d. m. s. , prof. Denga О. V.
d. m. s. , prof. Denga О. V.
 The stomatology of children's age is allocated among all stomatological disciplines, any physiological and pathological processes in child organism proceed immediately and all protective reactions are unstable (neuroendocrinal system, immunal status, etc. are not formated); In connection with features of formation and development of a child organism at various stages (growth of a skeleton, muscles, a fiber lack, formation of bodies and systems) it’s necessary to use various approaches to prophylaxis and treatment (it’s especially important in orthodontics); The pathological processes proceeding in the child organism, as a rule, are reversible unlike an adults organism (caries, parodontic diseases);
The stomatology of children's age is allocated among all stomatological disciplines, any physiological and pathological processes in child organism proceed immediately and all protective reactions are unstable (neuroendocrinal system, immunal status, etc. are not formated); In connection with features of formation and development of a child organism at various stages (growth of a skeleton, muscles, a fiber lack, formation of bodies and systems) it’s necessary to use various approaches to prophylaxis and treatment (it’s especially important in orthodontics); The pathological processes proceeding in the child organism, as a rule, are reversible unlike an adults organism (caries, parodontic diseases);
 For the children's dentist the most important are general medical knowledge, as a rule dentist first sees system diseases - especially important are diseases of blood, infringement of a bone metabolism, gastrointestinal tract, a pathology of kidneys, endocrinic and other pathologys; The bases of prophylaxis of stomatological diseases and the somatic pathology which is connected with them should be engaged by the stomatologistpediatrist even till the birth of the child and of course since first months of his life. The stomatological status depends not only on the general condition of an organism, but it also influences (M. A. Jasinovsky, V. P. Filatov, etc. ) on it.
For the children's dentist the most important are general medical knowledge, as a rule dentist first sees system diseases - especially important are diseases of blood, infringement of a bone metabolism, gastrointestinal tract, a pathology of kidneys, endocrinic and other pathologys; The bases of prophylaxis of stomatological diseases and the somatic pathology which is connected with them should be engaged by the stomatologistpediatrist even till the birth of the child and of course since first months of his life. The stomatological status depends not only on the general condition of an organism, but it also influences (M. A. Jasinovsky, V. P. Filatov, etc. ) on it.
 As a science and as a speciality the stomatology has arisen not occasionally. Its formation and development was preceded by accumulation of stomatological knowledge in Russia and studying of the heritage of outstanding doctors of ancient and a classical antiquity. In the ancient world the philosophy was the complex science including all natural knowledge, which include medicine and also different stomatological data. Thus in different works are cited isolated data about character of flowing of physiological and pathological processes in an oral cavity, means of treatment of various diseases of an oral cavity organs.
As a science and as a speciality the stomatology has arisen not occasionally. Its formation and development was preceded by accumulation of stomatological knowledge in Russia and studying of the heritage of outstanding doctors of ancient and a classical antiquity. In the ancient world the philosophy was the complex science including all natural knowledge, which include medicine and also different stomatological data. Thus in different works are cited isolated data about character of flowing of physiological and pathological processes in an oral cavity, means of treatment of various diseases of an oral cavity organs.
 The first stomatology documents that have reached us are dated 1900 B. C. - the papyrus of Edvin Smith's where is described doctor tactics of displacement joint treatment.
The first stomatology documents that have reached us are dated 1900 B. C. - the papyrus of Edvin Smith's where is described doctor tactics of displacement joint treatment.
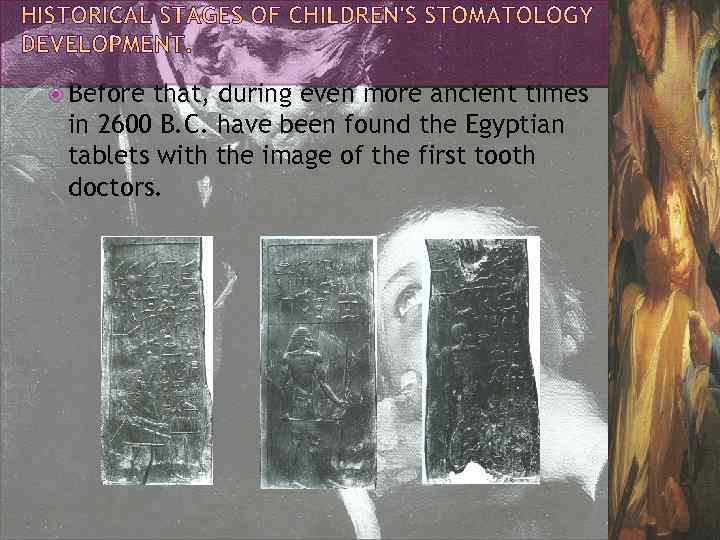 Before that, during even more ancient times in 2600 B. C. have been found the Egyptian tablets with the image of the first tooth doctors.
