de5f7c5f5303fc9e0a6d1e2e07a4cc41.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 103
 DARKROOM , PROCESSING & Artifacts REVIEW
DARKROOM , PROCESSING & Artifacts REVIEW
 Types of Safelights n n Kodak Wratten 6 B – brownish red filter 7. 5 to 15 watt bulb @ 4 feet above counter n Kodak GBX – brighter (reddish) light is directed upwards White walls and dust free n What type of film was amber filter used for? n
Types of Safelights n n Kodak Wratten 6 B – brownish red filter 7. 5 to 15 watt bulb @ 4 feet above counter n Kodak GBX – brighter (reddish) light is directed upwards White walls and dust free n What type of film was amber filter used for? n
 SAFELIGHTS
SAFELIGHTS
 Safelight distance?
Safelight distance?
 UNLOAD EXPOSED FILM
UNLOAD EXPOSED FILM
 FILM BIN - STORAGE
FILM BIN - STORAGE
 FILM ID PRINTER n n n What information Must be present For Legal reasons?
FILM ID PRINTER n n n What information Must be present For Legal reasons?
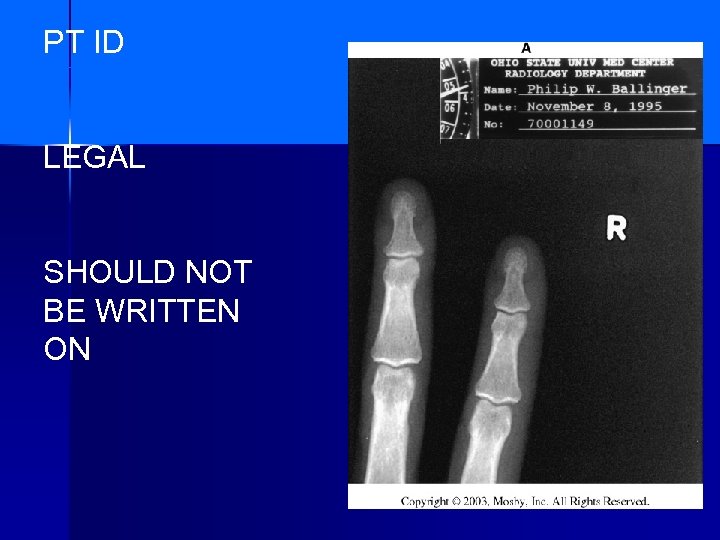 PT ID LEGAL SHOULD NOT BE WRITTEN ON
PT ID LEGAL SHOULD NOT BE WRITTEN ON
 Film/IMAGE Identification Pt name n Exam date & time n Pt x-ray number n Pt Birthday/DOB n Rt or Lt marker n Optional – Exam type – Dr. Name n
Film/IMAGE Identification Pt name n Exam date & time n Pt x-ray number n Pt Birthday/DOB n Rt or Lt marker n Optional – Exam type – Dr. Name n
 n Position of film travel on feed tray may determine type of artifact n What are the 3 classification?
n Position of film travel on feed tray may determine type of artifact n What are the 3 classification?
 Processing Film Floor model (LAB) Table top Close the lid Before leaving
Processing Film Floor model (LAB) Table top Close the lid Before leaving
 No longer in use in clinics DARKROOM DAYLIGHT Processor
No longer in use in clinics DARKROOM DAYLIGHT Processor

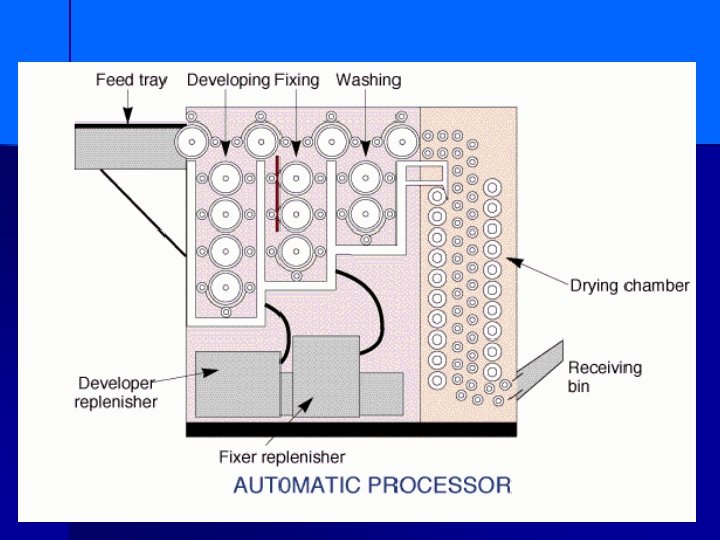
 NOTES ON PROCESSING n DEVELOPER n FIXER n WASH n DRY
NOTES ON PROCESSING n DEVELOPER n FIXER n WASH n DRY
 LOAD CASSETTE
LOAD CASSETTE
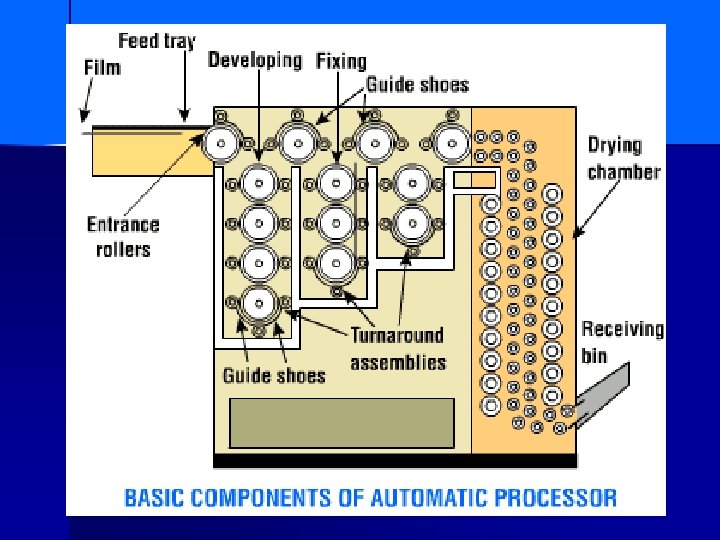


 n Stored on end prevents what type of artifact n Check expiration
n Stored on end prevents what type of artifact n Check expiration
 n DEVELOPER FIXER WASH DRY n WATER - SOLVENT n n n
n DEVELOPER FIXER WASH DRY n WATER - SOLVENT n n n
 Silver recovery
Silver recovery
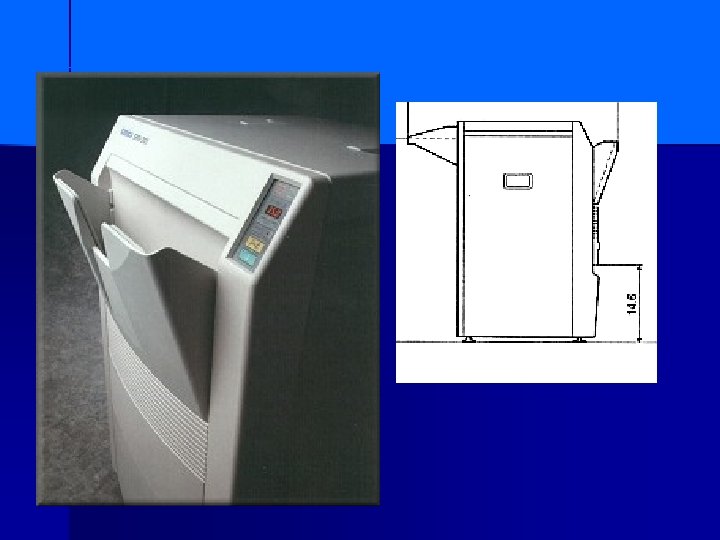
 silver recovery- see notes n n n A final consideration in film processing is silver recovery. This term is the process by which silver in the processing chemicals is reclaimed and recycled by a unit, such as the one shown in the illustration. This recycling is important for two reasons. Silver has economic value in its recycled form and helps recover some of the cost of the unexposed film, which is expensive, in part, because of the silver in it. Secondly, federal regulations require that heavy metals like silver be reclaimed from waste solutions before they are disposed of, to prevent pollution of the environment. Roughly half the silver in the film ends up dissolved in the fixer in the automatic processor. Different kinds of silver recovery units are used to process the used fixer to recover the silver.
silver recovery- see notes n n n A final consideration in film processing is silver recovery. This term is the process by which silver in the processing chemicals is reclaimed and recycled by a unit, such as the one shown in the illustration. This recycling is important for two reasons. Silver has economic value in its recycled form and helps recover some of the cost of the unexposed film, which is expensive, in part, because of the silver in it. Secondly, federal regulations require that heavy metals like silver be reclaimed from waste solutions before they are disposed of, to prevent pollution of the environment. Roughly half the silver in the film ends up dissolved in the fixer in the automatic processor. Different kinds of silver recovery units are used to process the used fixer to recover the silver.
 List the 3 types of silver recovery systems
List the 3 types of silver recovery systems
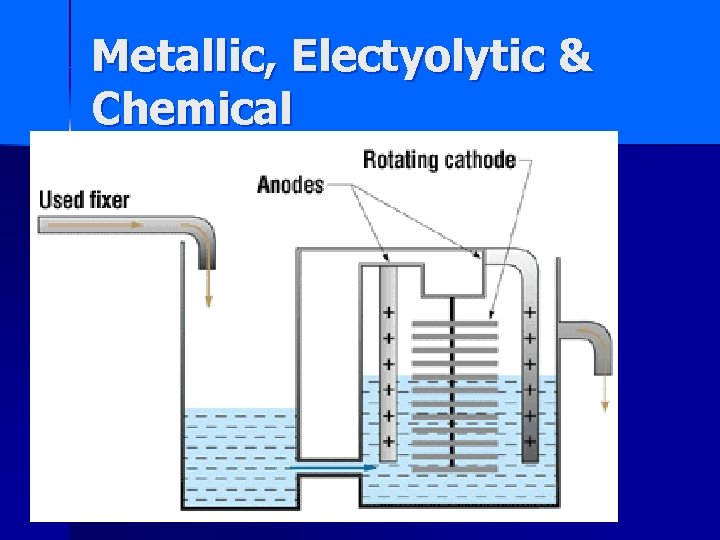 Metallic, Electyolytic & Chemical
Metallic, Electyolytic & Chemical
 “FILM” & IMAGE ARTIFACTS RT 244 REV 11/09
“FILM” & IMAGE ARTIFACTS RT 244 REV 11/09
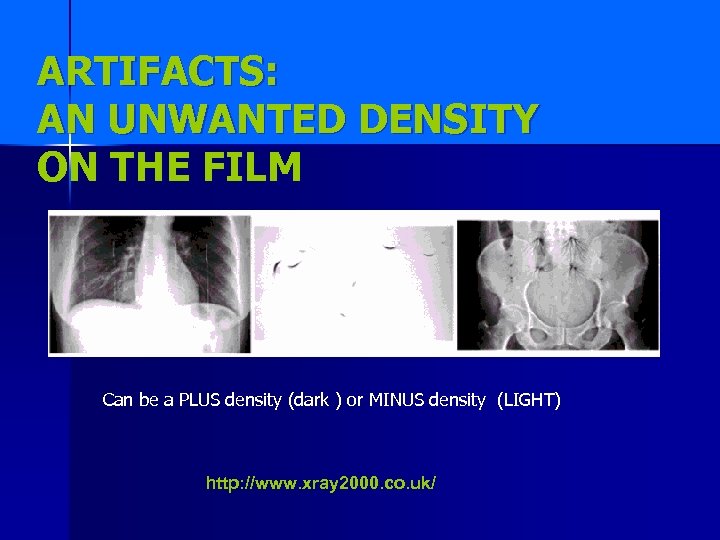 ARTIFACTS: AN UNWANTED DENSITY ON THE FILM Can be a PLUS density (dark ) or MINUS density (LIGHT) http: //www. xray 2000. co. uk/
ARTIFACTS: AN UNWANTED DENSITY ON THE FILM Can be a PLUS density (dark ) or MINUS density (LIGHT) http: //www. xray 2000. co. uk/
 Artifacts - Types n Processing Artifacts n Exposure Artifacts n Handling & Storage Artifacts
Artifacts - Types n Processing Artifacts n Exposure Artifacts n Handling & Storage Artifacts
 Exposure Artifacts Motion n Improper patient position n Wrong screen-film match n Poor film/screen contact n Double exposure n Warped cassette n Improper grid position n
Exposure Artifacts Motion n Improper patient position n Wrong screen-film match n Poor film/screen contact n Double exposure n Warped cassette n Improper grid position n
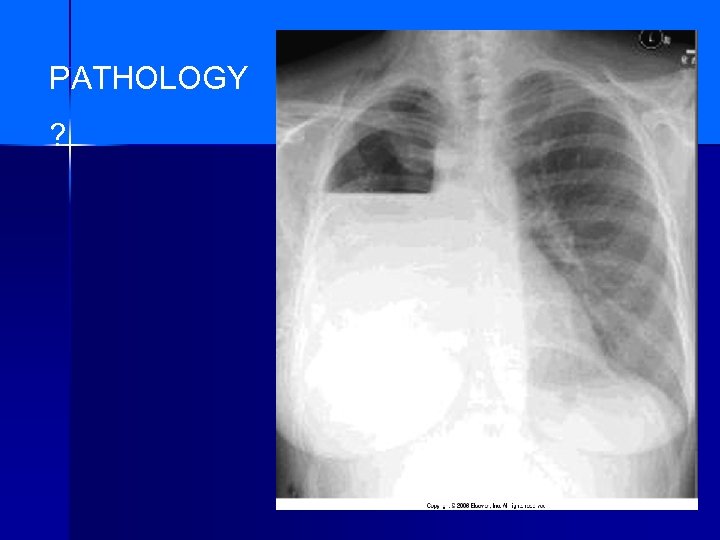 PATHOLOGY ?
