cf3b72eb9b4cf17f98944b8ed0dbd9ea.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
Data Fusion and Semantic Web: Meta-Models of Distributed Data and Decision Fusion. Project Report Vladimir Gorodetski, Oleg Karsaev, Vladimir Samoilov Intelligent System Laboratory of the St. Petersburg Institute for Informatics and Automation E-mail: {gor, ok, samovl}@mail. iias. spb. su http: //space. iias. spb. su/ai/english/gorodetski. htm 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland

Title of the Project “Autonomous Information Collection, Knowledge Discovery Techniques and Software Tool Prototype for Knowledge-Based Data Fusion” Project from European Office of Aerospace Research and Development (EOARD) –AFRL/IF (USA) (December 2000 - December 2003) 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland

Outline of the Project Presentation 1. Outline of the Data and Information Fusion problems 2. Project research objectives 3. Examples of case studies and applications used 4. Ontology-centered meta-model of data sources 5. Meta-model of decision fusion 6. Multi-agent architecture 7. Conclusion 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
Tasks and Applications of Data and Information Fusion Application Fields Critical areas of human society security, life support, security of critical state infrastructures, large-scale logistics, natural and man-made disasters, etc. Examples of Applications ь Assessment and prediction of situations, ь Resource management and rescue operation planning in large scale natural and man-made disasters, ь Decision making and planning of rescue operations in systems like US 911, Situational awareness and prediction for terrorist intents and anti-terrorist activity planning, ь Military situation assessment, ь Safeguard of critical plants like nuclear power stations, electrical power grids, etc. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
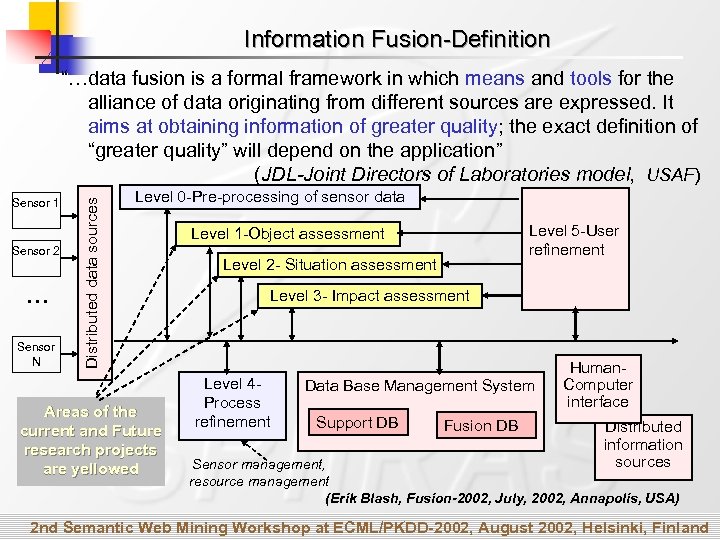
Information Fusion-Definition Sensor 1 Sensor 2 … Sensor N Distributed data sources “…data fusion is a formal framework in which means and tools for the alliance of data originating from different sources are expressed. It aims at obtaining information of greater quality; the exact definition of “greater quality” will depend on the application” (JDL-Joint Directors of Laboratories model, USAF) Level 0 -Pre-processing of sensor data Areas of the current and Future research projects are yellowed