ac96d209f046dd2fad31f0cfab8c8d63.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Data Mining and Virtual Observatory Yanxia Zhang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS DEC. 2 2004 1

Outline v Why v What v How 2

Astronomy is Facing a Major “Data Major Facing a Avalanche”: Data Avalanche Multi-Terabyte Sky Surveys and Archives (Soon: Multi-Petabyte), Billions of Detected Sources, Hundreds of Measured Attributes per Source … 3

Necessity Is the Mother of Invention Understanding of Complex Astrophysical Phenomena Requires Complex and Information-Rich Data Sets, and the Tools to Explore them … … This Will Lead to a Change in the nature of the Astronomical Discovery Process … … Which Requires A New Research Environment for Astronomy: VO 4
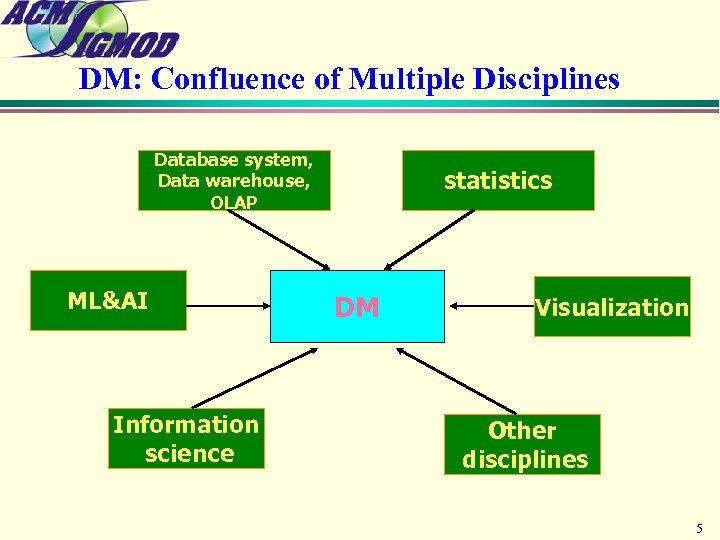
DM: Confluence of Multiple Disciplines Database system, Data warehouse, OLAP ML&AI Information science statistics DM Visualization Other disciplines 5