PATHOLOGY ?
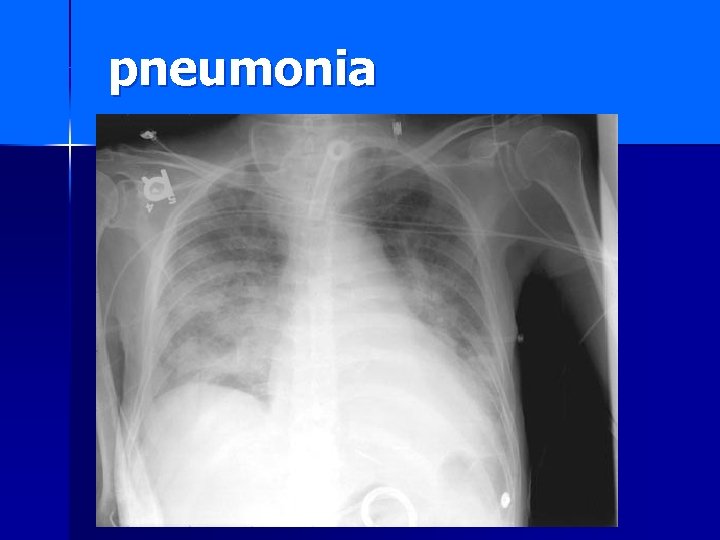 pneumonia
pneumonia
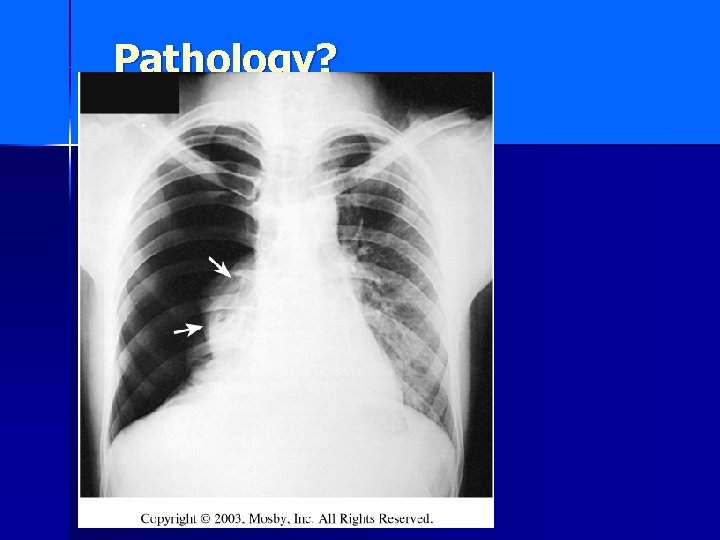 Pathology?
Pathology?
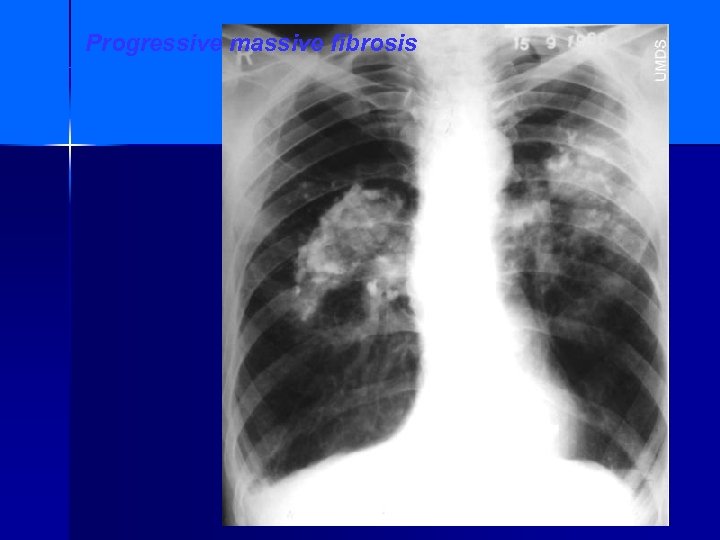 Progressive massive fibrosis
Progressive massive fibrosis
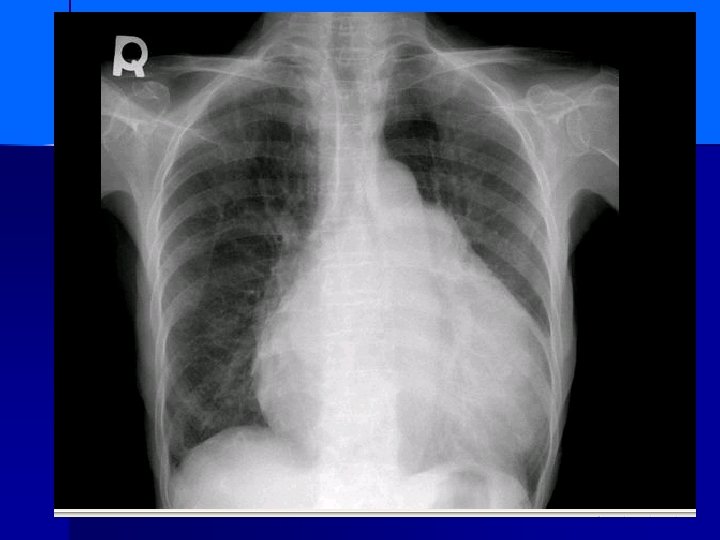
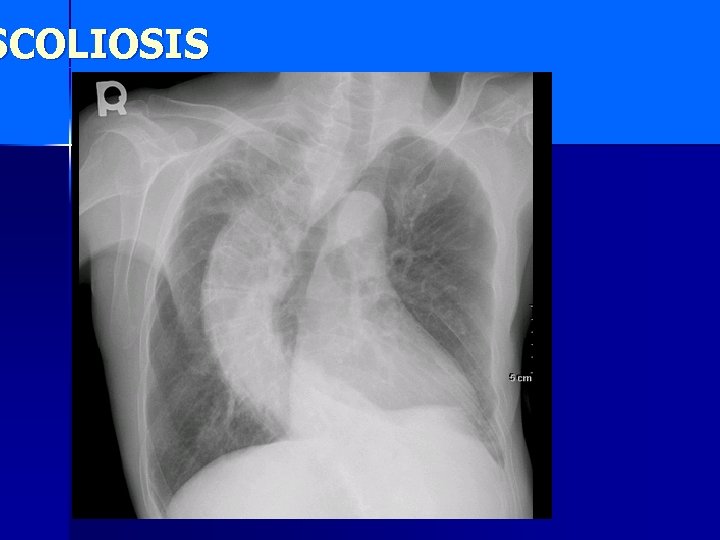 SCOLIOSIS
SCOLIOSIS
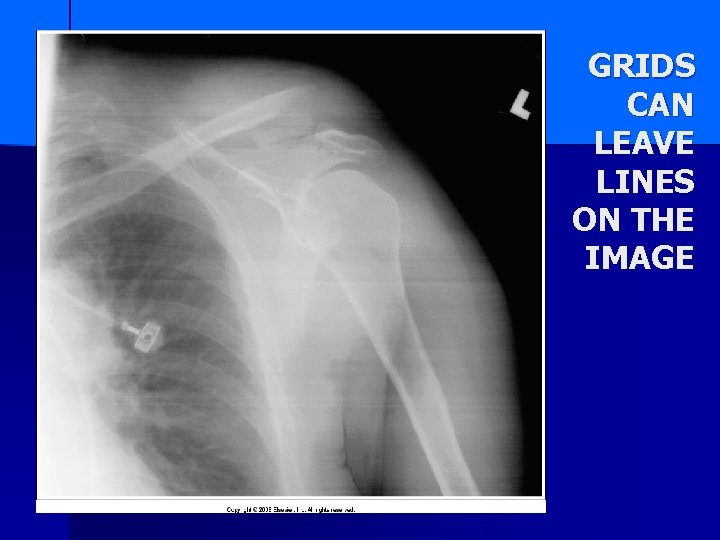 GRIDS CAN LEAVE LINES ON THE IMAGE
GRIDS CAN LEAVE LINES ON THE IMAGE
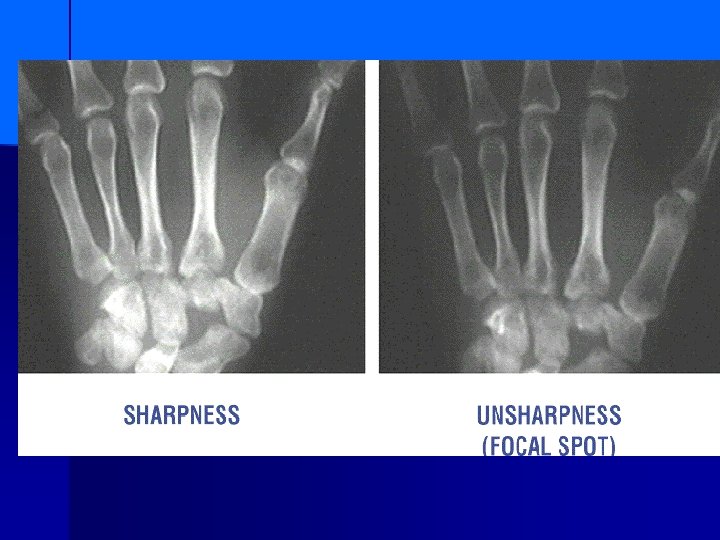
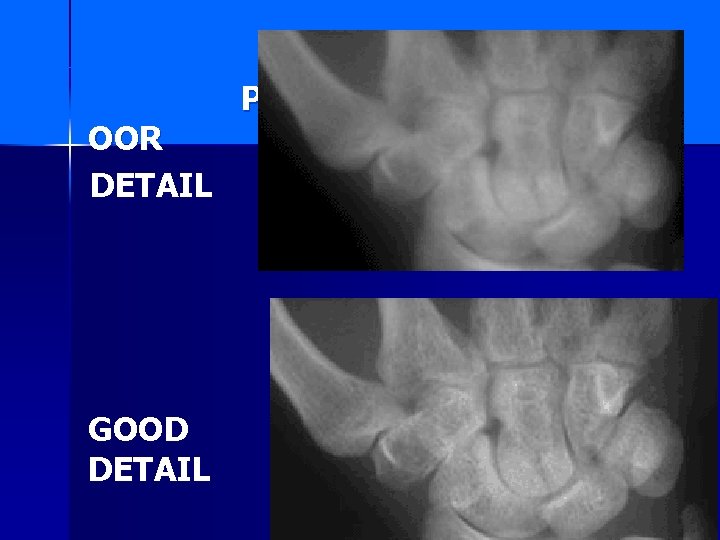 OOR DETAIL GOOD DETAIL P
OOR DETAIL GOOD DETAIL P
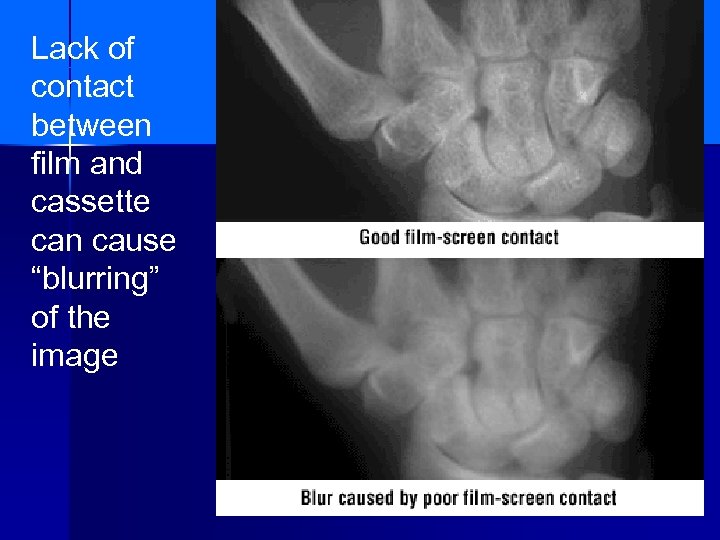 Lack of contact between film and cassette can cause “blurring” of the image
Lack of contact between film and cassette can cause “blurring” of the image
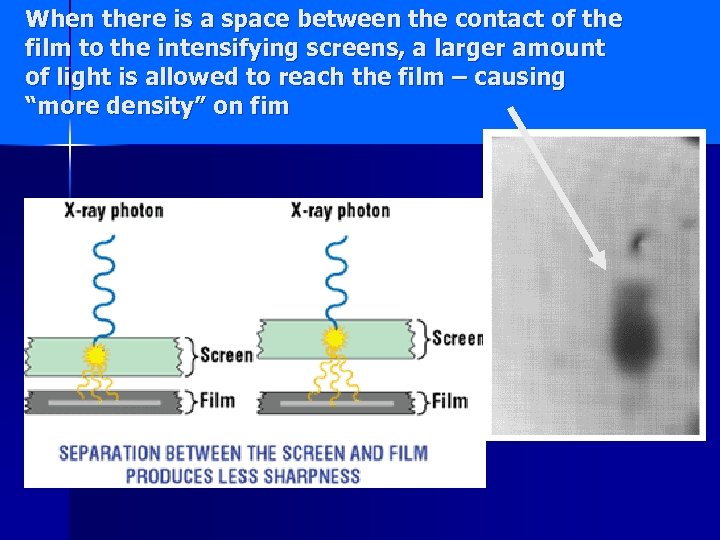 When there is a space between the contact of the film to the intensifying screens, a larger amount of light is allowed to reach the film – causing “more density” on fim
