786eb90ee1722ed25f4fc512b98a36b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Data Mining Process, Key Success Factors, Illustrations
Data Mining Process, Key Success Factors, Illustrations
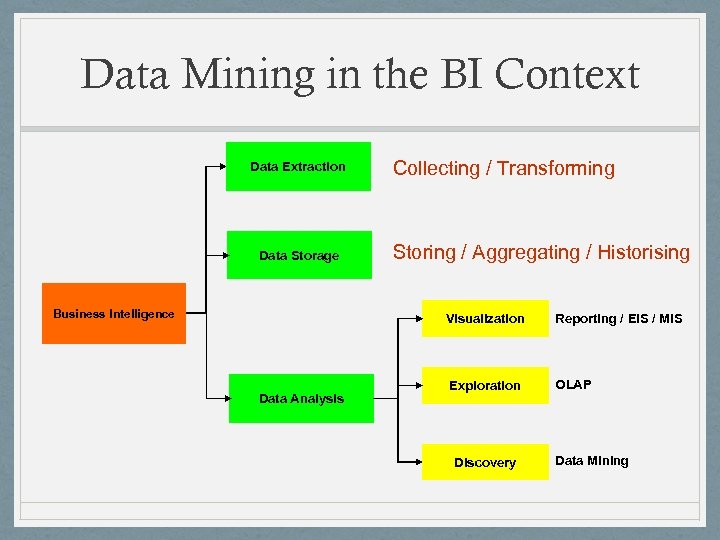 Data Mining in the BI Context Data Extraction Data Storage Business Intelligence Collecting / Transforming Storing / Aggregating / Historising Visualization Data Analysis Reporting / EIS / MIS Exploration OLAP Discovery Data Mining
Data Mining in the BI Context Data Extraction Data Storage Business Intelligence Collecting / Transforming Storing / Aggregating / Historising Visualization Data Analysis Reporting / EIS / MIS Exploration OLAP Discovery Data Mining
 What Is Data Mining? Business Definition • Deployment of business processes, supported by adequate analytical techniques, to: • Take further advantage of data • Discover relevant knowledge • Act on the results
What Is Data Mining? Business Definition • Deployment of business processes, supported by adequate analytical techniques, to: • Take further advantage of data • Discover relevant knowledge • Act on the results
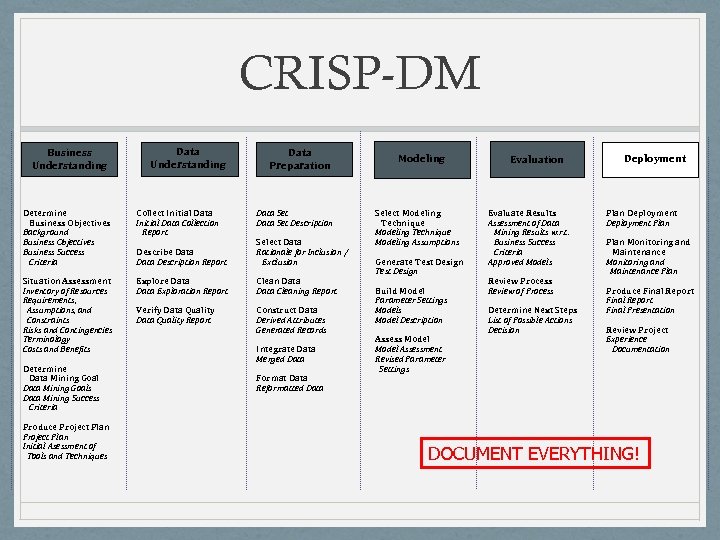 CRISP-DM Business Understanding Data Preparation Determine Business Objectives Background Business Objectives Business Success Criteria Collect Initial Data Collection Report Describe Data Description Report Select Data Rationale for Inclusion / Exclusion Situation Assessment Inventory of Resources Requirements, Assumptions, and Constraints Risks and Contingencies Terminology Costs and Benefits Explore Data Exploration Report Clean Data Cleaning Report Verify Data Quality Report Construct Data Derived Attributes Generated Records Determine Data Mining Goals Data Mining Success Criteria Produce Project Plan Initial Asessment of Tools and Techniques Data Set Description Integrate Data Merged Data Format Data Reformatted Data Modeling Select Modeling Technique Modeling Assumptions Generate Test Design Build Model Parameter Settings Model Description Assess Model Assessment Revised Parameter Settings Evaluation Evaluate Results Assessment of Data Mining Results w. r. t. Business Success Criteria Approved Models Review Process Review of Process Determine Next Steps List of Possible Actions Decision Deployment Plan Monitoring and Maintenance Plan Produce Final Report Final Presentation Review Project Experience Documentation DOCUMENT EVERYTHING!
