60dff57f5afb2b73714f3c5e13d99672.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Data Warehousing / Business Intelligence Good decisions by effectively managing data

Who Am I. . ► Loblaws – Director of Enterprise Data Warehousing ► Teradata – Sr. Professional Services Consultant ► Innovapost (Purolator) – Consulting Director Business Intelligence & Report Delivery

Forethought ►“Today every company is an information company but not all are prepared to deal with it. “ Mark Lahr – 3 M Corp ►"The CEO will always get good data, but the challenge is making it available to the masses. That’s the challenge, how do you democratize decision-making? " Eric Berg, chief administrative officer and former CIO-Goodyear.

What is a Data Warehouse ► Many definitions § A repository of an organizations electronically stored data. (Wikipedia) § A central repository for all or significant parts of the data that an enterprise's various business systems collect. (Search SQL) § A warehouse is a subject-oriented, integrated, timevariant and non-volatile collection of data in support of management's decision making process (Bill Inmon) § A data warehouse is a database system optimized for reporting. (Deakin University)

My favorite Definition –A potential white elephant bone yard of data and information. A scary place but it might also serve a purpose (Unknown)

Fine but what really is it… My Definition… Data warehouses collect relevant data from multiple different data sources, rationalize, summarize it and catalog it in large consistent, stable, accurate, long term data stores which allows for all types of questions to be answered which otherwise would be difficult or expensive to do. Data warehouses are optimized to provide insights into data to answer the same question asked multiple different ways to support the decision making process. A data warehouse can be fully customized for each installation, and every group using from the data warehouse can have a different perspective on the data contained within.

DW Definition ► More than just a database or single tool § Tools (Extract, Load, Transform, Aggregate, Mine, Analyze, Report, Manage) § Complex subject specific data models § Processes / Governance / Standards § People § Technology § Metadata
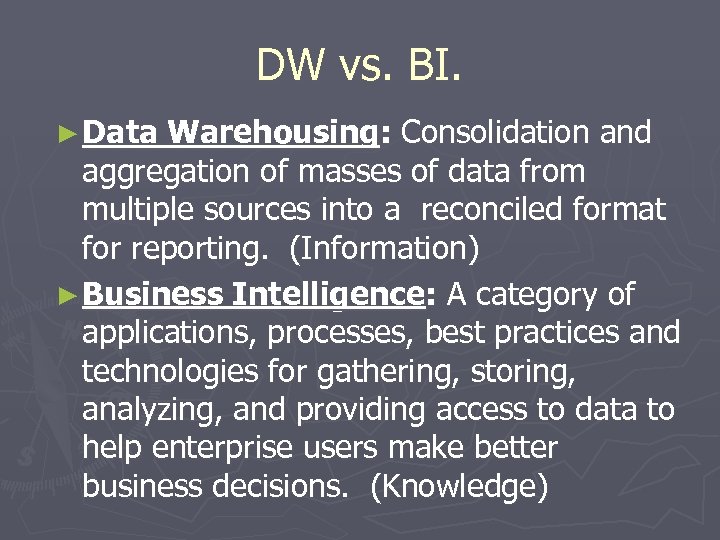
DW vs. BI. ► Data Warehousing: Consolidation and aggregation of masses of data from multiple sources into a reconciled format for reporting. (Information) ► Business Intelligence: A category of applications, processes, best practices and technologies for gathering, storing, analyzing, and providing access to data to help enterprise users make better business decisions. (Knowledge)

