19314bd8e729b887894d72e0d95f5161.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

Data Warehouses and Dashboard – A Primer Mr. Tod R. Massa Director, Policy Research & Data Warehousing, State Council of Higher Education for Virginia Dr. Dave Oehler Director of Assessment, Information and Analysis, Northwest Missouri State University 5/10/2005

Presentation Overview Ø Data Warehousing Ø Ø Goals of data warehousing Components of a data warehouse Data flow Dashboards Ø Ø Ø Goals of dashboards Components of dashboards “Drilling down” 5/10/2005 2

Presentation Overview Ø Data Warehousing Ø Ø Goals of data warehousing Components of a data warehouse Data flow Dashboards Ø Ø Ø Goals of dashboards Components of dashboards “Drilling down” 5/10/2005 3

What is a Data Warehouse? Ø Definition/use: Ø Ø A repository of data, frozen in time Scrubbed/cleansed Some portions captured “as is” Some portions massaged to facilitate faster computation/reporting 5/10/2005 4

Goals of Data Warehousing GOAL 1: Accessible information Ø Ø Intuitive and self-describing Labeled appropriately “Slicing and dicing” Minimal wait times 5/10/2005 5

Goals of Data Warehousing GOAL 2: Consistent information Ø Ø Carefully collected from multiple operational sources Cleansed and quality assured Common definitions Unique describing labels 5/10/2005 6

Goals of Data Warehousing GOAL 3: Flexible during change Ø Ø Designed to handle change Avoids invalidating existing data Minimal disruptions in existing applications and data Accountable for changes 5/10/2005 7

Goals of Data Warehousing GOAL 4: Secured information Ø Ø Ø “Crown Jewels” Usually contains sensitive business information Must effectively manage access 5/10/2005 8

Goals of Data Warehousing Ø Ø GOAL 5: Improved decision-making Data needed to make decisions Supply evidence to improve decisions Decision Support System 5/10/2005 9

Goals of Data Warehousing GOAL 6: Accepted among the organization Ø Ø Ø Extent of deployment after training Meeting the needs of management Use of system to make business decisions 5/10/2005 10

Presentation Overview Ø Data Warehousing Ø Ø Goals of data warehousing Components of a data warehouse Data flow Dashboards Ø Ø Ø Goals of dashboards Components of dashboards “Drilling down” 5/10/2005 11

Components Ø Operational source systems Ø Ø Ø Student information systems Financial information systems Alumni information systems Human resource information systems Other shadow information systems 5/10/2005 12
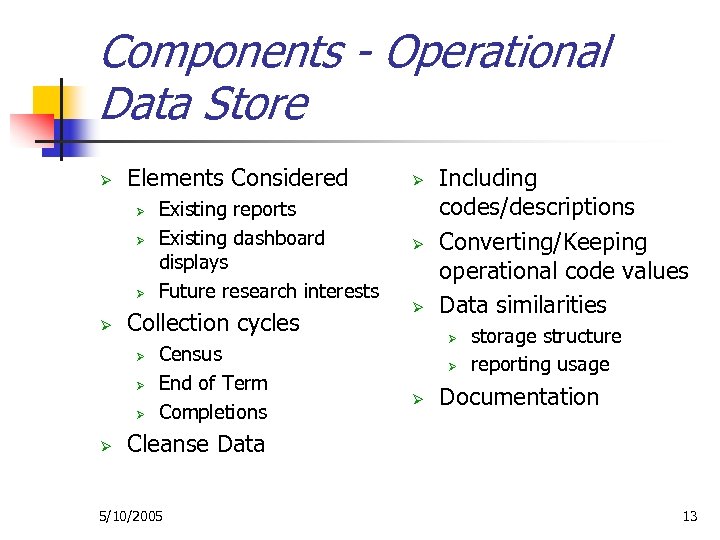
Components - Operational Data Store Ø Elements Considered Ø Ø Collection cycles Ø Ø Existing reports Existing dashboard displays Future research interests Census End of Term Completions Ø Ø Ø Including codes/descriptions Converting/Keeping operational code values Data similarities Ø Ø Ø storage structure reporting usage Documentation Cleanse Data 5/10/2005 13

Components Ø Data staging area (ETL) Ø Extract Ø Ø Transform Ø Ø Collect data records from operation information systems Massage data records (cleanse, combine, deduplicate) Load Ø Populating data records in the warehouse 5/10/2005 14

Components Ø Data presentation Ø Ø Ø Area accessible by management Integrated data marts (common dimensions and facts) Usually presented, stored, and accessed through dimensional schemas Contains detailed atomic data Operational by management 5/10/2005 15

