91fa804de058ae2ed625f17b2bb3a5f3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Data analytical issues with high-density oligonucleotide arrays A model for gene expression analysis and data quality assessment
Data analytical issues with high-density oligonucleotide arrays A model for gene expression analysis and data quality assessment
 Outline • Description of high-density oligonucleotide expression array data • Derivation of a model for gene expression estimation • Application of the model for data quality assessment
Outline • Description of high-density oligonucleotide expression array data • Derivation of a model for gene expression estimation • Application of the model for data quality assessment
 Gene Expression Analysis • Central Dogma: DNA -> m. RNA -> Protein • By comparing the abundance of m. RNA in different cells we can deduce the genes associated with cell condition. • Oligonucleotide arrays enable quantitative, highly parallel measurements of gene expression.
Gene Expression Analysis • Central Dogma: DNA -> m. RNA -> Protein • By comparing the abundance of m. RNA in different cells we can deduce the genes associated with cell condition. • Oligonucleotide arrays enable quantitative, highly parallel measurements of gene expression.
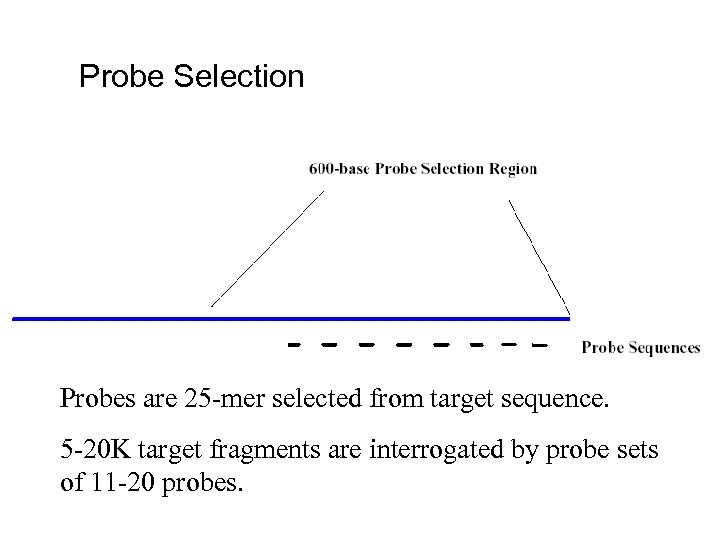 Probe Selection Probes are 25 -mer selected from target sequence. 5 -20 K target fragments are interrogated by probe sets of 11 -20 probes.
Probe Selection Probes are 25 -mer selected from target sequence. 5 -20 K target fragments are interrogated by probe sets of 11 -20 probes.
 Data preparation • RNA samples are prepared, labeled, and hybridized with arrays. • Arrays are scanned and the resulting image analyzed to produce an intensity value for each probe cell indicating how much hybridization occurred. • Of interest is to find a way to combine probe intensities for a given gene to produce an index of expression – an indicator of m. RNA abundance.
Data preparation • RNA samples are prepared, labeled, and hybridized with arrays. • Arrays are scanned and the resulting image analyzed to produce an intensity value for each probe cell indicating how much hybridization occurred. • Of interest is to find a way to combine probe intensities for a given gene to produce an index of expression – an indicator of m. RNA abundance.
