bcd1b4e457647522cc94fdace1de492b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 97

Data Warehousing Business Intelligence www. thinkingsolutions. be Erwin Moeyaert
Current Status What do I do? ? ? How do I increase sales? ? How do I make my product better? ? ? Business Users Mountains of Data
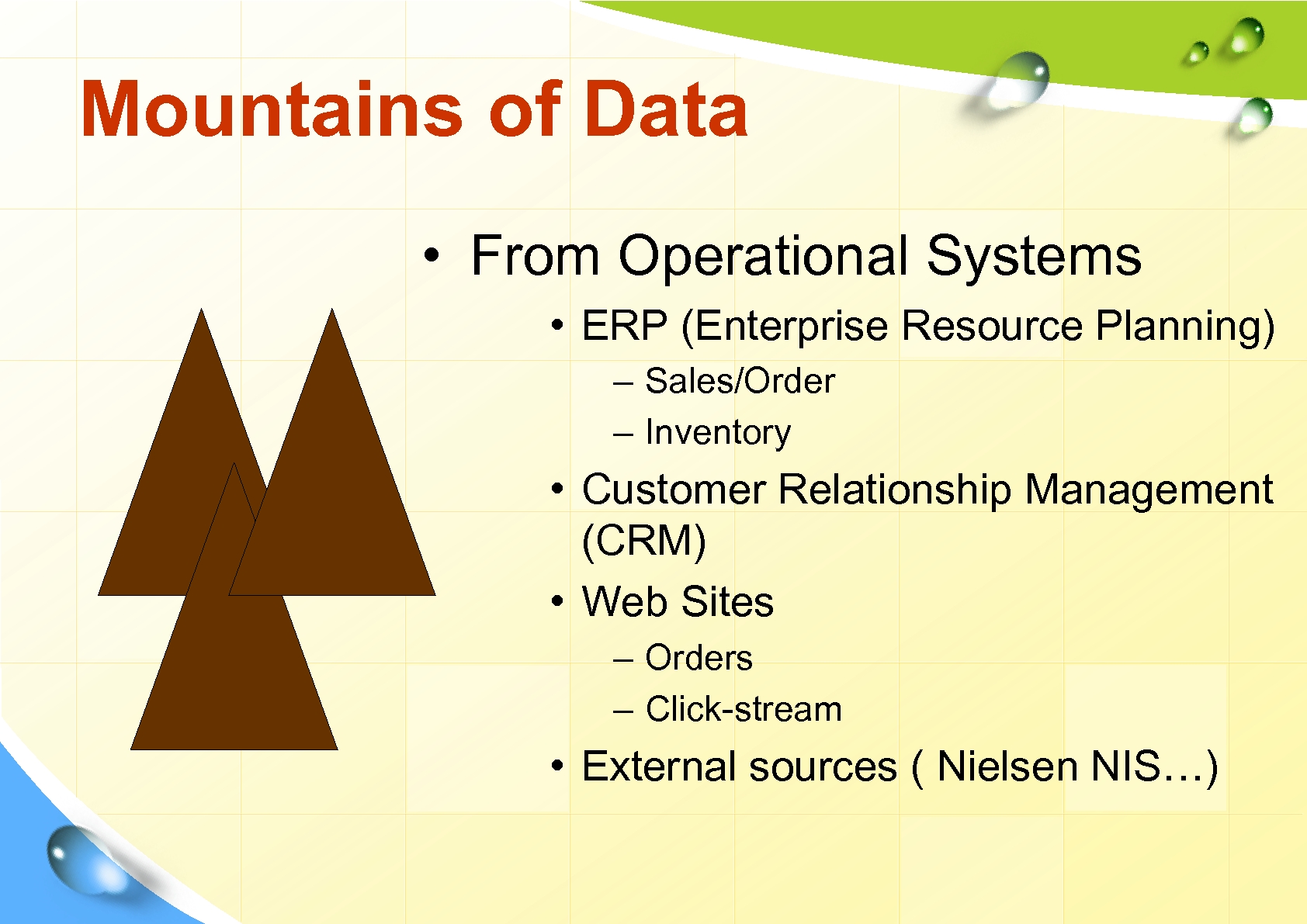
Mountains of Data • From Operational Systems • ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) – Sales/Order – Inventory • Customer Relationship Management (CRM) • Web Sites – Orders – Click-stream • External sources ( Nielsen NIS…)

Mountains of Data • Organizations have lots of data • Data is not in a form that is useful to decision-makers – Not easy to review – Not informative nor insightful
The Problem How do I retain customers? How do I increase sales? ? GAP How do I make my product better? ? ? Business People Mountains of Data
Today’s Information Flow • Business in 90’s invested in transactional systems: – – – Supply Chain Management (SCM) Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) Finance (budget, forecasting and reporting)
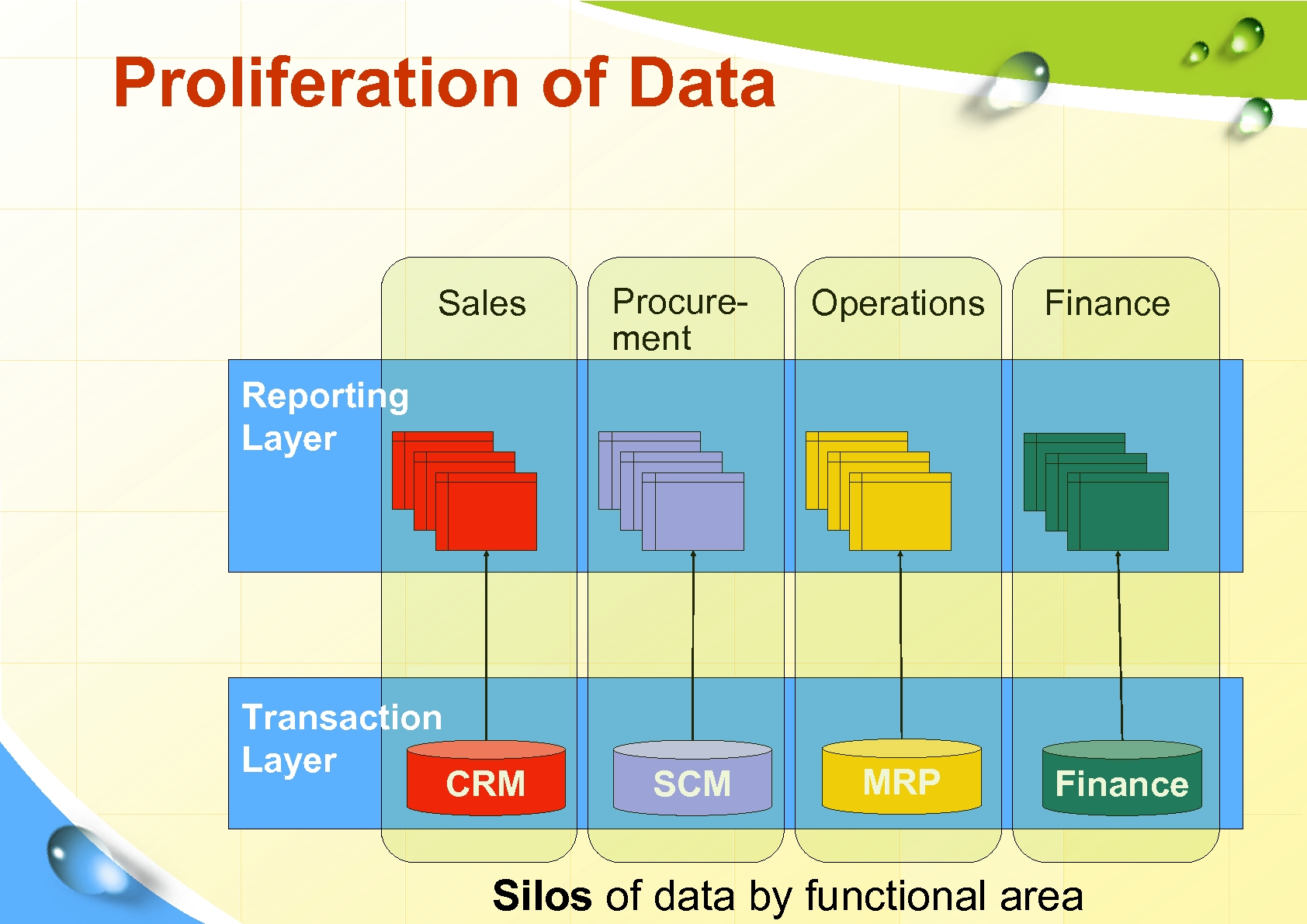
Proliferation of Data Sales Procurement Operations Finance Reporting Layer Transaction Layer CRM SCM MRP Finance Silos of data by functional area
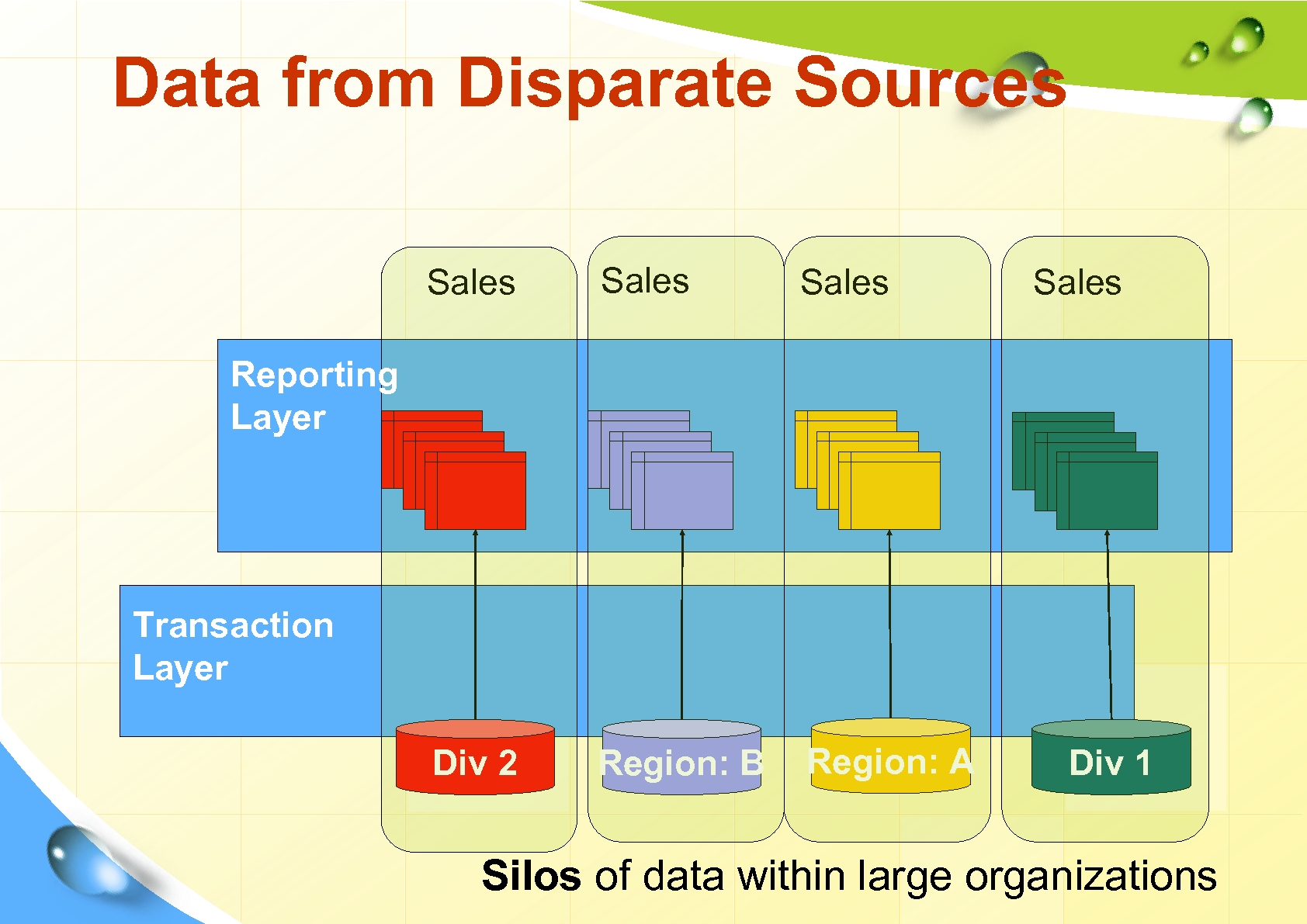
Data from Disparate Sources Sales Div 2 Region: B Region: A Sales Reporting Layer Transaction Layer Div 1 Silos of data within large organizations

