2d8bd0adb9fe6de24913f7f7abb942cc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 Data Grid Management Systems (DGMS) Arun Jagatheesan Arcot Rajasekar {arun, sekar}@sdsc. edu San Diego Supercomputer Center University of California, San Diego ACM SIGMOD Tutorial June 11, 2003 San Diego National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure University of Florida San Diego Supercomputer Center
Data Grid Management Systems (DGMS) Arun Jagatheesan Arcot Rajasekar {arun, sekar}@sdsc. edu San Diego Supercomputer Center University of California, San Diego ACM SIGMOD Tutorial June 11, 2003 San Diego National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure University of Florida San Diego Supercomputer Center
 Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II (Research Rubber hits the Road) • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II (Research Rubber hits the Road) • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Distributed Computing © Images courtesy of Computer History Museum National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Distributed Computing © Images courtesy of Computer History Museum National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Distributed Computing • ARPANET's goals : • <“quote> direct use of distributed hardware services; • direct retrieval from remote, one-of-a-kind databases; • and the sharing of software subroutines and packages not available on the users' primary computer due to incompatibility of hardware or languages. The Question: How to share (or use) physically distributed hardware and software seamlessly National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Distributed Computing • ARPANET's goals : • <“quote> direct use of distributed hardware services; • direct retrieval from remote, one-of-a-kind databases; • and the sharing of software subroutines and packages not available on the users' primary computer due to incompatibility of hardware or languages. The Question: How to share (or use) physically distributed hardware and software seamlessly National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Grid Computing • Computing and Storage Resources Ubiquitous • Small organizations also have lot of resources • Pull together ‘distributed-ly owned’ resources = grid • Coordinated resource sharing • Autonomous organizations join forces - Virtual Enterprise • Web = coordinated way of disseminate information; Grid = coordinated way to share computing, information storage resources and other devices National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Grid Computing • Computing and Storage Resources Ubiquitous • Small organizations also have lot of resources • Pull together ‘distributed-ly owned’ resources = grid • Coordinated resource sharing • Autonomous organizations join forces - Virtual Enterprise • Web = coordinated way of disseminate information; Grid = coordinated way to share computing, information storage resources and other devices National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Grid as Utility Computing National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Grid as Utility Computing National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Computing Grid Computing • The famous power grid analogy: • Computing and storage power can originate any where. • Plug-n-play-n-power up in the grid • Web required standard protocols like HTTP to provide coordinated and ease of information dissemination. • Grid for coordinated sharing of resources, requires standard means to advertise, discover, authorize, authenticate, access and manage inter-organizational communities that can join or leave a grid in a seamless manner National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Computing Grid Computing • The famous power grid analogy: • Computing and storage power can originate any where. • Plug-n-play-n-power up in the grid • Web required standard protocols like HTTP to provide coordinated and ease of information dissemination. • Grid for coordinated sharing of resources, requires standard means to advertise, discover, authorize, authenticate, access and manage inter-organizational communities that can join or leave a grid in a seamless manner National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 What is a Grid? Three point check-list for a grid: • “Coordinates resources that are not subject to centralized control • Uses standard, open, general-purpose protocols and interfaces • Delivers non-trivial qualities of service. ” Ian Foster, ANL Coordinated resource sharing and problem solving in dynamic, multi-institutional virtual organizations National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
What is a Grid? Three point check-list for a grid: • “Coordinates resources that are not subject to centralized control • Uses standard, open, general-purpose protocols and interfaces • Delivers non-trivial qualities of service. ” Ian Foster, ANL Coordinated resource sharing and problem solving in dynamic, multi-institutional virtual organizations National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Data Grids • A datagrid is a dynamic logical name space of global identifiers consisting of digital entities and information storage resources shared in coordination across administrative domains • Data Grid • Coordinated sharing of information storage • Dissemination of resources: data, services and storage • Requires multiple abstraction and transparency mechanisms • Computing grid and the datagrid part of the Grid. • Just different research camps National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 San Diego Supercomputer Center
Data Grids • A datagrid is a dynamic logical name space of global identifiers consisting of digital entities and information storage resources shared in coordination across administrative domains • Data Grid • Coordinated sharing of information storage • Dissemination of resources: data, services and storage • Requires multiple abstraction and transparency mechanisms • Computing grid and the datagrid part of the Grid. • Just different research camps National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 San Diego Supercomputer Center
 Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing Is it required some • Proliferation of Data Grids where? Or we just trying to find a • Data Grid Concepts problem for the answer • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing Is it required some • Proliferation of Data Grids where? Or we just trying to find a • Data Grid Concepts problem for the answer • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 NSF Gri. Phy. N/i. VDGL • Petabyte scale Virtual Data Grids • Gri. Phy. N/i. VDGL/PPDG – Trillium • Grid Physics Network • International Virtual Data Grid Laboratory • Particle Physics Data Grid • Enable groups of scientists distributed worldwide to harness Petascale processing, communication, and data resources • Data. TAG – Transatlantic with European Side National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
