7dd9f7f5c95d047aa56379d3331a8856.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 D-Link New IP DSLAM Solution Guide May, 2006 D-Link Corporation 1
D-Link New IP DSLAM Solution Guide May, 2006 D-Link Corporation 1
 Executive Summary • Functionality Advantage – – Versatile CPE to IP DSLAM Satisfy ISPs’ ADSL/2/2+ Broadband Service Gigabit, Multicast for Triple-Play Value-Added EMS Central Management System • Competitors – Alcatel(#1), Hwawei(#2). – Long Distance/Remote/Scarcity Population Cities 2
Executive Summary • Functionality Advantage – – Versatile CPE to IP DSLAM Satisfy ISPs’ ADSL/2/2+ Broadband Service Gigabit, Multicast for Triple-Play Value-Added EMS Central Management System • Competitors – Alcatel(#1), Hwawei(#2). – Long Distance/Remote/Scarcity Population Cities 2
 D-Link DAS-3324 • 24 -ports Harden • Triple Play IP DSLAM with ADSL/2/2+ 3
D-Link DAS-3324 • 24 -ports Harden • Triple Play IP DSLAM with ADSL/2/2+ 3
 Why D-Link IP DSLAM? • IGMP multicast to meet Triple-play. • Fiber Gigabit uplink to connect to. • Central management on Microsoft NT/SNMP, or Linux based Server GUI system. • From CPE to IP DSLAM, seamlessly operates and integrates, D-Link provides service providers with a complete ADSL Service solution. 4
Why D-Link IP DSLAM? • IGMP multicast to meet Triple-play. • Fiber Gigabit uplink to connect to. • Central management on Microsoft NT/SNMP, or Linux based Server GUI system. • From CPE to IP DSLAM, seamlessly operates and integrates, D-Link provides service providers with a complete ADSL Service solution. 4
 Contents • Product Application • Product Overview • New Technology • EMS Introduction • Trouble Shooting • D-Link’s Strength 5
Contents • Product Application • Product Overview • New Technology • EMS Introduction • Trouble Shooting • D-Link’s Strength 5