Presentation Overview Ø Data Warehousing Ø Ø Goals of data warehousing Components of a data warehouse Data flow Dashboards Ø Ø Ø Goals of dashboards Components of dashboards “Drilling down” 5/10/2005 16
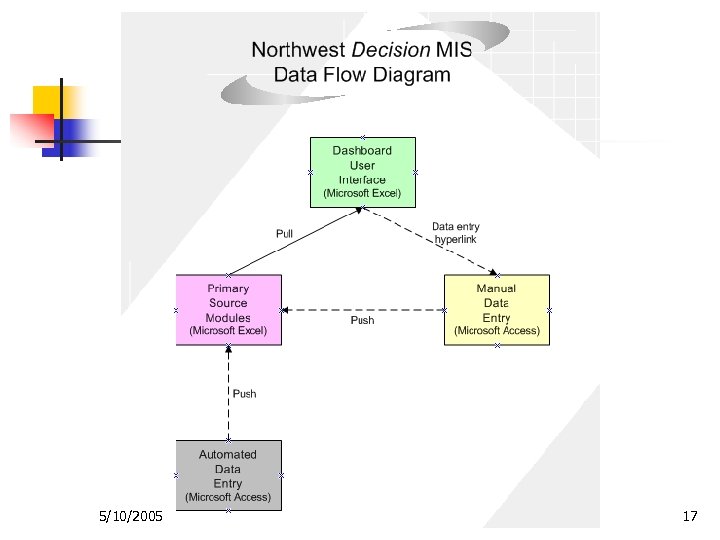
5/10/2005 17

5/10/2005 18
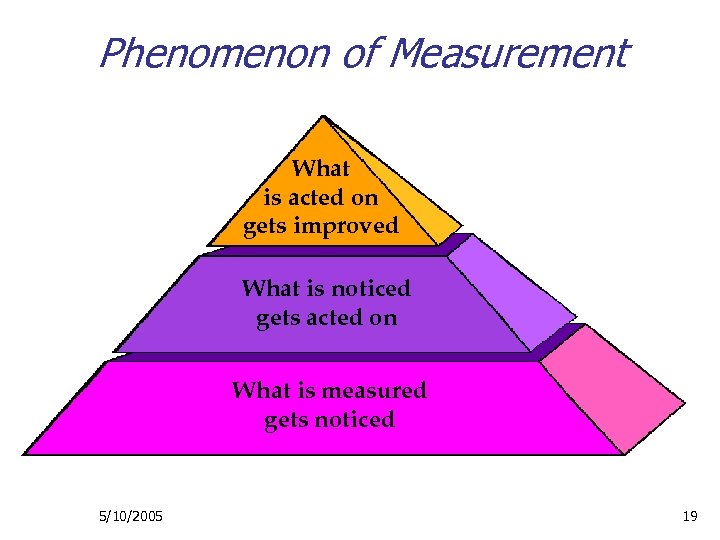
Phenomenon of Measurement This and the following slide were adapted from a Dee W. Hook presentation. What is acted on gets improved What is noticed gets acted on What is measured gets noticed 5/10/2005 19

Presentation Overview Ø Data Warehousing Ø Ø Goals of data warehousing Components of a data warehouse Data flow Dashboards Ø Ø Ø Goals of dashboards Components of dashboards “Drilling down” 5/10/2005 20

What is a Dashboard? Ø Definition/use: Ø Ø Both a process and a tool Looking for unfavorable trends or patterns and focusing energy on improving priority areas A (diagnostic) means for monitoring performance to ascertain what is working well and where additional attention is needed A few (4 -6) sets of indicators, representing the most central areas related to high performance 5/10/2005 21

How Does a Dashboard Focus Activities and Processes? Ø Ø Requires clear definition of outcomes Focuses on a manageable (small) set of key outcomes (results) Encourages cross-functional communication Requires fact-based decision processes Ø Ø Ø Data reporting structures Process improvement orientation Layering of detail (summative vs. formative) 5/10/2005 22

Time is Increasingly a Precious Resource Ø Ø Ø Dashboards help you know what’s important Dashboards focus on actions that make a difference Collect data to create information you can use, then use it 5/10/2005 23

