81eb51a100f785fe359f62ad8e446105.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
Data Modelling in ASAM ODS Presentation by Helmut J. Helpenstein, June 2005 1
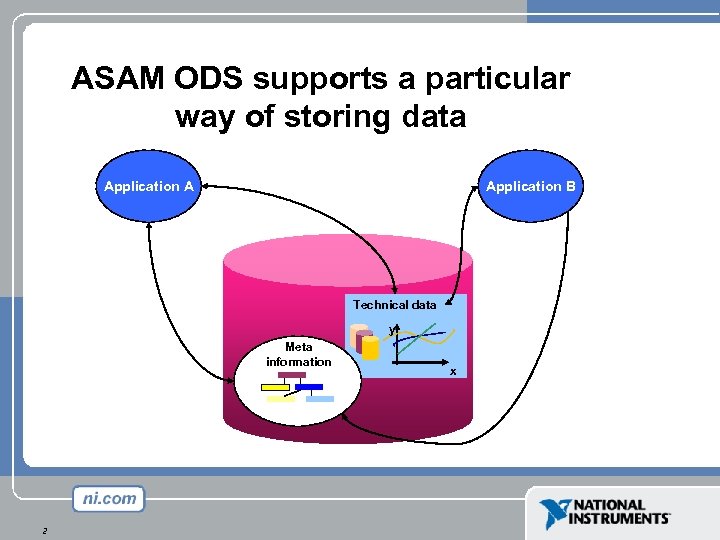
ASAM ODS supports a particular way of storing data Application A Application B Technical data y Meta information 2 x
Goals of ODS way • Combination of data and meta data • Meta data according to a Base Model The Base Model • defines common attributes and relationships for all test and measurement data • defines rules and methods how to derive customized (application specific) data models from the ASAM ODS Base Model 3
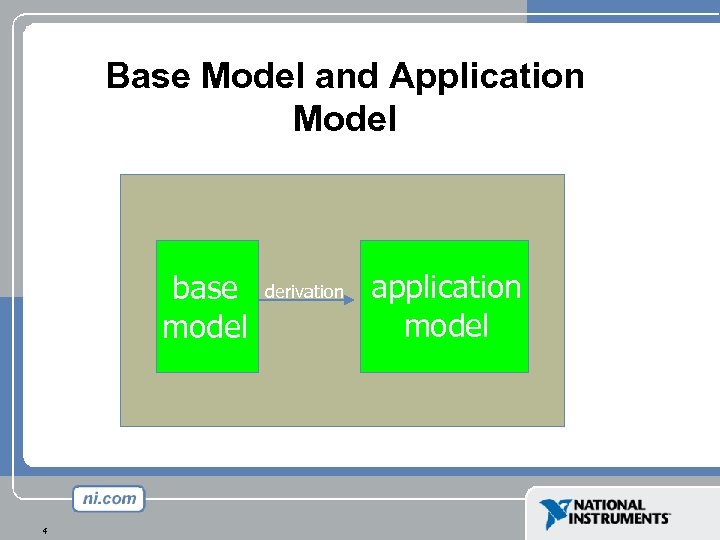
Base Model and Application Model base model 4 derivation application model
Application Model It has several tasks: • support the application • express any wanted details in a recognizable way • enable clients to understand semantics For each purpose the application model should use those constructs that are provided in the base model for that purpose. Base model influences application model. Application model influences data. 5