Before that, during even more ancient times in 2600 B. C. have been found the Egyptian tablets with the image of the first tooth doctors.
 In Rome in I century A. D. of our era already there were stomatologic tools
In Rome in I century A. D. of our era already there were stomatologic tools
 The first interesting data about a dentition are reflected in works of Hippocrat 460 -342 BC In the head of the known book of aphorisms Hippocrat wrote: «In the dentition period is observed: an itch in the of gums area, a fever» . He also connects all teeth diseases with accumulation in an organism of "bad juices» . This hypothesis has existed on almost till the end of XVIII century and was called «the humoral theory» .
The first interesting data about a dentition are reflected in works of Hippocrat 460 -342 BC In the head of the known book of aphorisms Hippocrat wrote: «In the dentition period is observed: an itch in the of gums area, a fever» . He also connects all teeth diseases with accumulation in an organism of "bad juices» . This hypothesis has existed on almost till the end of XVIII century and was called «the humoral theory» .
 It is known, that in Egypt more than 4 thousand years, and in China 2, 5 thousand years ago for treatment of gums diseases were applied herbs. Roman doctor Kornely Tsels (1 century BC - 1 century AD) recommended to treat diseases of gums by juice of unripe fruit. In his works there also instructions on sealing of caries cavities with canvas and lead.
It is known, that in Egypt more than 4 thousand years, and in China 2, 5 thousand years ago for treatment of gums diseases were applied herbs. Roman doctor Kornely Tsels (1 century BC - 1 century AD) recommended to treat diseases of gums by juice of unripe fruit. In his works there also instructions on sealing of caries cavities with canvas and lead.
 In canons of medical science of Ibn. Sina (10 -11 century of century AD) are resulted data on more than four hundred medical herbages, also is described operation concerning the cleftlip. In the works is paid the big attention to hygiene and preventive maintenance in stomatology and has put forward 8 points of conditions of preservation of health of a teeth.
In canons of medical science of Ibn. Sina (10 -11 century of century AD) are resulted data on more than four hundred medical herbages, also is described operation concerning the cleftlip. In the works is paid the big attention to hygiene and preventive maintenance in stomatology and has put forward 8 points of conditions of preservation of health of a teeth.
 Under illustration of Herodot (5 century of BC), at Scythians have been extended herbes fumigation of patients. In XII century in China doctor Agapit for calming of toothache applied mouth rinsings of the henbane broth, insertion in a tooth cavity of garlic, tincture of herbes roots. In "Herbalists" periodic journal in Russia were described healthgiving properties of plants and ways of their application for treatment of teeth diseases and gums.
Under illustration of Herodot (5 century of BC), at Scythians have been extended herbes fumigation of patients. In XII century in China doctor Agapit for calming of toothache applied mouth rinsings of the henbane broth, insertion in a tooth cavity of garlic, tincture of herbes roots. In "Herbalists" periodic journal in Russia were described healthgiving properties of plants and ways of their application for treatment of teeth diseases and gums.
 In the Middle Ages was continued qualitative development of stomatology (15 -18 centuries) teeth removal, hygiene, joint treatment.
In the Middle Ages was continued qualitative development of stomatology (15 -18 centuries) teeth removal, hygiene, joint treatment.