CRISP-DM Business Understanding Data Preparation Determine Business Objectives Background Business Objectives Business Success Criteria Collect Initial Data Collection Report Describe Data Description Report Select Data Rationale for Inclusion / Exclusion Situation Assessment Inventory of Resources Requirements, Assumptions, and Constraints Risks and Contingencies Terminology Costs and Benefits Explore Data Exploration Report Clean Data Cleaning Report Verify Data Quality Report Construct Data Derived Attributes Generated Records Determine Data Mining Goals Data Mining Success Criteria Produce Project Plan Initial Asessment of Tools and Techniques Data Set Description Integrate Data Merged Data Format Data Reformatted Data Modeling Select Modeling Technique Modeling Assumptions Generate Test Design Build Model Parameter Settings Model Description Assess Model Assessment Revised Parameter Settings Evaluation Evaluate Results Assessment of Data Mining Results w. r. t. Business Success Criteria Approved Models Review Process Review of Process Determine Next Steps List of Possible Actions Decision Deployment Plan Monitoring and Maintenance Plan Produce Final Report Final Presentation Review Project Experience Documentation DOCUMENT EVERYTHING!
 Data Mining Tasks • Summarization • Classification / Prediction • Classification, Concept learning, Regression • Clustering • Dependency modeling • Anomaly detection • Link Analysis
Data Mining Tasks • Summarization • Classification / Prediction • Classification, Concept learning, Regression • Clustering • Dependency modeling • Anomaly detection • Link Analysis
 Human Resources
Human Resources
 Survey and Online Game
Survey and Online Game
 Do They Know Us?
Do They Know Us?
 Who Plays?
Who Plays?
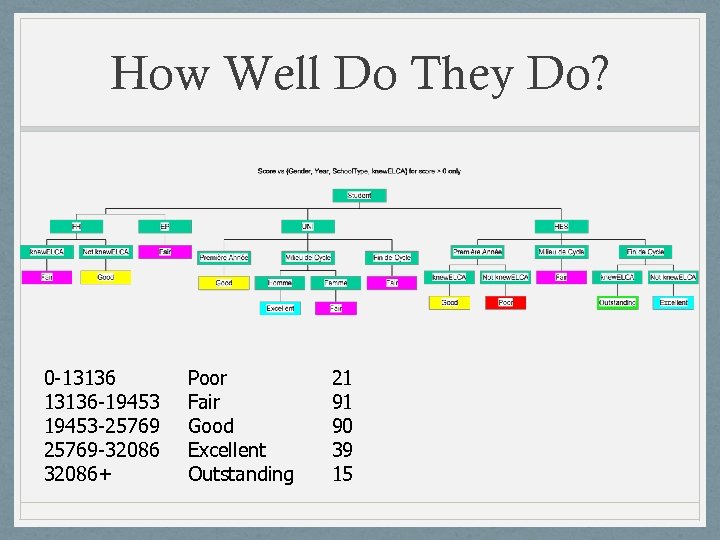 How Well Do They Do? 0 -13136 -19453 -25769 -32086+ Poor Fair Good Excellent Outstanding 21 91 90 39 15
How Well Do They Do? 0 -13136 -19453 -25769 -32086+ Poor Fair Good Excellent Outstanding 21 91 90 39 15
 Subscription Retail
Subscription Retail
 Situation & Goal • Poor understanding of customers and behaviors • Short audit: • Nice DWH, only 2 years old, not fully populated • Limited data on purchases and subscriptions • Potential goals: • Associations of products that sell together • Segmentation of customers
Situation & Goal • Poor understanding of customers and behaviors • Short audit: • Nice DWH, only 2 years old, not fully populated • Limited data on purchases and subscriptions • Potential goals: • Associations of products that sell together • Segmentation of customers
 Summarization / Aggregation • Revenue distribution • 80% generated by 41. 5% of subscribers • 60% generated by 18. 3% of subscribers • 42. 9% generated by top 5 products • Simple customer classes • Over 65 years old most profitable • Under 16 years old least profitable • Birthdate filled-in for only about 10% of subscribers!