BI vs. Data Warehouses ► Some companies claim you can do BI without a Data Warehouse…. You can also use a shoe as a hammer, it works but is not very effective! ► BI Needs cleaned, consistent large masses of data to work well.
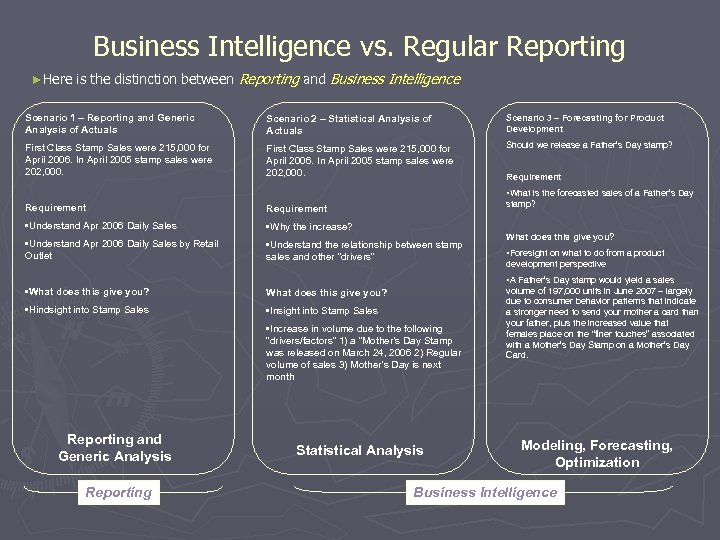
Business Intelligence vs. Regular Reporting ►Here is the distinction between Reporting and Business Intelligence Scenario 1 – Reporting and Generic Analysis of Actuals Scenario 2 – Statistical Analysis of Actuals Scenario 3 – Forecasting for Product Development First Class Stamp Sales were 215, 000 for April 2006. In April 2005 stamp sales were 202, 000. Should we release a Father’s Day stamp? Requirement • Understand Apr 2006 Daily Sales • Why the increase? • Understand Apr 2006 Daily Sales by Retail Outlet • Understand the relationship between stamp sales and other “drivers” • What does this give you? • Hindsight into Stamp Sales • Insight into Stamp Sales Requirement • What is the forecasted sales of a Father’s Day stamp? What does this give you? • Foresight on what to do from a product development perspective • A Father’s Day stamp would yield a sales • Increase in volume due to the following “drivers/factors” 1) a “Mother’s Day Stamp was released on March 24, 2006 2) Regular volume of sales 3) Mother’s Day is next month Reporting and Generic Analysis Reporting Statistical Analysis volume of 197, 000 units in June 2007 – largely due to consumer behavior patterns that indicate a stronger need to send your mother a card than your father, plus the increased value that females place on the “finer touches” associated with a Mother’s Day Stamp on a Mother’s Day Card. Modeling, Forecasting, Optimization Business Intelligence

Business Intelligence Definition – A Summary Business Intelligence is defined as the people, processes, • • • technology, and data that support — Getting consistent and quality information to the right person (or process) at the right time in an effective and efficient manner through the right delivery channel And using that information to — • Support management and/or operational decision-making • Provide insight into historical events • Provide answers to difficult business questions • Offer “fact-based” rationale for taking action • Based on a single version of the business • Debate the “Decisions” not the “Data”
Who Deploys DW / BI EVERYONE

How can a DW be used? ► Validation: Using empirical data to validate what is a commonly held hypothesis. ► Tactical Reporting: Standard listings of facts and figures. Sales / shipment / claims etc. ► Exploratory: Using the warehouse to find relationships or information that you did not know before.

Typical DW Applications ► ABC – Activity Based Costing ► Sales Forecasting ► Contract Renewal ► Shipping Simulation / Analysis ► Customer Segmentation ► GIS – Geographical Informational Systems ► Churn Analysis ► Customer Relationship Analysis ► Fraud Analysis

Data Warehousing at Loblaw’s ► Loblaw’s is the largest private employer in Canada 135, 000 employees ► Two Data Warehouses exist § § § Teradata 75 TB (773 tables) Oracle 11. 2 TB (521 Tables) 8 Reporting tools are used ► Over 50 external connections to other systems ► Environments support over 150, 000 reports per month. ► Data growing 450 GB / month

