74076101f5cf70e610087b6288cbdecd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

DAS/2: Next Generation Distributed Annotation System Gregg Helt 1, Steve Chervitz 1, Andrew Dalke 3, Allen Day 4, Ed Erwin 1, Andreas Prlic 2, and Lincoln Stein 4 with many other contributors (1) Affymetrix, Inc. (2) Sanger Institute (3) Dalke Scientific; (4) Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory

Development of DAS/2 Specification § DAS/2 development initially motivated by numerous suggestions for improvements to DAS on the DAS mailing list, and the series of RFCs collected on biodas. org site § Though informal, still a long process! § NIH grant awarded June 2004 for development of next-generation DAS/2 § Most recent DAS/2 specification is available at biodas. org/documents/das 2_protocol. html (tied to CVS repository) § DAS/2. 0 XML schema frozen since November 2006 – – Specified with Relax. NG Available in CVS repository at cvs. biodas. org, in file das/das 2_schemas. rnc § Feedback from the DAS developer and user communities will continue to guide future iterations of the DAS/2 specification – – – Biweekly teleconference, everyone is welcome to join in the discussion DAS/2 mailing list ( http: //lists. open-bio. org/mailman/listinfo/das 2 ) biodas. org site moving to wiki ( biodas. org/wiki )

“Things I would like to do with DAS, but currently can’t” (without extensions) § Achieve reasonable performance with large amounts of data § Represent features with more than two levels § Reliably refer to DAS features / sequences / etc. outside of DAS § Reliably relate feature types to a more structured ontology § Efficiently cache DAS feature queries § Easily identify when two DAS servers are using the same coordinate system (doable with help of Sanger DAS registry) § Have a standard way to create and edit DAS features

Preserving DAS 1 Strengths in DAS/2 § Specification is independent of implementation – – Many server implementations Many client implementations § Simple, simple – – HTTP for transport URLs for queries XML for responses REST-like style § No central annotation authority § Focus on location-based annotations of biological sequences § Couple XML response formats to URL request formats – Instead of XML formats on their own

Basic DAS/2 Queries § Net. Affx examples: http: //netaffxdas. affymetrix. com/das 2/ § Sources query: what genomes and versions of those genomes are available? § Segments query: what annotated sequences are available § Types query: what types of annotations are available § Features query: get features / annotations – Based on type – Based on segment range – Based on annotation ID
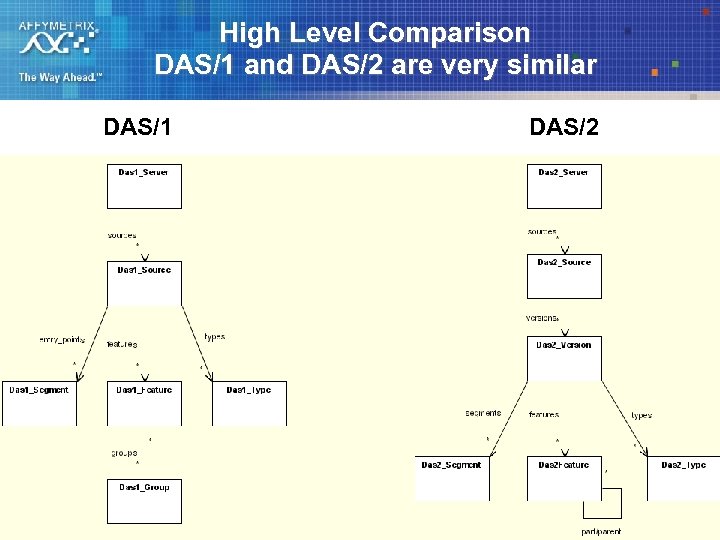
High Level Comparison DAS/1 and DAS/2 are very similar DAS/1 DAS/2

