debe2fceef324e965ae08111486d738e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Data Flow Diagrams DT 211 Stage 2 Software Engineering
Data Flow Diagrams DT 211 Stage 2 Software Engineering
 Where do they fit in? Life Cycle Phases Planning Feasibility Study Analysis Design Code and Unit test Analysis (What do we do? ) Fact finding investigate business process and the current system modelling the current and required systems deliverables requirements specification logical models of the required system
Where do they fit in? Life Cycle Phases Planning Feasibility Study Analysis Design Code and Unit test Analysis (What do we do? ) Fact finding investigate business process and the current system modelling the current and required systems deliverables requirements specification logical models of the required system
 Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) DFDs describe the flow of data or information into and out of a system what does the system do to the data? A DFD is a graphic representation of the flow of data or information through a system 3
Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) DFDs describe the flow of data or information into and out of a system what does the system do to the data? A DFD is a graphic representation of the flow of data or information through a system 3
 4 Main Elements external entity - people or organisations that send data into the system or receive data from the system process - models what happens to the data i. e. transforms incoming data into outgoing data store - represents permanent data that is used by the system data flow - models the actual flow of the data between the other elements
4 Main Elements external entity - people or organisations that send data into the system or receive data from the system process - models what happens to the data i. e. transforms incoming data into outgoing data store - represents permanent data that is used by the system data flow - models the actual flow of the data between the other elements
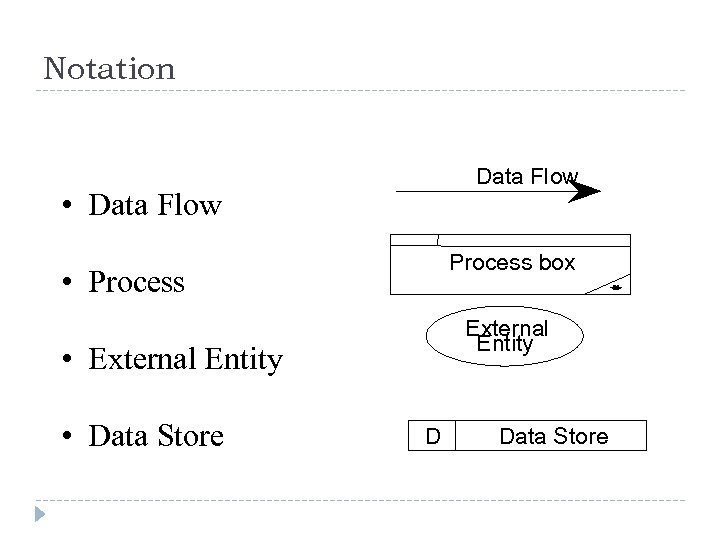 Notation Data Flow • Data Flow Process box • Process External Entity • External Entity • Data Store D Data Store
Notation Data Flow • Data Flow Process box • Process External Entity • External Entity • Data Store D Data Store
 Levelled DFDs Even a small system could have many processes and data flows and DFD could be large and messy use levelled DFDs - view system at different levels of detail one overview and many progressively greater detailed views 4
Levelled DFDs Even a small system could have many processes and data flows and DFD could be large and messy use levelled DFDs - view system at different levels of detail one overview and many progressively greater detailed views 4
 Level 0 - Context Diagram models system as one process box which represents scope of the system identifies external entities and related inputs and outputs Additional notation - system box
Level 0 - Context Diagram models system as one process box which represents scope of the system identifies external entities and related inputs and outputs Additional notation - system box
 Level 1 - overview diagram gives overview of full system identifies major processes and data flows between them identifies data stores that are used by the major processes boundary of level 1 is the context diagram
Level 1 - overview diagram gives overview of full system identifies major processes and data flows between them identifies data stores that are used by the major processes boundary of level 1 is the context diagram
 Level 2 - detailed diagram level 1 process is expanded into more detail each process in level 1 is decomposed to show its constituent processes boundary of level 2 is the level 1 process
Level 2 - detailed diagram level 1 process is expanded into more detail each process in level 1 is decomposed to show its constituent processes boundary of level 2 is the level 1 process
 Other Notation Duplicates marked by diagonal line in corner System Boundary Elementary Processes - star in corner Process that is levelled - dots on top
Other Notation Duplicates marked by diagonal line in corner System Boundary Elementary Processes - star in corner Process that is levelled - dots on top
 Rules for DFDs Numbering Labelling Balancing 5
Rules for DFDs Numbering Labelling Balancing 5
 Numbering On level 1 processes are numbered 1, 2, 3… On level 2 processes are numbered x. 1, x. 2, x. 3… where x is the number of the parent level 1 process Number is used to uniquely identify process not to represent any order of processing Data store numbers usually D 1, D 2, D 3. . .
Numbering On level 1 processes are numbered 1, 2, 3… On level 2 processes are numbered x. 1, x. 2, x. 3… where x is the number of the parent level 1 process Number is used to uniquely identify process not to represent any order of processing Data store numbers usually D 1, D 2, D 3. . .