Why Companies Deploy DW Lots of motivators behind why companies initially decide to deploy a DW. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Operational systems are being impacted because of reporting requests Operational systems cannot give a needed historical perspective The business is not getting consistent or timely answers (No single view of the “business”) Too expensive / Too difficult to tie source systems together for one-off reporting. No one knows the rules from legacy reporting systems. Because the competition has one. Investment in a BI tool wont work without
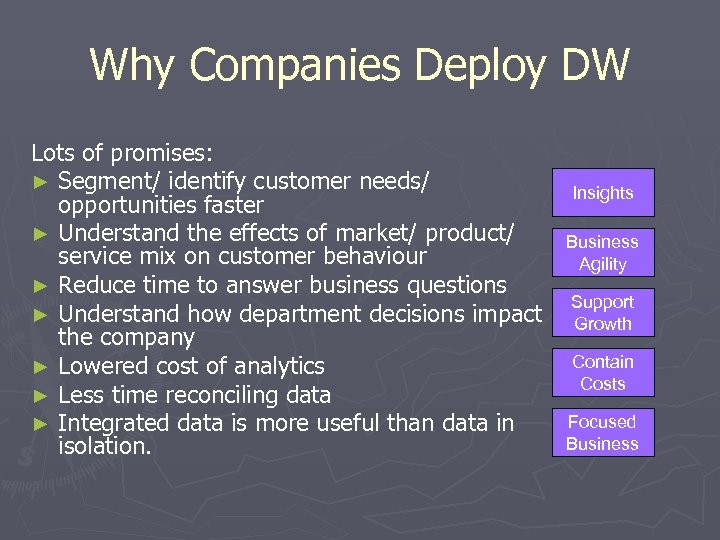
Why Companies Deploy DW Lots of promises: ► Segment/ identify customer needs/ opportunities faster ► Understand the effects of market/ product/ service mix on customer behaviour ► Reduce time to answer business questions ► Understand how department decisions impact the company ► Lowered cost of analytics ► Less time reconciling data ► Integrated data is more useful than data in isolation. Insights Business Agility Support Growth Contain Costs Focused Business

Why Companies Deploy A DW ► Even simple decisions – Buy / Not Buy / Discount often need lots of Inputs § § § Sales Information Transactional Context Inventory / Vendor Information Forecasting / Market Data / Trending Customer Information Promotional Information ► Now Repeat across every product you carry…
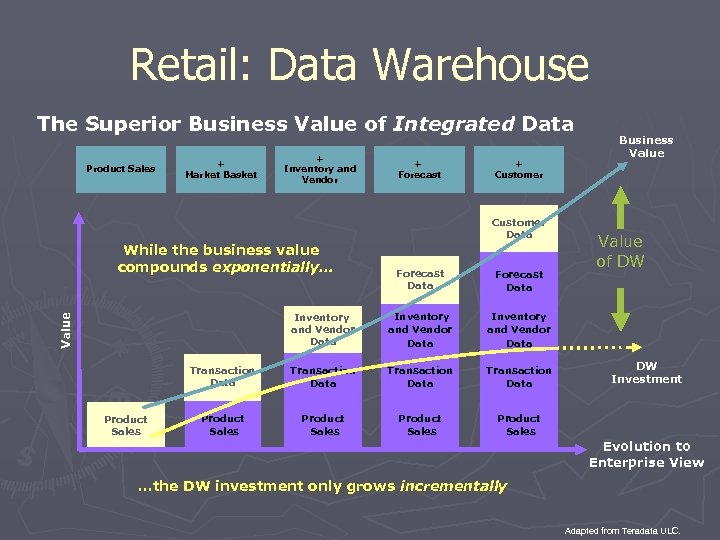
Retail: Data Warehouse The Superior Business Value of Integrated Data Product Sales + Market Basket + Inventory and Vendor + Forecast + Customer Data While the business value compounds exponentially… Forecast Data Inventory and Vendor Data Transaction Data Product Sales Value of DW Inventory and Vendor Data Product Sales Value Forecast Data Business Value DW Investment Evolution to Enterprise View …the DW investment only grows incrementally Adapted from Teradata ULC.
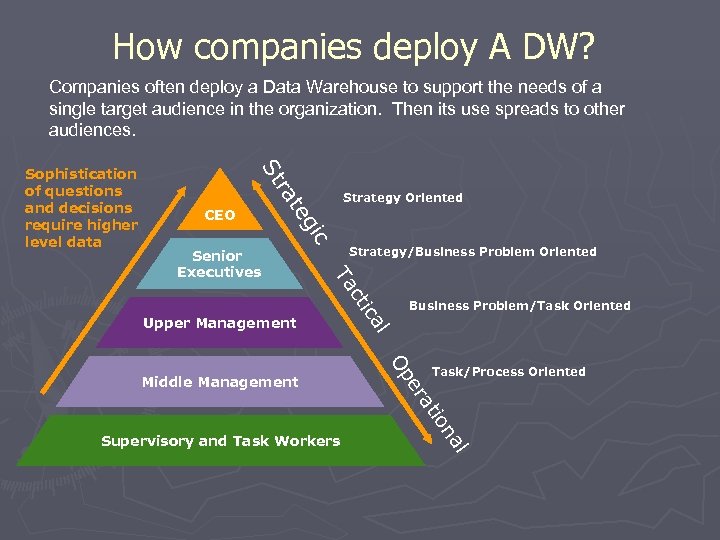
How companies deploy A DW? Companies often deploy a Data Warehouse to support the needs of a single target audience in the organization. Then its use spreads to other audiences. ra St Strategy/Business Problem Oriented Task/Process Oriented l na io at er Supervisory and Task Workers Op Middle Management Business Problem/Task Oriented l Upper Management ica ct Ta Senior Executives c gi CEO Strategy Oriented te Sophistication of questions and decisions require higher level data