Why BI? The Five Questions • • • What happened? What is happening? Why did it happen? Past Present What will happen? What do I want to happen? Data ERP CRM SCM 3 Pty Future Black books
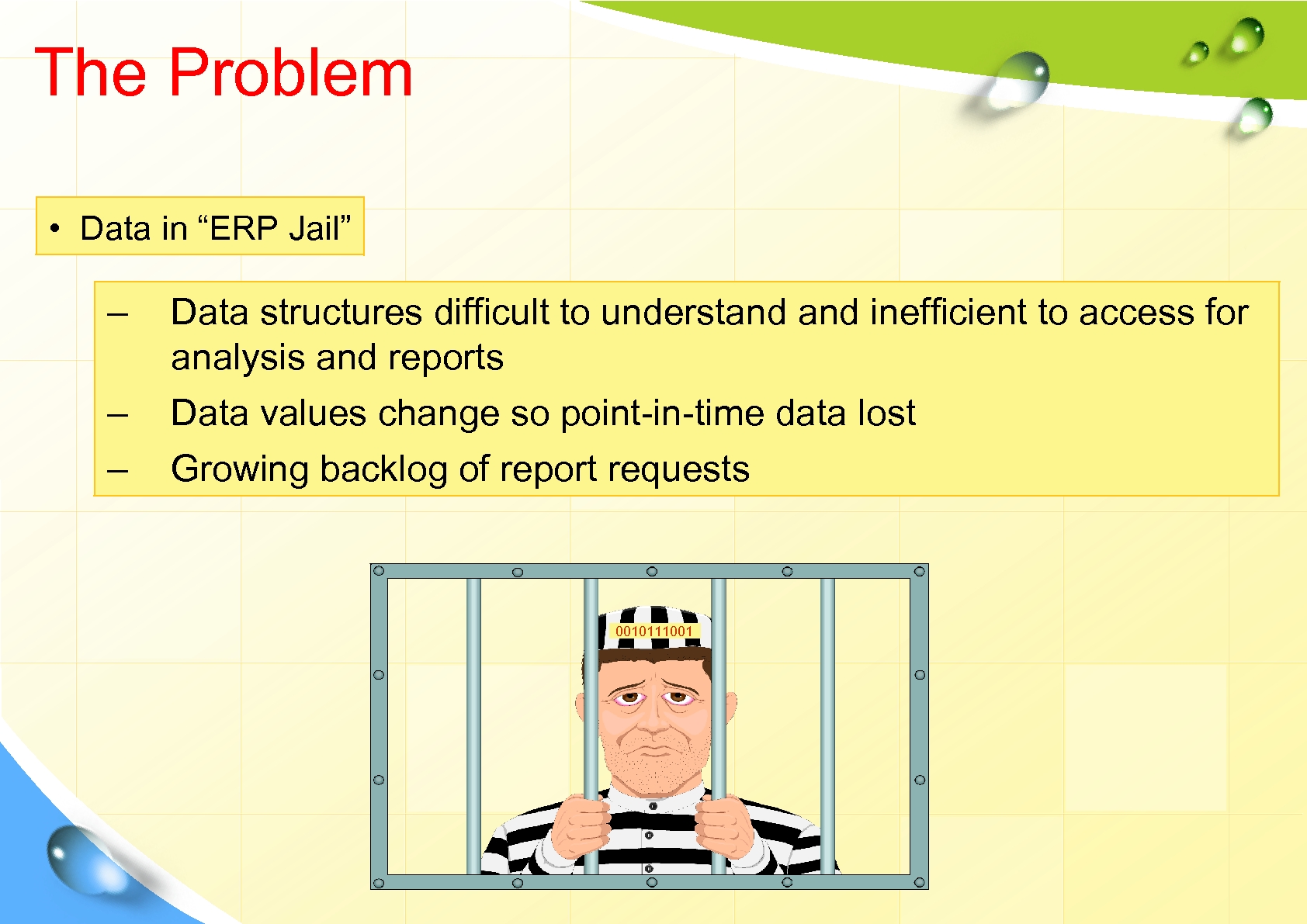
The Problem • Data in “ERP Jail” – – – Data structures difficult to understand inefficient to access for analysis and reports Data values change so point-in-time data lost Growing backlog of report requests 0010111001

The Solution • Initial charge – Build a data warehouse • Initial vision – Create business view of administrative data

Data Warehousing (DW) • Definition • A subject-oriented, integrated & non-volatile database updated on a typically rhythmic cycle from an enterprise’s various transaction databases. • Purpose • Accumulate data from disparate data sources for querying purposes • Separate reporting and analysis operations from transaction systems to maximize the performance of both Commonly very large repositories that house historical data

What is Business Intelligence? The process by which an organization manages large amounts of data, extracting pertinent information, and turning that information into knowledge upon which actions can be taken.

Reasons for BI • BI enables organizations to make well informed business decisions and gain competitive advantage. • BI enables organizations to use information to quickly and constantly respond to changes.
Benefits of BI • “Single Version of the truth” • Accurate, timely data available to all levels of the organization

BI Activities BI applications include the activities of: • decision support, • query and reporting, • online analytical processing (OLAP), • statistical analysis, • forecasting, and • data mining.

BI Users • There are many different users who can benefit from business intelligence – Executives – Business Decision Makers – Information Workers – Line Workers – Analysts

BI Solutions. How to make it happen • Two main components: – Data Consolidation and Storage – Data Retrieval, Analysis and Presentation
BI Curriculum • • • Multi-Dimensional Analysis Data Warehousing Data Mining Dimensional Modeling Data Visualization
Bridging the Gap • Need data storage structures to facilitate fast analysis of huge volumes of data • Need software to provide access to the data, allow flexible manipulation, and provide meaningful presentation
Data Warehouse Concepts & Architecture

Data Warehouse Concepts Why Do We Need A Data Warehouse ? We Can Only See - What We Can See ! BETTER ! FASTER ! CHEAPER ! FUNCTIONALLY COMPLETE !
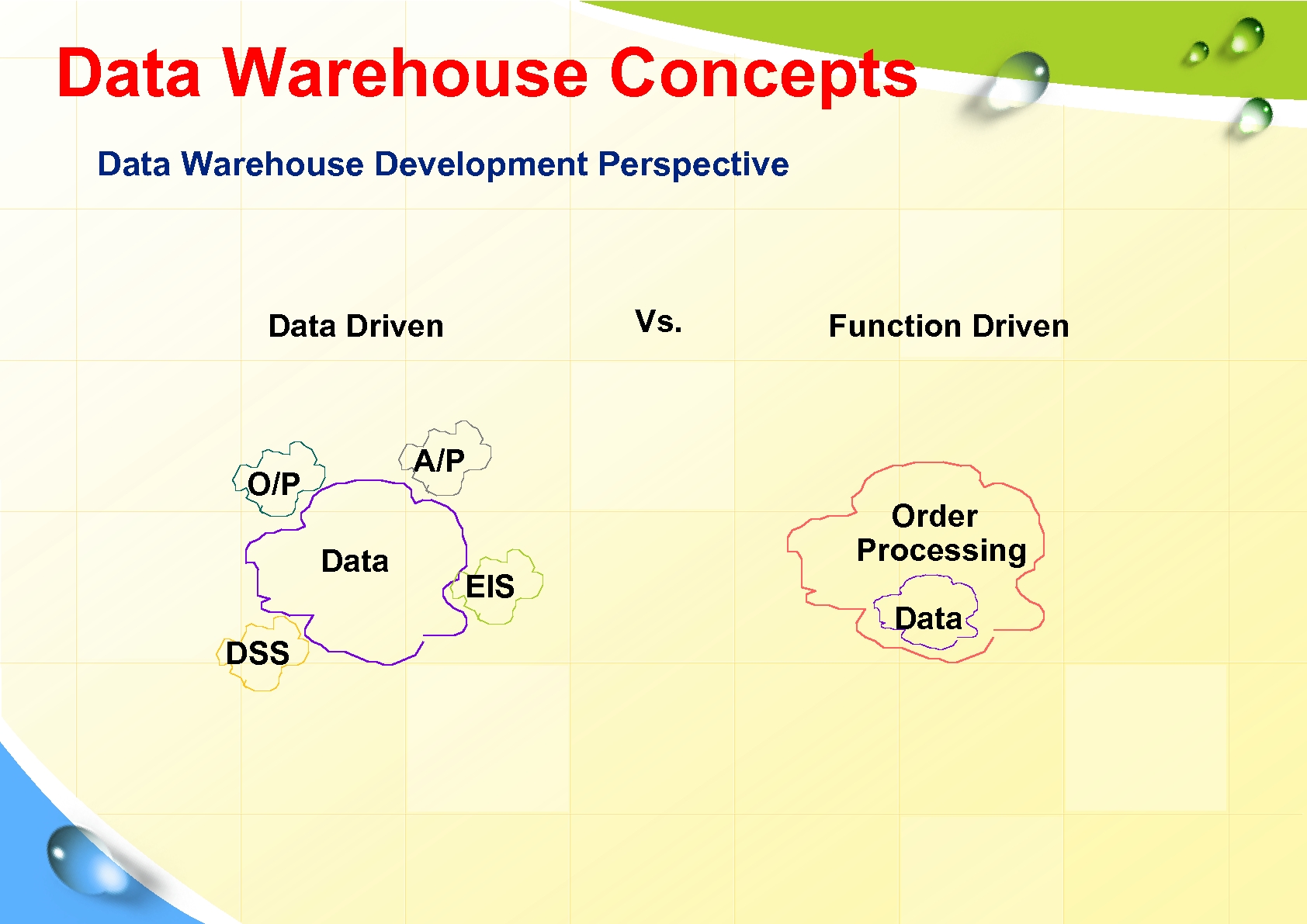
Data Warehouse Concepts Data Warehouse Development Perspective Vs. Data Driven A/P O/P Data DSS Function Driven Order Processing EIS Data