When there is a space between the contact of the film to the intensifying screens, a larger amount of light is allowed to reach the film – causing “more density” on fim
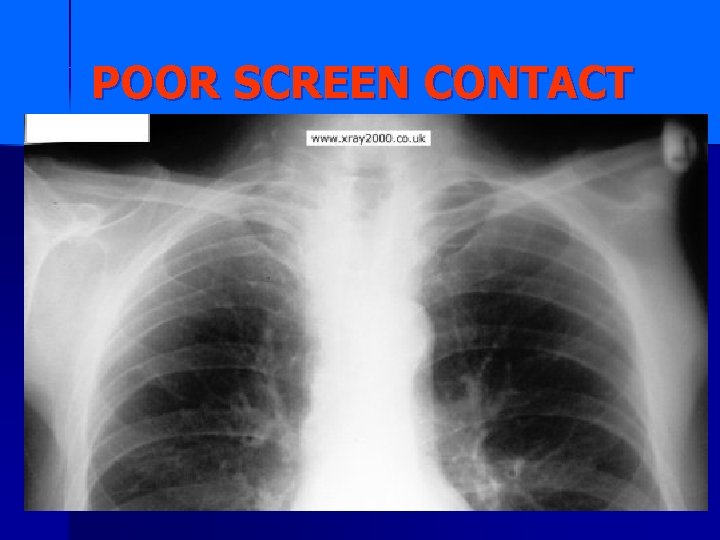 POOR SCREEN CONTACT
POOR SCREEN CONTACT
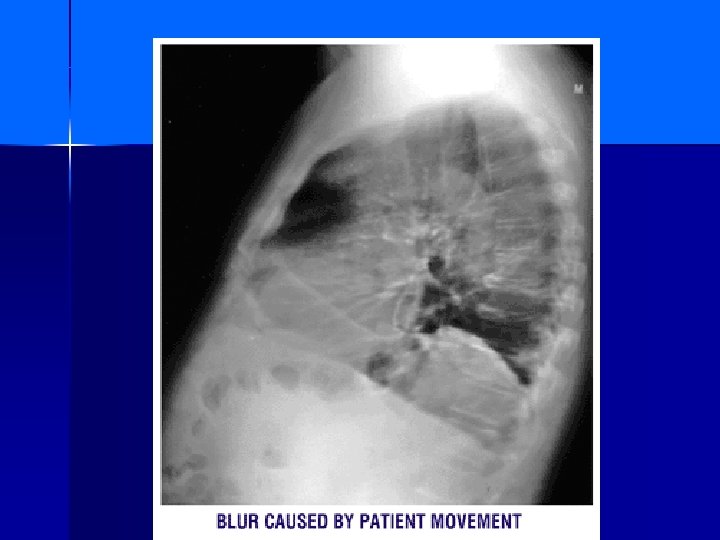
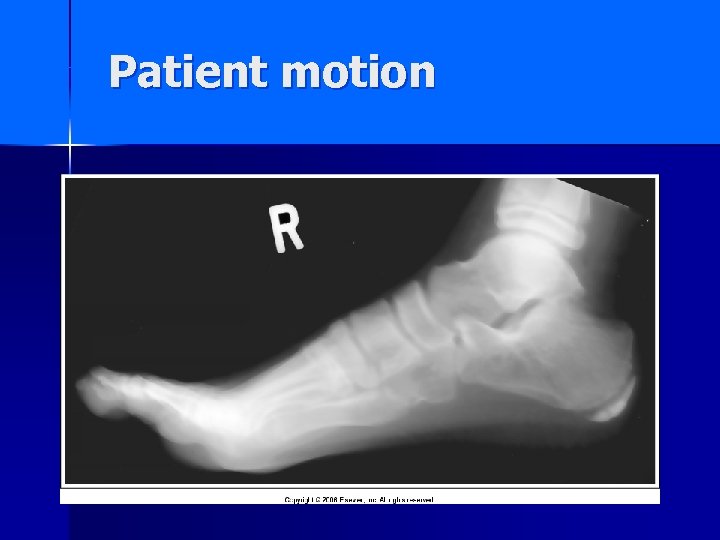 Patient motion
Patient motion
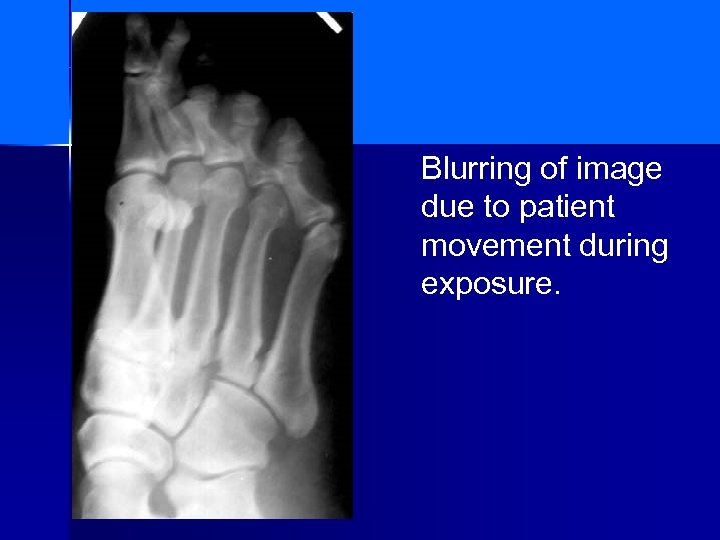 Blurring of image due to patient movement during exposure.
Blurring of image due to patient movement during exposure.
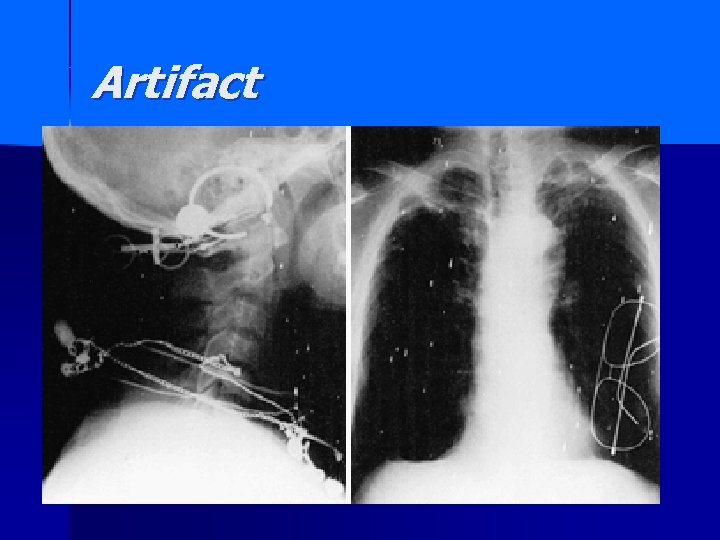 Artifact
Artifact
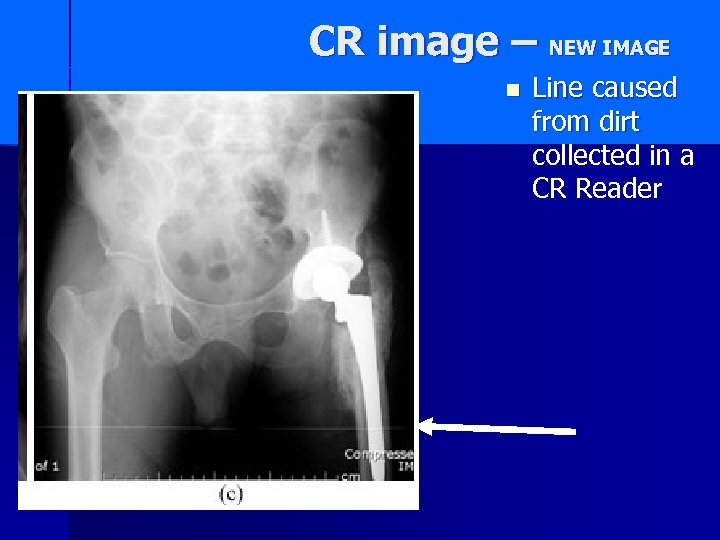 CR image – NEW IMAGE n Line caused from dirt collected in a CR Reader
CR image – NEW IMAGE n Line caused from dirt collected in a CR Reader
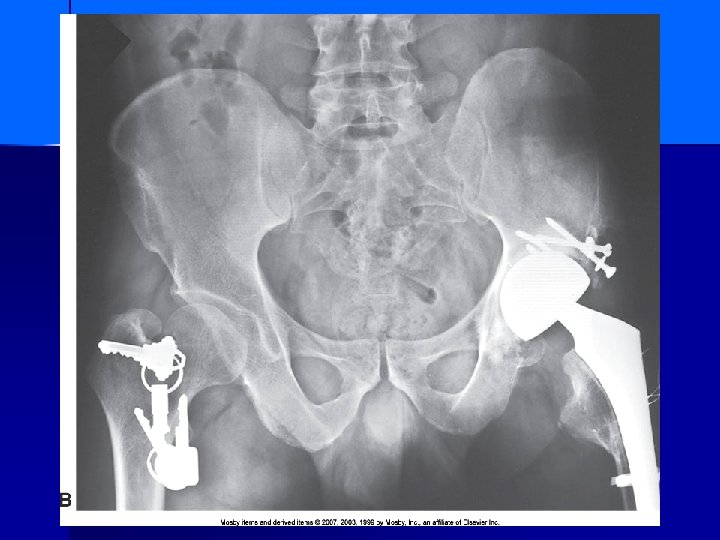
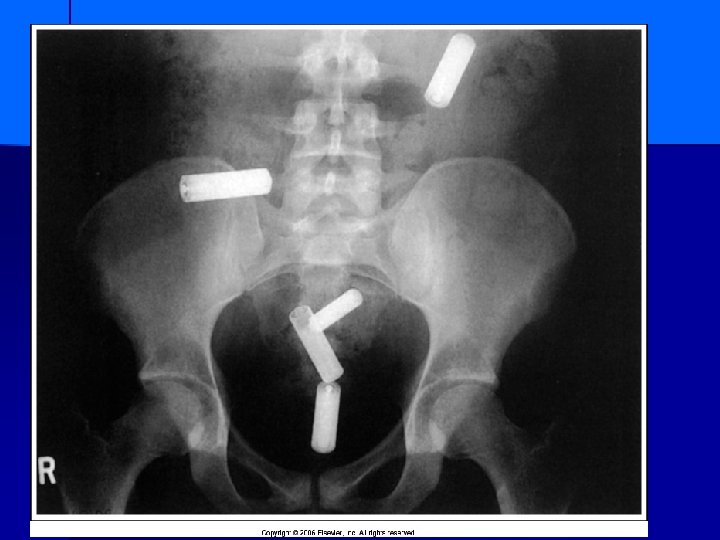
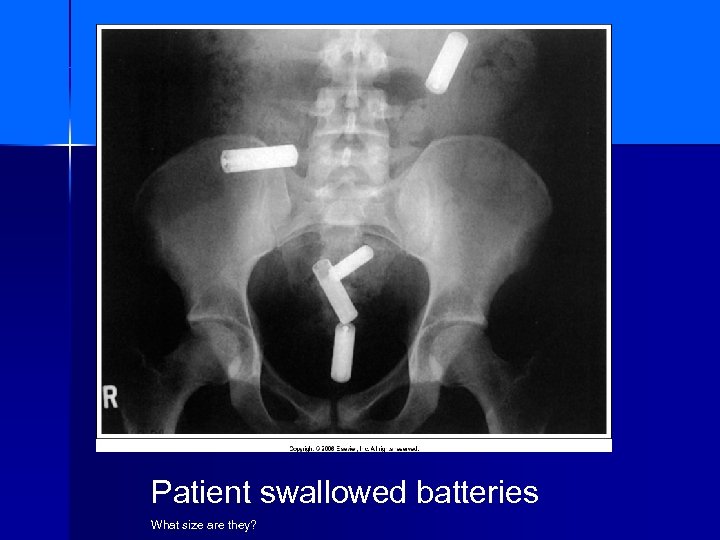 Patient swallowed batteries What size are they?