NSF Gri. Phy. N/i. VDGL • Petabyte scale Virtual Data Grids • Gri. Phy. N/i. VDGL/PPDG – Trillium • Grid Physics Network • International Virtual Data Grid Laboratory • Particle Physics Data Grid • Enable groups of scientists distributed worldwide to harness Petascale processing, communication, and data resources • Data. TAG – Transatlantic with European Side National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 US-i. VDGL Sites (Late Spring 2003) SKC LBL Wisconsin Michigan PSU Fermilab Argonne Indiana Caltech Oklahoma Vanderbilt UCSD/SDSC FSU Arlington Brownsville Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3 Boston U J. Hopkins Hampton Partners? u. EU u. CERN u. Brazil UF u. Australia u. Korea FIU u. Japan National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 BNL
US-i. VDGL Sites (Late Spring 2003) SKC LBL Wisconsin Michigan PSU Fermilab Argonne Indiana Caltech Oklahoma Vanderbilt UCSD/SDSC FSU Arlington Brownsville Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3 Boston U J. Hopkins Hampton Partners? u. EU u. CERN u. Brazil UF u. Australia u. Korea FIU u. Japan National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 BNL
 Tera Grid • Launched in August 2001 • SDSC, NCSA, ANL, CACR, PSC • 20 Tera flops of computing power • One peta byte of storage • Connected through 40 gigabits per second network (FASTEST network on planet) • “Building the Computational Infrastructure for Tomorrow's Scientific Discovery” National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tera Grid • Launched in August 2001 • SDSC, NCSA, ANL, CACR, PSC • 20 Tera flops of computing power • One peta byte of storage • Connected through 40 gigabits per second network (FASTEST network on planet) • “Building the Computational Infrastructure for Tomorrow's Scientific Discovery” National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 European Datagrid • European Union • Different Communities • High Energy Physics • Biology • Earth Science • Collaborate and complement other European and US projects National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
European Datagrid • European Union • Different Communities • High Energy Physics • Biology • Earth Science • Collaborate and complement other European and US projects National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 NIH BIRN • Biomedical Informatics Research Network • Access and analyze data at a variety of levels of aggregation • Data resources located at diverse sites throughout the country • A stable high performance grid based environment • Coordinate sharing of virtual data collections and data mining • Growing fast! National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
NIH BIRN • Biomedical Informatics Research Network • Access and analyze data at a variety of levels of aggregation • Data resources located at diverse sites throughout the country • A stable high performance grid based environment • Coordinate sharing of virtual data collections and data mining • Growing fast! National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
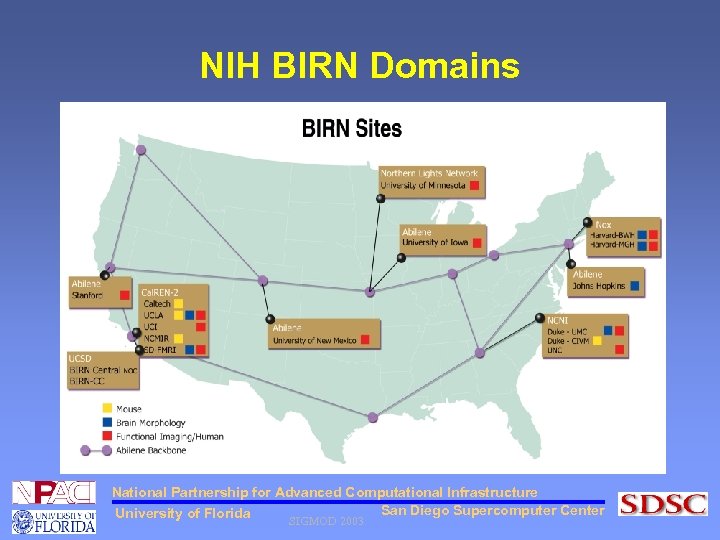 NIH BIRN Domains National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
NIH BIRN Domains National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 PRAGMA • Pacific Rim institutions collaborate to • Develop grid-enabled applications • Deploy the needed infrastructure • Allow data, computing, and other resource sharing • Multiple collaborators • Australia, China, India, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, Singapore, US … National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
PRAGMA • Pacific Rim institutions collaborate to • Develop grid-enabled applications • Deploy the needed infrastructure • Allow data, computing, and other resource sharing • Multiple collaborators • Australia, China, India, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, Singapore, US … National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Commonality in all these projects • Require collaborative and coordinated sharing • Resources (computing, data, storage, services and man power) • Seamless and coordinated access • multiple resources shared across multiple organizations • As data or information storage experts: • what is the state-of-art and standards in our domain to manage coordinated sharing of information and storage resources across multi-organizational collaborations? … • (Are we re-inventing data mediation/integration – Nope!) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Commonality in all these projects • Require collaborative and coordinated sharing • Resources (computing, data, storage, services and man power) • Seamless and coordinated access • multiple resources shared across multiple organizations • As data or information storage experts: • what is the state-of-art and standards in our domain to manage coordinated sharing of information and storage resources across multi-organizational collaborations? … • (Are we re-inventing data mediation/integration – Nope!) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
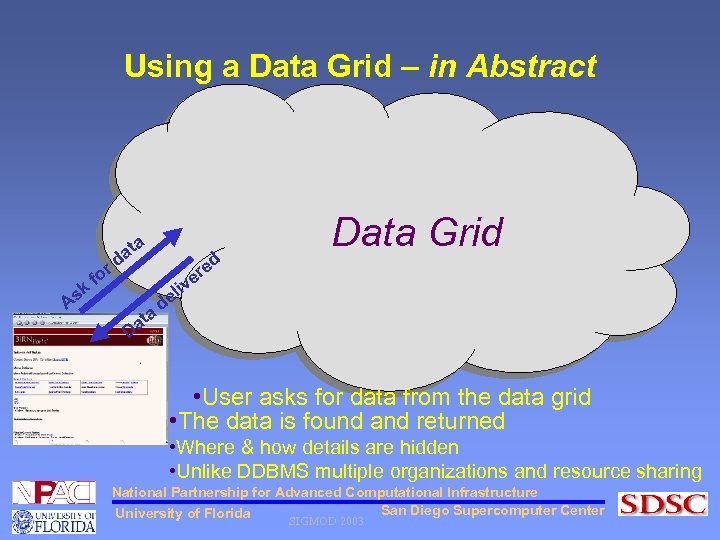 Using a Data Grid – in Abstract a sk A fo t da r d Data Grid e er v a t Da i el d • User asks for data from the data grid • The data is found and returned • Where & how details are hidden • Unlike DDBMS multiple organizations and resource sharing National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Using a Data Grid – in Abstract a sk A fo t da r d Data Grid e er v a t Da i el d • User asks for data from the data grid • The data is found and returned • Where & how details are hidden • Unlike DDBMS multiple organizations and resource sharing National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Data Grid Transparencies • Distributed information storage management • Requires transparencies and abstractions • Hide heterogeneity in storage devices, data formats, data access protocols, data location, data owner, grid community etc. , • Transparencies • Logical layers (not necessarily in a order) • Logical usage of data & behavior physically present on datagrid • Some RDBMS concepts stolen – thanks for 30+ years of R&D National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 San Diego Supercomputer Center
Data Grid Transparencies • Distributed information storage management • Requires transparencies and abstractions • Hide heterogeneity in storage devices, data formats, data access protocols, data location, data owner, grid community etc. , • Transparencies • Logical layers (not necessarily in a order) • Logical usage of data & behavior physically present on datagrid • Some RDBMS concepts stolen – thanks for 30+ years of R&D National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 San Diego Supercomputer Center
