13a91d1870148a8dd9d1e49e6f008ba1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Data Protection Regulations within Europol • Jan Ellermann • Data Protection and Confidentiality Unit • Belgrade, 10 February 2009
Data Protection Regulations within Europol • Jan Ellermann • Data Protection and Confidentiality Unit • Belgrade, 10 February 2009
 Impressions
Impressions
 General Overview
General Overview
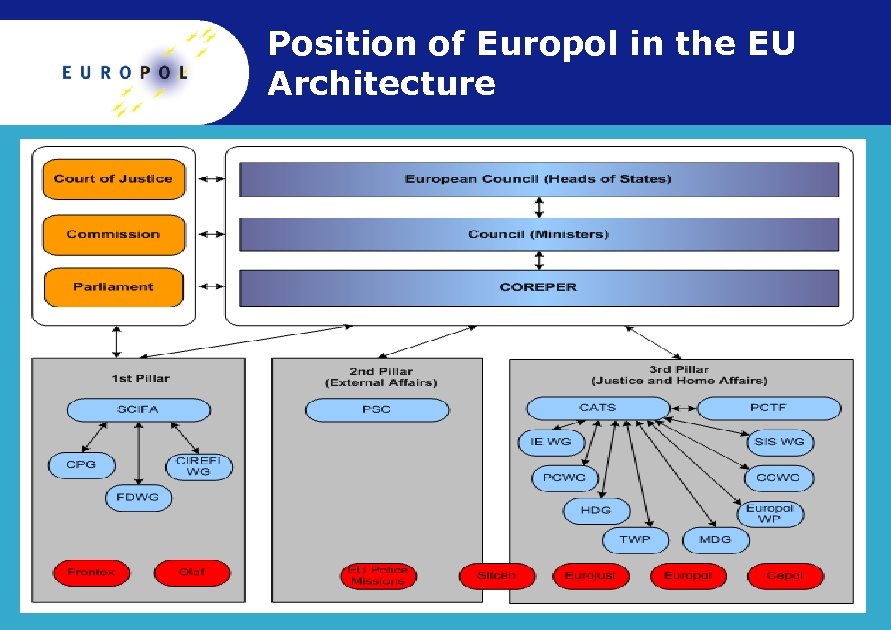 Position of Europol in the EU Architecture
Position of Europol in the EU Architecture
 EU Member States
EU Member States
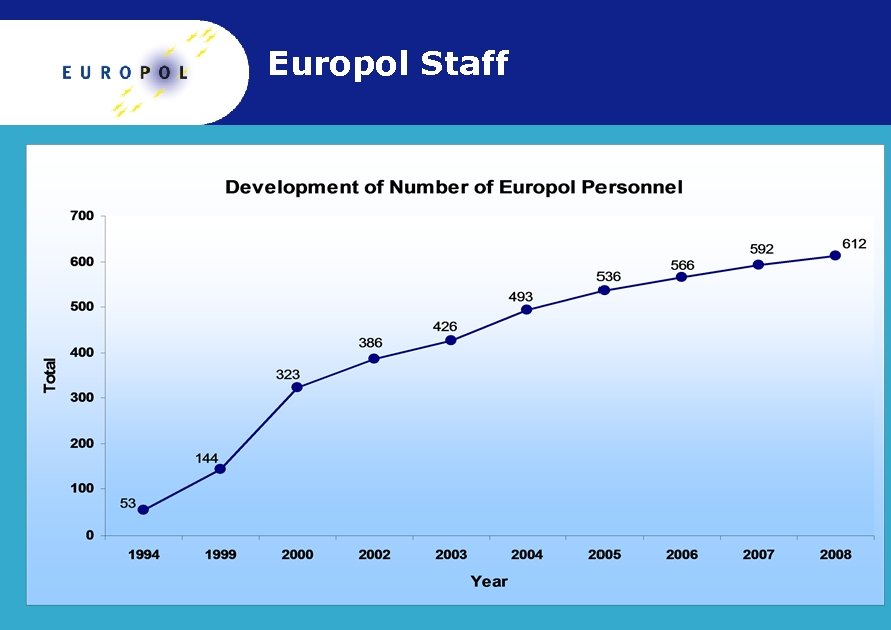 Europol Staff
Europol Staff
 Original Crime Areas
Original Crime Areas
 Since 2002: All crimes in annex to Convention q Crimes against life, limb or personal freedom q Crimes against property or public goods including fraud q Illegal trading and harm to the environment
Since 2002: All crimes in annex to Convention q Crimes against life, limb or personal freedom q Crimes against property or public goods including fraud q Illegal trading and harm to the environment
 Amendments to Europol Convention The Three Protocols: Agreed • 30. 11. 2000: Money Laundering Protocol • 28. 11. 2002: Joint Investigation Teams Protocol • 27. 11. 2003: Danish Protocol In force • 29. 03. 2007: Money Laundering Protocol • 29. 03. 2007: Joint Investigation Teams Protocol • 18. 04. 2007: Danish Protocol
Amendments to Europol Convention The Three Protocols: Agreed • 30. 11. 2000: Money Laundering Protocol • 28. 11. 2002: Joint Investigation Teams Protocol • 27. 11. 2003: Danish Protocol In force • 29. 03. 2007: Money Laundering Protocol • 29. 03. 2007: Joint Investigation Teams Protocol • 18. 04. 2007: Danish Protocol
 Europol Council Decision (ECD) • JHA Council agreed on 12 June 2007: Europol Convention should be replaced by a Council Decision • Increased flexibility since Council Decisions do not have to be ratified on national level • Unanimity on Council level required • Political agreement has been reached in 2008
Europol Council Decision (ECD) • JHA Council agreed on 12 June 2007: Europol Convention should be replaced by a Council Decision • Increased flexibility since Council Decisions do not have to be ratified on national level • Unanimity on Council level required • Political agreement has been reached in 2008
 Content of DCD • Competence of Europol will no longer be limited to organised crime • New systems processing personal data can be established • Europol will be financed from the general budget of the European Union • Institutionalisation of the Data Protection Officer as an independent internal control function
