87a56afdc15f15970fd4f5827ecc28a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Data Management in Globus and Datagrid This presentation is based on Globus tutorials and EU Data. Grid documents
Data Management Desired Functionality Globus Data. Grid Effords (see: http: //www. globus. org/datagrid/software. html) n Existing software n Future solutions EU Data. Grid Efford (GDMP) (http: //grid-data-management. web. cern. ch/grid-data -management/)
Examples of Desired Data Grid Functionality High-speed, reliable access to remote data Automated discovery of “best” copy of data Manage replication to improve performance Co-schedule compute, storage, network “Transparency” wrt delivered performance Enforce access control on data Allow representation of “global” resource allocation policies Central Q: How must Grid architecture be extended to support these functions?

Globus Datagrid Efford Grid. FTP: A high-performance, secure, robust data transfer mechanism Globus Replica Catalog: A mechanism for maintaining a catalog of dataset replicas. Globus Replica Management: A mechanism that ties together the Replica Catalog and Grid. FTP technologies, allowing applications to create and manage replicas of large datasets.

Globus Datagrid Efford software available to the public as components of the Globus Toolkit 2. 0 release tested and evaluated for more than a year by several external project teams (i. e. European Data. Grid used special relase of Globus Toolkit 2. 0 Beta 21)
Major Data Grid Projects Earth System Grid (DOE Office of Science) n DG technologies, climate applications European Data Grid (EU) n DG technologies & deployment in EU Gri. Phy. N (NSF ITR) n Investigation of “Virtual Data” concept Particle Physics Data Grid (DOE Science) n DG applications for HENP experiments
Why New Protocol ? Existing distributed data storage systems n n n DPSS, HPSS: focus on high-performance access, utilize parallel data transfer, striping DFS: focus on high-volume usage, dataset replication, local caching SRB: connects heterogeneous data collections, uniform client interface, metadata queries Problems n Incompatible (and proprietary) protocols w Each require custom client w Partitions available data sets and storage devices n Each protocol has subset of desired functionality
A Common, Secure, Efficient Data Access Protocol Common, extensible transfer protocol n Common protocol means all can interoperate Decouple low-level data transfer mechanisms from the storage service Advantages: n n New, specialized storage systems are automatically compatible with existing systems Existing systems have richer data transfer functionality Interface to many storage systems n n HPSS, DPSS, file systems Plan for SRB integration
A Universal Access/Transport Protocol Grid Security Infrastructure and Kerberos support Third-party control of data transfer Parallel data transfer Striped data transfer Partial file transfer Automatic negotiation of TCP buffer/window sizes Support for reliable and restartable data transfer
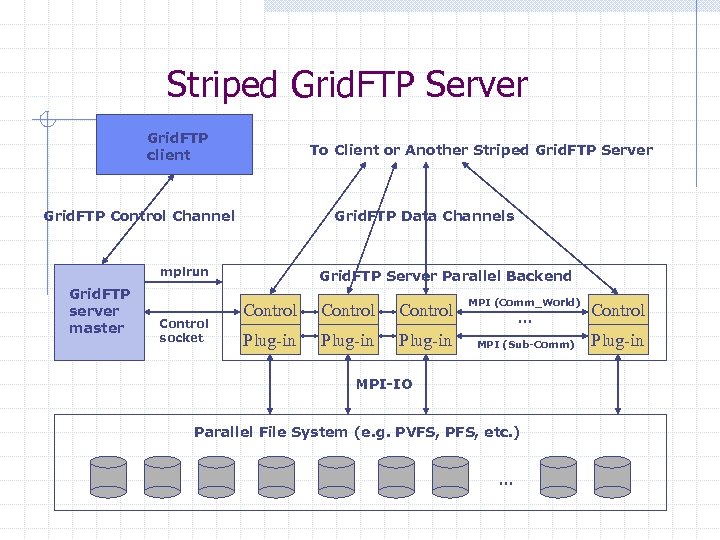
Striped Grid. FTP Server Grid. FTP client To Client or Another Striped Grid. FTP Server Grid. FTP Control Channel Grid. FTP Data Channels mpirun Grid. FTP server master Control socket Grid. FTP Server Parallel Backend Control Plug-in MPI (Comm_World) … MPI (Sub-Comm) MPI-IO Parallel File System (e. g. PVFS, PFS, etc. ) … Control Plug-in

And the Universal Protocol is … Grid. FTP Why FTP? n n n Ubiquity enables interoperation with many commodity tools Already supports many desired features, easily extended to support others Well understood and supported We use the term Grid. FTP to refer to n n Transfer protocol which meets requirements Family of tools which implement the protocol Note Grid. FTP > FTP Note that despite name, Grid. FTP is not restricted to file transfer!