Patient swallowed batteries What size are they?
 cast
cast
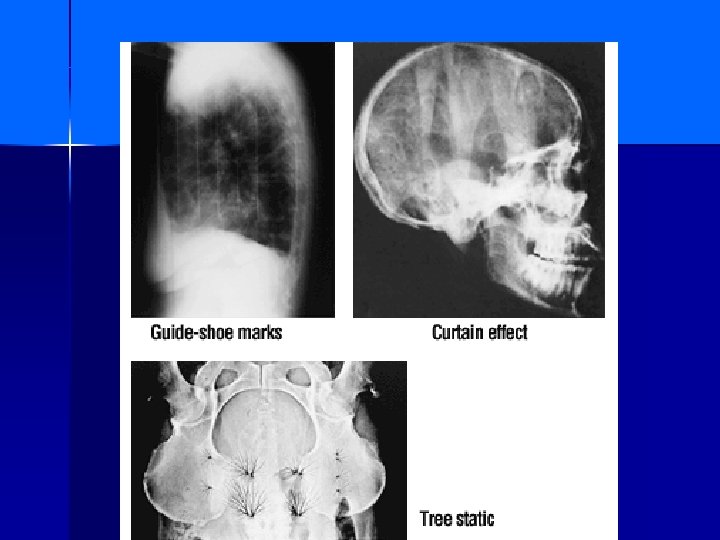
 Processing Artifacts Emulsion pickoff n Chemical fog n Guide-shoe marks n Water marks n Chemical spots n Guide-shoe & roller scratches n
Processing Artifacts Emulsion pickoff n Chemical fog n Guide-shoe marks n Water marks n Chemical spots n Guide-shoe & roller scratches n
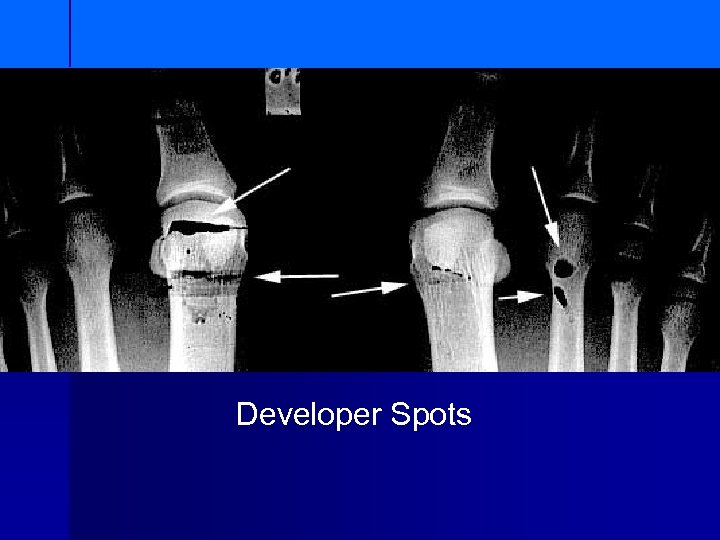 Developer Spots
Developer Spots
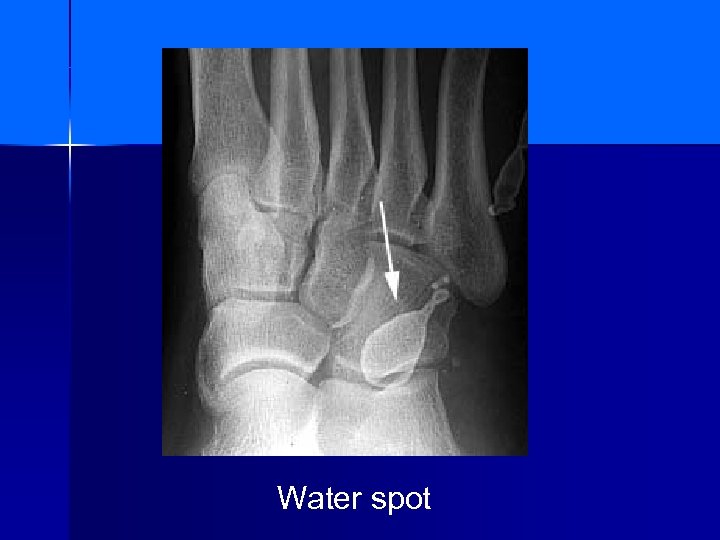 Water spot
Water spot
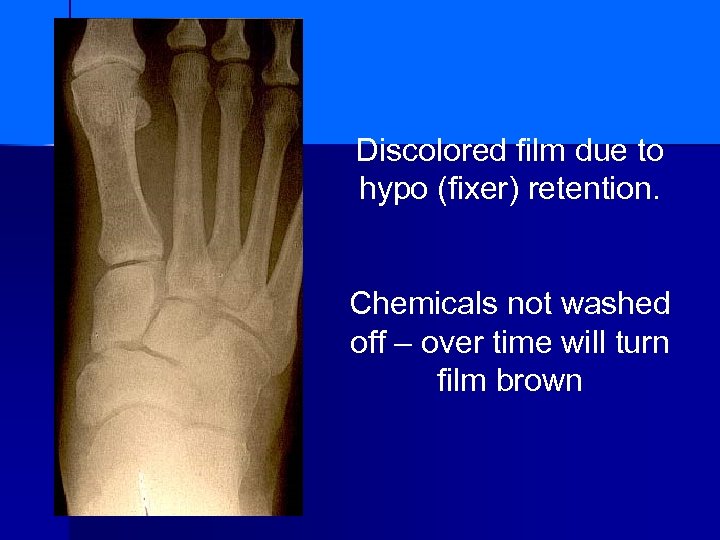 Discolored film due to hypo (fixer) retention. Chemicals not washed off – over time will turn film brown
Discolored film due to hypo (fixer) retention. Chemicals not washed off – over time will turn film brown
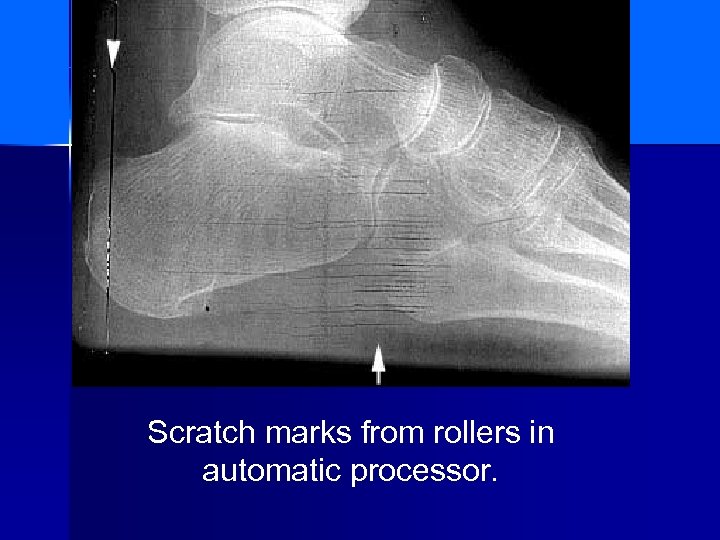 Scratch marks from rollers in automatic processor.
Scratch marks from rollers in automatic processor.
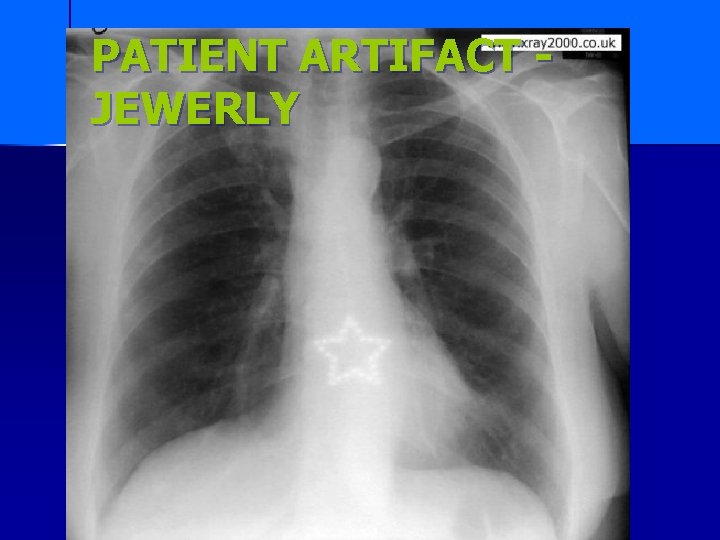 PATIENT ARTIFACT JEWERLY
PATIENT ARTIFACT JEWERLY
 Handling & Storage Artifacts Light fog n Radiation fog n Static n Kink marks n Scratches n Dirty cassettes n
Handling & Storage Artifacts Light fog n Radiation fog n Static n Kink marks n Scratches n Dirty cassettes n
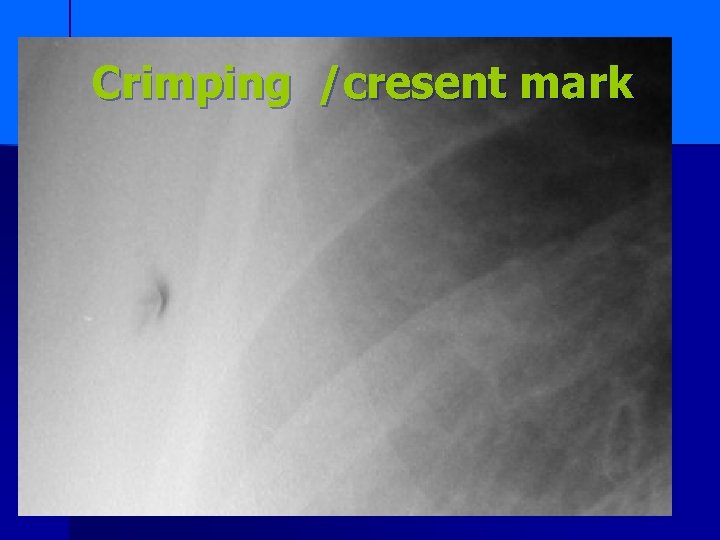 Crimping /cresent mark
Crimping /cresent mark
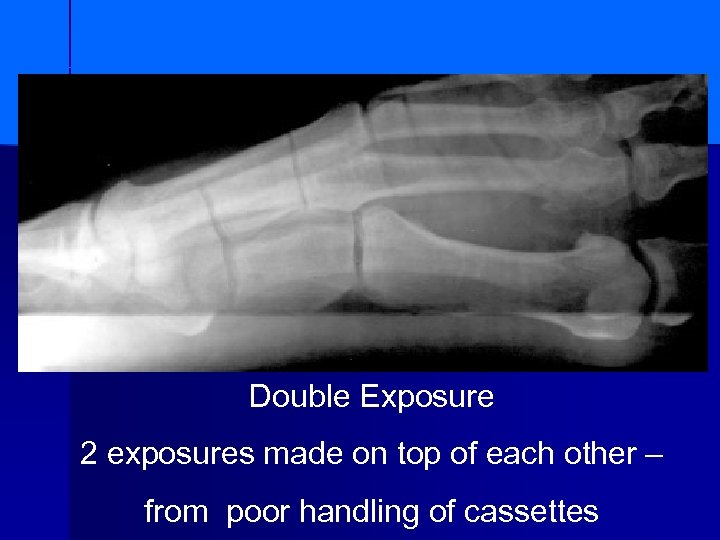 Double Exposure 2 exposures made on top of each other – from poor handling of cassettes
Double Exposure 2 exposures made on top of each other – from poor handling of cassettes
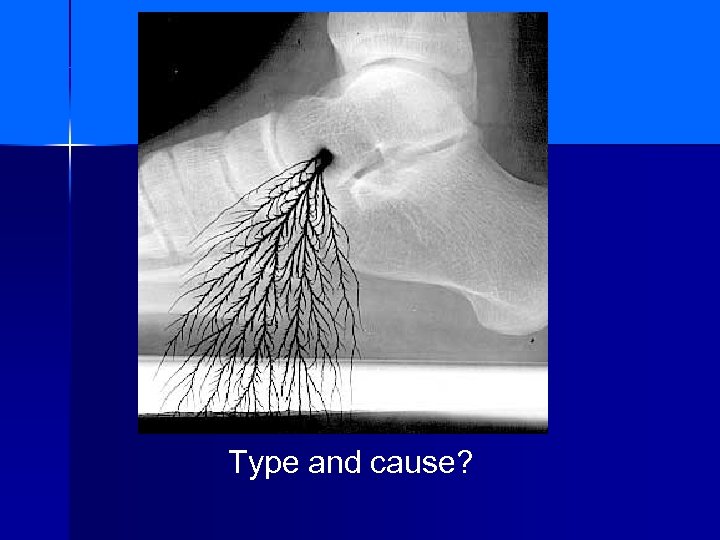 Type and cause?