 Value Proposition • Most Compact and Cost Effective Solution • Stackable with Virtual Single NE • Simple ‘Plug & Play’ – ‘Plug & Play’ IP based solutions – IP Based monitoring, provisioning & startup procedure • New revenue opportunities for operators & building owners through new service offerings such as: – Cost Effective Internet Access Service – Metro Ethernet Access – Secure LAN to LAN interconnect – Office Applications – IP Telephony 6
Value Proposition • Most Compact and Cost Effective Solution • Stackable with Virtual Single NE • Simple ‘Plug & Play’ – ‘Plug & Play’ IP based solutions – IP Based monitoring, provisioning & startup procedure • New revenue opportunities for operators & building owners through new service offerings such as: – Cost Effective Internet Access Service – Metro Ethernet Access – Secure LAN to LAN interconnect – Office Applications – IP Telephony 6
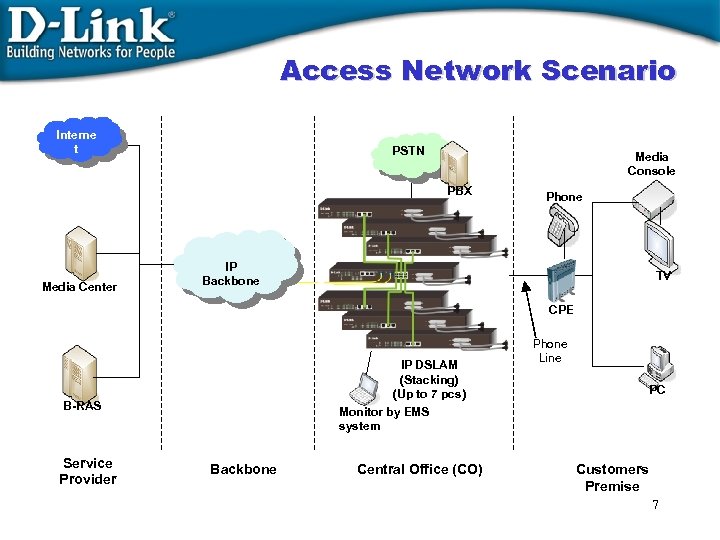 Access Network Scenario Interne t PSTN Media Console PBX Media Center Phone IP Backbone TV CPE IP DSLAM (Stacking) (Up to 7 pcs) Monitor by EMS system B-RAS Service Provider Backbone Central Office (CO) Phone Line PC Customers Premise 7
Access Network Scenario Interne t PSTN Media Console PBX Media Center Phone IP Backbone TV CPE IP DSLAM (Stacking) (Up to 7 pcs) Monitor by EMS system B-RAS Service Provider Backbone Central Office (CO) Phone Line PC Customers Premise 7
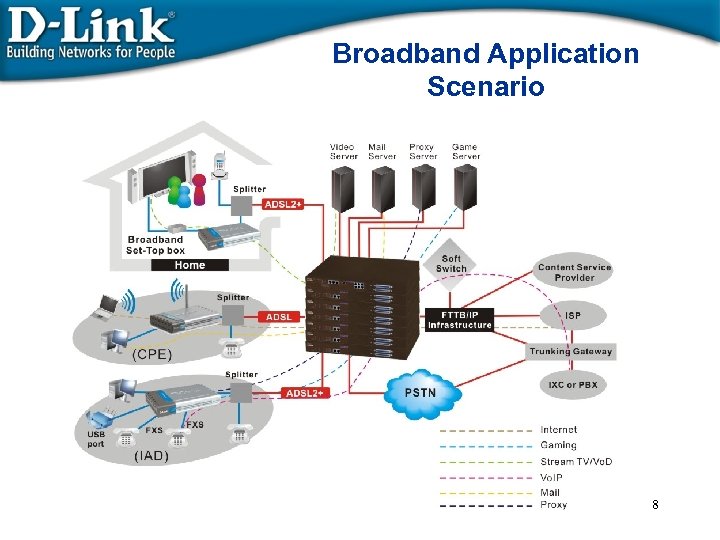 Broadband Application Scenario 8
Broadband Application Scenario 8
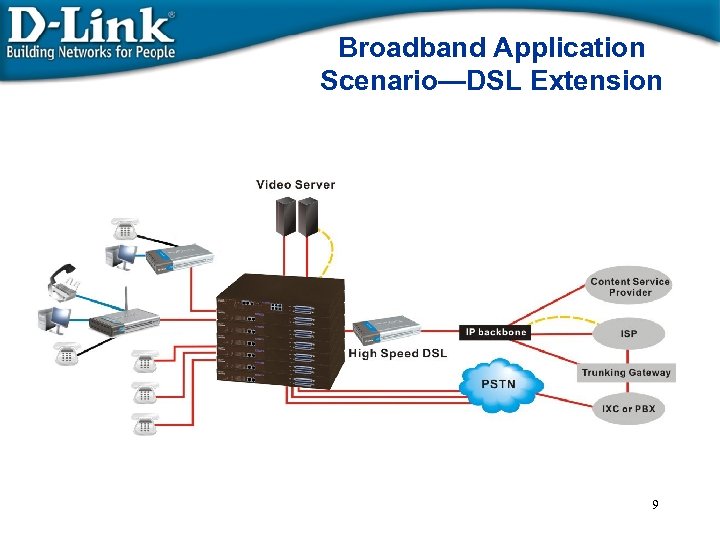 Broadband Application Scenario—DSL Extension 9
Broadband Application Scenario—DSL Extension 9
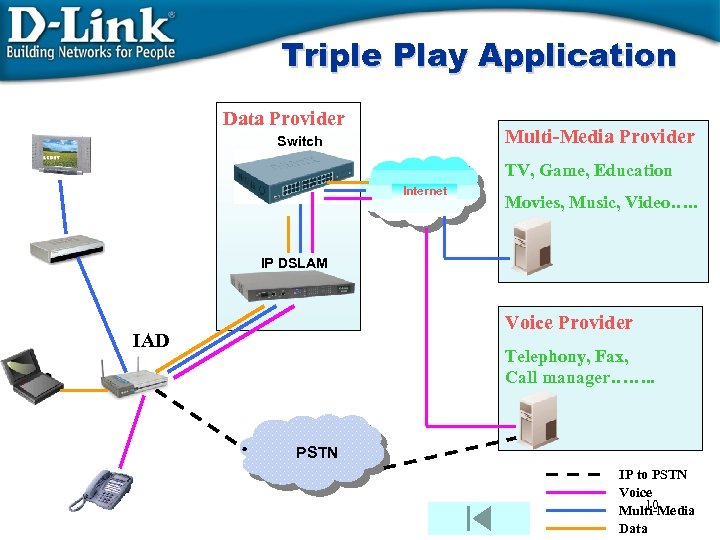 Triple Play Application Data Provider Multi-Media Provider Switch TV, Game, Education Internet Movies, Music, Video…. . IP DSLAM Voice Provider IAD Telephony, Fax, Call manager……. . PSTN IP to PSTN Voice 10 Multi-Media Data
Triple Play Application Data Provider Multi-Media Provider Switch TV, Game, Education Internet Movies, Music, Video…. . IP DSLAM Voice Provider IAD Telephony, Fax, Call manager……. . PSTN IP to PSTN Voice 10 Multi-Media Data