Application Model and Data application model 6 instantiation data
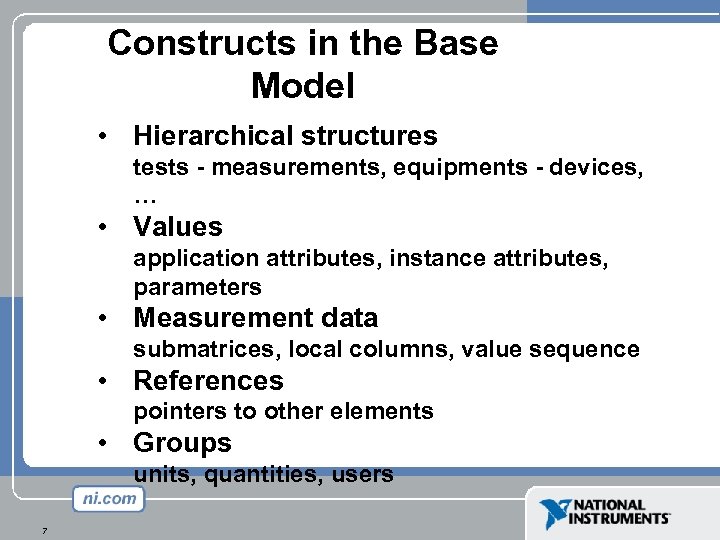
Constructs in the Base Model • Hierarchical structures tests - measurements, equipments - devices, … • Values application attributes, instance attributes, parameters • Measurement data submatrices, local columns, value sequence • References pointers to other elements • Groups units, quantities, users 7
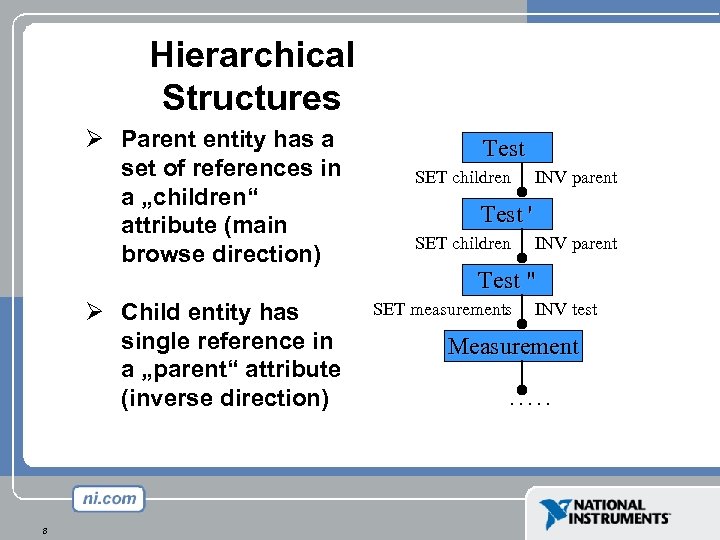
Hierarchical Structures Ø Parent entity has a set of references in a „children“ attribute (main browse direction) Ø Child entity has single reference in a „parent“ attribute (inverse direction) 8 Test SET children INV parent Test ' SET children INV parent Test " SET measurements INV test Measurement. . .
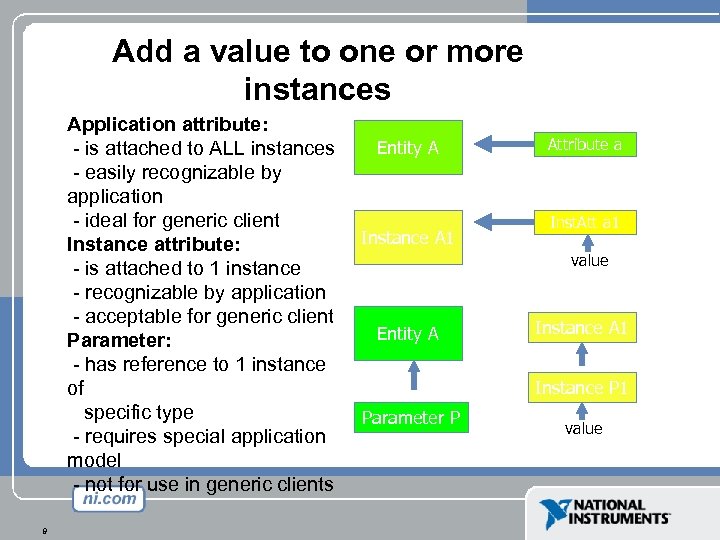
Add a value to one or more instances Application attribute: - is attached to ALL instances - easily recognizable by application - ideal for generic client Instance attribute: - is attached to 1 instance - recognizable