What is DM? The search for interesting patterns, in large databases, that were collected for other applications, using machine learning algorithms, high-performance computers and others methods for science and society! 6
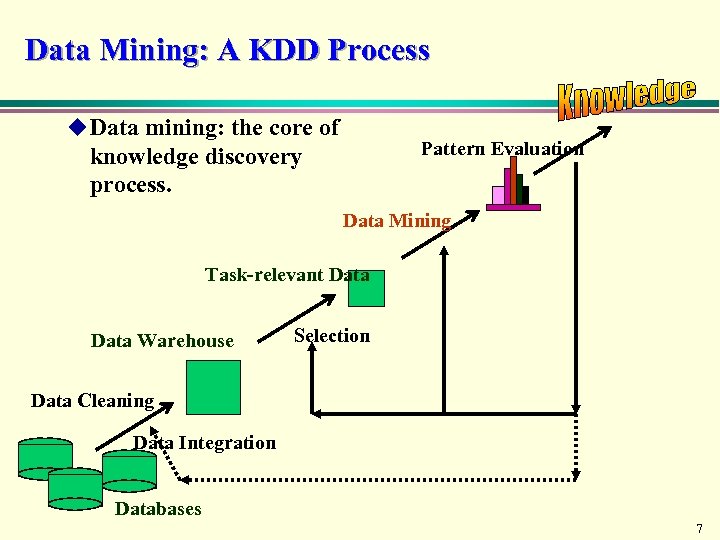
Data Mining: A KDD Process u Data mining: the core of Pattern Evaluation knowledge discovery process. Data Mining Task-relevant Data Warehouse Selection Data Cleaning Data Integration Databases 7
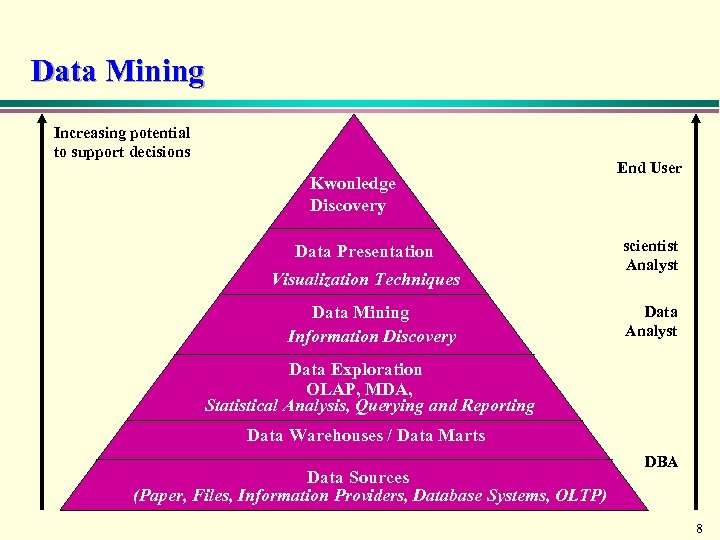
Data Mining Increasing potential to support decisions Kwonledge Discovery Data Presentation Visualization Techniques Data Mining Information Discovery End User scientist Analyst Data Exploration OLAP, MDA, Statistical Analysis, Querying and Reporting Data Warehouses / Data Marts Data Sources (Paper, Files, Information Providers, Database Systems, OLTP) DBA 8
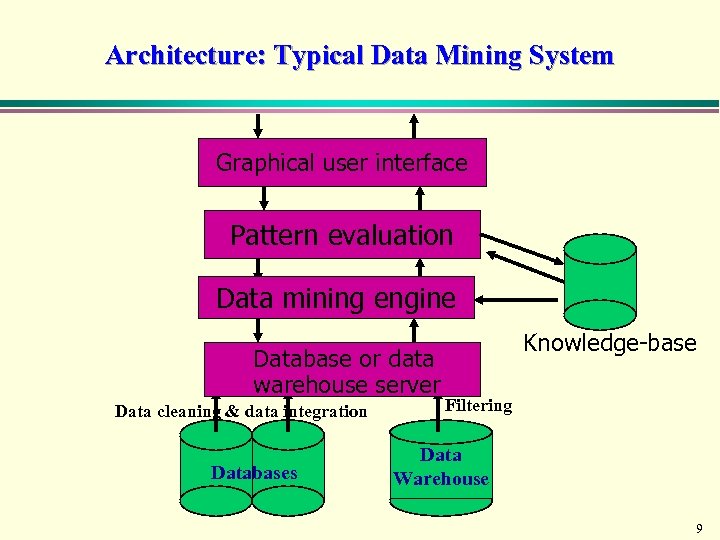
Architecture: Typical Data Mining System Graphical user interface Pattern evaluation Data mining engine Database or data warehouse server Data cleaning & data integration Databases Knowledge-base Filtering Data Warehouse 9