Level 5 -User refinement Level 1 -Object assessment Level 2 - Situation assessment Level 3 - Impact assessment Level 4 Process refinement Data Base Management System Support DB Fusion DB Human. Computer interface Distributed information sources Sensor management, resource management (Erik Blash, Fusion-2002, July, 2002, Annapolis, USA) 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland

Project Research Objectives Development of DF software tool providing support for design (first of all, for learning!) and implementation of DF applications of broad spectrum, in particular, providing support for : ь Development of ontology-based meta-models of data sources, meta-model of decision fusion and conceptual model of DF software tool, ь Development of Multi-agent architecture and ь Design and implementation of applications of broad spectrum. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
Examples of case studies and application used in Projects Case studies -KDD Cup 99 dataset -- Preprocessed relational data specifying Intrusion Detection task http: //kdd. ics. uci. edu/databases/kddcup 99. html -Landsat Multi-Spectral Scanner image dataset http: //www. dfc-grss. org/data/grss_dfc_0010. zip -STULONG dataset– Longitudinal Study of Atherosclerosis Risk Factors http: //euromise. vse. cz/challenge/en/projekt/index. php Application to be used in debugging and validation of MAS DK-DF - Intrusion detection learning system (Project also funded by EOARD/AFRL) 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
Subtasks of the Project matching Semantic Web Mining area 1. Design and implementation of meta-model of data sources caused by heterogeneity and distribution of data to be fused. 2. Design and implementation of meta-model of distributed learning. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
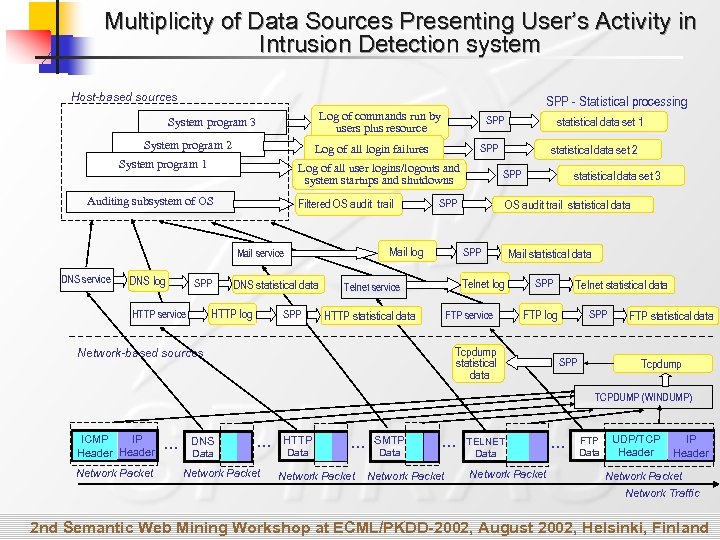
Multiplicity of Data Sources Presenting User’s Activity in Intrusion Detection system Host-based sources Log of commands run by users plus resource System program 3 System program 2 SPP Filtered OS audit trail statistical data SPP Mail log DNS statistical data HTTP log HTTP service statistical data set 2 SPP Mail service DNS log SPP Log of all user logins/logouts and system startups and shutdowns Auditing subsystem of OS DNS service SPP Log of all login failures System program 1 SPP - Statistical processing statistical program data set 1 SPP Telnet log Telnet service FTP service