33a627655f8fb987117141fa666b41e0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Data Linkage Strategies Shihfen Tu, Ph. D. University of Maine shihfen. tu@umit. maine. edu 1
Data Linkage Strategies Shihfen Tu, Ph. D. University of Maine shihfen. tu@umit. maine. edu 1
 Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship with the manufacturer(s) of the product(s) or provider(s) of the service(s) that will be discussed in my presentation. This presentation will not include discussion of pharmaceuticals or devices that have not been approved by the FDA. 2
Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship with the manufacturer(s) of the product(s) or provider(s) of the service(s) that will be discussed in my presentation. This presentation will not include discussion of pharmaceuticals or devices that have not been approved by the FDA. 2
 Acknowledgements • University of Maine – Quansheng Song – Cecilia Cobo-Lewis • Maine Bureau of Health – Kim Church – Pat Day – Ellie Mulcahy – Toni Wall 3
Acknowledgements • University of Maine – Quansheng Song – Cecilia Cobo-Lewis • Maine Bureau of Health – Kim Church – Pat Day – Ellie Mulcahy – Toni Wall 3
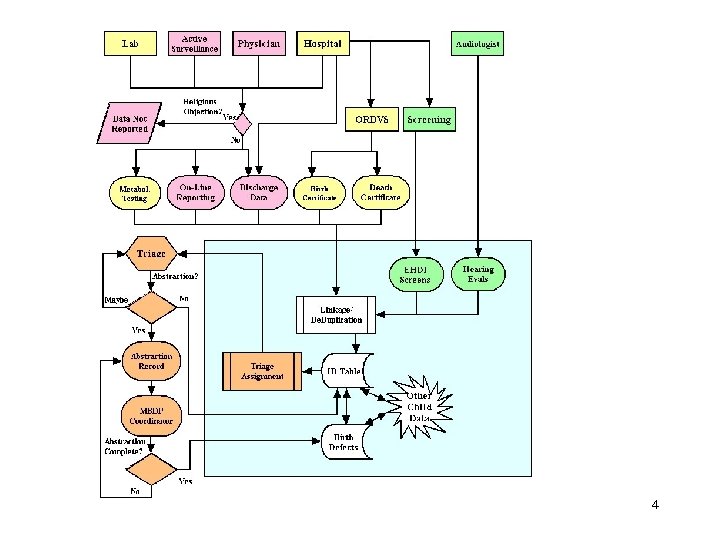 4
4
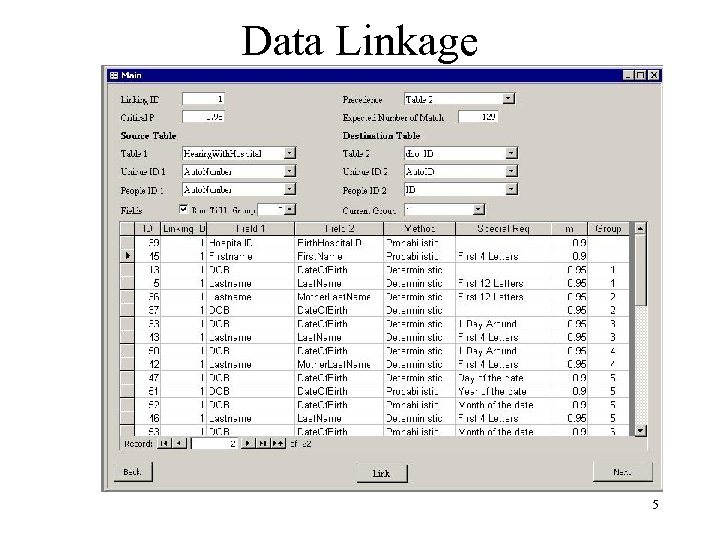 Data Linkage 5
Data Linkage 5
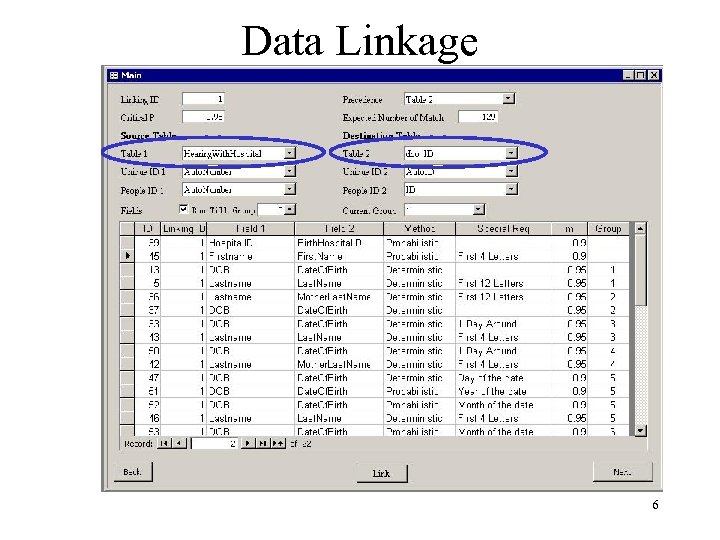 Data Linkage 6
Data Linkage 6
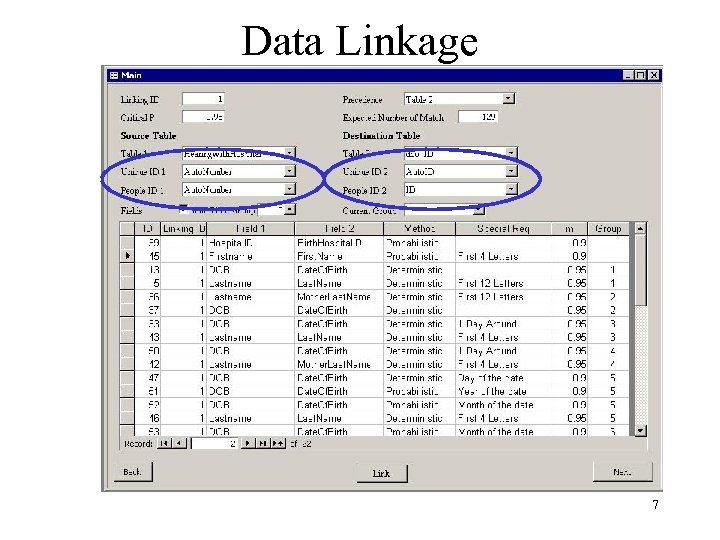 Data Linkage 7
Data Linkage 7
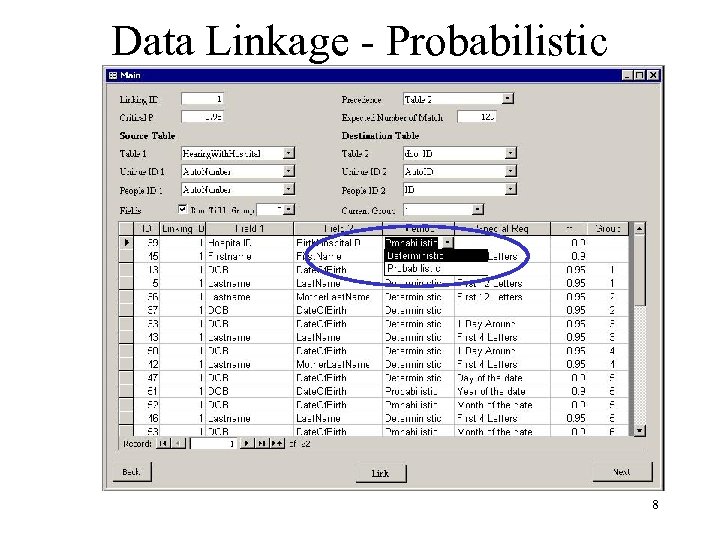 Data Linkage - Probabilistic 8
Data Linkage - Probabilistic 8
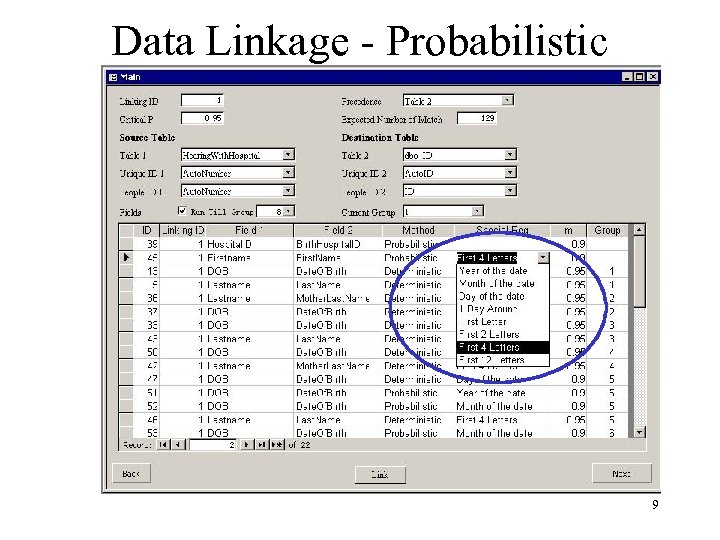 Data Linkage - Probabilistic 9
Data Linkage - Probabilistic 9
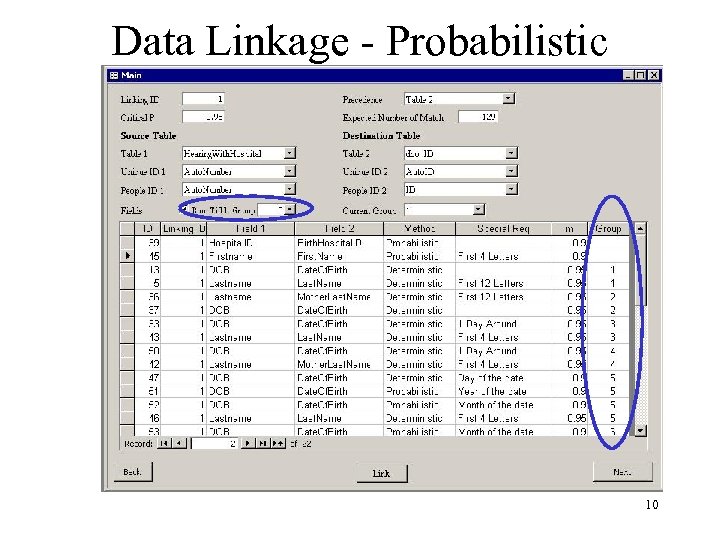 Data Linkage - Probabilistic 10
Data Linkage - Probabilistic 10
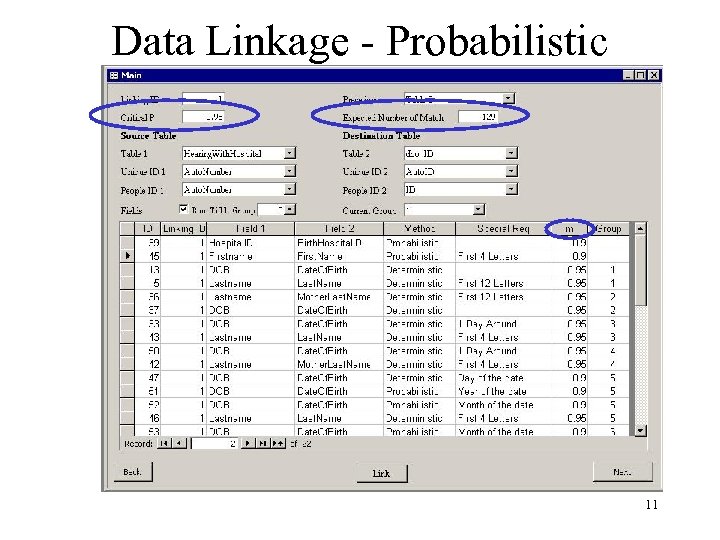 Data Linkage - Probabilistic 11
Data Linkage - Probabilistic 11
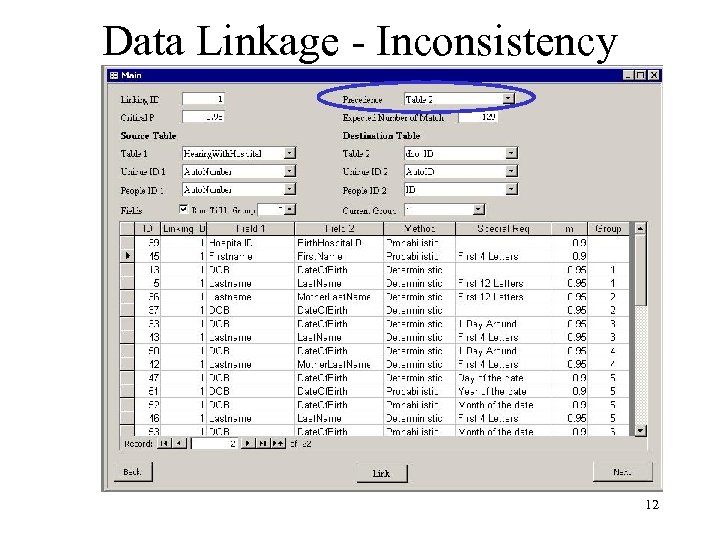 Data Linkage - Inconsistency 12
Data Linkage - Inconsistency 12
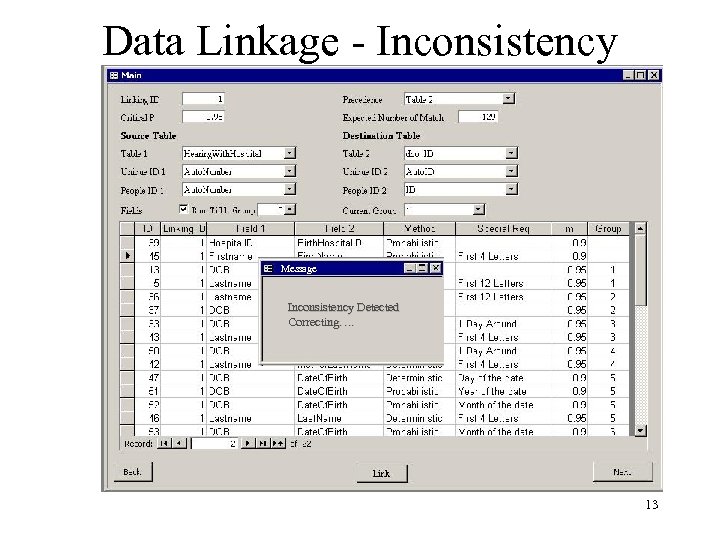 Data Linkage - Inconsistency Message Inconsistency Detected Correcting…. 13
Data Linkage - Inconsistency Message Inconsistency Detected Correcting…. 13