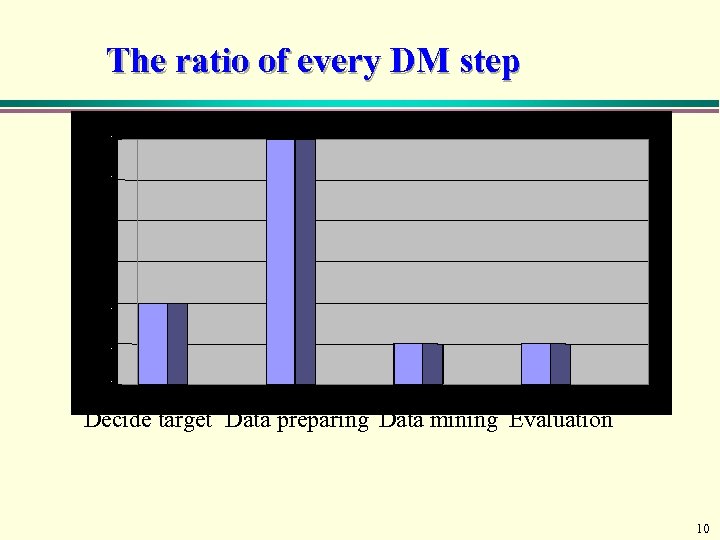
The ratio of every DM step Decide target Data preparing Data mining Evaluation 10

DM: On What Kind of Data? v Relational databases v Data warehouses v Transactional databases v Advanced DB systems and information repositories u Object-oriented and object-relational databases u Spatial databases u Time-series data and temporal data u Text databases and multimedia databases u Heterogeneous and legacy databases u WWW 11
Data Mining Functionality v Concept description v Association v Classification and Prediction v Clustering v Time-series analysis v Other pattern-directed or statistical analysis 12
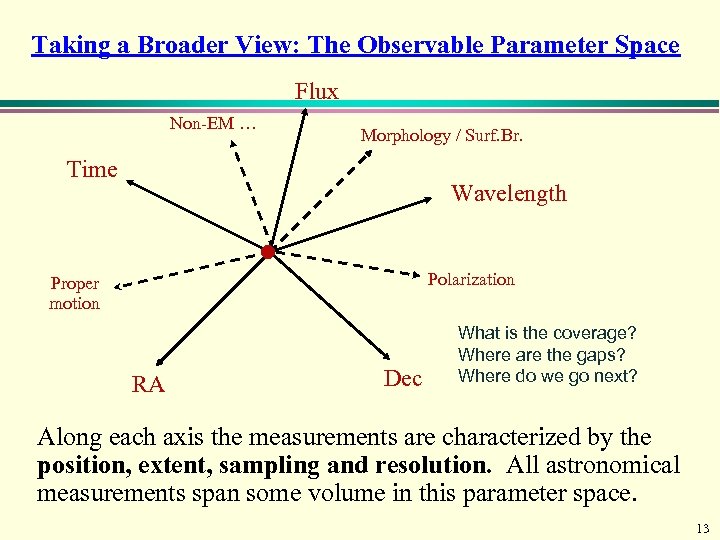
Taking a Broader View: The Observable Parameter Space Flux Non-EM … Morphology / Surf. Br. Time Wavelength Polarization Proper motion RA Dec What is the coverage? Where are the gaps? Where do we go next? Along each axis the measurements are characterized by the position, extent, sampling and resolution. All astronomical measurements span some volume in this parameter space. 13
