35e73e2395d5b4d59bddc795f18d8afe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Data Quality Assurance in Cooperative Information Systems: a Multi-dimension Quality Certificate Cinzia Cappiello 1, Chiara Francalanci 1, Barbara Pernici 1, Pierluigi Plebani 1, Monica Scannapieco 2 Politecnico di Milano, Italy {cappiell|francala|pernici|plebani}@elet. polimi. it 2 Università di Roma, “La Sapienza”, Rome, Italy IASI-CNR, Rome, Italy monscan@dis. uniroma 1. it 1 Cinzia Cappiello
Data Quality Assurance in Cooperative Information Systems: a Multi-dimension Quality Certificate Cinzia Cappiello 1, Chiara Francalanci 1, Barbara Pernici 1, Pierluigi Plebani 1, Monica Scannapieco 2 Politecnico di Milano, Italy {cappiell|francala|pernici|plebani}@elet. polimi. it 2 Università di Roma, “La Sapienza”, Rome, Italy IASI-CNR, Rome, Italy monscan@dis. uniroma 1. it 1 Cinzia Cappiello
 Outline Definitions of data quality dimensions Relevant data quality dimensions in CISs A Quality Management Architecture Data Quality Certificate Future work Cinzia Cappiello 2
Outline Definitions of data quality dimensions Relevant data quality dimensions in CISs A Quality Management Architecture Data Quality Certificate Future work Cinzia Cappiello 2
 Definitions of data quality dimensions The data quality literature provides a thorough classification of data quality dimensions. There is not general agreement on the definition of most dimensions. The selected definitions are founded on a survey of the quality dimensions proposed in the literature over the past 10 years [Catarci, Scannapieco 2002]. On the basis of this classification a basic set of data quality dimensions is defined including accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, interpretability and accessibility; which represent the dimensions considered by the majority of the authors. Timeliness is considered together with the other time related dimensions: currency and volatility. Cinzia Cappiello 3
Definitions of data quality dimensions The data quality literature provides a thorough classification of data quality dimensions. There is not general agreement on the definition of most dimensions. The selected definitions are founded on a survey of the quality dimensions proposed in the literature over the past 10 years [Catarci, Scannapieco 2002]. On the basis of this classification a basic set of data quality dimensions is defined including accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, interpretability and accessibility; which represent the dimensions considered by the majority of the authors. Timeliness is considered together with the other time related dimensions: currency and volatility. Cinzia Cappiello 3
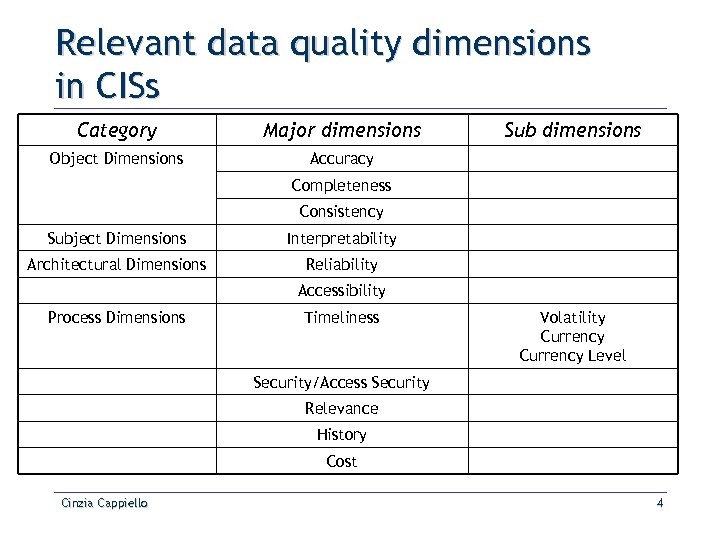 Relevant data quality dimensions in CISs Category Major dimensions Object Dimensions Sub dimensions Accuracy Completeness Consistency Subject Dimensions Interpretability Architectural Dimensions Reliability Accessibility Process Dimensions Timeliness Volatility Currency Level Security/Access Security Relevance History Cost Cinzia Cappiello 4