Data for Decision-making Ø Ø Assessment needs to answer questions Systems to collect, analyze, and report information need to be developed to support the specific information requirements 5/10/2005 24
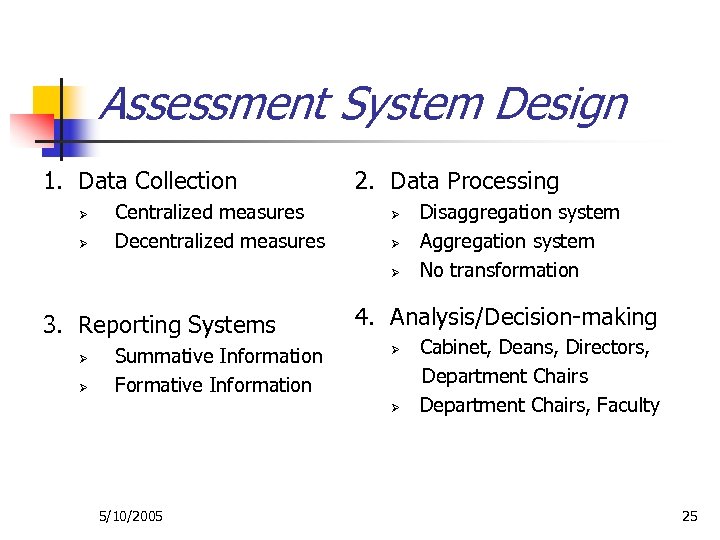
Assessment System Design 1. Data Collection Ø Ø Centralized measures Decentralized measures 2. Data Processing Ø Ø Ø 3. Reporting Systems Ø Ø Summative Information Formative Information 4. Analysis/Decision-making Ø Ø 5/10/2005 Disaggregation system Aggregation system No transformation Cabinet, Deans, Directors, Department Chairs, Faculty 25
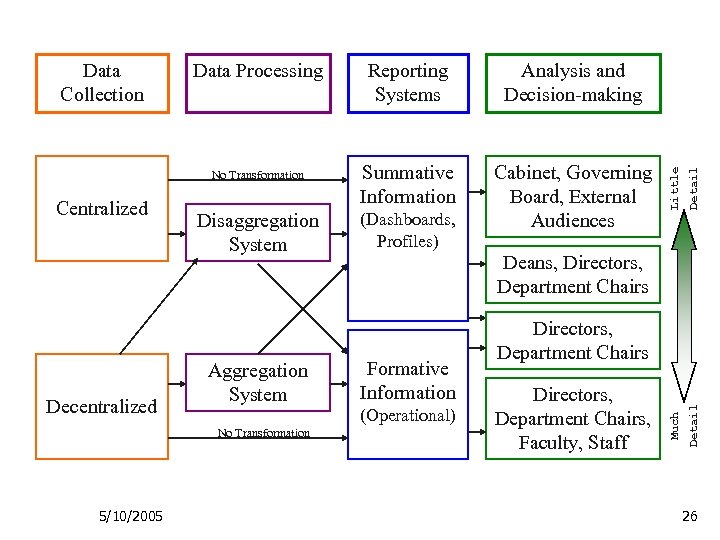
Decentralized Disaggregation System Aggregation System No Transformation 5/10/2005 Summative Information Cabinet, Governing Board, External Audiences (Dashboards, Profiles) Detail Centralized Analysis and Decision-making Deans, Directors, Department Chairs Formative Information (Operational) Directors, Department Chairs, Faculty, Staff Detail No Transformation Reporting Systems Little Data Processing Much Data Collection 26

Presentation Overview Ø Data Warehousing Ø Ø Goals of data warehousing Components of a data warehouse Data flow Dashboards Ø Ø Ø Goals of dashboards Components of dashboards “Drilling down” 5/10/2005 27