HTTP statistical data set 3 Mail statistical data SPP FTP log Tcpdump statistical data Network-based sources Telnet statistical data SPP FTP statistical data Tcpdump TCPDUMP (WINDUMP) IP ICMP Header Network Packet … DNS Data … Network Packet HTTP Data … Network Packet SMTP Data … Network Packet TELNET Data Network Packet … FTP Data UDP/TCP Header IP Header Network Packet Network Traffic 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland

Interrelation of Semantic Web and Ontology-oriented Research within the Project Semantic Web considers development and standardization of the ontology specification languages (XML, RDF, DAML+OIL), ontology-based query languages, ontology editors, etc). Semantic Web Mining considers specific problems of ontology design technology for (Web-based) Data Mining systems. Any DF system technology supposes (Web-based) distributed Data Mining and KDD and that is why it is a subarea of the Semantic Web Mining. Ontology-based Data and Information Fusion system design put a number of specific problems of technological sort. Among them, the most important one is a technology for distributed design of distributed ontology. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
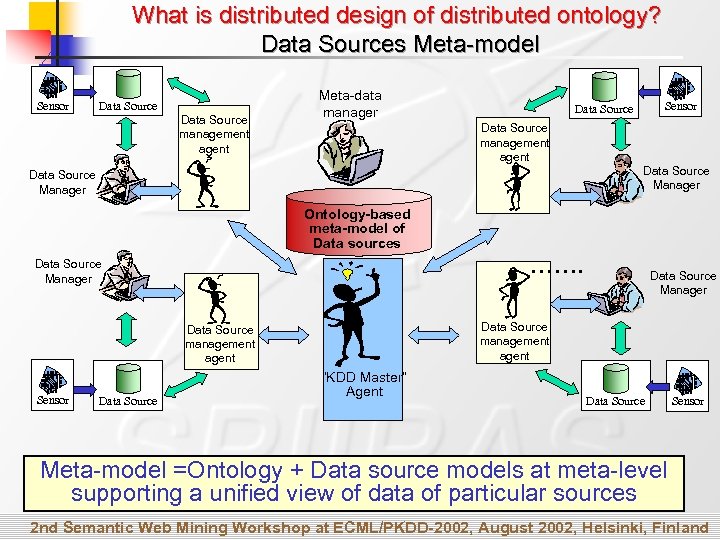
What is distributed design of distributed ontology? Data Sources Meta-model Sensor Data Source management agent Meta-data manager Sensor Data Source management agent Data Source Manager Ontology-based meta-model of Data sources ……. Data Source Manager Data Source management agent Sensor Data Source Manager “KDD Master” Agent Data Source Sensor Meta-model =Ontology + Data source models at meta-level supporting a unified view of data of particular sources 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
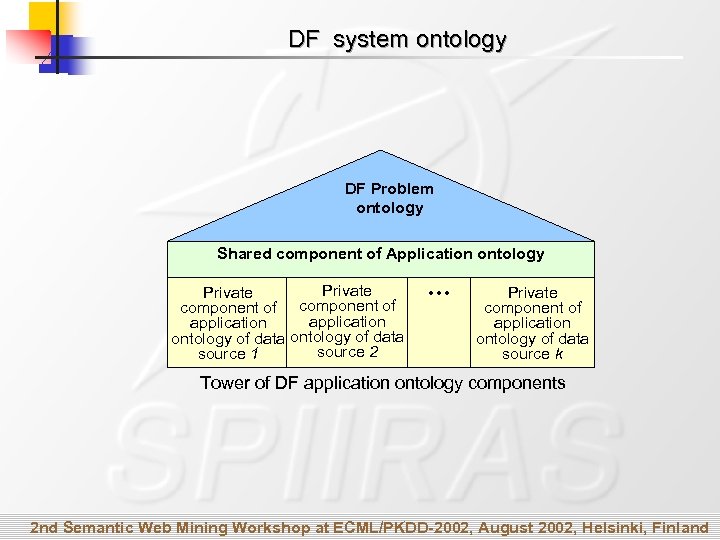
DF system ontology DF Problem ontology Shared component of Application ontology Private component of application ontology of data source 2 source 1 … Private component of application ontology of data source k Tower of DF application ontology components 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
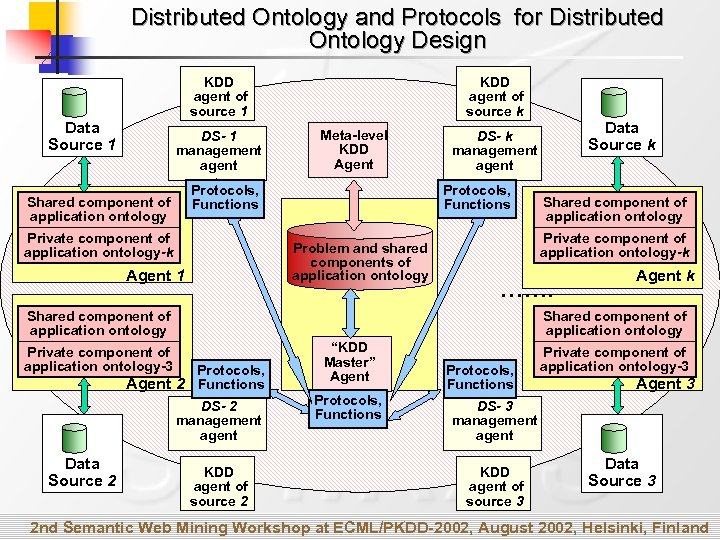