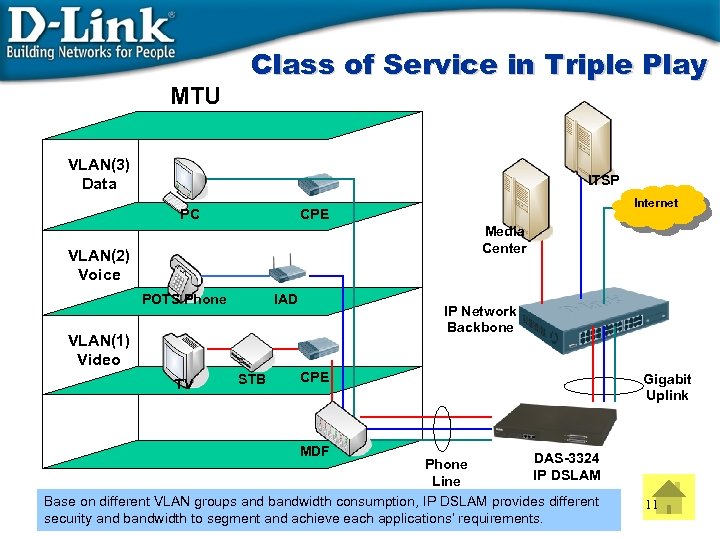 MTU Class of Service in Triple Play VLAN(3) Data ITSP PC Internet CPE Media Center VLAN(2) Voice POTS Phone IAD IP Network Backbone VLAN(1) Video TV STB CPE Gigabit Uplink MDF DAS-3324 Phone IP DSLAM Line Base on different VLAN groups and bandwidth consumption, IP DSLAM provides different security and bandwidth to segment and achieve each applications’ requirements. 11
MTU Class of Service in Triple Play VLAN(3) Data ITSP PC Internet CPE Media Center VLAN(2) Voice POTS Phone IAD IP Network Backbone VLAN(1) Video TV STB CPE Gigabit Uplink MDF DAS-3324 Phone IP DSLAM Line Base on different VLAN groups and bandwidth consumption, IP DSLAM provides different security and bandwidth to segment and achieve each applications’ requirements. 11
 Product Overview • Features of DAS-3324 • Roadmap of IP DSLAM 12
Product Overview • Features of DAS-3324 • Roadmap of IP DSLAM 12
 Features of DAS-3324 • Cost Saving Solution for ISP/SMB • • 24 ports ADSL/ADSL 2+ Subscriber Interface Build-in POTS Splitter Fiber Gigabit Uplinks to Backbones 7 units cascaded and managed as one unit • Excellent Management with Security • Microsoft NT, Linux SNMP-based GUI EMS System • Local RS-232 out-of-band CLI, and remote in-band SNMP/Telnet management • 3 -levels of user privilege system management • SNMP v 1, v 2 c support • Firmware upload/download via TFTP 13
Features of DAS-3324 • Cost Saving Solution for ISP/SMB • • 24 ports ADSL/ADSL 2+ Subscriber Interface Build-in POTS Splitter Fiber Gigabit Uplinks to Backbones 7 units cascaded and managed as one unit • Excellent Management with Security • Microsoft NT, Linux SNMP-based GUI EMS System • Local RS-232 out-of-band CLI, and remote in-band SNMP/Telnet management • 3 -levels of user privilege system management • SNMP v 1, v 2 c support • Firmware upload/download via TFTP 13
