3d2befd51e27690ea5df3db024dfd72e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

Database-Inspired Search David Konopnicki and Oded Shmueli IBM Haifa Technion

n Back in 1994 -95…
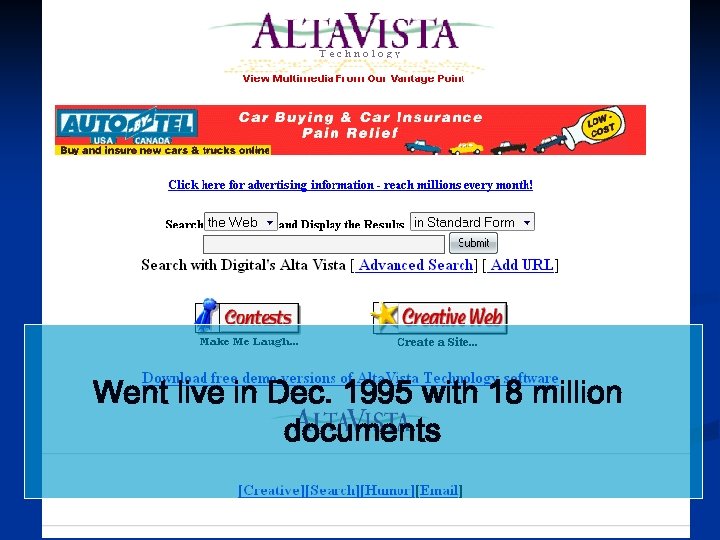
Went live in Dec. 1995 with 18 million documents
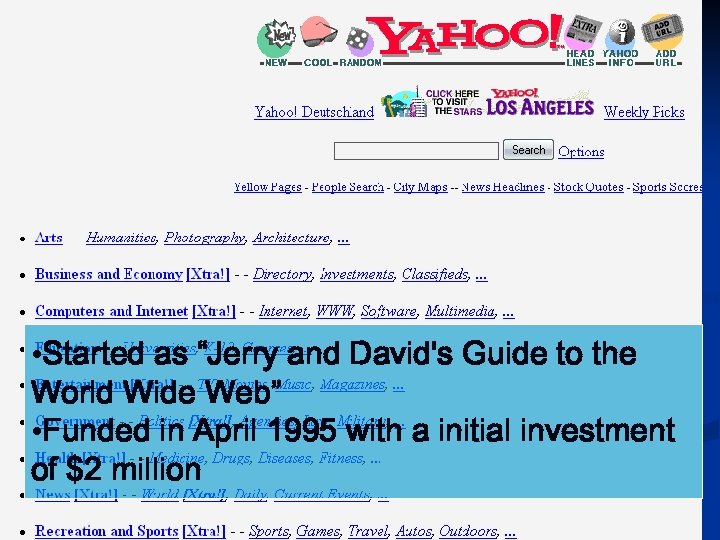
• Started as “Jerry and David's Guide to the World Wide Web” • Funded in April 1995 with a initial investment of $2 million
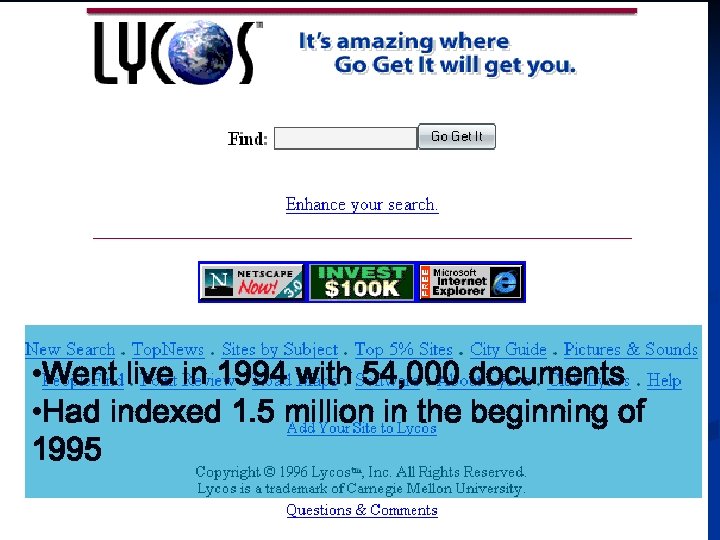
• Went live in 1994 with 54, 000 documents • Had indexed 1. 5 million in the beginning of 1995