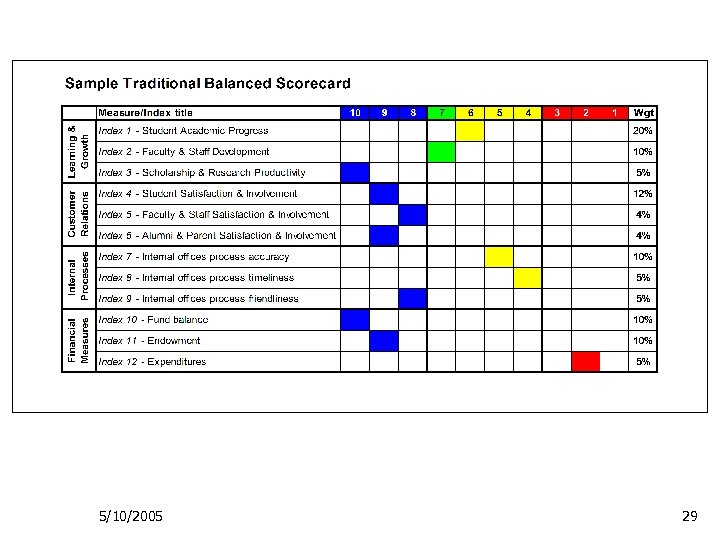
What Metrics are in a Dashboard? Ø The Dashboard includes a balanced view of an organization Ø Learning and Growth (student academic progress; faculty and staff development, scholarship and research productivity) Ø Customer Relations (students, faculty, staff, alumni, parent satisfaction and involvement) Ø Internal Processes (functional area performance – accuracy, timeliness, friendliness) Ø Financial Measures (fiscal health and viability) 5/10/2005 28
5/10/2005 29
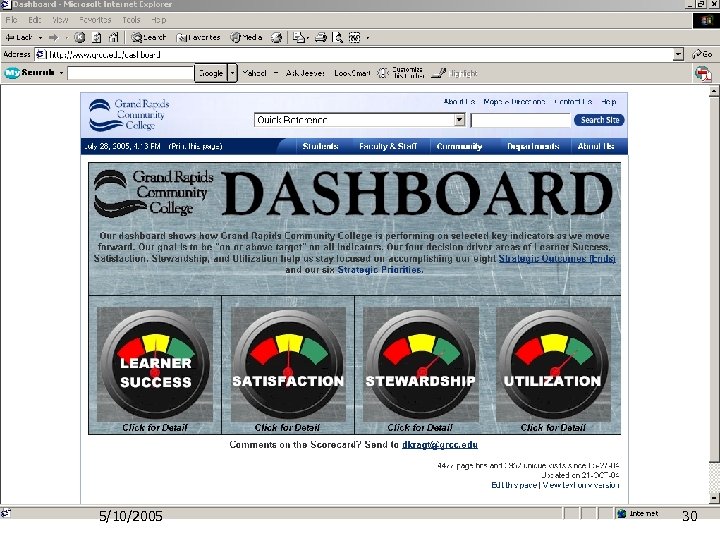
5/10/2005 30
Northwest’s Dashboard Model Ø Our model includes several types of information/report presentations ØDashboards – single screen current status ØTrend charts – key data element trends over time ØData tables –key data detail trends over time ØMajors, minors, advisees, degrees, SCH, financials ØSpecial interest charts/tables 5/10/2005 31

Features of the Northwest Balanced Scorecard System Ø Ø Ø Ø Dashboard “lights” to indicate current status Hyperlinks to navigate through workbooks Hyperlinks to “drill down” to detail Comparative data links for setting targets Real-time data updates Accommodates various data sources Modular design to facilitate upgrading Automated updating of modules 5/10/2005 32

5/10/2005 33

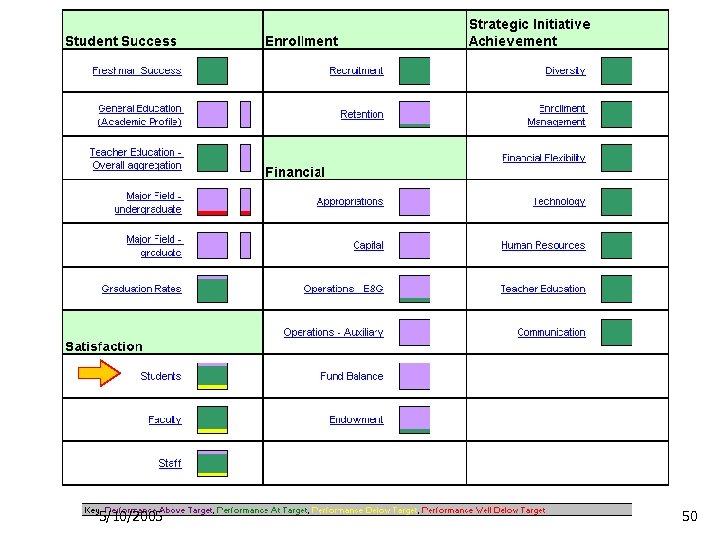
President’s Dashboard Ø General Dashboard categories: Ø Ø Ø Student Success Satisfaction Enrollment Financials Additional monitoring category: Ø Strategic Initiative Achievement 5/10/2005 34
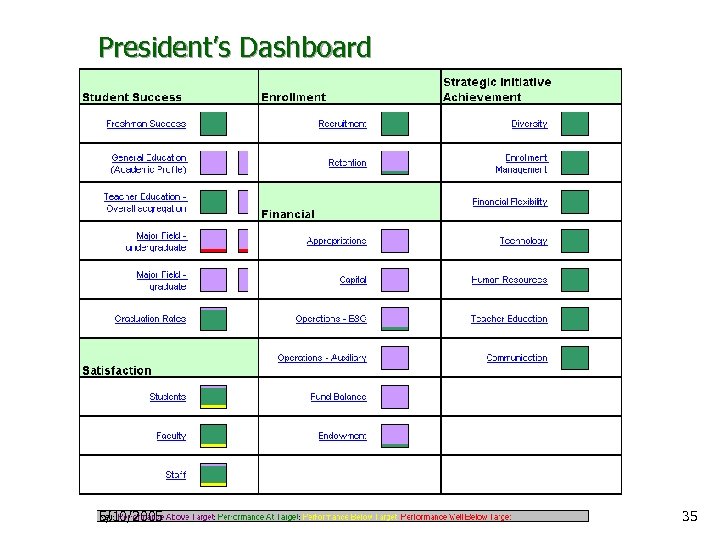
President’s Dashboard 5/10/2005 35

