 Data Marts and Star Schema Design Data Warehousing Lab. 박유림
Data Marts and Star Schema Design Data Warehousing Lab. 박유림
 Data Marts (1) 1. Data Marts vs Warehouse - subject-oriented, Integrated, nonvolatile, and time-variants - Warehouse : needs of the entire organization - Marts : subject areas or the needs of department or business function 2. Why Do You Need Data Marts? - rapid access to data - easier time navigating through data marts 2 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Data Marts (1) 1. Data Marts vs Warehouse - subject-oriented, Integrated, nonvolatile, and time-variants - Warehouse : needs of the entire organization - Marts : subject areas or the needs of department or business function 2. Why Do You Need Data Marts? - rapid access to data - easier time navigating through data marts 2 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
 Data Marts (2) 1. Data Marts replace a Data Warehouse - It avoids extraction repetition. - It ensures standard interpretation of enterprise data. - It provides a repository that is far more flexible than the denormalized structures in the high performance query, or data marts, layer. 2. Typical Technologies RDBMS, MDDB, OLAP, ROLAP, Oracle’s MDDB 3 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Data Marts (2) 1. Data Marts replace a Data Warehouse - It avoids extraction repetition. - It ensures standard interpretation of enterprise data. - It provides a repository that is far more flexible than the denormalized structures in the high performance query, or data marts, layer. 2. Typical Technologies RDBMS, MDDB, OLAP, ROLAP, Oracle’s MDDB 3 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
 Star Schema Design 1. In the vast majority of cases, the HPQS chosen to house relational data marts 2. Two kinds of table - Fact table is contains the actual transactions or values being analyzed - Multiple dimension table contain descriptive information about those transactions or values. 4 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Star Schema Design 1. In the vast majority of cases, the HPQS chosen to house relational data marts 2. Two kinds of table - Fact table is contains the actual transactions or values being analyzed - Multiple dimension table contain descriptive information about those transactions or values. 4 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
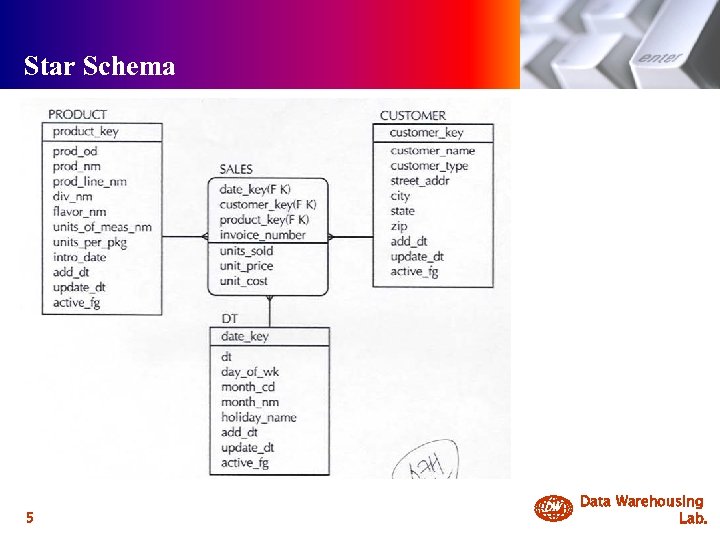 Star Schema 5 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Star Schema 5 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
 Fact Table Design 1. Contains a primary key made up of a concatenation of foreign keys to dimension tables and the facts or measures uniquely identified by primary key. 2. Invoice_number - integral to this investigation 3. Fact table is highly normalized structure. 6 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Fact Table Design 1. Contains a primary key made up of a concatenation of foreign keys to dimension tables and the facts or measures uniquely identified by primary key. 2. Invoice_number - integral to this investigation 3. Fact table is highly normalized structure. 6 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
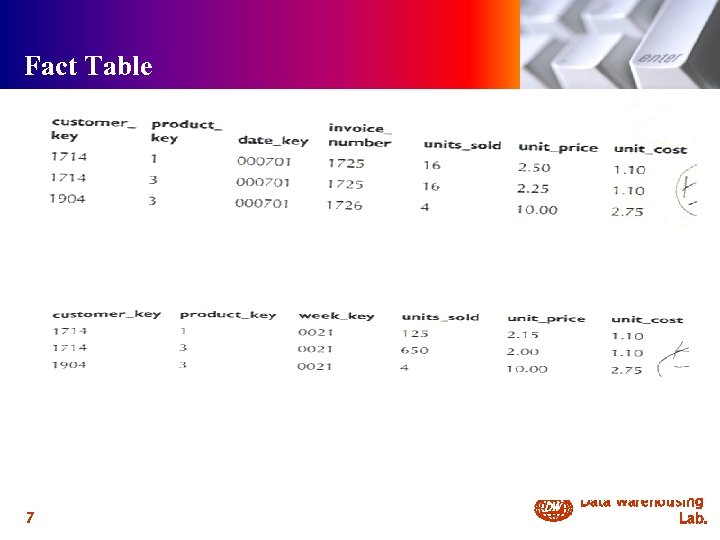 Fact Table 내용 7 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Fact Table 내용 7 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