 Labelling Process label - short description of what the process does, e. G. Price order Data flow label - noun representing the data flowing through it e. G. Customer payment Data store label - describes the type of data stored Make labels as meaningful as possible
Labelling Process label - short description of what the process does, e. G. Price order Data flow label - noun representing the data flowing through it e. G. Customer payment Data store label - describes the type of data stored Make labels as meaningful as possible
 Balancing and data stores Balancing any data flows entering or leaving a parent level must by equivalent to those on the child level Data stores data stores that are local to a process need not be included until the process is expanded
Balancing and data stores Balancing any data flows entering or leaving a parent level must by equivalent to those on the child level Data stores data stores that are local to a process need not be included until the process is expanded
 Data Flows Allowed to combine several data flows from lower level diagrams at a higher level under one data flow to reduce clutter Flows should be labelled except when data to or from a data store consists of all items in the data store
Data Flows Allowed to combine several data flows from lower level diagrams at a higher level under one data flow to reduce clutter Flows should be labelled except when data to or from a data store consists of all items in the data store
 Joe’s Yard Joe’s builders’ suppliers has a shop and a yard. His system is entirely manual. He has a stock list on the wall of his shop, complete with prices. When a builder wants to buy supplies, he goes into the shop and picks the stock items from the list. He writes his order on a duplicate docket and pays Joe, who stamps the docket as paid. The builder takes the duplicate docket and he goes to the yard and hands it to the yard foreman. The yard foreman gets the ordered items from the yard and gives them to the builder. The builder signs the duplicate docket and leaves one copy with the foreman and takes one copy as a receipt. Every week, Joe looks around the yard to see if any of his stock is running low. He rings up the relevant suppliers and reorders stock. He records the order in his order book, which is kept in the yard. The yard foreman takes delivery of the new stock and checks it against what has been ordered. He pays for it on delivery and staples the receipt into the order book. At the end of every month, Joe goes through all the dockets and the order book and produces a financial report for the shareholders. Draw a context level DFD and a level-1 DFD for this system.
Joe’s Yard Joe’s builders’ suppliers has a shop and a yard. His system is entirely manual. He has a stock list on the wall of his shop, complete with prices. When a builder wants to buy supplies, he goes into the shop and picks the stock items from the list. He writes his order on a duplicate docket and pays Joe, who stamps the docket as paid. The builder takes the duplicate docket and he goes to the yard and hands it to the yard foreman. The yard foreman gets the ordered items from the yard and gives them to the builder. The builder signs the duplicate docket and leaves one copy with the foreman and takes one copy as a receipt. Every week, Joe looks around the yard to see if any of his stock is running low. He rings up the relevant suppliers and reorders stock. He records the order in his order book, which is kept in the yard. The yard foreman takes delivery of the new stock and checks it against what has been ordered. He pays for it on delivery and staples the receipt into the order book. At the end of every month, Joe goes through all the dockets and the order book and produces a financial report for the shareholders. Draw a context level DFD and a level-1 DFD for this system.
 Context Diagram Find the people who send data into the system Often data is part of a PHYSICAL transaction When handing a bar of chocolate to a shopkeeper, you are handing him/her a barcode. Find the people who get data out of the system. The only data you need is data that is transformed or sent completely out of the system – not data that is handled by an operator within the system.
Context Diagram Find the people who send data into the system Often data is part of a PHYSICAL transaction When handing a bar of chocolate to a shopkeeper, you are handing him/her a barcode. Find the people who get data out of the system. The only data you need is data that is transformed or sent completely out of the system – not data that is handled by an operator within the system.
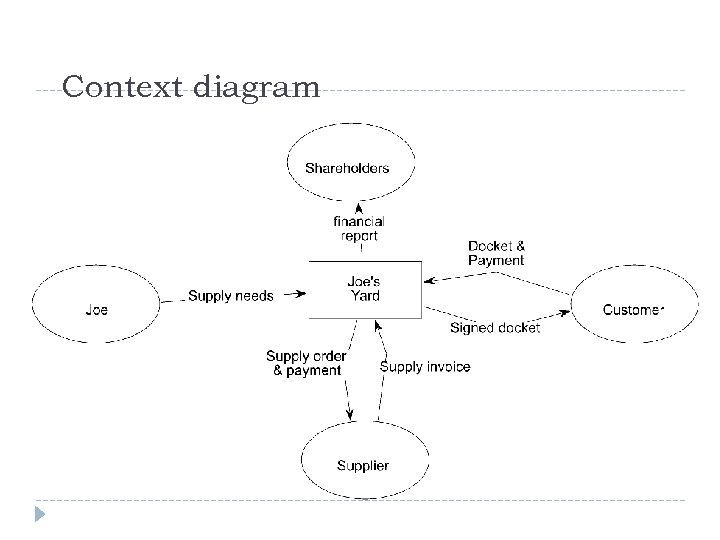 Context diagram
Context diagram
 Level-1 DFD processes Joe’s builders’ suppliers has a shop and a yard. His system is entirely manual. He has a stock list on the wall of his shop, complete with prices. When a builder wants to buy supplies, he goes into the shop and picks the stock items from the list. He writes his order on a duplicate docket and pays Joe, who stamps the docket as paid. The builder takes the duplicate docket and he goes to the yard and hands it to the yard foreman. The yard foreman gets the ordered items from the yard and gives them to the builder. The builder signs the duplicate docket and leaves one copy with the foreman and takes one copy as a receipt. Every week, Joe looks around the yard to see if any of his stock is running low. He rings up the relevant suppliers and reorders stock. He records the order in his order book, which is kept in the yard. The yard foreman takes delivery of the new stock and checks it against what has been ordered. He pays for it on delivery and staples the receipt into the order book. At the end of every month, Joe goes through all the dockets and the order book and produces a financial report for the shareholders.
