24f8704243685bacfcef7a12603baf5f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Data Communication & Computer Networks CS 1652 Jack Lange University of Pittsburgh The slides are adapted from the publisher’s material All material copyright 1996 -2009 J. F Kurose and K. W. Ross, All Rights Reserved 1 -1
Data Communication & Computer Networks CS 1652 Jack Lange University of Pittsburgh The slides are adapted from the publisher’s material All material copyright 1996 -2009 J. F Kurose and K. W. Ross, All Rights Reserved 1 -1
 Course Objectives q Understand modern data communication systems and computer networks Understand the key concepts v How they are designed & implemented v How they are operated v How they are likely to evolve in the future v q Course Approach Top-down : from what’s familiar to nuts and bolts v The Internet as the main focus v Hands-on experience on networked systems v 1 -2
Course Objectives q Understand modern data communication systems and computer networks Understand the key concepts v How they are designed & implemented v How they are operated v How they are likely to evolve in the future v q Course Approach Top-down : from what’s familiar to nuts and bolts v The Internet as the main focus v Hands-on experience on networked systems v 1 -2
 Administrativia q Instructor: Jack Lange v Email: jacklange@cs. pitt. edu v Office: Sennott Square #5407 v Office Hours: Weds. 2 -4 PM Teaching Assistant: TBD 1 -3
Administrativia q Instructor: Jack Lange v Email: jacklange@cs. pitt. edu v Office: Sennott Square #5407 v Office Hours: Weds. 2 -4 PM Teaching Assistant: TBD 1 -3
 Communication q Course homepage v v v http: //www. cs. pitt. edu/~jacklange/teaching/cs 1652 -f 13/ Announcements, clarifications, corrections Additional resources for projects q Google Group http: //groups. google. com/group/pitt-cs 1652 -f 13 v pitt-cs 1652 -f 13@googlegroups. com v Private discussion group v • Open venue for class discussions and questions v Based on email (Pitt addresses) • Email me if you want to use a different one
Communication q Course homepage v v v http: //www. cs. pitt. edu/~jacklange/teaching/cs 1652 -f 13/ Announcements, clarifications, corrections Additional resources for projects q Google Group http: //groups. google. com/group/pitt-cs 1652 -f 13 v pitt-cs 1652 -f 13@googlegroups. com v Private discussion group v • Open venue for class discussions and questions v Based on email (Pitt addresses) • Email me if you want to use a different one
 Text. Books q Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach James Kurose and Keith Ross v Fifth/Sixth Edition, Addison Wesley, 2010 v q TCP/IP Illustrated, Volume I: The Protocols Richard Stevens v Addison Wesley, 1994 v
Text. Books q Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach James Kurose and Keith Ross v Fifth/Sixth Edition, Addison Wesley, 2010 v q TCP/IP Illustrated, Volume I: The Protocols Richard Stevens v Addison Wesley, 1994 v
 Class meeting times q Lecture v Tues/Thurs: 4: 00 -5: 15 PM v Sennott Square, Rm. 6110 q Lab Sessions v Sennott Square, Rm. 5506 v Periodically replace lectures v Hands on exercises v Answer project question v Hopefully guest lectures 1 -6
Class meeting times q Lecture v Tues/Thurs: 4: 00 -5: 15 PM v Sennott Square, Rm. 6110 q Lab Sessions v Sennott Square, Rm. 5506 v Periodically replace lectures v Hands on exercises v Answer project question v Hopefully guest lectures 1 -6
 Networking Lab q Sennott Square, Rm. 5506 v 16 Linux machines (Fedore Core 13) v Login: Hopefully will be your Pitt login v Available for projects • Can use other machines, but… • Must work on lab equipment q Dual NICS v 1 internal network interface to be used for projects v 1 external network interface for external access 1 -11
Networking Lab q Sennott Square, Rm. 5506 v 16 Linux machines (Fedore Core 13) v Login: Hopefully will be your Pitt login v Available for projects • Can use other machines, but… • Must work on lab equipment q Dual NICS v 1 internal network interface to be used for projects v 1 external network interface for external access 1 -11
 Homework q Reading assignments v Expected to read before each class q Homework v 4 problem sets spaced over semester q Projects v Web server (20%) v TCP (50%) v Routing (30%) q Check Syllabus!
Homework q Reading assignments v Expected to read before each class q Homework v 4 problem sets spaced over semester q Projects v Web server (20%) v TCP (50%) v Routing (30%) q Check Syllabus!