Data Warehouse Concepts What Do We Need To Do ? Use Operational Legacy Systems’ Data: To Build Operational Data Store, That Integrate Into Corporate Data Warehouse, That Spin-off Data Marts. Some May Tell You To Develop These In Reverse!

Data Warehouse Concepts Our Goal for A Data Warehouse ? • Collect Data-Scrub, Integrate & Make It Accessible • Provide Information - For Our Businesses • Start Managing Knowledge • So Our Business Partners Will Gain Wisdom !
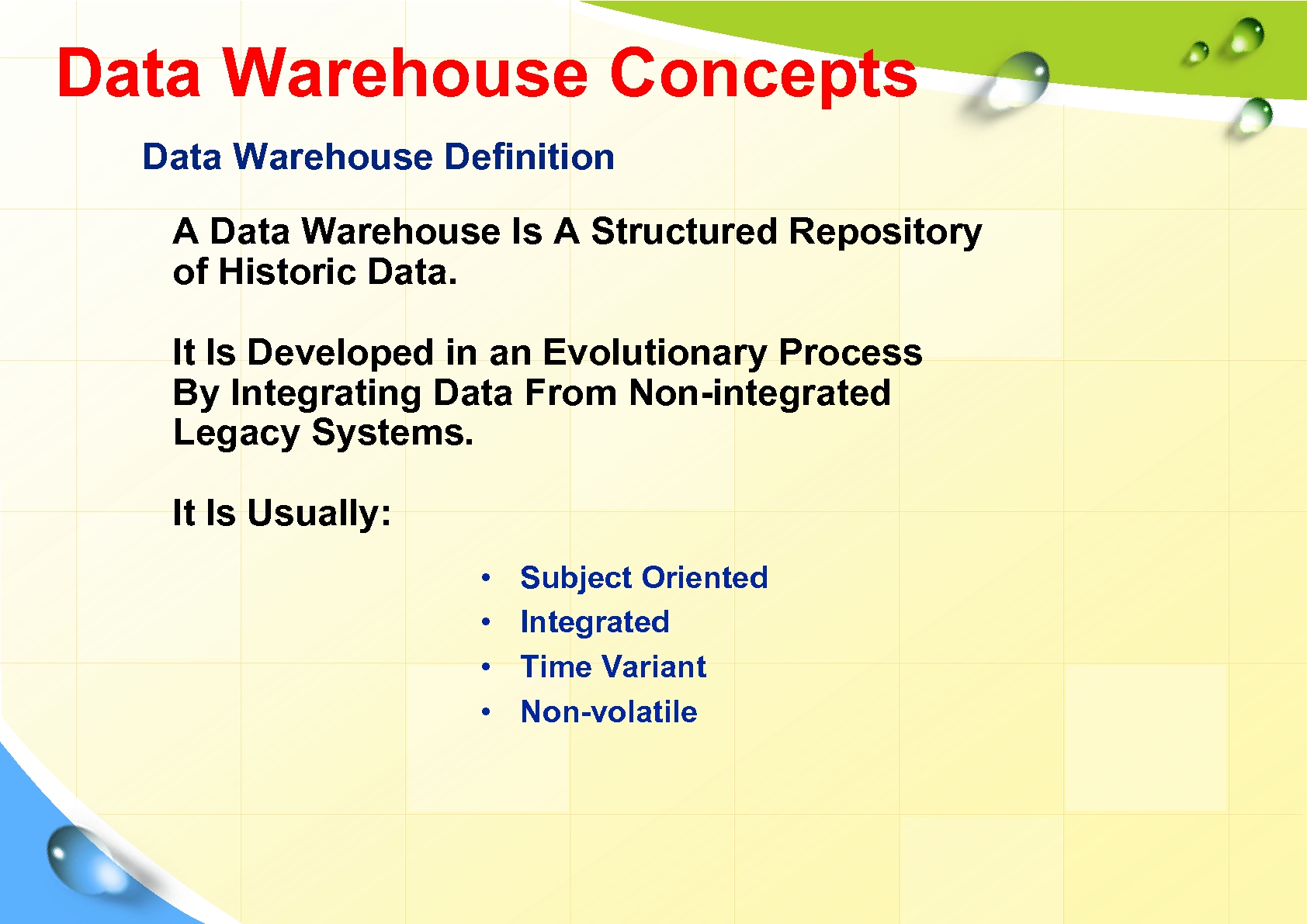
Data Warehouse Concepts Data Warehouse Definition A Data Warehouse Is A Structured Repository of Historic Data. It Is Developed in an Evolutionary Process By Integrating Data From Non-integrated Legacy Systems. It Is Usually: • • Subject Oriented Integrated Time Variant Non-volatile
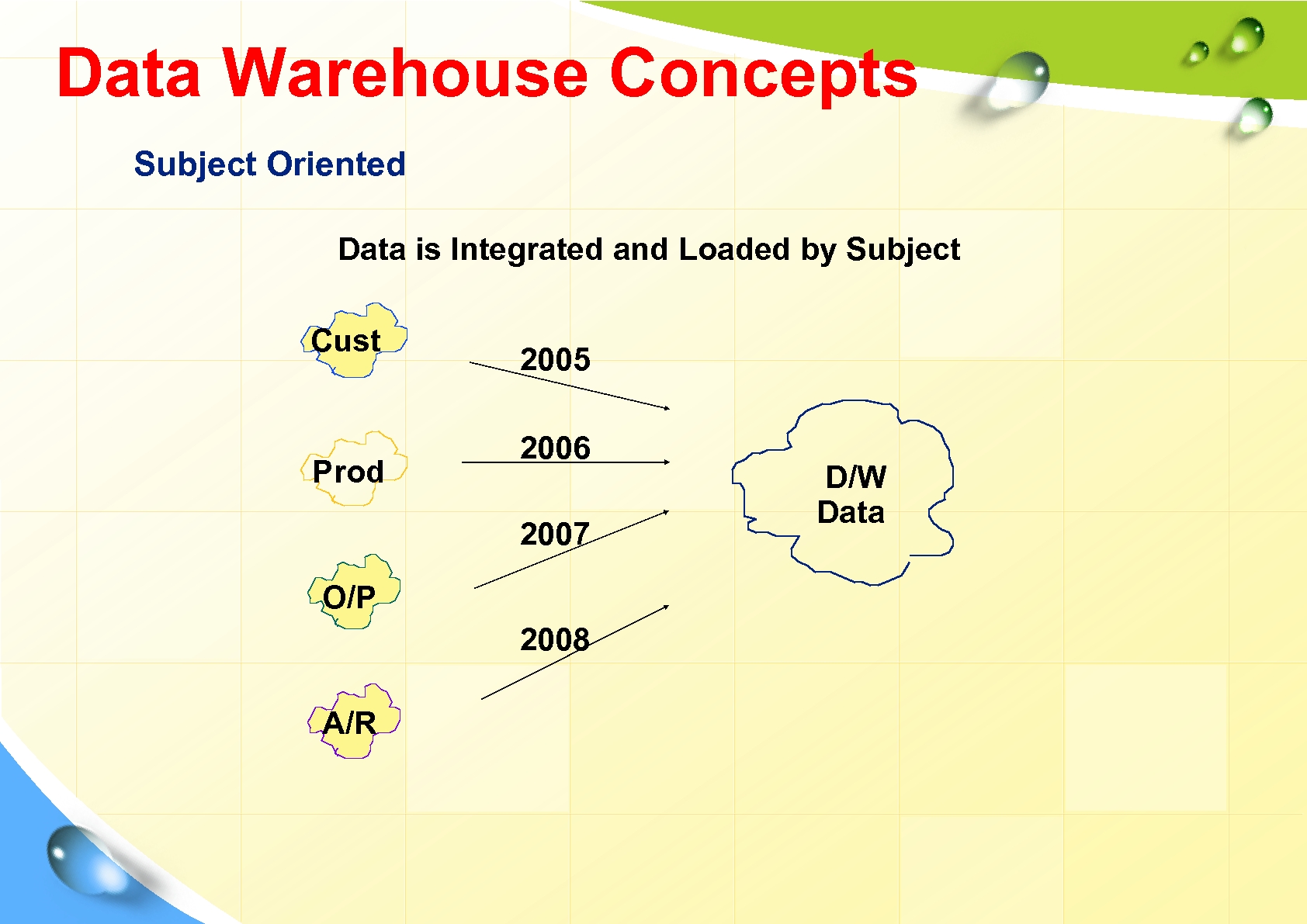
Data Warehouse Concepts Subject Oriented Data is Integrated and Loaded by Subject Cust Prod 2005 2006 2007 O/P 2008 A/R D/W Data