Level-1 DFD processes Joe’s builders’ suppliers has a shop and a yard. His system is entirely manual. He has a stock list on the wall of his shop, complete with prices. When a builder wants to buy supplies, he goes into the shop and picks the stock items from the list. He writes his order on a duplicate docket and pays Joe, who stamps the docket as paid. The builder takes the duplicate docket and he goes to the yard and hands it to the yard foreman. The yard foreman gets the ordered items from the yard and gives them to the builder. The builder signs the duplicate docket and leaves one copy with the foreman and takes one copy as a receipt. Every week, Joe looks around the yard to see if any of his stock is running low. He rings up the relevant suppliers and reorders stock. He records the order in his order book, which is kept in the yard. The yard foreman takes delivery of the new stock and checks it against what has been ordered. He pays for it on delivery and staples the receipt into the order book. At the end of every month, Joe goes through all the dockets and the order book and produces a financial report for the shareholders.
 Verbs from script Has (passive) Buy supplies Picks stock items Writes order Pays joe Stamps docket Takes docket to yard Hands it to foreman Gets items Gives them to builder Builder signs docket Takes copy as receipt Looks around yard and reorders Records order in order book Foreman takes delivery – checks Foreman pays supplier Staples receipt to order book Produces financial report
Verbs from script Has (passive) Buy supplies Picks stock items Writes order Pays joe Stamps docket Takes docket to yard Hands it to foreman Gets items Gives them to builder Builder signs docket Takes copy as receipt Looks around yard and reorders Records order in order book Foreman takes delivery – checks Foreman pays supplier Staples receipt to order book Produces financial report
 Remove passive verbs and queries Joe then Passive: has stock list Buy supplies Customer then Picks stock items (views list) Writes orders Pays joe Stamps docket Takes docket to yard Hands it to foreman Gets items Gives them to builder Builder signs docket Takes copy as receipt Foreman Looks around yard and reorders Records order in order book takes delivery – checks Foreman pays supplier Staples receipt to order book Joe Produces financial report
Remove passive verbs and queries Joe then Passive: has stock list Buy supplies Customer then Picks stock items (views list) Writes orders Pays joe Stamps docket Takes docket to yard Hands it to foreman Gets items Gives them to builder Builder signs docket Takes copy as receipt Foreman Looks around yard and reorders Records order in order book takes delivery – checks Foreman pays supplier Staples receipt to order book Joe Produces financial report