Distributed Ontology and Protocols for Distributed Ontology Design KDD agent of source 1 Data Source 1 DS- 1 management agent KDD agent of source k Meta-level KDD Agent Protocols, Functions Shared component of application ontology Private component of application ontology-k Protocols, Functions Problem and shared components of application ontology Agent 1 Shared component of application ontology Private component of application ontology-k ……. Shared component of application ontology Agent k Shared component of application ontology Private component of application ontology-3 Protocols, Agent 2 Functions DS- 2 management agent Data Source 2 Data Source k DS- k management agent KDD agent of source 2 “KDD Master” Agent Protocols, Functions Private component of application ontology-3 Agent 3 DS- 3 management agent KDD agent of source 3 Data Source 3 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland

Particular Tasks to Be Solved on the Basis of Metamodel of Data Sources • Providing for monosemantic understanding of terminology used in data specification by distributed analysts; • Solution of the entity identification problem; • Providing consistency of data representation (in case if the same attributes are presented differently in different data sources); • Providing a gateway between ontology and distributed databases accessibility making possible interaction between ontology and distributed databases, and several other tasks. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland

Meta-model of Data Sources: Ontology + Protocols => Monosemantic understanding of terminology among DF system components is provided by shared vocabulary used by DF system distributed entities for communication. This excludes different naming of the same entities and their properties in different sources, and equal naming of different entities within different data sources thus providing integrity and consistency of shared vocabulary. Protocols Supports distributed collaborative design of coherent ontology by distributed analysts. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
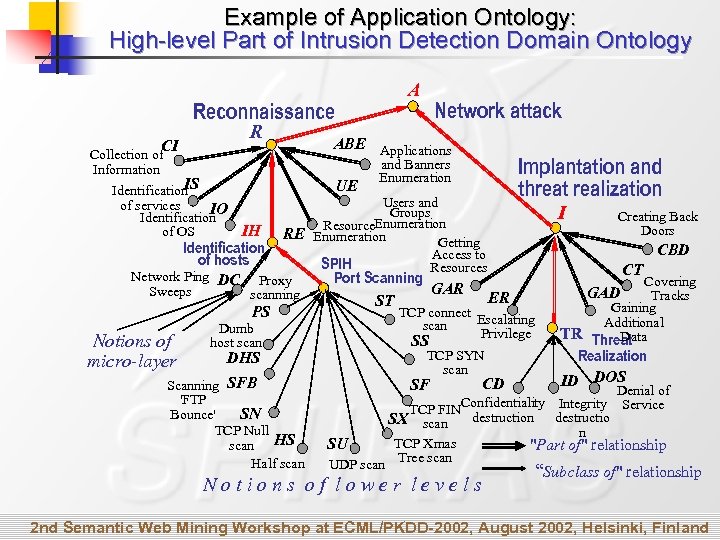
Example of Application Ontology: High-level Part of Intrusion Detection Domain Ontology A Reconnaissance CI Collection of Information R IS Identification of services IO Identification IH of OS Network attack ABE Applications UE and Banners Enumeration Implantation and threat realization Users and Groups I Creating Back Resource. Enumeration Doors RE Enumeration Getting Identification CBD Access to of hosts SPIH Resources CT Network Ping DC Proxy Port Scanning Covering GAR Sweeps GAD scanning Tracks ER ST Gaining PS TCP connect Escalating Additional scan Dumb Privilege TR Threat Data SS host scan Notions of TCP SYN Realization DHS micro-layer scan ID DOS CD Scanning SFB SF Denial of 'FTP Confidentiality Integrity Service TCP FIN Bounce' SN destruction destructio SX scan TCP Null n TCP Xmas SU scan HS "Part of" relationship Half scan UDP scan Tree scan Notions of lower levels “Subclass of" relationship 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
