9000873beffff8d1c5979d3a2aaafda5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Data Storage and Dissemination Outline Past/Existing data management overview Future data management: • Goals • Broad description of proposed solution • Key details of proposed solutions Challenges and lessons Next steps
Data Storage and Dissemination Outline Past/Existing data management overview Future data management: • Goals • Broad description of proposed solution • Key details of proposed solutions Challenges and lessons Next steps
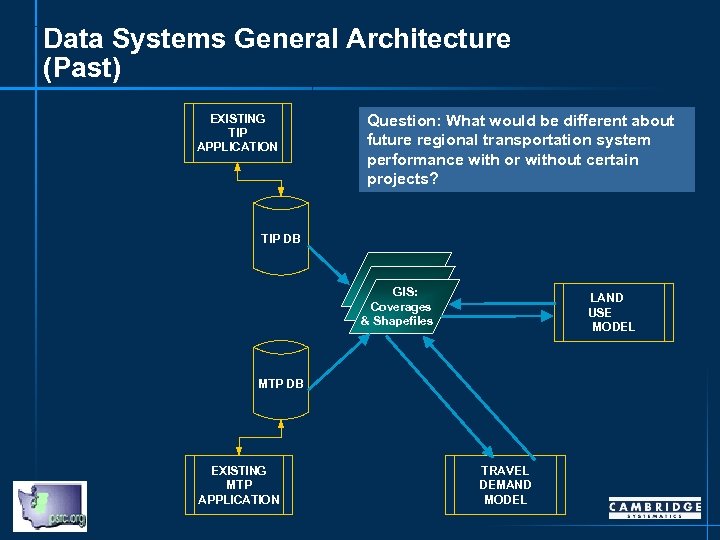 Data Systems General Architecture (Past) EXISTING TIP APPLICATION Question: What would be different about future regional transportation system performance with or without certain projects? TIP DB GIS: Coverages & Shapefiles LAND USE MODEL MTP DB EXISTING MTP APPLICATION TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL
Data Systems General Architecture (Past) EXISTING TIP APPLICATION Question: What would be different about future regional transportation system performance with or without certain projects? TIP DB GIS: Coverages & Shapefiles LAND USE MODEL MTP DB EXISTING MTP APPLICATION TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL
 Goals of proposed “Enterprise” Solution: Support model suite enhancements and future possibilities • Process automation • Quicker model run and analysis turnaround Support planning policy framework (Plan<->TIP<->PSRC project Approval) General efficiency and increased capability: • simultaneous multi-user access • automated data validation • In-your-face metadata Solid foundation for region-wide data sharing and publication (WWW) (note WA-TRANS FGDC Transportation Framework pilot, Summer 2005)
Goals of proposed “Enterprise” Solution: Support model suite enhancements and future possibilities • Process automation • Quicker model run and analysis turnaround Support planning policy framework (Plan<->TIP<->PSRC project Approval) General efficiency and increased capability: • simultaneous multi-user access • automated data validation • In-your-face metadata Solid foundation for region-wide data sharing and publication (WWW) (note WA-TRANS FGDC Transportation Framework pilot, Summer 2005)
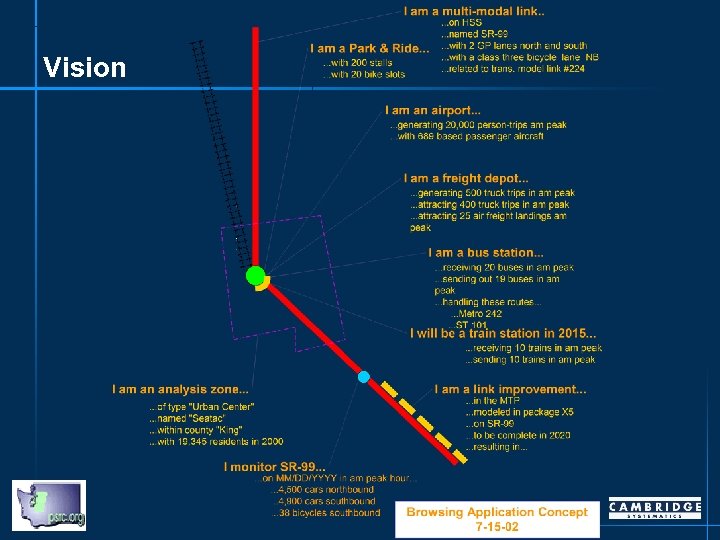 Vision
Vision