Data Warehouse Concepts Time Variant Operational System • View of The Business Today • Operational Time Frame • Key Need Not Have Data Warehouse • Designated Time Frame (3 - 10 Years) • One Snapshot Per Cycle • Key Includes Date

Data Warehouse Concepts Integrated
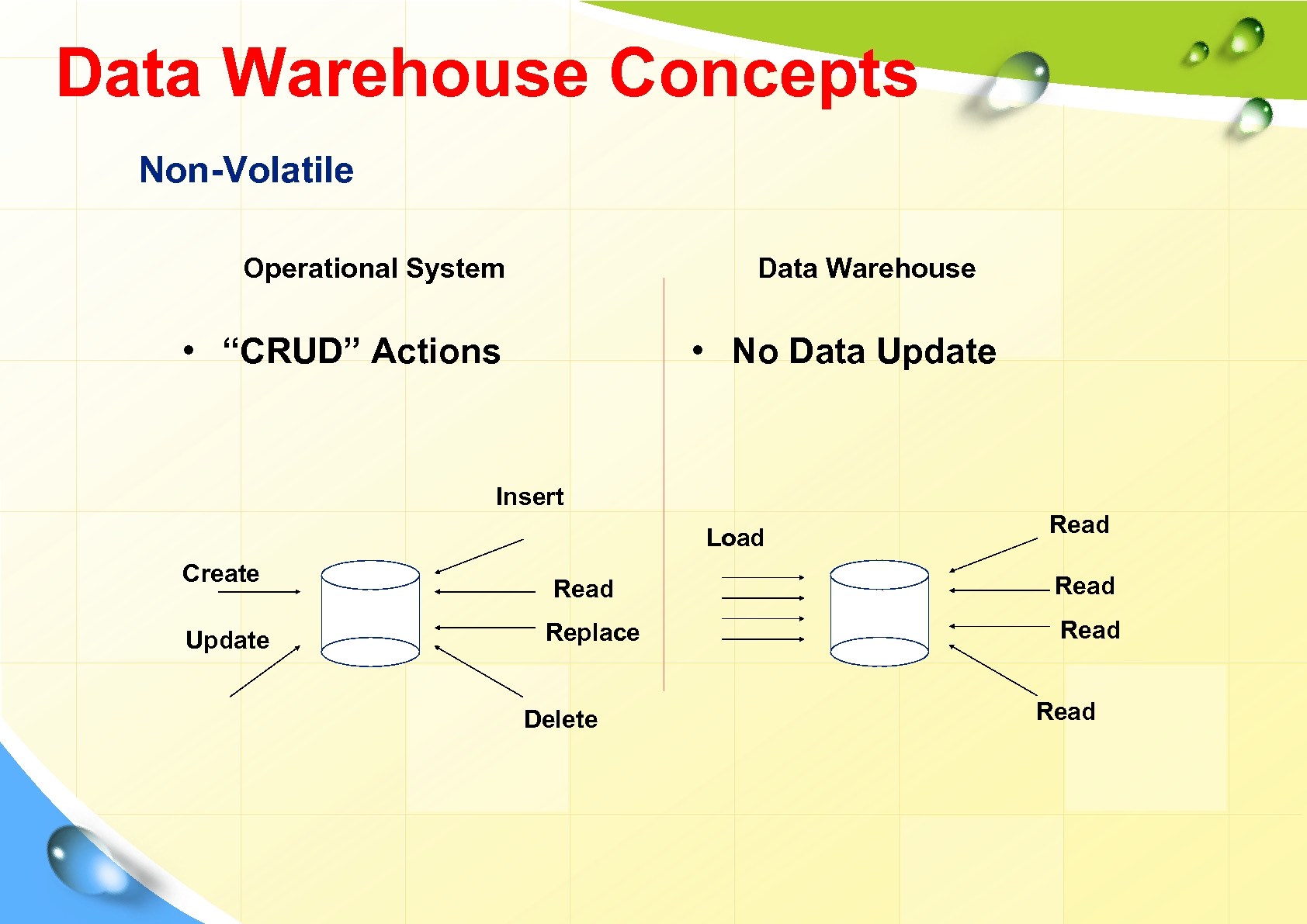
Data Warehouse Concepts Non-Volatile Operational System Data Warehouse • “CRUD” Actions • No Data Update Insert Load Create Update Read Replace Delete Read
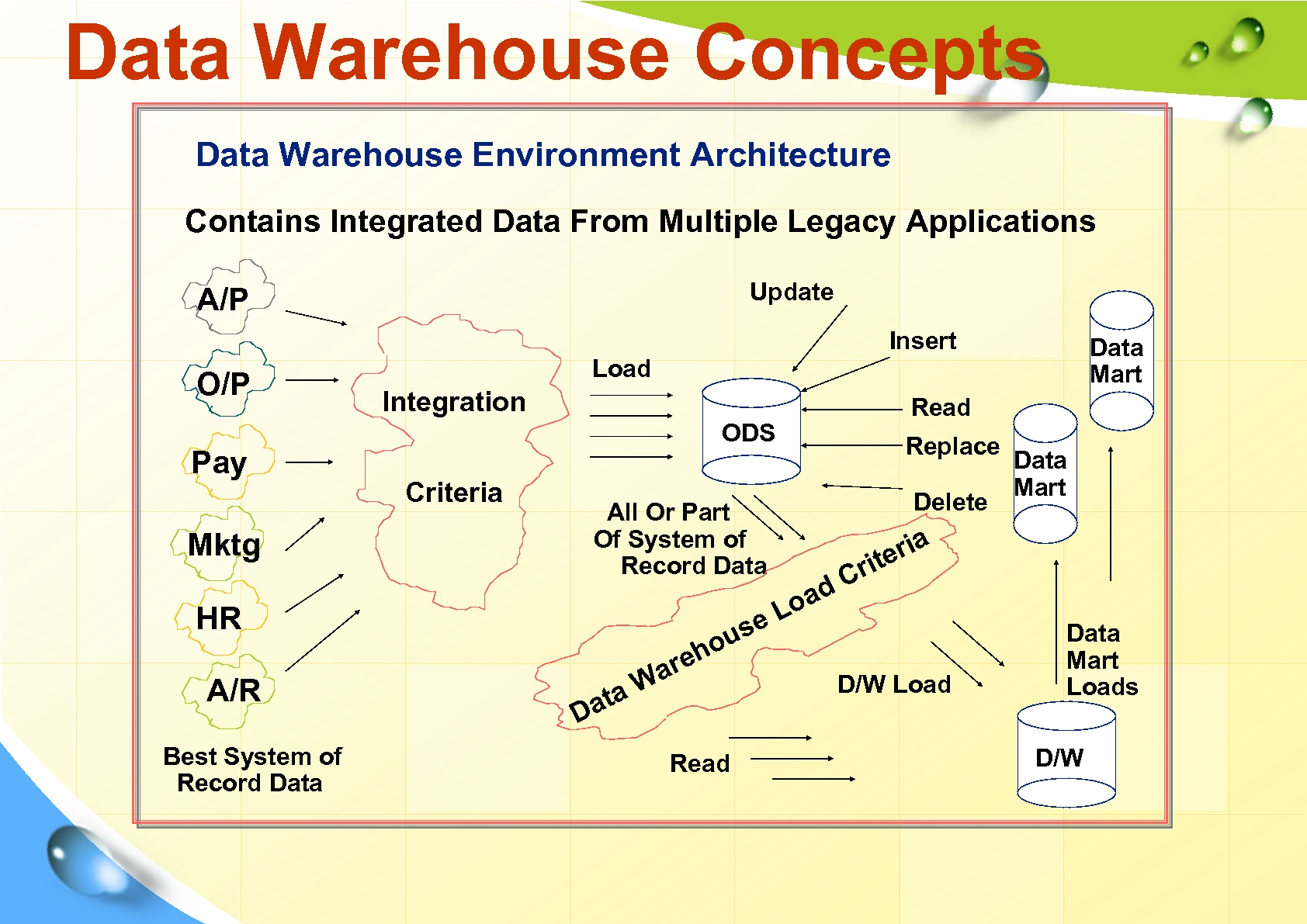
Data Warehouse Concepts Data Warehouse Environment Architecture Contains Integrated Data From Multiple Legacy Applications Update A/P Insert O/P Pay Mktg Load Integration Best System of Record Data Read ODS Criteria All Or Part Of System of Record Data ad Lo se u HR A/R Data Mart D ta a ho re a W Read Replace Delete Data Mart ria te ri C D/W Load Data Mart Loads D/W
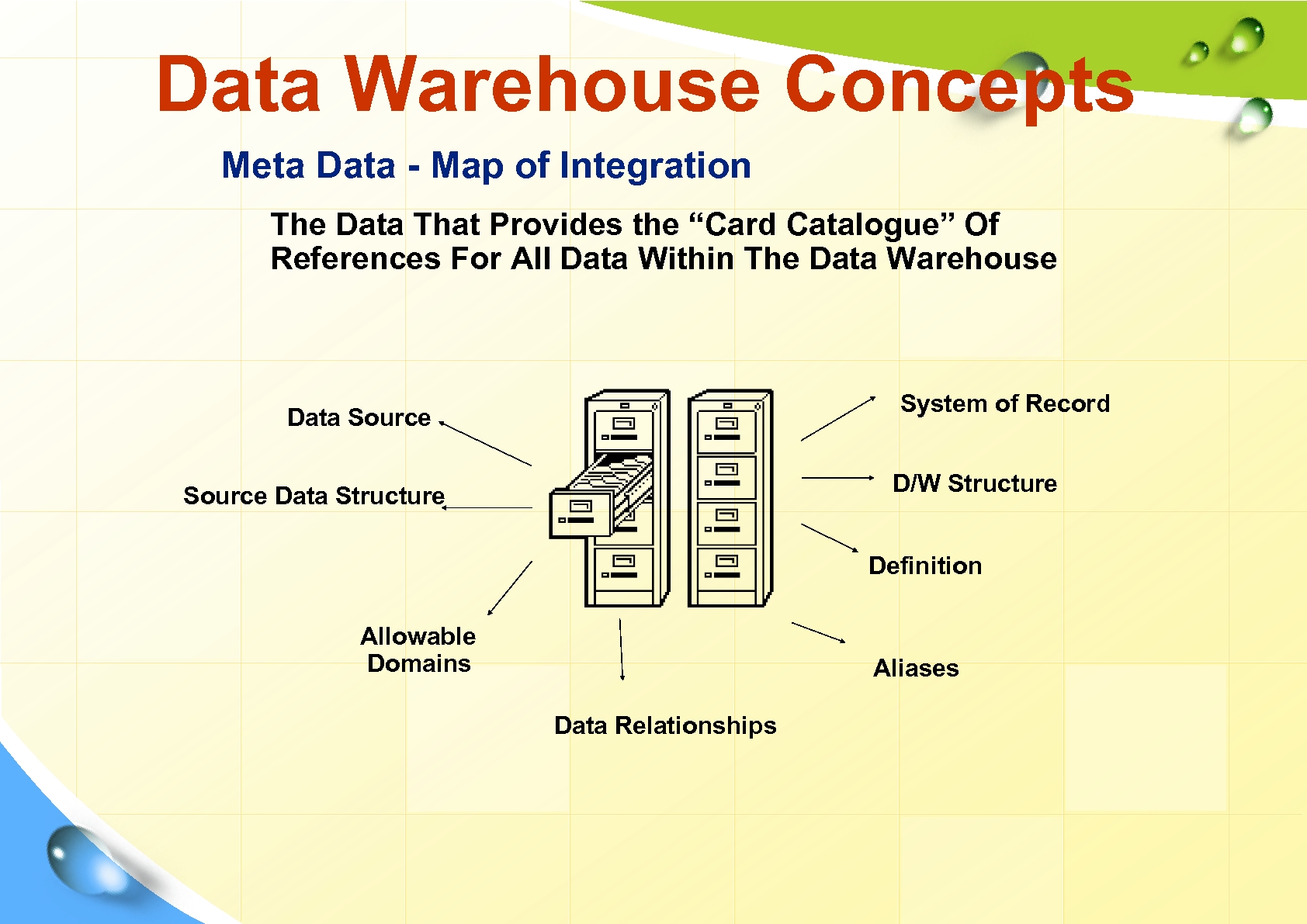