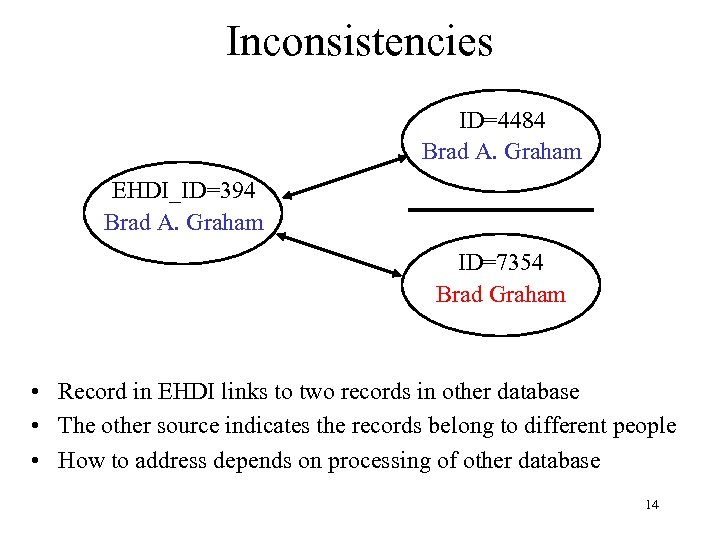 Inconsistencies ID=4484 Brad A. Graham EHDI_ID=394 Brad A. Graham ID=7354 Brad Graham • Record in EHDI links to two records in other database • The other source indicates the records belong to different people • How to address depends on processing of other database 14
Inconsistencies ID=4484 Brad A. Graham EHDI_ID=394 Brad A. Graham ID=7354 Brad Graham • Record in EHDI links to two records in other database • The other source indicates the records belong to different people • How to address depends on processing of other database 14
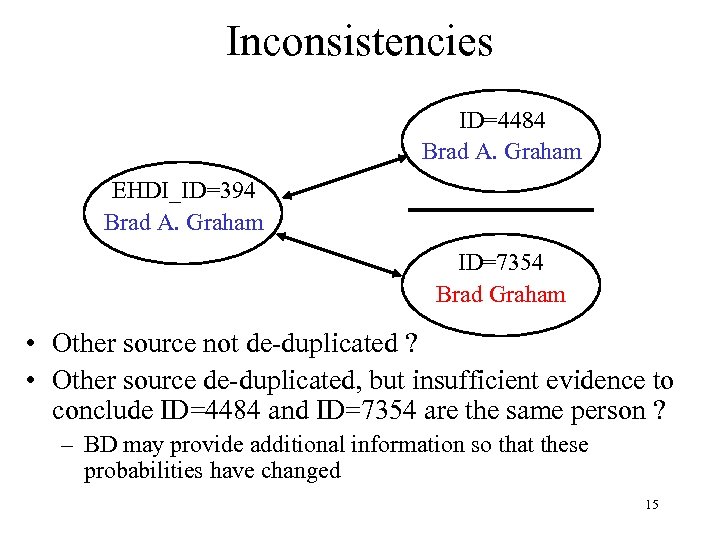 Inconsistencies ID=4484 Brad A. Graham EHDI_ID=394 Brad A. Graham ID=7354 Brad Graham • Other source not de-duplicated ? • Other source de-duplicated, but insufficient evidence to conclude ID=4484 and ID=7354 are the same person ? – BD may provide additional information so that these probabilities have changed 15
Inconsistencies ID=4484 Brad A. Graham EHDI_ID=394 Brad A. Graham ID=7354 Brad Graham • Other source not de-duplicated ? • Other source de-duplicated, but insufficient evidence to conclude ID=4484 and ID=7354 are the same person ? – BD may provide additional information so that these probabilities have changed 15