Type and cause?
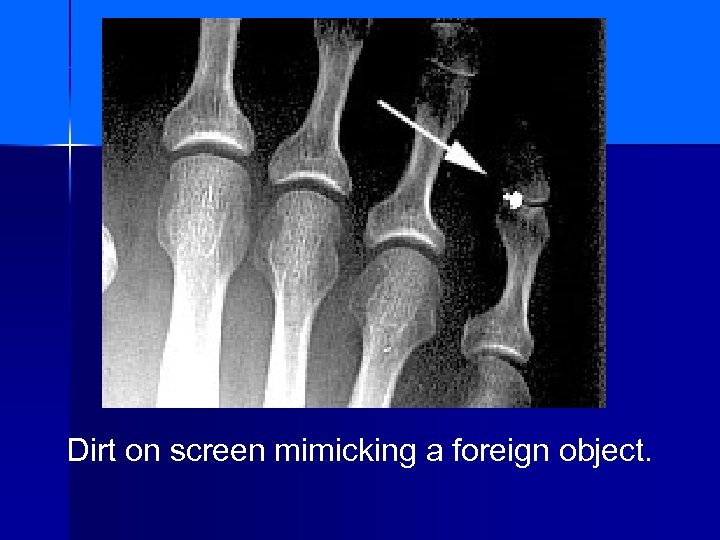 Dirt on screen mimicking a foreign object.
Dirt on screen mimicking a foreign object.
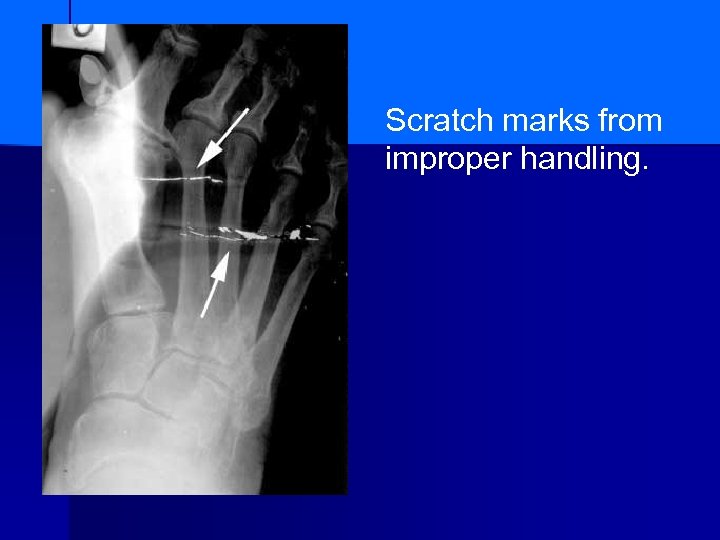 Scratch marks from improper handling.
Scratch marks from improper handling.
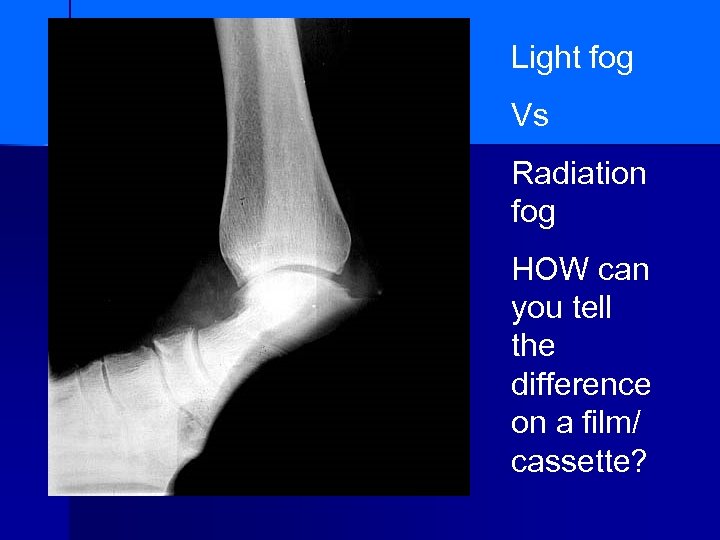 Light fog Vs Radiation fog HOW can you tell the difference on a film/ cassette?
Light fog Vs Radiation fog HOW can you tell the difference on a film/ cassette?
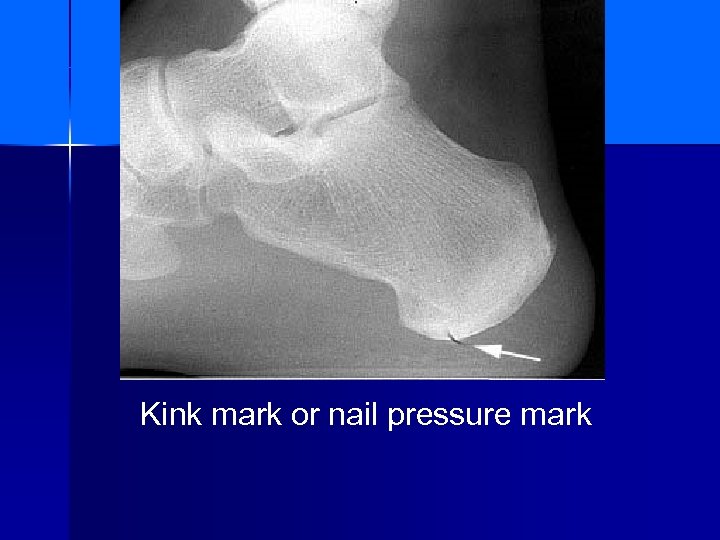 Kink mark or nail pressure mark
Kink mark or nail pressure mark
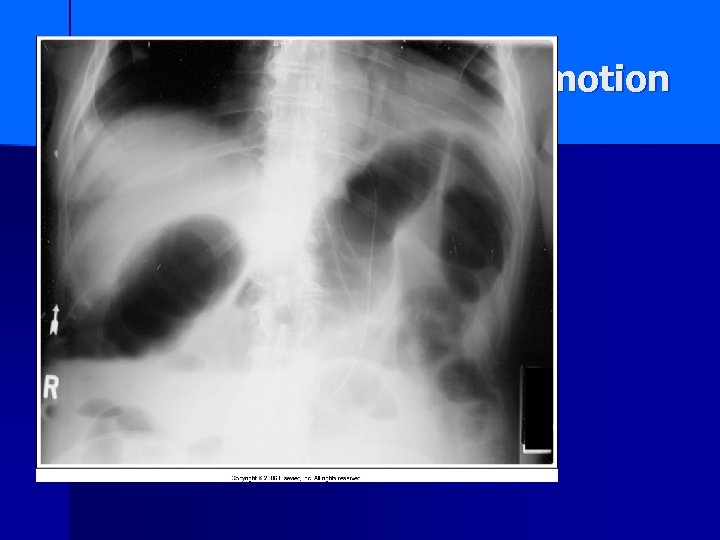 motion
motion
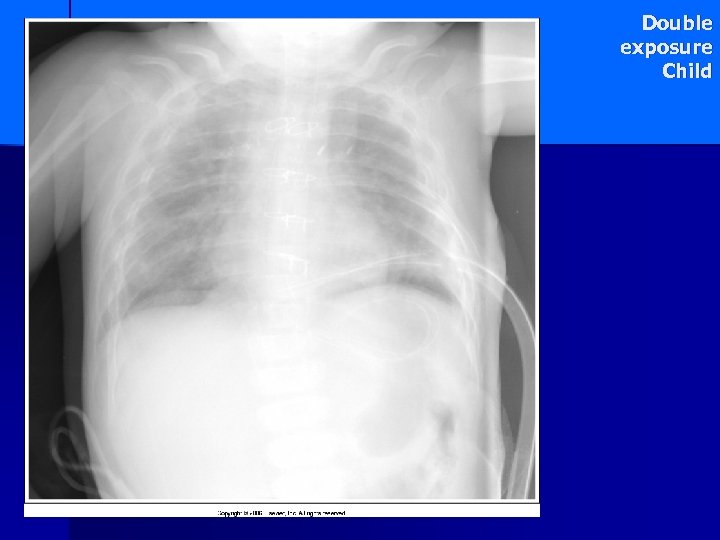 Double exposure Child
Double exposure Child
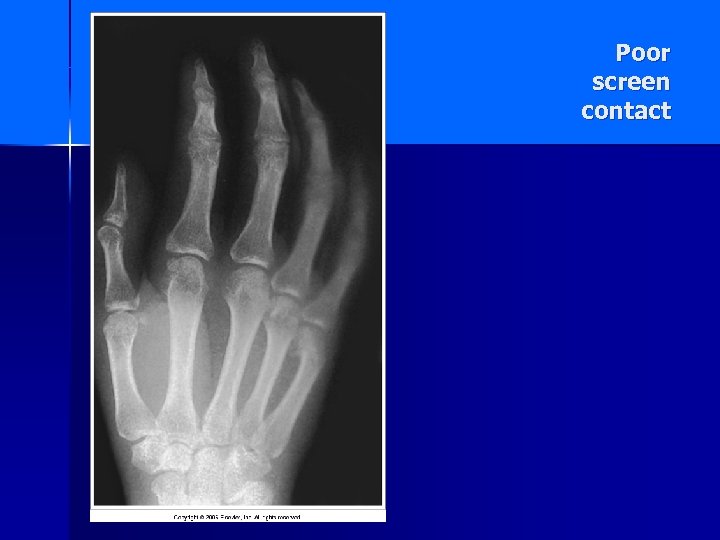 Poor screen contact
Poor screen contact
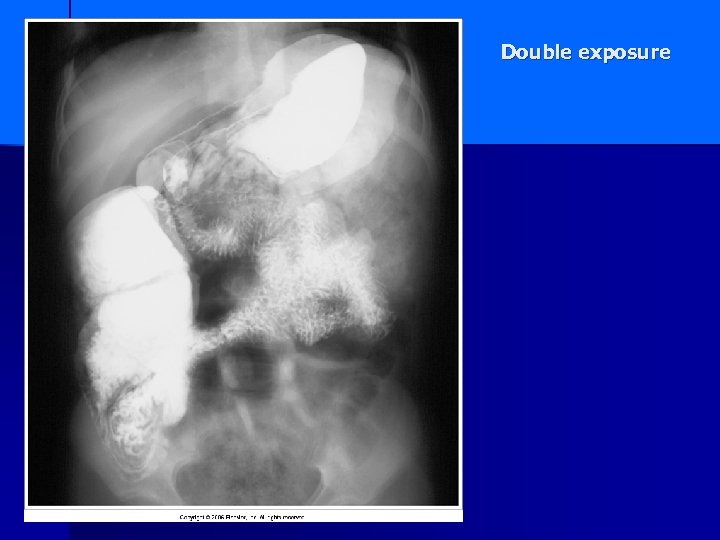 Double exposure
Double exposure
