a4846cedd9cb2c38bdb3a290d7a4b526.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9
Database Integration in the context of the GUS (“Genomics Unified Schema”) Data Warehouse Jonathan Crabtree Senior Programmer/Analyst Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory Center for Bioinformatics University of Pennsylvania http: //www. bil. upenn. edu c 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory
Outline • The problem(s) of database integration • A warehouse-based solution • The databases involved – GUS: an integrated warehouse of sequence data – RAD: a gene expression database • Resources developed using GUS and/or RAD • Queries enabled by the system • Future directions 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory

The Purpose of GUS • Integrate existing databases and tools – a single point of access to what is already known • Provide an automated “lab. notebook” – a permanent record of work in progress – e. g. , similarity searches, array data, etc. • And ultimately: support data mining – a potential source of novel discoveries 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory

What is GUS? • A relational schema with over 180 tables – integrates many types of data relevant to genomics – is based on the central dogma of biology – represents organisms, biological systems, projects • A relational data warehouse that contains – public sequence data – gene & genome annotation generated “in-house” – additional data sets from collaborators 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory

What is GUS (II)? • A Perl API and annotation subsystem – lightweight object layer – supports high-level programmatic access. . . – but does not mandate it (i. e. , SQL is an option) • A generic user interface – Java Servlet-based (Apache JServ) – supports browsing – and also restricted ad-hoc queries 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory
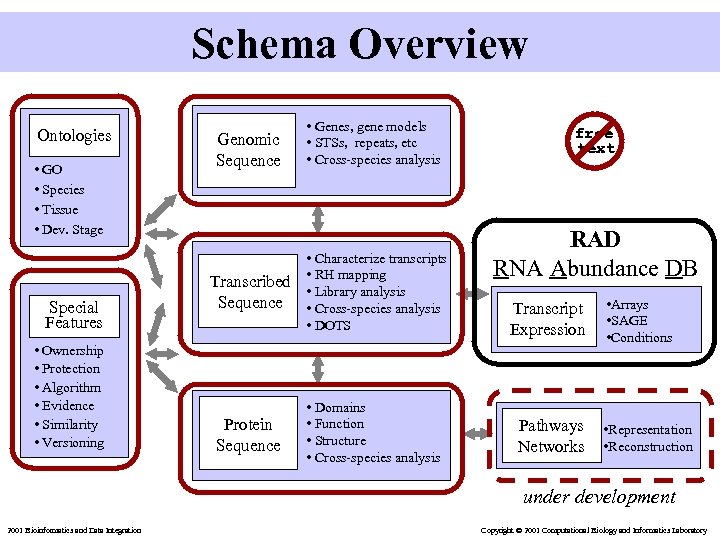
Schema Overview Ontologies • GO • Species • Tissue • Dev. Stage Special Features • Ownership • Protection • Algorithm • Evidence • Similarity • Versioning Genomic Sequence • Genes, gene models • STSs, repeats, etc • Cross-species analysis Transcribed Sequence • Characterize transcripts • RH mapping • Library analysis • Cross-species analysis • DOTS Protein Sequence • Domains • Function • Structure • Cross-species analysis free text RAD RNA Abundance DB Transcript Expression Pathways Networks • Arrays • SAGE • Conditions • Representation • Reconstruction under development 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory
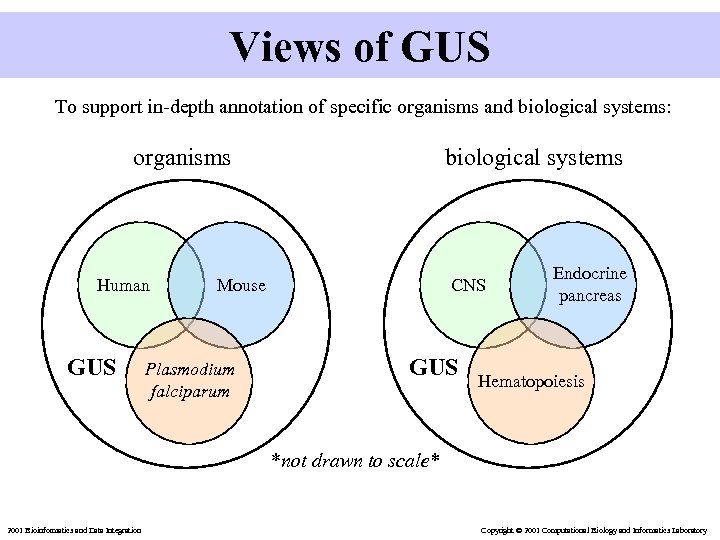
Views of GUS To support in-depth annotation of specific organisms and biological systems: organisms Human GUS biological systems Mouse Plasmodium falciparum CNS GUS Endocrine pancreas Hematopoiesis *not drawn to scale* 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory

URLs/References • UPenn. Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory (CBIL) – http: //www. bil. upenn. edu c • GUS (“Genomics Unified Schema”) – schema browser: • http: //www. llgenes a. org/cgi-bin/schema. Browser. pl? db=GUS – an example of a controlled vocabulary/ontology in GUS: • http: //www. bil. upenn. edu/anatomy. php 3 c – sites implemented (in part or whole) as views of GUS: • http: //www. llgenes a. org • http: //www. lasmodb. org p • http: //www. bil. upenn. edu/EPCon. DB c – reference: K 2/Kleisli and GUS: Experiments in Integrated Access to genomic data sources. Davidson, S. B. , Crabtree, J. , Brunk, B. P. , Schug, J. , Tannen, V. , Overton, G. C. , Stoeckert, C. J. , Jr. IBM Systems Journal: in press. 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory
URLs/References (II) • RAD (“RNA Abundance Database”) – schema browser: • http: //www. bil. upenn. edu/cgi-bin/RAD 2/schema. Browser. RAD c. pl – public web site: • http: //www. bil. upenn. edu/RAD 2 c – reference: A relational schema for both array-based and SAGE gene expression experiments. Stoeckert, C. , Pizarro, A. , Manduchi, E. , Gibson, M. , Brunk, B. , Crabtree, J. , Schug, J. , Shen-Orr, S. , Overton, G. C. Bioinformatics: in press. 2001 Bioinformatics and Data Integration Copyright © 2001 Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory
a4846cedd9cb2c38bdb3a290d7a4b526.ppt