Summarization / Aggregation • Revenue distribution • 80% generated by 41. 5% of subscribers • 60% generated by 18. 3% of subscribers • 42. 9% generated by top 5 products • Simple customer classes • Over 65 years old most profitable • Under 16 years old least profitable • Birthdate filled-in for only about 10% of subscribers!
 Product Association • About 21% of subscribers buy P 4, P 7 and P 9 • P 4 is most profitable product • P 7 is ranked 6 th • P 9 is ranked 15 th with only 2% of revenue • Several possible actions • Make a bundle offering of these products • Cross-sell from P 9 to P 4 • Temptation to remove P 9 should be resisted
Product Association • About 21% of subscribers buy P 4, P 7 and P 9 • P 4 is most profitable product • P 7 is ranked 6 th • P 9 is ranked 15 th with only 2% of revenue • Several possible actions • Make a bundle offering of these products • Cross-sell from P 9 to P 4 • Temptation to remove P 9 should be resisted
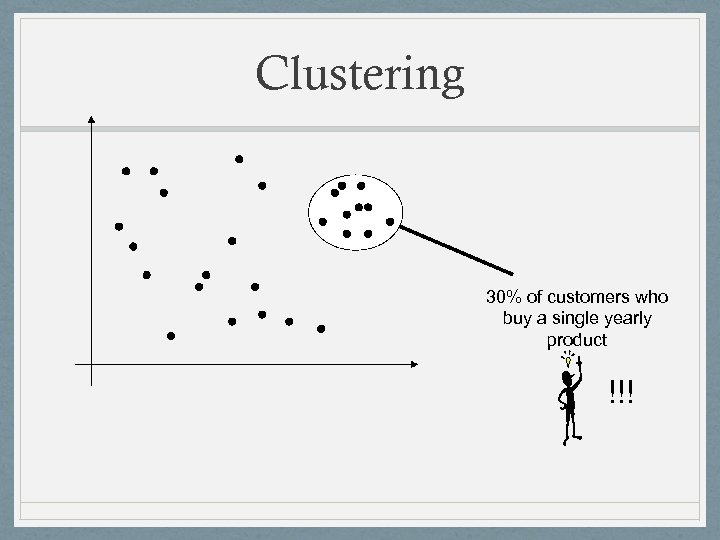 Clustering 30% of customers who buy a single yearly product !!!
Clustering 30% of customers who buy a single yearly product !!!
 Summary of Findings • Data Mining found: • A small percentage of the customers is responsible for a large share of the sales • Several groups of « strongly-connected » articles • A sizeable group of subscribers who buy a single article • Lessons learned: • First 2 findings: « we knew that! » (BUT: scientific confirmation of business observation) • 3 rd finding: « we could target these customers with a special offer! » • Lack of relevant data: the structure is in place but not being used systematically