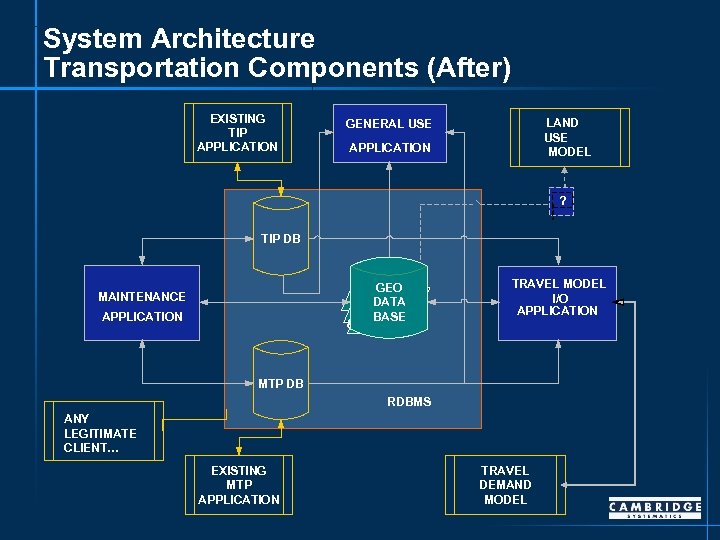 System Architecture Transportation Components (After) EXISTING TIP APPLICATION LAND USE MODEL GENERAL USE APPLICATION ? TIP DB GEO GIS: DATA Coverages BASE & Shapefiles MAINTENANCE APPLICATION TRAVEL MODEL I/O APPLICATION MTP DB RDBMS ANY LEGITIMATE CLIENT… EXISTING MTP APPLICATION TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL
System Architecture Transportation Components (After) EXISTING TIP APPLICATION LAND USE MODEL GENERAL USE APPLICATION ? TIP DB GEO GIS: DATA Coverages BASE & Shapefiles MAINTENANCE APPLICATION TRAVEL MODEL I/O APPLICATION MTP DB RDBMS ANY LEGITIMATE CLIENT… EXISTING MTP APPLICATION TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL
 Key Feature: Integrated Data Model Transportation Network (in progress) • Multimodal: One edge layer plus one junction layer for ALL modes (the “reference network”) • Granular: Ref net spatial layers plus related attribute tables encapsulate attributes for both directions and all times of day for present AND future possibilities • Dynamic: Possible future state(s) of the network determined by queries at runtime NOT in data Land use and demographic data (future) • Controlled: Results of data processes are “published” (along with metadata) once All data is transparent: accessible to all Data is secure: editable to few
Key Feature: Integrated Data Model Transportation Network (in progress) • Multimodal: One edge layer plus one junction layer for ALL modes (the “reference network”) • Granular: Ref net spatial layers plus related attribute tables encapsulate attributes for both directions and all times of day for present AND future possibilities • Dynamic: Possible future state(s) of the network determined by queries at runtime NOT in data Land use and demographic data (future) • Controlled: Results of data processes are “published” (along with metadata) once All data is transparent: accessible to all Data is secure: editable to few
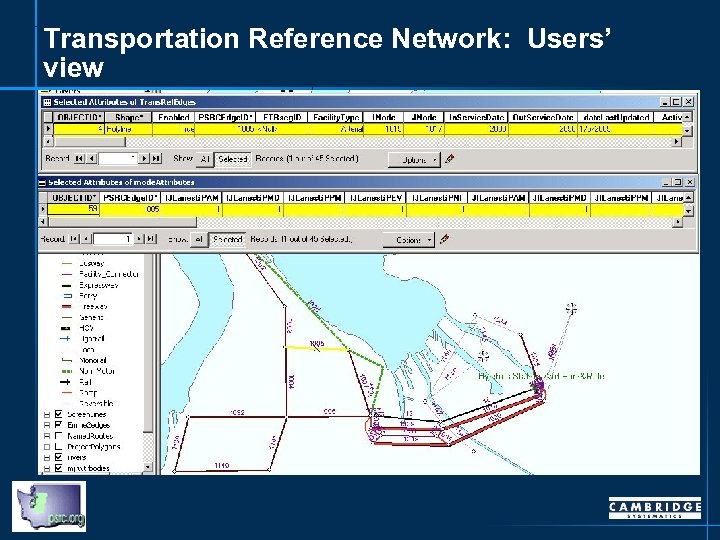 Transportation Reference Network: Users’ view
Transportation Reference Network: Users’ view
 Transportation: a Project-based Approach “Project” defined (for the data system): Future event with completion date Geographic location Alters transportation system Can be modeled