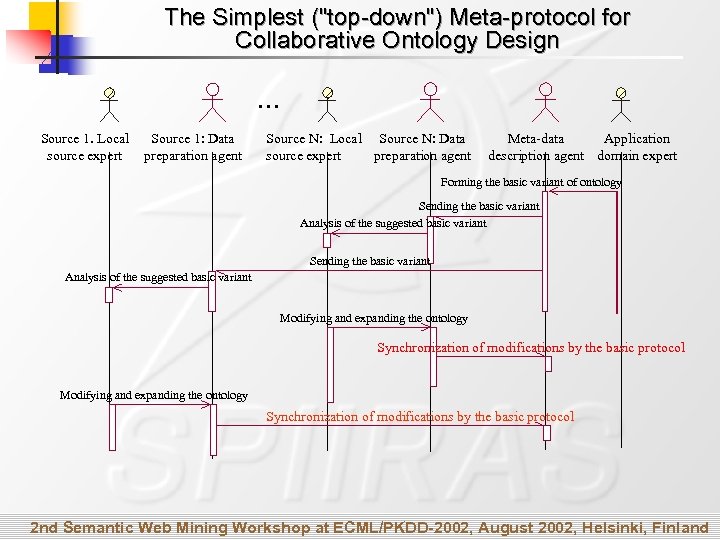
The Simplest ("top-down") Meta-protocol for Collaborative Ontology Design … Source 1. Local source expert Source 1: Data preparation agent Source N: Local Source N: Data source expert preparation agent Meta-data Application description agent domain expert Forming the basic variant of ontology Sending the basic variant Analysis of the suggested basic variant Modifying and expanding the ontology Synchronization of modifications by the basic protocol 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
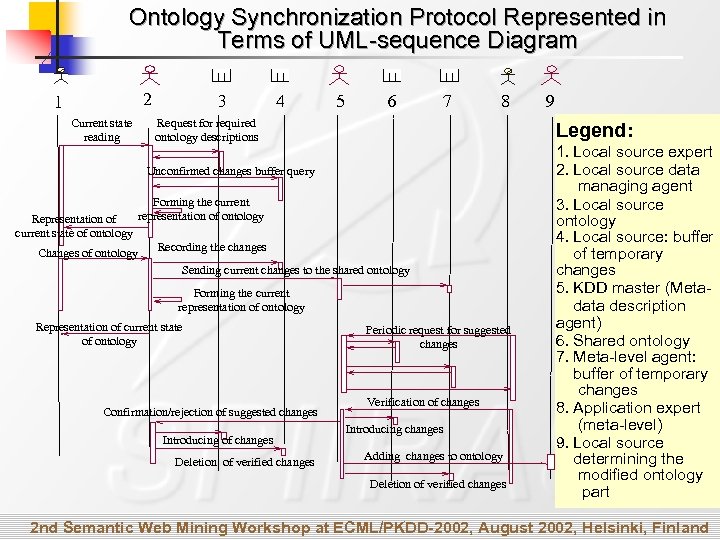
Ontology Synchronization Protocol Represented in Terms of UML-sequence Diagram 2 1 Current state reading 3 4 5 6 7 8 Request for required ontology descriptions Legend: Unconfirmed changes buffer query Representation of current state of ontology Forming the current representation of ontology Changes of ontology Recording the changes Sending current changes to the shared ontology Forming the current representation of ontology Representation of current state of ontology Confirmation/rejection of suggested changes Introducing of changes Deletion of verified changes 9 Periodic request for suggested changes Verification of changes Introducing changes Adding changes to ontology Deletion of verified changes 1. Local source expert 2. Local source data managing agent 3. Local source ontology 4. Local source: buffer of temporary changes 5. KDD master (Metadata description agent) 6. Shared ontology 7. Meta-level agent: buffer of temporary changes 8. Application expert (meta-level) 9. Local source determining the modified ontology part 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
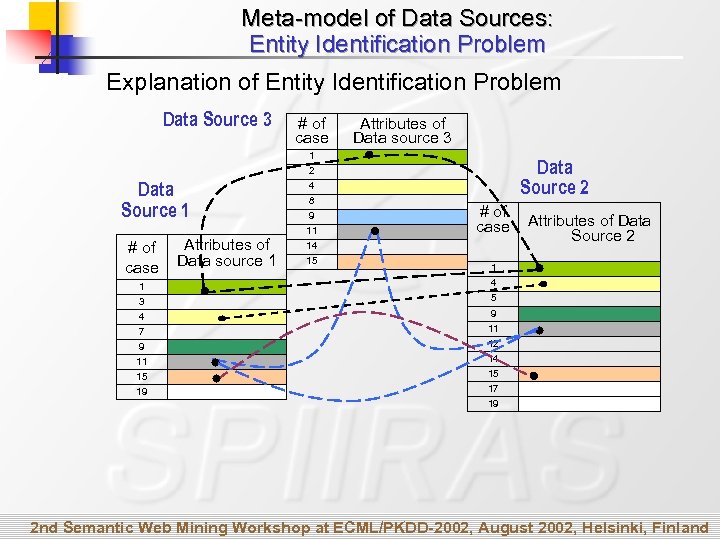
Meta-model of Data Sources: Entity Identification Problem Explanation of Entity Identification Problem Data Source 3 Data Source 1 # of case 1 3 4 7 9 11 15 19 Attributes of Data source 1 # of case 1 2 4 8 9 11 14 15 Attributes of Data source 3 Data Source 2 # of case Attributes of Data Source 2 1 4 5 9 11 12 14 15 17 19 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