 Except Ibn-Sina the big contribution to stomatology development was brought by other Arabian scientists - especially in 11 -12 century Ali-ibn-Al-Abbas (Ali ibn-al-Abbas) Abulqasis (936 -1013)
Except Ibn-Sina the big contribution to stomatology development was brought by other Arabian scientists - especially in 11 -12 century Ali-ibn-Al-Abbas (Ali ibn-al-Abbas) Abulqasis (936 -1013)
 Gwidon de Chauliac has written one of the first textbooks on surgery (Halen, Avizenna, Hipokrat);
Gwidon de Chauliac has written one of the first textbooks on surgery (Halen, Avizenna, Hipokrat);
 In the Middle Ages appeared the present scientific researches about treatment and prosthetics. Known French surgeon P. Fanchard in the book «the Tooth surgery or the treatise about a teeth» , published in 1728, in detail describes various methods of treatment and prosthetics of teeth. Later, in 1795 the French doctor Bordier publishes the book subsequently translated and published in Russia under the name «the Dentist or an easy way of observance of cleanliness in a mouth and preservations of a teeth»
In the Middle Ages appeared the present scientific researches about treatment and prosthetics. Known French surgeon P. Fanchard in the book «the Tooth surgery or the treatise about a teeth» , published in 1728, in detail describes various methods of treatment and prosthetics of teeth. Later, in 1795 the French doctor Bordier publishes the book subsequently translated and published in Russia under the name «the Dentist or an easy way of observance of cleanliness in a mouth and preservations of a teeth»


 At that time in Russia were persons (doctors, bloodletting persons, midwives, teeth exodonts) which considered teeth “treatment” as the basic work.
At that time in Russia were persons (doctors, bloodletting persons, midwives, teeth exodonts) which considered teeth “treatment” as the basic work.
 The stomatology status quo has confirmed Peter I. He has entered a rank of the dentist in 1710. By position, the one who has decided to be engaged in dentistry should take tests in Medical college. In 1721 the Senate has published the law, on prohibition to the persons who do not have a medical education to be engaged by treatment, removal and restoration of a teeth
The stomatology status quo has confirmed Peter I. He has entered a rank of the dentist in 1710. By position, the one who has decided to be engaged in dentistry should take tests in Medical college. In 1721 the Senate has published the law, on prohibition to the persons who do not have a medical education to be engaged by treatment, removal and restoration of a teeth
 Accordingly the stomatology acquires the right to a life. Its representatives by name were called in «the Russian medical list» which has started to come out in 1809. There were 19 of them. First was listed Illya Luzgin, he is considered as officially first dentist in Russia. In 1810 are issued “Rules about examinations” for the medical officials who wants to be tooth doctors. For permitting of independent practice it was necessary to pass exams in Medical-surgical academy or university. Since 1838 these specialists, according to the law, were called as dentists. However, the qualifying standards, were very low: they could have not only lack of the general educational qualification, but they also could even not know reading and writing bases.
Accordingly the stomatology acquires the right to a life. Its representatives by name were called in «the Russian medical list» which has started to come out in 1809. There were 19 of them. First was listed Illya Luzgin, he is considered as officially first dentist in Russia. In 1810 are issued “Rules about examinations” for the medical officials who wants to be tooth doctors. For permitting of independent practice it was necessary to pass exams in Medical-surgical academy or university. Since 1838 these specialists, according to the law, were called as dentists. However, the qualifying standards, were very low: they could have not only lack of the general educational qualification, but they also could even not know reading and writing bases.
 One of the first Russian doctors, who understood importance of children's stomatology was N. M. Ambodik. Maksimovich (1744 -1812), he was the founder of not only Russian obstetrics, but also pediatrics. In his works is given a lot of attention to stomatological diseases at children of early age. In work «Art of midwife, or a science about old wives business» the author mentions questions of children's stomatology, describes teeth and oral cavity diseases, gives many councils about hygiene of an oral cavity. In the three-volume textbook of Russian surgeon I. F. Bush «the Management on surgery teaching» 18071808 are illuminated the reasons of a wrong dentition and methods of their elimination, in that book are also a lot of questions of teeth “treatment”.
One of the first Russian doctors, who understood importance of children's stomatology was N. M. Ambodik. Maksimovich (1744 -1812), he was the founder of not only Russian obstetrics, but also pediatrics. In his works is given a lot of attention to stomatological diseases at children of early age. In work «Art of midwife, or a science about old wives business» the author mentions questions of children's stomatology, describes teeth and oral cavity diseases, gives many councils about hygiene of an oral cavity. In the three-volume textbook of Russian surgeon I. F. Bush «the Management on surgery teaching» 18071808 are illuminated the reasons of a wrong dentition and methods of their elimination, in that book are also a lot of questions of teeth “treatment”.
 In 1829 there was a book of staff-doctor A. M. Sobolev «Dentistic or tooth treatment art of with the appendix about children's hygiene» . In this book the author has informed «how to care children since the birth how to observe their health and to protect a teeth from damage» , there were offered the classification of bite anomalies with instructions of their aetiology and a way of treatment. Thus he notices, that «dentistic takes the important place and is closely connected with other medical specialities and based on the same laws» . N. P. Gundobin has published lectures about dentition at children. In the management «the General and private therapy of children's age» (1896) the author pays considerable attention to stomatological diseases at children.