Summary of Findings • Data Mining found: • A small percentage of the customers is responsible for a large share of the sales • Several groups of « strongly-connected » articles • A sizeable group of subscribers who buy a single article • Lessons learned: • First 2 findings: « we knew that! » (BUT: scientific confirmation of business observation) • 3 rd finding: « we could target these customers with a special offer! » • Lack of relevant data: the structure is in place but not being used systematically
 Campaign Management
Campaign Management
 Situation & Goal
Situation & Goal
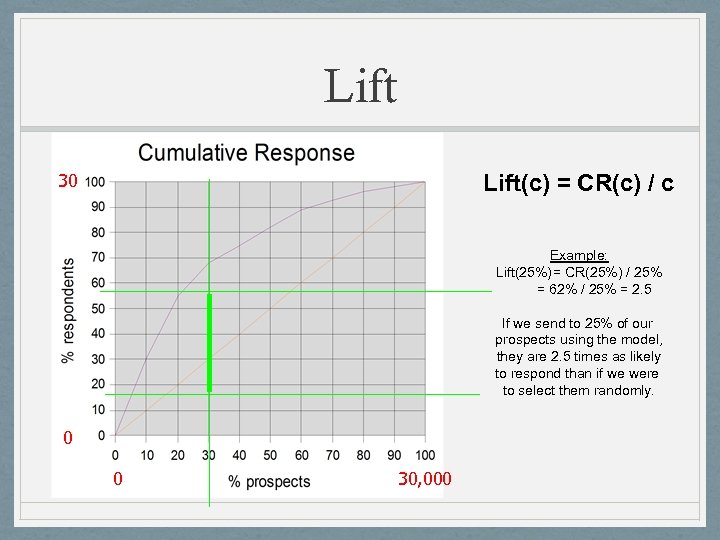 Lift 30 Lift(c) = CR(c) / c Example: Lift(25%)= CR(25%) / 25% = 62% / 25% = 2. 5 If we send to 25% of our prospects using the model, they are 2. 5 times as likely to respond than if we were to select them randomly. 0 0 30, 000
Lift 30 Lift(c) = CR(c) / c Example: Lift(25%)= CR(25%) / 25% = 62% / 25% = 2. 5 If we send to 25% of our prospects using the model, they are 2. 5 times as likely to respond than if we were to select them randomly. 0 0 30, 000
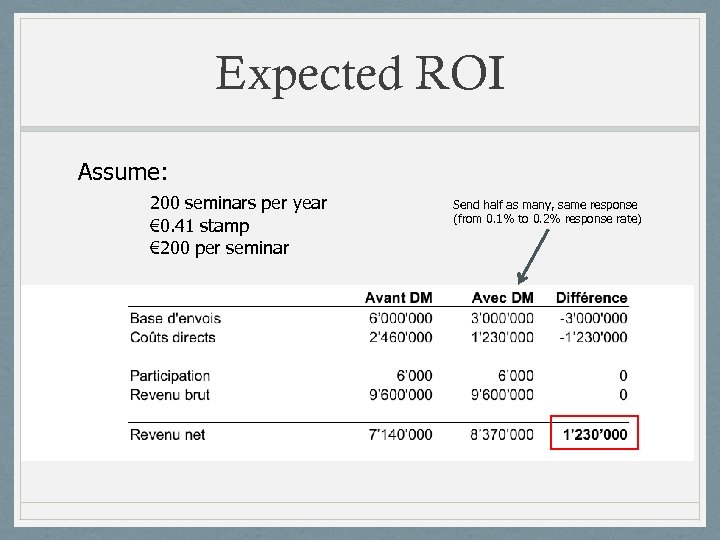 Expected ROI Assume: 200 seminars per year € 0. 41 stamp € 200 per seminar Send half as many, same response (from 0. 1% to 0. 2% response rate)
Expected ROI Assume: 200 seminars per year € 0. 41 stamp € 200 per seminar Send half as many, same response (from 0. 1% to 0. 2% response rate)
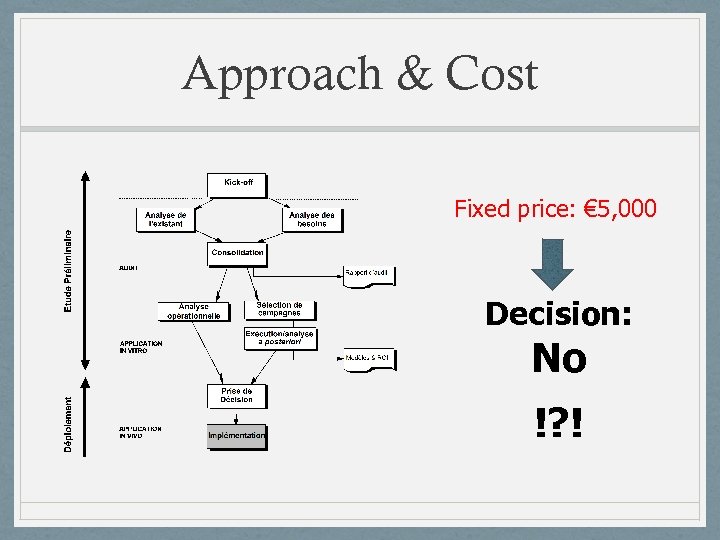 Approach & Cost Fixed price: € 5, 000 Decision: No !? !