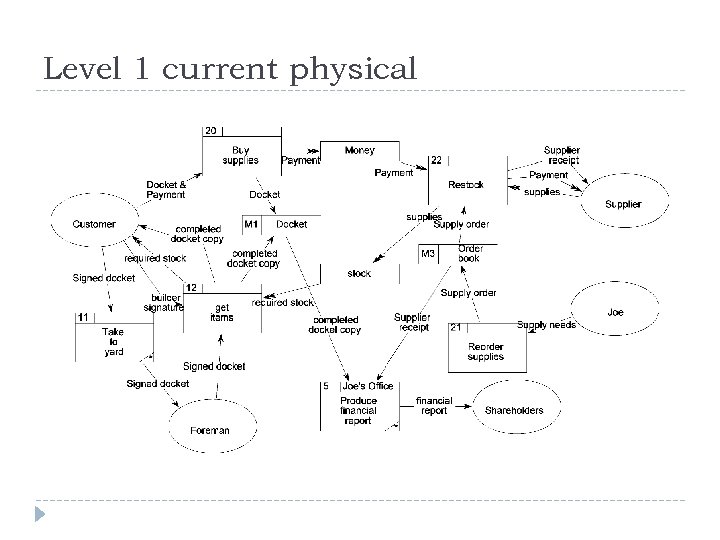 Level 1 current physical
Level 1 current physical
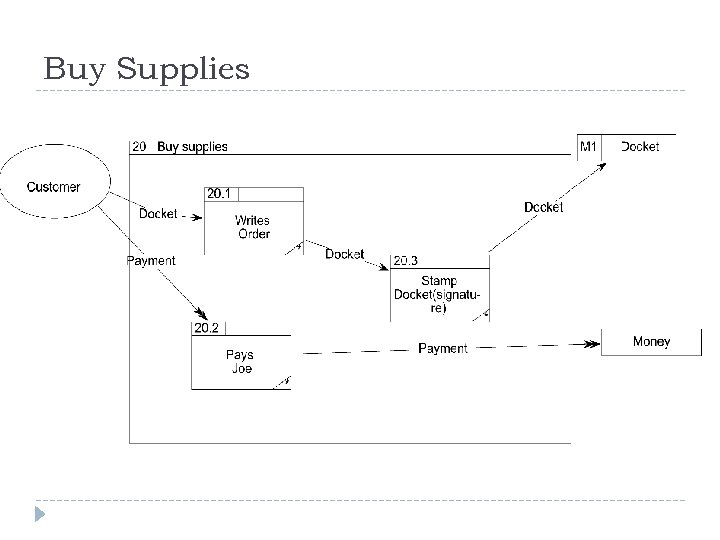 Buy Supplies
Buy Supplies
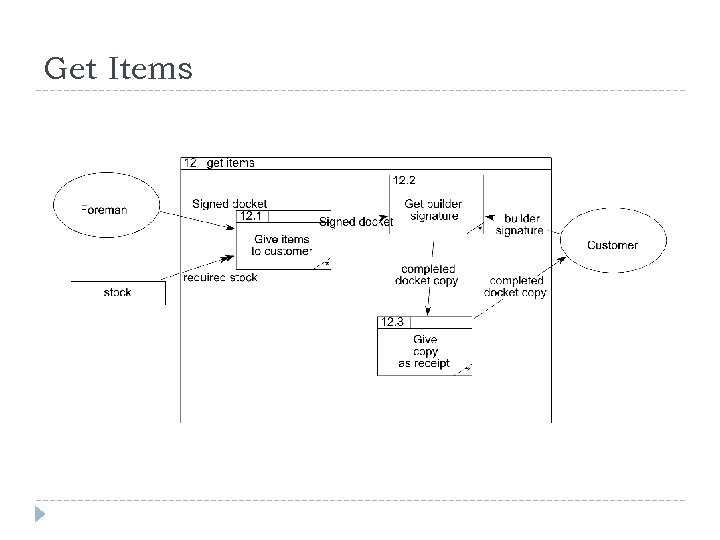 Get Items
Get Items
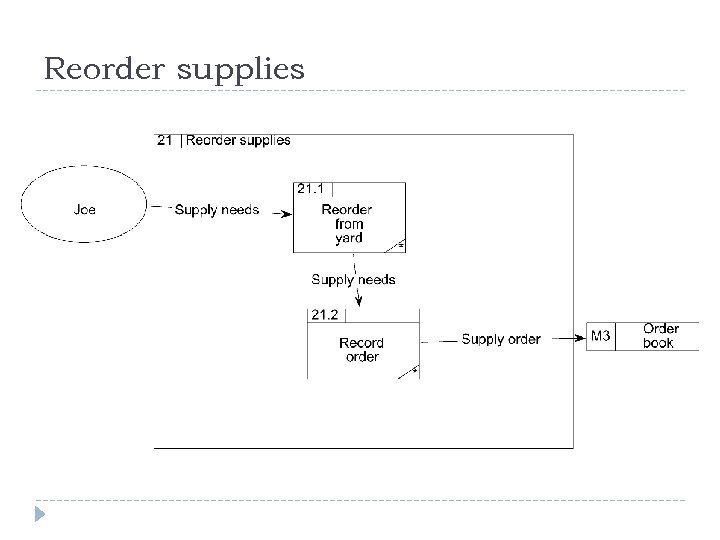 Reorder supplies
Reorder supplies
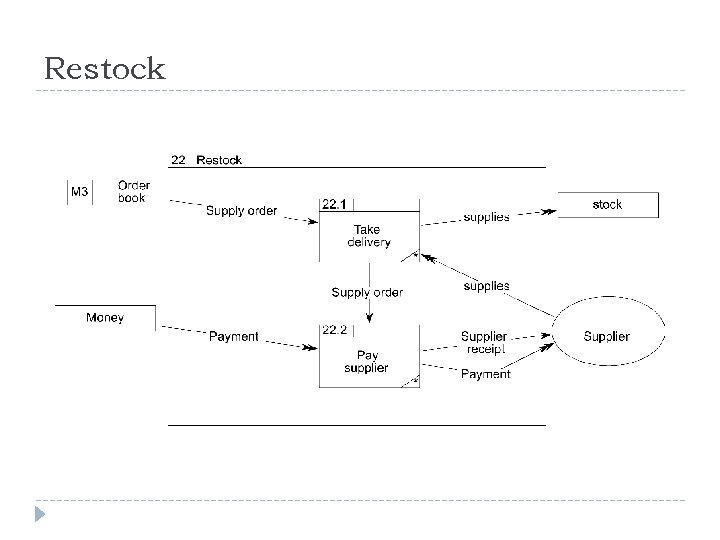 Restock
Restock
 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Steps: 1. Create a list of activities 2. Construct Context Level DFD (identifies external entities and processes) 3. Construct Level 0 DFD (identifies manageable sub process ) 4. Construct Level 1 - n DFD (identifies actual data flows and data stores ) 5. Check against rules of DFD
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Steps: 1. Create a list of activities 2. Construct Context Level DFD (identifies external entities and processes) 3. Construct Level 0 DFD (identifies manageable sub process ) 4. Construct Level 1 - n DFD (identifies actual data flows and data stores ) 5. Check against rules of DFD
 DFD Naming Guidelines External Entity Noun Data Flow Names of data Process verb phrase a system name a subsystem name Data Store Noun
DFD Naming Guidelines External Entity Noun Data Flow Names of data Process verb phrase a system name a subsystem name Data Store Noun
 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Lemonade Stand Example
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Lemonade Stand Example
 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example The operations of a simple lemonade stand will be used to demonstrate the creation of dataflow diagrams. Steps: 1. Create a list of activities • Old way: no Use-Case Diagram • New way: use Use-Case Diagram 2. Construct Context Level DFD (identifies sources and sink) 3. Construct Level 0 DFD (identifies manageable sub processes ) 4. Construct Level 1 - n DFD (identifies actual data flows and data stores )
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example The operations of a simple lemonade stand will be used to demonstrate the creation of dataflow diagrams. Steps: 1. Create a list of activities • Old way: no Use-Case Diagram • New way: use Use-Case Diagram 2. Construct Context Level DFD (identifies sources and sink) 3. Construct Level 0 DFD (identifies manageable sub processes ) 4. Construct Level 1 - n DFD (identifies actual data flows and data stores )