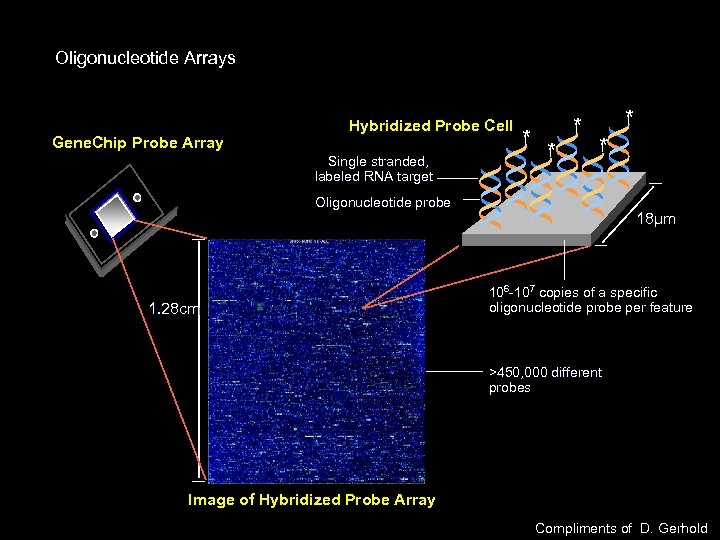 Oligonucleotide Arrays Gene. Chip Probe Array Hybridized Probe Cell Single stranded, labeled RNA target * * * Oligonucleotide probe 1. 28 cm 18µm 106 -107 copies of a specific oligonucleotide probe per feature >450, 000 different probes Image of Hybridized Probe Array Compliments of D. Gerhold
Oligonucleotide Arrays Gene. Chip Probe Array Hybridized Probe Cell Single stranded, labeled RNA target * * * Oligonucleotide probe 1. 28 cm 18µm 106 -107 copies of a specific oligonucleotide probe per feature >450, 000 different probes Image of Hybridized Probe Array Compliments of D. Gerhold
 Outline • Description of high-density oligonucleotide expression array data • Derivation of a model for gene expression analysis • Application of the model for data quality assessment
Outline • Description of high-density oligonucleotide expression array data • Derivation of a model for gene expression analysis • Application of the model for data quality assessment
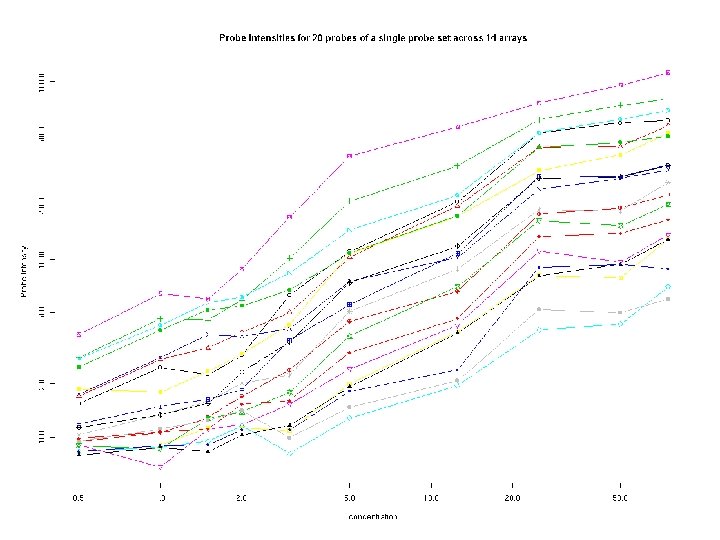 Probe Intensity vs conc ex 1
Probe Intensity vs conc ex 1
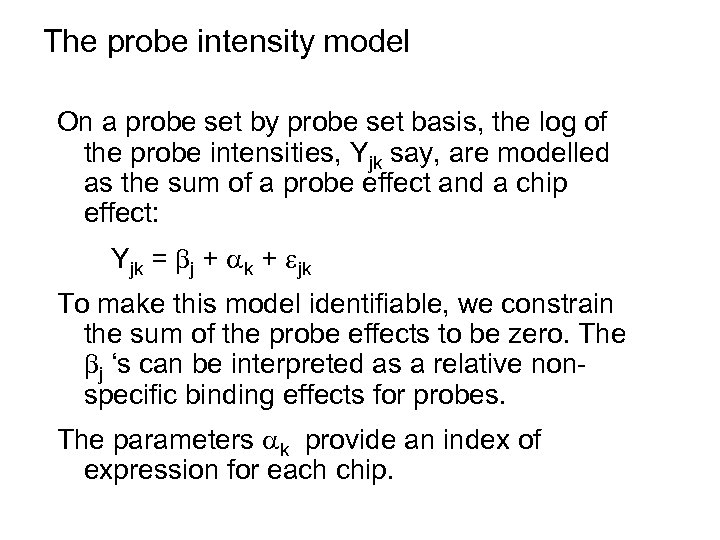 The probe intensity model On a probe set by probe set basis, the log of the probe intensities, Yjk say, are modelled as the sum of a probe effect and a chip effect: Yjk = j + k + jk To make this model identifiable, we constrain the sum of the probe effects to be zero. The j ‘s can be interpreted as a relative nonspecific binding effects for probes. The parameters k provide an index of expression for each chip.