Provost’s Dashboard Ø General Dashboard categories: Ø Ø Ø Student Academic Performance Student Satisfaction Student Success and Placement Academic Workload Additional monitoring category: Ø Strategic Initiative Action Plan Progress 5/10/2005 36
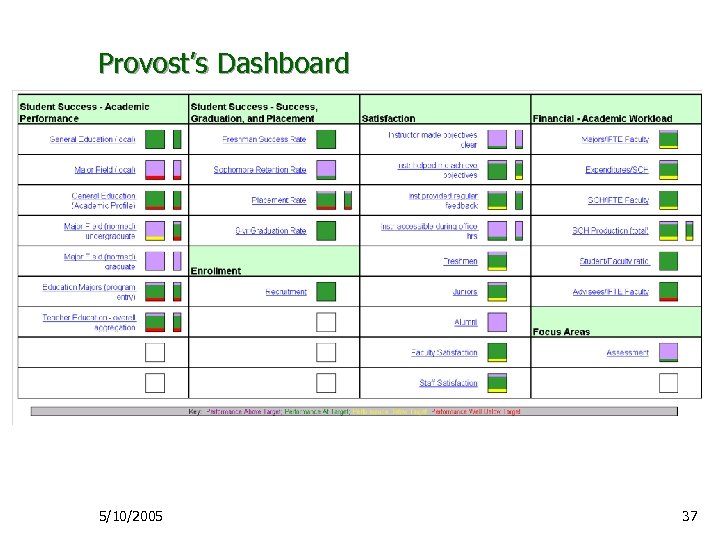
Provost’s Dashboard 5/10/2005 37

VP Student Affairs Dashboard Ø General Dashboard categories: Ø Ø Ø Student Engagement Student/Stakeholder Satisfaction Auxiliary (financial) 5/10/2005 38
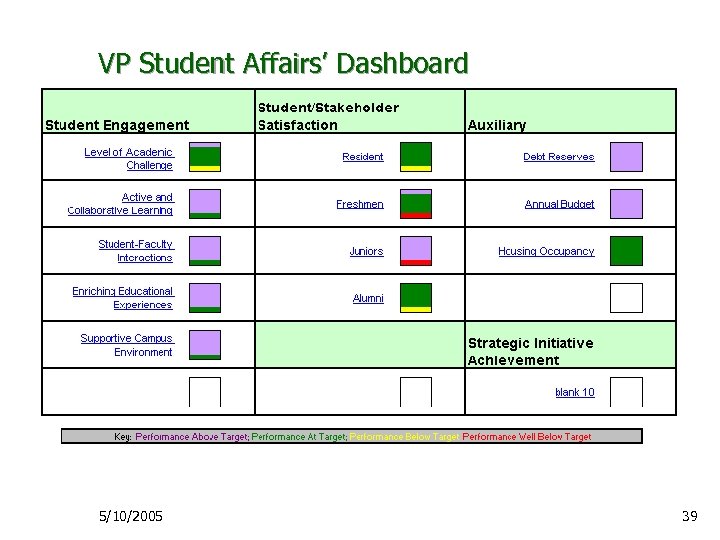
VP Student Affairs’ Dashboard 5/10/2005 39

Presentation Overview Ø Data Warehousing Ø Ø Goals of data warehousing Components of a data warehouse Data flow Dashboards Ø Ø Ø Goals of dashboards Components of dashboards “Drilling down” 5/10/2005 40