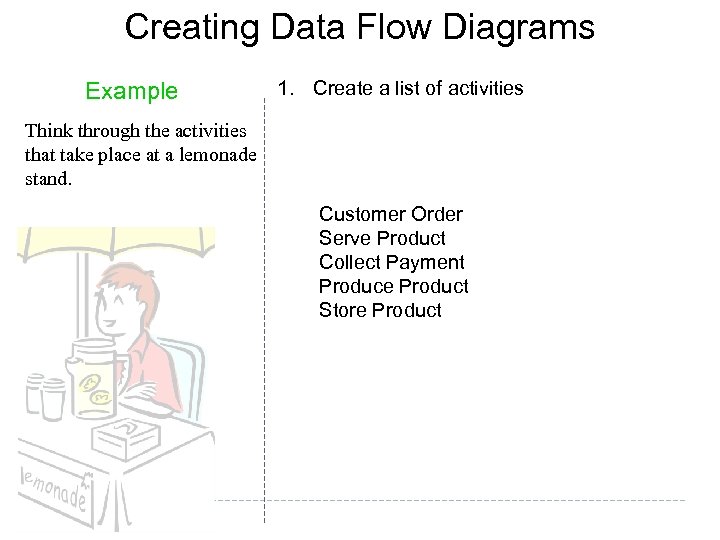 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example 1. Create a list of activities Think through the activities that take place at a lemonade stand. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example 1. Create a list of activities Think through the activities that take place at a lemonade stand. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product
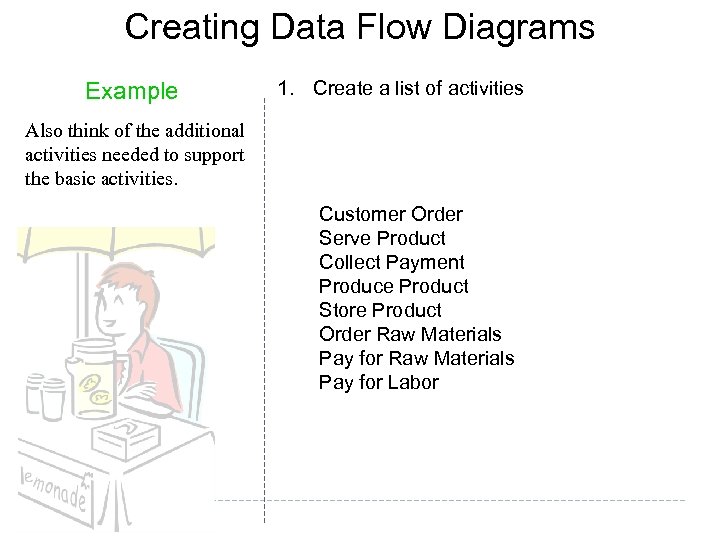 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example 1. Create a list of activities Also think of the additional activities needed to support the basic activities. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example 1. Create a list of activities Also think of the additional activities needed to support the basic activities. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor
 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example 1. Create a list of activities Group these activities in some logical fashion, possibly functional areas. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example 1. Create a list of activities Group these activities in some logical fashion, possibly functional areas. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor
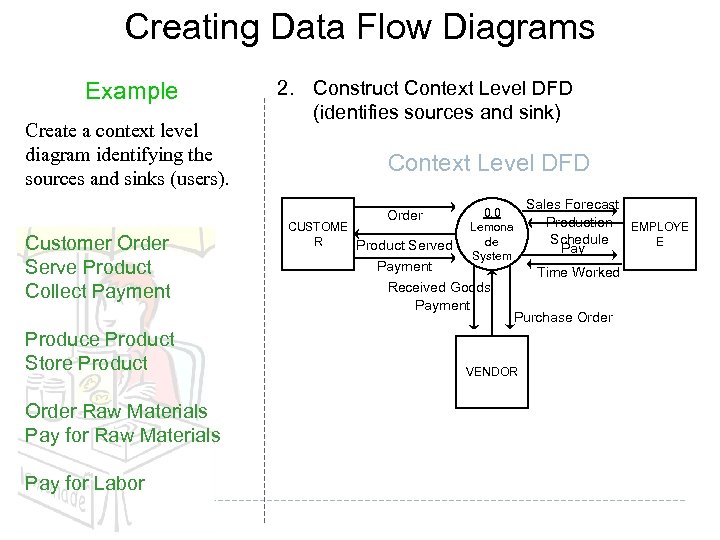 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a context level diagram identifying the sources and sinks (users). 2. Construct Context Level DFD (identifies sources and sink) Context Level DFD Order Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor CUSTOME R Product Served 0. 0 Lemona de System Payment Received Goods Payment Sales Forecast Production EMPLOYE Schedule E Pay Time Worked Purchase Order VENDOR
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a context level diagram identifying the sources and sinks (users). 2. Construct Context Level DFD (identifies sources and sink) Context Level DFD Order Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor CUSTOME R Product Served 0. 0 Lemona de System Payment Received Goods Payment Sales Forecast Production EMPLOYE Schedule E Pay Time Worked Purchase Order VENDOR
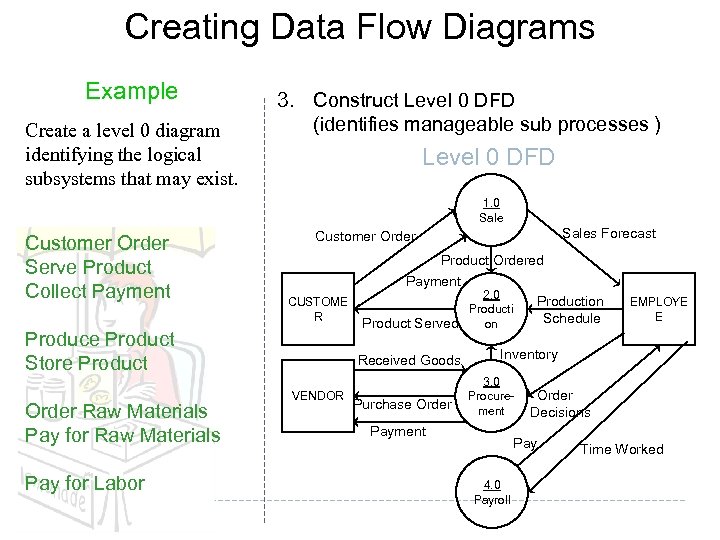 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 0 diagram identifying the logical subsystems that may exist. 3. Construct Level 0 DFD (identifies manageable sub processes ) Level 0 DFD 1. 0 Sale Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment CUSTOME R Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor Sales Forecast Customer Order Product Ordered Payment 2. 0 Production Producti Schedule Product Served on Received Goods VENDOR Purchase Order EMPLOYE E Inventory 3. 0 Procurement Payment Order Decisions Pay 4. 0 Payroll Time Worked
