f0988d7371576aef5e897821119231d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

Data to Biology Shankar Subramaniam University of California at San Diego
Many Dimensions of Biology • Scales: Molecules, Networks, Cells, Tissues… • Granularity: Structure, Function, Phenotype, Physiology… • Development: Stem cells, Differentiation, Tissue Engineering… • Species: Microorganisms, Unicellular Eukaryotes, Insects, Plants, Animals… • Length/Time: fempto, nano, micro, …. • Cell Processes: Metabolism, Regulation, Signaling… • Models: Micro, Meso, Macro…. • Model Systems: Microbes, Yeast, Worm/Fly, Plant, Mouse, Rat, Human UCSD-Bioinformatics & Systems Biology Group
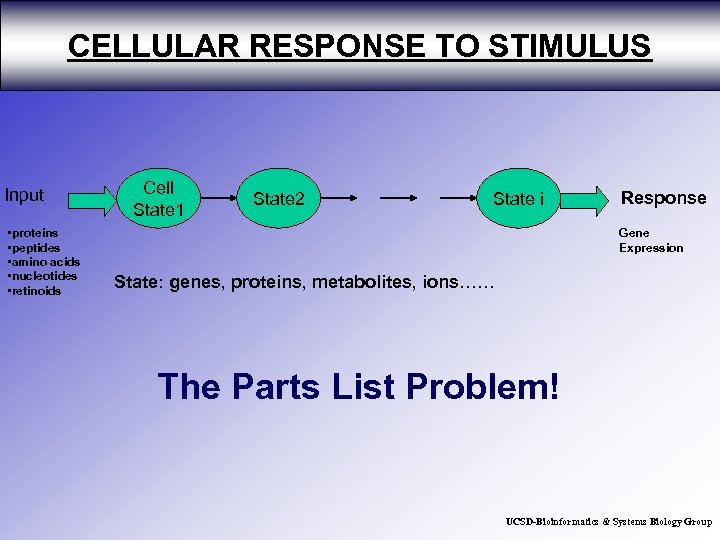
CELLULAR RESPONSE TO STIMULUS Input • proteins • peptides • amino acids • nucleotides • retinoids Cell State 1 State 2 State i Response Gene Expression State: genes, proteins, metabolites, ions…… The Parts List Problem! UCSD-Bioinformatics & Systems Biology Group
Automated sequencing machines at the Center for Genome Research in the Whitehead Institute UCSD-Bioinformatics & Systems Biology Group

Deconstructing Biology • Analysis of components, interactions and phenotypes – in context • Multiscale and high throughput measurements • Integration of data and knowledge • Coarse grained views of the system • Understanding larger scale function • Quantitative prediction of response to input at the systems level • Study of dynamical behavior of systems • Perturbation of components to produce changes in systemic response • Building dynamical models of systems

Challenges in building biochemical models • Complexity of proteomic states and interactions • Integration of diverse data to infer biochemical interactions and modules • Accounting for the temporal state of biochemical models
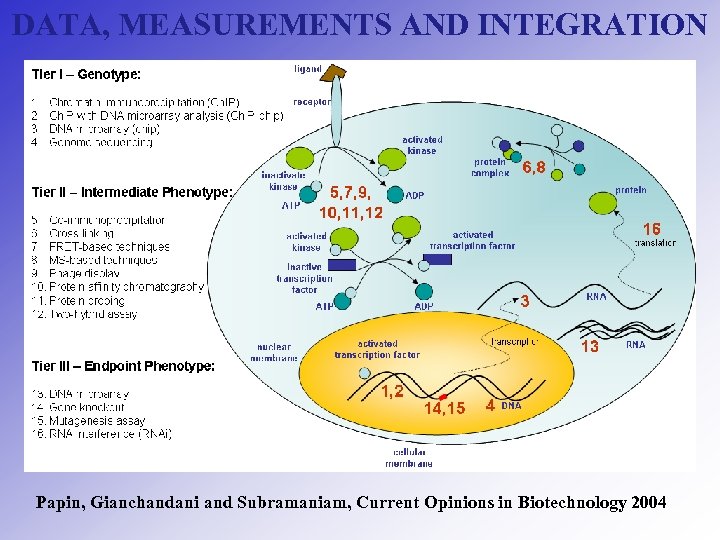
DATA, MEASUREMENTS AND INTEGRATION Papin, Gianchandani and Subramaniam, Current Opinions in Biotechnology 2004
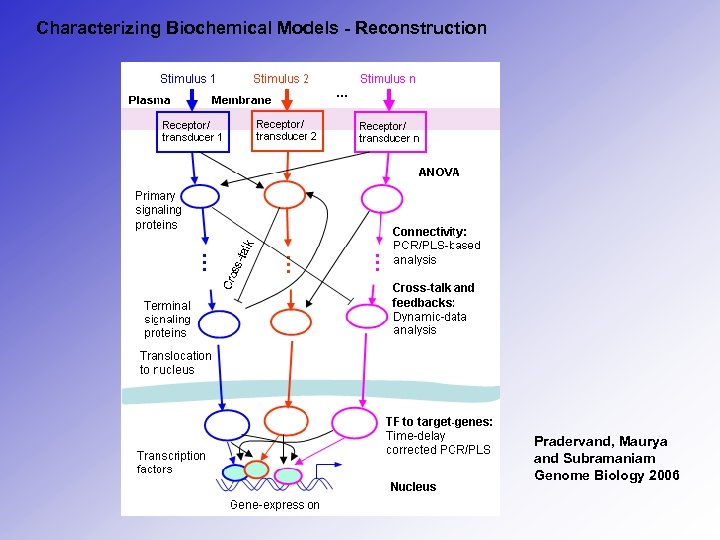
Characterizing Biochemical Models - Reconstruction Pradervand, Maurya and Subramaniam Genome Biology 2006