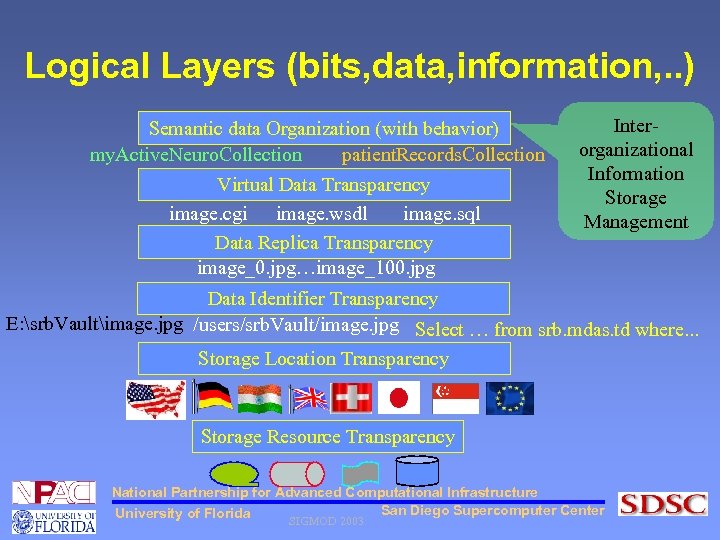 Logical Layers (bits, data, information, . . ) Semantic data Organization (with behavior) my. Active. Neuro. Collection patient. Records. Collection Virtual Data Transparency image. cgi image. wsdl image. sql Data Replica Transparency image_0. jpg…image_100. jpg Interorganizational Information Storage Management Data Identifier Transparency E: srb. Vaultimage. jpg /users/srb. Vault/image. jpg Select … from srb. mdas. td where. . . Storage Location Transparency Storage Resource Transparency National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Logical Layers (bits, data, information, . . ) Semantic data Organization (with behavior) my. Active. Neuro. Collection patient. Records. Collection Virtual Data Transparency image. cgi image. wsdl image. sql Data Replica Transparency image_0. jpg…image_100. jpg Interorganizational Information Storage Management Data Identifier Transparency E: srb. Vaultimage. jpg /users/srb. Vault/image. jpg Select … from srb. mdas. td where. . . Storage Location Transparency Storage Resource Transparency National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Storage Resource Transparency • Any storage resource • Archival systems, file systems, databases, FTP sites, … • Logical resources • Hide type and protocol of physical storage devices • Could be a combination of physical resources (e. g) an archival system along with a disk cache • User aware of logical resource names • Flexible to changes in the storage technology • “Be prepared” – optical mass storage is coming up • Software to handle data for 400+ years (Library of Congress) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Storage Resource Transparency • Any storage resource • Archival systems, file systems, databases, FTP sites, … • Logical resources • Hide type and protocol of physical storage devices • Could be a combination of physical resources (e. g) an archival system along with a disk cache • User aware of logical resource names • Flexible to changes in the storage technology • “Be prepared” – optical mass storage is coming up • Software to handle data for 400+ years (Library of Congress) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
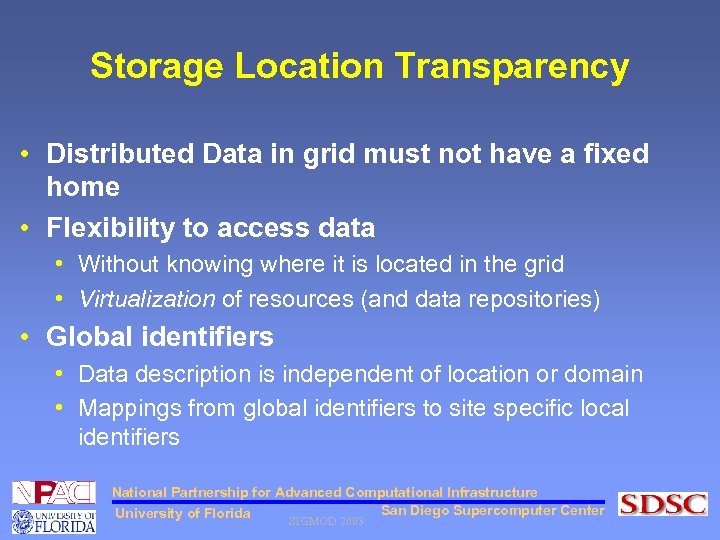 Storage Location Transparency • Distributed Data in grid must not have a fixed home • Flexibility to access data • Without knowing where it is located in the grid • Virtualization of resources (and data repositories) • Global identifiers • Data description is independent of location or domain • Mappings from global identifiers to site specific local identifiers National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Storage Location Transparency • Distributed Data in grid must not have a fixed home • Flexibility to access data • Without knowing where it is located in the grid • Virtualization of resources (and data repositories) • Global identifiers • Data description is independent of location or domain • Mappings from global identifiers to site specific local identifiers National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Data Identifier Transparency • Global identifiers might not be sufficient in datagrid • Data Identifier Transparency or Naming Transparency • Facilitate accessing data without knowing its identifier in grid • Data Access using attributes (meta-data) • Qualify the required data (Semantic Data? ) • Google-Like access • Dynamic discovery of data National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Data Identifier Transparency • Global identifiers might not be sufficient in datagrid • Data Identifier Transparency or Naming Transparency • Facilitate accessing data without knowing its identifier in grid • Data Access using attributes (meta-data) • Qualify the required data (Semantic Data? ) • Google-Like access • Dynamic discovery of data National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
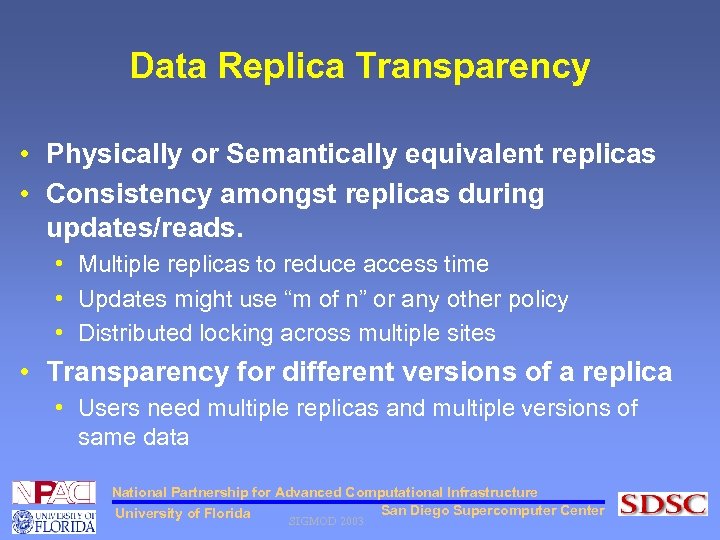 Data Replica Transparency • Physically or Semantically equivalent replicas • Consistency amongst replicas during updates/reads. • Multiple replicas to reduce access time • Updates might use “m of n” or any other policy • Distributed locking across multiple sites • Transparency for different versions of a replica • Users need multiple replicas and multiple versions of same data National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Data Replica Transparency • Physically or Semantically equivalent replicas • Consistency amongst replicas during updates/reads. • Multiple replicas to reduce access time • Updates might use “m of n” or any other policy • Distributed locking across multiple sites • Transparency for different versions of a replica • Users need multiple replicas and multiple versions of same data National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
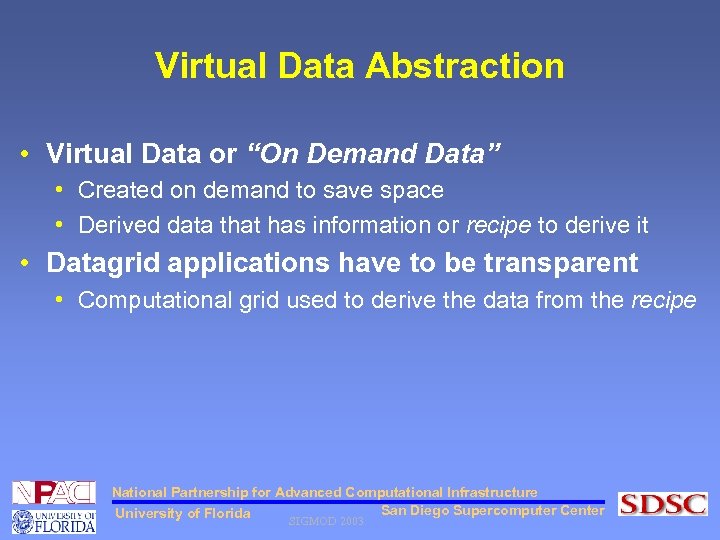 Virtual Data Abstraction • Virtual Data or “On Demand Data” • Created on demand to save space • Derived data that has information or recipe to derive it • Datagrid applications have to be transparent • Computational grid used to derive the data from the recipe National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Virtual Data Abstraction • Virtual Data or “On Demand Data” • Created on demand to save space • Derived data that has information or recipe to derive it • Datagrid applications have to be transparent • Computational grid used to derive the data from the recipe National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Data Organization • Physical Organization • Distributed Data • Heterogeneous resources • Multiple formats (structured and unstructured) • Logical Organization • Viewed as collections of semantically relevant or related data • Users create their own views (collections) of the data in the grid National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Data Organization • Physical Organization • Distributed Data • Heterogeneous resources • Multiple formats (structured and unstructured) • Logical Organization • Viewed as collections of semantically relevant or related data • Users create their own views (collections) of the data in the grid National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
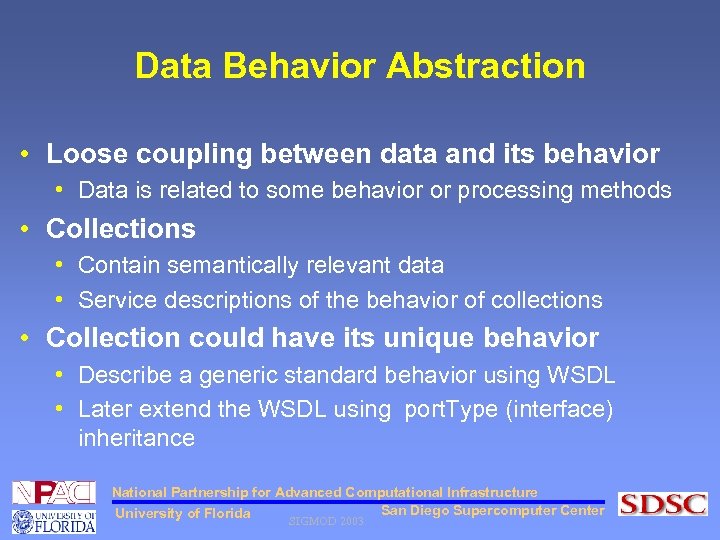 Data Behavior Abstraction • Loose coupling between data and its behavior • Data is related to some behavior or processing methods • Collections • Contain semantically relevant data • Service descriptions of the behavior of collections • Collection could have its unique behavior • Describe a generic standard behavior using WSDL • Later extend the WSDL using port. Type (interface) inheritance National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Data Behavior Abstraction • Loose coupling between data and its behavior • Data is related to some behavior or processing methods • Collections • Contain semantically relevant data • Service descriptions of the behavior of collections • Collection could have its unique behavior • Describe a generic standard behavior using WSDL • Later extend the WSDL using port. Type (interface) inheritance National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 DGMS Philosophy • Collective view of • Inter-organizational data • Operations on datagrid space • Local autonomy and global state consistency • Self-organizing collaborative datagrid communities • Self-describing and self-manipulating data • Horizontal and vertical behavior • Loose coupling between data and behavior (dynamically) • Referential integrities between a digital entity and its Physical locations, Logical names, Meta-data, Access National Partnership for control, Behavior Advanced Computational Infrastructure Center San Diego Supercomputer University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