Content of DCD • Competence of Europol will no longer be limited to organised crime • New systems processing personal data can be established • Europol will be financed from the general budget of the European Union • Institutionalisation of the Data Protection Officer as an independent internal control function
 Europol’s Tasks • Exchange of information between Member States • Obtain, collate and analyze information and intelligence • To support national investigations • Computerized system of collected information
Europol’s Tasks • Exchange of information between Member States • Obtain, collate and analyze information and intelligence • To support national investigations • Computerized system of collected information
 Why Data Protection ?
Why Data Protection ?
 Meaning of Data Protection for Europol • Europol as an “Intelligence Broker” • Enhance “intelligence led policing” Exchange of info between MS Europol Information System Analytical Workfiles (AWFs) Further systems processing personal data DP is one important element to be considered when measuring Europol’s operational powers and limits
Meaning of Data Protection for Europol • Europol as an “Intelligence Broker” • Enhance “intelligence led policing” Exchange of info between MS Europol Information System Analytical Workfiles (AWFs) Further systems processing personal data DP is one important element to be considered when measuring Europol’s operational powers and limits
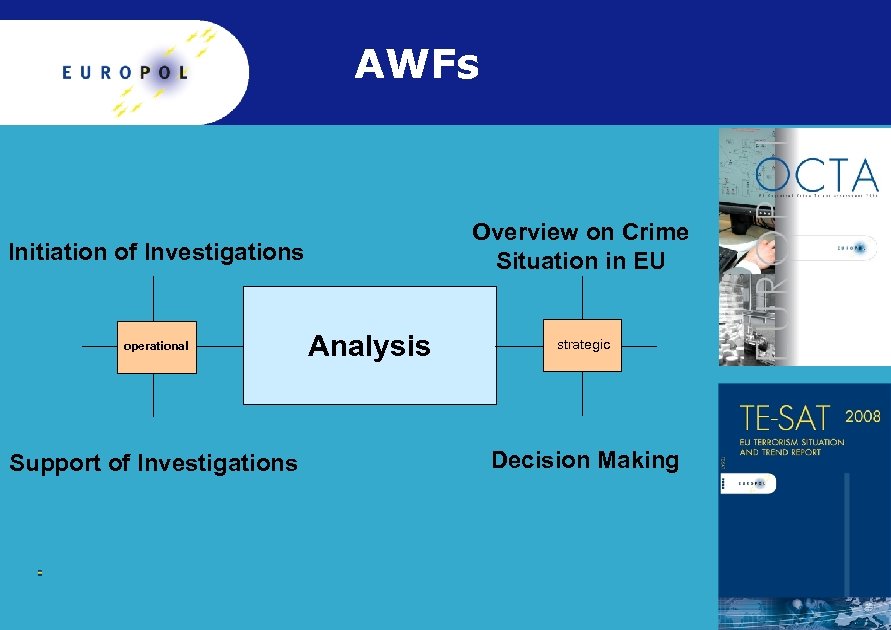 AWFs Overview on Crime Situation in EU Initiation of Investigations operational Support of Investigations Analysis strategic Decision Making
AWFs Overview on Crime Situation in EU Initiation of Investigations operational Support of Investigations Analysis strategic Decision Making
 OCTA • • Clear mandate Qualitative assessment Updated information Multi-agency concept • Holistic approach • Forward-looking
OCTA • • Clear mandate Qualitative assessment Updated information Multi-agency concept • Holistic approach • Forward-looking
 TE-SAT 2008 – main findings • 583 terrorist attacks in EU • Vast majority by separatist groups targeting France and Spain (517) • No successful Islamist terrorist attacks (2 failed and 2 attemped - DE, DK, UK) • 1044 individuals arrested (201 related to Islamist terrorism)
TE-SAT 2008 – main findings • 583 terrorist attacks in EU • Vast majority by separatist groups targeting France and Spain (517) • No successful Islamist terrorist attacks (2 failed and 2 attemped - DE, DK, UK) • 1044 individuals arrested (201 related to Islamist terrorism)