Basic Challenges for Systems Biology • How will we define and characterize a biological system? • How can we obtain the information on components of the system (qualitative and quantitative; static and dynamical)? Technologies and computational methods? • What mechanisms can we infer from the system behavior? • What are realistic models of a system? • How can we measure/compute input-phenotype characteristics of the system? • How will the model of the system be validated experimentally?
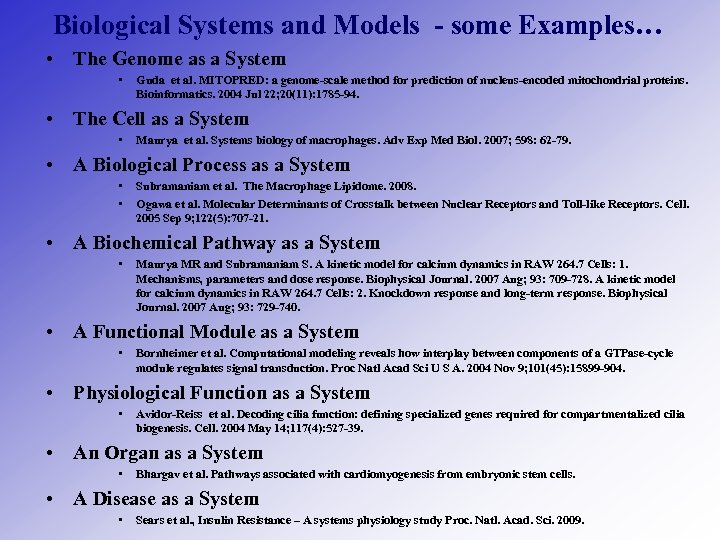
Biological Systems and Models - some Examples… • The Genome as a System • Guda et al. MITOPRED: a genome-scale method for prediction of nucleus-encoded mitochondrial proteins. Bioinformatics. 2004 Jul 22; 20(11): 1785 -94. • The Cell as a System • Maurya et al. Systems biology of macrophages. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007; 598: 62 -79. • A Biological Process as a System • • Subramaniam et al. The Macrophage Lipidome. 2008. Ogawa et al. Molecular Determinants of Crosstalk between Nuclear Receptors and Toll-like Receptors. Cell. 2005 Sep 9; 122(5): 707 -21. • A Biochemical Pathway as a System • Maurya MR and Subramaniam S. A kinetic model for calcium dynamics in RAW 264. 7 Cells: 1. Mechanisms, parameters and dose response. Biophysical Journal. 2007 Aug; 93: 709 -728. A kinetic model for calcium dynamics in RAW 264. 7 Cells: 2. Knockdown response and long-term response. Biophysical Journal. 2007 Aug; 93: 729 -740. • A Functional Module as a System • Bornheimer et al. Computational modeling reveals how interplay between components of a GTPase-cycle module regulates signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Nov 9; 101(45): 15899 -904. • Physiological Function as a System • Avidor-Reiss et al. Decoding cilia function: defining specialized genes required for compartmentalized cilia biogenesis. Cell. 2004 May 14; 117(4): 527 -39. • An Organ as a System • Bhargav et al. Pathways associated with cardiomyogenesis from embryonic stem cells. • A Disease as a System • Sears et al. , Insulin Resistance – A systems physiology study Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2009.
f0988d7371576aef5e897821119231d4.ppt