DGMS Philosophy • Collective view of • Inter-organizational data • Operations on datagrid space • Local autonomy and global state consistency • Self-organizing collaborative datagrid communities • Self-describing and self-manipulating data • Horizontal and vertical behavior • Loose coupling between data and behavior (dynamically) • Referential integrities between a digital entity and its Physical locations, Logical names, Meta-data, Access National Partnership for control, Behavior Advanced Computational Infrastructure Center San Diego Supercomputer University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
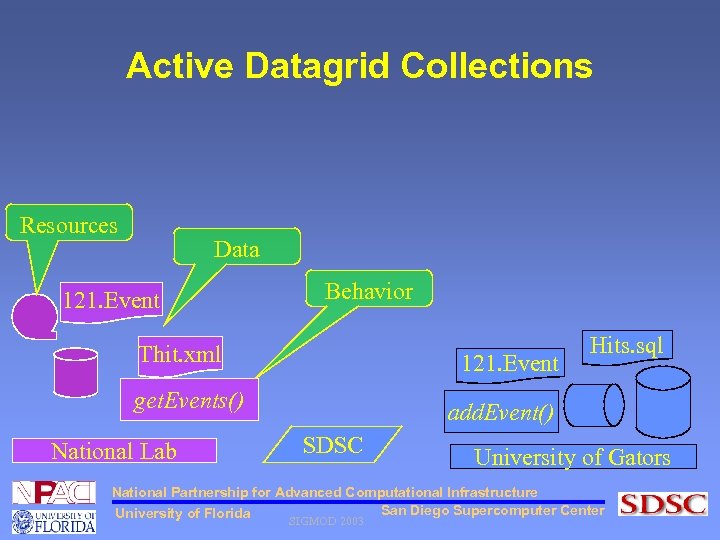 Active Datagrid Collections Resources Data 121. Event Behavior Thit. xml 121. Event get. Events() National Lab Hits. sql add. Event() SDSC University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Active Datagrid Collections Resources Data 121. Event Behavior Thit. xml 121. Event get. Events() National Lab Hits. sql add. Event() SDSC University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
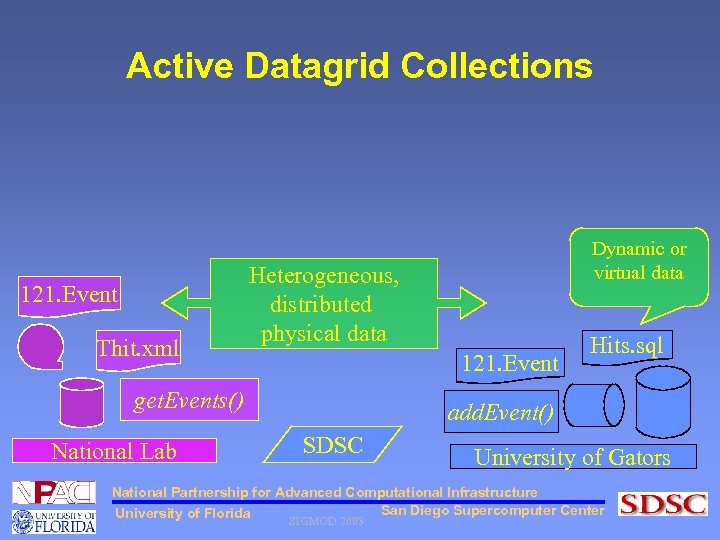 Active Datagrid Collections 121. Event Thit. xml Heterogeneous, distributed physical data 121. Event get. Events() National Lab Dynamic or virtual data Hits. sql add. Event() SDSC University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Active Datagrid Collections 121. Event Thit. xml Heterogeneous, distributed physical data 121. Event get. Events() National Lab Dynamic or virtual data Hits. sql add. Event() SDSC University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
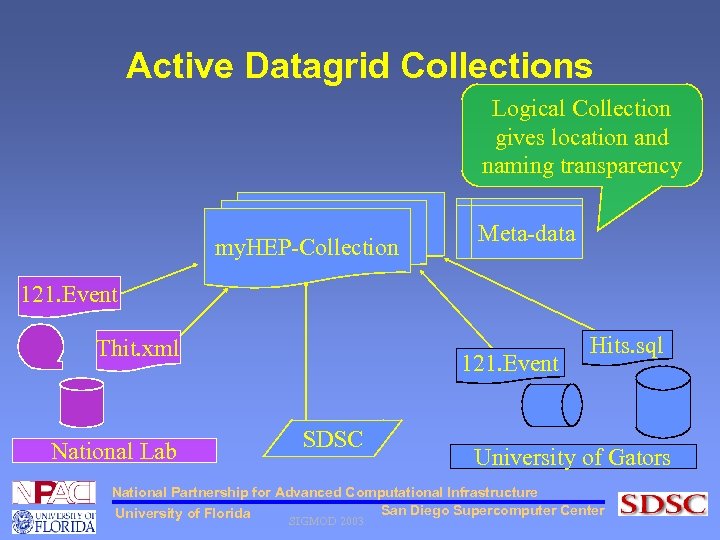 Active Datagrid Collections Logical Collection gives location and naming transparency my. HEP-Collection Meta-data 121. Event Thit. xml National Lab 121. Event SDSC Hits. sql University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Active Datagrid Collections Logical Collection gives location and naming transparency my. HEP-Collection Meta-data 121. Event Thit. xml National Lab 121. Event SDSC Hits. sql University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Active Datagrid Collections Now add behavior or services to this logical collection Collection state and services my. HEP-Collection Meta-data Horizontal Services 121. Event Thit. xml 121. Event get. Events() National Lab Hits. sql add. Event() SDSC University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Active Datagrid Collections Now add behavior or services to this logical collection Collection state and services my. HEP-Collection Meta-data Horizontal Services 121. Event Thit. xml 121. Event get. Events() National Lab Hits. sql add. Event() SDSC University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Active Datagrid Collections ADC Logical view of data & operations ADC specific Operations + Model View Controllers Collection state and services my. HEP-Collection Meta-data Horizontal Services 121. Event Thit. xml 121. Event get. Events() National Lab Hits. sql add. Event() SDSC University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Active Datagrid Collections ADC Logical view of data & operations ADC specific Operations + Model View Controllers Collection state and services my. HEP-Collection Meta-data Horizontal Services 121. Event Thit. xml 121. Event get. Events() National Lab Hits. sql add. Event() SDSC University of Gators National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
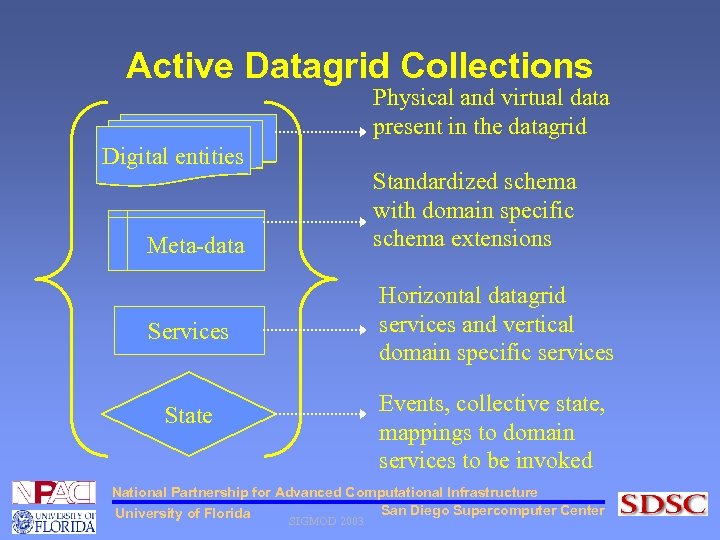 Active Datagrid Collections Physical and virtual data present in the datagrid Digital entities Standardized schema with domain specific schema extensions Meta-data Horizontal datagrid services and vertical domain specific services Services Events, collective state, mappings to domain services to be invoked State National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Active Datagrid Collections Physical and virtual data present in the datagrid Digital entities Standardized schema with domain specific schema extensions Meta-data Horizontal datagrid services and vertical domain specific services Services Events, collective state, mappings to domain services to be invoked State National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Active Datagrid Collections • Logical set consisting of related digital entities and references to their collective behavior for self-organization and manipulation of the data. • Basic unit or data model managed in DGMS Collections facilitate the transparencies and abstractions required to manage data in grids and inter-organizational enterprises National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Active Datagrid Collections • Logical set consisting of related digital entities and references to their collective behavior for self-organization and manipulation of the data. • Basic unit or data model managed in DGMS Collections facilitate the transparencies and abstractions required to manage data in grids and inter-organizational enterprises National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Datagrid Communities • Coordinated confluence of organizations • Inter-organizational datagrid communities or Virtual Enterprises • An organization could be in multiple communities • Datagrid communities share logical namespace of • Inter-organizational data described using Active Datagrid Collections • Storage Space National • Services Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure Center San Diego Supercomputer University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Datagrid Communities • Coordinated confluence of organizations • Inter-organizational datagrid communities or Virtual Enterprises • An organization could be in multiple communities • Datagrid communities share logical namespace of • Inter-organizational data described using Active Datagrid Collections • Storage Space National • Services Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure Center San Diego Supercomputer University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