In 1829 there was a book of staff-doctor A. M. Sobolev «Dentistic or tooth treatment art of with the appendix about children's hygiene» . In this book the author has informed «how to care children since the birth how to observe their health and to protect a teeth from damage» , there were offered the classification of bite anomalies with instructions of their aetiology and a way of treatment. Thus he notices, that «dentistic takes the important place and is closely connected with other medical specialities and based on the same laws» . N. P. Gundobin has published lectures about dentition at children. In the management «the General and private therapy of children's age» (1896) the author pays considerable attention to stomatological diseases at children.
 Till 1881 in Russia there were no special educational institutions for preparing of dentists. Dentist L. L. Jams the first has put forward idea of preparing of dental surgeries in special institutes. In work «About dentists» (1877) he wrote «the domestic laws about dental surgery business, do not correspond to a modern dentiatric condition and to requirements of a modern life» . In 1891 the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia has founded dental surgery schools with «the Normal Charter» , providing introduction in a curriculum of some basic medical disciplines.
Till 1881 in Russia there were no special educational institutions for preparing of dentists. Dentist L. L. Jams the first has put forward idea of preparing of dental surgeries in special institutes. In work «About dentists» (1877) he wrote «the domestic laws about dental surgery business, do not correspond to a modern dentiatric condition and to requirements of a modern life» . In 1891 the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia has founded dental surgery schools with «the Normal Charter» , providing introduction in a curriculum of some basic medical disciplines.
 First such school has been opened by L. L. Jams in Warsaw (1891). At the same time has been opened the dental surgery school in Odessa T. A. Tychinsky. The next years medical schools have been opened in Petersburg E. F. Vongl (1893), in Odessa - I. I. Margolin (1896), in Kiev - H. P. Blank(1897) and in Moscow - V. F. Greffe (1897), G. I. Vilga (1909).
First such school has been opened by L. L. Jams in Warsaw (1891). At the same time has been opened the dental surgery school in Odessa T. A. Tychinsky. The next years medical schools have been opened in Petersburg E. F. Vongl (1893), in Odessa - I. I. Margolin (1896), in Kiev - H. P. Blank(1897) and in Moscow - V. F. Greffe (1897), G. I. Vilga (1909).
 The great role in reforming of stomatological education belong to great russian surgeon N. V. Sklifosovsky. In 1879 on VI conferention of russian naturalists and doctors in his report “Teeth strength of people who leave in the capital cities” he for the first time has payed attention for teeth caries and its progression with the age. He was the first in Russia who gathered statistic material about teeth caries. He also was an initiator and organisator of the first teeth observations to learn the reasons of caries. N. V. Sklifosovsky first in the world during the operation og uraniscochasma applied local anesthesia with cocaine solution. He has made a reform of stomatological education. The main point of the reform was that the doctors-odontologists have to become the higher education on special chairs of medical universities. N. V. Sklifosovsky has also founded the first special private associate poffesure.
The great role in reforming of stomatological education belong to great russian surgeon N. V. Sklifosovsky. In 1879 on VI conferention of russian naturalists and doctors in his report “Teeth strength of people who leave in the capital cities” he for the first time has payed attention for teeth caries and its progression with the age. He was the first in Russia who gathered statistic material about teeth caries. He also was an initiator and organisator of the first teeth observations to learn the reasons of caries. N. V. Sklifosovsky first in the world during the operation og uraniscochasma applied local anesthesia with cocaine solution. He has made a reform of stomatological education. The main point of the reform was that the doctors-odontologists have to become the higher education on special chairs of medical universities. N. V. Sklifosovsky has also founded the first special private associate poffesure.