by application - acceptable for generic client Parameter: - has reference to 1 instance of specific type - requires special application model - not for use in generic clients 9 Entity A Instance A 1 Attribute a Inst. Att a 1 value Entity A Instance A 1 Instance P 1 Parameter P value
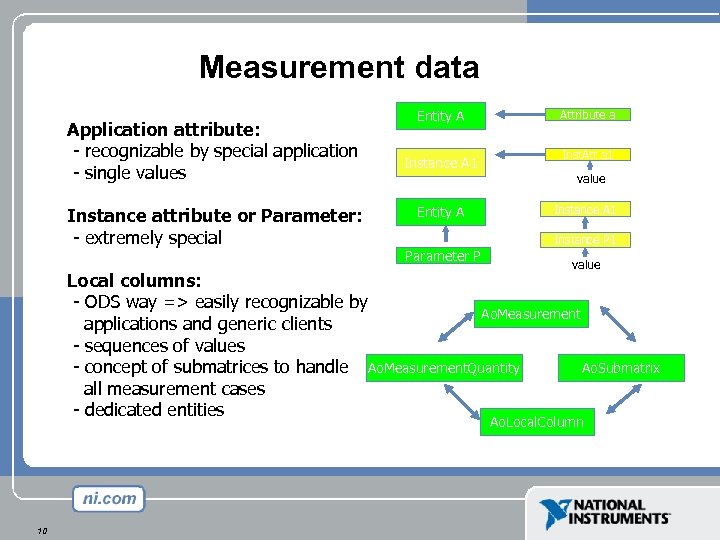
Measurement data Application attribute: - recognizable by special application - single values Instance attribute or Parameter: - extremely special Entity A Instance A 1 Entity A Parameter P Attribute a Inst. Att a 1 value Instance A 1 Instance P 1 value Local columns: - ODS way => easily recognizable by Ao. Measurement applications and generic clients - sequences of values - concept of submatrices to handle Ao. Measurement. Quantity Ao. Submatrix all measurement cases - dedicated entities Ao. Local. Column 10
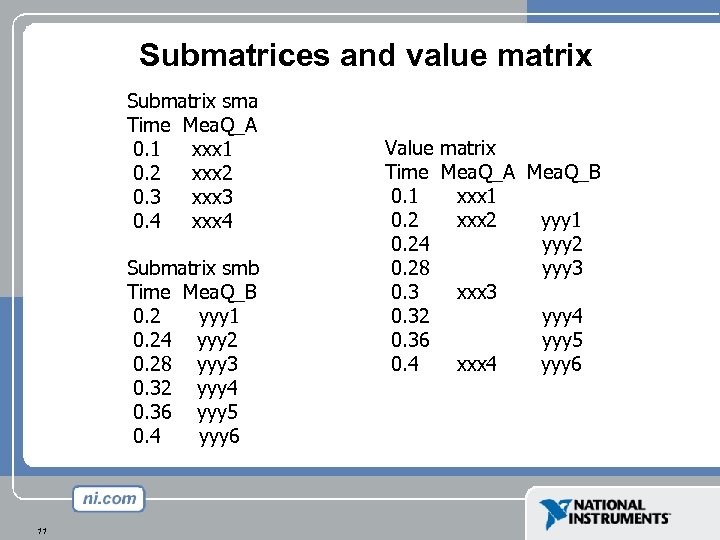
Submatrices and value matrix Submatrix sma Time Mea. Q_A 0. 1 xxx 1 0. 2 xxx 2 0. 3 xxx 3 0. 4 xxx 4 Submatrix smb Time Mea. Q_B 0. 2 yyy 1 0. 24 yyy 2 0. 28 yyy 3 0. 