EQI Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

EPIC – Phase 1 • • Baseline data collection Training of Infection Teams – MD, RN, QI Review of published literature Meeting to share findings Identify Critical Pathways & Incidents Qualitative research – identify Failure Modes Data analysis – identify practice differences associated with outcome variation • Develop Change Strategy Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

EPIC – Phase 2 • Staff communication and training – group sessions, information packages • Prepare supporting materials, e. g. prompts printed on order sheets • Publicize information, posters, newsletters • Implement EPIC • 3 -monthly feedback – Control Charts • Revise strategies, reinforce change Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
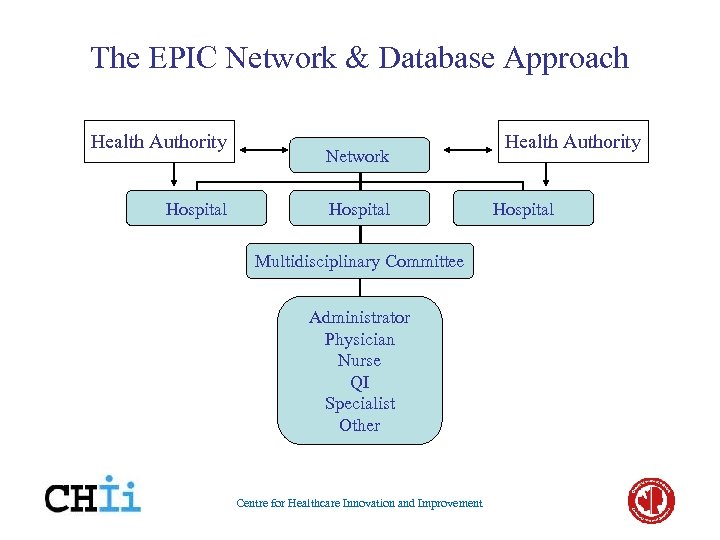
The EPIC Network & Database Approach Health Authority Hospital Network Hospital Multidisciplinary Committee Administrator Physician Nurse QI Specialist Other Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement Health Authority Hospital