 This years N. I. Pirogov (1810 -1881) made the first plastic surgery operations on children faces, including and heyloplastic. M. М. Chemodanov - 1902 р. had substantiated the amputaton method of primariy dentition with pulpits, he said that the physiological root resorbtion is not disturbed. So, even in prerevolutionary Russia the great personalities in medicine payed a lot of attention to stomatology of children age
This years N. I. Pirogov (1810 -1881) made the first plastic surgery operations on children faces, including and heyloplastic. M. М. Chemodanov - 1902 р. had substantiated the amputaton method of primariy dentition with pulpits, he said that the physiological root resorbtion is not disturbed. So, even in prerevolutionary Russia the great personalities in medicine payed a lot of attention to stomatology of children age
 P. G. Dauge marked that it is necessary to revse radical the work of stomatologacal institutions. He said that when we replace accidentlyindividual caries control with regular prophylaxis, it will be no caries at all
P. G. Dauge marked that it is necessary to revse radical the work of stomatologacal institutions. He said that when we replace accidentlyindividual caries control with regular prophylaxis, it will be no caries at all
 1. april 1928 in Odessa was opened the first official Ukrainian science-investigatory institute of dentistry. A lot of time it was the only investigatory institute of stomatological profile in USSR. Onli in 1962 in Moscow was opened Central science-investigatory institute of stomatology. The main tasks of the institute were the analysis of reasons, which proceeds deseases of an oral cavity and different methods of their treatment and prophylaxis.
1. april 1928 in Odessa was opened the first official Ukrainian science-investigatory institute of dentistry. A lot of time it was the only investigatory institute of stomatological profile in USSR. Onli in 1962 in Moscow was opened Central science-investigatory institute of stomatology. The main tasks of the institute were the analysis of reasons, which proceeds deseases of an oral cavity and different methods of their treatment and prophylaxis.
 In 1981 in the list of medical specialities was written the official speciality of children age dentist In 1963 are organisated chairs of children age stomatology in Moscow. Then later in Perm, Kalinin, Poltava, Lvov and Minsk
In 1981 in the list of medical specialities was written the official speciality of children age dentist In 1963 are organisated chairs of children age stomatology in Moscow. Then later in Perm, Kalinin, Poltava, Lvov and Minsk
 In 1986 in Odessa medical university was founded the chair of children age stomatology. The head of the chair was d. m. s, prof. Rudenko M. M. The main base of the chair was Odessa children dentistry polyclinic № 5. Since 1993 the educational proccess is made according to the new educational plans, that is improved every year
In 1986 in Odessa medical university was founded the chair of children age stomatology. The head of the chair was d. m. s, prof. Rudenko M. M. The main base of the chair was Odessa children dentistry polyclinic № 5. Since 1993 the educational proccess is made according to the new educational plans, that is improved every year
 Since 2006 the main scientific directions of the chair are: 1. Adaptogenic prophylaxis and treatment of teeth caries, fluorosis, gingivitis, teeth-maxilary anomalies (correction of adaptativecompensatory reactions in organism and oral cavity at children with the help of herbal adaptogenic preparations – biological active materials, antioxidants, proteins, influence of millimeter electromagnetic waves, direct current. of physiological magnitude, lasers therapy). 2. The developent of functional express-diagnostic methods and investigations of teeth hard tissues. Pulp, parodontic tissues, microcapillary channel, nonspecific resistance in oral cavity (spectrocolorymetry, electrophysical aand biophysical methods). 3. Monitoring of caries and fluorosis morbidity, morbidity of parodontic tissues, teeth-maxilary anomalies at children of 7, 12 and 15 years okd of different regions of Ukraine. 4. The specificity of teeth caries treatment at children of different regions of Ukraine 6. Correction of adaptogenic reactions of chirdren during ortodontic treatment (diagnostic, prediction, complication prophylaxis, osteogenesis correction).
Since 2006 the main scientific directions of the chair are: 1. Adaptogenic prophylaxis and treatment of teeth caries, fluorosis, gingivitis, teeth-maxilary anomalies (correction of adaptativecompensatory reactions in organism and oral cavity at children with the help of herbal adaptogenic preparations – biological active materials, antioxidants, proteins, influence of millimeter electromagnetic waves, direct current. of physiological magnitude, lasers therapy). 2. The developent of functional express-diagnostic methods and investigations of teeth hard tissues. Pulp, parodontic tissues, microcapillary channel, nonspecific resistance in oral cavity (spectrocolorymetry, electrophysical aand biophysical methods). 3. Monitoring of caries and fluorosis morbidity, morbidity of parodontic tissues, teeth-maxilary anomalies at children of 7, 12 and 15 years okd of different regions of Ukraine. 4. The specificity of teeth caries treatment at children of different regions of Ukraine 6. Correction of adaptogenic reactions of chirdren during ortodontic treatment (diagnostic, prediction, complication prophylaxis, osteogenesis correction).