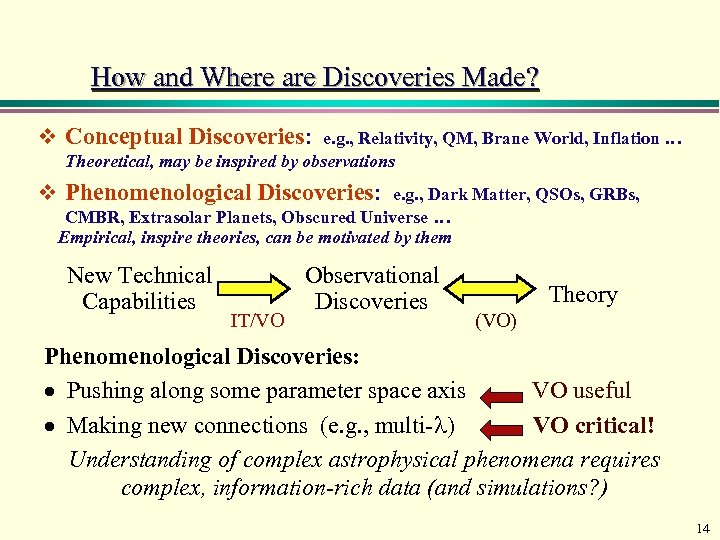
How and Where are Discoveries Made? v Conceptual Discoveries: e. g. , Relativity, QM, Brane World, Inflation … Theoretical, may be inspired by observations v Phenomenological Discoveries: e. g. , Dark Matter, QSOs, GRBs, CMBR, Extrasolar Planets, Obscured Universe … Empirical, inspire theories, can be motivated by them New Technical Capabilities IT/VO Observational Discoveries Theory (VO) Phenomenological Discoveries: Pushing along some parameter space axis VO useful Making new connections (e. g. , multi- ) VO critical! Understanding of complex astrophysical phenomena requires complex, information-rich data (and simulations? ) 14
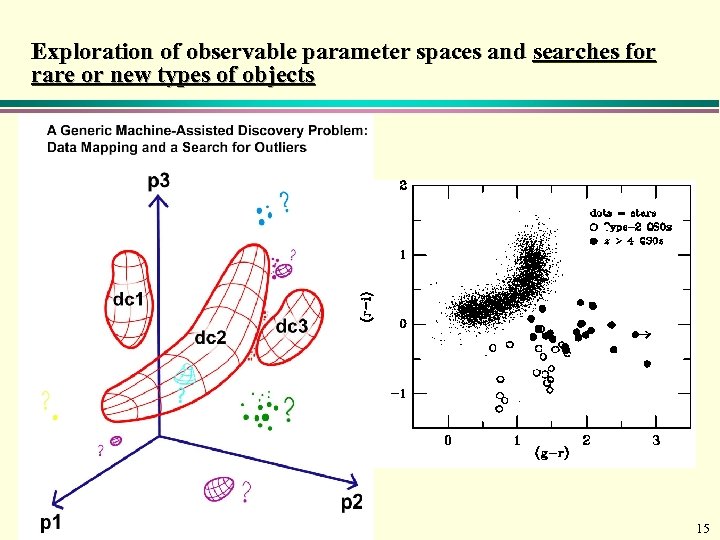
Exploration of observable parameter spaces and searches for rare or new types of objects 15
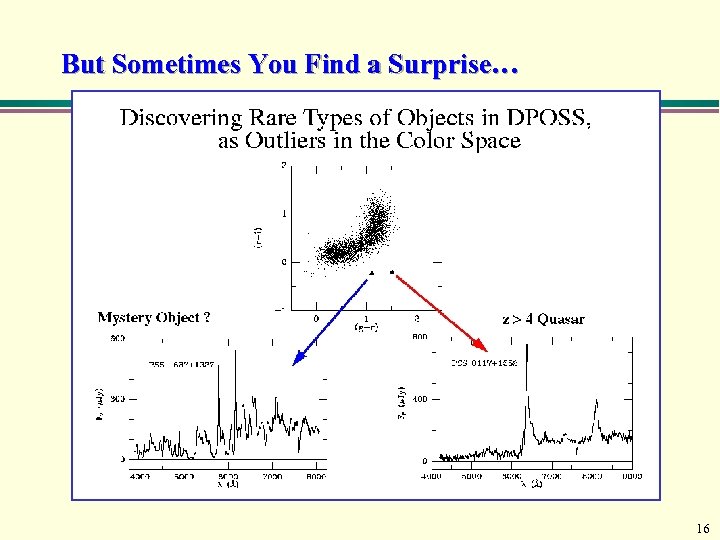
But Sometimes You Find a Surprise… 16
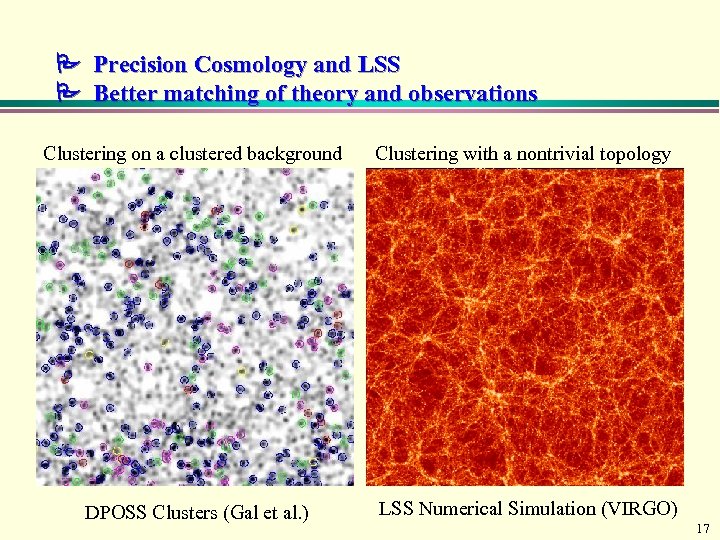
Precision Cosmology and LSS Better matching of theory and observations Clustering on a clustered background Clustering with a nontrivial topology DPOSS Clusters (Gal et al. ) LSS Numerical Simulation (VIRGO) 17