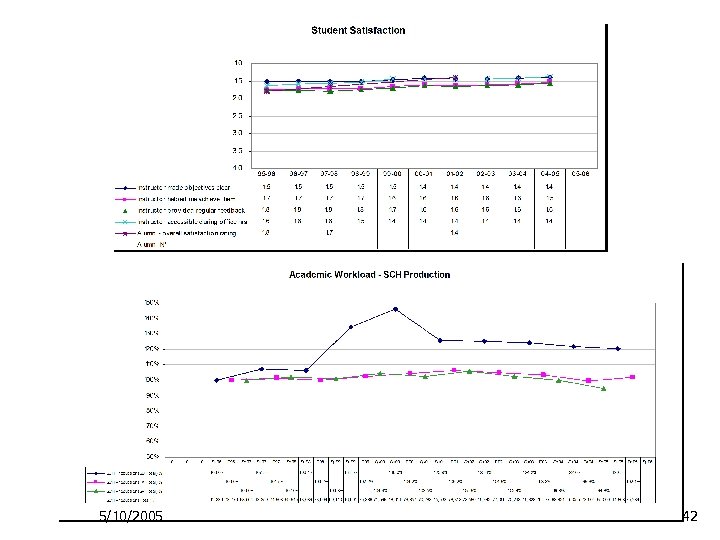
Comparative Data Ø In order to judge how good your performance is, results should be put into some context Ø Ø Trends over time Comparisons to other internal units Comparisons with peer groups Comparisons outside of the education sector 5/10/2005 41
