5a80edfc176b432e4f3e3dccef81b9db.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Data Links Technology
Problem Domain Addressed. . . l l l 70%-95% (or more) of data resides in file systems as compared to databases Ù Internet has exacerbated this divide Legacy applications using file systems abound, and new ones being developed involving unstructured data Ù Applications using file systems here to stay for a long time File system limitations Ù Search Ù Security Ù Integrity -- referential, domain, etc. Ù Transactional semantics Ù Administration
Problem Domain Addressed l l New e-business applications and certain existing and emerging applications need to integrate database systems with existing and new file systems Ù They all need database level integrity, security, backup and recovery, replication and transaction consistency Storing files in BLOBs gives it DBMS capabilities Ù Files must be copied/migrated to the BLOBs 3 Coexistence with existing and emerging applications using file system interfaces Ù Performance issues 3 Ability to deliver data isochronously 3 Scalability of a single database server
DB 2 UDB Data Links l Extends the following database management capabilities to file data in file systems Ù Referential Integrity Ù Value-based security Ù Coordinated backup & recovery All with transaction semantics l Allows management of files AS IF it were stored in the database l Retains file system performance, APIs and "look and feel" l Leaves data where it is and manages it Fusion of database and file system technologies
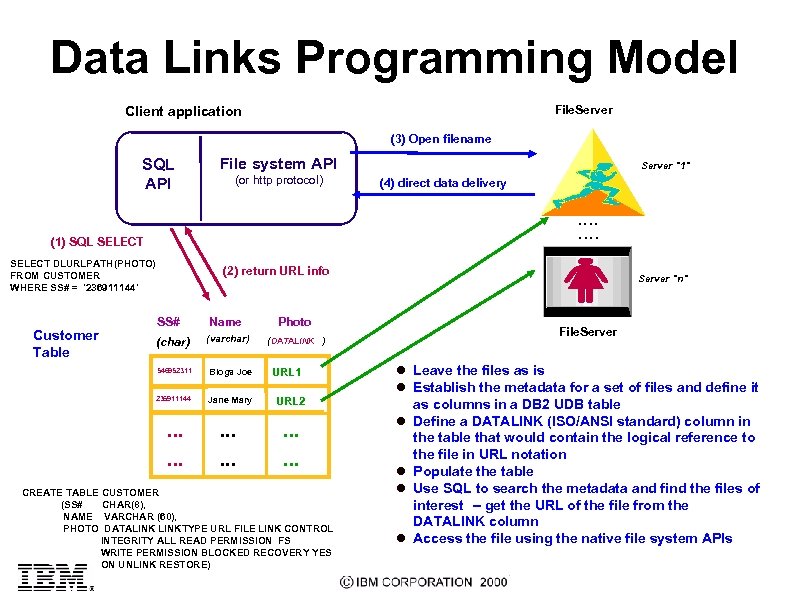
Data Links Programming Model Client application File. Server (3) Open filename SQL API File system API (or http protocol) Server "1" (4) direct data delivery . . . . (1) SQL SELECT DLURLPATH(PHOTO) FROM CUSTOMER WHERE SS# = '236911144' Customer Table (2) return URL info SS# (char) Name Photo (varchar) (DATALINK ) 546952311 Blogs Joe 236911144 Jane Mary URL 2 . . . . Server "n" URL 1 CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER (SS# CHAR(8), NAME VARCHAR (60), PHOTO DATALINKTYPE URL FILE LINK CONTROL INTEGRITY ALL READ PERMISSION FS WRITE PERMISSION BLOCKED RECOVERY YES