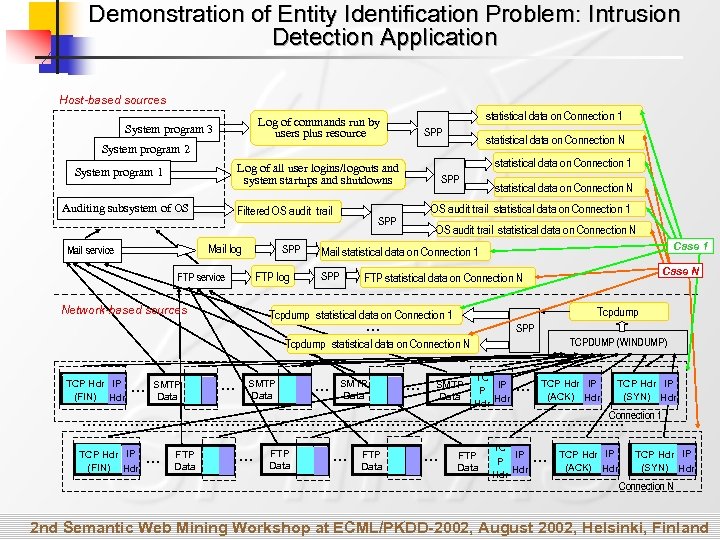
Demonstration of Entity Identification Problem: Intrusion Detection Application Host-based sources statistical data on Connection 1 Log of commands run by users plus resource System program 3 SPP statistical data on Connection N System program 2 statistical data on Connection 1 Log of all user logins/logouts and system startups and shutdowns System program 1 Auditing subsystem of OS Filtered OS audit trail Mail log Mail service SPP FTP log FTP service Network-based sources SPP statistical data on Connection N OS audit trail statistical data on Connection 1 SPP OS audit trail statistical data on Connection N Case 1 Mail statistical data on Connection 1 SPP Case N FTP statistical data on Connection N Tcpdump statistical data on Connection 1 … SPP TCPDUMP (WINDUMP) Tcpdump statistical data on Connection N TCP Hdr IP (FIN) Hdr … SMTP Data TC IP P Hdr … TCP Hdr IP (ACK) Hdr TCP Hdr IP (SYN) Hdr Connection 1 …………………………………………… TCP Hdr IP (FIN) Hdr … FTP Data TC IP P Hdr … TCP Hdr IP (ACK) Hdr TCP Hdr IP (SYN) Hdr Connection N 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
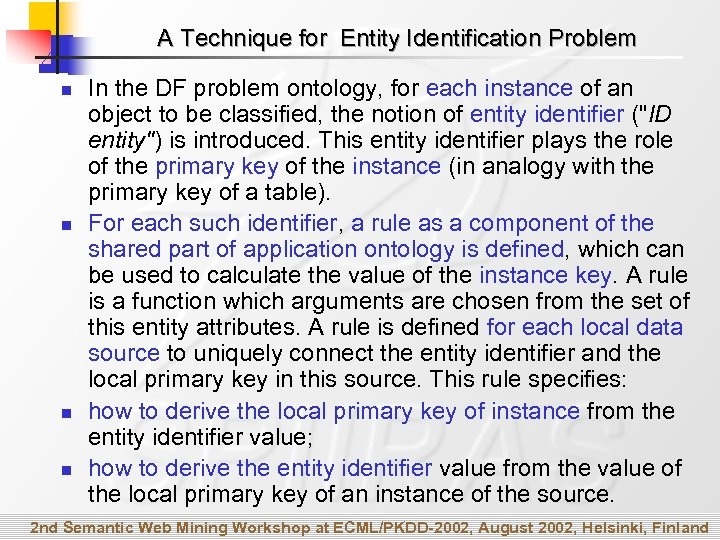
A Technique for Entity Identification Problem n n In the DF problem ontology, for each instance of an object to be classified, the notion of entity identifier ("ID entity") is introduced. This entity identifier plays the role of the primary key of the instance (in analogy with the primary key of a table). For each such identifier, a rule as a component of the shared part of application ontology is defined, which can be used to calculate the value of the instance key. A rule is a function which arguments are chosen from the set of this entity attributes. A rule is defined for each local data source to uniquely connect the entity identifier and the local primary key in this source. This rule specifies: how to derive the local primary key of instance from the entity identifier value; how to derive the entity identifier value from the value of the local primary key of an instance of the source. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