 Grading q Grading v Midterm (20%) v Final (20%) v 4 Homework (10%) v 3 Projects (50%) q Late policy v Submit by midnight of the due date v 10% penalty for every day late
Grading q Grading v Midterm (20%) v Final (20%) v 4 Homework (10%) v 3 Projects (50%) q Late policy v Submit by midnight of the due date v 10% penalty for every day late
 Projects q Work in groups of 2 v C/C++ is required q Lot of work, but will be worth it v Build a TCP stack and a Web server that runs on it v IP routing q Highly Recommended: OS or having some familiarity with Unix systems programming, preferably in C or C++ v Minet is in C++ v BUILDING software is 50% of the grade of this class 1 -9
Projects q Work in groups of 2 v C/C++ is required q Lot of work, but will be worth it v Build a TCP stack and a Web server that runs on it v IP routing q Highly Recommended: OS or having some familiarity with Unix systems programming, preferably in C or C++ v Minet is in C++ v BUILDING software is 50% of the grade of this class 1 -9
 Today’s topic q Computer Networks Overview v What’s the Internet? • Nuts and bolts vs. service view v What’s a protocol? • A set of rules between communicating entities v Network edge/core • Hosts, access networks, physical media • Packet switching/circuit switching, Internet structure q Goal Get “feel” and terminology v More depth, detail later in course v 1 -12
Today’s topic q Computer Networks Overview v What’s the Internet? • Nuts and bolts vs. service view v What’s a protocol? • A set of rules between communicating entities v Network edge/core • Hosts, access networks, physical media • Packet switching/circuit switching, Internet structure q Goal Get “feel” and terminology v More depth, detail later in course v 1 -12
 What is the internet? q Flows, packets, and bits q Optical light, electricity, and radio waves q Servers, clients, and peers q Hosts, switches, and routers
What is the internet? q Flows, packets, and bits q Optical light, electricity, and radio waves q Servers, clients, and peers q Hosts, switches, and routers
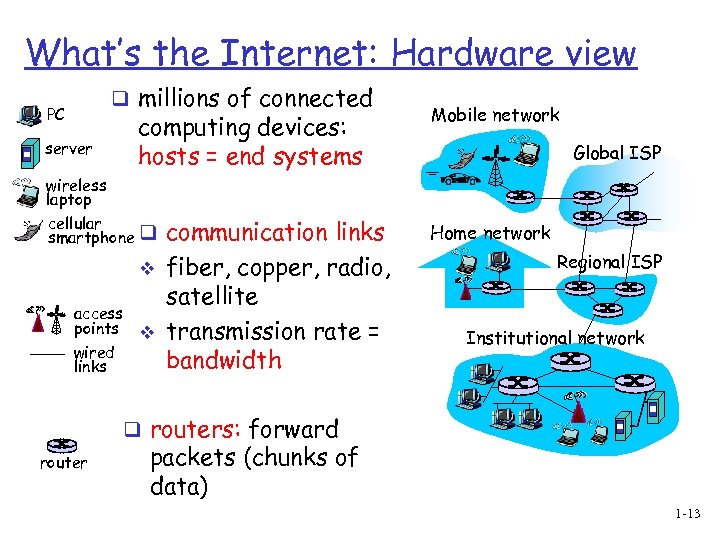 What’s the Internet: Hardware view q millions of connected PC server computing devices: hosts = end systems wireless laptop cellular smartphone q v access points v wired links communication links fiber, copper, radio, satellite transmission rate = bandwidth Mobile network Global ISP Home network Regional ISP Institutional network q routers: forward router packets (chunks of data) 1 -13
What’s the Internet: Hardware view q millions of connected PC server computing devices: hosts = end systems wireless laptop cellular smartphone q v access points v wired links communication links fiber, copper, radio, satellite transmission rate = bandwidth Mobile network Global ISP Home network Regional ISP Institutional network q routers: forward router packets (chunks of data) 1 -13