 Staff 10, 25 basic rates – 25 research workers (12 by-workers) 3 Doctors of medical sciences (2 proffessors); 15 candidate of medical sciences (3 docents, 5 s. s. s. ); 7 assistances – without scientific degree (4 – have already finished their scientific works for candidate degree, 3 – are ready for planning);
Staff 10, 25 basic rates – 25 research workers (12 by-workers) 3 Doctors of medical sciences (2 proffessors); 15 candidate of medical sciences (3 docents, 5 s. s. s. ); 7 assistances – without scientific degree (4 – have already finished their scientific works for candidate degree, 3 – are ready for planning);
 On the chair are educated: 13 master students(8 english -speaking ); 11 clinical ordinators english (9 -speaking ); 4 aspirants(1 work is finished pre-term ); 2 works for degree of d. m. s are planned work is finished pre-term (1 );
On the chair are educated: 13 master students(8 english -speaking ); 11 clinical ordinators english (9 -speaking ); 4 aspirants(1 work is finished pre-term ); 2 works for degree of d. m. s are planned work is finished pre-term (1 );
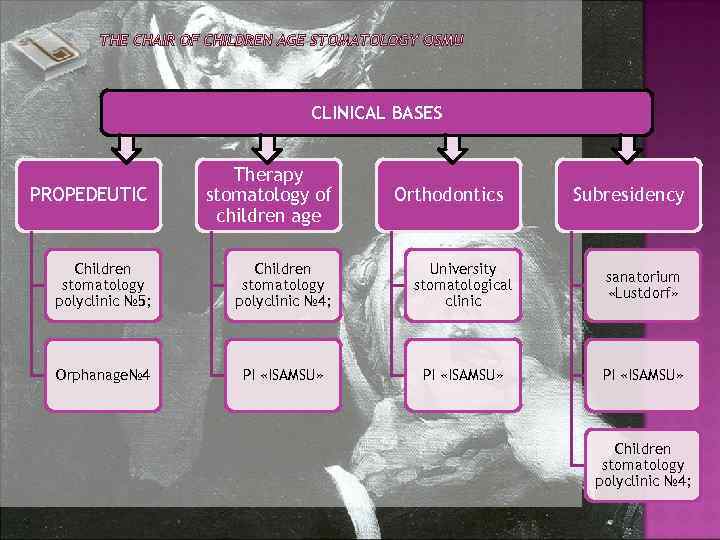 CLINICAL BASES PROPEDEUTIC Therapy stomatology of children age Children stomatology polyclinic № 5; Children stomatology polyclinic № 4; University stomatological clinic sanatorium «Lustdorf» Orphanage№ 4 PI «ISAMSU» Orthodontics Subresidency Children stomatology polyclinic № 4;
CLINICAL BASES PROPEDEUTIC Therapy stomatology of children age Children stomatology polyclinic № 5; Children stomatology polyclinic № 4; University stomatological clinic sanatorium «Lustdorf» Orphanage№ 4 PI «ISAMSU» Orthodontics Subresidency Children stomatology polyclinic № 4;
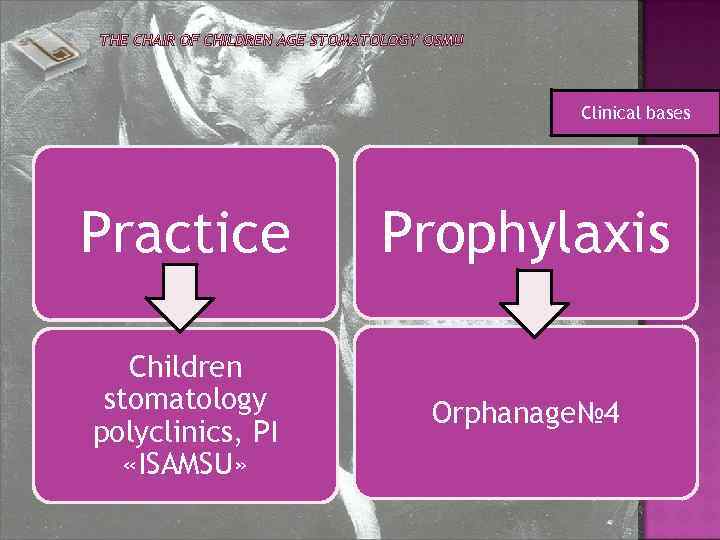 Clinical bases Practice Prophylaxis Children stomatology polyclinics, PI «ISAMSU» Orphanage№ 4
Clinical bases Practice Prophylaxis Children stomatology polyclinics, PI «ISAMSU» Orphanage№ 4
 monography publishing activities(20052007) • Алгоритмы организации оказания амбулаторнополиклинической стоматологической помощи (Изд. «Мед. книга» , Москва, 2008); • Особенности эндодонтического лечения зубов у детей раннего возраста (Изд. «Печатный мир» , Запорожье, 2006 • Протоколи надання медичної допомоги населенню України (Изд. «Медінформ» , Київ 2006, 2007); • Лечение пульпита у детей (Ивано-Франковск, 2008)
monography publishing activities(20052007) • Алгоритмы организации оказания амбулаторнополиклинической стоматологической помощи (Изд. «Мед. книга» , Москва, 2008); • Особенности эндодонтического лечения зубов у детей раннего возраста (Изд. «Печатный мир» , Запорожье, 2006 • Протоколи надання медичної допомоги населенню України (Изд. «Медінформ» , Київ 2006, 2007); • Лечение пульпита у детей (Ивано-Франковск, 2008)