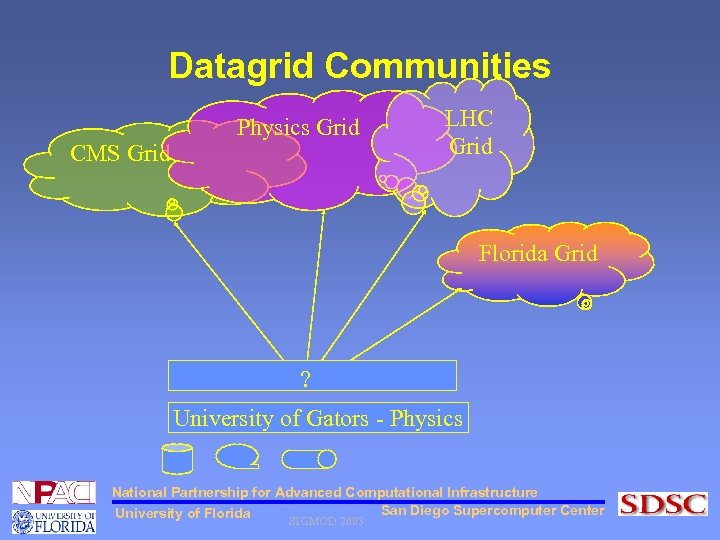 Datagrid Communities CMS Grid Physics Grid LHC Grid Florida Grid ? University of Gators - Physics National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Datagrid Communities CMS Grid Physics Grid LHC Grid Florida Grid ? University of Gators - Physics National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Datagrid Communities • Each organization needs a system to • Join or leave in one or more datagrid communities dynamically • Disseminate its own inter-organizational data in the grid • Discover and use data from other datagrid communities • Coordinate its local policies with policies of each datagrid community to share resources Yes, it is DGMS. But, please wait till we introduce it officially the next slide National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Datagrid Communities • Each organization needs a system to • Join or leave in one or more datagrid communities dynamically • Disseminate its own inter-organizational data in the grid • Discover and use data from other datagrid communities • Coordinate its local policies with policies of each datagrid community to share resources Yes, it is DGMS. But, please wait till we introduce it officially the next slide National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 DGMS • Datagrid Management System consists of a set of services (protocols) and a hierarchical framework for: • Confluence of datagrid communities • Coordinated sharing of inter-organizational information storage space and active datagrid collections • DGMS manages • • State information of the datagrid collections (data) Knowledge of events, rules and services (behavior) Collaborative communities (users and their resources) Differs from DDBMS in that it manages “communityowned” unstructured data along with behavior and interorganizational resources. Computational Infrastructure National Partnership for Advanced University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 San Diego Supercomputer Center
DGMS • Datagrid Management System consists of a set of services (protocols) and a hierarchical framework for: • Confluence of datagrid communities • Coordinated sharing of inter-organizational information storage space and active datagrid collections • DGMS manages • • State information of the datagrid collections (data) Knowledge of events, rules and services (behavior) Collaborative communities (users and their resources) Differs from DDBMS in that it manages “communityowned” unstructured data along with behavior and interorganizational resources. Computational Infrastructure National Partnership for Advanced University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 San Diego Supercomputer Center
 Datagrid Broker • A datagrid broker acts as an agent for an administrative domain in a DGMS framework. • Datagrid communities • formed by confluence of datagrid brokers • Peer 2 peer network of brokers resulting in DGMS • Datagrid brokers facilitate • sharing of services and data as components of active datagrid collections in the datagrid. • Ensure the users in its domain are benefited by participating in datagrid communities. National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Datagrid Broker • A datagrid broker acts as an agent for an administrative domain in a DGMS framework. • Datagrid communities • formed by confluence of datagrid brokers • Peer 2 peer network of brokers resulting in DGMS • Datagrid brokers facilitate • sharing of services and data as components of active datagrid collections in the datagrid. • Ensure the users in its domain are benefited by participating in datagrid communities. National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
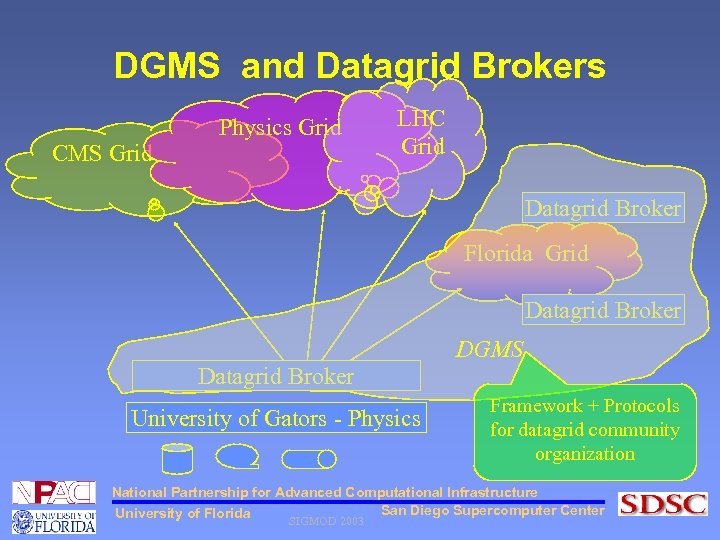 DGMS and Datagrid Brokers CMS Grid Physics Grid LHC Grid Datagrid Broker Florida Grid Datagrid Broker DGMS Datagrid Broker University of Gators - Physics Framework + Protocols for datagrid community organization National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
DGMS and Datagrid Brokers CMS Grid Physics Grid LHC Grid Datagrid Broker Florida Grid Datagrid Broker DGMS Datagrid Broker University of Gators - Physics Framework + Protocols for datagrid community organization National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
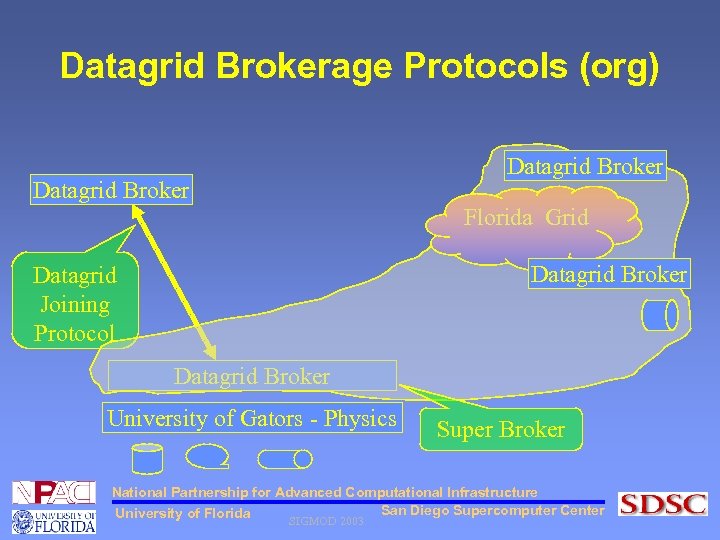 Datagrid Brokerage Protocols (org) Datagrid Broker Florida Grid Datagrid Broker Datagrid Joining Protocol Datagrid Broker University of Gators - Physics Super Broker National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Datagrid Brokerage Protocols (org) Datagrid Broker Florida Grid Datagrid Broker Datagrid Joining Protocol Datagrid Broker University of Gators - Physics Super Broker National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Datagrid Brokerage Protocols (org) New-community member Datagrid Broker University of Gators - Physics Super Broker National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Datagrid Brokerage Protocols (org) New-community member Datagrid Broker University of Gators - Physics Super Broker National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Datagrid Brokerage Protocols (org) • Organizing datagrid community • Managing the inter-organizational data • Datagrid Operations • Converted into datagrid brokerage protocols • Protocols implemented as services by the datagrid brokers • Hence, DGMS is nothing but these datagrid brokers which form these communities and the protocols (services) which operate on the collections National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Datagrid Brokerage Protocols (org) • Organizing datagrid community • Managing the inter-organizational data • Datagrid Operations • Converted into datagrid brokerage protocols • Protocols implemented as services by the datagrid brokers • Hence, DGMS is nothing but these datagrid brokers which form these communities and the protocols (services) which operate on the collections National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
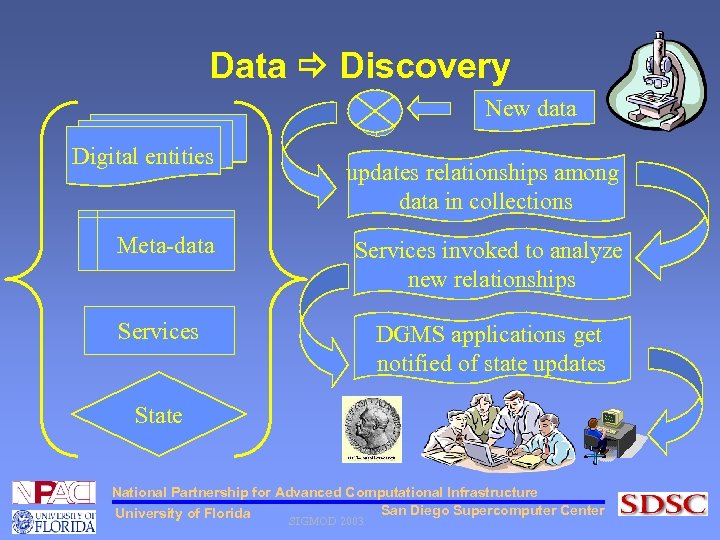 Data Discovery New data Digital entities updates relationships among data in collections Meta-data Services invoked to analyze new relationships Services DGMS applications get notified of state updates State National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Data Discovery New data Digital entities updates relationships among data in collections Meta-data Services invoked to analyze new relationships Services DGMS applications get notified of state updates State National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Data Discovery (Issues) • “More data; More discovery” – Fermi National Lab • DGMS applications to automate knowledge discovery • Work flow Management Systems (Wf. MS) subscribe to updates in datagrid collections • DBMS - Trigger like mechanism on this large scale dynamic and distributed data is MUST • Dynamic rule description and execution based on events • Semantic Mediation of datagrid collections • [SDSC Grid Enabled Mediation (Ge. MS)] National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Data Discovery (Issues) • “More data; More discovery” – Fermi National Lab • DGMS applications to automate knowledge discovery • Work flow Management Systems (Wf. MS) subscribe to updates in datagrid collections • DBMS - Trigger like mechanism on this large scale dynamic and distributed data is MUST • Dynamic rule description and execution based on events • Semantic Mediation of datagrid collections • [SDSC Grid Enabled Mediation (Ge. MS)] National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 DGMS Research Issues • Self-organization datagrid communities • Using knowledge relationships across the datagrids • Inter-datagrid operations based on semantics of data in the communities (different ontologies) • High speed data transfer • Terabyte to transfer - TCP/IP not final answer • Protocols, routers needed • Latency Management • Data source speed > data sink speed • Datagrid Constraints • Data placement and scheduling • How many replicas, where to place them… National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