 What’s a protocol? human protocols: q “what’s the time? ” q “I have a question” q introductions network protocols: q machines rather than humans q all communication activity in Internet governed by protocols … specific msgs sent … specific actions taken when msgs received, or other events protocols define format, order of msgs sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on msg transmission, receipt 1 -17
What’s a protocol? human protocols: q “what’s the time? ” q “I have a question” q introductions network protocols: q machines rather than humans q all communication activity in Internet governed by protocols … specific msgs sent … specific actions taken when msgs received, or other events protocols define format, order of msgs sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on msg transmission, receipt 1 -17
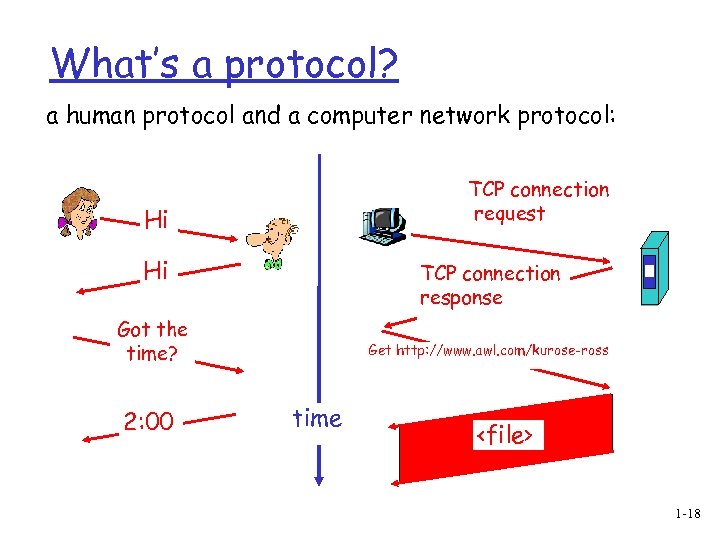 What’s a protocol? a human protocol and a computer network protocol: TCP connection request Hi Hi TCP connection response Got the time? 2: 00 Get http: //www. awl. com/kurose-ross time
What’s a protocol? a human protocol and a computer network protocol: TCP connection request Hi Hi TCP connection response Got the time? 2: 00 Get http: //www. awl. com/kurose-ross time
 Where are we? q What’s the Internet? v Nuts and bolts vs. service view q What’s the protocol? q Network edge/core Hosts, access networks, physical media v Packet switching/circuit switching, Internet structure v 1 -19
Where are we? q What’s the Internet? v Nuts and bolts vs. service view q What’s the protocol? q Network edge/core Hosts, access networks, physical media v Packet switching/circuit switching, Internet structure v 1 -19
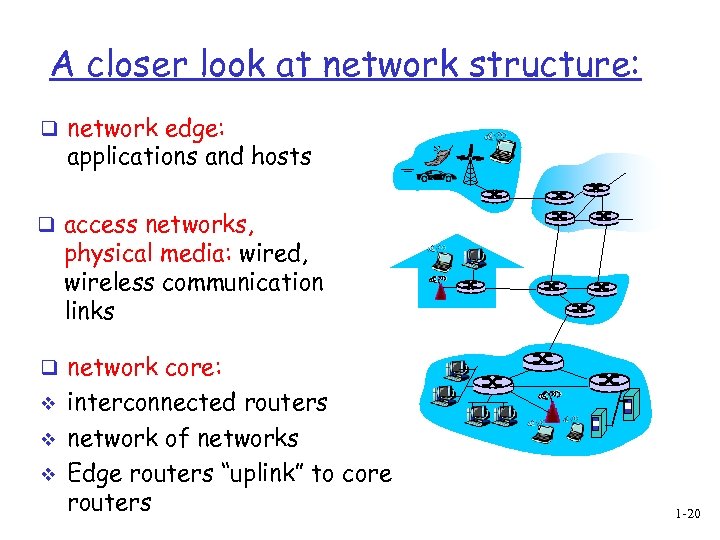 A closer look at network structure: q network edge: applications and hosts q access networks, physical media: wired, wireless communication links q network core: v v v interconnected routers network of networks Edge routers “uplink” to core routers 1 -20
A closer look at network structure: q network edge: applications and hosts q access networks, physical media: wired, wireless communication links q network core: v v v interconnected routers network of networks Edge routers “uplink” to core routers 1 -20
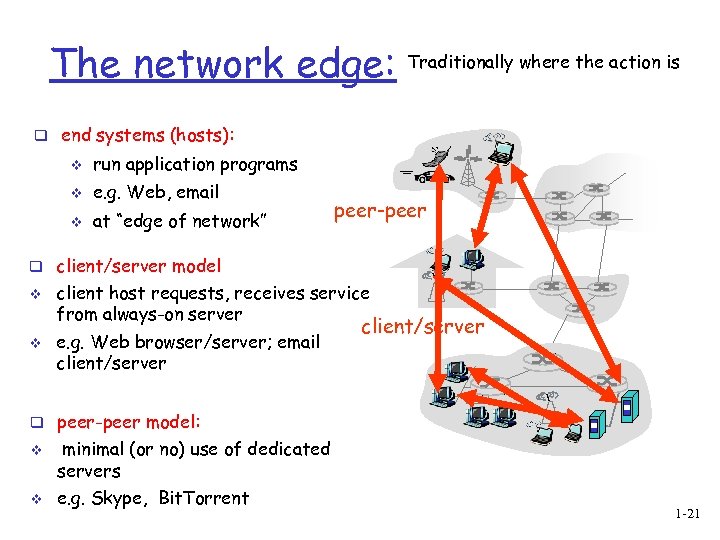 The network edge: Traditionally where the action is q end systems (hosts): v run application programs v e. g. Web, email v at “edge of network” peer-peer q client/server model v v client host requests, receives service from always-on server e. g. Web browser/server; email client/server q peer-peer model: v v minimal (or no) use of dedicated servers e. g. Skype, Bit. Torrent 1 -21
