6e92b1c4e2613d169afdfc5d64be757b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Database System Implementation Spring 2001 Prof. Sang Ho Lee School of Computing, Soongsil Univ. shlee@computing. soongsil. ac. kr Chapter 1 1
Isn’t Implementing a Database System Simple? Relations Statements Chapter 1 Results 2

Introducing the Database Management System • The latest from Megatron Labs • Incorporates latest relational technology • UNIX compatible Chapter 1 3
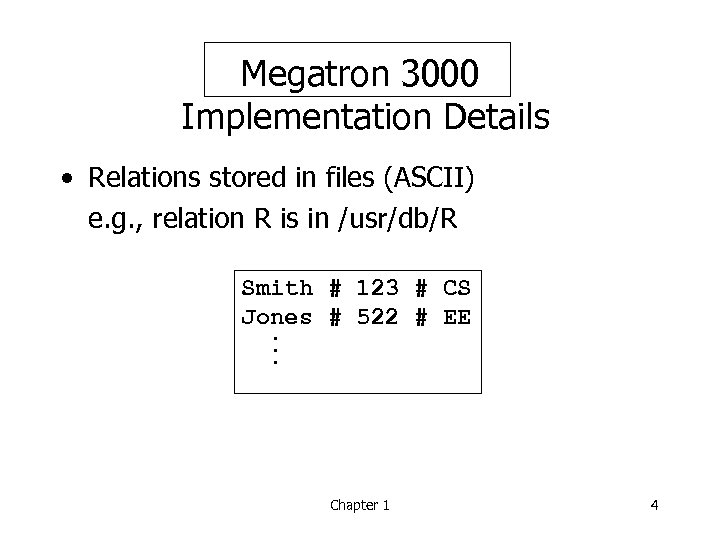
Megatron 3000 Implementation Details • Relations stored in files (ASCII) e. g. , relation R is in /usr/db/R Smith # 123 # CS Jones # 522 # EE. . . Chapter 1 4
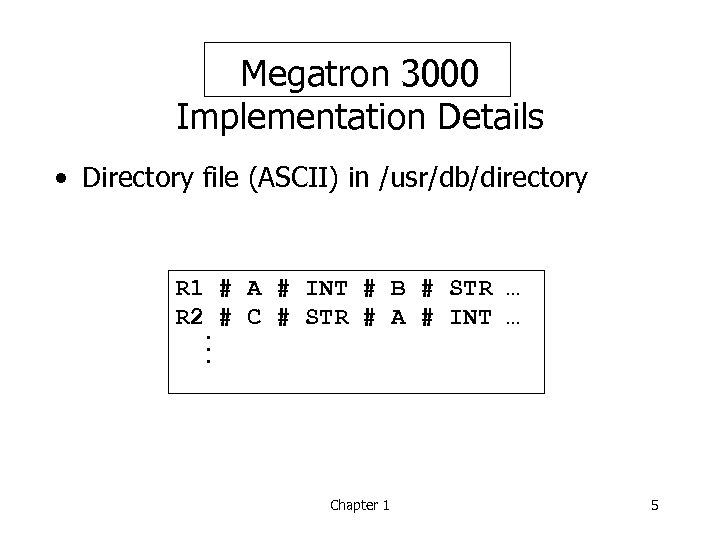
Megatron 3000 Implementation Details • Directory file (ASCII) in /usr/db/directory R 1 # A # INT # B # STR … R 2 # C # STR # A # INT …. . . Chapter 1 5