W 3 QL – W 3 QS: A database approach to Web data n n A way to “improve” search results A database language for searching the web Using full-text indexes as starting points Had conditions on “semi-structured” formats: n 1. format eq “Latex File” && n 1. section[3]. content =~ /zoo/ n Would record form fillings and re-execute them automatically n Basically, a way to define personal crawlers

Contemporary Systems n First generation languages: Web. SQL (Mihaila, Mendelzon and Milo) n Second generation languages: Weblog (Lakshmanan, Sadri, and Subramania) , Florid (Ludascher, Himmeroder, Lausen, May and Schlepphorst) n n Web restructuring languages: Web. OQL (Arocena and Mendelzon) , Stru. QL (Fernandez, Florescu, Kang, Levy and Suciu), Araneus (Mecca, Atzeni, Masci, Merialdo and Sindoni) Lorel (Abiteboul, Quass, Mc. Hugh, Widom and Wiener)

Present Trends n n Certainly, nowadays search engines are bigger and faster and more accurate A few new features: Clusty n Is searching the web easier? Teoma

Limitations Remain the Same Visually parsing results n Search in context n Searching beyond the first page of results n Integrated search from my desktop, my enterprise and on to the world n
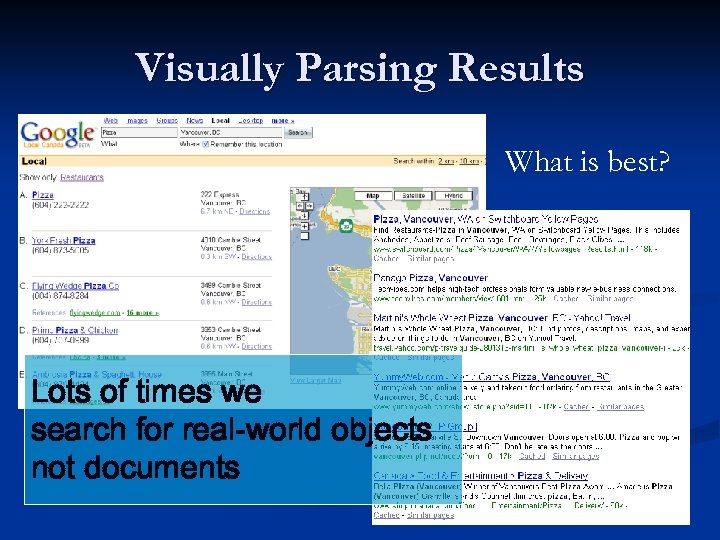
Visually Parsing Results What is best? Lots of times we search for real-world objects not documents
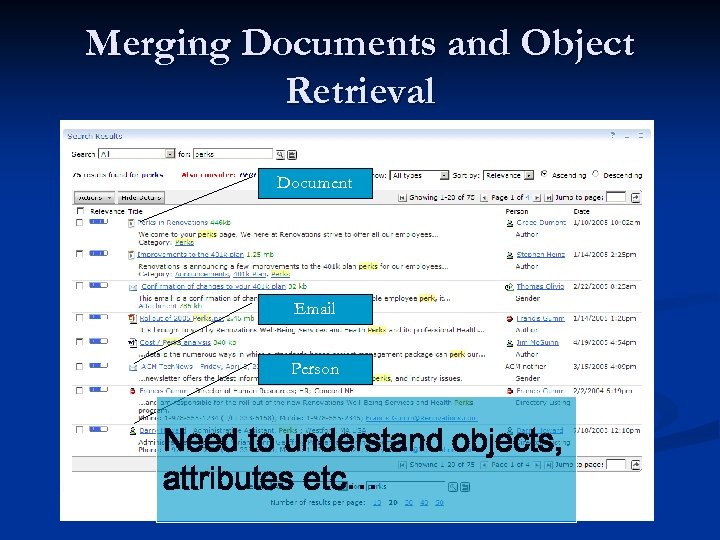
Merging Documents and Object Retrieval Document Email Person Need to understand objects, attributes etc…
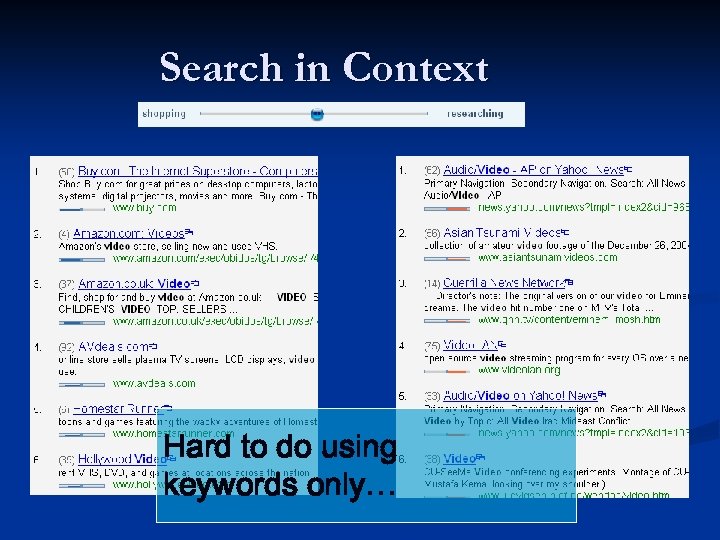
Search in Context Hard to do using keywords only…