The network edge: Traditionally where the action is q end systems (hosts): v run application programs v e. g. Web, email v at “edge of network” peer-peer q client/server model v v client host requests, receives service from always-on server e. g. Web browser/server; email client/server q peer-peer model: v v minimal (or no) use of dedicated servers e. g. Skype, Bit. Torrent 1 -21
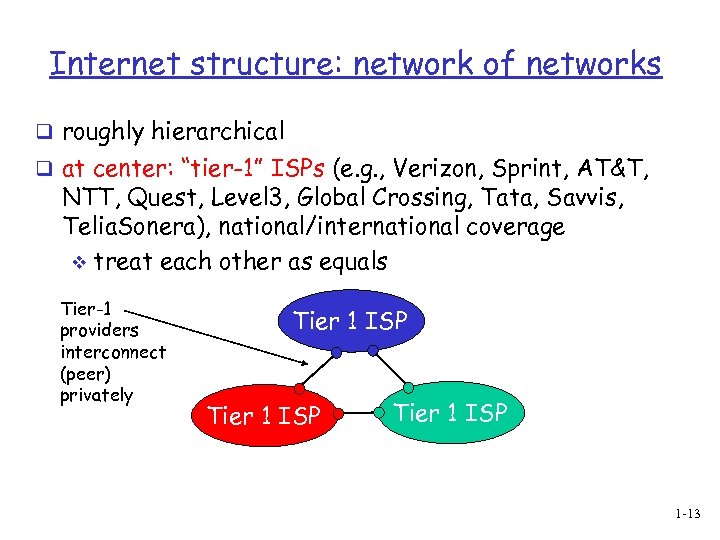 Internet structure: network of networks q roughly hierarchical q at center: “tier-1” ISPs (e. g. , Verizon, Sprint, AT&T, NTT, Quest, Level 3, Global Crossing, Tata, Savvis, Telia. Sonera), national/international coverage v treat each other as equals Tier-1 providers interconnect (peer) privately Tier 1 ISP 1 -13
Internet structure: network of networks q roughly hierarchical q at center: “tier-1” ISPs (e. g. , Verizon, Sprint, AT&T, NTT, Quest, Level 3, Global Crossing, Tata, Savvis, Telia. Sonera), national/international coverage v treat each other as equals Tier-1 providers interconnect (peer) privately Tier 1 ISP 1 -13
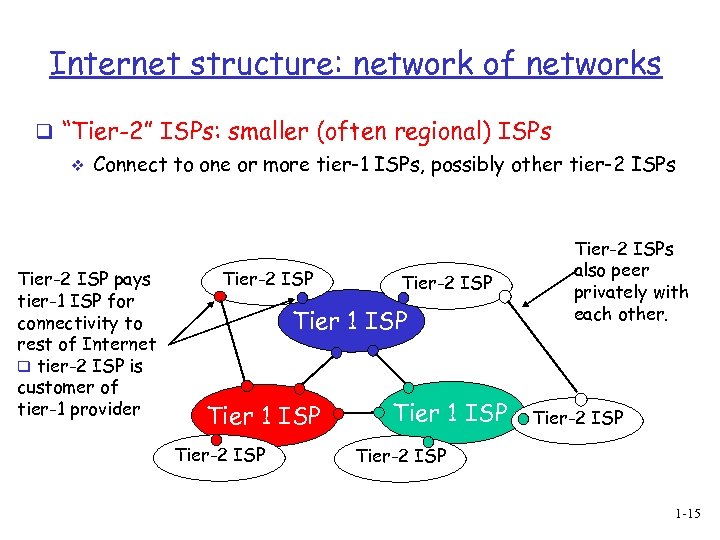 Internet structure: network of networks q “Tier-2” ISPs: smaller (often regional) ISPs v Connect to one or more tier-1 ISPs, possibly other tier-2 ISPs Tier-2 ISP pays tier-1 ISP for connectivity to rest of Internet q tier-2 ISP is customer of tier-1 provider Tier-2 ISP Tier 1 ISP Tier-2 ISPs also peer privately with each other. Tier-2 ISP 1 -15
Internet structure: network of networks q “Tier-2” ISPs: smaller (often regional) ISPs v Connect to one or more tier-1 ISPs, possibly other tier-2 ISPs Tier-2 ISP pays tier-1 ISP for connectivity to rest of Internet q tier-2 ISP is customer of tier-1 provider Tier-2 ISP Tier 1 ISP Tier-2 ISPs also peer privately with each other. Tier-2 ISP 1 -15
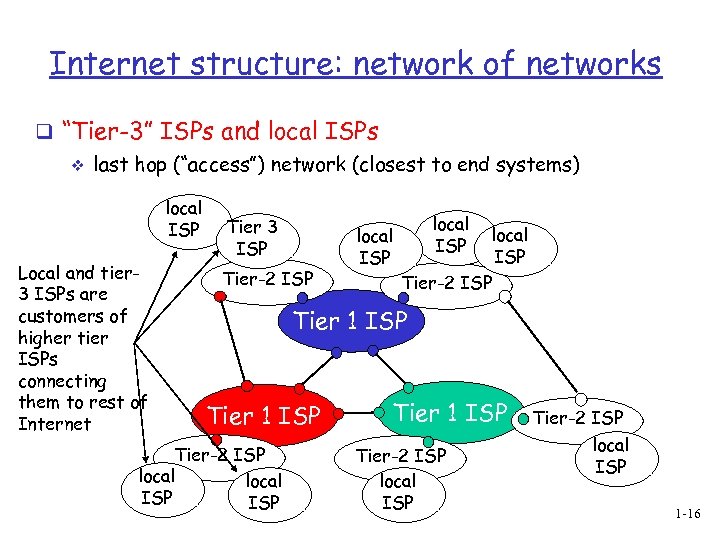 Internet structure: network of networks q “Tier-3” ISPs and local ISPs v last hop (“access”) network (closest to end systems) local ISP Local and tier 3 ISPs are customers of higher tier ISPs connecting them to rest of Internet Tier 3 ISP Tier-2 ISP local ISP Tier-2 ISP Tier 1 ISP Tier-2 ISP local ISP 1 -16
Internet structure: network of networks q “Tier-3” ISPs and local ISPs v last hop (“access”) network (closest to end systems) local ISP Local and tier 3 ISPs are customers of higher tier ISPs connecting them to rest of Internet Tier 3 ISP Tier-2 ISP local ISP Tier-2 ISP Tier 1 ISP Tier-2 ISP local ISP 1 -16
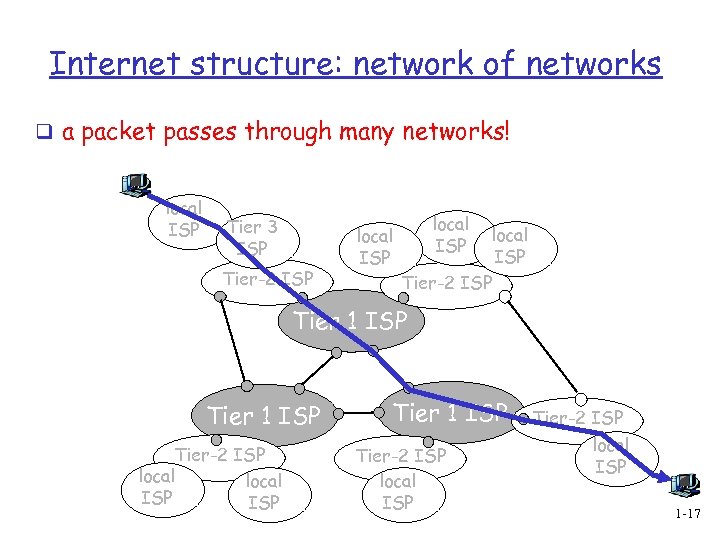 Internet structure: network of networks q a packet passes through many networks! local ISP Tier 3 ISP Tier-2 ISP local ISP Tier-2 ISP Tier 1 ISP Tier-2 ISP local ISP 1 -17
Internet structure: network of networks q a packet passes through many networks! local ISP Tier 3 ISP Tier-2 ISP local ISP Tier-2 ISP Tier 1 ISP Tier-2 ISP local ISP 1 -17
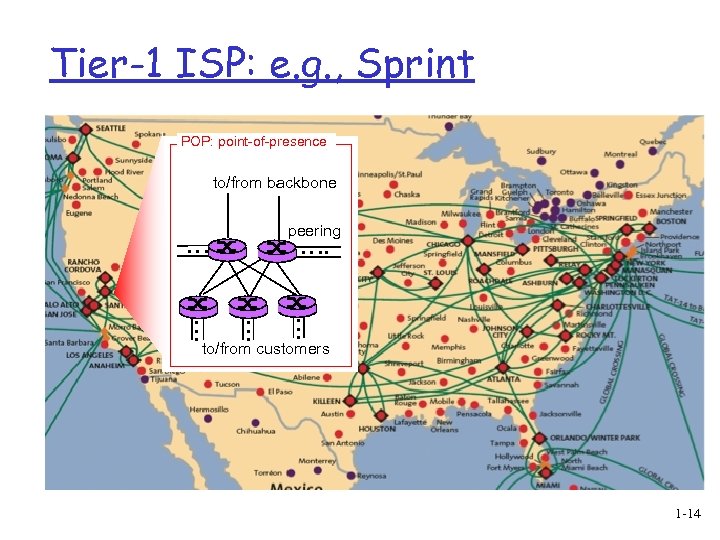 Tier-1 ISP: e. g. , Sprint POP: point-of-presence to/from backbone peering … … … to/from customers 1 -14