Relevant data quality dimensions in CISs Category Major dimensions Object Dimensions Sub dimensions Accuracy Completeness Consistency Subject Dimensions Interpretability Architectural Dimensions Reliability Accessibility Process Dimensions Timeliness Volatility Currency Level Security/Access Security Relevance History Cost Cinzia Cappiello 4
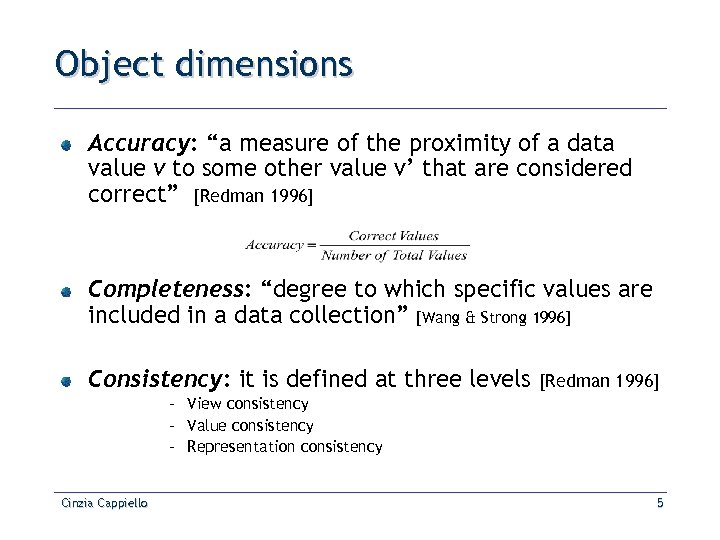 Object dimensions Accuracy: “a measure of the proximity of a data value v to some other value v’ that are considered correct” [Redman 1996] Completeness: “degree to which specific values are included in a data collection” [Wang & Strong 1996] Consistency: it is defined at three levels [Redman 1996] – View consistency – Value consistency – Representation consistency Cinzia Cappiello 5
Object dimensions Accuracy: “a measure of the proximity of a data value v to some other value v’ that are considered correct” [Redman 1996] Completeness: “degree to which specific values are included in a data collection” [Wang & Strong 1996] Consistency: it is defined at three levels [Redman 1996] – View consistency – Value consistency – Representation consistency Cinzia Cappiello 5
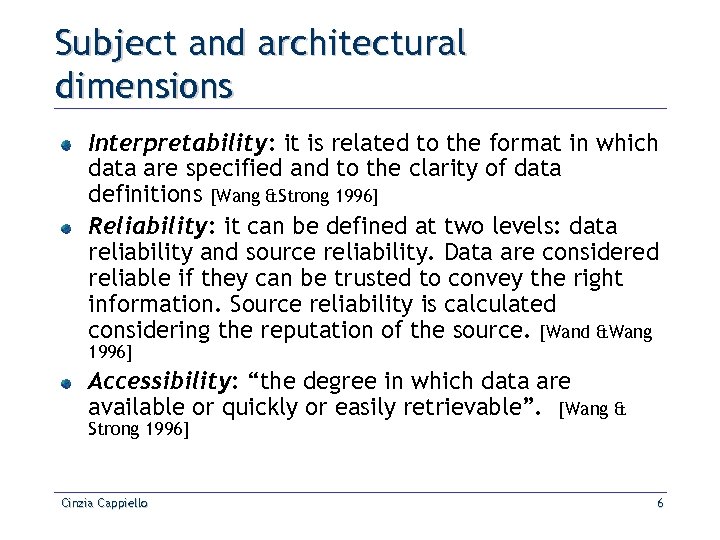 Subject and architectural dimensions Interpretability: it is related to the format in which data are specified and to the clarity of data definitions [Wang &Strong 1996] Reliability: it can be defined at two levels: data reliability and source reliability. Data are considered reliable if they can be trusted to convey the right information. Source reliability is calculated considering the reputation of the source. [Wand &Wang 1996] Accessibility: “the degree in which data are available or quickly or easily retrievable”. [Wang & Strong 1996] Cinzia Cappiello 6
Subject and architectural dimensions Interpretability: it is related to the format in which data are specified and to the clarity of data definitions [Wang &Strong 1996] Reliability: it can be defined at two levels: data reliability and source reliability. Data are considered reliable if they can be trusted to convey the right information. Source reliability is calculated considering the reputation of the source. [Wand &Wang 1996] Accessibility: “the degree in which data are available or quickly or easily retrievable”. [Wang & Strong 1996] Cinzia Cappiello 6
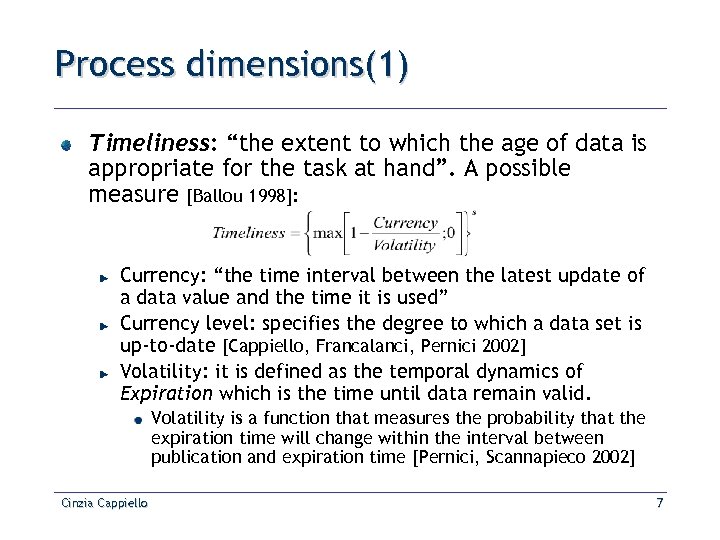 Process dimensions(1) Timeliness: “the extent to which the age of data is appropriate for the task at hand”. A possible measure [Ballou 1998]: Currency: “the time interval between the latest update of a data value and the time it is used” Currency level: specifies the degree to which a data set is up-to-date [Cappiello, Francalanci, Pernici 2002] Volatility: it is defined as the temporal dynamics of Expiration which is the time until data remain valid. Volatility is a function that measures the probability that the expiration time will change within the interval between publication and expiration time [Pernici, Scannapieco 2002] Cinzia Cappiello 7