Integrative Processes Administrative Clinical Research Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Comparing Outcomes Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Population and Policy Implications Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
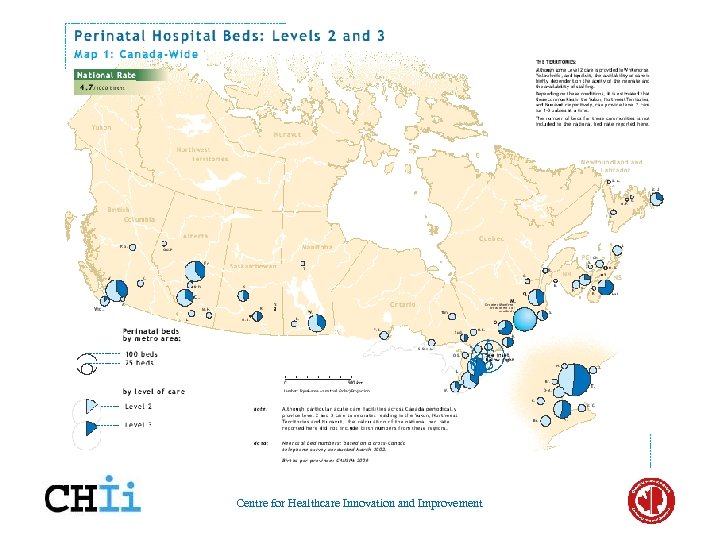
Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
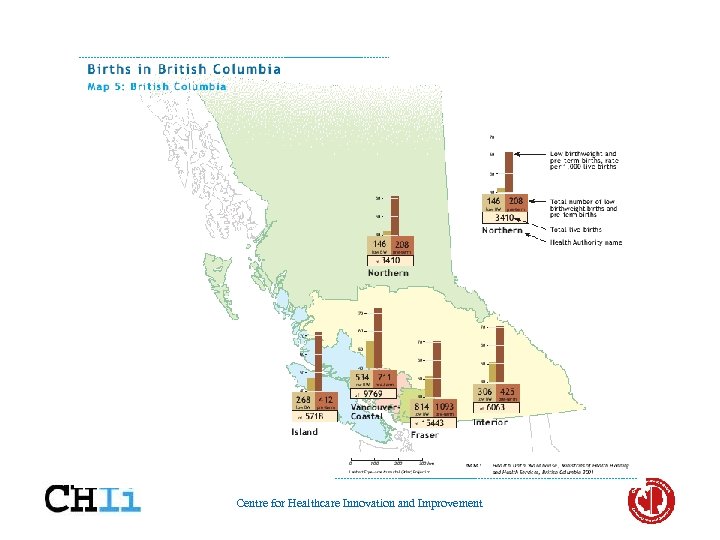
Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
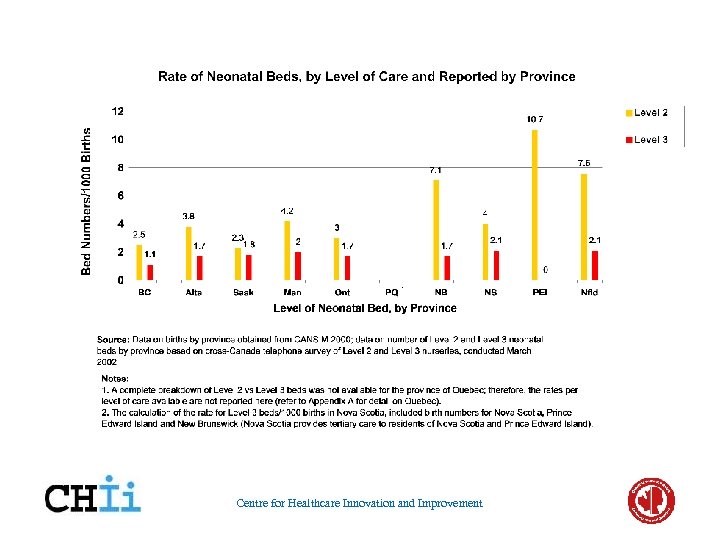
Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
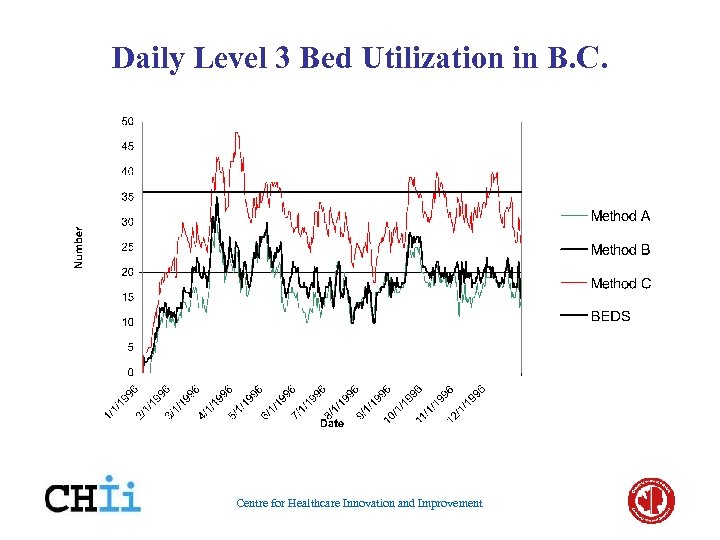
Daily Level 3 Bed Utilization in B. C. Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
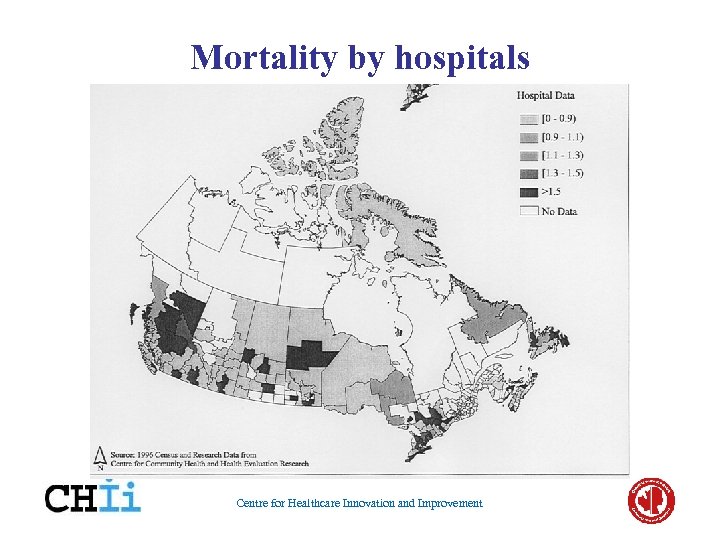
Mortality by hospitals Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
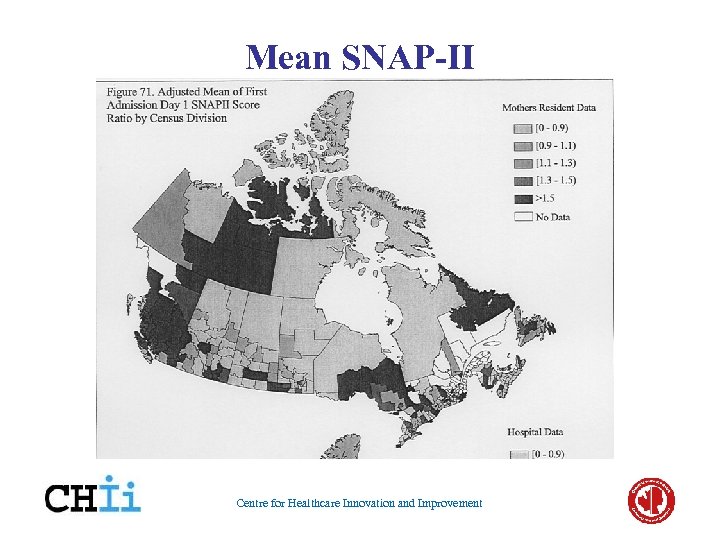
Mean SNAP-II Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Manpower Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
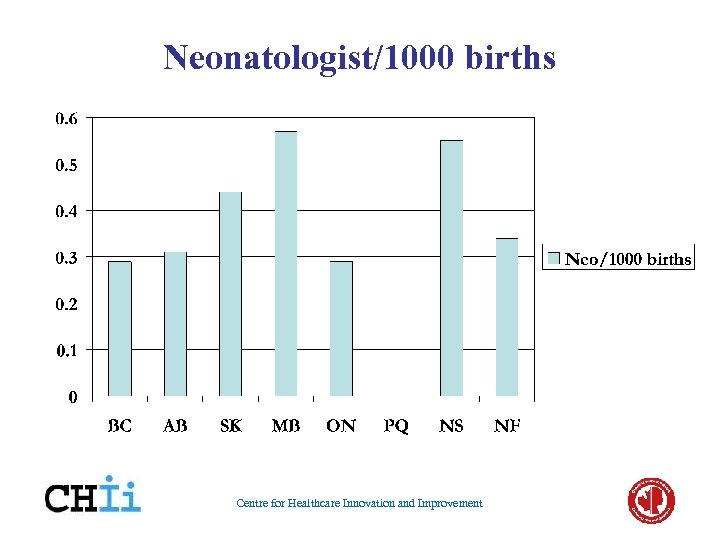
Neonatologist/1000 births Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Normative values Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