Transportation: a Project-based Approach “Project” defined (for the data system): Future event with completion date Geographic location Alters transportation system Can be modeled
 Key feature: future year networks derived from operation on reference and project layers + BASE YEAR NETWORK = FUTURE PROJECTS FUTURE NETWORK
Key feature: future year networks derived from operation on reference and project layers + BASE YEAR NETWORK = FUTURE PROJECTS FUTURE NETWORK
 Key feature: model automation Automated, query-based scenario creation • In/out service years • Other selection criteria (optional) • Other rule-based network thinning (optional) Automated travel model (in progress) and LU model (future) inputs generation Automated travel model (in progress) and LU model (future) forecast retrieval into Geodatabase
Key feature: model automation Automated, query-based scenario creation • In/out service years • Other selection criteria (optional) • Other rule-based network thinning (optional) Automated travel model (in progress) and LU model (future) inputs generation Automated travel model (in progress) and LU model (future) forecast retrieval into Geodatabase
 Key feature: data maintenance support Software “helper” application together with server features… • Ensures validity across all dependant layers • Maintains relationships between different databases • Maintains metadata (such as datestamps)
Key feature: data maintenance support Software “helper” application together with server features… • Ensures validity across all dependant layers • Maintains relationships between different databases • Maintains metadata (such as datestamps)
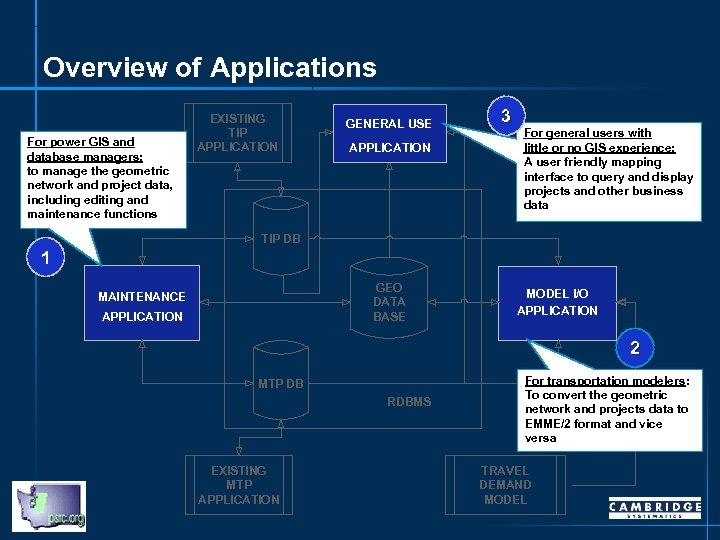 Overview of Applications For power GIS and database managers: to manage the geometric network and project data, including editing and maintenance functions EXISTING TIP APPLICATION GENERAL USE APPLICATION 3 For general users with little or no GIS experience: A user friendly mapping interface to query and display projects and other business data TIP DB 1 GEO DATA BASE MAINTENANCE APPLICATION MODEL I/O APPLICATION 2 MTP DB RDBMS EXISTING MTP APPLICATION For transportation modelers: To convert the geometric network and projects data to EMME/2 format and vice versa TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL
Overview of Applications For power GIS and database managers: to manage the geometric network and project data, including editing and maintenance functions EXISTING TIP APPLICATION GENERAL USE APPLICATION 3 For general users with little or no GIS experience: A user friendly mapping interface to query and display projects and other business data TIP DB 1 GEO DATA BASE MAINTENANCE APPLICATION MODEL I/O APPLICATION 2 MTP DB RDBMS EXISTING MTP APPLICATION For transportation modelers: To convert the geometric network and projects data to EMME/2 format and vice versa TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL
 Maintenance Application: User View Additional Option: Scan project DB’s for all projects that need to be mapped
Maintenance Application: User View Additional Option: Scan project DB’s for all projects that need to be mapped
 Maintenance Application: Mapping a project
Maintenance Application: Mapping a project
 General Use Application: Data Loading and Metadata
General Use Application: Data Loading and Metadata
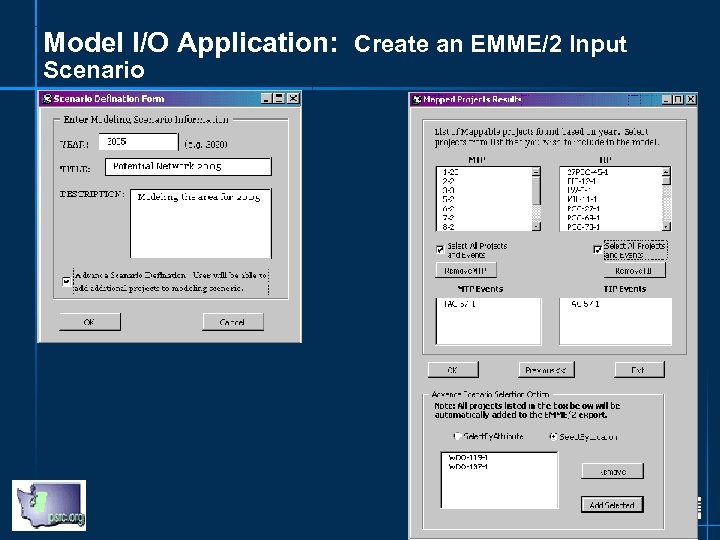 Model I/O Application: Create an EMME/2 Input Scenario
Model I/O Application: Create an EMME/2 Input Scenario
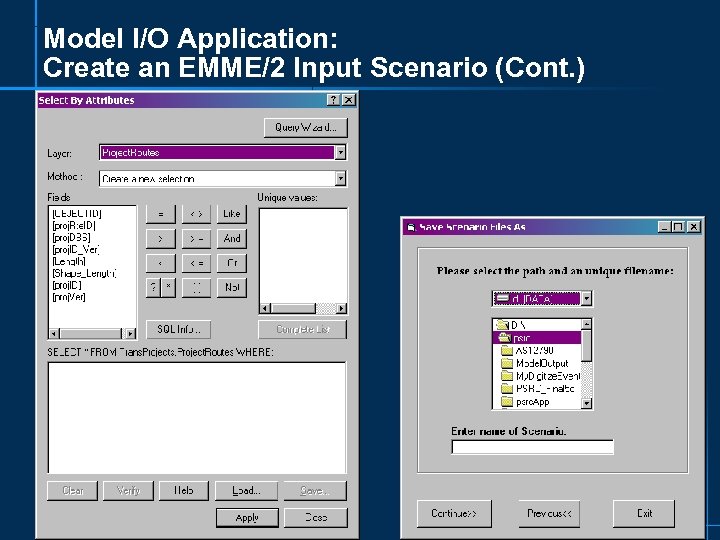 Model I/O Application: Create an EMME/2 Input Scenario (Cont. )
Model I/O Application: Create an EMME/2 Input Scenario (Cont. )
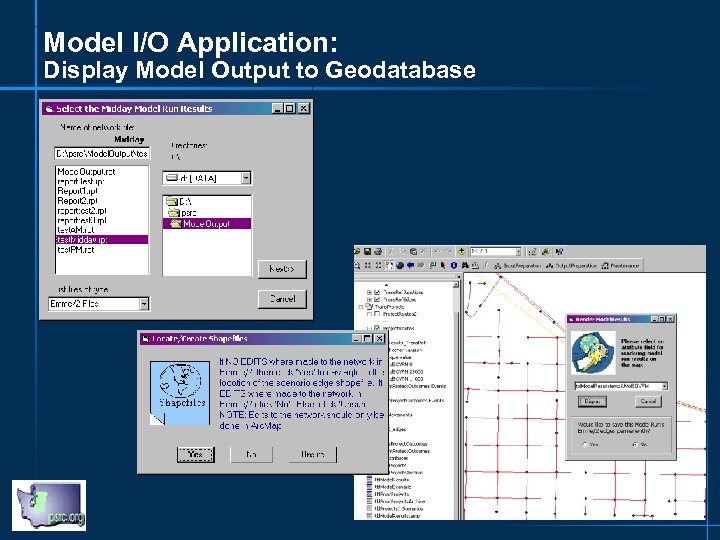 Model I/O Application: Display Model Output to Geodatabase
Model I/O Application: Display Model Output to Geodatabase
 Status Transportation: in beta test cycle Demographic & LU data plus any supporting application(s): about to restart design External data import/export: future
Status Transportation: in beta test cycle Demographic & LU data plus any supporting application(s): about to restart design External data import/export: future
 Lessons Learned Migrating legacy data to new system: more huge than you ever think Software and data model development: proceed together in many small steps Question: your data integration success stories or lessons?
Lessons Learned Migrating legacy data to new system: more huge than you ever think Software and data model development: proceed together in many small steps Question: your data integration success stories or lessons?
 Questions?
Questions?