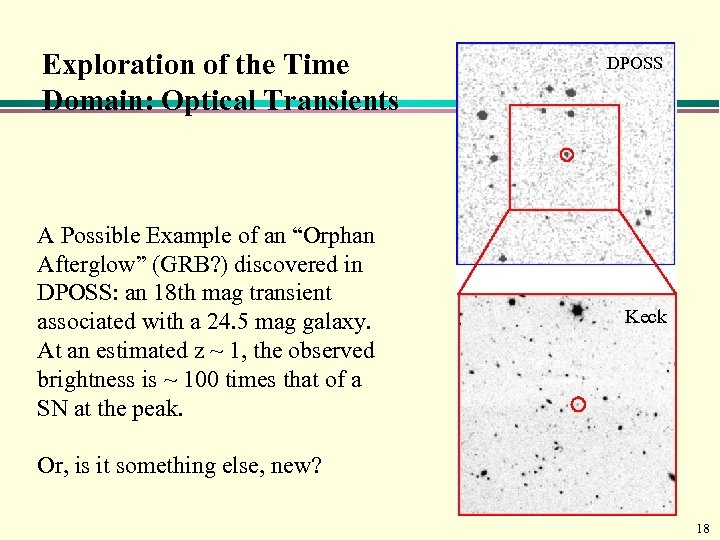
Exploration of the Time Domain: Optical Transients A Possible Example of an “Orphan Afterglow” (GRB? ) discovered in DPOSS: an 18 th mag transient associated with a 24. 5 mag galaxy. At an estimated z ~ 1, the observed brightness is ~ 100 times that of a SN at the peak. DPOSS Keck Or, is it something else, new? 18

Exploration of the Time Domain: Faint, Fast Transients (Tyson et al. ) 19
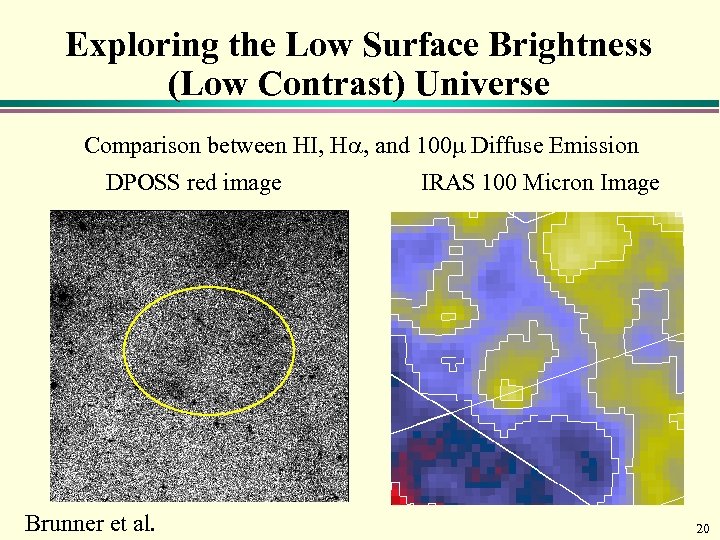
Exploring the Low Surface Brightness (Low Contrast) Universe Comparison between HI, Ha, and 100 m Diffuse Emission DPOSS red image Brunner et al. IRAS 100 Micron Image 20
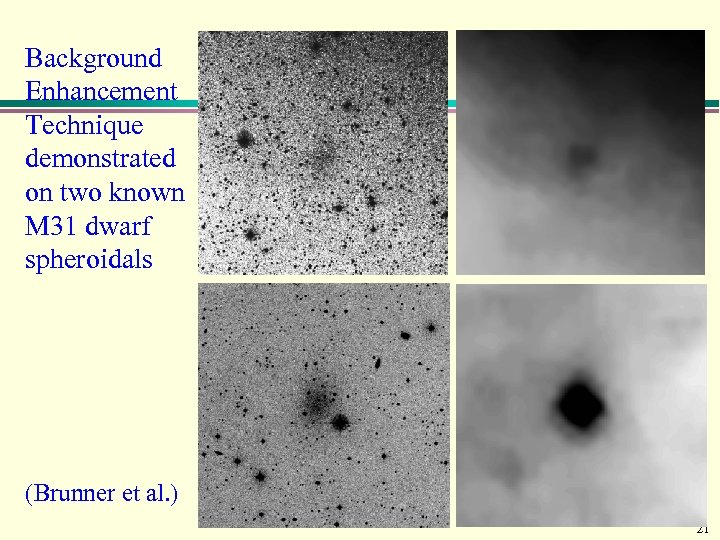
Background Enhancement Technique demonstrated on two known M 31 dwarf spheroidals (Brunner et al. ) 21

Data Mining in the Image Domain: Can We Discover New Types of Phenomena Using Automated Pattern Recognition? (Every object detection algorithm has its biases and limitations) 22
