7b5f0aa18d2ff243b7bba45065cadc66.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Database Design 1

Course Description – This course will focus on topics related to database design. The course will begin with a brief review of modeling, and then discuss the evolution of the resulting products (e. g. , the data models) into an actual design. This will include normalization, de-normalization, logical and physical design, and a variety of other topics that have design implications (VLDBs, data warehousing, OLTP, OLAP, Data Mining, RAID, etc). 2

Course Topics • Basic data modeling concepts: – Entities, attributes, relationships, dependencies. • Logical and physical database design: – Normal forms, normalization, object (i. e. , table and index) placement. • Design configurations: – On-line transaction processing, decision support, data warehousing, VLDBs. Note that this course will not attempt to present a process, but will rather focus on a variety of common database problems and issues. 3

Course Outline – – – – Introduction Modeling & Design Overview Normal Forms Normalization Logical & Physical Design (Object Placement) Data Warehousing & VLDBs De-normalization RAID 4

What Is Data Modeling? Information modeling is a technique that supports many of the activities needed to manage information as an asset. Information modeling is a technique for describing information structures. -Designing Quality Databases with IDEF 1 X Information Models by Thomas A. Bruce. 5

Data Modeling Languages & Processes • Relational Based: – – – IDEF 1 X Chen Information Engineering NIAM MERISE • Others: – – Bachman Associative Data Modeling Semantic Information Modeling IBM’s Repository Modeling Language 6
Data Modeling Products • Relational modeling typically defines: – – Entities Attributes Keys (candidate, primary, foreign, alternate, secondary) Relationships (cardinality, type) • The above are summarized in a variety of different types of diagrams: – – – Entity relationship diagram Key based model Project information model Fully attributed model Transformation model Enterprise model 7
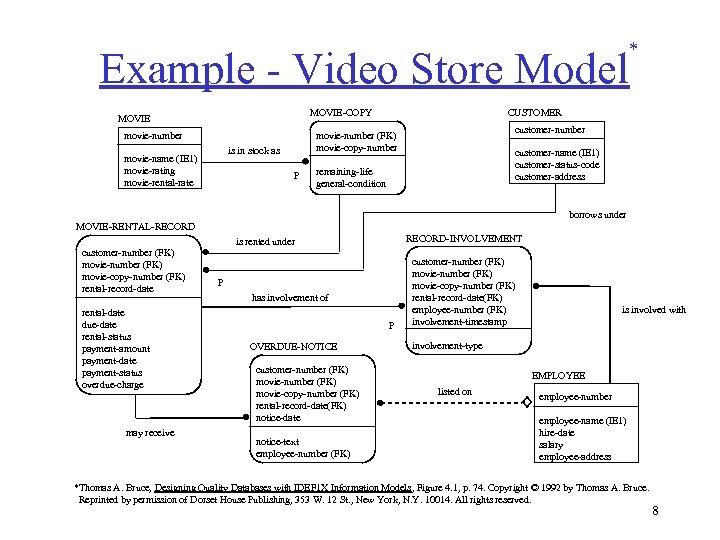
Example - Video Store Model CUSTOMER MOVIE-COPY MOVIE movie-number customer-number movie-number (FK) movie-copy-number is in stock as movie-name (IE 1) movie-rating movie-rental-rate P * customer-name (IE 1) customer-status-code customer-address remaining-life general-condition borrows under MOVIE-RENTAL-RECORD customer-number (FK) movie-copy-number (FK) rental-record-date rental-date due-date rental-status payment-amount payment-date payment-status overdue-charge may receive RECORD-INVOLVEMENT is rented under P has involvement of P OVERDUE-NOTICE customer-number (FK) movie-copy-number (FK) rental-record-date(FK) notice-date notice-text employee-number (FK) customer-number (FK) movie-copy-number (FK) rental-record-date(FK) employee-number (FK) involvement-timestamp is involved with involvement-type EMPLOYEE listed on employee-number employee-name (IE 1) hire-date salary employee-address *Thomas A. Bruce, Designing Quality Databases with IDEF 1 X Information Models, Figure 4. 1, p. 74. Copyright © 1992 by Thomas A. Bruce. Reprinted by permission of Dorset House Publishing, 353 W. 12 St. , New York, N. Y. 10014. All rights reserved. 8

Data Modeling Tools Power Designer 2000 ER/Studio ERwin Data Modeler Visio Professional Vivid Clarity Easy. ER/Easy. Object - Sybase - Oracle - Embarcadero - Logic Works - Iconix - Visio Corporation - Intek Technologies - Visible Systems And the list goes on. . . see www. dbmsmag. com/pccase. shtml 9

Database Design • Database design decisions made during modeling phases: – Selection of entities, attributes, relationships, etc. , • Such decisions have a direct impact on database design: – – Entities => tables Attributes => columns Search Keys => indices Relationships => triggers, referential constraints • Many design decisions are not made during modeling: – De-normalization – Index selection – Object placement 10
Components Of A Database Design • Tables – columns (type, constraints) – keys (primary, foreign) – triggers • Object Placement – index placement – table placement • Device Configuration • Indices – column selection – column index order – index type (clustered, nonclustered, hashed, bitmap) – mirroring – striping 11

Course Focus • Problems and issues that arise throughout the database life-cycle, from modeling to administration. • Topics considered will have direct implications for database design. • All discussion will be in the context of the relational model (as opposed to the network, hierarchical, or object-oriented models). 12
7b5f0aa18d2ff243b7bba45065cadc66.ppt