ON UNLINK RESTORE) File. Server l Leave the files as is l Establish the metadata for a set of files and define it l l as columns in a DB 2 UDB table Define a DATALINK (ISO/ANSI standard) column in the table that would contain the logical reference to the file in URL notation Populate the table Use SQL to search the metadata and find the files of interest -- get the URL of the file from the DATALINK column Access the file using the native file system APIs
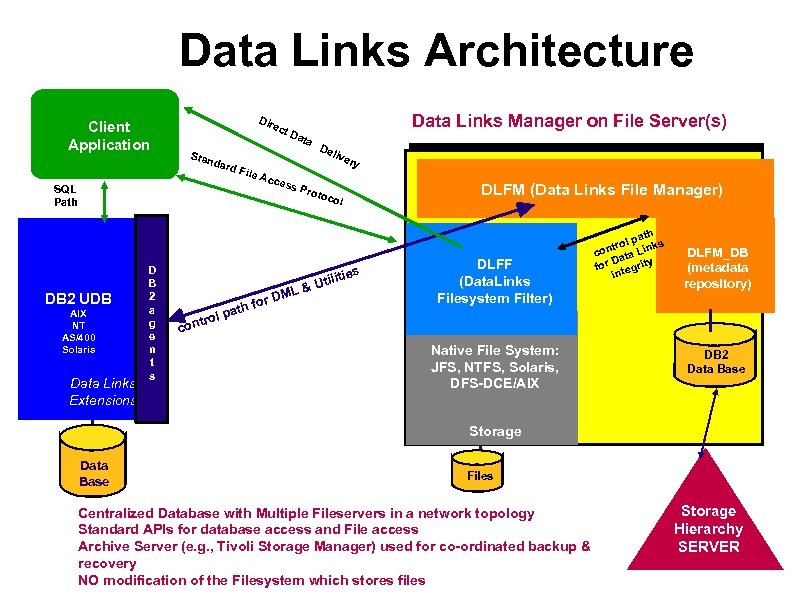
Data Links Architecture Client Application Client Dir ect Stan dard SQL Path File DB 2 UDB AIX NT AS/400 Solaris Data Links Extensions D B 2 a g e n t s trol con Data Links Manager on File Server(s) De live ry Acc ess r. D th fo pa Da ta Prot ML oco l tili &U ties DLFM (Data Links File Manager) DLFF (Data. Links Filesystem Filter) Native File System: JFS, NTFS, Solaris, DFS-DCE/AIX h pat trol Links con ata D for tegrity in DLFM_DB (metadata repository) DB 2 Data Base Storage Data Base Files Centralized Database with Multiple Fileservers in a network topology Standard APIs for database access and File access Archive Server (e. g. , Tivoli Storage Manager) used for co-ordinated backup & recovery NO modification of the Filesystem which stores files Storage Hierarchy SERVER
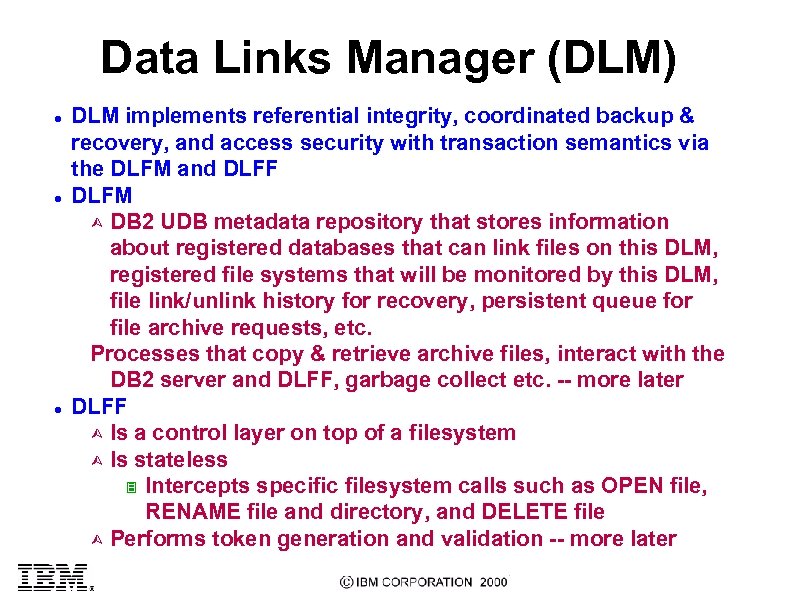
Data Links Manager (DLM) l l l DLM implements referential integrity, coordinated backup & recovery, and access security with transaction semantics via the DLFM and DLFF DLFM Ù DB 2 UDB metadata repository that stores information about registered databases that can link files on this DLM, registered file systems that will be monitored by this DLM, file link/unlink history for recovery, persistent queue for file archive requests, etc. Processes that copy & retrieve archive files, interact with the DB 2 server and DLFF, garbage collect etc. -- more later DLFF Ù Is a control layer on top of a filesystem Ù Is stateless 3 Intercepts specific filesystem calls such as OPEN file, RENAME file and directory, and DELETE file Ù Performs token generation and validation -- more later
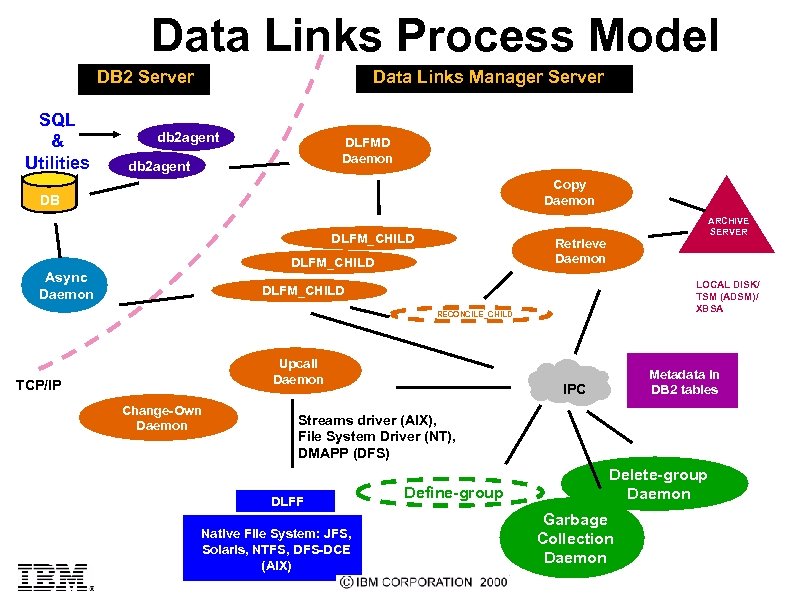