Process dimensions(1) Timeliness: “the extent to which the age of data is appropriate for the task at hand”. A possible measure [Ballou 1998]: Currency: “the time interval between the latest update of a data value and the time it is used” Currency level: specifies the degree to which a data set is up-to-date [Cappiello, Francalanci, Pernici 2002] Volatility: it is defined as the temporal dynamics of Expiration which is the time until data remain valid. Volatility is a function that measures the probability that the expiration time will change within the interval between publication and expiration time [Pernici, Scannapieco 2002] Cinzia Cappiello 7
 Process dimensions (2) Security/Access Security: it is defined as “the extent to which access to data can be restricted and hence kept secure” [Wang & Strong 1996]. We have listed the security requirements that should be satisfied to assure data security. The percentage of satisfied requirements in IS can be a measure of the value of this dimension. Relevance: it is a measure of the appropriateness of the data extracted for the requested task. Cinzia Cappiello 8
Process dimensions (2) Security/Access Security: it is defined as “the extent to which access to data can be restricted and hence kept secure” [Wang & Strong 1996]. We have listed the security requirements that should be satisfied to assure data security. The percentage of satisfied requirements in IS can be a measure of the value of this dimension. Relevance: it is a measure of the appropriateness of the data extracted for the requested task. Cinzia Cappiello 8
 Process dimensions (3) History: the storage of what operations of quality improvement have been performed on data allows to build a certificate in which all the operations that have modified data are listed. For each operation has to be stored: – Type of operation – Execution date – Percentage of improvement Cost: Dimensions that is able to evaluate the cost impact of the errors due to bad data quality Cinzia Cappiello 9
Process dimensions (3) History: the storage of what operations of quality improvement have been performed on data allows to build a certificate in which all the operations that have modified data are listed. For each operation has to be stored: – Type of operation – Execution date – Percentage of improvement Cost: Dimensions that is able to evaluate the cost impact of the errors due to bad data quality Cinzia Cappiello 9
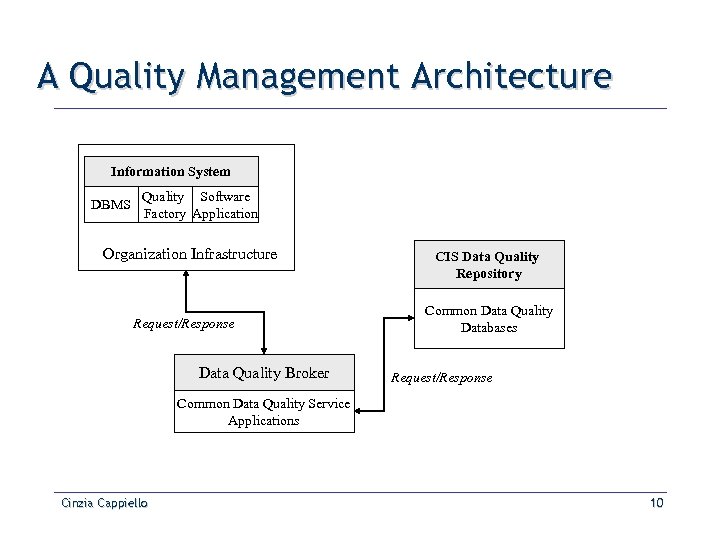 A Quality Management Architecture Information System DBMS Quality Software Factory Application Organization Infrastructure Request/Response Data Quality Broker CIS Data Quality Repository Common Data Quality Databases Request/Response Common Data Quality Service Applications Cinzia Cappiello 10
A Quality Management Architecture Information System DBMS Quality Software Factory Application Organization Infrastructure Request/Response Data Quality Broker CIS Data Quality Repository Common Data Quality Databases Request/Response Common Data Quality Service Applications Cinzia Cappiello 10