Grid. FTP Protocol Specifications Existing standards n n RFC 949: File Transfer Protocol RFC 2228: FTP Security Extensions RFC 2389: Feature Negotiation for the File Transfer Protocol Draft: FTP Extensions New drafts n Grid. FTP: Protocol Extensions to FTP for the Grid w Grid Forum Data Working Group

The Grid. FTP Family of Tools Patches to existing FTP code – gsiwuftpd tools– (Globus 1. 3) Globus Toolkit V 2. 0 Grid. FTP server (GT 2 Grid. FTP) Grid. FTP client tools, client library, control library – No Grid. FTP client !
Grid. FTP – tools API/library : globus_ftp_control n globus_ftp_client include interfaces for adding software plugins n w customized reliability w fault tolerance w performance monitoring w extended data processing.
Grid. FTP – tools API/library n globus_gass_copy Command line tool n globus_url_copy integrates Grid. FTP, HTTP, and local file I/O to enable secure transfers using any combination of these protocols. Adapted wu-ftp package
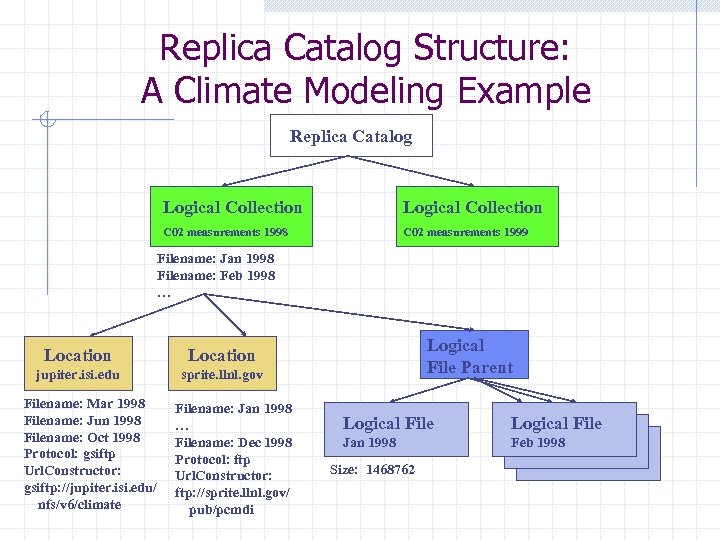
Replica Catalog Structure: A Climate Modeling Example Replica Catalog Logical Collection C 02 measurements 1998 C 02 measurements 1999 Filename: Jan 1998 Filename: Feb 1998 … Location jupiter. isi. edu Logical File Parent Location sprite. llnl. gov Filename: Mar 1998 Filename: Jun 1998 Filename: Oct 1998 Protocol: gsiftp Url. Constructor: gsiftp: //jupiter. isi. edu/ nfs/v 6/climate Filename: Jan 1998 … Filename: Dec 1998 Protocol: ftp Url. Constructor: ftp: //sprite. llnl. gov/ pub/pcmdi Logical File Jan 1998 Feb 1998 Size: 1468762