Tier-1 ISP: e. g. , Sprint POP: point-of-presence to/from backbone peering … … … to/from customers 1 -14
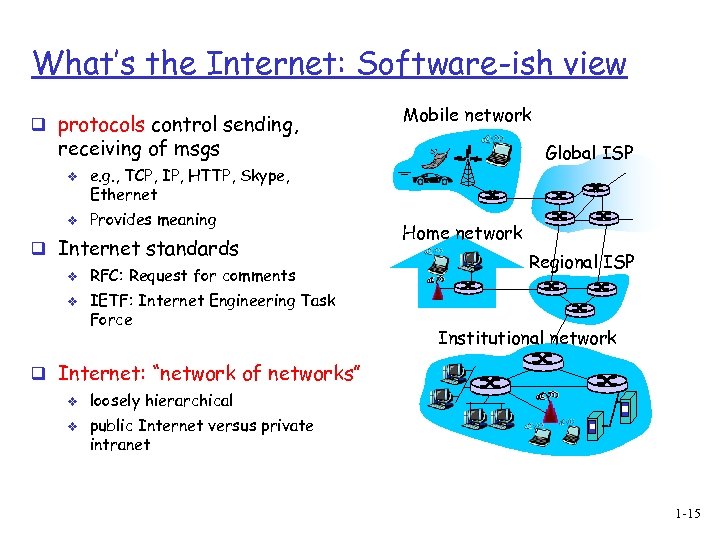 What’s the Internet: Software-ish view q protocols control sending, Mobile network receiving of msgs v v e. g. , TCP, IP, HTTP, Skype, Ethernet Provides meaning q Internet standards v v Global ISP RFC: Request for comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force Home network Regional ISP Institutional network q Internet: “network of networks” v v loosely hierarchical public Internet versus private intranet 1 -15
What’s the Internet: Software-ish view q protocols control sending, Mobile network receiving of msgs v v e. g. , TCP, IP, HTTP, Skype, Ethernet Provides meaning q Internet standards v v Global ISP RFC: Request for comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force Home network Regional ISP Institutional network q Internet: “network of networks” v v loosely hierarchical public Internet versus private intranet 1 -15
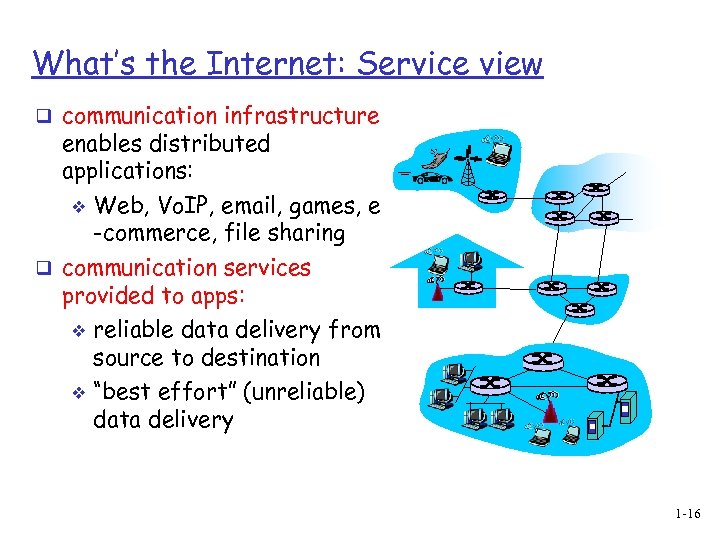 What’s the Internet: Service view q communication infrastructure enables distributed applications: v Web, Vo. IP, email, games, e -commerce, file sharing q communication services provided to apps: v reliable data delivery from source to destination v “best effort” (unreliable) data delivery 1 -16
What’s the Internet: Service view q communication infrastructure enables distributed applications: v Web, Vo. IP, email, games, e -commerce, file sharing q communication services provided to apps: v reliable data delivery from source to destination v “best effort” (unreliable) data delivery 1 -16
 Access networks and physical media Q: How to connect end systems to edge router? q residential access nets q institutional access networks (school, company) q mobile access networks Keep in mind: q bandwidth (bits per second) of access network? q shared or dedicated? 1 -22
Access networks and physical media Q: How to connect end systems to edge router? q residential access nets q institutional access networks (school, company) q mobile access networks Keep in mind: q bandwidth (bits per second) of access network? q shared or dedicated? 1 -22
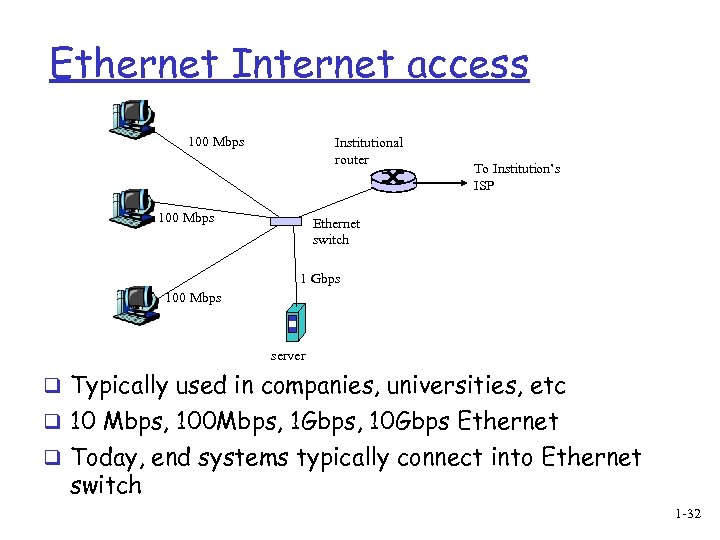 Ethernet Internet access 100 Mbps Institutional router 100 Mbps To Institution’s ISP Ethernet switch 1 Gbps 100 Mbps server q Typically used in companies, universities, etc q 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps Ethernet q Today, end systems typically connect into Ethernet switch 1 -32
Ethernet Internet access 100 Mbps Institutional router 100 Mbps To Institution’s ISP Ethernet switch 1 Gbps 100 Mbps server q Typically used in companies, universities, etc q 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps Ethernet q Today, end systems typically connect into Ethernet switch 1 -32