DAS/2 Enhancements: Performance § One of the biggest complaints about DAS 1 : Performance – Very verbose annotation XML, which hinders performance at the server, network, and client § DAS/2 Solution #1: Refactoring annotation XML – Much smaller minimum footprint § DAS/2 Solution #2: Alternative return formats – – – All servers can return defined das 2 xml annotation format Servers can also specify additional return formats per annotation type Clients can choose from alternative formats if they desire Not restricted to XML, or even text Examples: GFF 3, BED, PSL, binary. PSL Extreme performance improvements possible
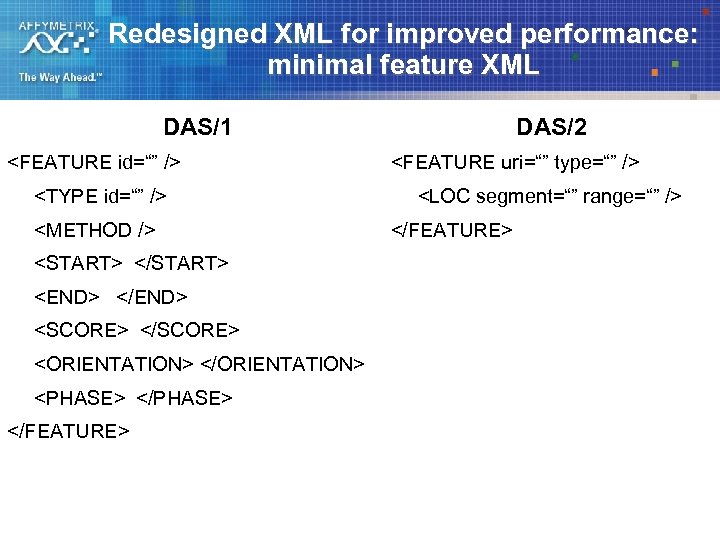
Redesigned XML for improved performance: minimal feature XML DAS/2 DAS/1 <FEATURE id=“” /> <TYPE id=“” /> <METHOD /> <START> </START> <END> </END> <SCORE> </SCORE> <ORIENTATION> </ORIENTATION> <PHASE> </FEATURE> <FEATURE uri=“” type=“” /> <LOC segment=“” range=“” /> </FEATURE>
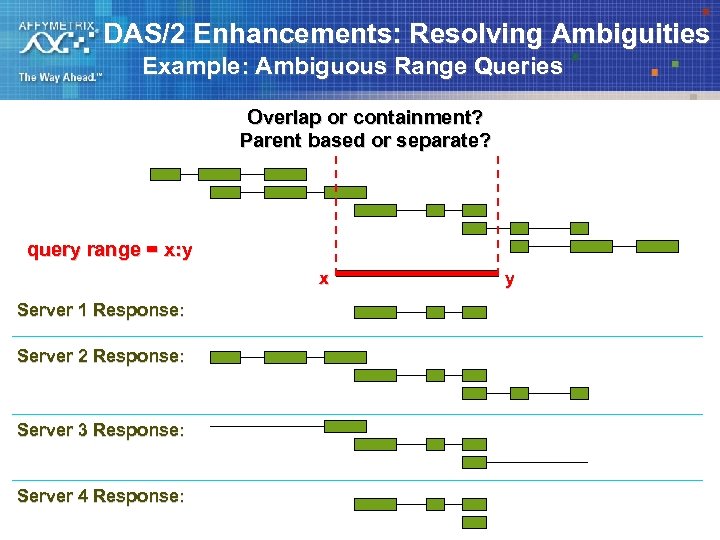
DAS/2 Enhancements: Resolving Ambiguities Example: Ambiguous Range Queries Overlap or containment? Parent based or separate? query range = x: y x Server 1 Response: Server 2 Response: Server 3 Response: Server 4 Response: y

DAS/2 Solution #1 – remove spec ambiguity Example: Ambiguous Range Queries § Be specific about whether feature query range filter is overlap, containment, etc. § Add different region filters for different possibilities – – Overlaps Contains Within Identical § Allow boolean combinations of these and other filters in the query URL – A smart client could used these combinations to optimize queries § Return full feature closure ( all parents and parts ) – This also allows streaming processing

Solution #2: DAS/2 Validation Suite § Verify whether a DAS/2 server is compliant with the specification. – Critical for improving interoperability between clients and servers developed by different groups. § Standalone tool and web application, written in Python – – Enter a DAS/2 URL query or XML response Get an HTML report about DAS/2 compliance § Performs schema-based validation – also validates some parts of protocol not formalized in schema, such as URL query parameters § Web application at http: //cgi. biodas. org: 8080/ – – – Moving soon Plan is to eventually integrate into DAS/2 registry server Source code available at: http: //sourceforge. net/projects/dasypus
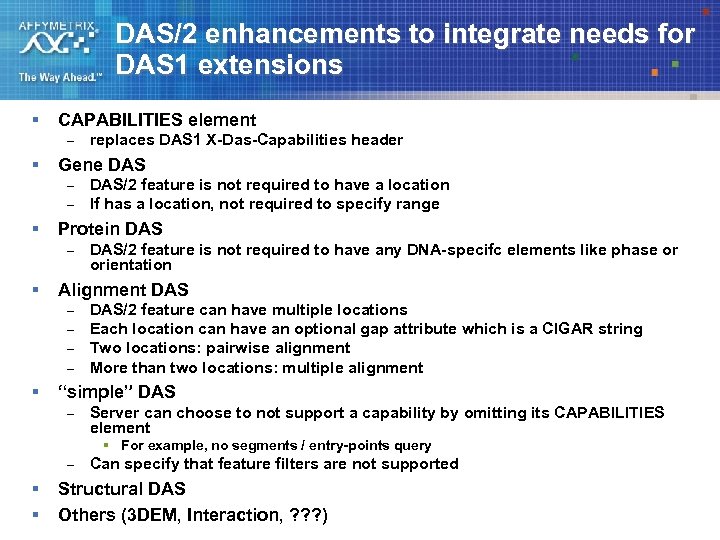
DAS/2 enhancements to integrate needs for DAS 1 extensions § CAPABILITIES element – § Gene DAS – – § DAS/2 feature is not required to have any DNA-specifc elements like phase or orientation Alignment DAS – – § DAS/2 feature is not required to have a location If has a location, not required to specify range Protein DAS – § replaces DAS 1 X-Das-Capabilities header DAS/2 feature can have multiple locations Each location can have an optional gap attribute which is a CIGAR string Two locations: pairwise alignment More than two locations: multiple alignment “simple” DAS – Server can choose to not support a capability by omitting its CAPABILITIES element § For example, no segments / entry-points query – § § Can specify that feature filters are not supported Structural DAS Others (3 DEM, Interaction, ? ? ? )