 Key lesson: Many small cyclical steps Each iteration of schema prompts application update… …application test reveals data or schema issue… …which when fixed allows a new application feature to be attempted… …for which the feasible application solutions prompt a schema update…
Key lesson: Many small cyclical steps Each iteration of schema prompts application update… …application test reveals data or schema issue… …which when fixed allows a new application feature to be attempted… …for which the feasible application solutions prompt a schema update…
 Key challenge: Discovering what new capabilities and limits are present in commercial software Geometric network (only feature available when project started) exposes insufficient spatial relationship tools New relational database capability is significant advance…but has performance and functional issues Stock loading and validation tools cumbersome and implement only part of underlying data provider capabilities
Key challenge: Discovering what new capabilities and limits are present in commercial software Geometric network (only feature available when project started) exposes insufficient spatial relationship tools New relational database capability is significant advance…but has performance and functional issues Stock loading and validation tools cumbersome and implement only part of underlying data provider capabilities
 Key lesson: migration timing and planning Document the migration (in detail) so that the entire process can be repeated easily Revise migration plan with each schema/application iteration to foresee migration implications Data migration is the bulk of the work Assume more manual work than marketing flyers imply
Key lesson: migration timing and planning Document the migration (in detail) so that the entire process can be repeated easily Revise migration plan with each schema/application iteration to foresee migration implications Data migration is the bulk of the work Assume more manual work than marketing flyers imply
 GIS Contacts at PSRC Jeff Frkonja Senior Planner Puget Sound Regional Council 206 -464 -6180 jfrkonja@psrc. org Andy Norton Senior GIS Analyst Puget Sound Regional Council 206 -464 -7527 anorton@psrc. org
GIS Contacts at PSRC Jeff Frkonja Senior Planner Puget Sound Regional Council 206 -464 -6180 jfrkonja@psrc. org Andy Norton Senior GIS Analyst Puget Sound Regional Council 206 -464 -7527 anorton@psrc. org
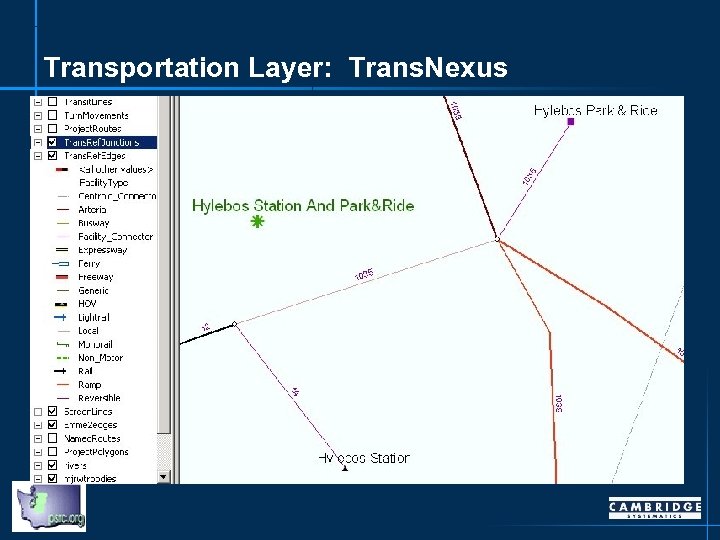 Transportation Layer: Trans. Nexus
Transportation Layer: Trans. Nexus
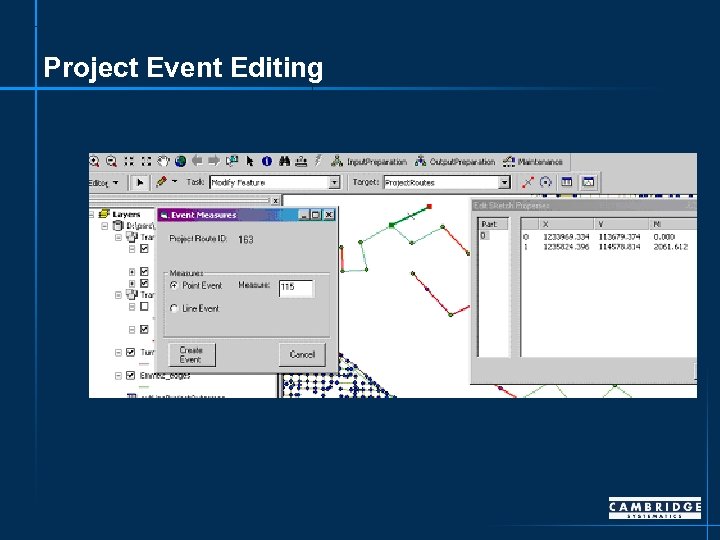 Project Event Editing
Project Event Editing
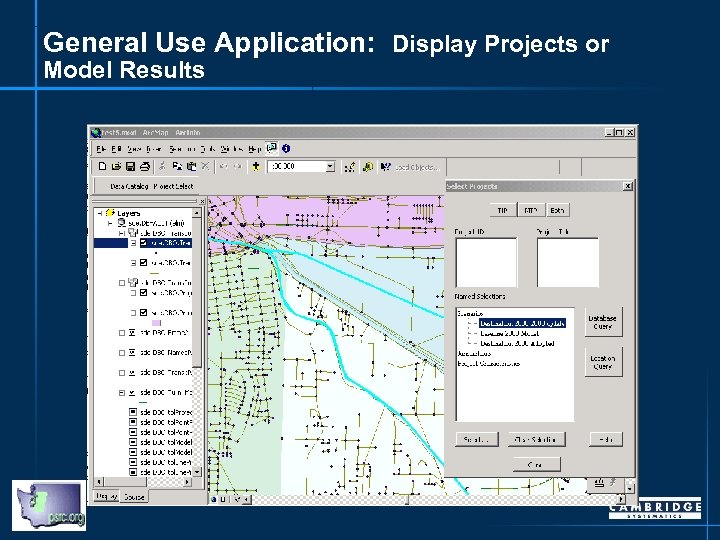 General Use Application: Display Projects or Model Results
General Use Application: Display Projects or Model Results
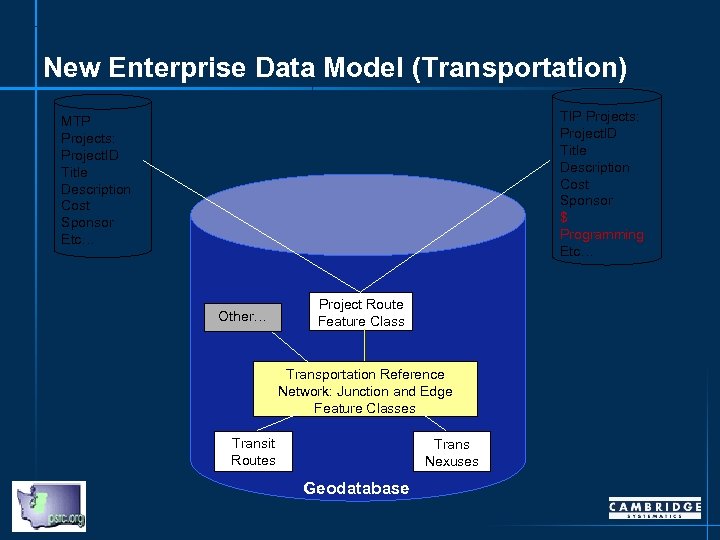 New Enterprise Data Model (Transportation) TIP Projects: Project. ID Title Description Cost Sponsor $ Programming Etc… MTP Projects: Project. ID Title Description Cost Sponsor Etc… Other… Project Route Feature Class Transportation Reference Network: Junction and Edge Feature Classes Transit Routes Trans Nexuses Geodatabase
New Enterprise Data Model (Transportation) TIP Projects: Project. ID Title Description Cost Sponsor $ Programming Etc… MTP Projects: Project. ID Title Description Cost Sponsor Etc… Other… Project Route Feature Class Transportation Reference Network: Junction and Edge Feature Classes Transit Routes Trans Nexuses Geodatabase