Data Warehouse Concepts Meta Data - Map of Integration The Data That Provides the “Card Catalogue” Of References For All Data Within The Data Warehouse System of Record Data Source D/W Structure Source Data Structure Definition Allowable Domains Aliases Data Relationships
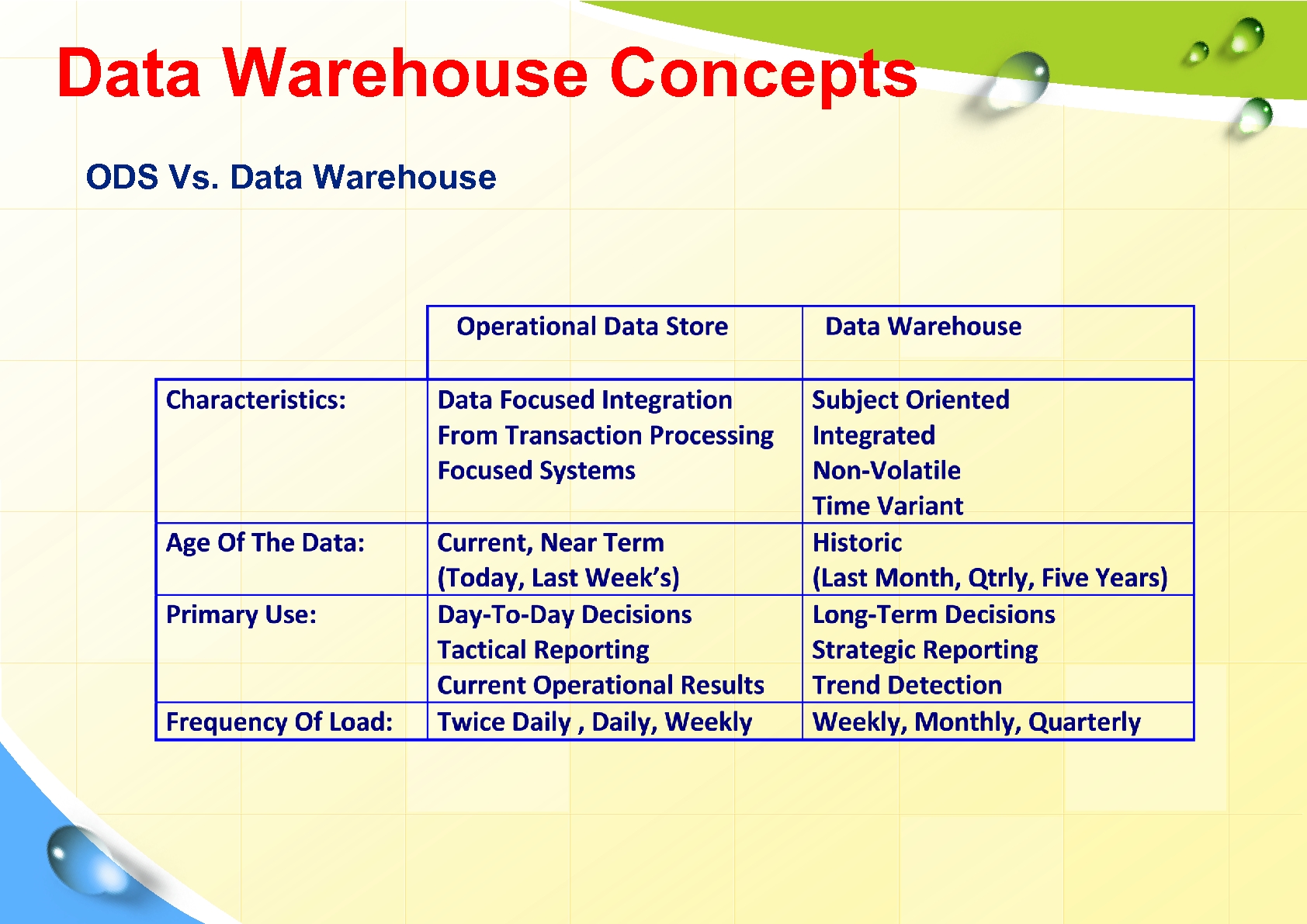
Data Warehouse Concepts ODS Vs. Data Warehouse
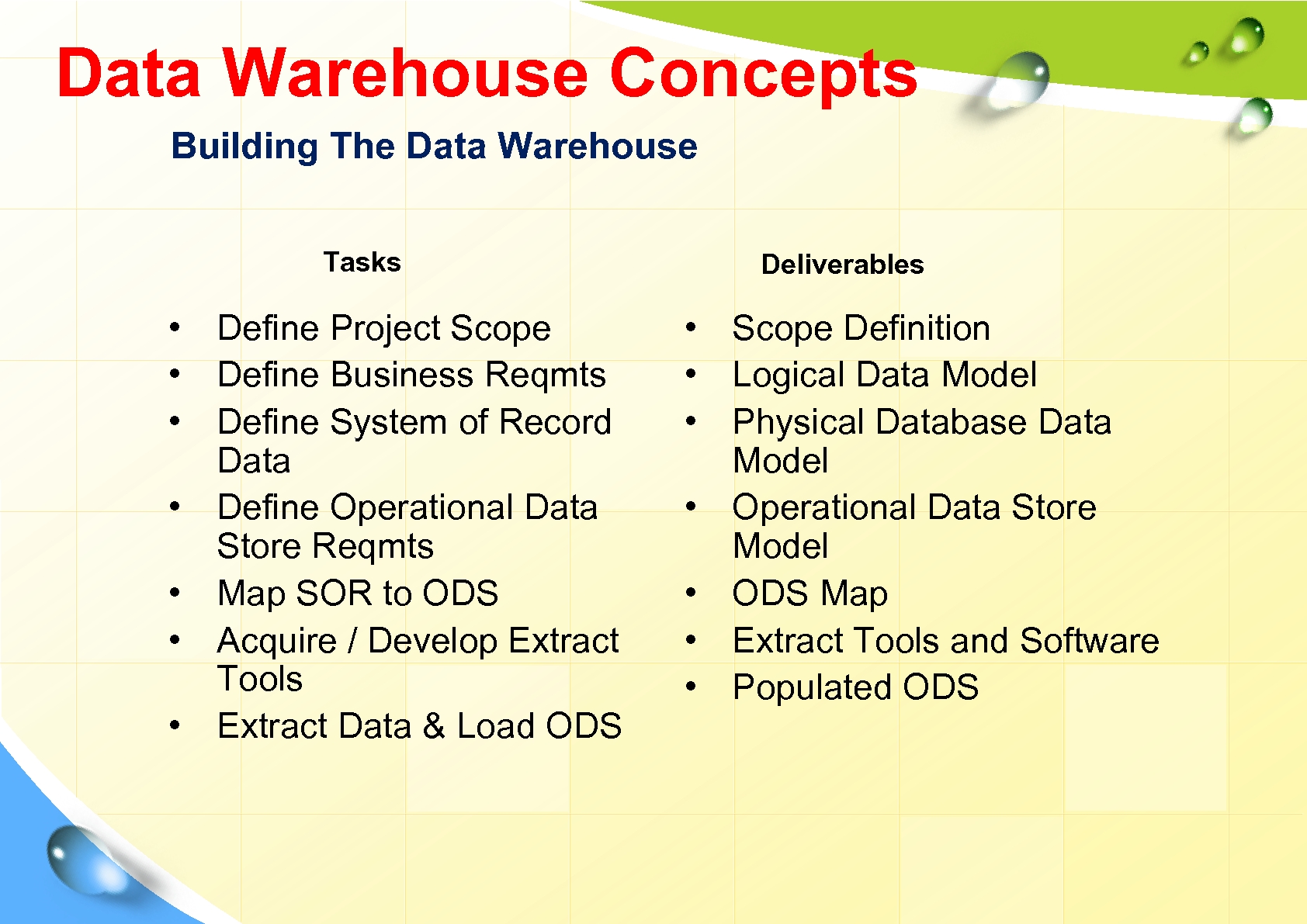
Data Warehouse Concepts Building The Data Warehouse Tasks • Define Project Scope • Define Business Reqmts • Define System of Record Data • Define Operational Data Store Reqmts • Map SOR to ODS • Acquire / Develop Extract Tools • Extract Data & Load ODS Deliverables • Scope Definition • Logical Data Model • Physical Database Data Model • Operational Data Store Model • ODS Map • Extract Tools and Software • Populated ODS
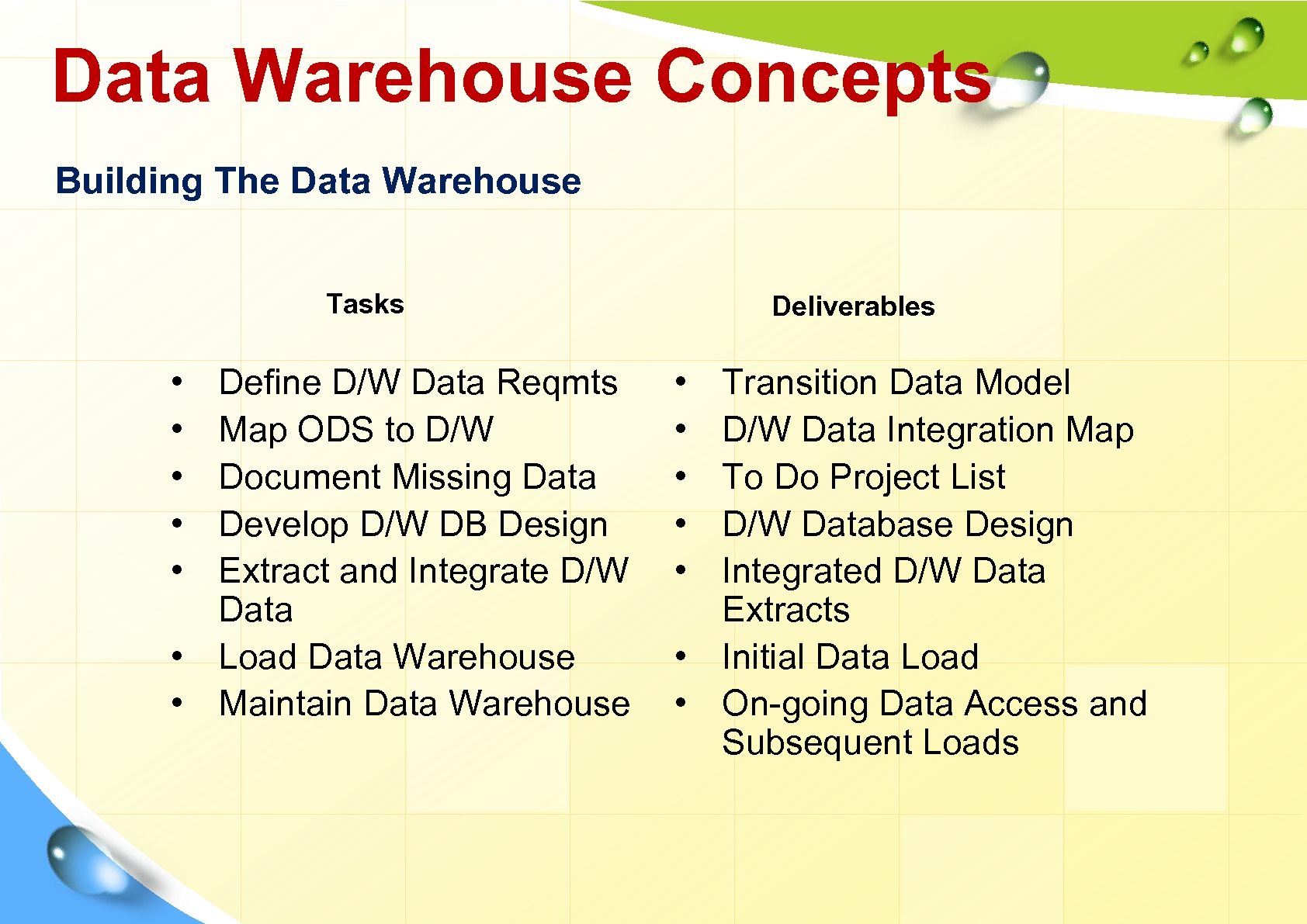
Data Warehouse Concepts Building The Data Warehouse Tasks • • • Define D/W Data Reqmts Map ODS to D/W Document Missing Data Develop D/W DB Design Extract and Integrate