Data Links Process Model DB 2 Server SQL & Utilities Data Links Manager Server db 2 agent DLFMD Daemon db 2 agent Copy Daemon DB DLFM_CHILD Retrieve Daemon DLFM_CHILD Async Daemon ARCHIVE SERVER LOCAL DISK/ TSM (ADSM)/ XBSA DLFM_CHILD RECONCILE_CHILD Upcall Daemon TCP/IP Change-Own Daemon Metadata in DB 2 tables IPC Streams driver (AIX), File System Driver (NT), DMAPP (DFS) DLFF Native File System: JFS, Solaris, NTFS, DFS-DCE (AIX) Define-group Delete-group Daemon Garbage Collection Daemon
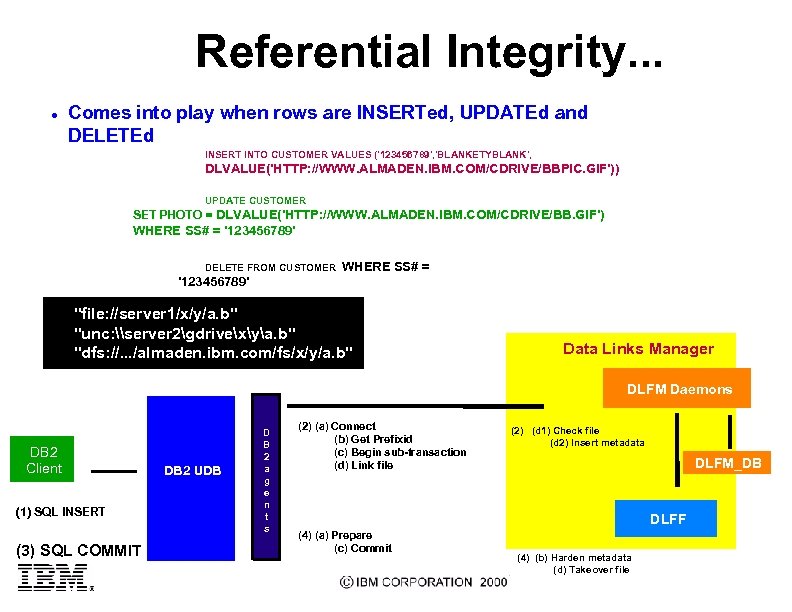
Referential Integrity. . . l Comes into play when rows are INSERTed, UPDATEd and DELETEd INSERT INTO CUSTOMER VALUES ('123456789', 'BLANKETYBLANK', DLVALUE('HTTP: //WWW. ALMADEN. IBM. COM/CDRIVE/BBPIC. GIF')) UPDATE CUSTOMER SET PHOTO = DLVALUE('HTTP: //WWW. ALMADEN. IBM. COM/CDRIVE/BB. GIF') WHERE SS# = '123456789' DELETE FROM CUSTOMER WHERE SS# = '123456789' "file: //server 1/x/y/a. b" "unc: \server 2gdrivexya. b" "dfs: //. . . /almaden. ibm. com/fs/x/y/a. b" Data Links Manager DLFM Daemons DB 2 Client (1) SQL INSERT (3) SQL COMMIT DB 2 UDB D B 2 a g e n t s (2) (a) Connect (b) Get Prefixid (c) Begin sub-transaction (d) Link file (2) (d 1) Check file (d 2) Insert metadata DLFM_DB DLFF (4) (a) Prepare (c) Commit (4) (b) Harden metadata (d) Takeover file

Referential Integrity l l Action on linked file when database row is DELETEd, or DATALINK column is set to NULL (or another DATALINK value) depends upon the "ON UNLINK" option in the DATALINK column attributes Ù "ON UNLINK RESTORE" causes the file permissions and ownership to be restored to what they were before they were first linked Ù "ON UNLINK DELETE" causes the linked file to be deleted Action when a user tries to use filesystem commands to DELETE or RENAME the file l DLFF intercepts these commands, and interacts with the UPCALL daemon to determine if the file is linked, in which case the DELETE or RENAME is prohibited
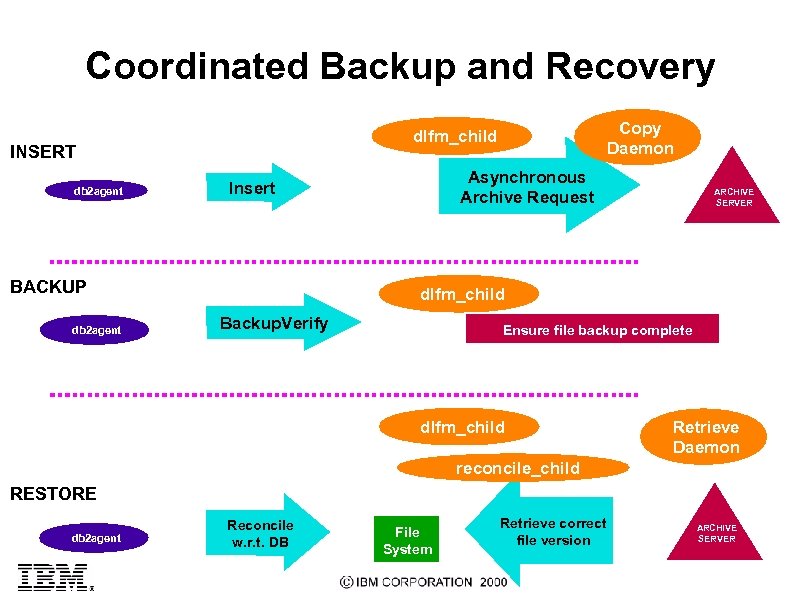
Coordinated Backup and Recovery INSERT db 2 agent Asynchronous Archive Request Insert BACKUP db 2 agent Copy Daemon dlfm_child ARCHIVE SERVER dlfm_child Backup. Verify Ensure file backup complete dlfm_child Retrieve Daemon reconcile_child RESTORE db 2 agent Reconcile w. r. t. DB File System Retrieve correct file version ARCHIVE SERVER