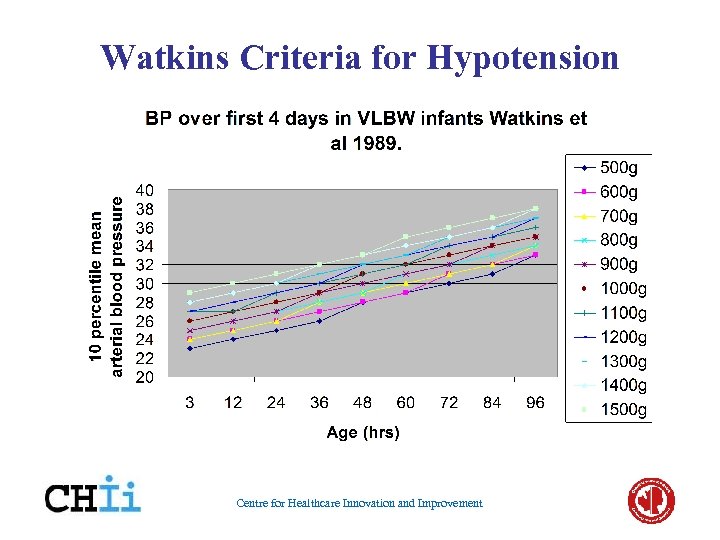
Watkins Criteria for Hypotension Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
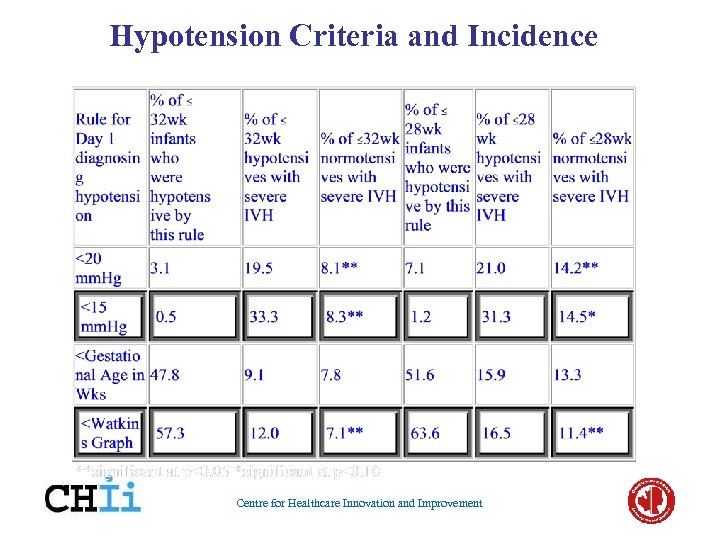
Hypotension Criteria and Incidence Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Evaluate Expert Guidelines Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Cost-effectiveness ROP screening Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Develop new clinical guidelines Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
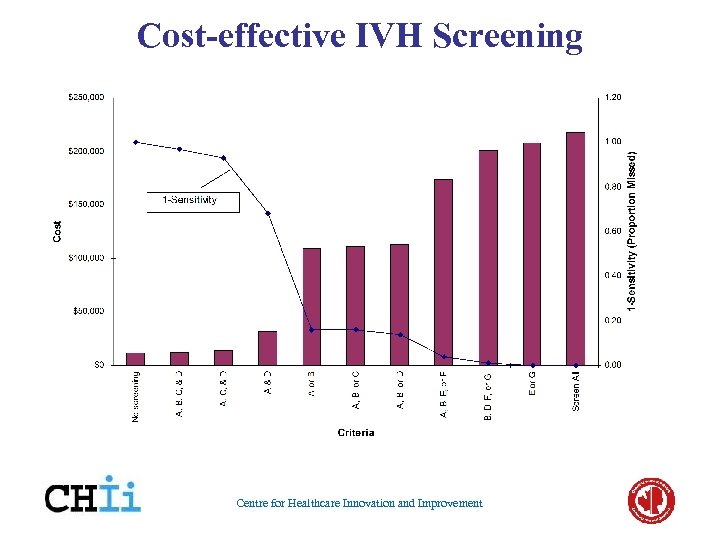
Cost-effective IVH Screening Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Assess guideline use Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
Antenatal Steroid Use • 1996 -97: incidence of use = 59% among infants 24 -34 weeks gestation • Variation in use: Inborn 25% – 96% Outborn 8% - 94% • Potential to decrease neonatal deaths by 10% Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Planning and Policy Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
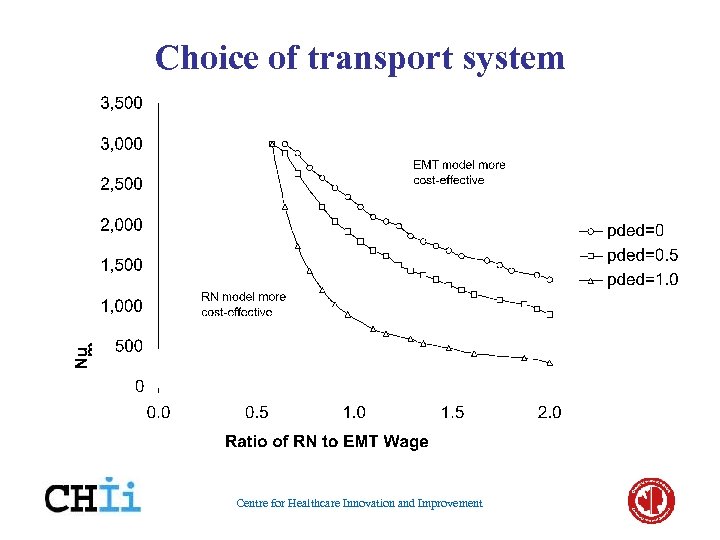
Choice of transport system Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Regional variations in outcomes and resource allocation planning Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Planning for future Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

10 year Projections Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Summary • • • Databases can be useful But use data and interpretation with CARE Clinical input is vital Database should meet your needs and goals Societal versus institutional goals Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Concerns • • • Public impact of information Privacy and confidentiality Conformity versus innovation Barrier to clinical trials “Big brother” control Not “real” hypothesis-driven research Not high quality evidence (e. g. clinical trials) Research versus Quality Improvement Clinician versus “real” researchers Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

www. canadianneonatalnetwork. org Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement

Centre for Healthcare Innovation and Improvement
713a8edc2432a324b5dd09676c1c3af0.ppt