32 yyy 4 0. 36 yyy 5 0. 4 yyy 6 11 Value matrix Time Mea. Q_A Mea. Q_B 0. 1 xxx 1 0. 2 xxx 2 yyy 1 0. 24 yyy 2 0. 28 yyy 3 0. 3 xxx 3 0. 32 yyy 4 0. 36 yyy 5 0. 4 xxx 4 yyy 6
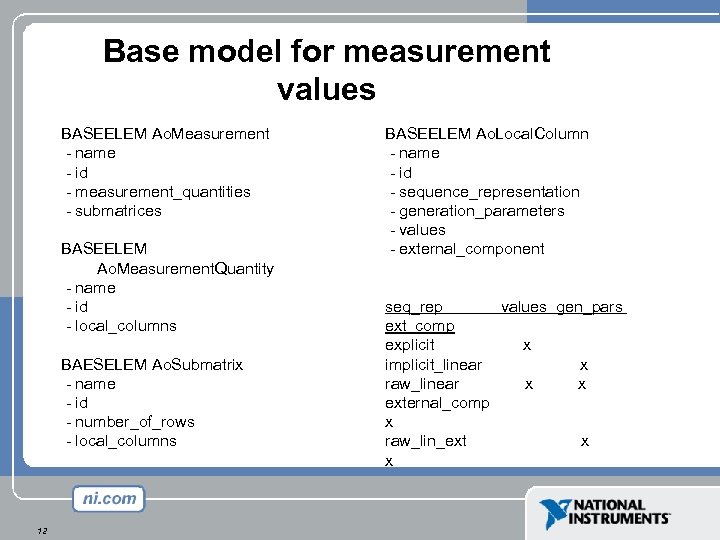
Base model for measurement values BASEELEM Ao. Measurement - name - id - measurement_quantities - submatrices BASEELEM Ao. Measurement. Quantity - name - id - local_columns BAESELEM Ao. Submatrix - name - id - number_of_rows - local_columns 12 BASEELEM Ao. Local. Column - name - id - sequence_representation - generation_parameters - values - external_component seq_rep values gen_pars ext_comp explicit x implicit_linear x raw_linear x x external_comp x raw_lin_ext x x
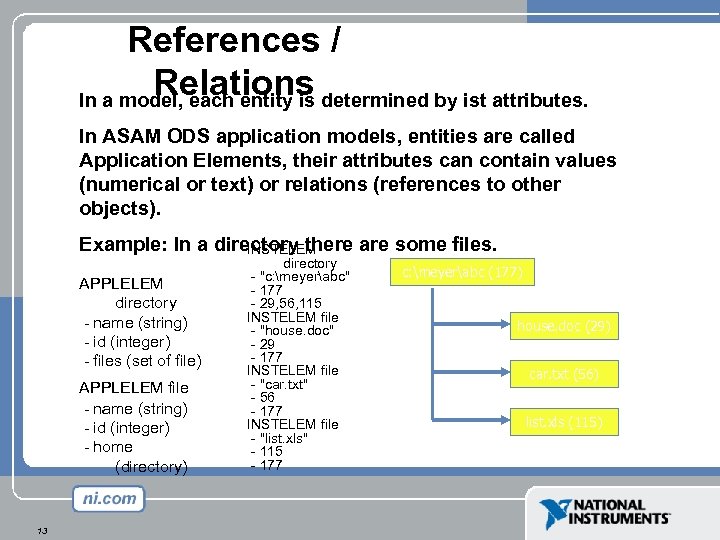
References / Relations In a model, each entity is determined by ist attributes. In ASAM ODS application models, entities are called Application Elements, their attributes can contain values (numerical or text) or relations (references to other objects). Example: In a directory there are some files. INSTELEM APPLELEM directory - name (string) - id (integer) - files (set of file) APPLELEM file - name (string) - id (integer) - home (directory) 13 directory - "c: meyerabc" - 177 - 29, 56, 115 INSTELEM file - "house. doc" - 29 - 177 INSTELEM file - "car. txt" - 56 - 177 INSTELEM file - "list. xls" - 115 - 177 c: meyerabc (177) house. doc (29) car. txt (56) list. xls (115)
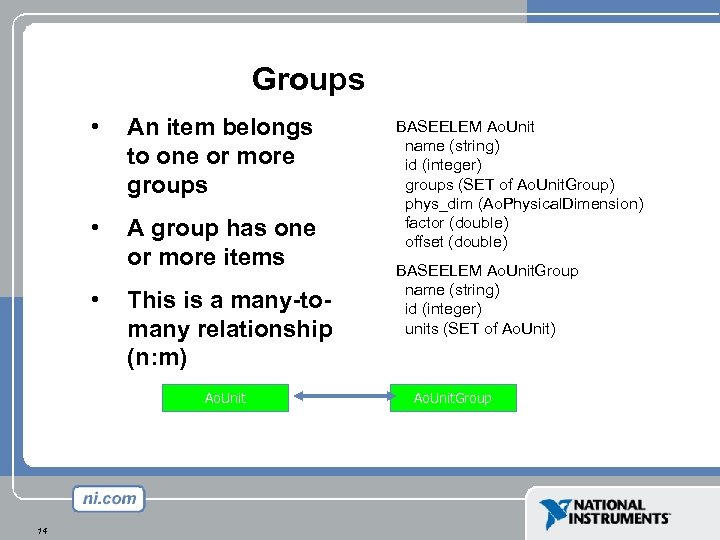
Groups • An item belongs to one or more groups • A group has one or more items • This is a many-tomany relationship (n: m) Ao. Unit 14 BASEELEM Ao. Unit name (string) id (integer) groups (SET of Ao. Unit. Group) phys_dim (Ao. Physical. Dimension) factor (double) offset (double) BASEELEM Ao. Unit. Group name (string) id (integer) units (SET of Ao. Unit) Ao. Unit. Group
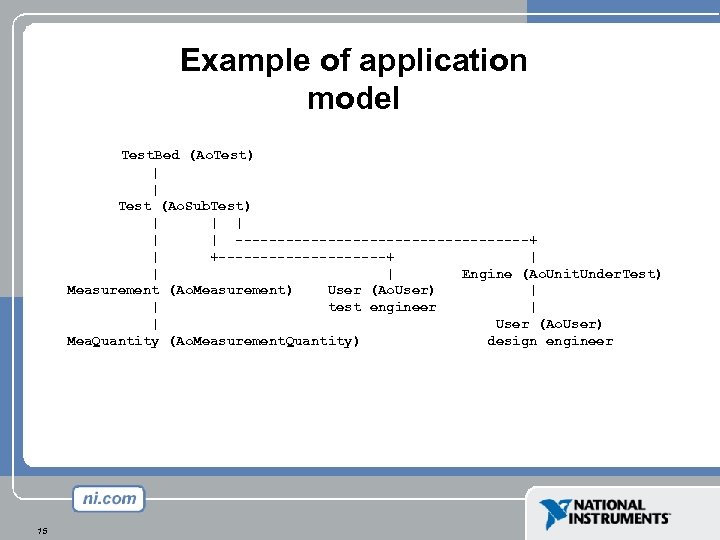
Example of application model Test. Bed (Ao. Test) | | Test (Ao. Sub. Test) | | | ------------------+ | +----------+ | | | Engine (Ao. Unit. Under. Test) Measurement (Ao. Measurement) User (Ao. User) | | test engineer | | User (Ao. User) Mea. Quantity (Ao. Measurement. Quantity) design engineer 15