Data Warehouse Considerations ► Forces different areas of the business to standardize around definitions, metrics and common hierarchies. ► Requires investments from across the business. ► Has a significant start-up cost before any real value / payback. ► Requires data be treated like a corporate asset. ► Imposes discipline and cost into every new project being brought into the organization.
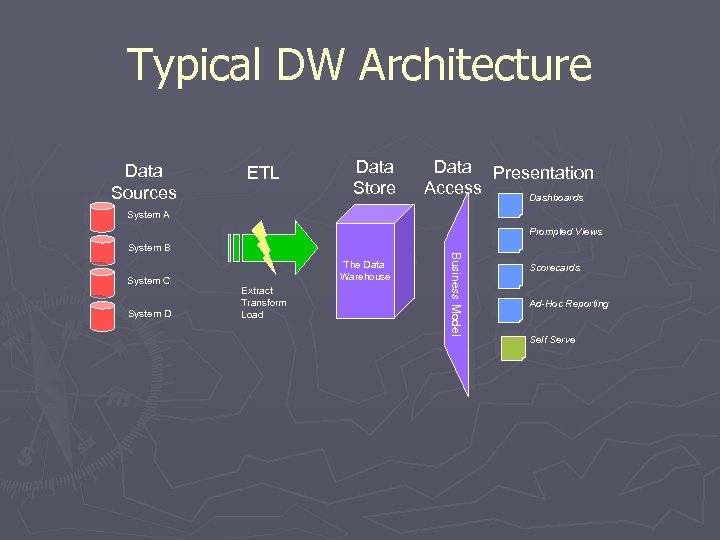
Typical DW Architecture Data Sources ETL Data Store Data Presentation Access Dashboards System A Prompted Views System C System D The Data Warehouse Extract Transform Load Business Model System B Scorecards Ad-Hoc Reporting Self Serve
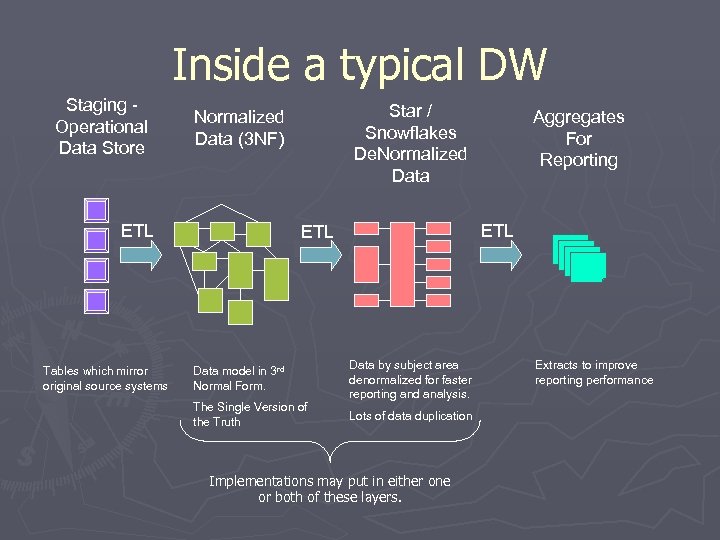
Inside a typical DW Staging Operational Data Store ETL Tables which mirror original source systems Star / Snowflakes De. Normalized Data (3 NF) ETL Data model in 3 rd Normal Form. The Single Version of the Truth Aggregates For Reporting Data by subject area denormalized for faster reporting and analysis. Lots of data duplication Implementations may put in either one or both of these layers. Extracts to improve reporting performance
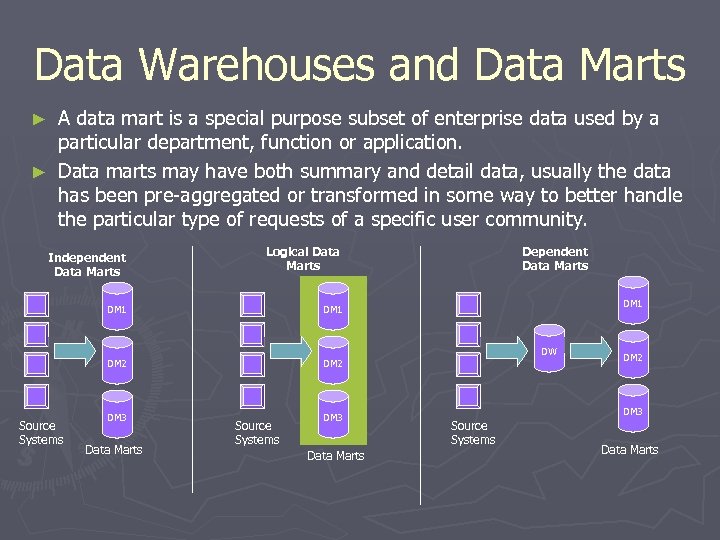
Data Warehouses and Data Marts A data mart is a special purpose subset of enterprise data used by a particular department, function or application. ► Data marts may have both summary and detail data, usually the data has been pre-aggregated or transformed in some way to better handle the particular type of requests of a specific user community. ► Independent Data Marts Logical Data Marts DM 1 Source Systems DM 2 DM 3 DM 1 DM 2 Dependent Data Marts Source Systems Data Marts DW DM 2 DM 3 Source Systems Data Marts