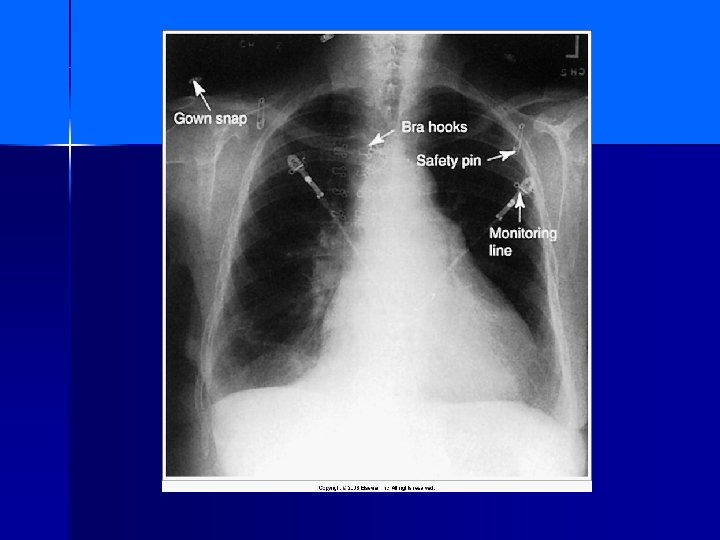
 Exposure Artifacts n Could be corrected before exposure = Jewelry n Hands in the anatomy n Something on the patient n
Exposure Artifacts n Could be corrected before exposure = Jewelry n Hands in the anatomy n Something on the patient n
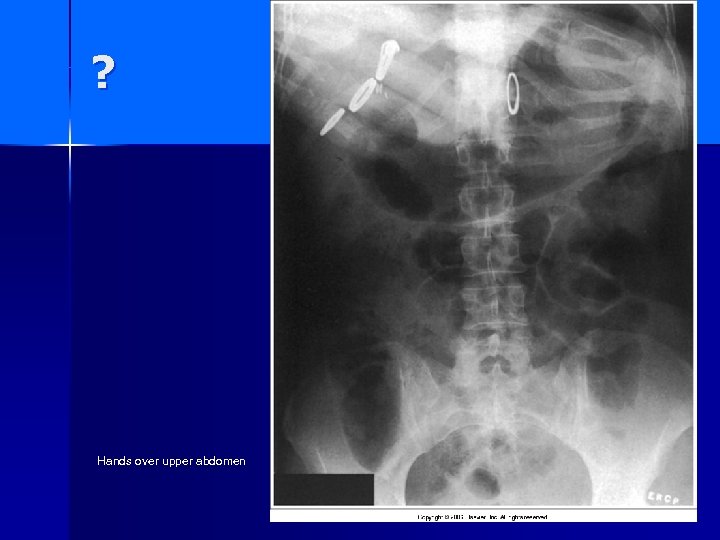 ? Hands over upper abdomen
? Hands over upper abdomen
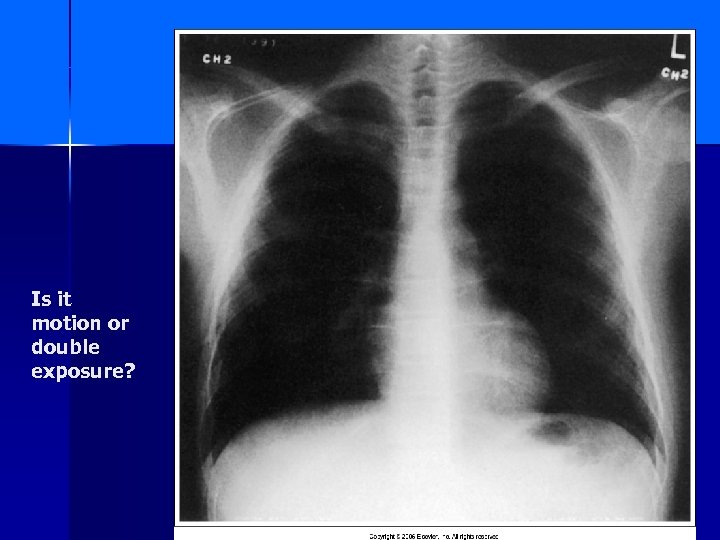 Is it motion or double exposure?
Is it motion or double exposure?
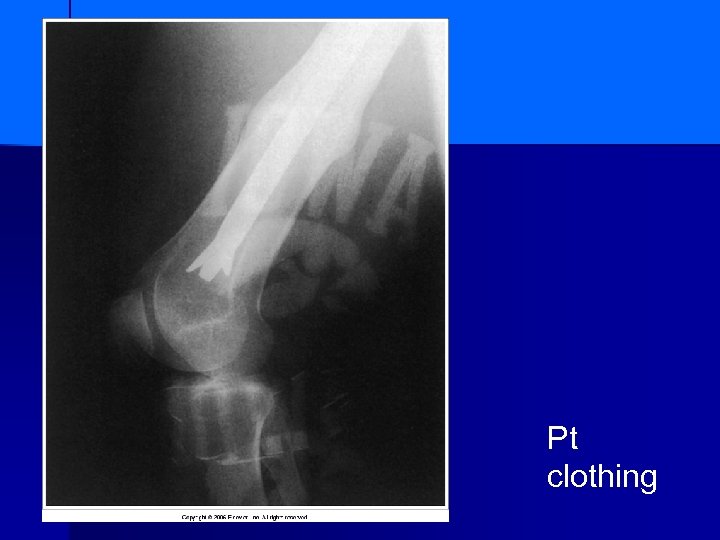 Pt clothing
Pt clothing
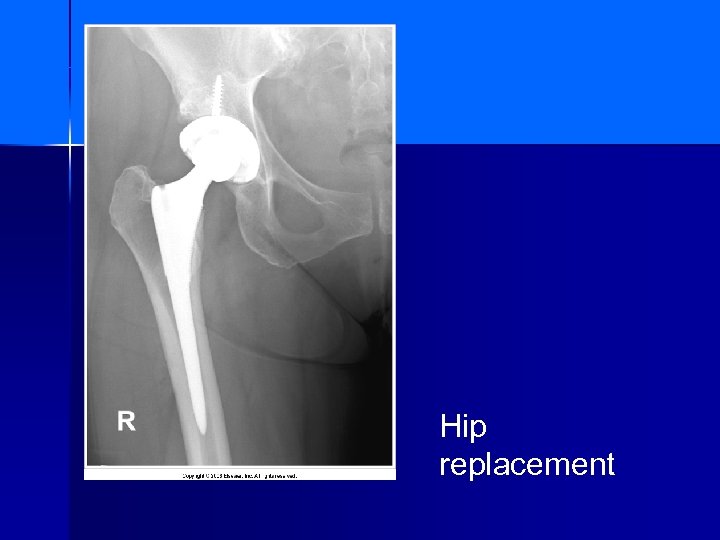 Hip replacement
Hip replacement
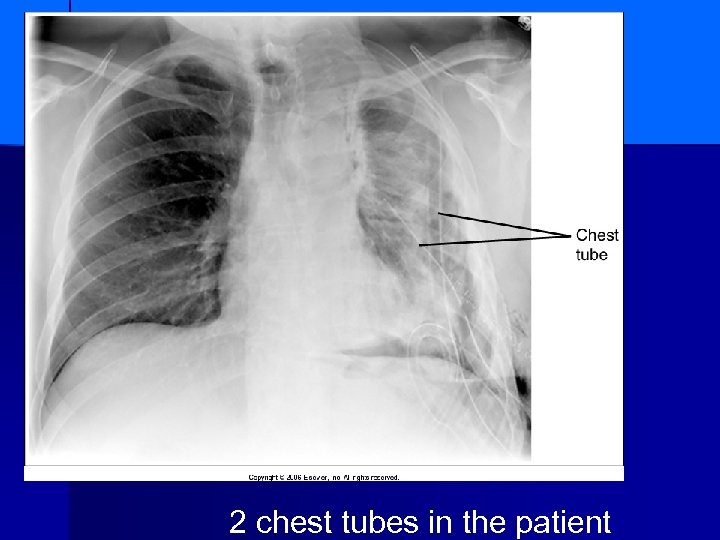 2 chest tubes in the patient
2 chest tubes in the patient
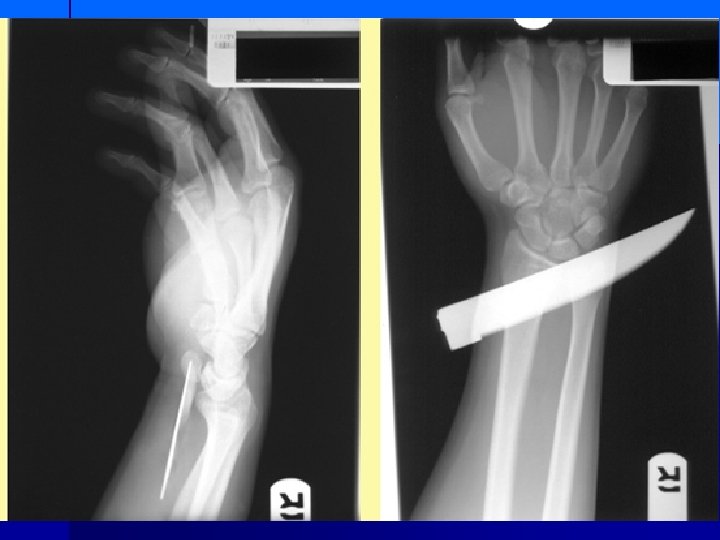
 PATHOLOGY NOT ARTIFACT
PATHOLOGY NOT ARTIFACT
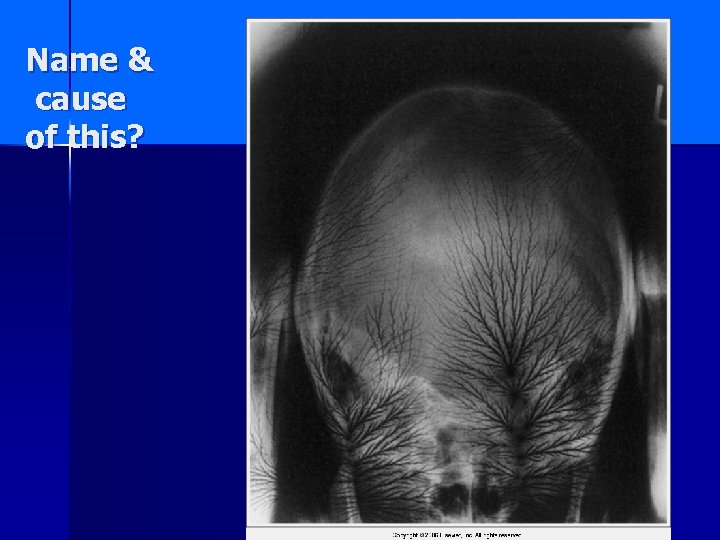 Name & cause of this?
Name & cause of this?