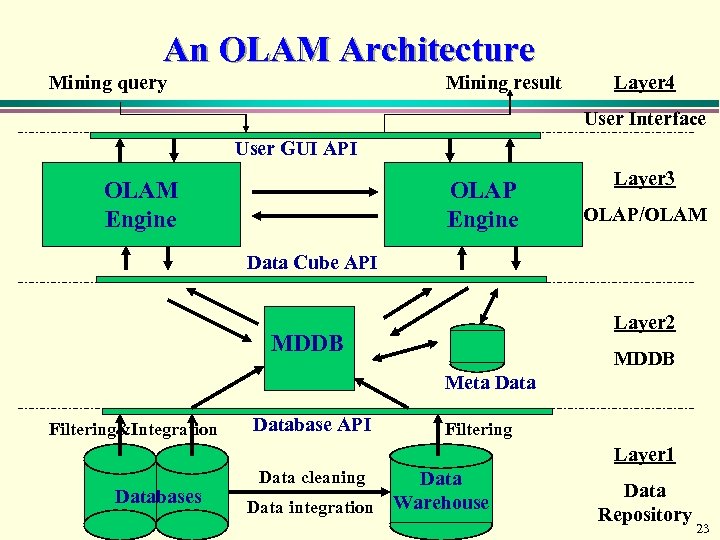
An OLAM Architecture Mining query Mining result Layer 4 User Interface User GUI API OLAM Engine OLAP Engine Layer 3 OLAP/OLAM Data Cube API Layer 2 MDDB Meta Data Filtering&Integration Database API Filtering Layer 1 Databases Data cleaning Data integration Warehouse Data Repository 23
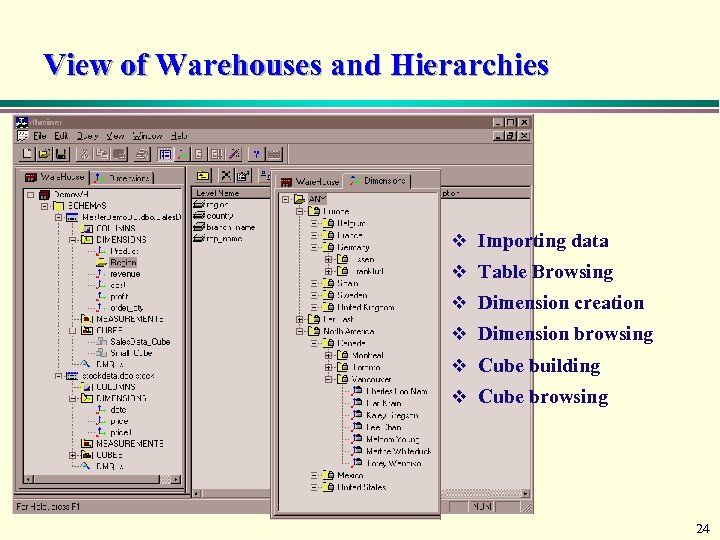
View of Warehouses and Hierarchies v Importing data v Table Browsing v Dimension creation v Dimension browsing v Cube building v Cube browsing 24
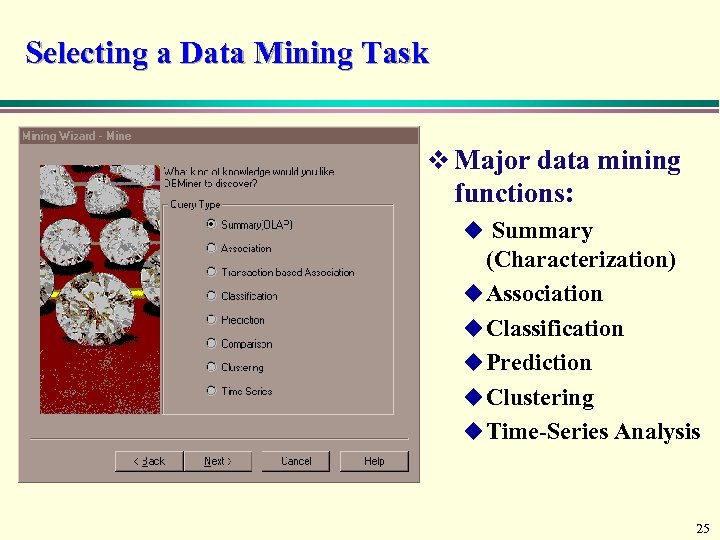
Selecting a Data Mining Task v Major data mining functions: u Summary (Characterization) u Association u Classification u Prediction u Clustering u Time-Series Analysis 25
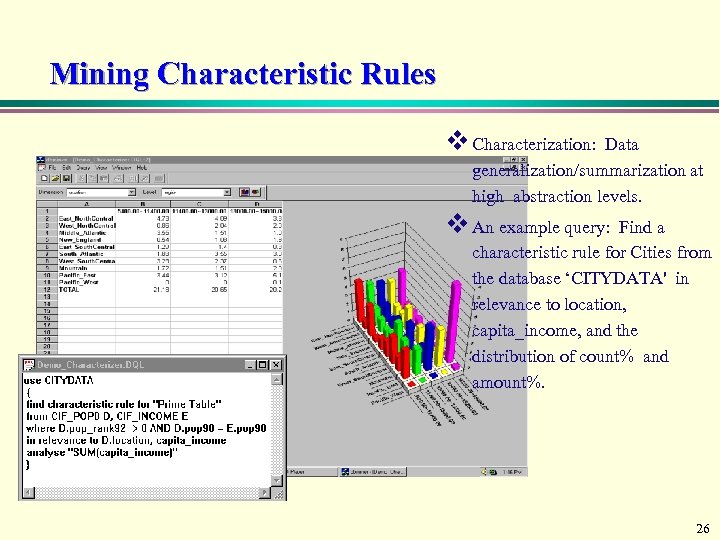
Mining Characteristic Rules v Characterization: Data generalization/summarization at high abstraction levels. v An example query: Find a characteristic rule for Cities from the database ‘CITYDATA' in relevance to location, capita_income, and the distribution of count% and amount%. 26