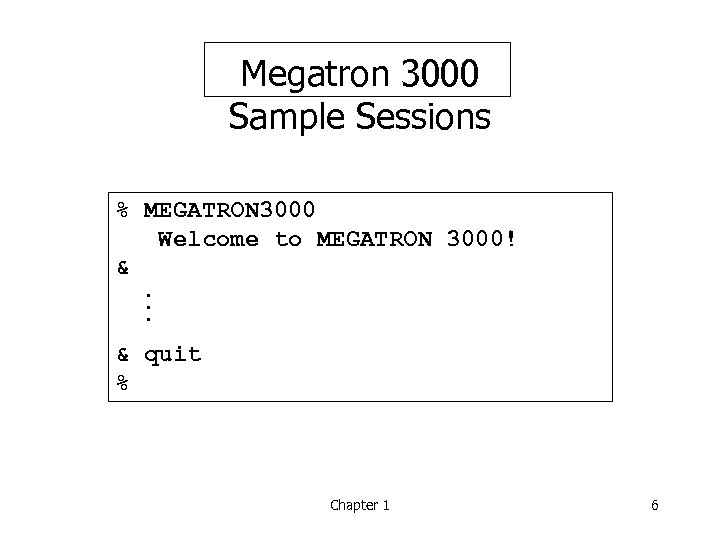
Megatron 3000 Sample Sessions % MEGATRON 3000 Welcome to MEGATRON 3000! &. . . & quit % Chapter 1 6
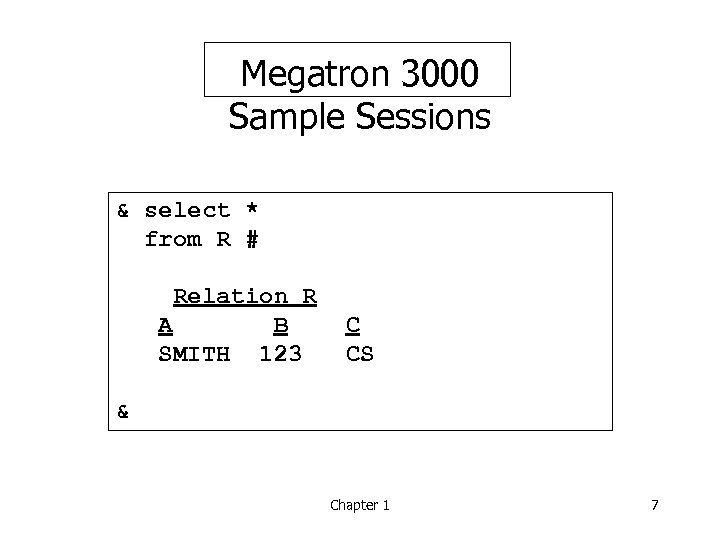
Megatron 3000 Sample Sessions & select * from R # Relation R A B SMITH 123 C CS & Chapter 1 7
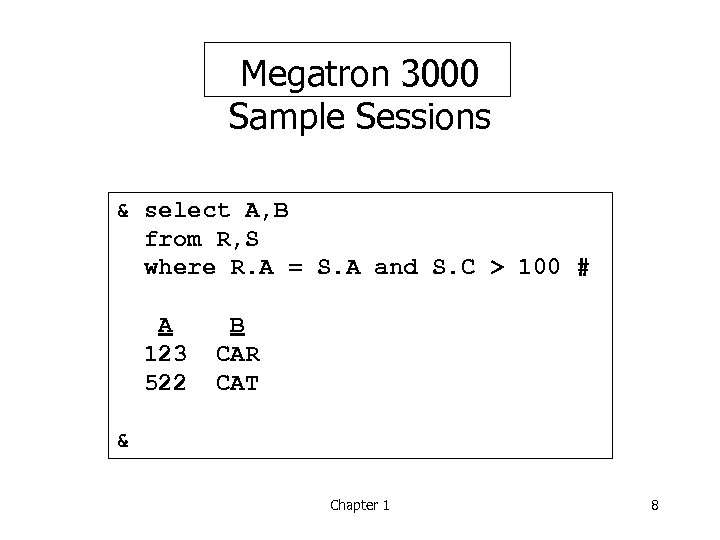
Megatron 3000 Sample Sessions & select A, B from R, S where R. A = S. A and S. C > 100 # A 123 522 B CAR CAT & Chapter 1 8
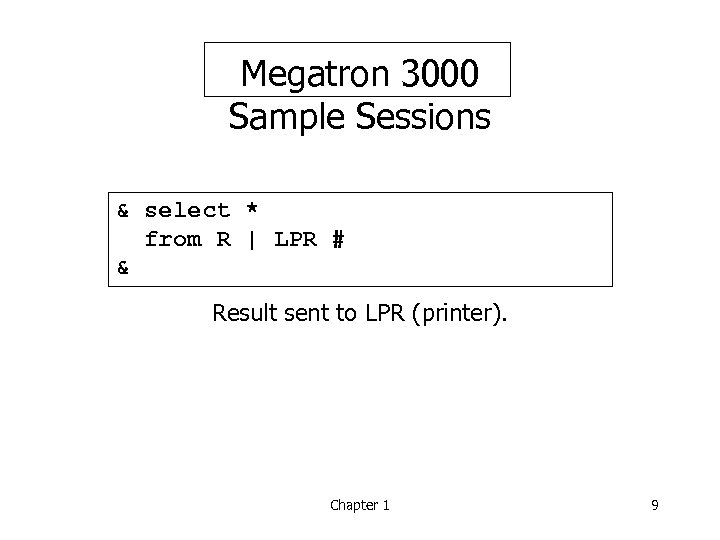
Megatron 3000 Sample Sessions & select * from R | LPR # & Result sent to LPR (printer). Chapter 1 9
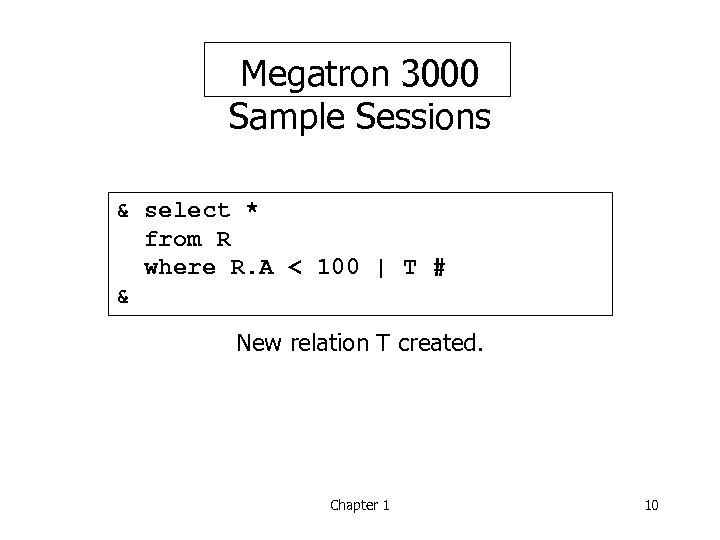
Megatron 3000 Sample Sessions & select * from R where R. A < 100 | T # & New relation T created. Chapter 1 10