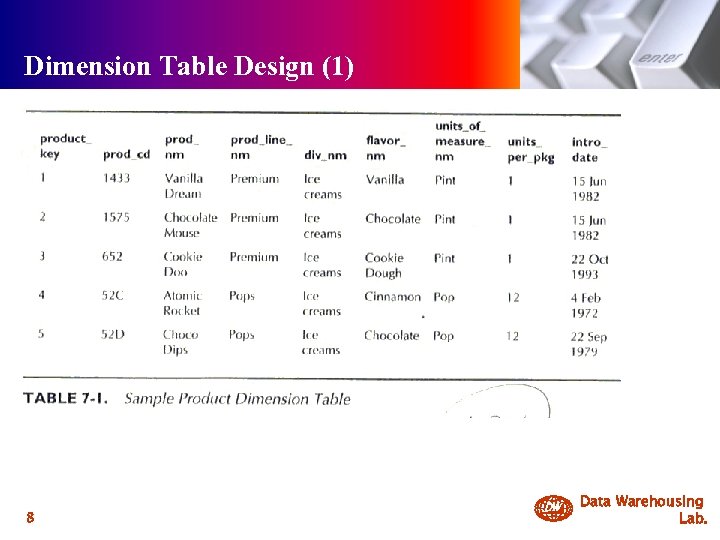 Dimension Table Design (1) 8 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Dimension Table Design (1) 8 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
 Dimension Table Design (2) 1. Dimension Table Features 1. 2. Wide 3. Short 4. Use Surrogate Keys 5. Contains Links to Corresponding Records in Source Tables 6. 9 Denormalized Contains Additional Date and Active Flag Fields DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Dimension Table Design (2) 1. Dimension Table Features 1. 2. Wide 3. Short 4. Use Surrogate Keys 5. Contains Links to Corresponding Records in Source Tables 6. 9 Denormalized Contains Additional Date and Active Flag Fields DW Data Warehousing Lab.
 Snowflake Schema 1. Snowflake schema is just like a star with normalized demension tables. Summary Tables 1. Materialized Views 1. It allows you to use Oracle 8 i query rewrite capabilities 2. It allows you to push the work of maintaining 2. The Effect on Dimension Tables - layered star : fully denormalized into dimension tables at that level - snowflake schema : date and month those two tables would have to be joined at query time 10 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Snowflake Schema 1. Snowflake schema is just like a star with normalized demension tables. Summary Tables 1. Materialized Views 1. It allows you to use Oracle 8 i query rewrite capabilities 2. It allows you to push the work of maintaining 2. The Effect on Dimension Tables - layered star : fully denormalized into dimension tables at that level - snowflake schema : date and month those two tables would have to be joined at query time 10 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
 Common Design Complexities 1. Example 1. 2. While his Michigan business is closing 3. 2. Suppose that Jeff’s Quickie Mart, a customer of Wonderscoop Jeff decides to move to Florida and take his business with him. Problem - All the sales that Wonderscoop made to Jeff in the past will look like they are Florida sales even though they actually occurred in Michigan 3. Solution -The new record has a new Customer key. 1. 2. 11 We did update it with information indicating that it is no longer an active record. All they need do is query the customer dimension table where active_fg = true DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Common Design Complexities 1. Example 1. 2. While his Michigan business is closing 3. 2. Suppose that Jeff’s Quickie Mart, a customer of Wonderscoop Jeff decides to move to Florida and take his business with him. Problem - All the sales that Wonderscoop made to Jeff in the past will look like they are Florida sales even though they actually occurred in Michigan 3. Solution -The new record has a new Customer key. 1. 2. 11 We did update it with information indicating that it is no longer an active record. All they need do is query the customer dimension table where active_fg = true DW Data Warehousing Lab.
 Conclusion -Data marts are the databases that users actually go to for information. -These are usually built with either multidimensional or relational technologies. 12 DW Data Warehousing Lab.
Conclusion -Data marts are the databases that users actually go to for information. -These are usually built with either multidimensional or relational technologies. 12 DW Data Warehousing Lab.