DGMS Research Issues • Self-organization datagrid communities • Using knowledge relationships across the datagrids • Inter-datagrid operations based on semantics of data in the communities (different ontologies) • High speed data transfer • Terabyte to transfer - TCP/IP not final answer • Protocols, routers needed • Latency Management • Data source speed > data sink speed • Datagrid Constraints • Data placement and scheduling • How many replicas, where to place them… National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Legion & Avaki • A Worldwide Virtual Computer (one out of many) • Runs above existing OSs • Local systems provide storage, CPUs etc • Legion combines resources into single system • OS-Centric Approach – Grid as single virtual machine • Security, Data grid and Local System transparency, High-performance • Started in 1993 at University of Virginia’s research lab - Now Avaki National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Legion & Avaki • A Worldwide Virtual Computer (one out of many) • Runs above existing OSs • Local systems provide storage, CPUs etc • Legion combines resources into single system • OS-Centric Approach – Grid as single virtual machine • Security, Data grid and Local System transparency, High-performance • Started in 1993 at University of Virginia’s research lab - Now Avaki National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Globus • The Globus Project is developing fundamental technologies needed to build computational grids • Movement started by Ian Foster(ANL) and Carl Kesselman (ISI) • Has become synonymous with computational grids • Open-source development; standards-based • Toolkit used or evaluated in major grid projects in USA and Europe • http: //www. globus. org National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Globus • The Globus Project is developing fundamental technologies needed to build computational grids • Movement started by Ian Foster(ANL) and Carl Kesselman (ISI) • Has become synonymous with computational grids • Open-source development; standards-based • Toolkit used or evaluated in major grid projects in USA and Europe • http: //www. globus. org National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Gri. Phy. N Chimera • Data Provenance - facilitate on-demand derivation • Chimera Virtual Data System • Virtual data catalog and virtual data language • Capture and manage relationships amongst data derivations • Collaborative derivation of datasets • Store the recipe to derive a large data on demand (Virtual Data) • Or cache the derived data to serve it without a computeintensive derivation (Virtual Service) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Gri. Phy. N Chimera • Data Provenance - facilitate on-demand derivation • Chimera Virtual Data System • Virtual data catalog and virtual data language • Capture and manage relationships amongst data derivations • Collaborative derivation of datasets • Store the recipe to derive a large data on demand (Virtual Data) • Or cache the derived data to serve it without a computeintensive derivation (Virtual Service) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 OGSA-DAI • GGF – Global Grid Forum • OGSA - Open Grid Services Architecture • Future standard for Grid Computing by GGF • Stateful services - Service data • Works with W 3 C • OGSA-DAI (Data Access and Integration) • Standard interfaces to access (and control) disparate, heterogeneous data resources as though they were a single logical resource National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
OGSA-DAI • GGF – Global Grid Forum • OGSA - Open Grid Services Architecture • Future standard for Grid Computing by GGF • Stateful services - Service data • Works with W 3 C • OGSA-DAI (Data Access and Integration) • Standard interfaces to access (and control) disparate, heterogeneous data resources as though they were a single logical resource National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids • Data Grid Concepts • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 SDSC SRB – The History • Started in 1995 funded by DARPA • Massive Data Analysis System (MDAS) • PI: Reagan Moore • Support data-intensive applications that manipulate very large data sets by building upon object-relational database technology and archival storage technology • Multiple projects for multiple federal agencies • Do. D, NSF, NARA, NIH, Do. E, NLM, Library of Congress, NASA • Commercial version by General Atomics (Nirvana) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
SDSC SRB – The History • Started in 1995 funded by DARPA • Massive Data Analysis System (MDAS) • PI: Reagan Moore • Support data-intensive applications that manipulate very large data sets by building upon object-relational database technology and archival storage technology • Multiple projects for multiple federal agencies • Do. D, NSF, NARA, NIH, Do. E, NLM, Library of Congress, NASA • Commercial version by General Atomics (Nirvana) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 SDSC SRB Team (Data “R” Us : -) • Camera-shy • • Wayne Schroeder Vicky Rowley Lucas Gilbert Marcio Faerman SCEC • Not in picture students & SRB emeritus • • • Erik Vandekieft Reena Thomas Xi (Cynthia) Sheng Allen Ding Grace Lin • Is he the world’s first employee with title ‘datagrid engineer’? National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
SDSC SRB Team (Data “R” Us : -) • Camera-shy • • Wayne Schroeder Vicky Rowley Lucas Gilbert Marcio Faerman SCEC • Not in picture students & SRB emeritus • • • Erik Vandekieft Reena Thomas Xi (Cynthia) Sheng Allen Ding Grace Lin • Is he the world’s first employee with title ‘datagrid engineer’? National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 SRB Statistics (SDSC) Still Counting; More R&D; Over 50 Tera Bytes of data/information storage management National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
SRB Statistics (SDSC) Still Counting; More R&D; Over 50 Tera Bytes of data/information storage management National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