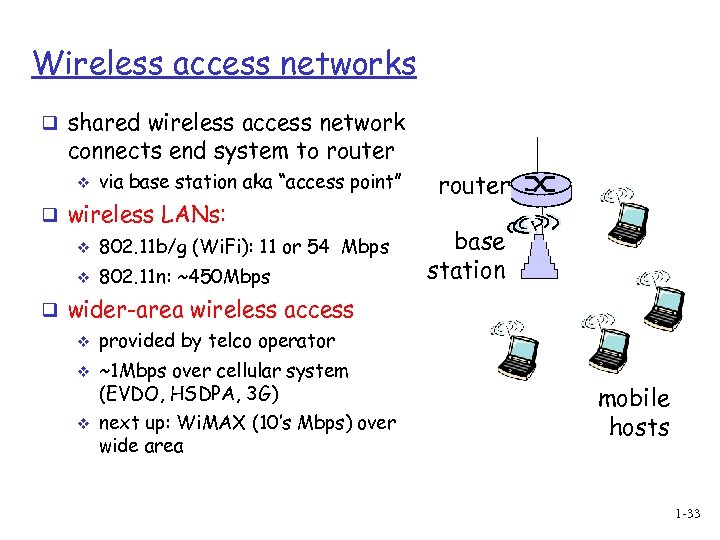 Wireless access networks q shared wireless access network connects end system to router v via base station aka “access point” q wireless LANs: v 802. 11 b/g (Wi. Fi): 11 or 54 Mbps v 802. 11 n: ~450 Mbps router base station q wider-area wireless access v v v provided by telco operator ~1 Mbps over cellular system (EVDO, HSDPA, 3 G) next up: Wi. MAX (10’s Mbps) over wide area mobile hosts 1 -33
Wireless access networks q shared wireless access network connects end system to router v via base station aka “access point” q wireless LANs: v 802. 11 b/g (Wi. Fi): 11 or 54 Mbps v 802. 11 n: ~450 Mbps router base station q wider-area wireless access v v v provided by telco operator ~1 Mbps over cellular system (EVDO, HSDPA, 3 G) next up: Wi. MAX (10’s Mbps) over wide area mobile hosts 1 -33
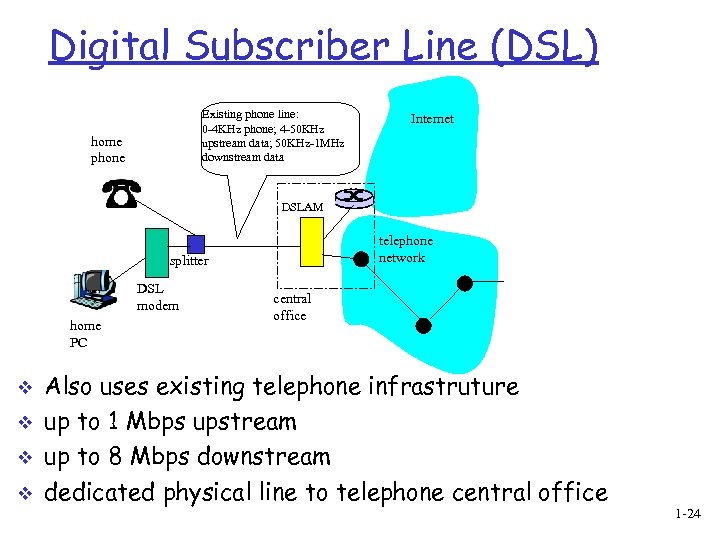 Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Existing phone line: 0 -4 KHz phone; 4 -50 KHz upstream data; 50 KHz-1 MHz downstream data home phone Internet DSLAM telephone network splitter DSL modem home PC v v central office Also uses existing telephone infrastruture up to 1 Mbps upstream up to 8 Mbps downstream dedicated physical line to telephone central office 1 -24
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Existing phone line: 0 -4 KHz phone; 4 -50 KHz upstream data; 50 KHz-1 MHz downstream data home phone Internet DSLAM telephone network splitter DSL modem home PC v v central office Also uses existing telephone infrastruture up to 1 Mbps upstream up to 8 Mbps downstream dedicated physical line to telephone central office 1 -24
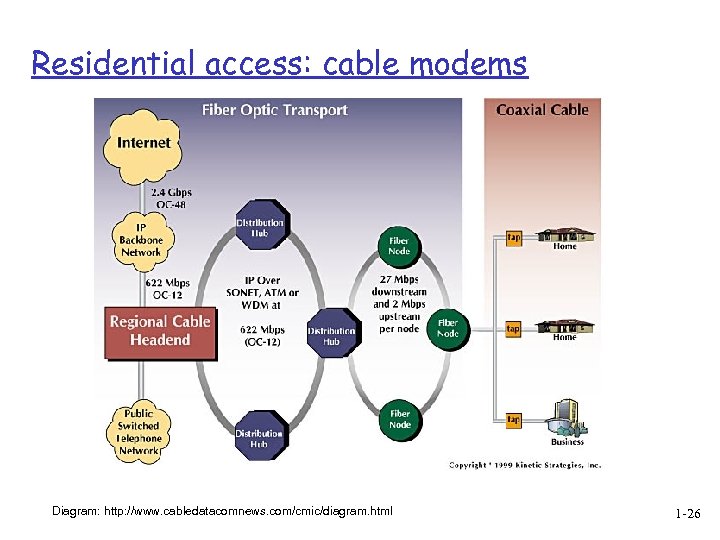 Residential access: cable modems Diagram: http: //www. cabledatacomnews. com/cmic/diagram. html 1 -26
Residential access: cable modems Diagram: http: //www. cabledatacomnews. com/cmic/diagram. html 1 -26
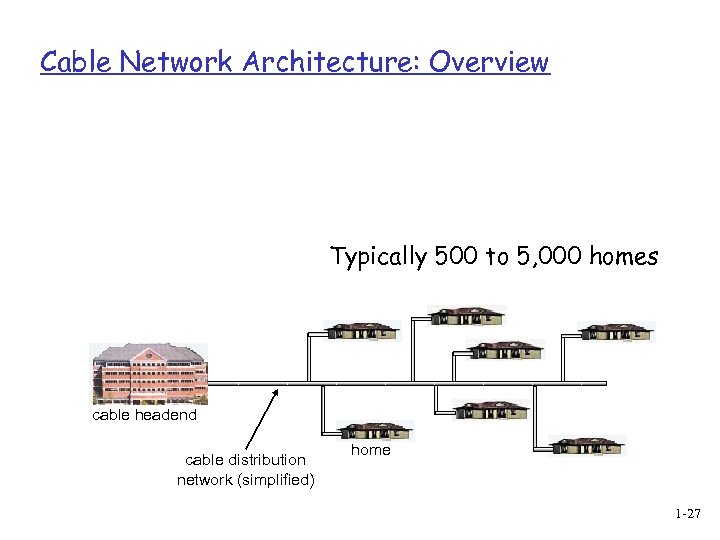 Cable Network Architecture: Overview Typically 500 to 5, 000 homes cable headend cable distribution network (simplified) home 1 -27
Cable Network Architecture: Overview Typically 500 to 5, 000 homes cable headend cable distribution network (simplified) home 1 -27
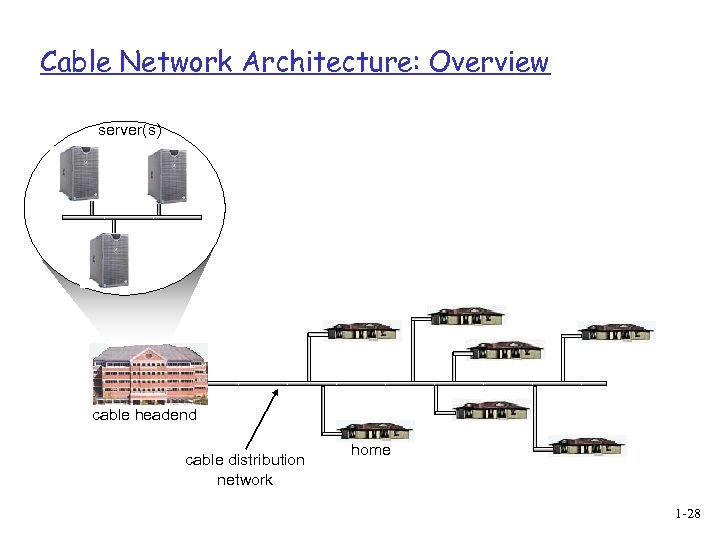 Cable Network Architecture: Overview server(s) cable headend cable distribution network home 1 -28
Cable Network Architecture: Overview server(s) cable headend cable distribution network home 1 -28
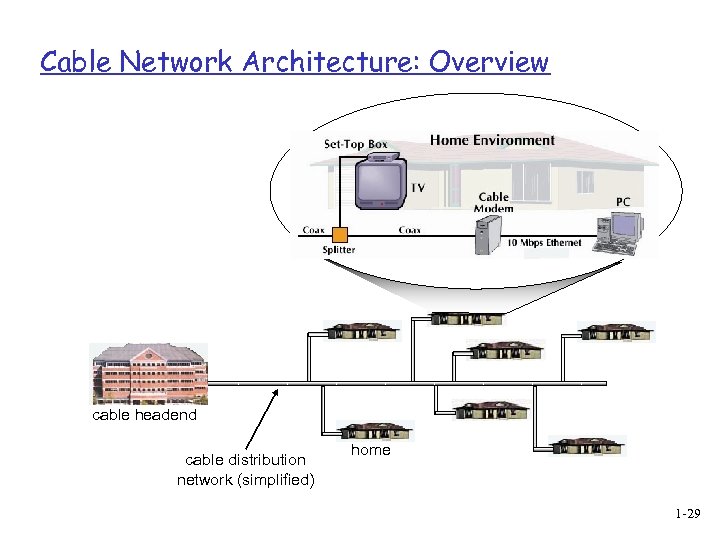 Cable Network Architecture: Overview cable headend cable distribution network (simplified) home 1 -29
Cable Network Architecture: Overview cable headend cable distribution network (simplified) home 1 -29
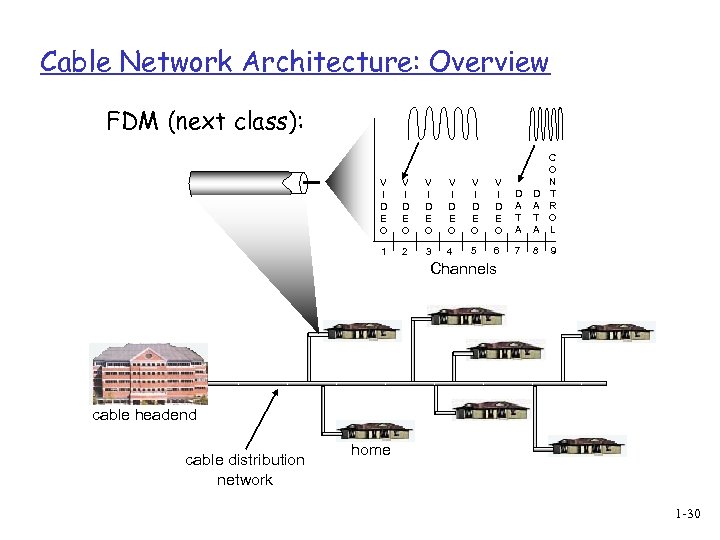 Cable Network Architecture: Overview FDM (next class): V I D E O V I D E O D A T A C O N T R O L 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Channels cable headend cable distribution network home 1 -30