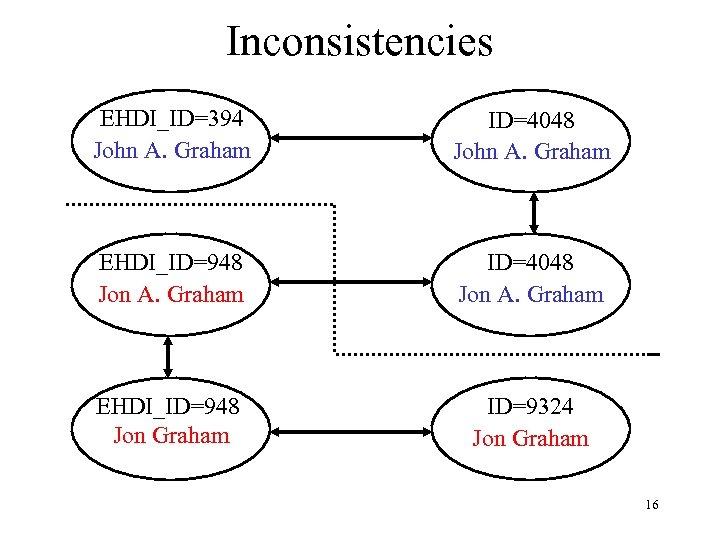 Inconsistencies EHDI_ID=394 John A. Graham ID=4048 John A. Graham EHDI_ID=948 Jon A. Graham ID=4048 Jon A. Graham EHDI_ID=948 Jon Graham ID=9324 Jon Graham 16
Inconsistencies EHDI_ID=394 John A. Graham ID=4048 John A. Graham EHDI_ID=948 Jon A. Graham ID=4048 Jon A. Graham EHDI_ID=948 Jon Graham ID=9324 Jon Graham 16
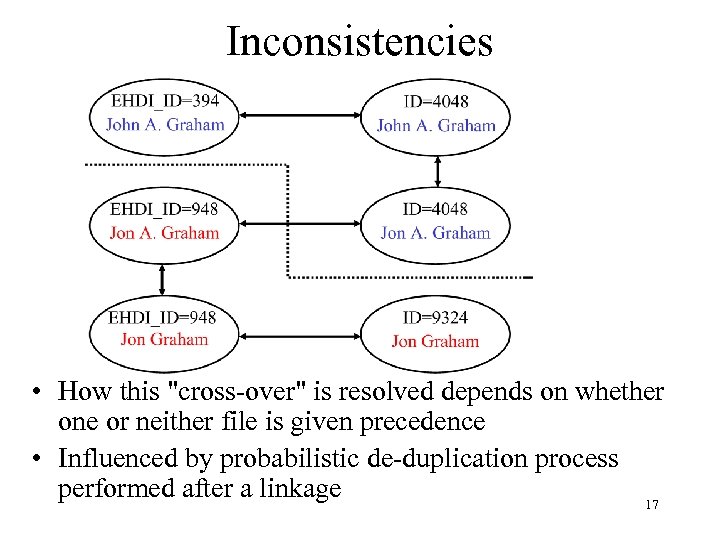 Inconsistencies • How this "cross-over" is resolved depends on whether one or neither file is given precedence • Influenced by probabilistic de-duplication process performed after a linkage 17
Inconsistencies • How this "cross-over" is resolved depends on whether one or neither file is given precedence • Influenced by probabilistic de-duplication process performed after a linkage 17
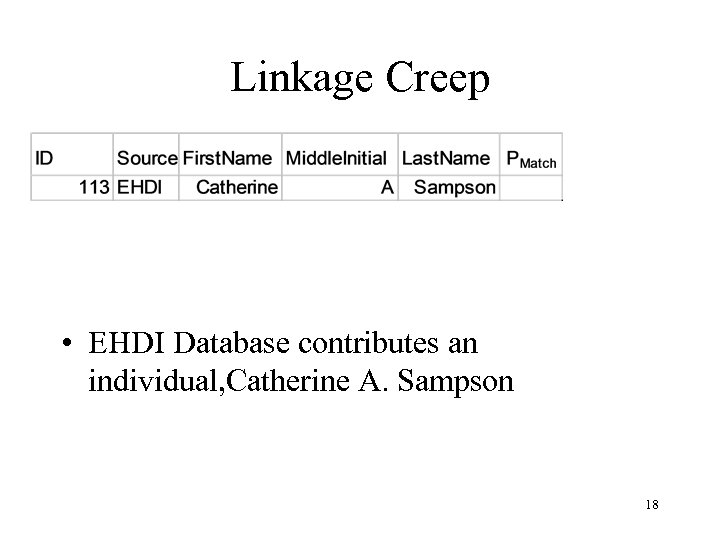 Linkage Creep • EHDI Database contributes an individual, Catherine A. Sampson 18
Linkage Creep • EHDI Database contributes an individual, Catherine A. Sampson 18
 Linkage Creep • Link the Electronic Birth Certificate – Name is Catherine A. Simpson – Are these the same person? – Perform probabilistic match • Require. 85 probability of a match to conclude two similar records are the same (Critical p =. 85) • Probability is. 90, we conclude they’re the same person 19