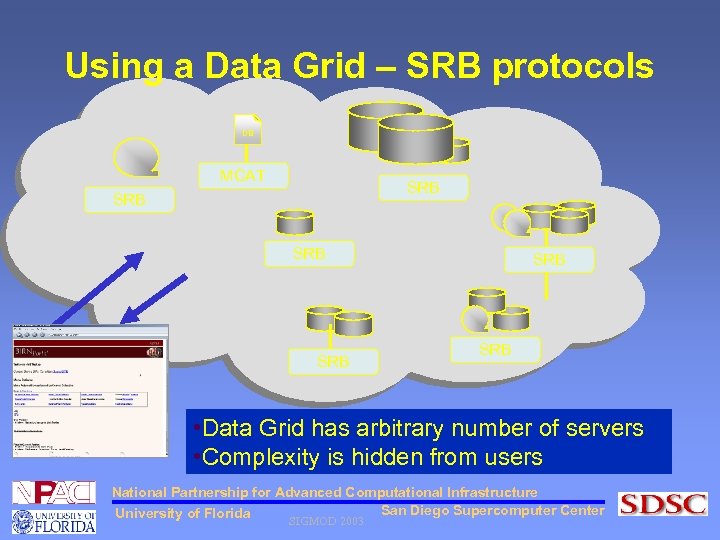 Using a Data Grid – SRB protocols DB MCAT SRB SRB SRB • Data Grid has arbitrary number of servers • Complexity is hidden from users National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Using a Data Grid – SRB protocols DB MCAT SRB SRB SRB • Data Grid has arbitrary number of servers • Complexity is hidden from users National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Data Grids – An SRB View • Manage data in a distributed environment • • Logical name space, provide global identifier Data access, storage system abstraction Replication, disaster back up Uniform access, common API across file systems, archives, and databases • Use Metadata to integrate data - information • Single sign-on, authenticate across administration domains • Integration of collection-based management of digital entities, with • Remote data access through storage system abstraction • Catalog access through information repository abstraction • Automation through collection-owned data National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Data Grids – An SRB View • Manage data in a distributed environment • • Logical name space, provide global identifier Data access, storage system abstraction Replication, disaster back up Uniform access, common API across file systems, archives, and databases • Use Metadata to integrate data - information • Single sign-on, authenticate across administration domains • Integration of collection-based management of digital entities, with • Remote data access through storage system abstraction • Catalog access through information repository abstraction • Automation through collection-owned data National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Digital Libraries – An SRB View • Provide services on the data collection • • • Ingestion, loading of attribute values Extensibility, definition of new attributes Discovery, queries on attributes Browsing, hierarchical listing Presentation, formatting specified data models • Communities • Digital library • Global Grid Forum, Databases and the Grid working group • OMG, Common Warehouse Meta-model National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Digital Libraries – An SRB View • Provide services on the data collection • • • Ingestion, loading of attribute values Extensibility, definition of new attributes Discovery, queries on attributes Browsing, hierarchical listing Presentation, formatting specified data models • Communities • Digital library • Global Grid Forum, Databases and the Grid working group • OMG, Common Warehouse Meta-model National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Persistent Archives – An SRB View • Manage technology evolution • Storage system abstraction, support data migration across storage systems • Information repository abstraction, support catalog migration to new databases • Logical name space, support global persistent identifier • Communities • Persistent archive community • Global Grid Forum, Persistent archive working group National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Persistent Archives – An SRB View • Manage technology evolution • Storage system abstraction, support data migration across storage systems • Information repository abstraction, support catalog migration to new databases • Logical name space, support global persistent identifier • Communities • Persistent archive community • Global Grid Forum, Persistent archive working group National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
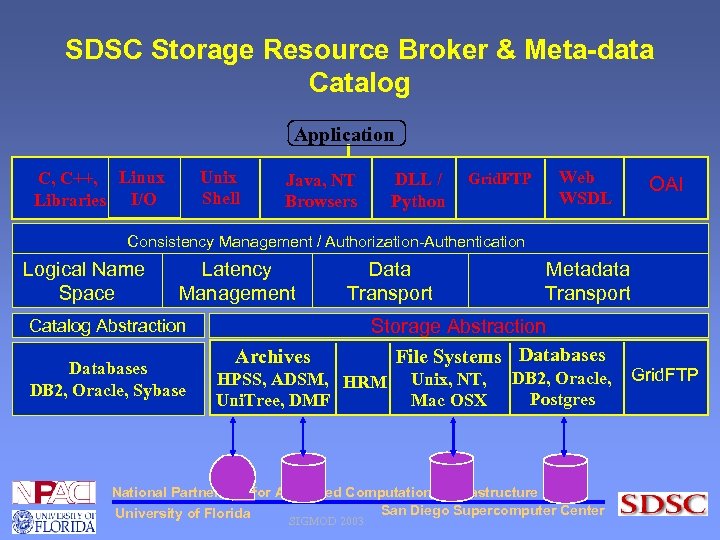 SDSC Storage Resource Broker & Meta-data Catalog Application Unix Shell C, C++, Linux Libraries I/O DLL / Python Java, NT Browsers Grid. FTP Web WSDL OAI Consistency Management / Authorization-Authentication Logical Name Space Latency Management Data Transport Catalog Abstraction Databases DB 2, Oracle, Sybase Archives Metadata Transport Storage Abstraction File Systems Databases HPSS, ADSM, HRM Uni. Tree, DMF Unix, NT, Mac OSX DB 2, Oracle, Postgres National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 Grid. FTP
SDSC Storage Resource Broker & Meta-data Catalog Application Unix Shell C, C++, Linux Libraries I/O DLL / Python Java, NT Browsers Grid. FTP Web WSDL OAI Consistency Management / Authorization-Authentication Logical Name Space Latency Management Data Transport Catalog Abstraction Databases DB 2, Oracle, Sybase Archives Metadata Transport Storage Abstraction File Systems Databases HPSS, ADSM, HRM Uni. Tree, DMF Unix, NT, Mac OSX DB 2, Oracle, Postgres National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 Grid. FTP
 SRB Concepts to Features • Abstraction of Data and Collections • Virtual Collections: Persistent Identifier and Global Name Space • Organization independent of physical location & resource type • Virtual Data Management and Movement • • Replication & Consistency Maintenance Data Aggregation: Containers Seamless Cache Management and Data Placement Copy, Move, Link, … • Metadata & Data Discovery – semantic linking • • System Metadata - metadata needed to run a data grid User-defined Metadata – Structural & Descriptive Application, Schema-based, Domain-centric Attribute-based Access (path names become irrelevant) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
SRB Concepts to Features • Abstraction of Data and Collections • Virtual Collections: Persistent Identifier and Global Name Space • Organization independent of physical location & resource type • Virtual Data Management and Movement • • Replication & Consistency Maintenance Data Aggregation: Containers Seamless Cache Management and Data Placement Copy, Move, Link, … • Metadata & Data Discovery – semantic linking • • System Metadata - metadata needed to run a data grid User-defined Metadata – Structural & Descriptive Application, Schema-based, Domain-centric Attribute-based Access (path names become irrelevant) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 SRB Concepts to Features • Abstraction of User Space – Global User Space • Single sign-on & Seamless Authorization • Certificates, (secure) passwords, tickets, group permissions, roles • Abstraction of Methods • • APIs, Command Line, GUI Browsers, Web-Access (Portal, WSDL, CGI) • Parallel Access with both Client and Server-driven strategies • Fault-tolerant and Reliable data management • Proxy and Remote Operations UCLA Duke NCMIR Abstraction of Resources - Resource Virtualisation • Resource Location, Type & Access transparency • Logical Resource Definitions – bundling Virtual Data Grid (SRB) Cal. Tech SDSC National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 MCAT
SRB Concepts to Features • Abstraction of User Space – Global User Space • Single sign-on & Seamless Authorization • Certificates, (secure) passwords, tickets, group permissions, roles • Abstraction of Methods • • APIs, Command Line, GUI Browsers, Web-Access (Portal, WSDL, CGI) • Parallel Access with both Client and Server-driven strategies • Fault-tolerant and Reliable data management • Proxy and Remote Operations UCLA Duke NCMIR Abstraction of Resources - Resource Virtualisation • Resource Location, Type & Access transparency • Logical Resource Definitions – bundling Virtual Data Grid (SRB) Cal. Tech SDSC National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 MCAT