D/W Data • Load Data Warehouse • Maintain Data Warehouse Deliverables • • • Transition Data Model D/W Data Integration Map To Do Project List D/W Database Design Integrated D/W Data Extracts • Initial Data Load • On-going Data Access and Subsequent Loads
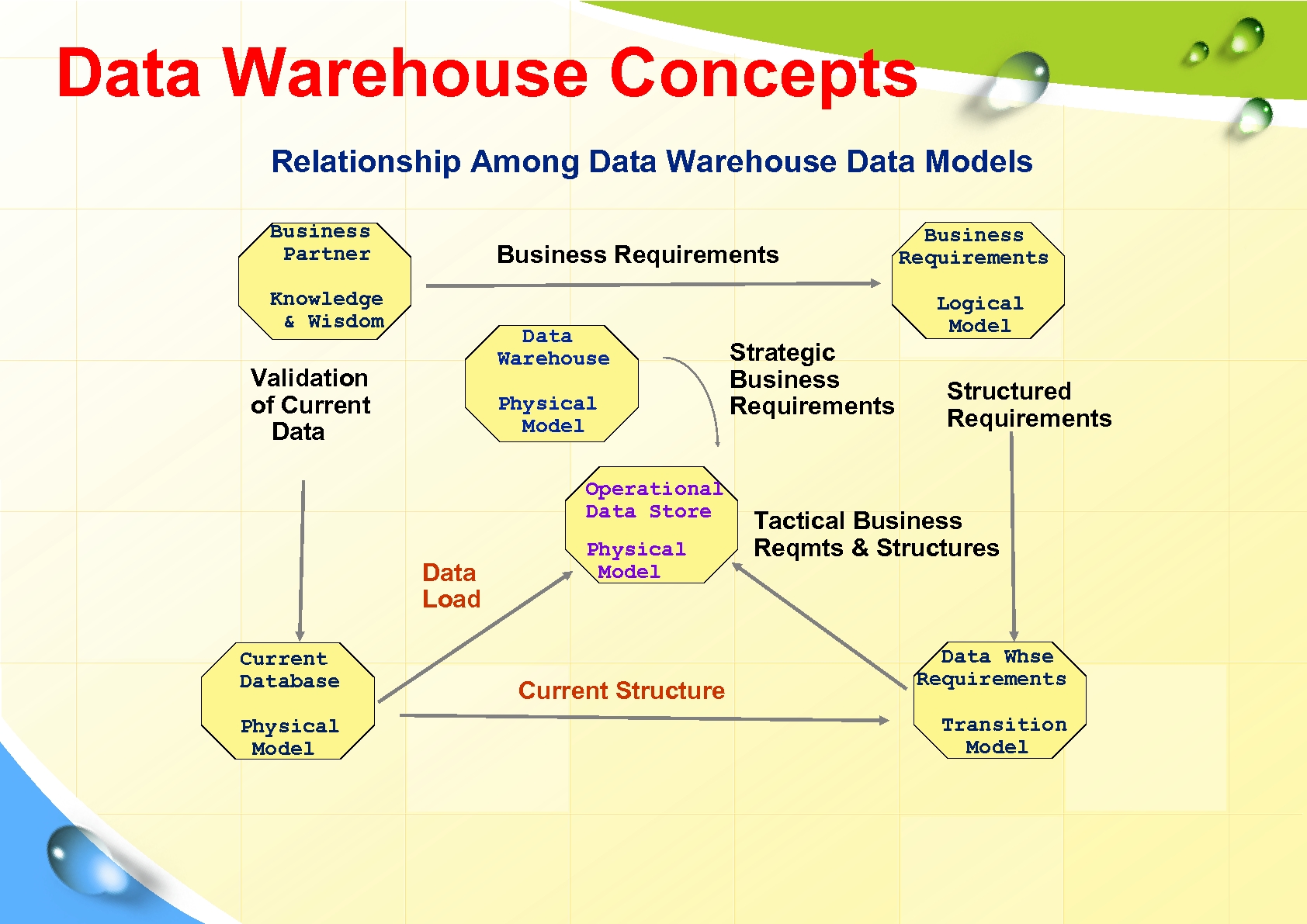
Data Warehouse Concepts Relationship Among Data Warehouse Data Models Business Partner Business Requirements Knowledge & Wisdom Data Warehouse Validation of Current Data Physical Model Operational Data Store Data Load Current Database Physical Model Current Structure Business Requirements Logical Model Strategic Business Requirements Structured Requirements Tactical Business Reqmts & Structures Data Whse Requirements Transition Model
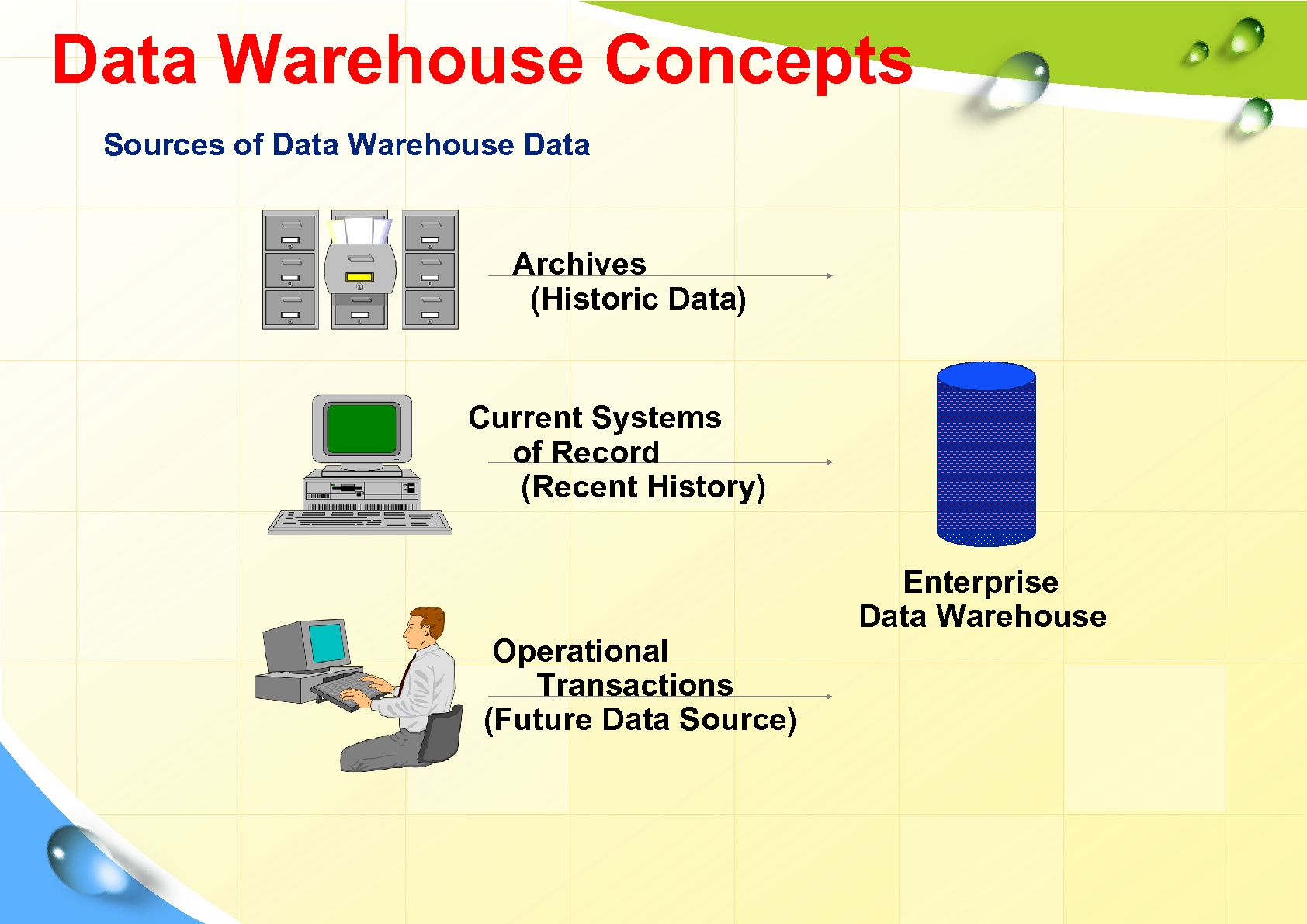
Data Warehouse Concepts Sources of Data Warehouse Data Archives (Historic Data) Current Systems of Record (Recent History) Operational Transactions (Future Data Source) Enterprise Data Warehouse