The probe intensity model On a probe set by probe set basis, the log of the probe intensities, Yjk say, are modelled as the sum of a probe effect and a chip effect: Yjk = j + k + jk To make this model identifiable, we constrain the sum of the probe effects to be zero. The j ‘s can be interpreted as a relative nonspecific binding effects for probes. The parameters k provide an index of expression for each chip.
 Example - detecting differential expression Fit the model to 24 chips with common source of RNA + 12 RNA spiked in at 2 -fold p. M concentrations between the two groups of 12.
Example - detecting differential expression Fit the model to 24 chips with common source of RNA + 12 RNA spiked in at 2 -fold p. M concentrations between the two groups of 12.
 MVA A vs B
MVA A vs B
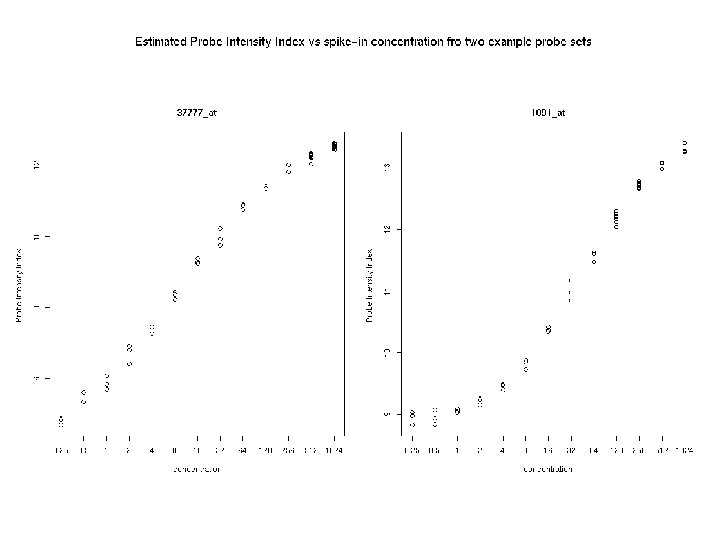 Index vs Conc
Index vs Conc
 Robust procedures perform well under a range of possible models and greatly facilitates the detection of anomalous data points. Why robust? • Image artifacts • Bad probes • Bad chips • Quality assessment
Robust procedures perform well under a range of possible models and greatly facilitates the detection of anomalous data points. Why robust? • Image artifacts • Bad probes • Bad chips • Quality assessment
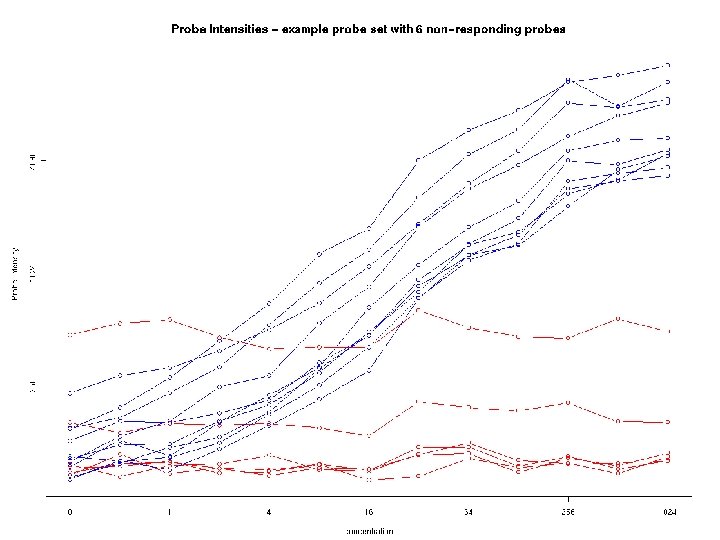 Robust fit example A
Robust fit example A
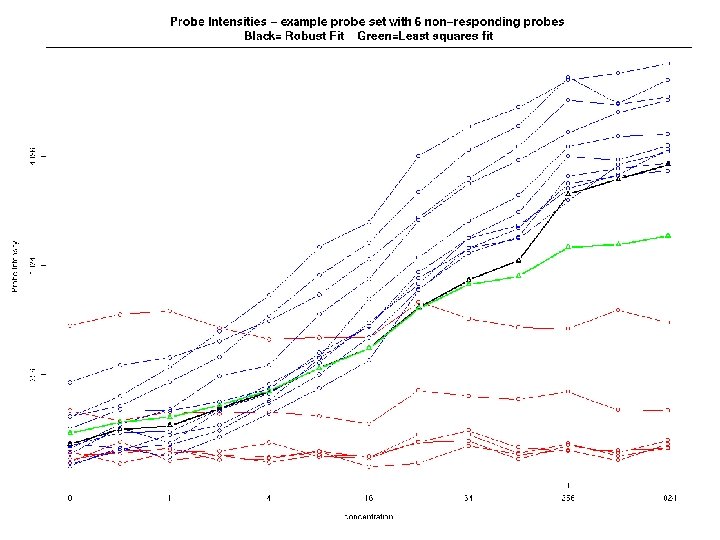 Robust fit example B
Robust fit example B
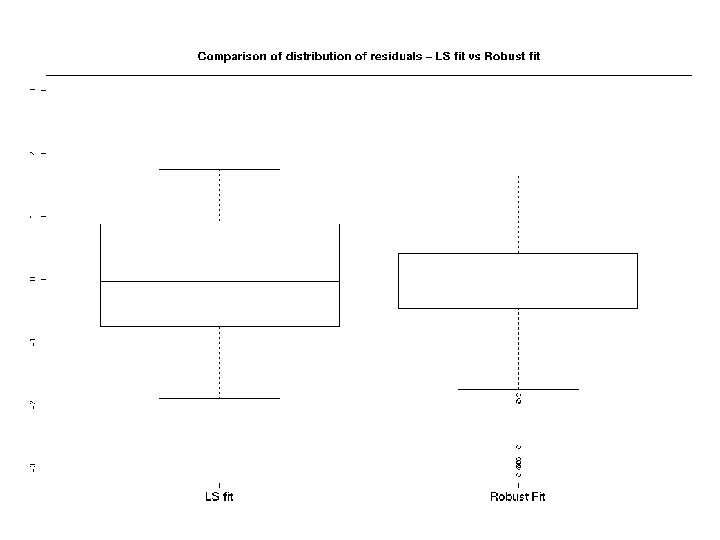 Residuals from fit
Residuals from fit
 Outline • Description of high-density oligonucleotide expression array data • Derivation of a model for gene expression estimation • Application of the model to data quality assessment
Outline • Description of high-density oligonucleotide expression array data • Derivation of a model for gene expression estimation • Application of the model to data quality assessment
 Chip manufacturer QA protocols • Starting RNA QA – look at gel patterns and RNA quantification. • Post hybridization QA – image examination, chip intensity parameters, expressions for control genes of various sorts, house keeping genes, percent present calls.
Chip manufacturer QA protocols • Starting RNA QA – look at gel patterns and RNA quantification. • Post hybridization QA – image examination, chip intensity parameters, expressions for control genes of various sorts, house keeping genes, percent present calls.
 Goal: measuring expression data quality Manufacturer QA guidelines emphasize maintenance of data comparability across chips in analysis set. We seek assessments that measure data quality as it pertains to expression values. In particular, would like to provide quantitative measures that can help making decisions – Accept, Reject or Adjust.
Goal: measuring expression data quality Manufacturer QA guidelines emphasize maintenance of data comparability across chips in analysis set. We seek assessments that measure data quality as it pertains to expression values. In particular, would like to provide quantitative measures that can help making decisions – Accept, Reject or Adjust.