Cable Network Architecture: Overview FDM (next class): V I D E O V I D E O D A T A C O N T R O L 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Channels cable headend cable distribution network home 1 -30
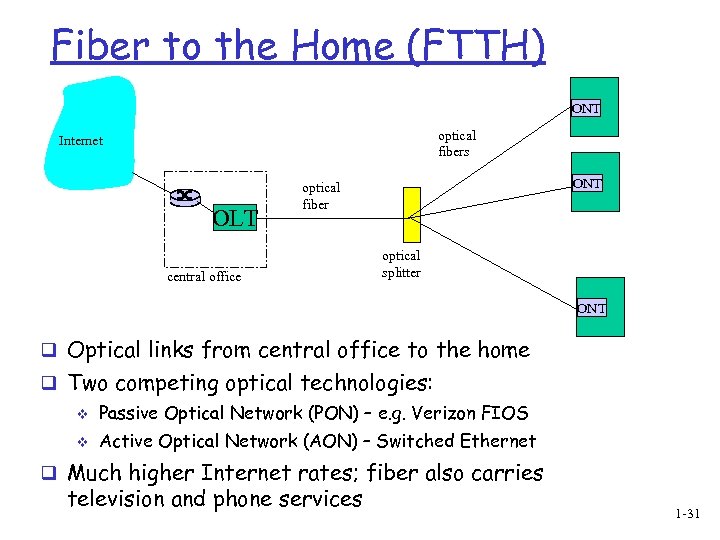 Fiber to the Home (FTTH) ONT optical fibers Internet OLT ONT optical fiber central office optical splitter ONT q Optical links from central office to the home q Two competing optical technologies: v Passive Optical Network (PON) – e. g. Verizon FIOS v Active Optical Network (AON) – Switched Ethernet q Much higher Internet rates; fiber also carries television and phone services 1 -31
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) ONT optical fibers Internet OLT ONT optical fiber central office optical splitter ONT q Optical links from central office to the home q Two competing optical technologies: v Passive Optical Network (PON) – e. g. Verizon FIOS v Active Optical Network (AON) – Switched Ethernet q Much higher Internet rates; fiber also carries television and phone services 1 -31
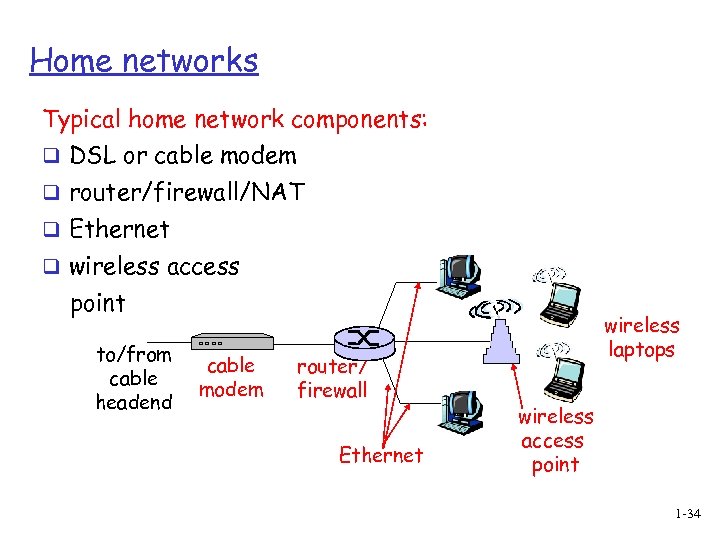 Home networks Typical home network components: q DSL or cable modem q router/firewall/NAT q Ethernet q wireless access point to/from cable headend cable modem router/ firewall Ethernet wireless laptops wireless access point 1 -34
Home networks Typical home network components: q DSL or cable modem q router/firewall/NAT q Ethernet q wireless access point to/from cable headend cable modem router/ firewall Ethernet wireless laptops wireless access point 1 -34
 Physical media q Bit: propagates between transmitter/rcvr pairs q physical link: what lies between transmitter & receiver q guided media: v signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax Twisted Pair (TP) q two insulated copper wires v v Category 3: traditional phone wires, 10 Mbps Ethernet Category 5: 100 Mbps Ethernet q unguided media: v signals propagate freely, e. g. , radio 1 -35
Physical media q Bit: propagates between transmitter/rcvr pairs q physical link: what lies between transmitter & receiver q guided media: v signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax Twisted Pair (TP) q two insulated copper wires v v Category 3: traditional phone wires, 10 Mbps Ethernet Category 5: 100 Mbps Ethernet q unguided media: v signals propagate freely, e. g. , radio 1 -35
 Physical media: coax, fiber Coaxial cable: q two concentric copper conductors q bidirectional q baseband: v single channel on cable • Digital signal v legacy Ethernet Fiber optic cable: q glass fiber carrying light pulses, each pulse a bit q high-speed operation: v high-speed point-to-point transmission (e. g. , 10’s-100’s Gps) q low error rate: repeaters spaced far apart ; immune to electromagnetic noise q broadband: v multiple channels on cable • Analog Signal v HFC 1 -36