Data Warehouse Concepts Appropriate Uses of Data Warehouse Data • Produce Reports For Long Term Trend Analysis • Produce Reports Aggregating Enterprise Data • Produce Reports of Multiple Dimensions (Earned revenue by month by product by branch)

Data Warehouse Concepts Inappropriate Uses of Data Warehouse Data • Replace Operational Systems’ Reports • Analyze Current Operational Results
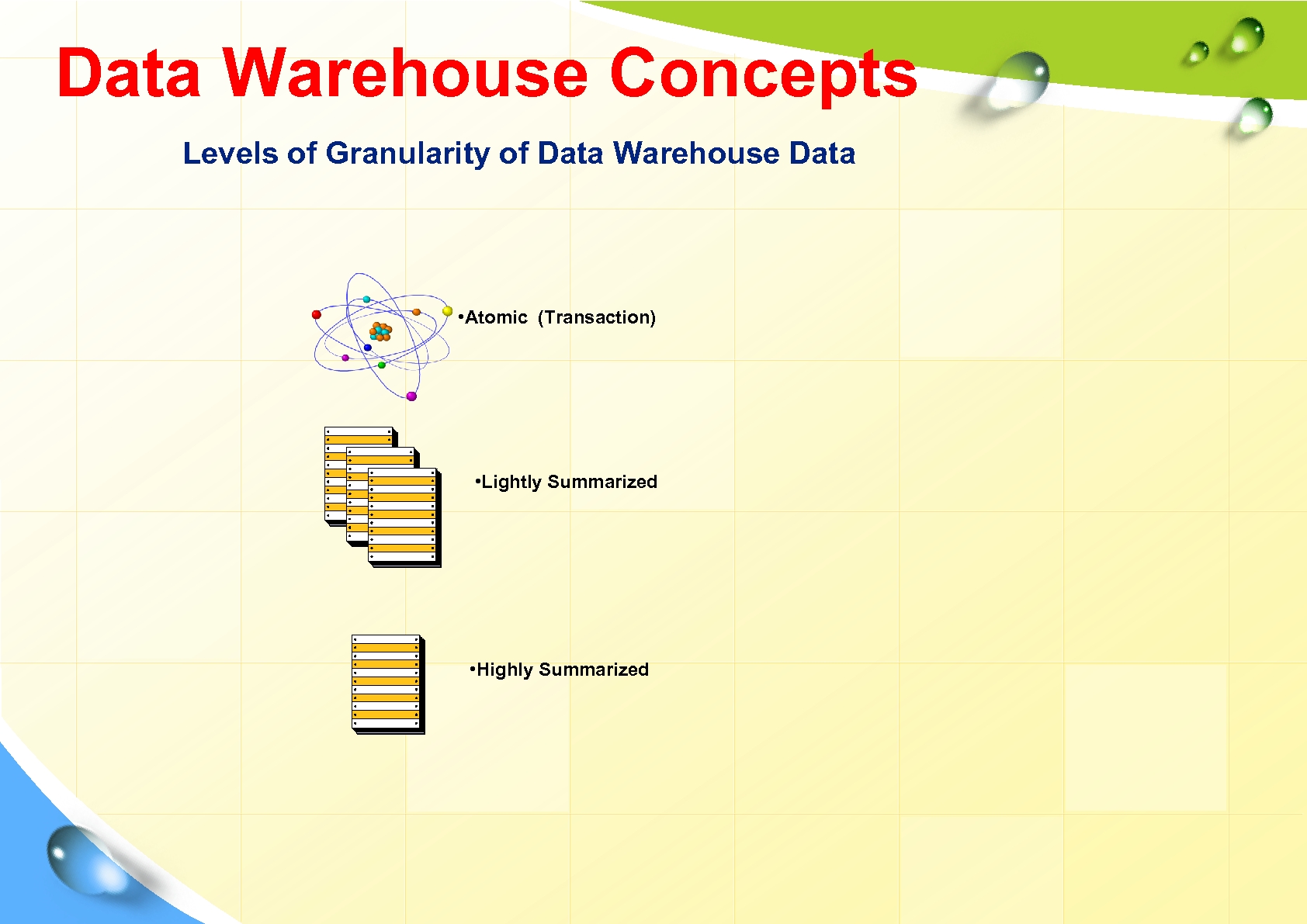
Data Warehouse Concepts Levels of Granularity of Data Warehouse Data • Atomic (Transaction) • Lightly Summarized • Highly Summarized

Common Data Warehouse Components • Staging Area • A preparatory repository where transaction data can be transformed for use in the data warehouse • Data Mart • • Traditional dimensionally modeled set of dimension and fact tables Per Kimball, a data warehouse is the union of a set of data marts • Operational Data Store (ODS) • • Modeled to support near real-time reporting needs Contains traits of both relational and dimensional modeling techniques

Data Warehouse Modeling • Data warehouses typically use a denormalized method called dimensional modeling made up of the following components: • Dimension • • An entity defined in its entirety with a single primary key Examples: Customer, Product, Sales Force, Calendar • Fact • • Details (often numerical) regarding a set of dimensions Example: Order Details
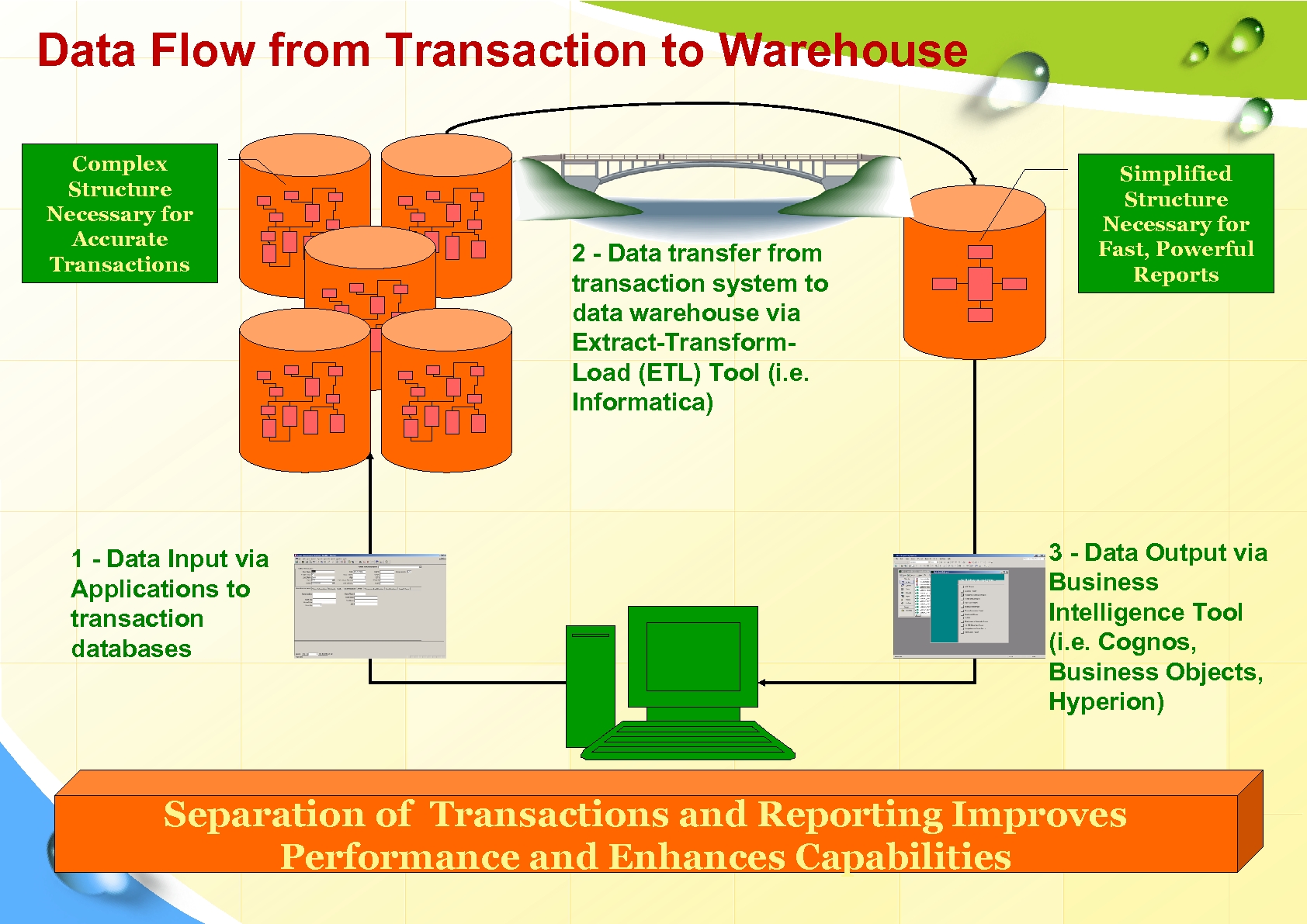
Data Flow from Transaction to Warehouse Complex Structure Necessary for Accurate Transactions 1 - Data Input via Applications to transaction databases 2 - Data transfer from transaction system to data warehouse via Extract-Transform. Load (ETL) Tool (i. e. Informatica) Simplified Structure Necessary for Fast, Powerful Reports 3 - Data Output via Business Intelligence Tool (i. e. Cognos, Business Objects, Hyperion) Separation of Transactions and Reporting Improves Performance and Enhances Capabilities