Linkage Creep • Link the Electronic Birth Certificate – Name is Catherine A. Simpson – Are these the same person? – Perform probabilistic match • Require. 85 probability of a match to conclude two similar records are the same (Critical p =. 85) • Probability is. 90, we conclude they’re the same person 19
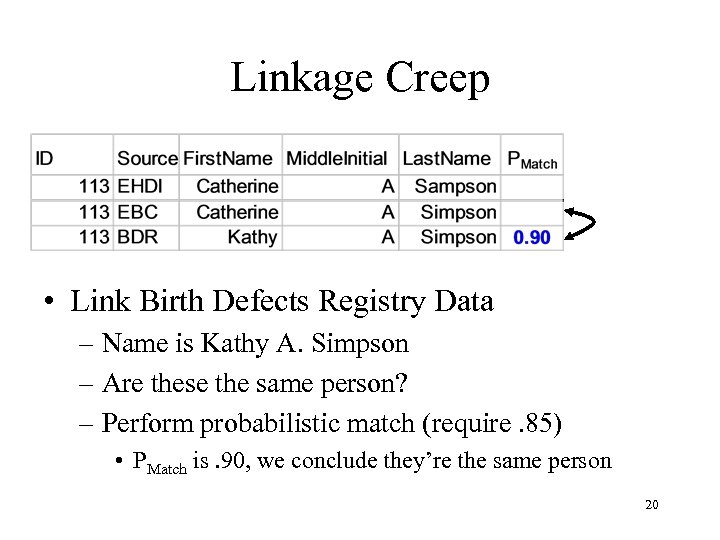 Linkage Creep • Link Birth Defects Registry Data – Name is Kathy A. Simpson – Are these the same person? – Perform probabilistic match (require. 85) • PMatch is. 90, we conclude they’re the same person 20
Linkage Creep • Link Birth Defects Registry Data – Name is Kathy A. Simpson – Are these the same person? – Perform probabilistic match (require. 85) • PMatch is. 90, we conclude they’re the same person 20
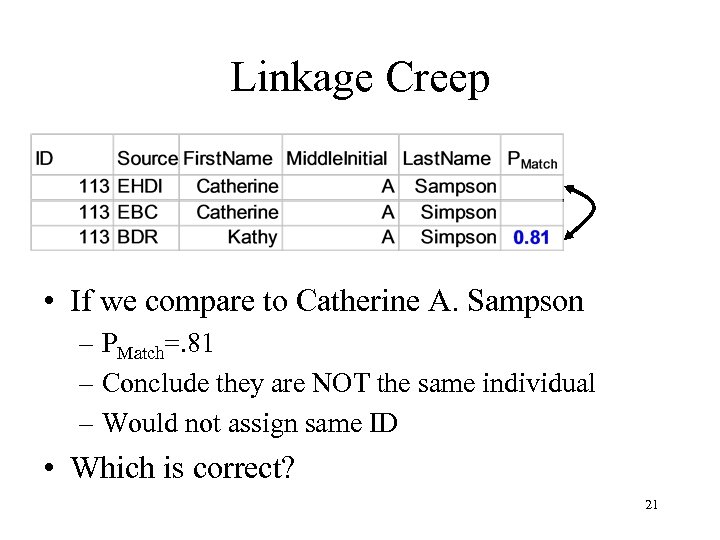 Linkage Creep • If we compare to Catherine A. Sampson – PMatch=. 81 – Conclude they are NOT the same individual – Would not assign same ID • Which is correct? 21