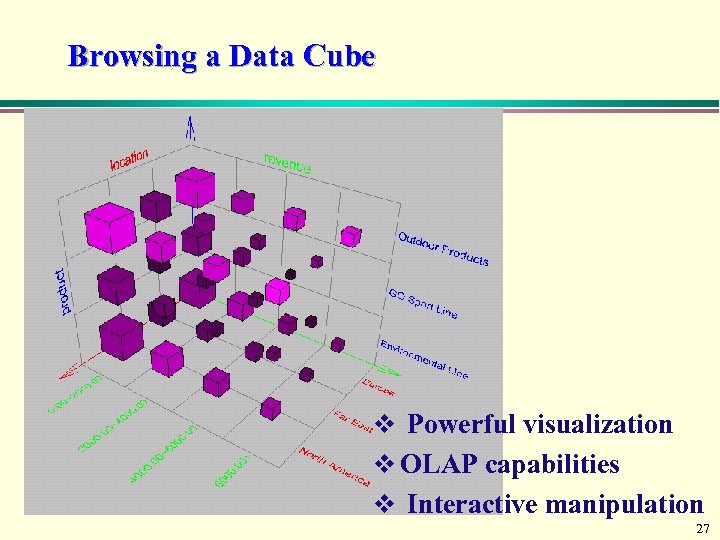
Browsing a Data Cube v Powerful visualization v OLAP capabilities v Interactive manipulation 27
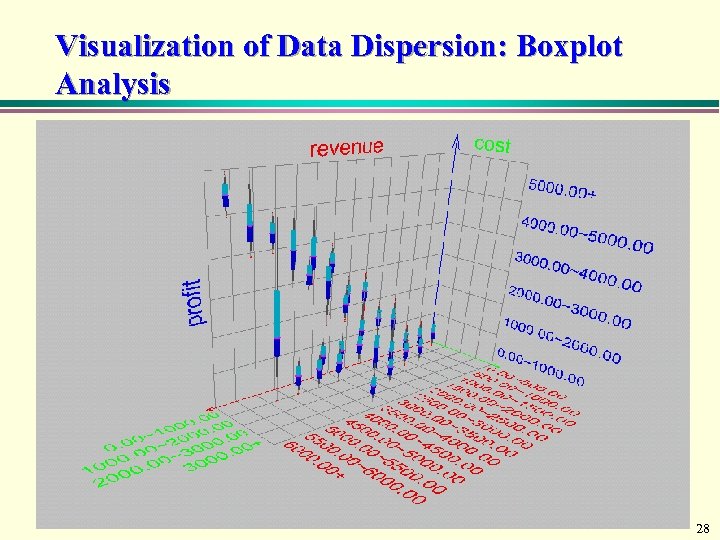
Visualization of Data Dispersion: Boxplot Analysis 28
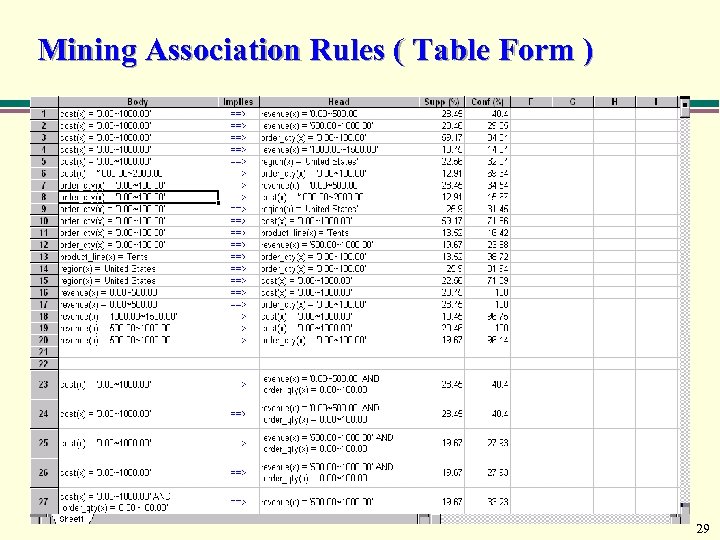
Mining Association Rules ( Table Form ) 29
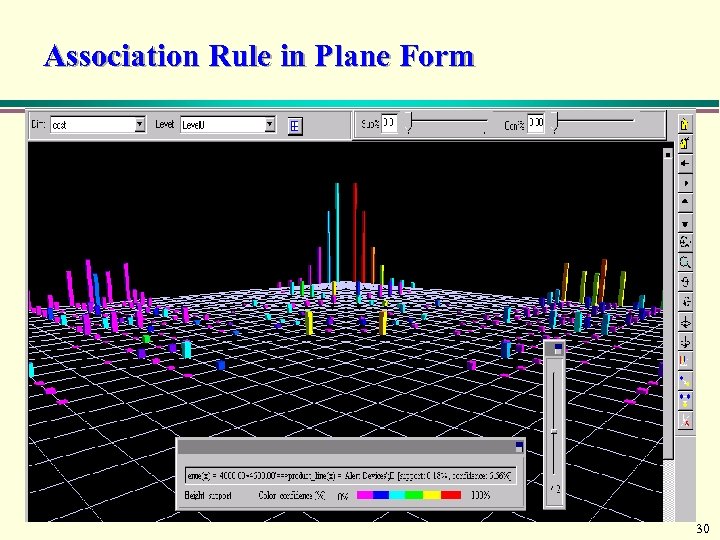
Association Rule in Plane Form 30
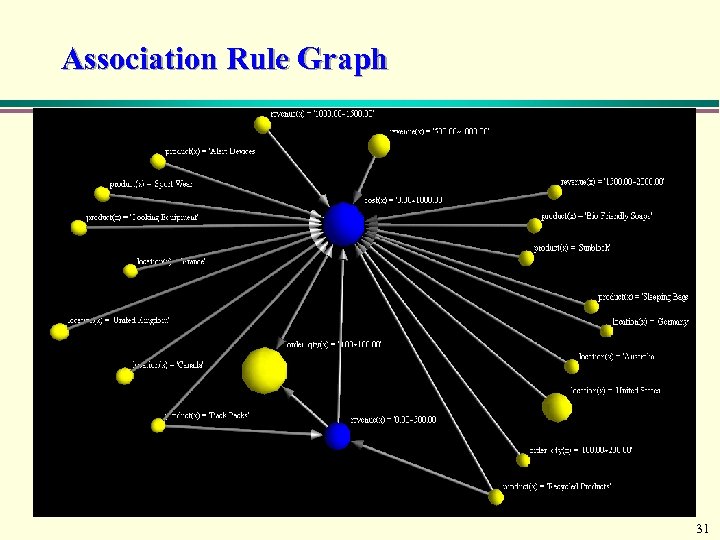
Association Rule Graph 31
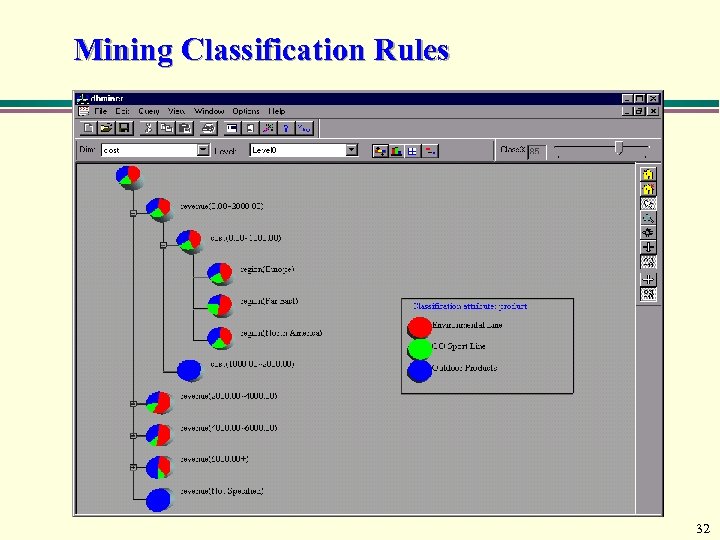
Mining Classification Rules 32
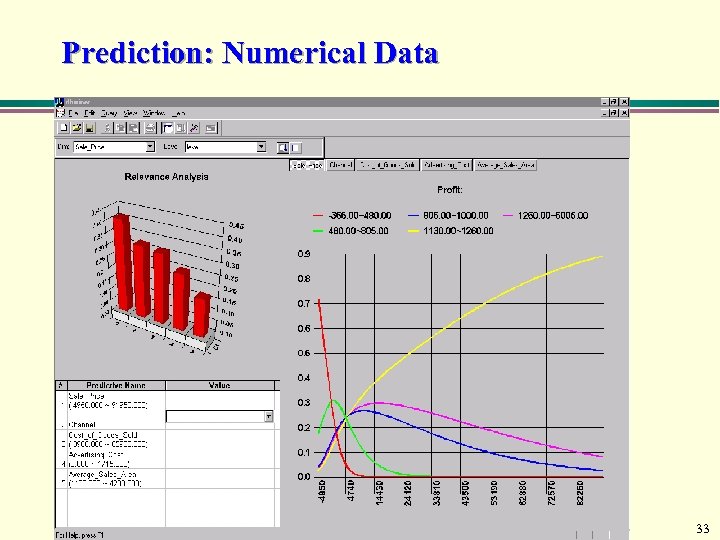
Prediction: Numerical Data 33
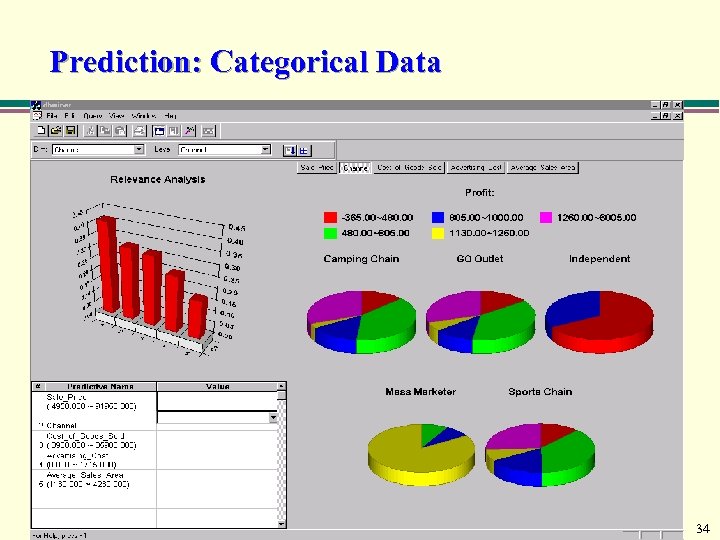
Prediction: Categorical Data 34
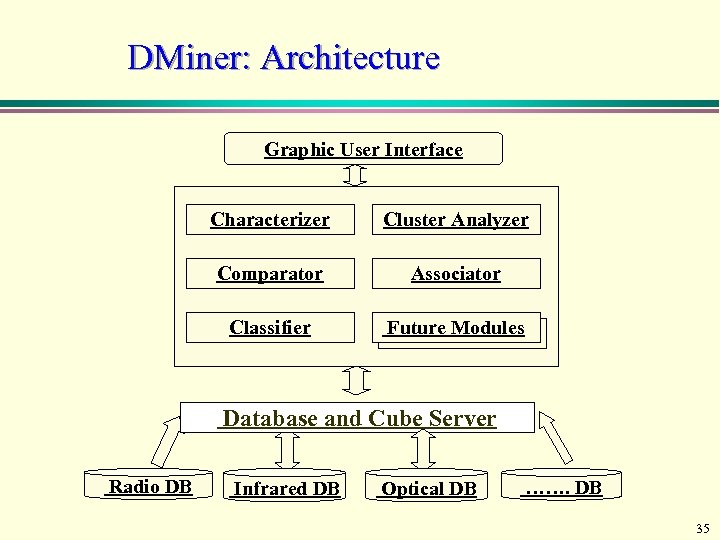
DMiner: Architecture Graphic User Interface Characterizer Cluster Analyzer Comparator Associator Classifier Future Modules Database and Cube Server Radio DB Infrared DB Optical DB ……. DB 35
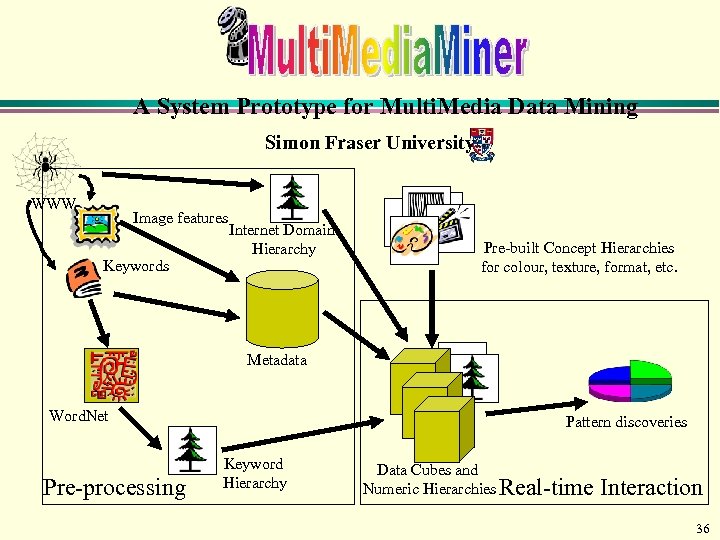