 What is personal data ? • Any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person • An identifiable person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identification number or to one or more factors specific to his physical, physiological, mental, economic, cultural or social identity
What is personal data ? • Any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person • An identifiable person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identification number or to one or more factors specific to his physical, physiological, mental, economic, cultural or social identity
 Processing of personal data • Processing of personal data includes the collection, recording, organisation, storage, adaptation or alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure by transmission, dissemination or otherwise making available, alignment or combination, blocking, erasure or destruction of personal data any operation performed on personal data
Processing of personal data • Processing of personal data includes the collection, recording, organisation, storage, adaptation or alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure by transmission, dissemination or otherwise making available, alignment or combination, blocking, erasure or destruction of personal data any operation performed on personal data
 … which means that Europol in a large number of cases will have to comply with … The 13 DP principles • • • • Lawfulness of Processing Purpose of Transmission Quality of Data Proportionality Time Limits Communication to non-EU states and bodies Sensitive Data Security Transparency Liability Supervisory Authorities Drawing up Reports
… which means that Europol in a large number of cases will have to comply with … The 13 DP principles • • • • Lawfulness of Processing Purpose of Transmission Quality of Data Proportionality Time Limits Communication to non-EU states and bodies Sensitive Data Security Transparency Liability Supervisory Authorities Drawing up Reports
 Data Protection acquis at Europol • The Europol Convention / Council Decision • Implementing Rules, e. g. the Analysis Rules • Council of Europe Convention 108 from 1981 • Council of Europe Recommendation R(87)15 – Use of personal data in the police sector • Regulation (EC) 45/2001 • Framework Decision on Data Protection in 3 rd Pillar?
Data Protection acquis at Europol • The Europol Convention / Council Decision • Implementing Rules, e. g. the Analysis Rules • Council of Europe Convention 108 from 1981 • Council of Europe Recommendation R(87)15 – Use of personal data in the police sector • Regulation (EC) 45/2001 • Framework Decision on Data Protection in 3 rd Pillar?