5/10/2005 42
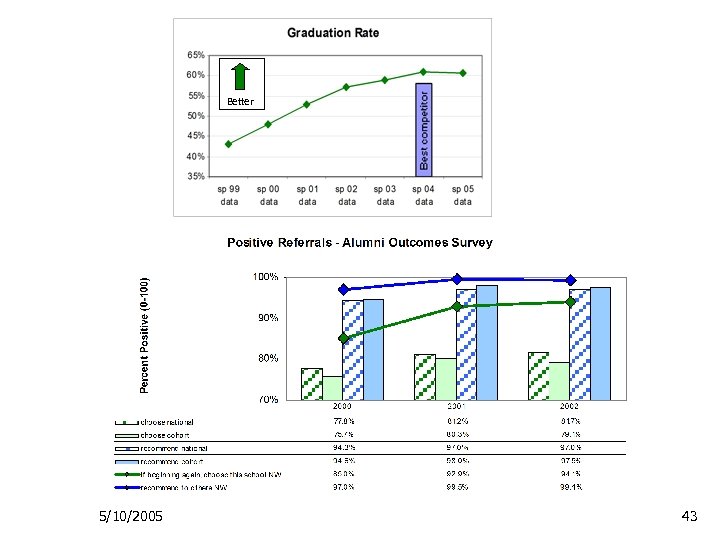
Better 5/10/2005 43
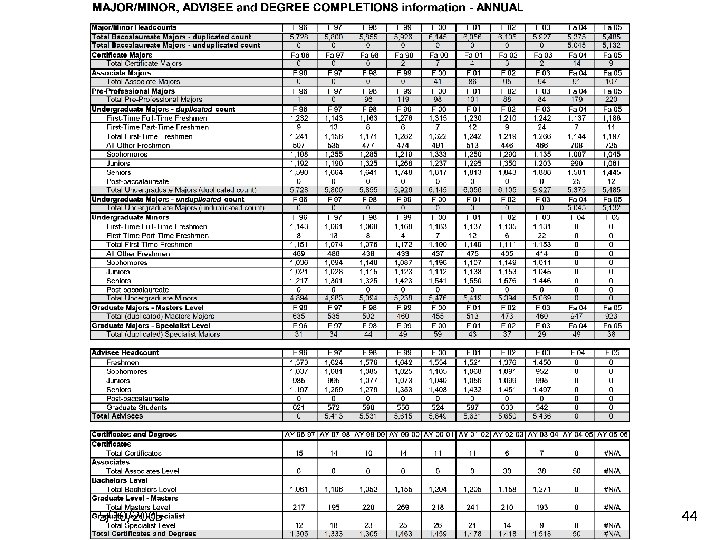
5/10/2005 44
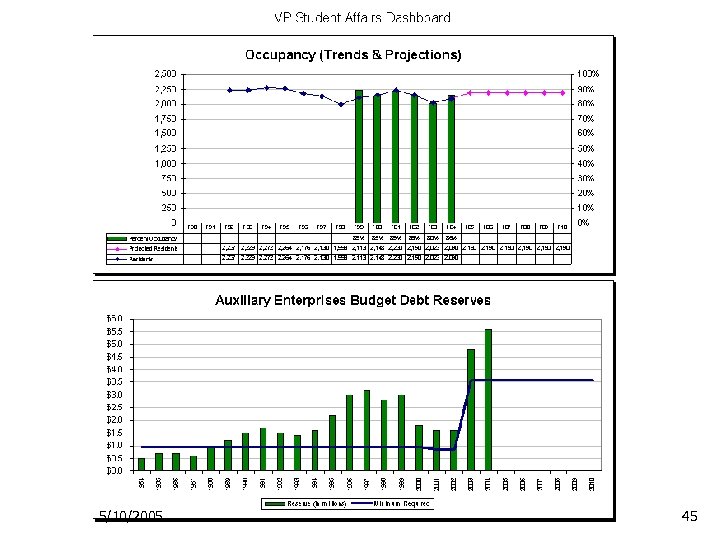
5/10/2005 45
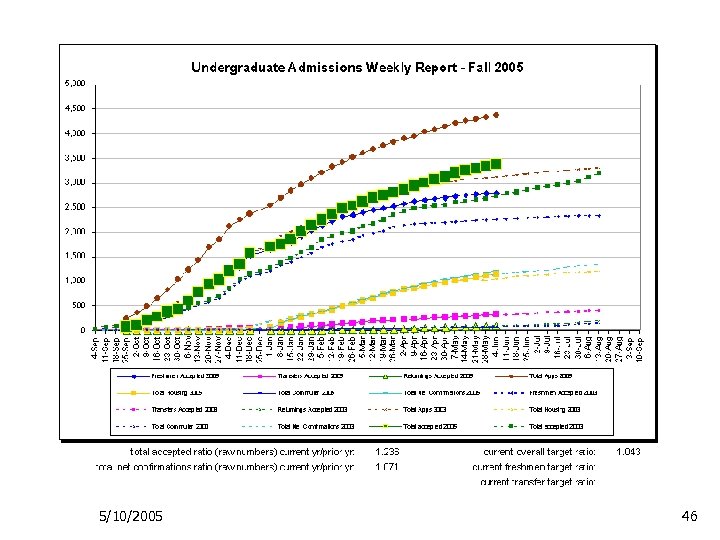
5/10/2005 46
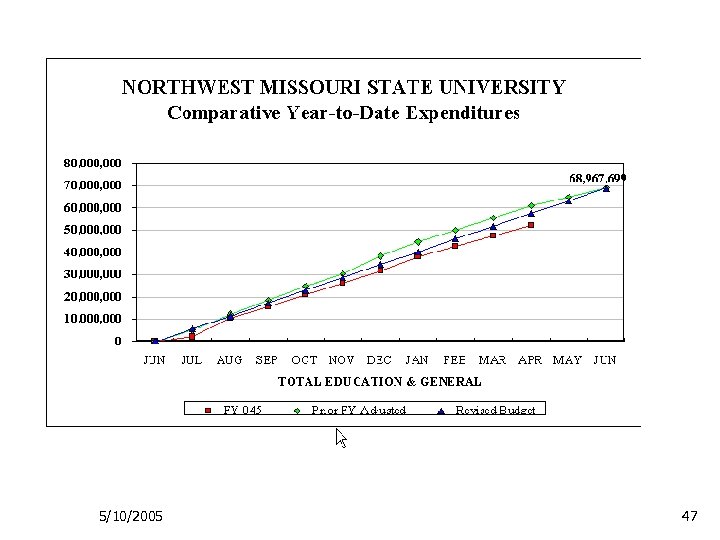
5/10/2005 47