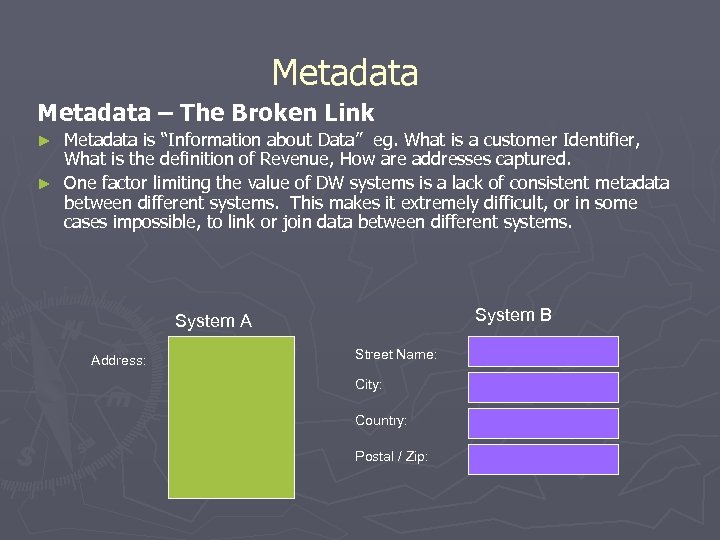
Metadata – The Broken Link Metadata is “Information about Data” eg. What is a customer Identifier, What is the definition of Revenue, How are addresses captured. ► One factor limiting the value of DW systems is a lack of consistent metadata between different systems. This makes it extremely difficult, or in some cases impossible, to link or join data between different systems. ► System B System A Address: Street Name: City: Country: Postal / Zip:
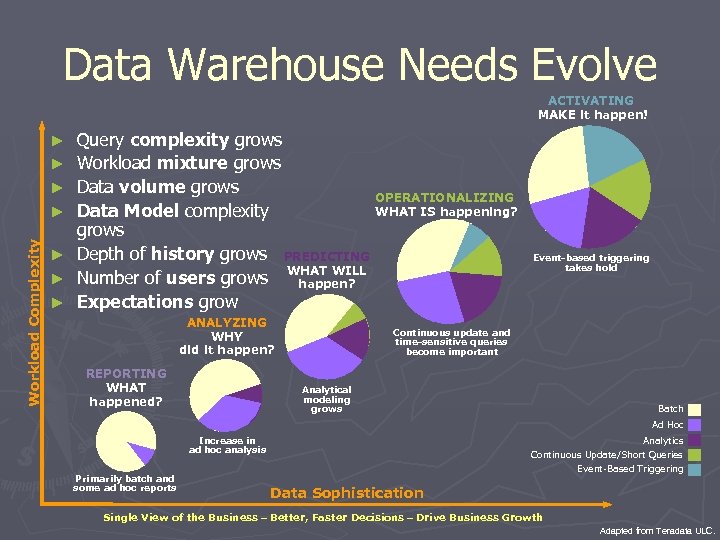
Data Warehouse Needs Evolve ACTIVATING MAKE it happen! ► ► ► Workload Complexity ► ► Query complexity grows Workload mixture grows Data volume grows OPERATIONALIZING WHAT IS happening? Data Model complexity grows Depth of history grows PREDICTING WHAT WILL Number of users grows happen? Expectations grow ANALYZING WHY did it happen? REPORTING WHAT happened? Event-based triggering takes hold Continuous update and time-sensitive queries become important Analytical modeling grows Batch Ad Hoc Increase in ad hoc analysis Primarily batch and some ad hoc reports Analytics Continuous Update/Short Queries Event-Based Triggering Data Sophistication Single View of the Business – Better, Faster Decisions – Drive Business Growth Adapted from Teradata ULC.