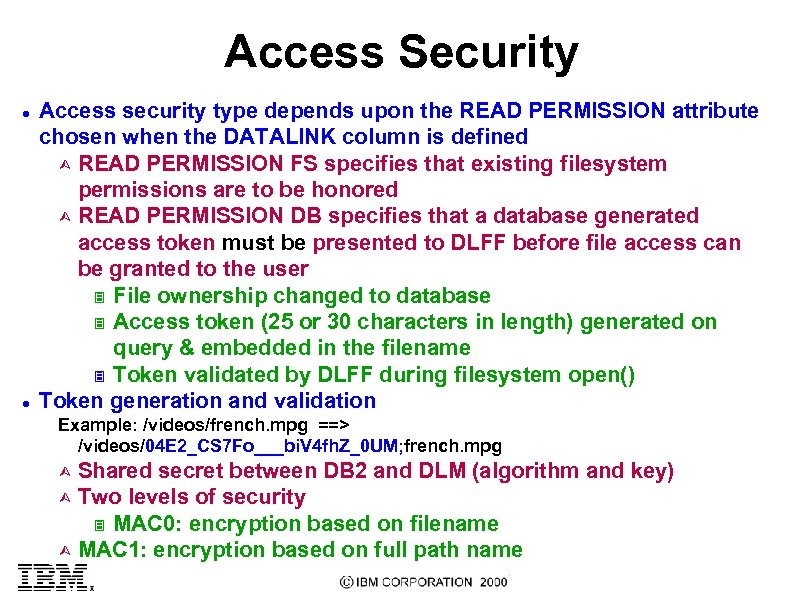
Access Security l l Access security type depends upon the READ PERMISSION attribute chosen when the DATALINK column is defined Ù READ PERMISSION FS specifies that existing filesystem permissions are to be honored Ù READ PERMISSION DB specifies that a database generated access token must be presented to DLFF before file access can be granted to the user 3 File ownership changed to database 3 Access token (25 or 30 characters in length) generated on query & embedded in the filename 3 Token validated by DLFF during filesystem open() Token generation and validation Example: /videos/french. mpg ==> /videos/04 E 2_CS 7 Fo___bi. V 4 fh. Z_0 UM; french. mpg Shared secret between DB 2 and DLM (algorithm and key) Ù Two levels of security 3 MAC 0: encryption based on filename Ù MAC 1: encryption based on full path name Ù
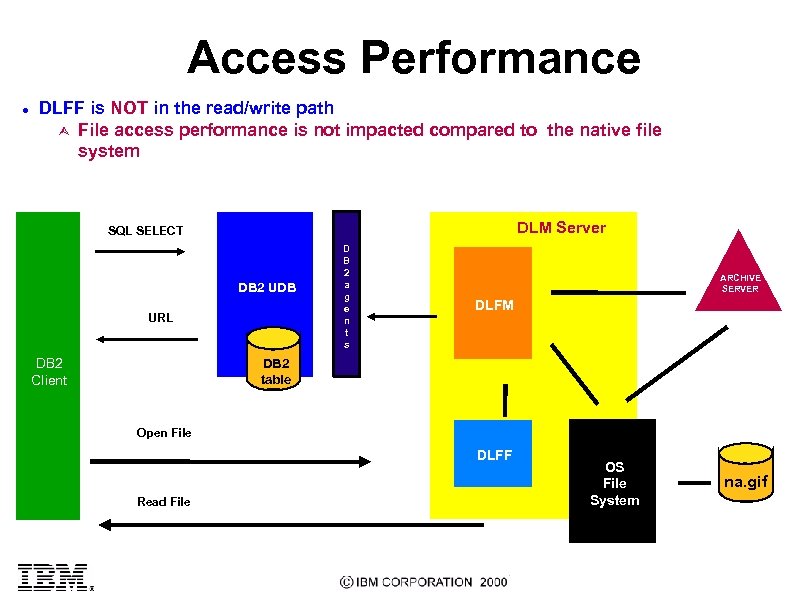
Access Performance l DLFF is NOT in the read/write path Ù File access performance is not impacted compared to the native file system DLM Server SQL SELECT DB 2 UDB URL DB 2 Client D B 2 a g e n t s ARCHIVE SERVER DLFM DB 2 table Open File DLFF Read File OS File System na. gif

Utilities. . . All input formats to LOAD and IMPORT supported for tables containing DATALINK columns Ù DATALINK SPECIFICATION provides flexibility for transforming DATALINK values in data files Ù SAVECOUNT in LOAD causes consistency points for files linked in DLMs Ù Exceptions for DATALINK column(s) reported in exception table 3 LOAD COPY and LOAD REPLACE options not supported l EXPORT Ù DB 2 EXPORT command generates control file (TAR or ZIP) containing file references l dlfm_export generates a TAR (ZIP on NT) file based on control file l IMPORT Ù dlfm-import uses the control file and TAR (ZIP on NT) file to materialize files prior to running IMPORT on DB 2 Ù See DB 2 Data Movements Guide for details l
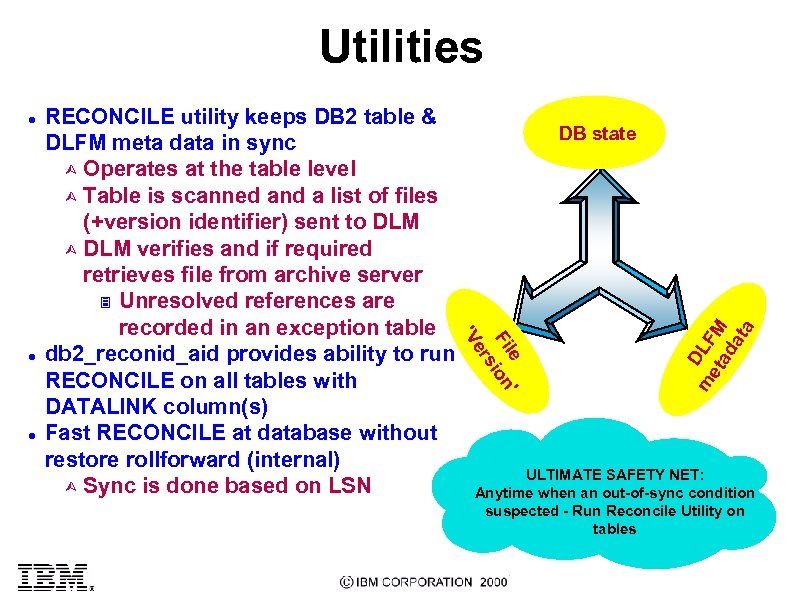