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 0 diagram identifying the logical subsystems that may exist. 3. Construct Level 0 DFD (identifies manageable sub processes ) Level 0 DFD 1. 0 Sale Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment CUSTOME R Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor Sales Forecast Customer Order Product Ordered Payment 2. 0 Production Producti Schedule Product Served on Received Goods VENDOR Purchase Order EMPLOYE E Inventory 3. 0 Procurement Payment Order Decisions Pay 4. 0 Payroll Time Worked
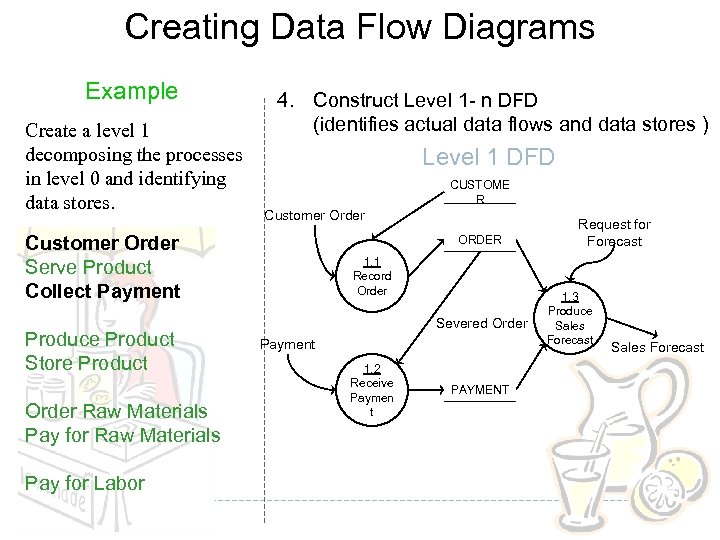 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 1 decomposing the processes in level 0 and identifying data stores. 4. Construct Level 1 - n DFD (identifies actual data flows and data stores ) Level 1 DFD CUSTOME R Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor ORDER 1. 1 Record Order Severed Order Payment 1. 2 Receive Paymen t PAYMENT Request for Forecast 1. 3 Produce Sales Forecast
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 1 decomposing the processes in level 0 and identifying data stores. 4. Construct Level 1 - n DFD (identifies actual data flows and data stores ) Level 1 DFD CUSTOME R Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor ORDER 1. 1 Record Order Severed Order Payment 1. 2 Receive Paymen t PAYMENT Request for Forecast 1. 3 Produce Sales Forecast
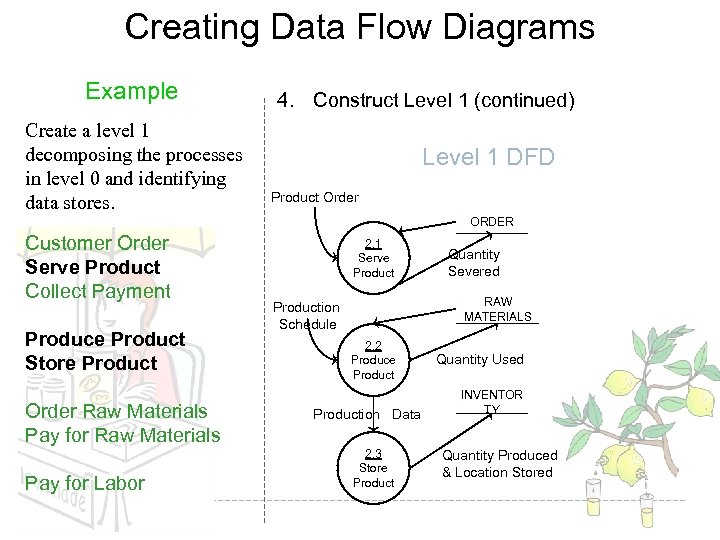 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 1 decomposing the processes in level 0 and identifying data stores. 4. Construct Level 1 (continued) Level 1 DFD Product Order ORDER Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor 2. 1 Serve Product Quantity Severed RAW MATERIALS Production Schedule 2. 2 Produce Production Data 2. 3 Store Product Quantity Used INVENTOR TY Quantity Produced & Location Stored
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 1 decomposing the processes in level 0 and identifying data stores. 4. Construct Level 1 (continued) Level 1 DFD Product Order ORDER Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Labor 2. 1 Serve Product Quantity Severed RAW MATERIALS Production Schedule 2. 2 Produce Production Data 2. 3 Store Product Quantity Used INVENTOR TY Quantity Produced & Location Stored
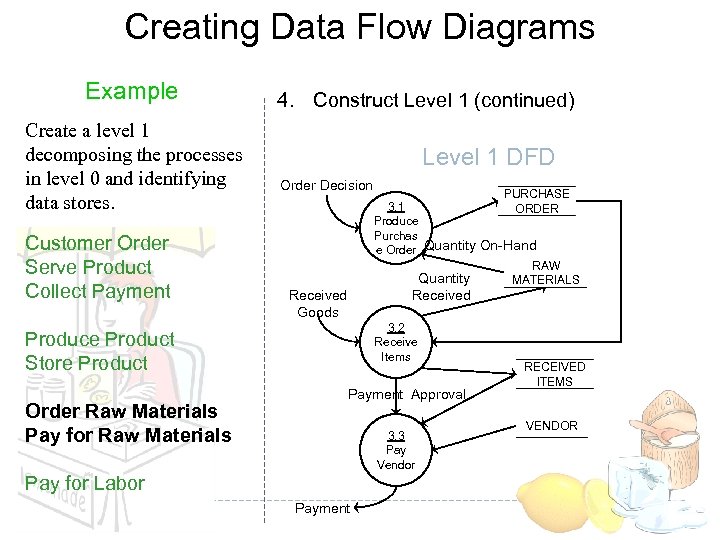 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 1 decomposing the processes in level 0 and identifying data stores. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment 4. Construct Level 1 (continued) Level 1 DFD Order Decision Received Goods 3. 2 Receive Items Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Raw Materials PURCHASE 3. 1 ORDER Produce Purchas e Order Quantity On-Hand RAW Quantity MATERIALS Payment Approval 3. 3 Pay Vendor Pay for Labor Payment RECEIVED ITEMS VENDOR