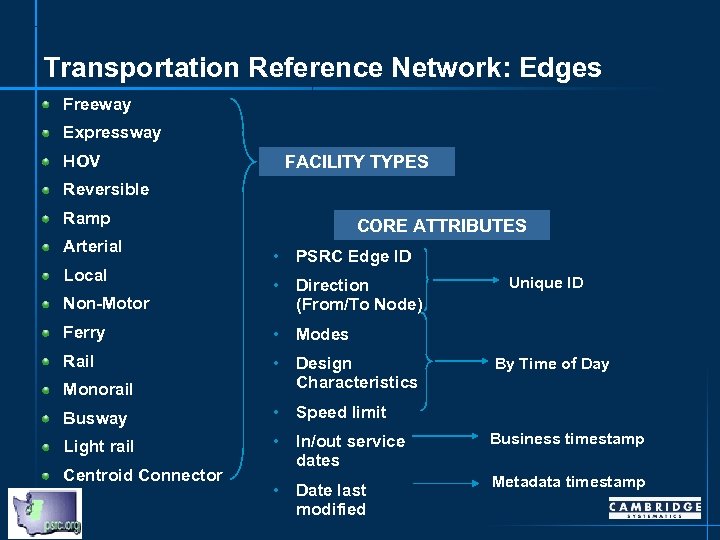 Transportation Reference Network: Edges Freeway Expressway HOV FACILITY TYPES Reversible Ramp Arterial Local CORE ATTRIBUTES • PSRC Edge ID Unique ID Non-Motor • Direction (From/To Node) Ferry • Modes Rail Monorail • Design Characteristics Busway • Speed limit Light rail • In/out service dates Business timestamp • Date last modified Metadata timestamp Centroid Connector By Time of Day
Transportation Reference Network: Edges Freeway Expressway HOV FACILITY TYPES Reversible Ramp Arterial Local CORE ATTRIBUTES • PSRC Edge ID Unique ID Non-Motor • Direction (From/To Node) Ferry • Modes Rail Monorail • Design Characteristics Busway • Speed limit Light rail • In/out service dates Business timestamp • Date last modified Metadata timestamp Centroid Connector By Time of Day
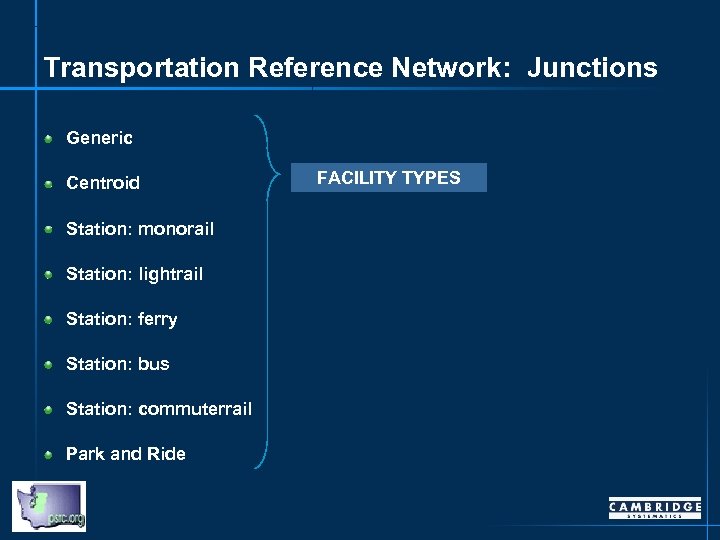 Transportation Reference Network: Junctions Generic Centroid Station: monorail Station: lightrail Station: ferry Station: bus Station: commuterrail Park and Ride FACILITY TYPES
Transportation Reference Network: Junctions Generic Centroid Station: monorail Station: lightrail Station: ferry Station: bus Station: commuterrail Park and Ride FACILITY TYPES
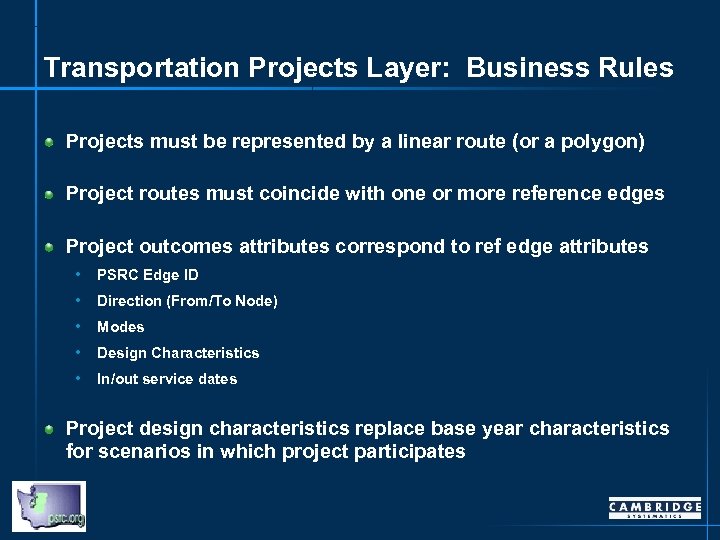 Transportation Projects Layer: Business Rules Projects must be represented by a linear route (or a polygon) Project routes must coincide with one or more reference edges Project outcomes attributes correspond to ref edge attributes • PSRC Edge ID • Direction (From/To Node) • Modes • Design Characteristics • In/out service dates Project design characteristics replace base year characteristics for scenarios in which project participates