Utilities le ' Fi ion s er l DB state 'V l RECONCILE utility keeps DB 2 table & DLFM meta data in sync Ù Operates at the table level Ù Table is scanned and a list of files (+version identifier) sent to DLM Ù DLM verifies and if required retrieves file from archive server 3 Unresolved references are recorded in an exception table db 2_reconid_aid provides ability to run RECONCILE on all tables with DATALINK column(s) Fast RECONCILE at database without restore rollforward (internal) Ù Sync is done based on LSN m DLF et M ad at a l ULTIMATE SAFETY NET: Anytime when an out-of-sync condition suspected - Run Reconcile Utility on tables
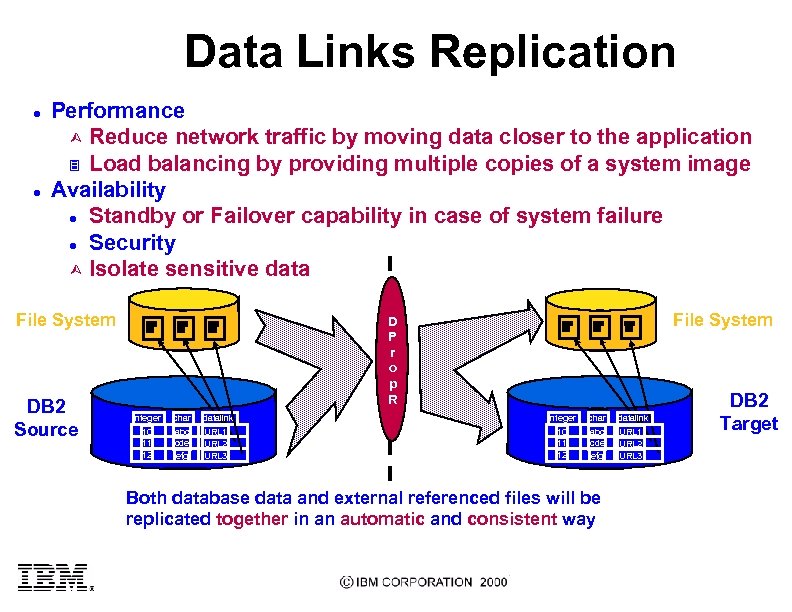
Data Links Replication l l Performance Ù Reduce network traffic by moving data closer to the application 3 Load balancing by providing multiple copies of a system image Availability l Standby or Failover capability in case of system failure l Security Ù Isolate sensitive data File System DB 2 Source File System D P r o p R integer char datalink 10 11 12 abc cde efg URL 1 URL 2 URL 3 Both database data and external referenced files will be DB 2 replicated together in an automatic and consistent way DB 2 Target
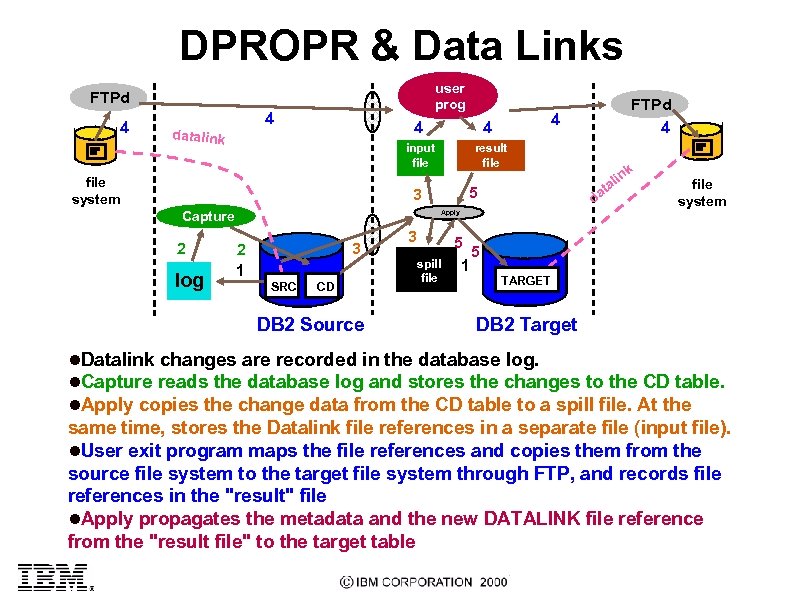
DPROPR & Data Links user prog FTPd 4 4 datalink 4 file system result file system Apply Capture log k in al t da 5 3 2 4 4 input file FTPd 4 3 2 1 SRC CD DB 2 Source 3 spill file 5 5 1 TARGET DB 2 Target l. Datalink changes are recorded in the database log. l. Capture reads the database log and stores the changes to the CD table. l. Apply copies the change data from the CD table to a spill file. At the same time, stores the Datalink file references in a separate file (input file). l. User exit program maps the file references and copies them from the source file system to the target file system through FTP, and records file references in the "result" file l. Apply propagates the metadata and the new DATALINK file reference from the "result file" to the target table
Data Links Applications. . . l l e. Commerce Ù Product catalogs, price lists, brochures, thumbnail and full images, video, etc. 3 Integrity of file content 3 Integrity of file reference Supply Chain Management (SCM) Ù Common in automotive and aerospace industry for engineering designs 3 Large automotive manufacturer outsources 70% of a vehicle design u requires content sharing between different enterprises u needs replication of both the engineering drawings (files) and the metadata (database) Ù Customer support document system 3 Large airplane manufacturer needs to deliver maintenance documents in common format to relevant airlines