How DW is different ► Data Volumes are huge ► History is maintained for long periods of ► Slowly changing dimensions ► Summary and Detailed Data ► Denormalized Data ► Data architecture and governance ► Long Running Queries – Casual delivery ► Mixed workloads ► Enterprise view and focus ► Read vs. Inserts time

Challenges / Pitfalls ► The challenges facing a Data Warehouse Implementation are summarized as the 4 P’s. § People § Process § Platform § Politics

Challenges / Pitfalls - People ► For a data warehouse people need to be trained differently then for other types of applications. ► Poorly or improperly trained people will result in a poorly performing, unsustainable solution. ► Typically a BI/DW focused team member takes several years of dedication to the subject to be truly competent.

Challenges / Pitfalls - Process A DW usually runs processing 24 x 7 ► A DW initiative requires implementing processes for creating standards ► § § § ► Data definitions Standard Hierarchies Managing History / Retention Data corrections / Data completeness Processing failures SLA’s The absence of good processes will result in a poor solution which likely will fail to match business needs

Challenges / Pitfalls - Platform ► Wrong selection of tools and technologies will result in unnecessary expense, frustration by both IT and business and potentially an unworkable solution. ► Tools and technology need to be matched to the skills, training and needs of the business. ► ETL, Database Engine, Backups, Scheduling, Archiving, Report Delivery are key choices

Challenges / Pitfalls - Politics ► Because a DW is an expensive, shared asset politics play a big role in derailing projects. § Sponsorship § Data Democracy § Charge backs § Priorities § Architecture / Data Marts § Standards

Conclusion Implementing a Data Warehouse or Business Intelligence initiatives are not projects, but a long term commitment to implement continuously improving business intelligence practices… Business Intelligence needs to be a strategy and thought pattern applied to all projects, departments and initiatives, across the enterprise!
60dff57f5afb2b73714f3c5e13d99672.ppt