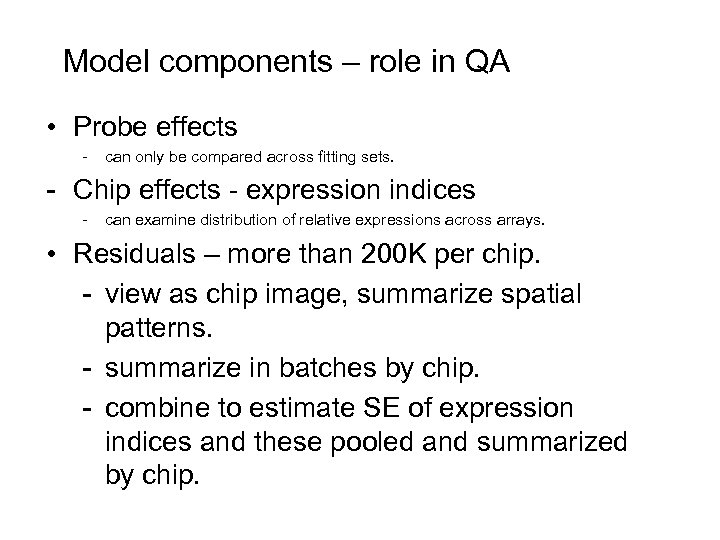 Model components – role in QA • Probe effects - can only be compared across fitting sets. - Chip effects - expression indices - can examine distribution of relative expressions across arrays. • Residuals – more than 200 K per chip. - view as chip image, summarize spatial patterns. - summarize in batches by chip. - combine to estimate SE of expression indices and these pooled and summarized by chip.
Model components – role in QA • Probe effects - can only be compared across fitting sets. - Chip effects - expression indices - can examine distribution of relative expressions across arrays. • Residuals – more than 200 K per chip. - view as chip image, summarize spatial patterns. - summarize in batches by chip. - combine to estimate SE of expression indices and these pooled and summarized by chip.
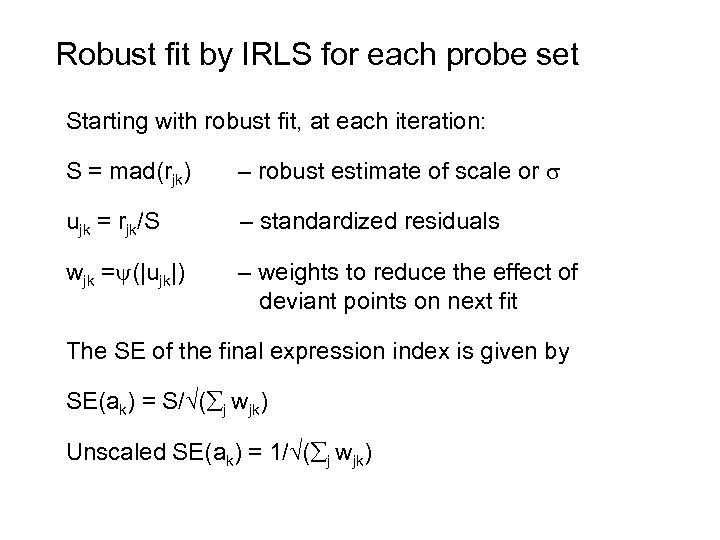 Robust fit by IRLS for each probe set Starting with robust fit, at each iteration: S = mad(rjk) – robust estimate of scale or ujk = rjk/S – standardized residuals wjk = (|ujk|) – weights to reduce the effect of deviant points on next fit The SE of the final expression index is given by SE(ak) = S/ ( j wjk) Unscaled SE(ak) = 1/ ( j wjk)
Robust fit by IRLS for each probe set Starting with robust fit, at each iteration: S = mad(rjk) – robust estimate of scale or ujk = rjk/S – standardized residuals wjk = (|ujk|) – weights to reduce the effect of deviant points on next fit The SE of the final expression index is given by SE(ak) = S/ ( j wjk) Unscaled SE(ak) = 1/ ( j wjk)
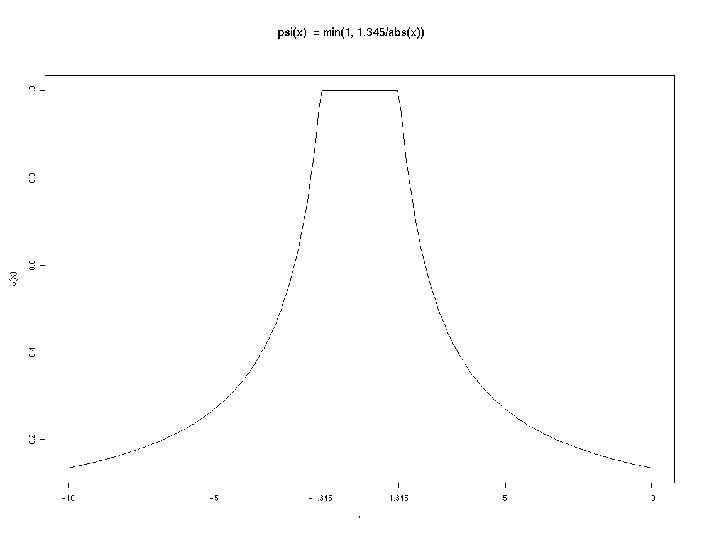 function
function
 Images of weights • For 24 chips from Affymetrix, look at patterns of weights on chip real estate.