Physical media: coax, fiber Coaxial cable: q two concentric copper conductors q bidirectional q baseband: v single channel on cable • Digital signal v legacy Ethernet Fiber optic cable: q glass fiber carrying light pulses, each pulse a bit q high-speed operation: v high-speed point-to-point transmission (e. g. , 10’s-100’s Gps) q low error rate: repeaters spaced far apart ; immune to electromagnetic noise q broadband: v multiple channels on cable • Analog Signal v HFC 1 -36
 Physical media: radio q signal carried in electromagnetic spectrum q no physical “wire” q bidirectional q propagation environment effects: v reflection v obstruction by objects v interference Radio link types: q terrestrial microwave v e. g. up to 45 Mbps channels q LAN (e. g. , Wifi) v 11 Mbps, 54 Mbps q wide-area (e. g. , cellular) v 3 G cellular: ~ 1 Mbps q satellite v Kbps to 45 Mbps channel (or multiple smaller channels) v 270 msec end-end delay v geosynchronous versus low altitude 1 -37
Physical media: radio q signal carried in electromagnetic spectrum q no physical “wire” q bidirectional q propagation environment effects: v reflection v obstruction by objects v interference Radio link types: q terrestrial microwave v e. g. up to 45 Mbps channels q LAN (e. g. , Wifi) v 11 Mbps, 54 Mbps q wide-area (e. g. , cellular) v 3 G cellular: ~ 1 Mbps q satellite v Kbps to 45 Mbps channel (or multiple smaller channels) v 270 msec end-end delay v geosynchronous versus low altitude 1 -37
 Summary q The Internet can be defined as A set of hosts running distributed applications communicating via routers v Infrastructure providing popular services v q Protocols define the message formats, orders, actions on transmission and reception q Access networks: at the network edge Residential (dial-up, DSL, Cable, FTTH) v Institutional (Ethernet) v Wireless (Wi-fi, Wi. MAX) v 1 -38
Summary q The Internet can be defined as A set of hosts running distributed applications communicating via routers v Infrastructure providing popular services v q Protocols define the message formats, orders, actions on transmission and reception q Access networks: at the network edge Residential (dial-up, DSL, Cable, FTTH) v Institutional (Ethernet) v Wireless (Wi-fi, Wi. MAX) v 1 -38
 Cable modems q Does not use telephone infrastructure v Instead uses cable TV infrastructure q HFC: hybrid fiber coax v asymmetric: up to 30 Mbps downstream, 2 Mbps upstream q network of cable and fiber attaches homes to ISP router v homes share access to router v unlike DSL, which has dedicated access 1 -25
Cable modems q Does not use telephone infrastructure v Instead uses cable TV infrastructure q HFC: hybrid fiber coax v asymmetric: up to 30 Mbps downstream, 2 Mbps upstream q network of cable and fiber attaches homes to ISP router v homes share access to router v unlike DSL, which has dedicated access 1 -25