Data Links Applications l l Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Ù Holistic view of customer touchpoint interactions -- voice, e-mail, fax, web, database, etc. 3 Integrity of file content Ù Integrity of file reference ERP Ù Patient Information System where information is exchanged between hospitals and clinic -- Xrays, ECG charts, Doctor comments, medical history, etc. Ù Catalog distribution system -- catalogs include metadata & file data Ù Automotive insurance (vehicle damage pictures, claim forms, etc. ) CAD/CAM Ù Engineering drawings Asset & Configuration Management Ù Content Management 3 Integrated Document Management 3 Media Access Management 3 Web Asset Management
BLOBs versus Data Links Storing files in BLOBs gives it DBMS capabilities Data. Links allows files to remain as is, while extending DBMS capabilities to them l Use Data. Links when Ù Performance & scalability are of concern Coexistence with existing and emerging applications that use the file system natively is required l BLOBs appropriate when above issues not a concern DB 2 UDB is unique in the industry in offering the customer the choice to either implement BLOBs or Data Links Lets the customer decide which option is most appropriate for their particular application requirement (Single application may adopt both technologies)

Conclusions
Conclusions Explosive growth in data stored in files critical to e-business l e-business applications Ù Integrate structured and unstructured information from diverse sources Ù Co-exist with existing and emerging file system based applications Demand mission critical capabilities of scalability, availability, security and integrity l Data Links addresses e-business application demands by Ù Extending to file systems, the umbrella of mission-critical RDBMS capabilities of referential integrity, value-based security, transaction consistency and co-ordinated backup and recovery Ù Supporting coordinated database & file replication for load balancing, high availability and B 2 B requirements Ù Providing a scaleable multi-platform solution