 Methodological guidances and recommendations publishing activities(2005 -2007) • Методическое руководство для стоматологов по внедрению комплексной системы профилактики стоматологических заболеваний у детского населения Украины • Організація первинної профілактики стоматологічних захворювань в дошкільних дитячих закладах та школах • Проведення стоматологічного епідеміологічного обстеження населення України • Ультрафонофорез катамаса в комплексній терапії хронічного катарального гінгівіту в осіб зі зниженною неспецифічною резистентністю • Лікування ускладненого карієсу зубів з несформованим коренем • Діагностика алергічних реакцій в стоматології • Здоровий спосіб життя – основа первинної профілактики карієсу зубів • Застосування склоіономірного цементу 3 M ESPE Vitremer ТМ при лікуванні карієсу тимчасових та постійних зубів • Гігієнічні аспекти первинної профілактики стоматологічних захворювань у дітей • Комплексный метод профилактики и лечения кариеса зубов у детей дошкольного возраста с множественным кариесом зубов на фоне синдрома избыточного бактериального роста • Экспериментальные методы исследования остеогенеза
Methodological guidances and recommendations publishing activities(2005 -2007) • Методическое руководство для стоматологов по внедрению комплексной системы профилактики стоматологических заболеваний у детского населения Украины • Організація первинної профілактики стоматологічних захворювань в дошкільних дитячих закладах та школах • Проведення стоматологічного епідеміологічного обстеження населення України • Ультрафонофорез катамаса в комплексній терапії хронічного катарального гінгівіту в осіб зі зниженною неспецифічною резистентністю • Лікування ускладненого карієсу зубів з несформованим коренем • Діагностика алергічних реакцій в стоматології • Здоровий спосіб життя – основа первинної профілактики карієсу зубів • Застосування склоіономірного цементу 3 M ESPE Vitremer ТМ при лікуванні карієсу тимчасових та постійних зубів • Гігієнічні аспекти первинної профілактики стоматологічних захворювань у дітей • Комплексный метод профилактики и лечения кариеса зубов у детей дошкольного возраста с множественным кариесом зубов на фоне синдрома избыточного бактериального роста • Экспериментальные методы исследования остеогенеза
 Learning aids and information letters publishing activities (2005 -2007) • Сборник алгоритмов практических навыков и умений (пособие) • Комплексный практически ориентированный государственный экзамен (пособие) • Індивідуальна профілактика рецидивів хронічного катарального гінгівіту у дітей • Застосування склоіономірного цементу Ketac™ Molar Easymix при лікуванні карі’єу тимчасових зубів • Комплексні діагностика, профілактика та лікування флюорозу зубів у дітей • Поетапна профілакика карієсу у дітей
Learning aids and information letters publishing activities (2005 -2007) • Сборник алгоритмов практических навыков и умений (пособие) • Комплексный практически ориентированный государственный экзамен (пособие) • Індивідуальна профілактика рецидивів хронічного катарального гінгівіту у дітей • Застосування склоіономірного цементу Ketac™ Molar Easymix при лікуванні карі’єу тимчасових зубів • Комплексні діагностика, профілактика та лікування флюорозу зубів у дітей • Поетапна профілакика карієсу у дітей