Meta-model of Data Sources: Diversity of Measurement Scales of the Same Attributes in Different Data Sources Let X be an attribute in application ontology that is measured differently in different sources. 1. In the shared component of application ontology, the type and the measurement unit of the attribute X are determined. Selection of attribute X specification within shared part of application ontology is made by experts during negotiations according to a synchronization protocol. 2. In all the sources where X is present, expressions are determined for this attribute, through which it can further be converted into the same scale in all the sources. This allows using the values of attributes on the metalevel regardless of the data source from which they originated. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
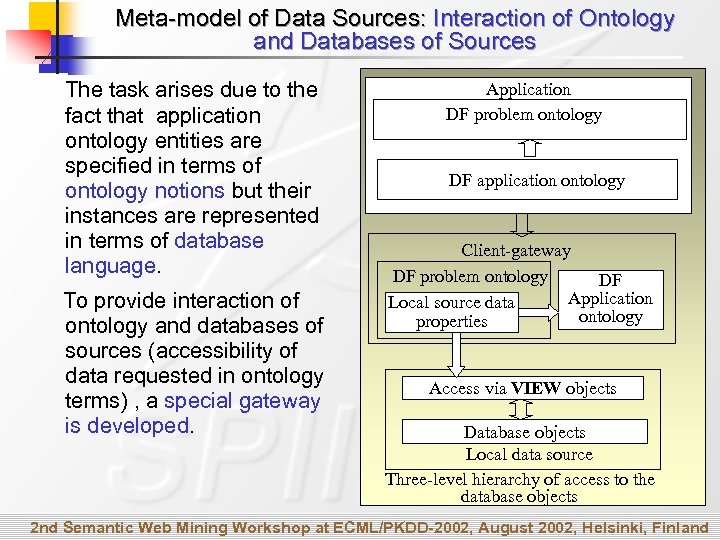
Meta-model of Data Sources: Interaction of Ontology and Databases of Sources The task arises due to the fact that application ontology entities are specified in terms of ontology notions but their instances are represented in terms of database language. To provide interaction of ontology and databases of sources (accessibility of data requested in ontology terms) , a special gateway is developed. Application DF problem ontology DF application ontology Client-gateway DF problem ontology DF Application Local source data ontology properties Access via VIEW objects Database objects Local data source Three-level hierarchy of access to the database objects 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
Meta-model of Distributed Learning Components of meta-model of distributed learning: • Meta-model of decision making and combining decisions of multiple base-level classifiers; • Model of distributed data management (allocation training and testing data sets for learning particular classifiers; management by computation of metadata for upper level example-based learning, etc. ); • Approaches and formal techniques used for combining decisions. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland

Conclusion: Future work. 1. Development of sophisticated ontology editor supporting distributed design of a distributed ontology. 2. Further design and Implementation of Data Fusion System software tool for development and implementation of particular distributed applications in Data Fusion area. 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland

Thank you! For more information and related publications please contact E-mail: gor@mail. iias. spb. su http: //space. iias. spb. su/ai/english/gorodetski. htm Acknowledgement This research is funded by AFRL/IF (EOARD), 1999 -2003 2 nd Semantic Web Mining Workshop at ECML/PKDD-2002, August 2002, Helsinki, Finland
cf3b72eb9b4cf17f98944b8ed0dbd9ea.ppt