Supporting Foils
Data. Links Terminology. . . l l l Access Token Ù Embedded token in the filename that can be used to open files that are owned by the DB DATALINK Ù A base datatype whose value is a URL Ù Final Draft International Standard (FDIS) stage of ISO/ANSI standard (Database Language: SQL - Part 9: SQL/MED (Management of External Data) -- expected to be published as a standard in early 2001 DLFF Ù Data. Links Filesystem Filter Ù Sub-component of DLM Ù Kernel/user level subsystem that sits atop the native filesystem to provide RI and access control
Data. Links Terminology l l DLFM Ù Data Links File Manager Ù Sub-component of DLM dealing with file metadata processing, user-process level daemons l Interacts with DLFF and DB 2 DLM Ù Data Link Manager Ù Data. Links application that is installed on the file server DProp. R Ù IBM's replication technology Prefix Ù The mount point of the DLFF monitored filesystem
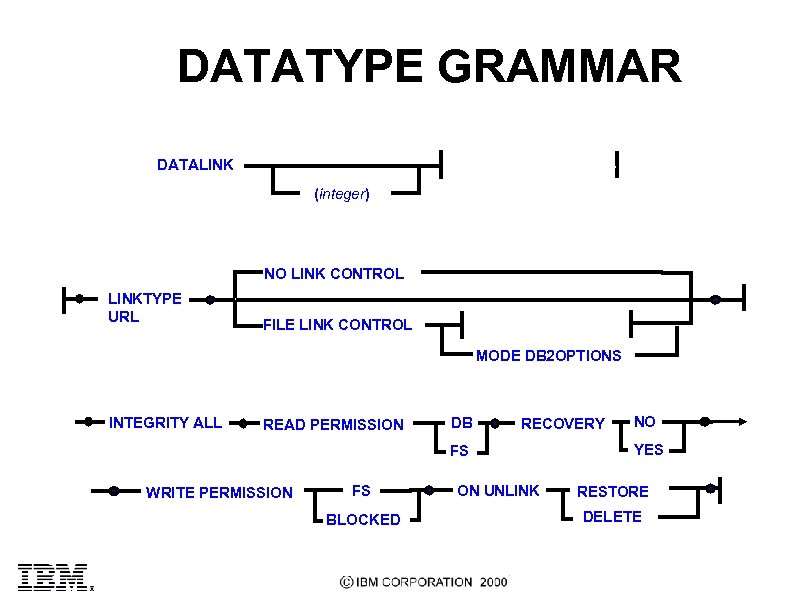
DATATYPE GRAMMAR DATALINK datalink-options-clause (integer) datalink-options-clause: NO LINK CONTROL LINKTYPE URL FILE LINK CONTROL file-link-options-clause MODE DB 2 OPTIONS file-link-options-clause: INTEGRITY ALL READ PERMISSION DB RECOVERY FS WRITE PERMISSION FS BLOCKED ON UNLINK NO YES RESTORE DELETE
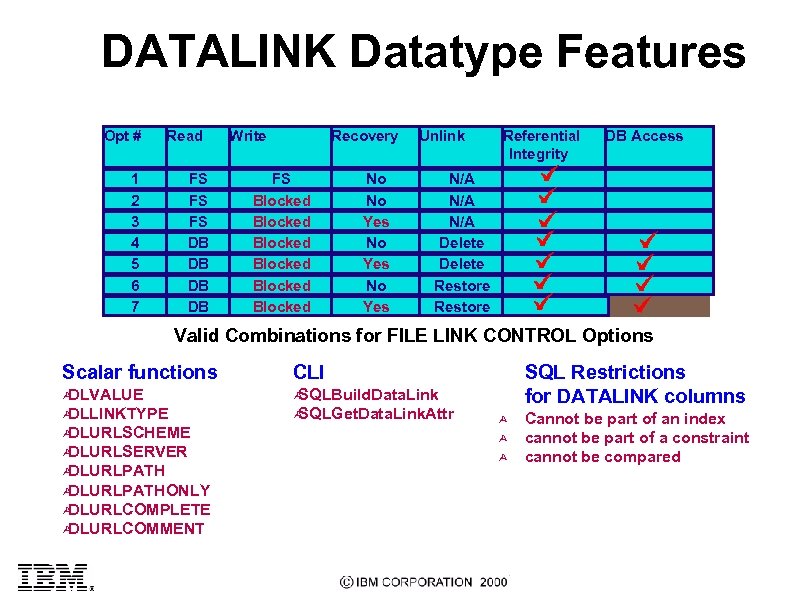
DATALINK Datatype Features Opt # Read 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 FS FS FS DB DB Write Recovery FS Blocked Blocked No No Yes Unlink Referential Integrity DB Access N/A N/A Delete Restore Valid Combinations for FILE LINK CONTROL Options Scalar functions CLI Ù DLVALUE Ù SQLBuild. Data. Link Ù DLLINKTYPE Ù SQLGet. Data. Link. Attr Ù DLURLSCHEME Ù DLURLSERVER Ù DLURLPATHONLY Ù DLURLCOMPLETE Ù DLURLCOMMENT SQL Restrictions for DATALINK columns Ù Ù Ù Cannot be part of an index cannot be part of a constraint cannot be compared
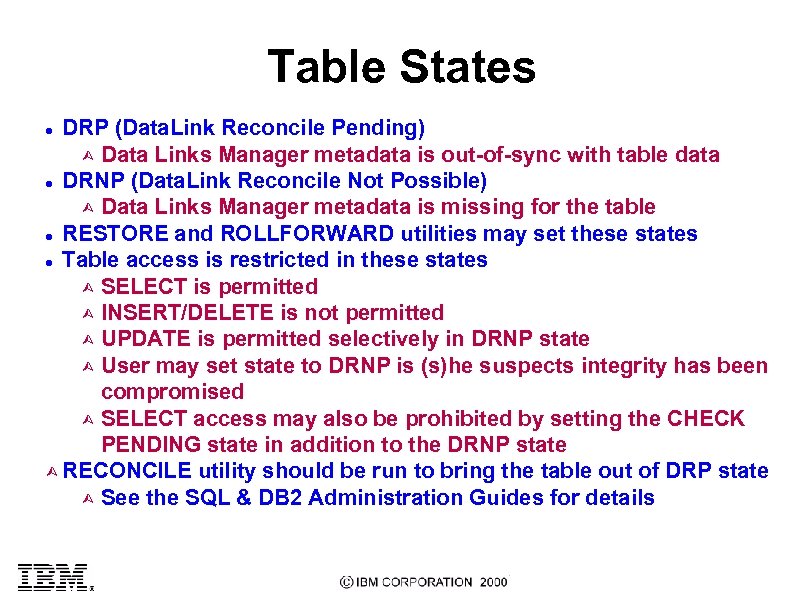