Search Only the First Page of Results n From a recent study on 12, 500 queries: n n n 73. 9% of Ask Jeeves first page results were unique to Ask Jeeves 71. 2% of Yahoo first page results were unique to Yahoo 70. 8% of MSN search first page results were unique to MSN search 66. 4% of Google first page results were unique to Google Need an automated way to search beyond the first page on several search engines simultaneously Full-text indexes are just starting points

Desktop Search Quite different than web search n No links - cannot use link analysis n Information discovery versus locating information n

Enterprise Search n Quite different too: Data integration from lots of systems n Critical intranet service n n IBM Intranet Search 10, 000 websites n 6 million indexed documents n A new product called Omni. Find n
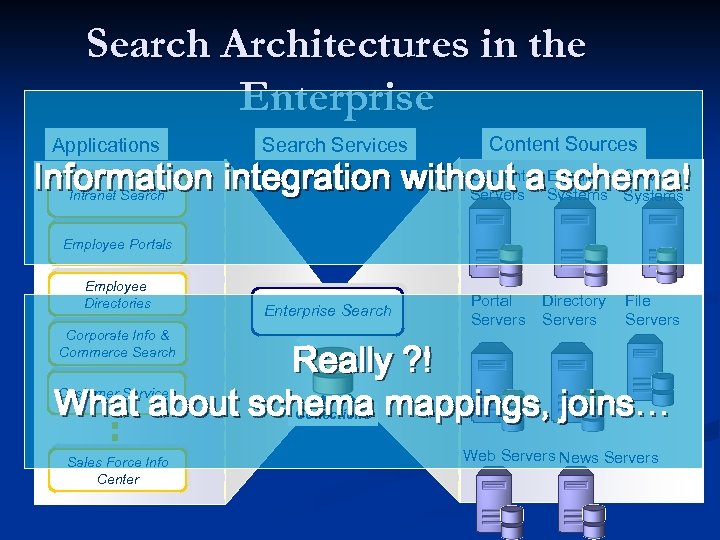
Search Architectures in the Enterprise Applications Search Services Content Sources Content Information integration without a. E-mail CRM schema! Servers Systems Intranet Search Employee Portals Employee Directories Enterprise Search Corporate Info & Commerce Search C E C Portal o Directory- File R Servers m Servers. M n t a S e i y n l s t t e P S S m o Web Servers News Servers s e y r r s t v t a e e l Really ? ! What about schema mappings, joins… Customer Services Collections Sales Force Info Center
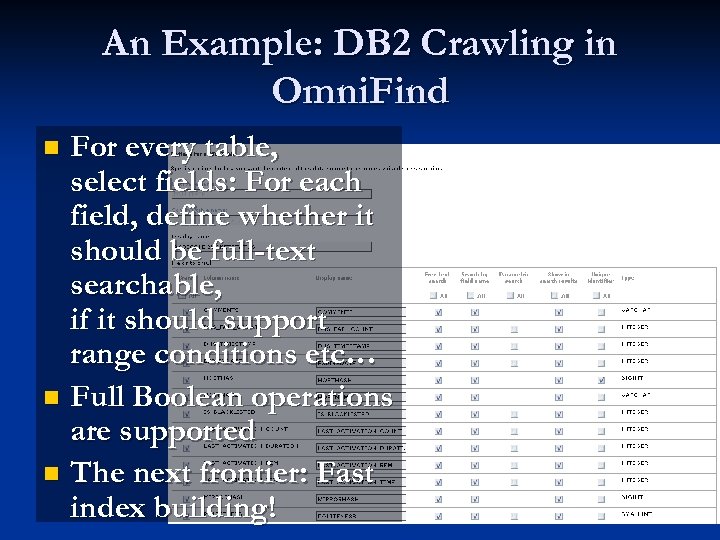