A System Prototype for Multi. Media Data Mining Simon Fraser University WWW Image features Keywords Internet Domain Hierarchy Pre-built Concept Hierarchies for colour, texture, format, etc. Metadata Word. Net Pre-processing Pattern discoveries Keyword Hierarchy Data Cubes and Numeric Hierarchies Real-time Interaction 36
Simon Fraser University 37
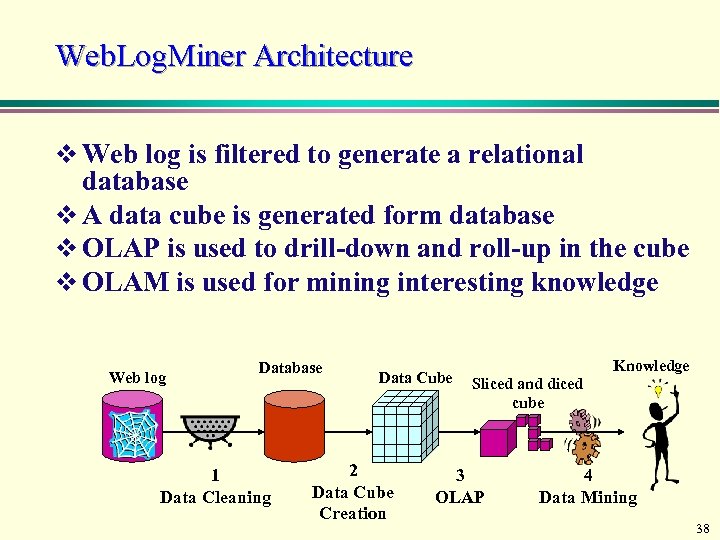
Web. Log. Miner Architecture v Web log is filtered to generate a relational database v A data cube is generated form database v OLAP is used to drill-down and roll-up in the cube v OLAM is used for mining interesting knowledge Web log Database 1 Data Cleaning Data Cube 2 Data Cube Creation Knowledge Sliced and diced cube 3 OLAP 4 Data Mining 38
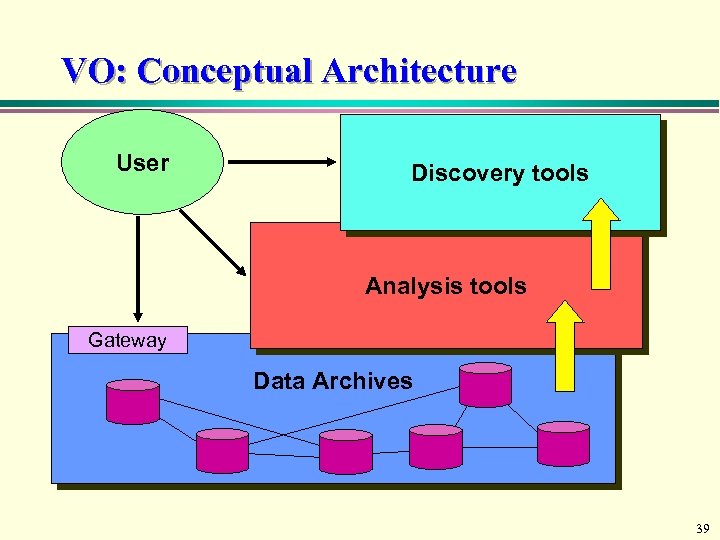
VO: Conceptual Architecture User Discovery tools Analysis tools Gateway Data Archives 39
Conclusion ◆ Development and application of DM in astronomy; ◆ Automated DM, visulized DM and audio DM; ◆ Integrate VO and DM. The next golden age of discovery in astronomy come eariler! 40

Q&A? Thank you !!! 41
ac96d209f046dd2fad31f0cfab8c8d63.ppt