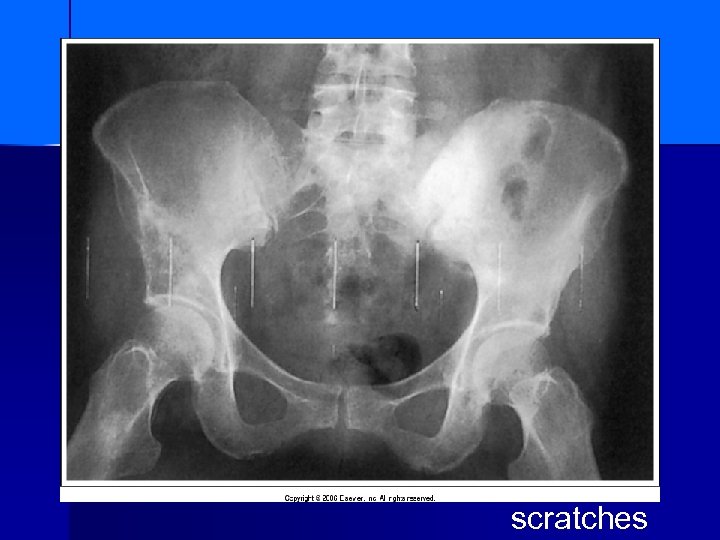 scratches
scratches
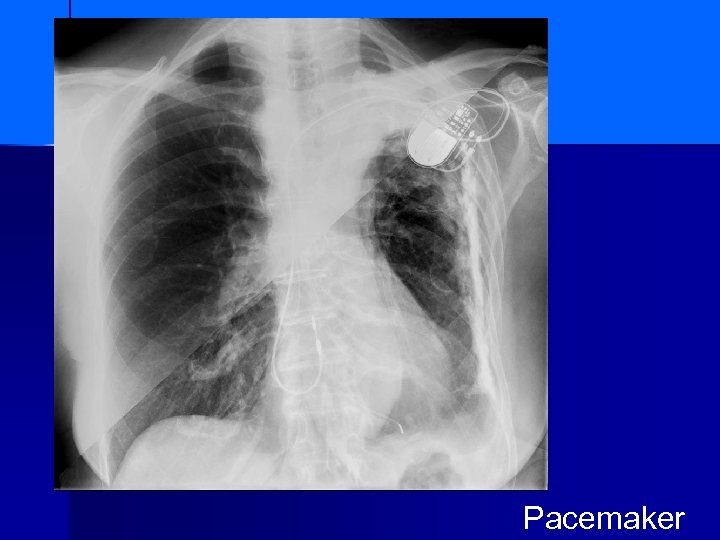 Pacemaker
Pacemaker
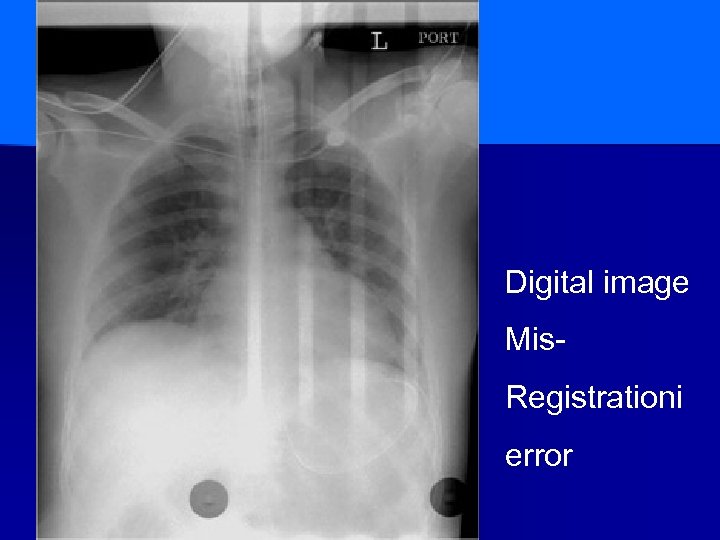 Digital image Mis. Registrationi error
Digital image Mis. Registrationi error
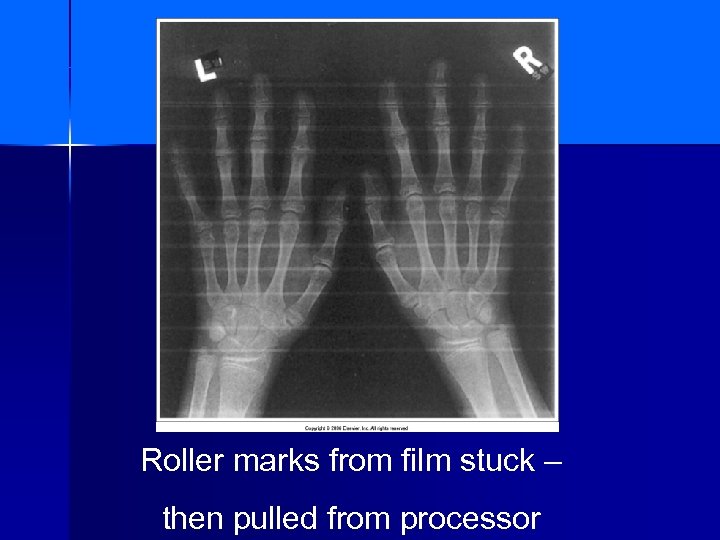 Roller marks from film stuck – then pulled from processor
Roller marks from film stuck – then pulled from processor
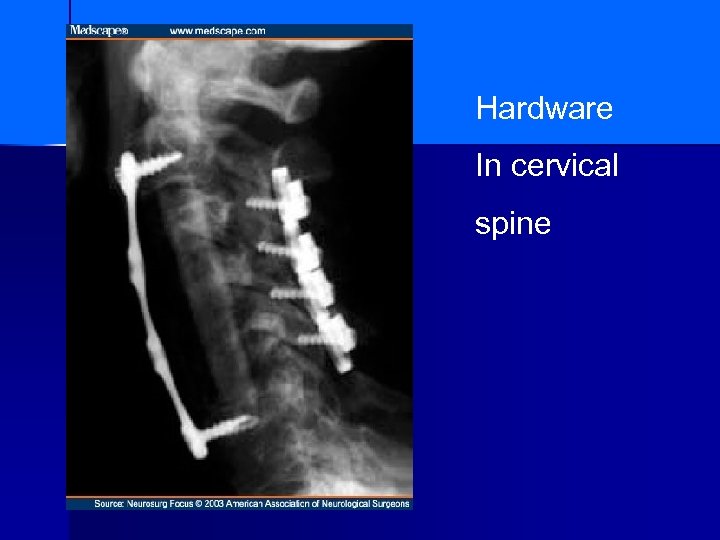 Hardware In cervical spine
Hardware In cervical spine
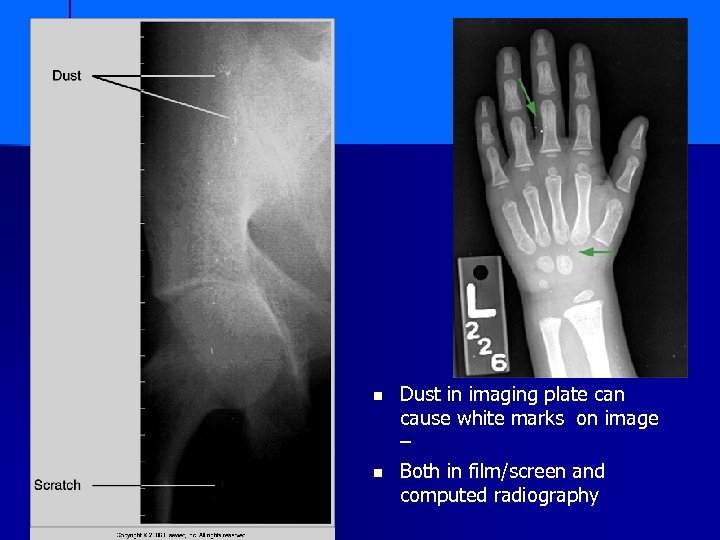 n n Dust in imaging plate can cause white marks on image – Both in film/screen and computed radiography
n n Dust in imaging plate can cause white marks on image – Both in film/screen and computed radiography
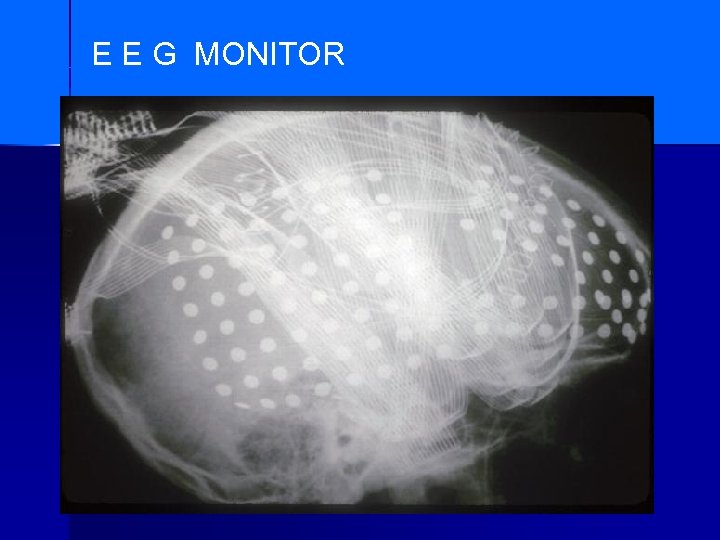 E E G MONITOR
E E G MONITOR
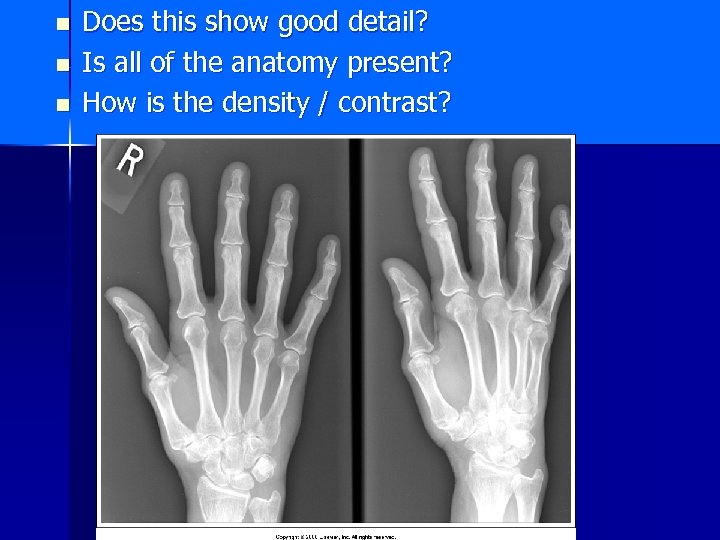 n n n Does this show good detail? Is all of the anatomy present? How is the density / contrast?
n n n Does this show good detail? Is all of the anatomy present? How is the density / contrast?