 WHY ? What is the idea behind those data protection principles ? • Define rights of the data subject • Define obligations on those who process PD • Define obligations on those who exercise control over data processing • Ensure quality, proportionality, liabilities, remedies and sanctions
WHY ? What is the idea behind those data protection principles ? • Define rights of the data subject • Define obligations on those who process PD • Define obligations on those who exercise control over data processing • Ensure quality, proportionality, liabilities, remedies and sanctions
 “Data Protection hinders effective law enforcement” !? • Common prejudice in the law enforcement community
“Data Protection hinders effective law enforcement” !? • Common prejudice in the law enforcement community
 Why we are sitting in one boat… • Data Protection leads to high quality of data • A bad reputation of Europol in terms of data protection might prevent the criminal from being convicted • Cases of imminent criminal danger are subject to exemption rules within the data protection legal framework
Why we are sitting in one boat… • Data Protection leads to high quality of data • A bad reputation of Europol in terms of data protection might prevent the criminal from being convicted • Cases of imminent criminal danger are subject to exemption rules within the data protection legal framework
 …on the other hand: … criminals might occasionally benefit from data protection - that is due to the fact that preventing and combating crime in a democratic society means: Don’t pay any price for achieving these important aims ! Europol’s mission is to enhance an Area of Freedom, Security and Justice
…on the other hand: … criminals might occasionally benefit from data protection - that is due to the fact that preventing and combating crime in a democratic society means: Don’t pay any price for achieving these important aims ! Europol’s mission is to enhance an Area of Freedom, Security and Justice
 Data Protection Regulations in ECD
Data Protection Regulations in ECD
 Most important changes in ECD related to data protection • Art. 9. 3 (d): Bilateral MS exchange outside Europol’s mandate • Art. 10: New Databases processing personal data • Art. 25: Information from private parties and persons including open sources • Art. 28: Institutionalised independent Data Protection Officer • Art. 39. 6: Responsibility for administrative data protection
Most important changes in ECD related to data protection • Art. 9. 3 (d): Bilateral MS exchange outside Europol’s mandate • Art. 10: New Databases processing personal data • Art. 25: Information from private parties and persons including open sources • Art. 28: Institutionalised independent Data Protection Officer • Art. 39. 6: Responsibility for administrative data protection
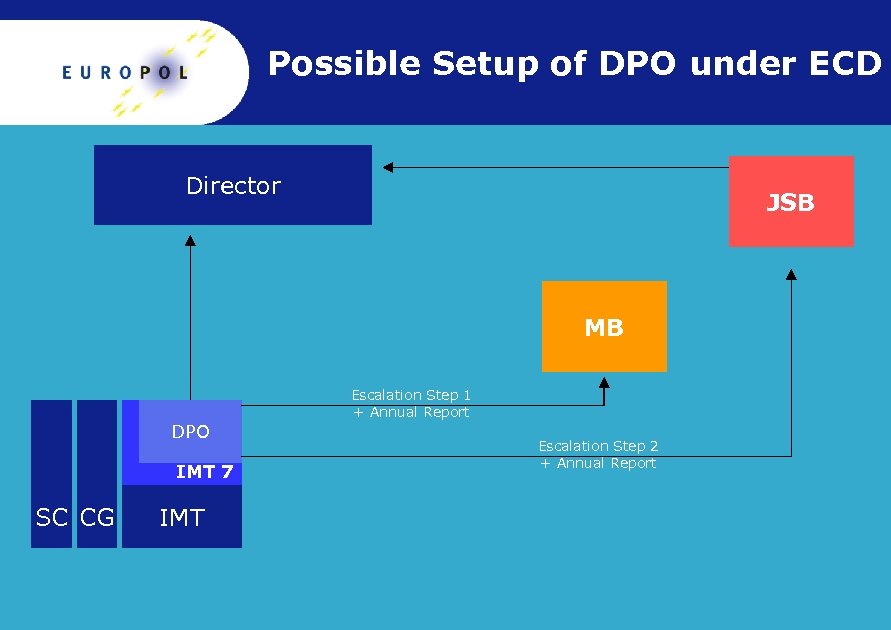 Possible Setup of DPO under ECD Director JSB MB Escalation Step 1 + Annual Report DPO IMT 7 SC CG IMT Escalation Step 2 + Annual Report
Possible Setup of DPO under ECD Director JSB MB Escalation Step 1 + Annual Report DPO IMT 7 SC CG IMT Escalation Step 2 + Annual Report
 Relations with third States & third bodies
Relations with third States & third bodies
 Co-operation with third States & third bodies • Regulated in Art. 22 ff. ECD and implementing rules • General rule: Exchange on the basis of an agreement • Exchange possible without an agreement in limited cases only on the basis of decision by Europol Director (essential interests, preventing imminent criminal danger – data protection level needs to be considered)
Co-operation with third States & third bodies • Regulated in Art. 22 ff. ECD and implementing rules • General rule: Exchange on the basis of an agreement • Exchange possible without an agreement in limited cases only on the basis of decision by Europol Director (essential interests, preventing imminent criminal danger – data protection level needs to be considered)
 Europol - beyond the European Union • Operational agreements − Australia, Canada, Croatia, Iceland, Norway, Switzerland, USA − Eurojust, Interpol • Strategic agreements − Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Colombia, FYROM, Moldova, Montenegro, Russian Federation, Serbia, Turkey − CEPOL, Commission, ECB, EMCDDA, FRONTEX, OLAF, WCO, UNODC, Sit. Cen • Agreements in development − China, Israel, Morocco, Ukraine