 Medical work In medical work are participated: Ø 1 honoured doctor of Ukraine. Ø 14 chair assistents have higher doctors cathegoryr. Ø Chair research workers treat children on all clinical bases on children therapeutic stomatology, prophylaxis and orthodontics. Ø Proffessors and associate professors of the chair have consultative work
Medical work In medical work are participated: Ø 1 honoured doctor of Ukraine. Ø 14 chair assistents have higher doctors cathegoryr. Ø Chair research workers treat children on all clinical bases on children therapeutic stomatology, prophylaxis and orthodontics. Ø Proffessors and associate professors of the chair have consultative work
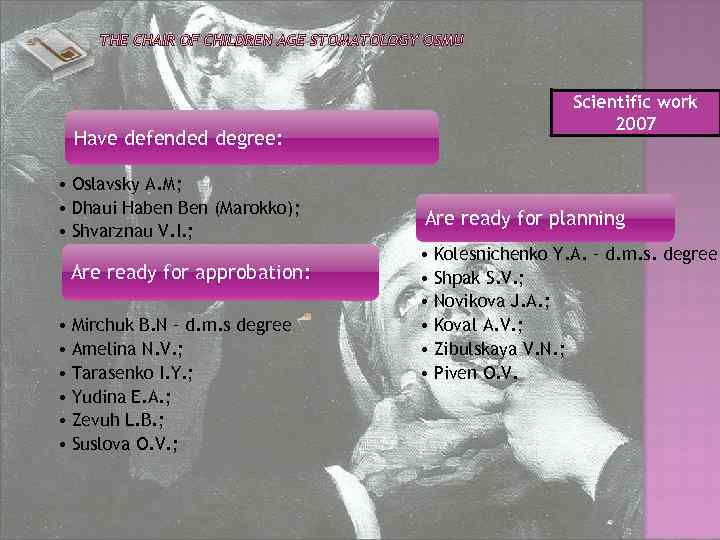 Have defended degree: • Oslavsky А. М; • Dhaui Haben Ben (Marokko); • Shvarznau V. I. ; Are ready for approbation: • Mirchuk B. N – d. m. s degree • Amelina N. V. ; • Tarasenko I. Y. ; • Yudina E. А. ; • Zevuh L. B. ; • Suslova О. V. ; Scientific work 2007 Are ready for planning • Kolesnichenko Y. А. – d. m. s. degree • Shpak S. V. ; • Novikova J. А. ; • Koval А. V. ; • Zibulskaya V. N. ; • Piven О. V.
Have defended degree: • Oslavsky А. М; • Dhaui Haben Ben (Marokko); • Shvarznau V. I. ; Are ready for approbation: • Mirchuk B. N – d. m. s degree • Amelina N. V. ; • Tarasenko I. Y. ; • Yudina E. А. ; • Zevuh L. B. ; • Suslova О. V. ; Scientific work 2007 Are ready for planning • Kolesnichenko Y. А. – d. m. s. degree • Shpak S. V. ; • Novikova J. А. ; • Koval А. V. ; • Zibulskaya V. N. ; • Piven О. V.
 Scientific work Internetional collaboration ü STAR (Associasion of stomatologists in Russia) – prophylaxis and hygienists sections; ü Belorussia state university, Bel MAPO ICD ü Baltimour medical university (USA); ü Utrech medical university (Nitherlands); ü Athene medical university (Greece); ü Association of stomatologists Baden-Wuertenburg (Germany).
Scientific work Internetional collaboration ü STAR (Associasion of stomatologists in Russia) – prophylaxis and hygienists sections; ü Belorussia state university, Bel MAPO ICD ü Baltimour medical university (USA); ü Utrech medical university (Nitherlands); ü Athene medical university (Greece); ü Association of stomatologists Baden-Wuertenburg (Germany).
 Scientific work Internetional collaboration ü Scientific reports: § Stomatological congress (Russia, 2006); § Stomatological congress of Belorussia (2006); § Symposium «Actual stomatological questions» (Germany, 2006); § Baltimour medical university – report about stomatological status in Ukraine (USA, 2007).
Scientific work Internetional collaboration ü Scientific reports: § Stomatological congress (Russia, 2006); § Stomatological congress of Belorussia (2006); § Symposium «Actual stomatological questions» (Germany, 2006); § Baltimour medical university – report about stomatological status in Ukraine (USA, 2007).