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 1 decomposing the processes in level 0 and identifying data stores. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment 4. Construct Level 1 (continued) Level 1 DFD Order Decision Received Goods 3. 2 Receive Items Produce Product Store Product Order Raw Materials Pay for Raw Materials PURCHASE 3. 1 ORDER Produce Purchas e Order Quantity On-Hand RAW Quantity MATERIALS Payment Approval 3. 3 Pay Vendor Pay for Labor Payment RECEIVED ITEMS VENDOR
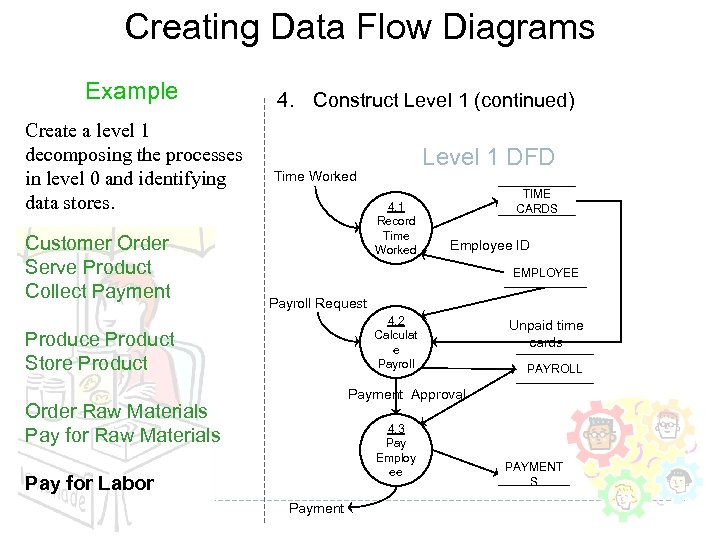 Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 1 decomposing the processes in level 0 and identifying data stores. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment 4. Construct Level 1 (continued) Level 1 DFD Time Worked 4. 1 Record Time Worked TIME CARDS Employee ID EMPLOYEE Payroll Request 4. 2 Calculat e Payroll Produce Product Store Product Unpaid time cards PAYROLL Payment Approval Order Raw Materials Pay for Raw Materials 4. 3 Pay Employ ee Pay for Labor Payment PAYMENT S
Creating Data Flow Diagrams Example Create a level 1 decomposing the processes in level 0 and identifying data stores. Customer Order Serve Product Collect Payment 4. Construct Level 1 (continued) Level 1 DFD Time Worked 4. 1 Record Time Worked TIME CARDS Employee ID EMPLOYEE Payroll Request 4. 2 Calculat e Payroll Produce Product Store Product Unpaid time cards PAYROLL Payment Approval Order Raw Materials Pay for Raw Materials 4. 3 Pay Employ ee Pay for Labor Payment PAYMENT S
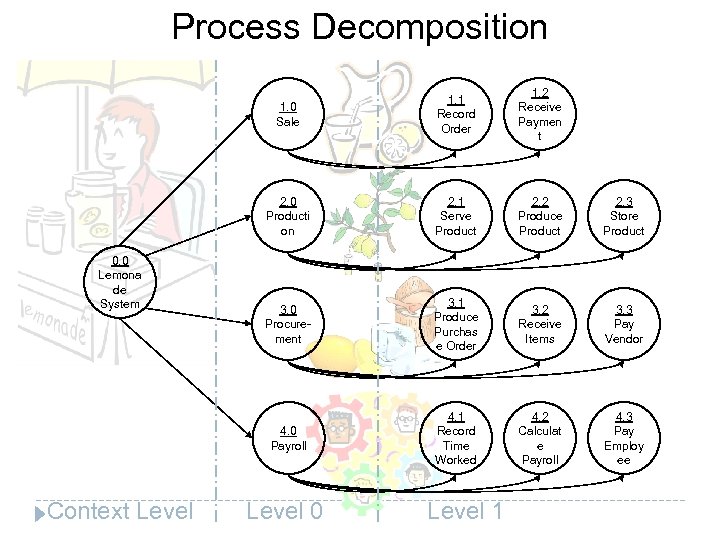 Process Decomposition 1. 0 Sale 2. 1 Serve Product 2. 2 Produce Product 2. 3 Store Product 3. 0 Procurement 3. 1 Produce Purchas e Order 3. 2 Receive Items 3. 3 Pay Vendor 4. 0 Payroll Context Level 1. 2 Receive Paymen t 2. 0 Producti on 0. 0 Lemona de System 1. 1 Record Order 4. 1 Record Time Worked 4. 2 Calculat e Payroll 4. 3 Pay Employ ee Level 0 Level 1
Process Decomposition 1. 0 Sale 2. 1 Serve Product 2. 2 Produce Product 2. 3 Store Product 3. 0 Procurement 3. 1 Produce Purchas e Order 3. 2 Receive Items 3. 3 Pay Vendor 4. 0 Payroll Context Level 1. 2 Receive Paymen t 2. 0 Producti on 0. 0 Lemona de System 1. 1 Record Order 4. 1 Record Time Worked 4. 2 Calculat e Payroll 4. 3 Pay Employ ee Level 0 Level 1
 DFD Example: Bus Garage Repairs Buses come to a garage for repairs. A mechanic and helper perform the repair, record the reason for the repair and record the total cost of all parts used on a Shop Repair Order. Information on labor, parts and repair outcome is used for billing by the Accounting Department, parts monitoring by the inventory management computer system and a performance review by the supervisor.