Transportation Projects Layer: Business Rules Projects must be represented by a linear route (or a polygon) Project routes must coincide with one or more reference edges Project outcomes attributes correspond to ref edge attributes • PSRC Edge ID • Direction (From/To Node) • Modes • Design Characteristics • In/out service dates Project design characteristics replace base year characteristics for scenarios in which project participates
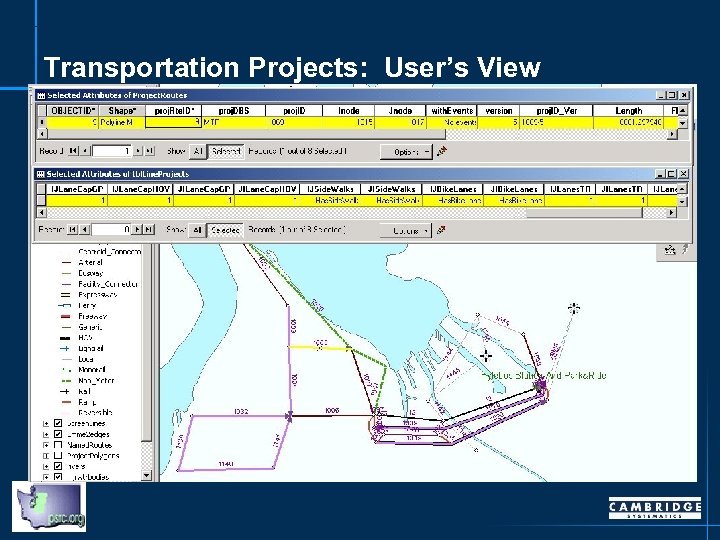 Transportation Projects: User’s View
Transportation Projects: User’s View
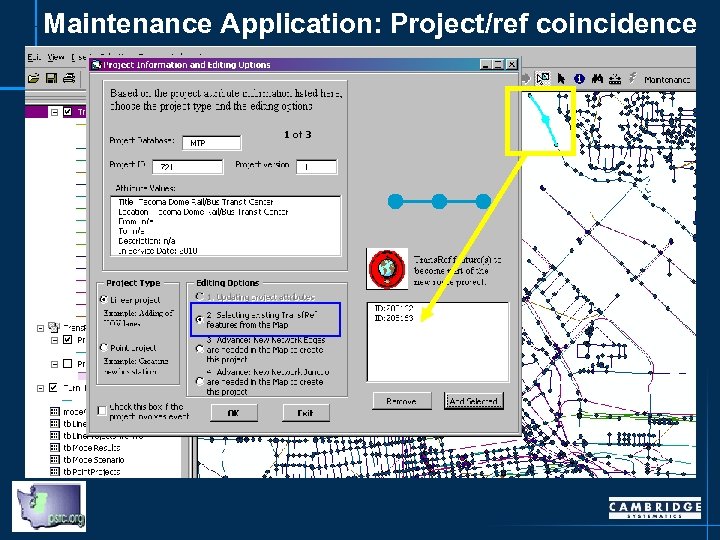 Maintenance Application: Project/ref coincidence
Maintenance Application: Project/ref coincidence
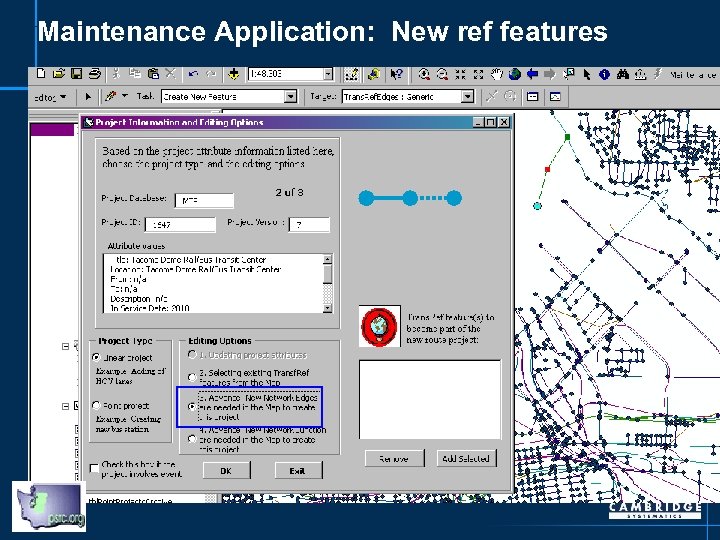 Maintenance Application: New ref features
Maintenance Application: New ref features
 Key challenge: Articulate business rules for Geodatabase-to-EMME/2 data exchange Goal clarity: separating what should be from what is • Legacy model manipulated exogenous data to achieve calibration (i. e. , a road with 2. 3 northbound lanes) Triage: which chosen design goals are best met in which system component (Geodatabase, application, or model? ) • More realistic network representation=>Geodb Complexity: can rule-based automation work? • “Shadow” HOV and weave links one geodatabase edge becomes separate SOV and HOV links in model
Key challenge: Articulate business rules for Geodatabase-to-EMME/2 data exchange Goal clarity: separating what should be from what is • Legacy model manipulated exogenous data to achieve calibration (i. e. , a road with 2. 3 northbound lanes) Triage: which chosen design goals are best met in which system component (Geodatabase, application, or model? ) • More realistic network representation=>Geodb Complexity: can rule-based automation work? • “Shadow” HOV and weave links one geodatabase edge becomes separate SOV and HOV links in model