An Example: DB 2 Crawling in Omni. Find For every table, select fields: For each field, define whether it should be full-text searchable, if it should support range conditions etc… n Full Boolean operations are supported n The next frontier: Fast index building! n
UIMA: Unstructured Information Management Architecture n An open architecture n A software framework for processing unstructured information n Plug-n-Play with back-end Search Technologies n Freely Available on IBM Alpha. Works
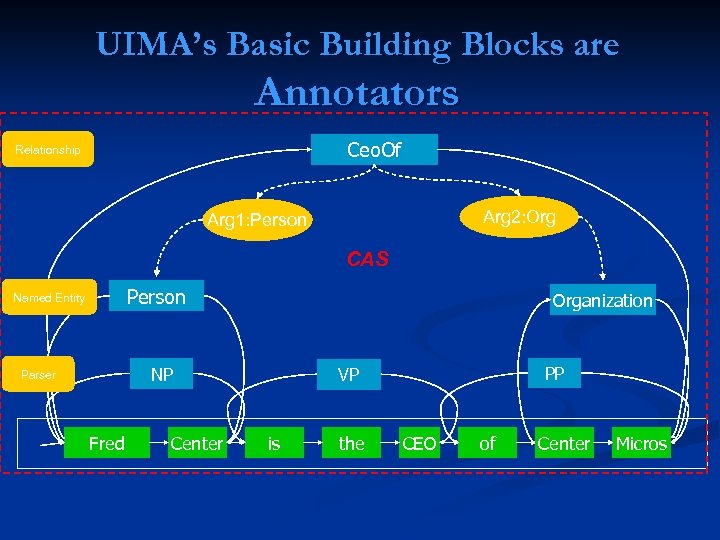
UIMA’s Basic Building Blocks are Annotators Ceo. Of Relationship Arg 2: Org Arg 1: Person CAS Person Named Entity Organization NP Parser Fred Center PP VP is the CEO of Center Micros
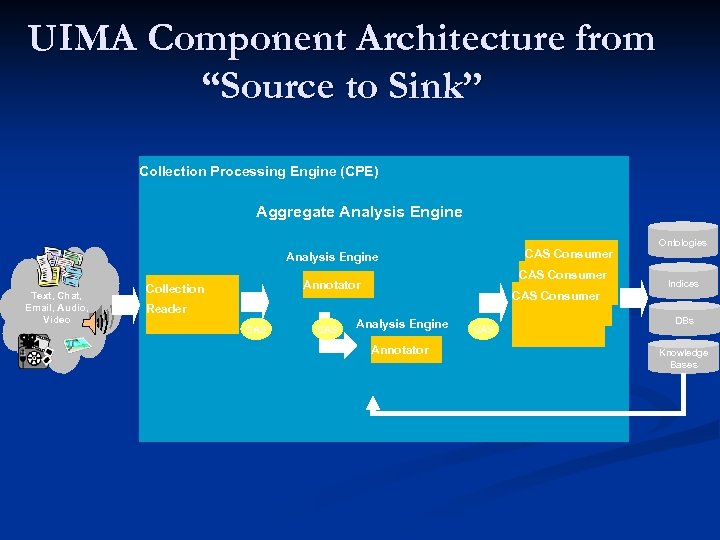
UIMA Component Architecture from “Source to Sink” Collection Processing Engine (CPE) Aggregate Analysis Engine CAS Consumer Analysis Engine Text, Chat, Email, Audio, Video CAS Consumer Annotator Collection CAS Consumer Reader CAS Analysis Engine Annotator CAS Ontologies Indices DBs Knowledge Bases
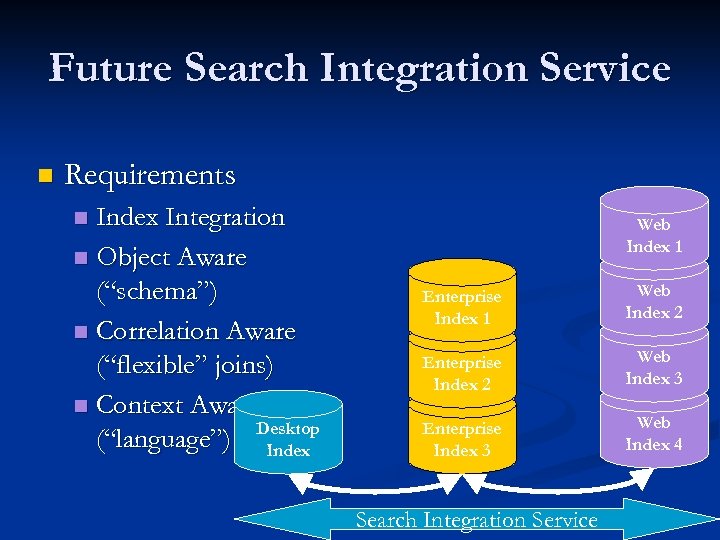
Future Search Integration Service n Requirements Index Integration n Object Aware (“schema”) n Correlation Aware (“flexible” joins) n Context Aware (“language”) Desktop Index n Web Index 1 Enterprise Index 1 Web Index 2 Enterprise Index 2 Web Index 3 Enterprise Index 3 Web Index 4 Search Integration Service