Approach & Cost Fixed price: € 5, 000 Decision: No !? !
 Laws of Data Mining
Laws of Data Mining
 Eight Laws (I) • Business/domain objectives are the origin of every data mining solution • Business/domain knowledge is central to every step of the data mining process • Data preparation is more than half of every data mining process • The right model for a given application can only be discovered by experiment
Eight Laws (I) • Business/domain objectives are the origin of every data mining solution • Business/domain knowledge is central to every step of the data mining process • Data preparation is more than half of every data mining process • The right model for a given application can only be discovered by experiment
 Eight Laws (II) • There always patterns • Data mining amplifies perception in the domain • The value of data mining results is not determined by the accuracy or stability of predictive models • All patterns are subject to change
Eight Laws (II) • There always patterns • Data mining amplifies perception in the domain • The value of data mining results is not determined by the accuracy or stability of predictive models • All patterns are subject to change
 The Right Expectation • Data Mining is unlikely to produce surprising results that will utterly transform a business. Rather: • Early results: insights about data and scientific confirmation of human experience/intuition • Beyond: steady improvement to an already successful organization • Occasionally: discovery of one rare/highly valuable piece of knowledge
The Right Expectation • Data Mining is unlikely to produce surprising results that will utterly transform a business. Rather: • Early results: insights about data and scientific confirmation of human experience/intuition • Beyond: steady improvement to an already successful organization • Occasionally: discovery of one rare/highly valuable piece of knowledge
 The Right Organization • Data Mining is not sophisticated enough to be substituted for domain knowledge or for experience in analysis and model building. • Rather: • Data Mining is a joint venture • “… put teams together that have a variety of skills (e. g. , statistics, business and IT skills), are creative and are close to the business thinking. ”
The Right Organization • Data Mining is not sophisticated enough to be substituted for domain knowledge or for experience in analysis and model building. • Rather: • Data Mining is a joint venture • “… put teams together that have a variety of skills (e. g. , statistics, business and IT skills), are creative and are close to the business thinking. ”
 Key Success Factors • Have a clearly articulated business problem that needs to be solved and for which Data Mining is the adequate technology • Ensure that the problem being pursued is supported by the right type of data of sufficient quality and in sufficient quantity • Recognize that Data Mining is a process with many components and dependencies • Plan to learn from the Data Mining process whatever the outcome
Key Success Factors • Have a clearly articulated business problem that needs to be solved and for which Data Mining is the adequate technology • Ensure that the problem being pursued is supported by the right type of data of sufficient quality and in sufficient quantity • Recognize that Data Mining is a process with many components and dependencies • Plan to learn from the Data Mining process whatever the outcome
 Essential Tips
Essential Tips
 Tips (I) • Don’t wait to get started – the competition is only a mouse click away • Begin with the end in mind • It’s the decision maker, stupid! • Unless there’s a method, there’s madness • Better data means better results
Tips (I) • Don’t wait to get started – the competition is only a mouse click away • Begin with the end in mind • It’s the decision maker, stupid! • Unless there’s a method, there’s madness • Better data means better results
 Tips (II) • Twyman’s law: any statistic that appears interesting is almost certainly a mistake (double-check all findings) • Avoid the OLAP trap • Deployment is the key to data mining ROI • Champions train so they can win the race
Tips (II) • Twyman’s law: any statistic that appears interesting is almost certainly a mistake (double-check all findings) • Avoid the OLAP trap • Deployment is the key to data mining ROI • Champions train so they can win the race
 Crawl, Walk, Run • Exploratory Workshop / Brainstorm • Identify potential profitable applications • Data Audit • Assess data quality and relevance • Identify shortcomings • Suggest ways to enrich data (internal and external) • Domain-relevant Case Studies (start small) • Refine list of applications to produce well-defined, actionable, domain-relevant case studies • Select 1 or more case studies as « pilots » • Scale-up
Crawl, Walk, Run • Exploratory Workshop / Brainstorm • Identify potential profitable applications • Data Audit • Assess data quality and relevance • Identify shortcomings • Suggest ways to enrich data (internal and external) • Domain-relevant Case Studies (start small) • Refine list of applications to produce well-defined, actionable, domain-relevant case studies • Select 1 or more case studies as « pilots » • Scale-up