DFD Example: Bus Garage Repairs Buses come to a garage for repairs. A mechanic and helper perform the repair, record the reason for the repair and record the total cost of all parts used on a Shop Repair Order. Information on labor, parts and repair outcome is used for billing by the Accounting Department, parts monitoring by the inventory management computer system and a performance review by the supervisor.
 DFD Example: Bus Garage Repairs (cont’d) External Entities: Bus, Mechanic, Helper, Supervisor, Inventory Management System, Accounting Department, etc. Key process (“the system”): performing repairs and storing information related to repairs Processes: Record Bus ID and reason for repair Determine parts needed Perform repair Calculate parts extended and total cost Record labor hours, cost
DFD Example: Bus Garage Repairs (cont’d) External Entities: Bus, Mechanic, Helper, Supervisor, Inventory Management System, Accounting Department, etc. Key process (“the system”): performing repairs and storing information related to repairs Processes: Record Bus ID and reason for repair Determine parts needed Perform repair Calculate parts extended and total cost Record labor hours, cost
 DFD Example: Bus Garage Repairs (cont’d) Data stores: Personnel file Repairs file Bus master list Parts list Data flows: Repair order Bus record Parts record Employee timecard Invoices
DFD Example: Bus Garage Repairs (cont’d) Data stores: Personnel file Repairs file Bus master list Parts list Data flows: Repair order Bus record Parts record Employee timecard Invoices
 Bus Garage Context Diagram Bus Fixed mechanical problems Mechanical problem to be repaired Helper Labor Mechanic Bus Repair Process System Labor, parts cost details Repair summary List of parts used Supervisor Inventory Management System Accountin g
Bus Garage Context Diagram Bus Fixed mechanical problems Mechanical problem to be repaired Helper Labor Mechanic Bus Repair Process System Labor, parts cost details Repair summary List of parts used Supervisor Inventory Management System Accountin g
 CSUB Burger’s Order Processing System Draw the CSUB Burger’s context diagram System External entities Order processing system Kitchen Restaurant Customer Processes Customer order Receipt Food order Management report
CSUB Burger’s Order Processing System Draw the CSUB Burger’s context diagram System External entities Order processing system Kitchen Restaurant Customer Processes Customer order Receipt Food order Management report