Images of weights • For 24 chips from Affymetrix, look at patterns of weights on chip real estate.
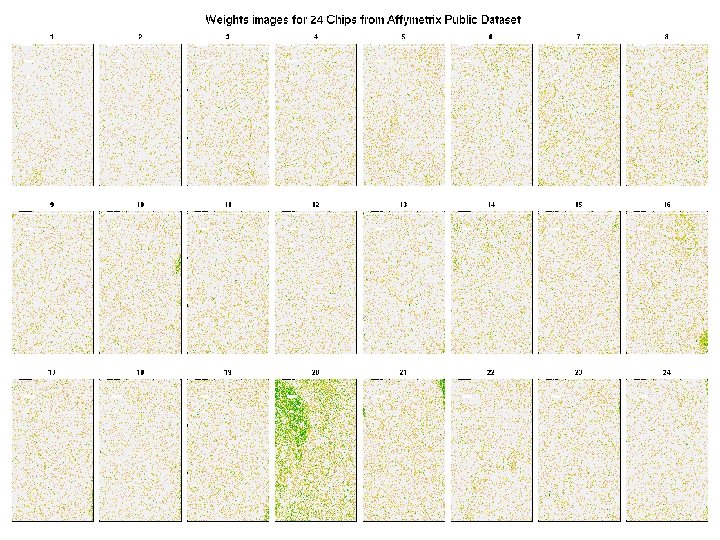 Images of weights
Images of weights
 Images sign of residuals • For 24 chips from Affymetrix, look at patterns of sign of residuals on chip real estate.
Images sign of residuals • For 24 chips from Affymetrix, look at patterns of sign of residuals on chip real estate.
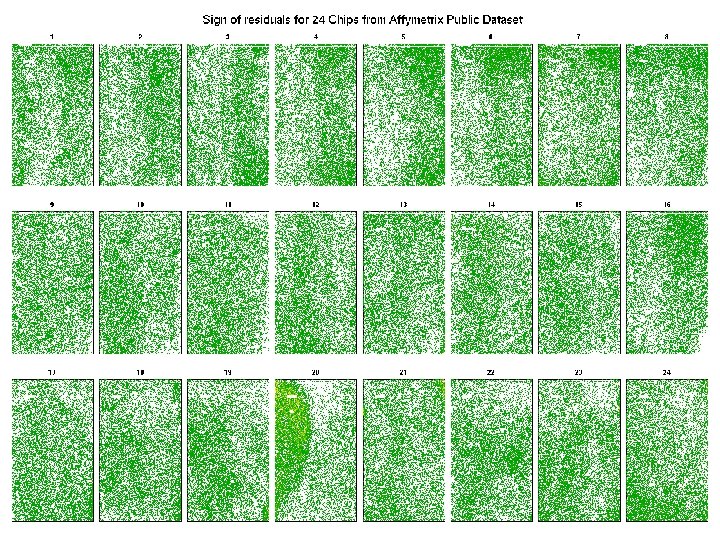 Images of sign of residuals
Images of sign of residuals
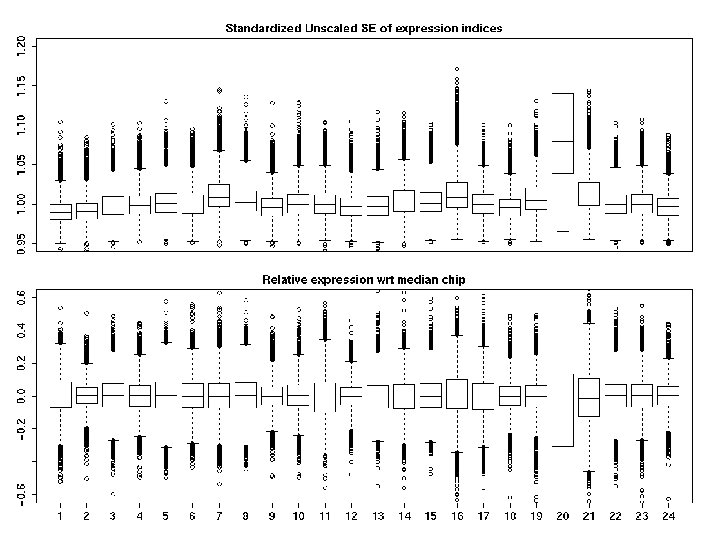 Residual summaries
Residual summaries
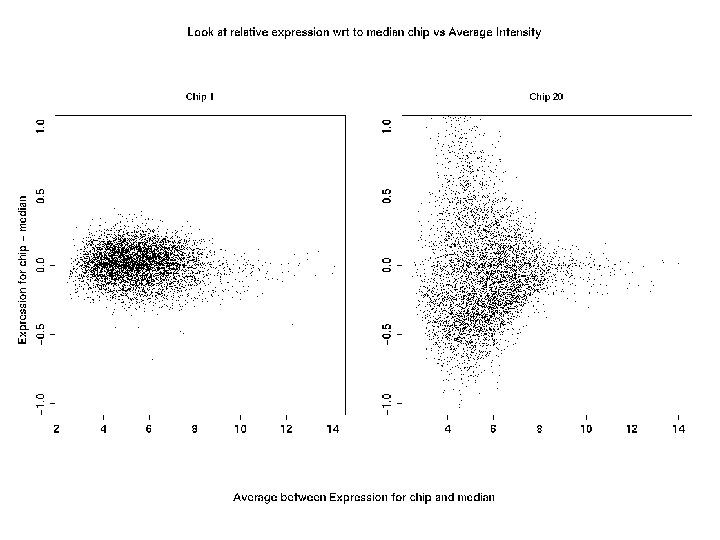 MVA exp index
MVA exp index
 Future developments Develop quality assessment measures for routine use in large throughput environment. Assess relationships among various QA measures. Develop diagnostics to assign causes to departures from quality standards. Other applications Identify non-performing or cross-hybridizing probes, qualify probe sets.
Future developments Develop quality assessment measures for routine use in large throughput environment. Assess relationships among various QA measures. Develop diagnostics to assign causes to departures from quality standards. Other applications Identify non-performing or cross-hybridizing probes, qualify probe sets.
 References 1. New Statistical Algorithms for Monitoring Gene Expression on Gene. Chip® Probe Arrays, Affymetrix technical report. 2. Array Design for the Gene. Chip® Human Genome U 133 Set, Affymetrix technical note. 3. Discussion on Background, Ben Bolstad. 4. Bolstad BM, et. al. (2003), A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data basedon variance and bias. Bioinformatics. 