Search Integration Services Capabilities n n Need APIs for querying and control Control capabilities n n n Specifying the number of results, result chunks Total size of results Degree of validity, recency, trust, security-level… Time constraints, cost constraints, privacy constraints, security constraints May specify tradeoffs Semantic capabilities: APIs n n Relevant ontologies Description of resources

A Changing Landscape Search Integration Services n Semantic web capabilities n Technologies for Supporting Comprehensive Search: n n n XML search NL annotation servers collaborative bookmarks domain-specific services

What kind of Applications are we considering? n n n n n Generally involves a comprehensive answer to a question Not the kind you can perform by viewing a single result page – although these are very important Very time consuming with current tools May involve public and proprietary information May involve information from various sources May involve personal information May involve payment for certain resources May be time constrained May be of adjustable levels of dependability, clarity, recency

Kinds of Questions Informational: U. S. educational spending in cities with population of at least one million n Recommendation: What treatment is recommended for X n Technical: detailed techniques for water purification n Workflow: How do I organize a trip to Y: visa, flights, vaccinations, money exchange, cellular service, consulate, emergencies n Compositional: How do I perform a task electronically by composing various services These are difficult to answer with current tools n

n n Towards a Comprehensive Platform A language and a system supporting it Why an additional language? n n n To take advantage of a collection of sophisticated services – search engines, semantics, collaborative tools, advanced techniques … To provide a context to search services To enable better result presentation services To enable personalization of the task at hand When required, look at ‘raw’ data rather than only derived products To enable optimization
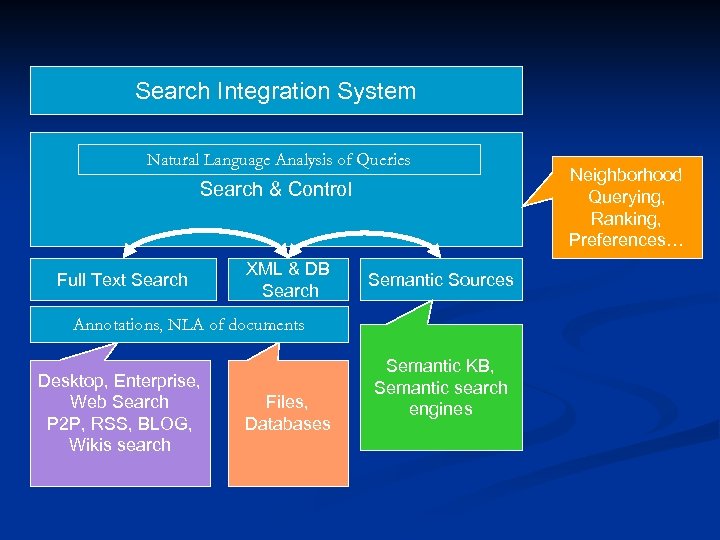
Search Integration System Natural Language Analysis of Queries Search & Control Full Text Search XML & DB Search Semantic Sources Annotations, NLA of documents Desktop, Enterprise, Web Search P 2 P, RSS, BLOG, Wikis search Files, Databases Semantic KB, Semantic search engines Neighborhood Querying, Ranking, Preferences…