Business Intelligence Software • Definition • A set of tools that allow users to access enterprise data via reports, Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) cubes, graphs/charts, ad-hoc queries and dashboards • Purpose • Allow users to view the data from all levels of the enterprise • Provide users with information necessary to make timely, well-informed business decisions The tools must be easy for the end user to understand manipulate

Some Components In The BI Toolkit • Reports (Example) • • Commonly needed data can be structured in a set of canned reports made available to large numbers of users Flexibility can be given to users through ad-hoc querying and filters • Cubes (Example) • • Multi-dimensional, allowing the user the view the data from multiple angles Interactive, giving the user the ability to change what is viewable on the fly

Some Components In The BI Toolkit • Charts & Graphs (Example) • • Graphical Representation of data Commonly used in presentations and statistical analysis • Dashboards (Example) • • Actively updating graphical displays that provides business users with updates on key metrics Some dashboards provide drill through capability, allowing users to start with summary data and dive in to the details

Report Example

Cube Example Dimensions and facts can be dragged and dropped on the to display to view the data in different ways

Chart/Graph Example

Dashboard Example

How It All Works Together Data Input Disparate Data Sources OLTP Extract Transform Load Single Reporting Repository Real-time Dashboards AIMSPC OLTP TIMS DW Static and Ad-hoc Reporting RECBASS OLTP ATRRS Other Possible Data Sources RATSS RFMSS Graphical Data Analysis

Data Consolidation & Storage Customers Sales Procurement Suppliers Operations Finance Shared Reporting Shared Data Layer Transaction Layer SCM Data Warehouse CRM MRP Finance • Operations and financial information is shared across the organization from same core data

How is data consolidated? • This is difficult!!!!! – Data is often spread across multiple systems, stored in different formats, and may even be localized for different countries

Transforming Data • Data must be transformed for consistency and meaning – Transformations may be as simple as copying columns or may be incredibly complex – Common transformations include: • Hard-coded changes (‘T’ to 1) • Looking up values in a table (mapping a customer number across disparate systems) • Inserting dummy records and mapping them to unknowns (inserting an ‘Unknown’ customer)

Cleansing Data • Data must be cleansed to be meaningful – All companies have “bad” data in their systems – Data may be missing – Data may be inconsistent – Data may be wrong

Data Warehouses • ETL (extract, transform and load) processes are needed to create data warehouses – This is an arduous and technical process that can account for a large percentage of a BI project cost!!!!

The Result Runs Every Night ERP Data Extract Transform Load Other Data Sources Process Checks Data Warehouse Ready For Access & Query

The Result 41 ERP Tables 1 Warehouse Table EMPLOYEE_STATUS_DIMENSION

Business Intelligence • Business is now investing in Business Intelligence • Business Intelligence is about making effective business decisions

Multi-Dimensional Databases • Measures – Any quantitative expression – Some are designated as Key Performance Indicators (KPI) – Appropriate to the business process. • Dimensions – How we describe the measures: Product/Customer/Region/Time – These are the “By’s – “What were our Customer Sales by Product Line by Region by Quarter for the past two years? ”.

Multi-Dimensional Databases OLAP • What is OLAP ? – – – On-Line Analytical Processing Ad-hoc reports Slice & Dice Drill-down (hierarchies) Drill-through (details)

Building a Cube 1 Dimension les Sa les U Sa r sts olla lar Co D gin ar ol D M n% rgi Ma nit Dimension 1: Measures

Building a Cube 2 Dimensions Dimension 2: Time January February March April May June les Sa r sts lla Co Do ar gin ar oll M D n% gi ar M nit U Dimension 1: Measures

Building a Cube Beef Stew Lasagne Paper Towels Fizzy Light Fizzy Classic Strong Cola 3 Dimensies Dimension 2: Time January February March Dimension 3: Products April May June les Sa les U Sa r sts lla Co Do gin ar ar oll M D n% rgi Ma nit Dimension 1: Measures

Building a Cube Beef Stew Lasagne Paper Towels Fizzy Light Fizzy Classic String Cola Multi-dimensional Cube Dimension 2: Time January February March April Dimension 3: Products May June les Sa les U Sa r sts lla Co Do gin ar ar oll M D n% rgi Ma nit Dimension 1: Measures

OLAP: An Example Products Strong Cola January Paper Towel Beef Stew February March $6, 745 April “For Beef Stew, show me the margin for February” May Margin Sales $ Units Cost Measures Time

Dimensions

Facts

Star Scheme

Analytics • Reporting Applications – Limited user interaction – Fulfill a significant portion of an organization’s information needs • Analytic Applications – Allow users to visualize and explore data following their train of thought – Extensive interactivity



Analytic Application

Data Mining • The process of identifying patterns in data • Goes beyond simple querying of the database • Goes beyond multi-dimensional database queries as well

Data Mining • Data Mining works for problems like: – Develop a general profile for credit card customers … – Differentiate individuals who are poor credit risks … – Determine what characteristics differentiate male & female investors.

Data Mining vs. Data Query • Use data query if you already almost know what you are looking for. • Use data mining to find regularities in data that are not obvious.

Data Mining Applications • • Fraud detection Targeted Marketing Risk Management Business Analysis

Origins of Data Mining • Mathematics – Statistics – Numerical Analysis • Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning • Computer Science – Data Storage and Manipulation

Keys To Success • Sponsorship • High level endorsement is essential to ensuring you have the authority to drive the effort • Funding • You have to spend money to save/make money • Time • • This can be a years long effort to implement Maintenance is ever-present • Central Governance • Without strict governance over components of your enterprise data warehouse, you risk stove piping

Summary • Data is Key • Whether coming in or going out, data is the foundation of all business applications and should be structured to properly meet the need • Solutions are Complex • There are many components to a good BI strategy…and they all have to work • Diligence Required • • • Data will change Technology will change Be assured…user requirements will change

Business Intelligence Vision Improving organizations by providing business insights to all employees leading to better, faster, more relevant decisions Advanced Analytics Self Service Reporting End-User Analysis Business Performance Management Operational Applications Embedded Analytics

The End Result

General View BI Actions Data Acquisition and Integration Source Data Operational Application Data Warehouse Storage Group ODS User BI Reporting Predefined Reports ADS Data MART Public Folders Interactive reports OLAP Data Quality Repository Metadata Repository Data Quality Database Metadata Database Data Quality Measurements Metadata Measurements

Jobs • • Business Analyst Data Analyst Functional Analyst Marketing Analyst

Jobs • • Report Developer Data Modeler ETL Developer Data Architect Data Warehouse Designer Data Warehouse Developer Data Warehouse Administrator Database Administrator

Jobs • • Business Intelligence Consultant Business Intelligence Developer Business Intelligence Analyst Business Intelligence Project Team Member

Jobs • One of the fastest growing segments of IT • Less likely to be outsourced • May exist in business units rather than IT • Knowledge/understanding of the organization is key

Microsoft BI Platform

Microsoft BI Platform

SQL Server Database Management SQL Server Relational Database – provides a robust, scalable and enterprise-ready Data Warehouse platform. Microsoft SQL Server 2005 has improved partitioning, manageability, and query optimizations to streamline data warehouse operations and increase performance. Many Business Solutions and systems currently use this database. Business Intelligence Platform Analysis Services Reporting Services SQL 2005 Integration Services Database Management

SQL Server Analysis Services Allows for Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), commonly referred to as “cubes”. Includes advanced analytical features such as complete data mining and key performance indicator frameworks. Enables organizations to accommodate multiple analytic needs within one solution. Business Intelligence Platform Analysis Services Reporting Services SQL 2005 Integration Services Database Management

SQL Server Reporting Services Provides a complete reporting platform so that end-users can view data using a Web browser or desk top. Includes report authoring tools for both technical developers and business users. Allows web-based viewing and rendering in popular document formats such as Microsoft Excel and PDF. Contains robust e-mail subscription capability. Business Intelligence Platform Analysis Services Reporting Services SQL 2005 Integration Services Database Management

Microsoft BI Platform

Microsoft Excel 2007 End User Tools & Performance Management

Office Performance. Point Server 2007 Planning § Drive strategic objectives and goals into the planning and budgeting process to ensure departmental plans align with corporate strategy. Monitoring and Analysis § Powerful analytics capabilities empower business users to access data and to perform analyses on their own so that they can make better, faster decisions. Release scheduled for Q 4, 2007 End User Tools & Performance Management

Microsoft BI Platform

Microsoft Office Share. Point Server Key Benefit: makes information easy to access and use. Brings the “Self-Service” to BI. Serves as the central access point for all reports and business data. Provides integration to Reporting Services, Microsoft Excel, Pro. Clarity Analytics, Dashboards (currently known as Business Scorecard Manager) and Performance. Point Server. Allows users to collaborate, annotate and search. Stores documents in a document library. Collaboration earch S Reports Dashboards Point Server Delivery Share Excel Workbooks Scorecards Conten t Mana gemen t Analytic Views Plans
bcd1b4e457647522cc94fdace1de492b.ppt