2003 Jan 22; 19(2): 185 -193. 5. Irizarry, R. et. al (2003) Summaries of Affymetrix Gene. Chip probe level data, Nucleic Acids Research, 2003, Vol. 31, No. 4 e 15 6. Irizarry, R. et. al. (2003) Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics, in press. 7. http: //array. mc. vanderbilt. edu/Pages/VMSR_Info/Sample_submission. htm
References 1. New Statistical Algorithms for Monitoring Gene Expression on Gene. Chip® Probe Arrays, Affymetrix technical report. 2. Array Design for the Gene. Chip® Human Genome U 133 Set, Affymetrix technical note. 3. Discussion on Background, Ben Bolstad. 4. Bolstad BM, et. al. (2003), A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data basedon variance and bias. Bioinformatics. 2003 Jan 22; 19(2): 185 -193. 5. Irizarry, R. et. al (2003) Summaries of Affymetrix Gene. Chip probe level data, Nucleic Acids Research, 2003, Vol. 31, No. 4 e 15 6. Irizarry, R. et. al. (2003) Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics, in press. 7. http: //array. mc. vanderbilt. edu/Pages/VMSR_Info/Sample_submission. htm
 Background correction - to correct for differential background due to experimental processing effects and to put the estimated differential expression on a proper scale. Normalization – to correct for systematic differences in the distribution of probe intensities
Background correction - to correct for differential background due to experimental processing effects and to put the estimated differential expression on a proper scale. Normalization – to correct for systematic differences in the distribution of probe intensities