Semantic Web: Search and Integration n n Look at mixed resources – involving traditional as well as semantic layers (annotation). Search the semantic web (as in Swoogle) n n n Use ontologies to resolve ambiguities Include reasoning capabilities Use various measures for semantic proximity Combine information from multiple sources and resolve conflicts (trust, easier for intranets) Use ontologies to organize results in human readable form Supply explanations – how is information deduced

Semantic Web: Search and Integration n Search semantic data (KB) to obtain access to described traditional resources (as in TAP) n n Resolve ambiguities at the data level Deduce keywords for traditional search engines to obtain additional information Examine likely sources (e. g. , IMDB) Continue further exploration of described resources

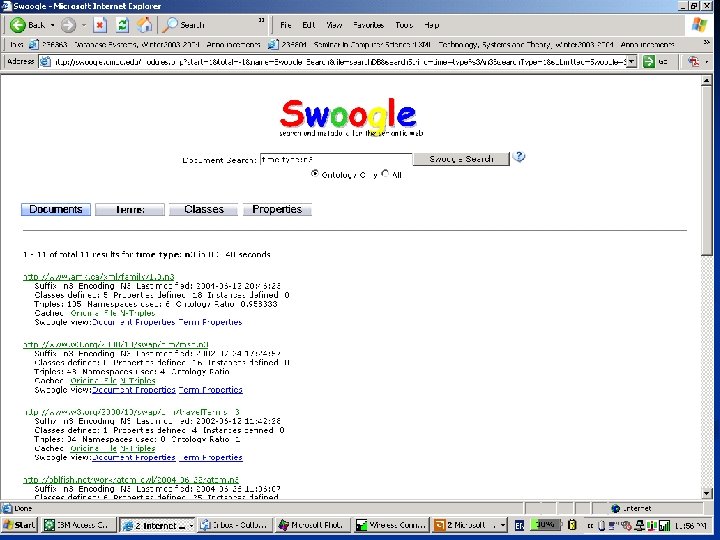
Swoogle (extracted from the site) n n Swoogle is a crawler-based indexing and retrieval system for the Semantic Web -- RDF and OWL documents encoded in XML or N 3 Swoogle extracts metadata for each discovered document, and computes relations among them Swoogle is intended as a resource to support services needed by software agents and programs via web service interfaces and also for semantic web researchers to use directly via the web interface It is not designed to support casual users seeking to answer queries on the web (e. g. , "what is the population of the capital of India? ")

Tap (extracted from the site) n n n The TAP KB is a shallow but broad knowledge base containing basic lexical and taxonomic information about a wide range of popular objects Our goal is to bootstrap the Semantic Web by providing a comprehensive source of basic information about popular objects The KB currently includes knowledge about, n n n Music: Popular music, musicians & groups, instruments, styles, composers Movies: Top Movies, actors, television shows Authors: Top book authors, classic books Sports: Athletes, sports teams, equipment ….

The KB </rdfs: Class> <rdfs: Class rdf: ID="http: //tap. stanford. edu/data/United. States. Senator"> <rdfs: label xml: lang="en">Sen. </rdfs: label> <rdfs: label xml: lang="en">Senator</rdfs: label> <rdfs: sub. Class. Of rdf: resource="http: //tap. stanford. edu/data/Politician"/> <tap: plural>senator</tap: plural> </rdfs: Class> <tap: United. States. Senator rdf: ID="http: //tap. stanford. edu/data/Politician. Dodd, _Christopher"> <rdfs: label xml: lang="en">Christopher Dodd</rdfs: label> <tap: represents. Place rdf: resource="http: //tap. stanford. edu/data/Connecticut. State"/> <tap: member. Of rdf: resource="http: //tap. stanford. edu/data/USDemocratic. Party"/> </tap: United. States. Senator>