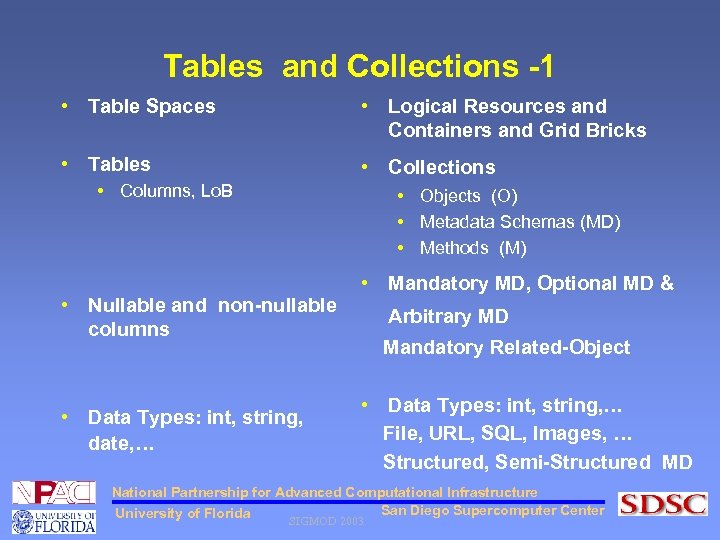 Tables and Collections -1 • Table Spaces • Logical Resources and Containers and Grid Bricks • Tables • Collections • Columns, Lo. B • Objects (O) • Metadata Schemas (MD) • Methods (M) • Nullable and non-nullable columns • Data Types: int, string, date, … • Mandatory MD, Optional MD & Arbitrary MD Mandatory Related-Object • Data Types: int, string, … File, URL, SQL, Images, … Structured, Semi-Structured MD National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tables and Collections -1 • Table Spaces • Logical Resources and Containers and Grid Bricks • Tables • Collections • Columns, Lo. B • Objects (O) • Metadata Schemas (MD) • Methods (M) • Nullable and non-nullable columns • Data Types: int, string, date, … • Mandatory MD, Optional MD & Arbitrary MD Mandatory Related-Object • Data Types: int, string, … File, URL, SQL, Images, … Structured, Semi-Structured MD National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tables and Collections - 2 • Indexes: on primary keys, columns • Triggers: Used to perform operations on updates/inserts • Integrity Constraints: Checking for data correctness • Multiple types of indices: textual, image, GIS, 3 -D (polygonal), 4 -D (time), ontological (topic maps), Indices on MD • Ingestion & Modification Checks: (ex: automatic metadata extraction, thumbnail generation, DICOM anonymize checking • Data Format, Checksum, Validation, Authenticity, National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure Reserved Words San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tables and Collections - 2 • Indexes: on primary keys, columns • Triggers: Used to perform operations on updates/inserts • Integrity Constraints: Checking for data correctness • Multiple types of indices: textual, image, GIS, 3 -D (polygonal), 4 -D (time), ontological (topic maps), Indices on MD • Ingestion & Modification Checks: (ex: automatic metadata extraction, thumbnail generation, DICOM anonymize checking • Data Format, Checksum, Validation, Authenticity, National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure Reserved Words San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tables and Collections - 3 • When a row is inserted • When an Object is Ingested • Row is inserted in a particular tablespace • Integrity constraint checked • Foreign key relationships checked • Indices created in particular tablespaces • Triggers executed • Object created in a Logical resource or container • Integrity constraints and format specs checked • Reserved keywords and related objects checked • Indices created (eg. Data cutter indexing) • Ingestion Methods applied National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tables and Collections - 3 • When a row is inserted • When an Object is Ingested • Row is inserted in a particular tablespace • Integrity constraint checked • Foreign key relationships checked • Indices created in particular tablespaces • Triggers executed • Object created in a Logical resource or container • Integrity constraints and format specs checked • Reserved keywords and related objects checked • Indices created (eg. Data cutter indexing) • Ingestion Methods applied National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
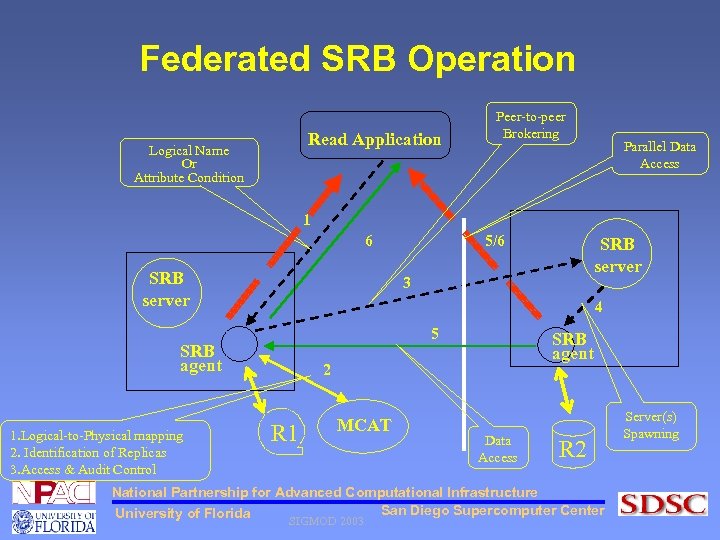 Federated SRB Operation Read Application Logical Name Or Attribute Condition Peer-to-peer Brokering Parallel Data Access 1 6 SRB server 3 4 5 SRB agent 1. Logical-to-Physical mapping 2. Identification of Replicas 3. Access & Audit Control 5/6 SRB agent 2 R 1 MCAT Data Access R 2 National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 Server(s) Spawning
Federated SRB Operation Read Application Logical Name Or Attribute Condition Peer-to-peer Brokering Parallel Data Access 1 6 SRB server 3 4 5 SRB agent 1. Logical-to-Physical mapping 2. Identification of Replicas 3. Access & Audit Control 5/6 SRB agent 2 R 1 MCAT Data Access R 2 National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003 Server(s) Spawning
 SRB Clients • Programmatic API for C, C++ • High-level API for Posix like interface • Low-level API for storage repository abstraction • SRB Manager API for administration • Command Level Interface - Scommands • Graphical User Interfaces - in. Q, Java, Admin Tool • Web Interface/utilities – my. SRB • Web Services – WSDL/SOAP Interface • Portals – GRid. Port, Telescience, BIRNPort, … National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
SRB Clients • Programmatic API for C, C++ • High-level API for Posix like interface • Low-level API for storage repository abstraction • SRB Manager API for administration • Command Level Interface - Scommands • Graphical User Interfaces - in. Q, Java, Admin Tool • Web Interface/utilities – my. SRB • Web Services – WSDL/SOAP Interface • Portals – GRid. Port, Telescience, BIRNPort, … National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids Research Rubber hits • Data Grid Concepts the Road • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Outline PART I • Introduction to Grid Computing • Proliferation of Data Grids Research Rubber hits • Data Grid Concepts the Road • Data Grid Management Systems • Data Grid Management – Open Research Issues • Tools and applications available PART II • Overview and Hands on SDSC Storage Resource Broker (SRB) National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 Tutorial Summary • Grids are evolving; coming soon to a domain near you • DGMS • Coordinate collaborative management of interorganizational information storage using Active Datagrid Collections • Tools are available from research and academia. • Industry getting involved. • SDSC SRB provides the abstraction mechanisms required to implement data grids, digital libraries and persistent archives • Open Research issues for • Distributed databases, Information Infrastructure National Partnership for Advanced Computational management and Semantic web researchers San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
Tutorial Summary • Grids are evolving; coming soon to a domain near you • DGMS • Coordinate collaborative management of interorganizational information storage using Active Datagrid Collections • Tools are available from research and academia. • Industry getting involved. • SDSC SRB provides the abstraction mechanisms required to implement data grids, digital libraries and persistent archives • Open Research issues for • Distributed databases, Information Infrastructure National Partnership for Advanced Computational management and Semantic web researchers San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
 National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003
National Partnership for Advanced Computational Infrastructure San Diego Supercomputer Center University of Florida SIGMOD 2003