Linkage Creep • If we compare to Catherine A. Sampson – PMatch=. 81 – Conclude they are NOT the same individual – Would not assign same ID • Which is correct? 21
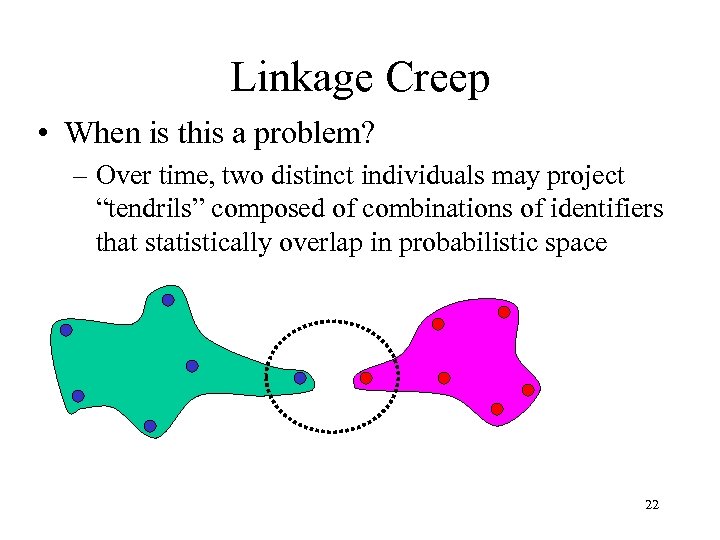 Linkage Creep • When is this a problem? – Over time, two distinct individuals may project “tendrils” composed of combinations of identifiers that statistically overlap in probabilistic space 22
Linkage Creep • When is this a problem? – Over time, two distinct individuals may project “tendrils” composed of combinations of identifiers that statistically overlap in probabilistic space 22
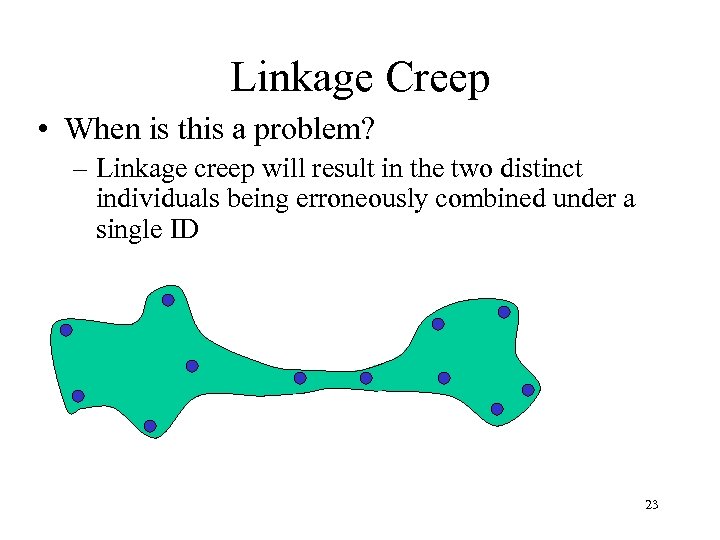 Linkage Creep • When is this a problem? – Linkage creep will result in the two distinct individuals being erroneously combined under a single ID 23
Linkage Creep • When is this a problem? – Linkage creep will result in the two distinct individuals being erroneously combined under a single ID 23
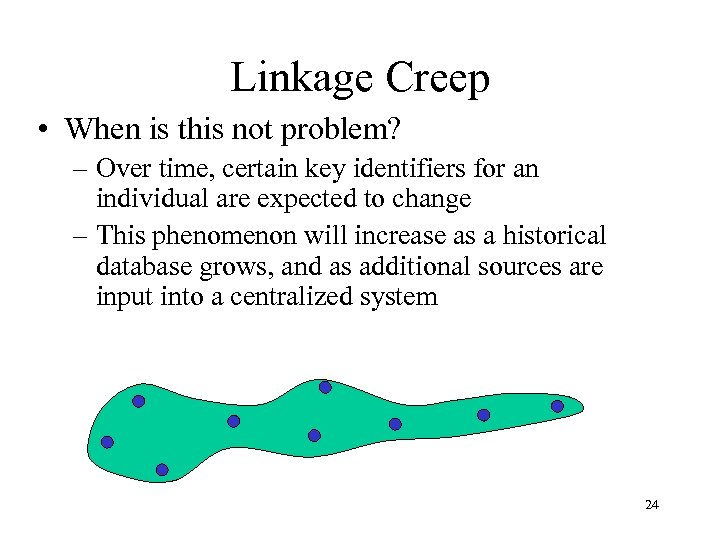 Linkage Creep • When is this not problem? – Over time, certain key identifiers for an individual are expected to change – This phenomenon will increase as a historical database grows, and as additional sources are input into a centralized system 24