 n Does this show good detail? – YES n Is all of the anatomy present? – No (part of the little finger is not seen) n n n How is the density / contrast? Density – a little “light” underexposed Contrast is good
n Does this show good detail? – YES n Is all of the anatomy present? – No (part of the little finger is not seen) n n n How is the density / contrast? Density – a little “light” underexposed Contrast is good
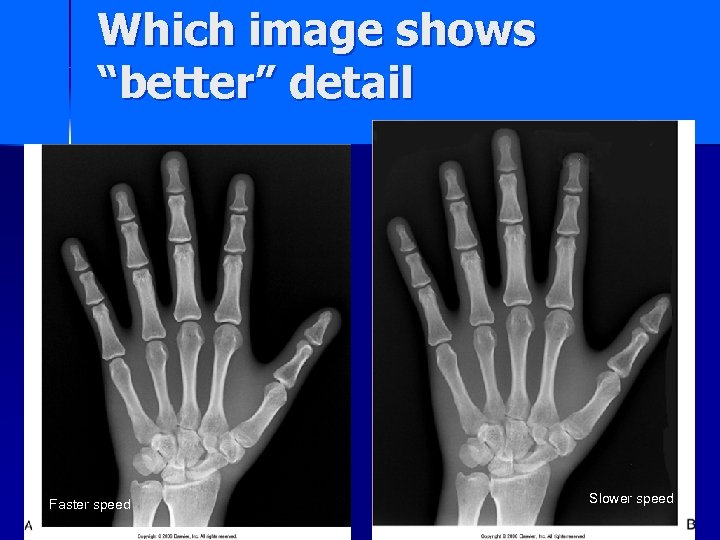 Which image shows “better” detail Faster speed Slower speed
Which image shows “better” detail Faster speed Slower speed
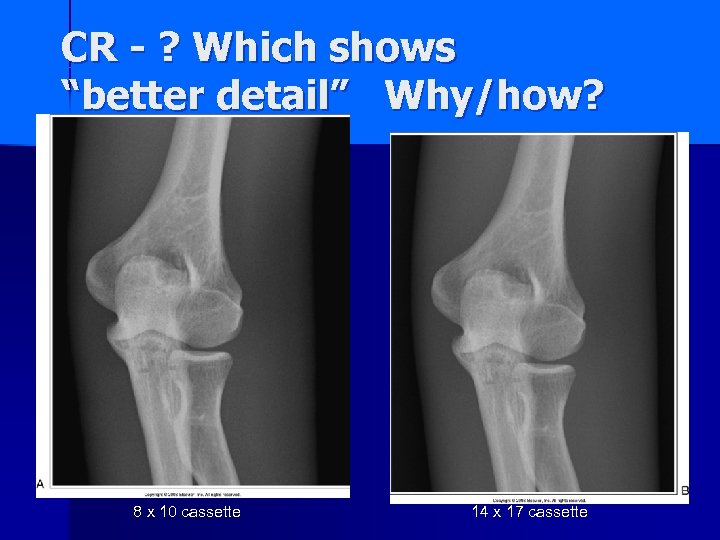 CR - ? Which shows “better detail” Why/how? 8 x 10 cassette 14 x 17 cassette
CR - ? Which shows “better detail” Why/how? 8 x 10 cassette 14 x 17 cassette
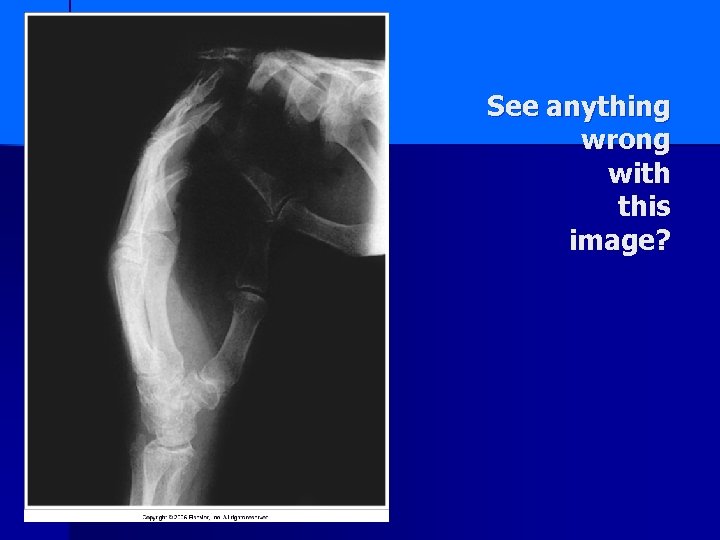 See anything wrong with this image?
See anything wrong with this image?
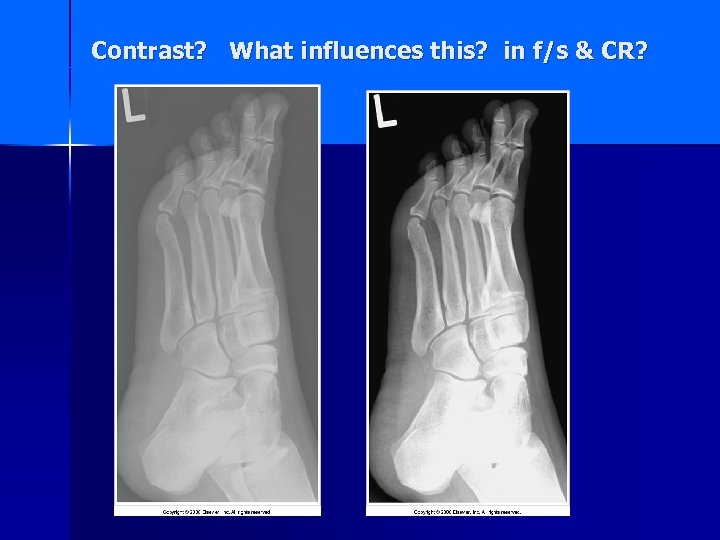 Contrast? What influences this? in f/s & CR?
Contrast? What influences this? in f/s & CR?
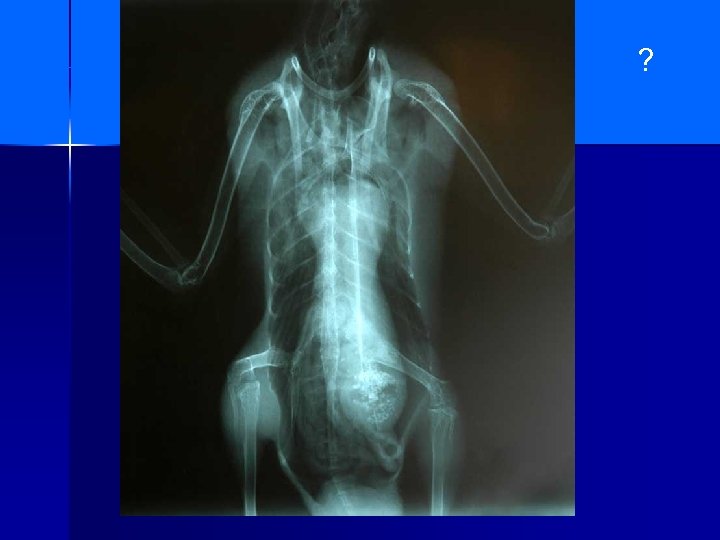 ?
?
 What are the following types of artifact classifications? Handling/Storage Exposure Processing (Chemical)
What are the following types of artifact classifications? Handling/Storage Exposure Processing (Chemical)
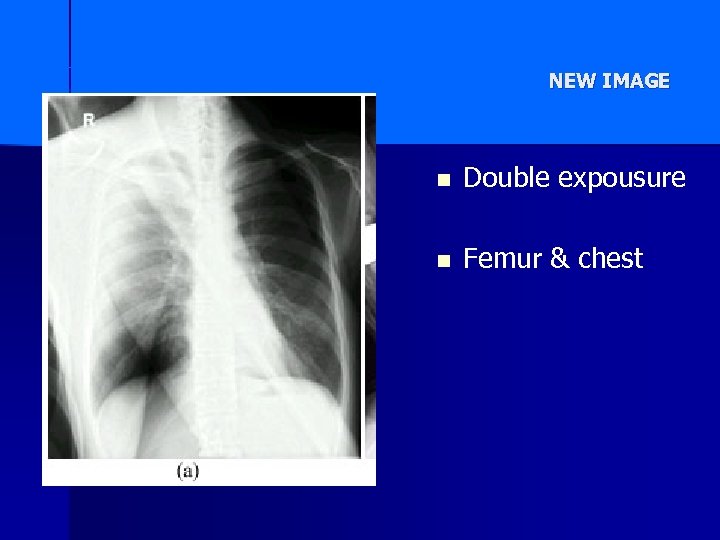 NEW IMAGE n Double expousure n Femur & chest
NEW IMAGE n Double expousure n Femur & chest
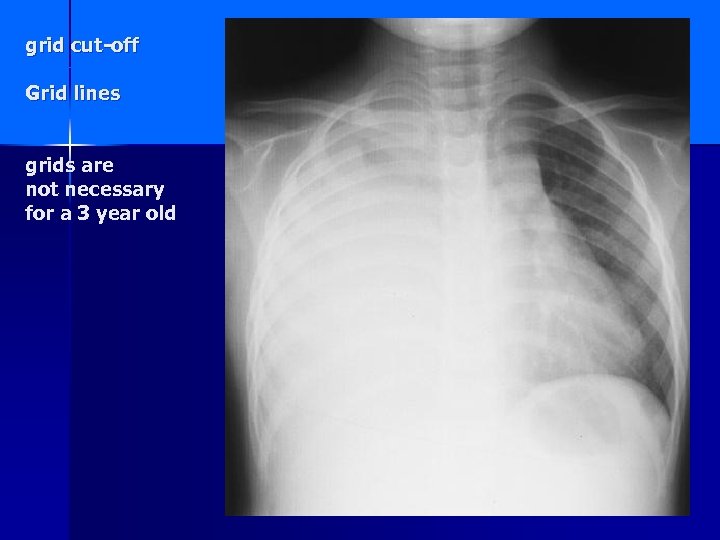 grid cut-off Grid lines grids are not necessary for a 3 year old
grid cut-off Grid lines grids are not necessary for a 3 year old
 Review of some CR artifacts
Review of some CR artifacts
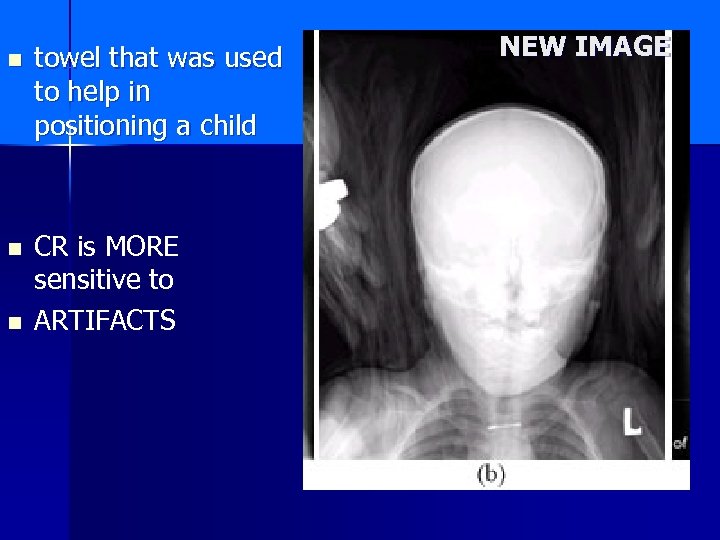 n towel that was used to help in positioning a child n CR is MORE sensitive to ARTIFACTS n NEW IMAGE
n towel that was used to help in positioning a child n CR is MORE sensitive to ARTIFACTS n NEW IMAGE
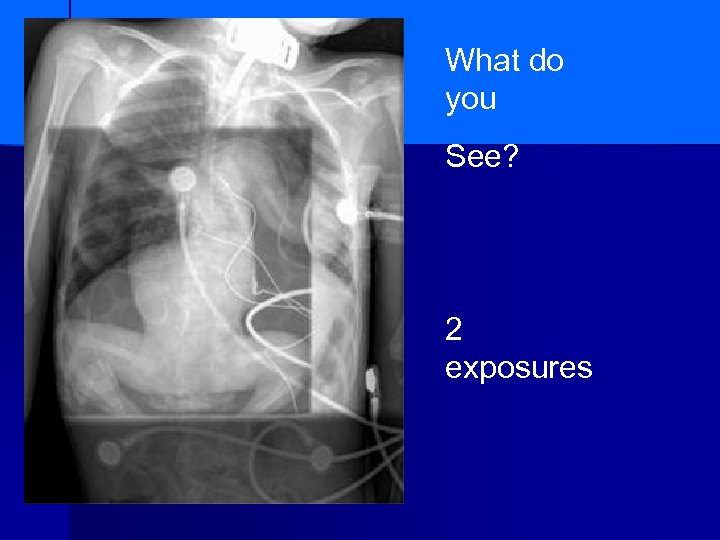 What do you See? 2 exposures
What do you See? 2 exposures
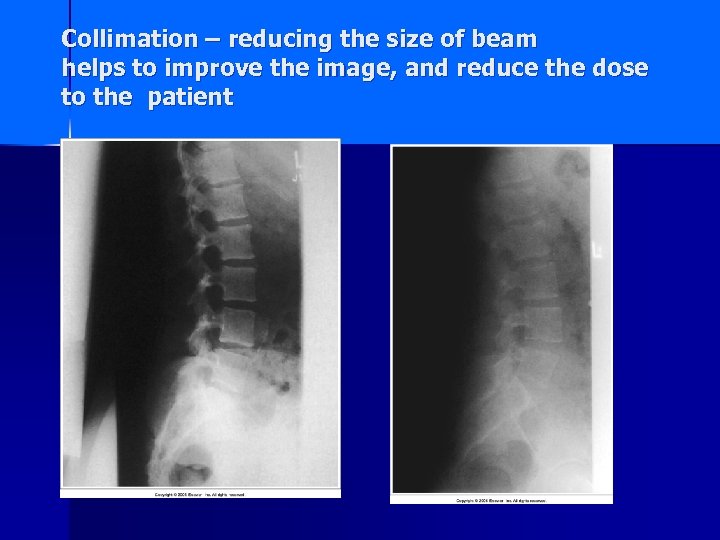 Collimation – reducing the size of beam helps to improve the image, and reduce the dose to the patient
Collimation – reducing the size of beam helps to improve the image, and reduce the dose to the patient
 Discarded x-ray film used to make ♫ records ♫
Discarded x-ray film used to make ♫ records ♫