Semantic Web: Task Formation n Use ontologies to deduce a workflow for performing a task Applicable to composing web services n The task itself may involve a number of sites n Parts may be executable: n n on the web n via other means n via web services n The output may be a complete or partial task fulfillment

Business Trip Planner Agent Example-1 n Present coherent information for trip planning n n Dates, constraints, preferences, organizational policy Company resources and clients in the area n n Destination conditions based on historical data n n History of contacts, clients, deals, prospects weather, tourist information, official holidays Latest news at destination and vicinity n commercial, political, religious, security, crime, medical

Business Trip Planner Agent Example-2 n Additional information for trip planning n n n Airline, hotel, car rental data Suggest itinerary based on constraints Prepare to make reservations on-line Personal friends, family in the area Must visit tourist attractions n n Major seasonal attractions n n dates, rates, photos, video, historical background, links festivals, concerts, theatre Once information is machine “understandable” one should be able to construct a trip planner agent

Technologies for Supporting Comprehensive Search 1. Querying Modes and Control n n 2. Ranking n 3. The exact structure may not always be known and relationships need be specified in a flexible way; various semantics are possible Declaratively stating priorities Ranking is a critical component, both in weighting different scores as well as controlling the ordering of result presentation Neighborhood Querying n Imprecise querying mode in which similar or near entities/objects are retrieved

1. Querying Modes and Control n NL understanding n n Flexible Querying n n Web pages contain phrases whose similarity is not just based on syntactical matching; the meaning may depend on context, language usage and more The exact structure may not always be known and relationships need be specified in a flexible way; various semantics are possible Query control: Preferences n A search may involve resources and tradeoffs may need to be specified; preferences may also address quality, recency, amount, language and other factors

Querying Modes and Controls Example n n n n Trying to locate information about a movie based on fairly vague recollections It is based on a book It deals with military political issues, maybe a coup or a coup attempt, or a kidnapping From the fifties or sixties The lead role is a famous movie star of that time It’s not the one with Peter Sellers and it’s not Failsafe and not the one with submarines The plot involves Generals, Colonels and the President, maybe not all of them and there might also be a Senator or two

Querying Modes and Controls Example n Solving the above may utilize n n n a movie database with an associated ontology a flexible querying language that attempts at maximal subset satisfaction a web search engine with some NL understanding (of the plot)

Querying Modes and Controls Example Con’t. n While I’m really interested, please n n n Work on it for no more than an hour Don’t spend more that a dollar finding the answer Use only highly trusted sources Obtain photos and video clips if possible, especially those involving the lead star, Washington sites, trucks and airplanes The most important items are how much the movie grossed and whether the lead star was nominated for an Oscar for this movie

2. Ranking n Composition n n Top-k Queries n n n Various “judges” may score differently; allow scoring of search terms, services, relevancy Multidimensional objects; monotone aggregation function on attributes; on each attribute, a list in rank order; find k top ranked objects Many variations; e. g. , applications for finding “best” pages based on ranking by various services Ranked Query Results n Ranking query results in desired order also applies to the semantic web, important for retaining user attention as well as in specifying sub queries during compilation/execution

Ranking Example n n n Continuing the previous example, textual information may be provided by various search engines – rank the information based on the weights awarded to these engines Various photos may score differently on the star, Washington sites, airplanes and trucks, find best Rank results, for example those that answer the most conditions that are judged to be the most important

3. Neighborhood Querying flexibility n k Nearest Neighbors n n Complex Similarity Queries n n Locate near-by objects in a multidimensional space, objects may be pages, or traditional objects, where each dimension corresponds to a property (attribute) Identify similar objects, to a given object set Detecting “identical objects”

Neighborhood Querying Example n n n Continuing the example, if a coup or kidnapping plot is not found, a close one may be a plot of some other type, for example an overthrow, and instead of the military it may involve the secret service Maybe it was some other vehicle rather than trucks or planes Perhaps the movie was an Oscar candidate in some other category or its director/star were Oscar winners for other movies

Moving on… n The landscape is complex n n n n Sophisticated tagging and information aggregation Merging object and document retrieval Focused search New “sources” including RSS, Blogs, Wikis … Useful result presentation Cooperative bookmarks management We explored some ways to take advantage of this emerging landscape for sophisticated search and integration tasks

Thank You!
3d2befd51e27690ea5df3db024dfd72e.ppt