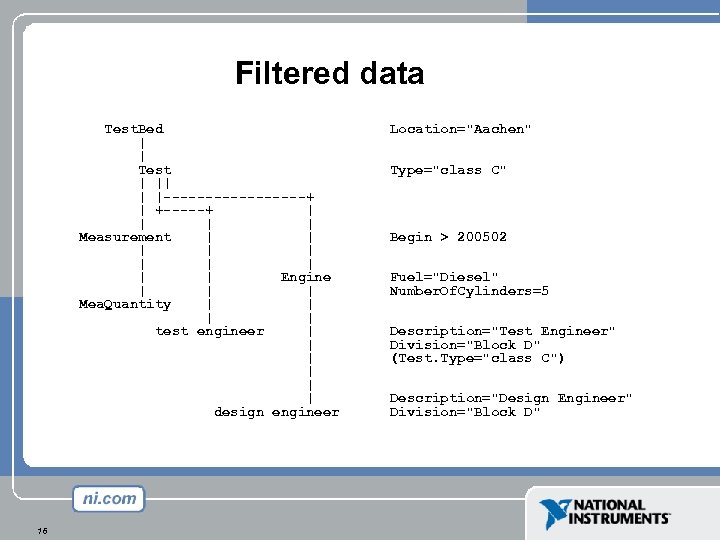
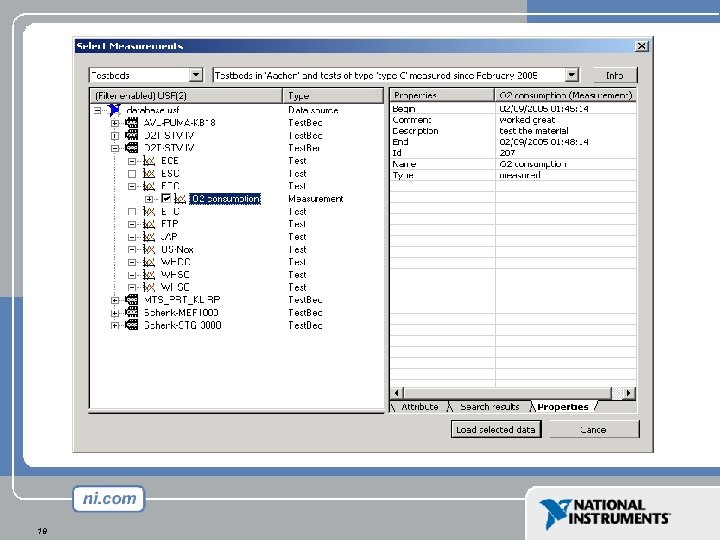
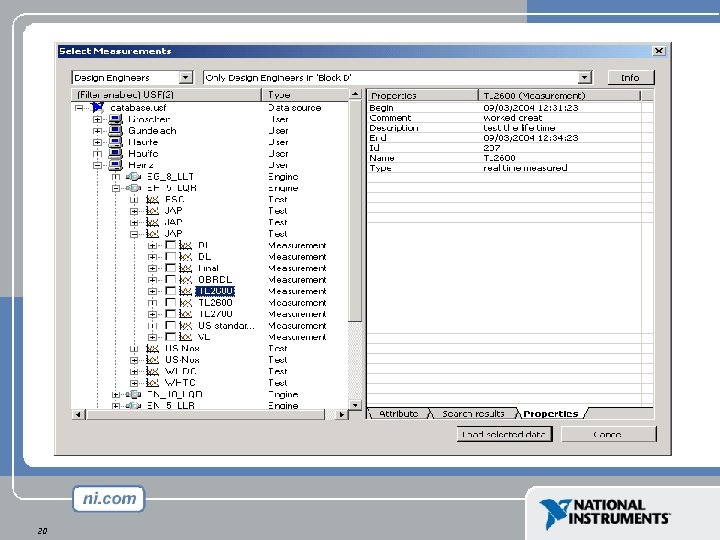
Filtered data Test. Bed | | Test | || | |---------+ | +-----+ | | Measurement | | | | | Engine | | | Mea. Quantity | | test engineer | | | design engineer 16 Location="Aachen" Type="class C" Begin > 200502 Fuel="Diesel" Number. Of. Cylinders=5 Description="Test Engineer" Division="Block D" (Test. Type="class C") Description="Design Engineer" Division="Block D"
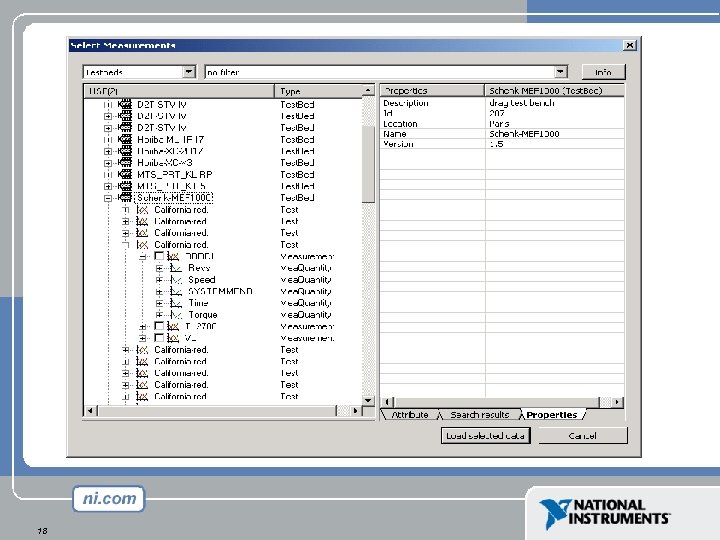
• • • 17 Select Measurements in DIAdem Precondition: Modelling according to ODS way Size of example data: 45 MB many Test. Beds, each with many Tests Measurements can be imported with their Measurement. Quantities We want to find data in a limited set, described by filtering with conditions enabled by modelling in ODS way Measurement. Quantities can be displayed Screenshots display the filtering process
18
19
20
21

Thank you for your attention. 22
81eb51a100f785fe359f62ad8e446105.ppt