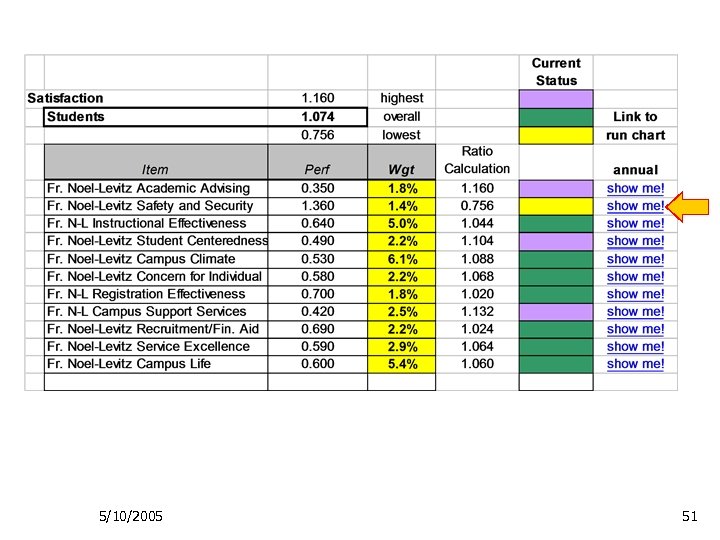
Interpreting Dashboard Indicators Ø To follow up on indicators of interest, use hyperlinks to access increasing levels of detail Ø Student satisfaction as an example ØPresident’s dashboard to ØProvost’s dashboard to ØNoel-Levitz Student Satisfaction Inventory data trends 5/10/2005 48
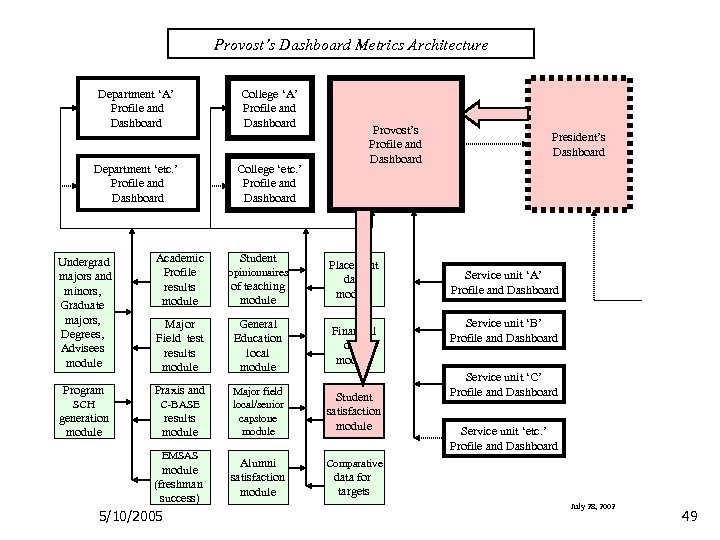
Provost’s Dashboard Metrics Architecture Department ‘A’ Profile and Dashboard Department ‘etc. ’ Profile and Dashboard College ‘A’ Profile and Dashboard College ‘etc. ’ Profile and Dashboard Provost’s Profile and Dashboard Undergrad majors and minors, Graduate majors, Degrees, Advisees module Academic Profile results module Major Field test results module General Education local module Financial data module Program Praxis and SCH C-BASE generation module results module Major field local/senior capstone module Student satisfaction module Alumni satisfaction module President’s Dashboard Comparative EMSAS module (freshman success) 5/10/2005 Student opinionnaires of teaching module Placement data module Service unit ‘A’ Profile and Dashboard Service unit ‘B’ Profile and Dashboard Service unit ‘C’ Profile and Dashboard Service unit ‘etc. ’ Profile and Dashboard data for targets July 28, 2002 49
5/10/2005 50
5/10/2005 51
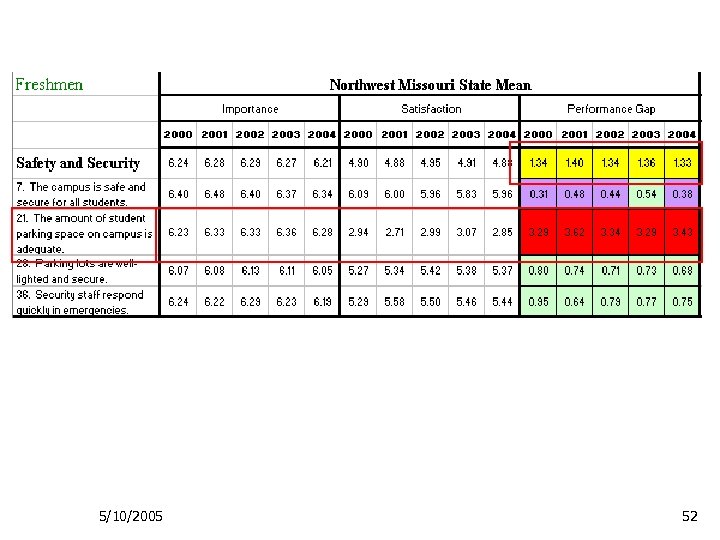
5/10/2005 52
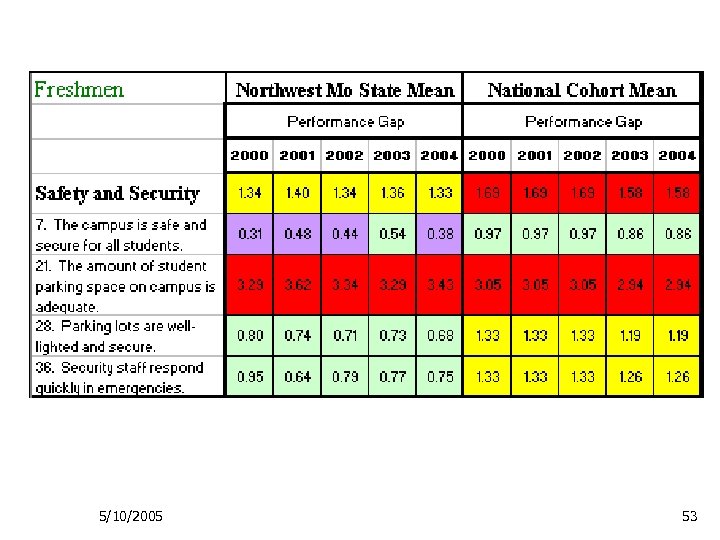
5/10/2005 53

Data Warehouses and Dashboards – A Primer Ø Contact information: Ø Ø Ø Ø Tod Massa State Council of Higher Education for Virginia 804. 225. 3147 (voice) todmassa@schev. edu Dave Oehler Northwest Missouri State University 660. 562. 1527 (voice) oehler@nwmissouri. edu 5/10/2005 54
19314bd8e729b887894d72e0d95f5161.ppt