Table States DRP (Data. Link Reconcile Pending) Ù Data Links Manager metadata is out-of-sync with table data l DRNP (Data. Link Reconcile Not Possible) Ù Data Links Manager metadata is missing for the table l RESTORE and ROLLFORWARD utilities may set these states l Table access is restricted in these states Ù SELECT is permitted Ù INSERT/DELETE is not permitted Ù UPDATE is permitted selectively in DRNP state Ù User may set state to DRNP is (s)he suspects integrity has been compromised Ù SELECT access may also be prohibited by setting the CHECK PENDING state in addition to the DRNP state Ù RECONCILE utility should be run to bring the table out of DRP state Ù See the SQL & DB 2 Administration Guides for details l
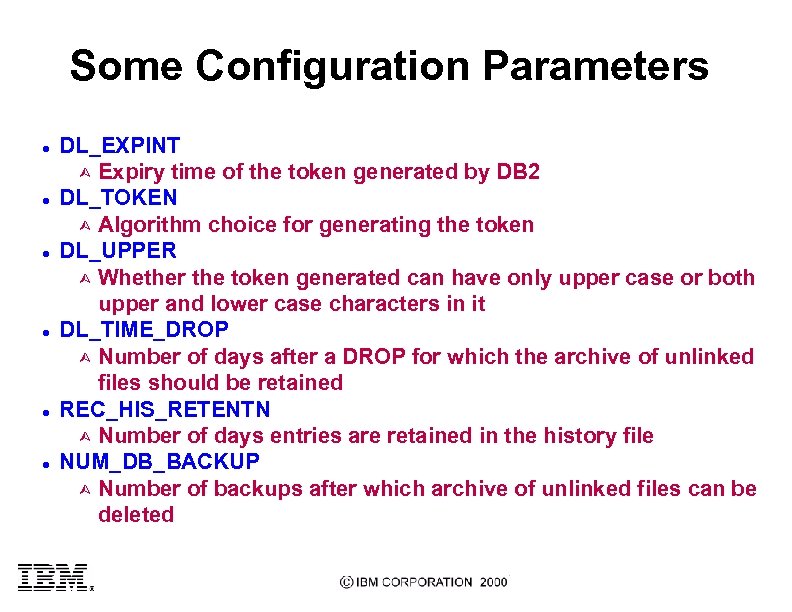
Some Configuration Parameters l l l DL_EXPINT Ù Expiry time of the token generated by DB 2 DL_TOKEN Ù Algorithm choice for generating the token DL_UPPER Ù Whether the token generated can have only upper case or both upper and lower case characters in it DL_TIME_DROP Ù Number of days after a DROP for which the archive of unlinked files should be retained REC_HIS_RETENTN Ù Number of days entries are retained in the history file NUM_DB_BACKUP Ù Number of backups after which archive of unlinked files can be deleted
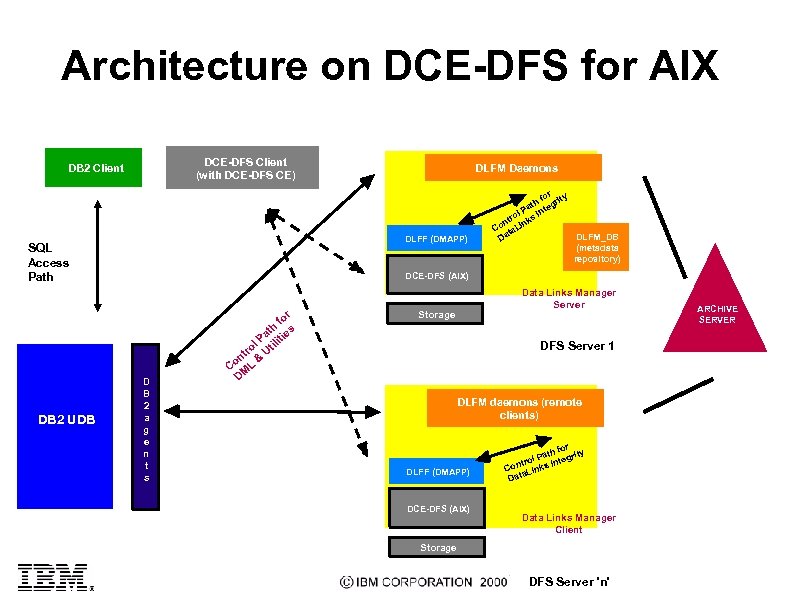
Architecture on DCE-DFS for AIX DCE-DFS Client (with DCE-DFS CE) DB 2 Client DLFF (DMAPP) SQL Access Path DB 2 UDB DLFM Daemons r fo rity ath teg l P In ro s nt ink Co ta. L DLFM_DB Da (metadata repository) DCE-DFS (AIX) D B 2 a g e n t s r fo h s at ie l P tilit ro U nt & Co ML D Data Links Manager Server Storage DFS Server 1 DLFM daemons (remote clients) DLFF (DMAPP) DCE-DFS (AIX) or y th f t l Pa ntegri ro ont inks I C a. L Data Links Manager Client Storage DFS Server 'n' ARCHIVE SERVER
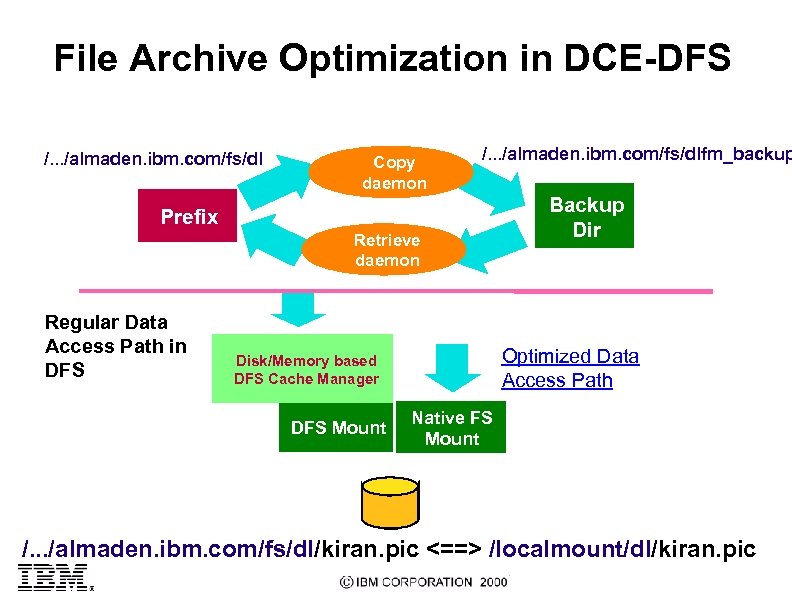
File Archive Optimization in DCE-DFS /. . . /almaden. ibm. com/fs/dl Copy daemon /. . . /almaden. ibm. com/fs/dlfm_backup Prefix Retrieve daemon Regular Data Access Path in DFS Optimized Data Access Path Disk/Memory based DFS Cache Manager DFS Mount Backup Dir Native FS Mount /. . . /almaden. ibm. com/fs/dl/kiran. pic <==> /localmount/dl/kiran. pic
5a80edfc176b432e4f3e3dccef81b9db.ppt