Replica Catalog -implementation API, library and a command line tool running against standard LDAP server, but constructed independently globus-replica-catalog HOST OBJECT ACTION
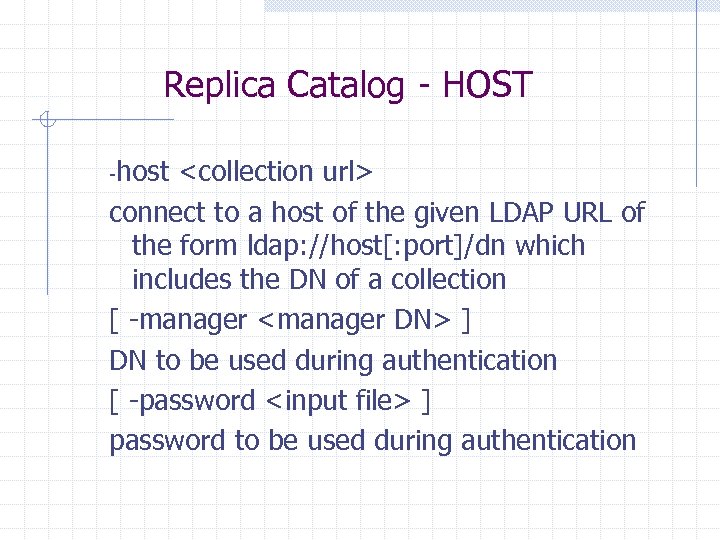
Replica Catalog - HOST -host <collection url> connect to a host of the given LDAP URL of the form ldap: //host[: port]/dn which includes the DN of a collection [ -manager <manager DN> ] DN to be used during authentication [ -password <input file> ] password to be used during authentication

Replica Catalog - OBJECT -collection act on the collection given in the DN of the LDAP URL -location <location name> act on the given location name -logicalfile <logical file name> act on the given logicalfile name
![Replica Catalog - ACTION -create [ <input file> ] | -create <location url> [ Replica Catalog - ACTION -create [ <input file> ] | -create <location url> [](https://present5.com/presentation/87a56afdc15f15970fd4f5827ecc28a8/image-20.jpg)
Replica Catalog - ACTION -create [ <input file> ] | -create <location url> [ <input file> ]| -create <size> w a collection with filenames in the given input file, w a location with the given location url and optional set of filenames in the given input file w a logicalfile. -delete w delete a collection, location, or logical file

Replica Manager-API &command tool Session handlers Rollback Restart Creating catalog entries File registration Copying files Publishing files Deleting files
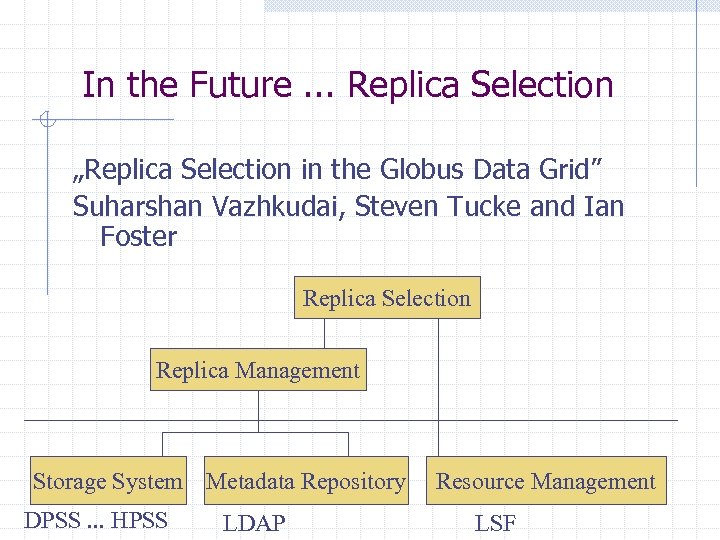
In the Future. . . Replica Selection „Replica Selection in the Globus Data Grid” Suharshan Vazhkudai, Steven Tucke and Ian Foster Replica Selection Replica Management Storage System Metadata Repository DPSS. . . HPSS LDAP Resource Management LSF

Replica Selection & MDS LDAP-based GRIS demon on each storage resource GRIS demon collects: n n n static attributes (configuration files) dynamic attributes via shell scripts (i. e. df) network performance (via monitoring storage performance, historical information) GRIS can be registered with GIIS, that can be queried by a user