Europol - beyond the European Union • Operational agreements − Australia, Canada, Croatia, Iceland, Norway, Switzerland, USA − Eurojust, Interpol • Strategic agreements − Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Colombia, FYROM, Moldova, Montenegro, Russian Federation, Serbia, Turkey − CEPOL, Commission, ECB, EMCDDA, FRONTEX, OLAF, WCO, UNODC, Sit. Cen • Agreements in development − China, Israel, Morocco, Ukraine
 Data Subject’s Rights
Data Subject’s Rights
 Right of Access • Data subject has a right to be informed of all data relating to him/her that is processed at Europol on request • Such access shall only be refused to the extent that this is necessary to enable Europol to fulfil its tasks properly, to protect security and public order in the Member States or to prevent crime, to guarantee that national investigations will not be jeopardised and to protect the rights and freedoms of third parties • Request to be made in MS of choice
Right of Access • Data subject has a right to be informed of all data relating to him/her that is processed at Europol on request • Such access shall only be refused to the extent that this is necessary to enable Europol to fulfil its tasks properly, to protect security and public order in the Member States or to prevent crime, to guarantee that national investigations will not be jeopardised and to protect the rights and freedoms of third parties • Request to be made in MS of choice
 Right of Correction & Deletion • Data subject has a right to correction or deletion of personal data relating to him or her where it is shown to be inaccurate.
Right of Correction & Deletion • Data subject has a right to correction or deletion of personal data relating to him or her where it is shown to be inaccurate.
 Right of Compensation • An individual has a right to obtain compensation for damages suffered as a consequence of incorrect data processing. The Member State where the damage occurred is liable for such damages; however, where such damage is caused by Europol, Europol must reimburse the Member State
Right of Compensation • An individual has a right to obtain compensation for damages suffered as a consequence of incorrect data processing. The Member State where the damage occurred is liable for such damages; however, where such damage is caused by Europol, Europol must reimburse the Member State
 Data Protection Supervision
Data Protection Supervision
 Joint Supervisory Body • Independent Control Body supervising processing of personal data by or through Europol • Right of inspecting all Europol files at any time • Appeals committee as regards right of access, correction and deletion
Joint Supervisory Body • Independent Control Body supervising processing of personal data by or through Europol • Right of inspecting all Europol files at any time • Appeals committee as regards right of access, correction and deletion
 National Supervisory Bodies • Monitor independently, in accordance with national law, communication of personal data to and from Europol • Access at national unit and at liaison offices on Europol premises • Data subject has a right to request national supervisory body to ensure that input or communication of personal data to Europol are lawful
National Supervisory Bodies • Monitor independently, in accordance with national law, communication of personal data to and from Europol • Access at national unit and at liaison offices on Europol premises • Data subject has a right to request national supervisory body to ensure that input or communication of personal data to Europol are lawful
 “Europol has recognised the importance of data protection not just as a necessary element of meeting its human rights obligations but also a means of providing reassurance to contributing Member States. ” Mr. David Smith, Chairman of the JSB 28 th January 2008
“Europol has recognised the importance of data protection not just as a necessary element of meeting its human rights obligations but also a means of providing reassurance to contributing Member States. ” Mr. David Smith, Chairman of the JSB 28 th January 2008
 Questions ? Thank you for your attention !
Questions ? Thank you for your attention !