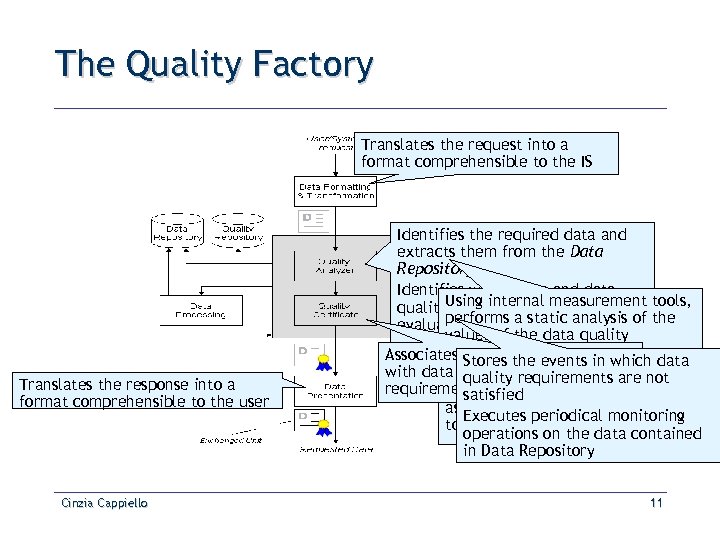 The Quality Factory Translates the request into a format comprehensible to the IS Translates the response into a format comprehensible to the user Cinzia Cappiello Identifies the required data and extracts them from the Data Repository Identifies which data and data quality. Using internal measurement tools, dimensions have been performs a static analysis of the evaluated values of the data quality dimension certificate Associates Stores the events in which data a quality with data that satisfy quality satisfy not If data values do not quality requirements are requirements quality satisfied assessment sends an alert message Executes periodical monitoring to the Monitoring module operations on the data contained in Data Repository 11
The Quality Factory Translates the request into a format comprehensible to the IS Translates the response into a format comprehensible to the user Cinzia Cappiello Identifies the required data and extracts them from the Data Repository Identifies which data and data quality. Using internal measurement tools, dimensions have been performs a static analysis of the evaluated values of the data quality dimension certificate Associates Stores the events in which data a quality with data that satisfy quality satisfy not If data values do not quality requirements are requirements quality satisfied assessment sends an alert message Executes periodical monitoring to the Monitoring module operations on the data contained in Data Repository 11
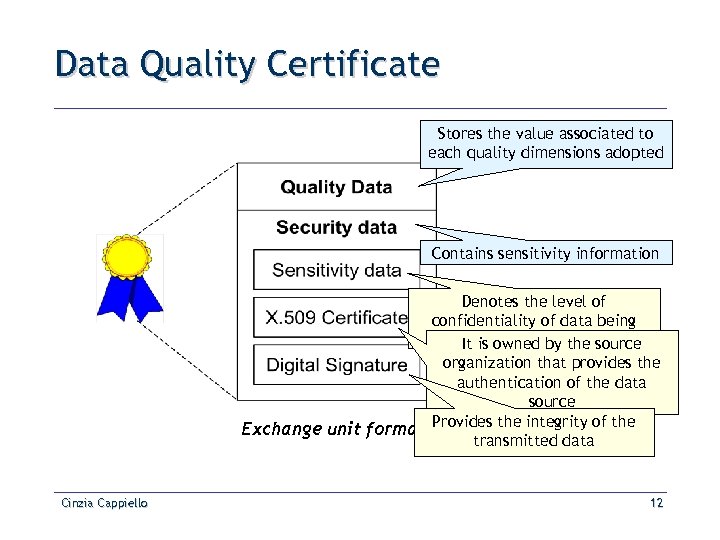 Data Quality Certificate Stores the value associated to each quality dimensions adopted Contains sensitivity information Denotes the level of confidentiality of data being transferred It is owned by the source organization that provides the authentication of the data source Exchange unit format Provides the integrity of the transmitted data Cinzia Cappiello 12
Data Quality Certificate Stores the value associated to each quality dimensions adopted Contains sensitivity information Denotes the level of confidentiality of data being transferred It is owned by the source organization that provides the authentication of the data source Exchange unit format Provides the integrity of the transmitted data Cinzia Cappiello 12
 Future work Software implementation of quality factory architecture and data quality certificate Application of the data quality certificate to evaluate the quality of Web services in a cooperative environment Evaluation of the impact of data replication and distribution on data quality dimensions Cinzia Cappiello 13
Future work Software implementation of quality factory architecture and data quality certificate Application of the data quality certificate to evaluate the quality of Web services in a cooperative environment Evaluation of the impact of data replication and distribution on data quality dimensions Cinzia Cappiello 13