Megatron 3000 • To execute “select * from R where condition”: (1) Read dictionary to get R attributes (2) Read R file, for each line: (a) Check condition (b) If OK, display Chapter 1 11

Megatron 3000 • To execute “select * from R where condition | T”: (1) Process select as before (2) Write results to new file T (3) Append new line to dictionary Chapter 1 12

Megatron 3000 • To execute “select A, B from R, S where condition”: (1) Read dictionary to get R, S attributes (2) Read R file, for each line: (a) Read S file, for each line: (i) Create join tuple (ii) Check condition (iii) Display if OK Chapter 1 13

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? Chapter 1 14

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • Tuple layout on disk – Change string from ‘Cat’ to ‘Cats’ and we have to rewrite file – ASCII storage is expensive – Deletions are expensive Chapter 1 15

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • Search expensive; no indexes – Cannot find tuple with given key quickly – Always have to read full relation Chapter 1 16
What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • Brute force query processing e. g. , select * from R, S where R. A = S. A and S. B > 1000 - Do select first? - More efficient join? Chapter 1 17
What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • No buffer manager e. g. , Need caching Chapter 1 18

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • No concurrency control Chapter 1 19

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • No reliability e. g. , - Can lose data - Can leave operations half done Chapter 1 20

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • No security e. g. , - File system insecure - File system security is coarse Chapter 1 21
What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • No application program interface (API) e. g. , How can a payroll program get at the data? Chapter 1 22

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • Cannot interact with other DBMSs. Chapter 1 23

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • Poor dictionary facilities Chapter 1 24

What’s wrong with the Megatron 3000 DBMS? • No GUI Chapter 1 25

Course Overview • File & System Structure Records in blocks, dictionary, buffer management, … • Indexing & Hashing B-Trees, hashing, … • Query Processing Query costs, join strategies, … • Crash Recovery Failures, stable storage, … Chapter 1 26

Course Overview • Concurrency Control Correctness, locks, … • Transaction Processing Logs, deadlocks, … • Security & Integrity Authorization, encryption, … • Distributed Databases Interoperation, distributed recovery, … Chapter 1 27
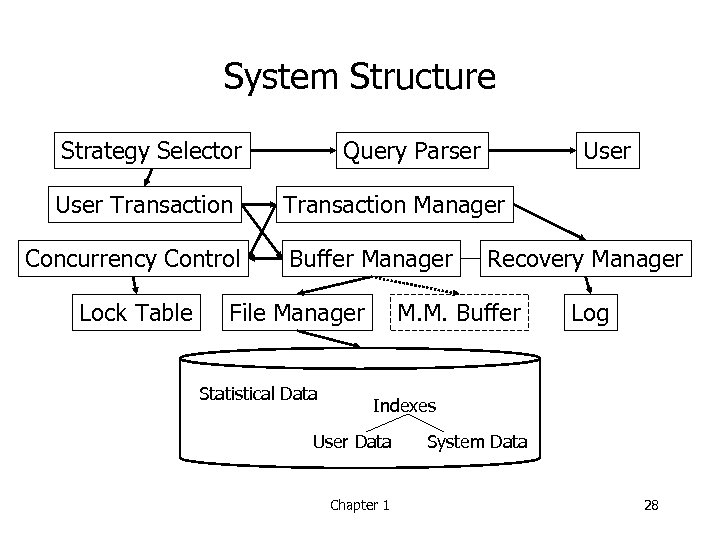
System Structure Strategy Selector User Transaction Concurrency Control Lock Table Query Parser User Transaction Manager Buffer Manager File Manager Statistical Data Recovery Manager M. M. Buffer Log Indexes User Data Chapter 1 System Data 28

Course Details • LECTURES: Tuesday 9: 00 – 11: 50 am • TEXTBOOK: Garcia-Molina, Ullman, Widom; "DATABASE SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION“, Prentice Hall, 2000 • ASSIGNMENTS: Written homework assignments. No programming. Significant reading assignments • GRADING: – 3 -4 times exams. (90%) – Attendance and homework (10%) • WEB SITE: http: //orion. soongsil. ac. kr (Please check it periodically for last minute announcements) Chapter 1 29

Read Carefully • Course prerequisite – Undergraduate database courses – A First Course in Database Systems J. Ullman and J. Widom, Prentice Hall, 1997 • Should be familiar with – ER/Relational/OO Data models – Database design theory (FD, normalization, …) – Relational algebra, SQL, OQL, … Chapter 1 30

Notice that • This course requires considerable amount of self-reading. • I do not cover every part of this book, but the exams do. • My primary concern is about how to encourage you to study databases • It will not be easy for you !!! Chapter 1 31
6e92b1c4e2613d169afdfc5d64be757b.ppt