Linkage Creep • When is this not problem? – Over time, certain key identifiers for an individual are expected to change – This phenomenon will increase as a historical database grows, and as additional sources are input into a centralized system 24
 Linkage Creep • Complexity of “creep” in longitudinal datasets – Black records are related to all records – Yellow and Blue records are NOT related to White record – Yellow record is also not related to Red record at 25
Linkage Creep • Complexity of “creep” in longitudinal datasets – Black records are related to all records – Yellow and Blue records are NOT related to White record – Yellow record is also not related to Red record at 25
 Linkage Creep • Forbidding “creep” will result in a single individual being divided into two IDs over time • Further challenge—where to divide records into additional IDs? 26
Linkage Creep • Forbidding “creep” will result in a single individual being divided into two IDs over time • Further challenge—where to divide records into additional IDs? 26
 Tools for Evaluating Linkage • Inconsistencies can occur in deterministic linkage, but are more common in probabilistic linkages • Probabilities that create potential for problems provide a valuable tool for evaluating linkages – Instead of a “are two records the same person ? ” Yes/No – Estimates or indices of how likely it is that two records are the same person • Should be able to estimate the number of erroneous linkages • Possible to conduct a detailed examination of quality by ignoring very strong and very weak pairings, and only focusing on pairings that are ambiguous 27
Tools for Evaluating Linkage • Inconsistencies can occur in deterministic linkage, but are more common in probabilistic linkages • Probabilities that create potential for problems provide a valuable tool for evaluating linkages – Instead of a “are two records the same person ? ” Yes/No – Estimates or indices of how likely it is that two records are the same person • Should be able to estimate the number of erroneous linkages • Possible to conduct a detailed examination of quality by ignoring very strong and very weak pairings, and only focusing on pairings that are ambiguous 27