More DAS/2 Enhancements § IDs are URIs – – – Could be LSIDs or URLs Allows for integration with many other web technologies xml: base § “Writeback” spec to allow DAS/2 clients to create and edit annotations on DAS/2 servers – Spec has been frozen, but client and server implementation are still preliminary § Ontologies for feature types § Feature hierarchies § DAS/2 Registry § And more…
DAS/2 Server Implementations § GMOD-based DAS/2 server – – – Deployed at http: //das. biopackages. net/das/genome Uses Bio. Perl for middleware Plugin architecture for data backend Currently most developed plugin is for CHADO database Source code available via anonymous CVS as part of GMOD § See http: //www. gmod. org for access details. § Genometry DAS/2 server – – Deployed at http: //netaffxdas. affymetrix. com/das 2/sources Designed for performance § (Mostly) In-memory object datastore § Quickly transmit hundreds of thousands of features § Quickly transmit millions of graph data points – – – Only supports fairly simple annotations Supports alternative content formats Supports some DAS/2 caching via If-Modified-Since header § Simple files exposed on web server § Easing migration: DAS 1 DAS/2 transformational proxy server § Other implementations?

DAS/2 Client Implementations § IGB (“ig-bee”) - genome visualization app developed at Affymetrix – Implemented in Java in the Integrated Genome Browser § Supports data loading via a variety of formats and mechanisms § Contains both DAS 1 and DAS/2 clients – Handles large amounts of genome-scale data § § § – Loads hundreds of thousands of sequence annotations at once Loads dense quantitative graphs with millions of data points Maintains real-time responsiveness to user interactions Includes features to support exploratory data analysis Plugin architecture for customized extensions Source code released under Common Public License § http: //genoviz. sourceforge. net § Also available as a Web. Start-managed application at Affymetrix or Sourceforge web sites § Other implementations? – – GBrowse Dasypus validator DAS/2 Registry ? ? ?

DAS/2 Registry § Main registry implementation developed by Andreas Prlic § Evolving from Sanger DAS 1 registry § Multiple ways to access registry – Andreas’ talk later § One elegant way: DAS/2 registry is simply a DAS/2 server – – – Most info needed for a registry are already available in DAS/2 XML responses So any DAS/2 server that aggregates DAS/2 sources in its sources XML doc can be considered a DAS/2 registry This works because of the RESTful approach to specifying URLs for accessing particular versioned source capabilities “Simple” DAS/2 registries can even be static documents Very useful for in-house DAS/2 registries § More sophisticated DAS/2 registries can have query filters for the sources query (not developed yet)

DAS/2 Writeback § Uses HTTP POST § DAS 2 XML POSTed to DAS/2 writeback server § Atomic transactional unit is the HTTP call § Locking mechanism § Spec stable § Only partial client and server implementations, expect spec to change as implementations are further developed

Future DAS/2 developments § Short term – – More documentation of specification More documentation of existing client and server implementations Continued improvements to client and server implementations Most work needed on client and server writeback implementation § Help install and/or develop DAS/2 servers at model organism database sites § Mapping servers § Interclient communications protocol § Extreme DAS caching § [ 3 D structure ] § Extensions – – Extended via CAPABILITIES element General Principles: § If entity is independent enough to have an ID, the ID shoud be a URI § …

Acknowledgements § DAS & DAS 2 mailing list participants!
74076101f5cf70e610087b6288cbdecd.ppt