Class. Ads for Replica Selection Hostname=‘comet. xyz. com’; reqd. Space=5 GB reqd. RDBandwidth= 50 K/Sec rank= other. available. Space>5 GB && other. Max. RDBandwidth>50 K/Sec
Storage Broker Actions Searching n n Query Replica Catalog for all physical locations Query each physical location (GRIS servers) Matching (Class. Ads mechanism like in Condor) Accessing (Grid. FTP)
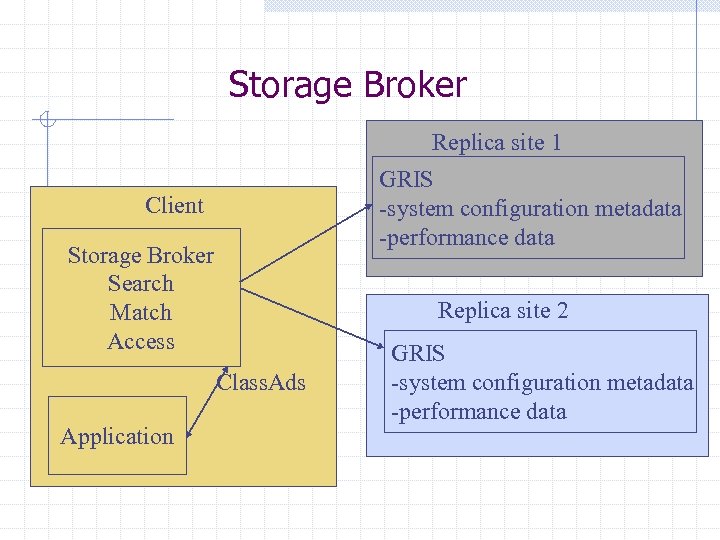
Storage Broker Replica site 1 GRIS -system configuration metadata -performance data Client Storage Broker Search Match Access Replica site 2 Class. Ads Application GRIS -system configuration metadata -performance data
EU Datagrid WP 2 Grid Data Mirroring Package (GDMP) User Guide for GDMP v 2. 1 currently available Collaboration with Particle Physics Data Grid Uses Globus Replica Catalog from GT 2. 0 Beta release
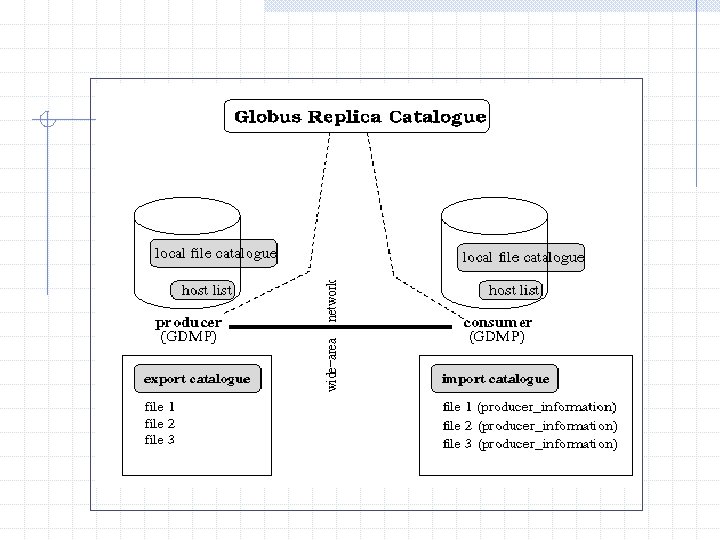

Quick Start Guide to GDMP Run GDMB server on site A and site B Subscribe host B to the host list at site A n n n gdmp_host_subscribe command on site B must have grid proxy (grid_proxy_init on B) results in info about B in configuration file at A Register local files on site A n n gdmp_register_local_file command on site A results in entry in local file at A

Quick Start Guide to GDMP -ctd Publish Catalog on site A n n gdmp_publish_cataloge command at site A must have grid proxy (grid_proxy_init at A) results in import (site. B) and export (site. A) files Replica Catalog is updated by default (can be distabled) Get Replica from A to B n n gdmp_replicate_get command at site A results in transfering files in the case of Objectivity file, the files are attached to the federation at site B Replica Catalog is updated by default (can be disabled)
87a56afdc15f15970fd4f5827ecc28a8.ppt