 Features of DAS-3324 • Advanced Function for Broadband Service Offering – IGMP Snooping – Up to 8 VCs – 802. 1 p Qo. S – 802. 1 d Spanning Tree – 802. 3 ad Uplink Aggregation – Up to 4096 VLAN(0, 1 reserve) – 64 MAC Addresses per DSL port, 4 K MAC per System – Static VLAN and port-based VLAN support – Configurable packet size (64 to 1536 bytes) – Security functions: VLAN filtering, MAC Filtering, IP Filtering, MAC-based and IP-based Access Control List (ACL) – MAC-based and IP-based rate limiting 14
Features of DAS-3324 • Advanced Function for Broadband Service Offering – IGMP Snooping – Up to 8 VCs – 802. 1 p Qo. S – 802. 1 d Spanning Tree – 802. 3 ad Uplink Aggregation – Up to 4096 VLAN(0, 1 reserve) – 64 MAC Addresses per DSL port, 4 K MAC per System – Static VLAN and port-based VLAN support – Configurable packet size (64 to 1536 bytes) – Security functions: VLAN filtering, MAC Filtering, IP Filtering, MAC-based and IP-based Access Control List (ACL) – MAC-based and IP-based rate limiting 14
 ADSL 2+ IP DSLAM Target Market • IP Metro Ethernet Networks § § • Outdoor Remote application Central Office Enterprise Market § Hotel/Private Property § SOHO • Master Mini-DSLAM § Low density and/or limited space CO application § ILEC or CLEC • Desktop-DSLAM § § MTU/MDU applications Campuses Slave 15
ADSL 2+ IP DSLAM Target Market • IP Metro Ethernet Networks § § • Outdoor Remote application Central Office Enterprise Market § Hotel/Private Property § SOHO • Master Mini-DSLAM § Low density and/or limited space CO application § ILEC or CLEC • Desktop-DSLAM § § MTU/MDU applications Campuses Slave 15
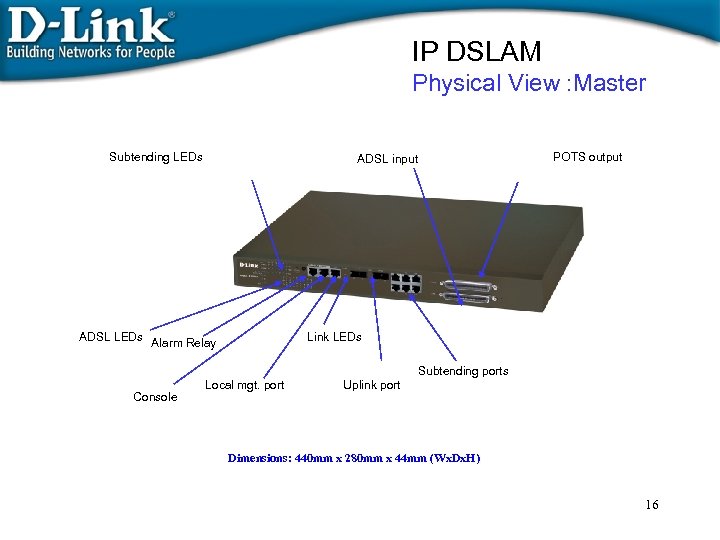 IP DSLAM Physical View : Master Subtending LEDs POTS output ADSL input ADSL LEDs Alarm Relay Link LEDs Subtending ports Console Local mgt. port Uplink port Dimensions: 440 mm x 280 mm x 44 mm (Wx. Dx. H) 16
IP DSLAM Physical View : Master Subtending LEDs POTS output ADSL input ADSL LEDs Alarm Relay Link LEDs Subtending ports Console Local mgt. port Uplink port Dimensions: 440 mm x 280 mm x 44 mm (Wx. Dx. H) 16
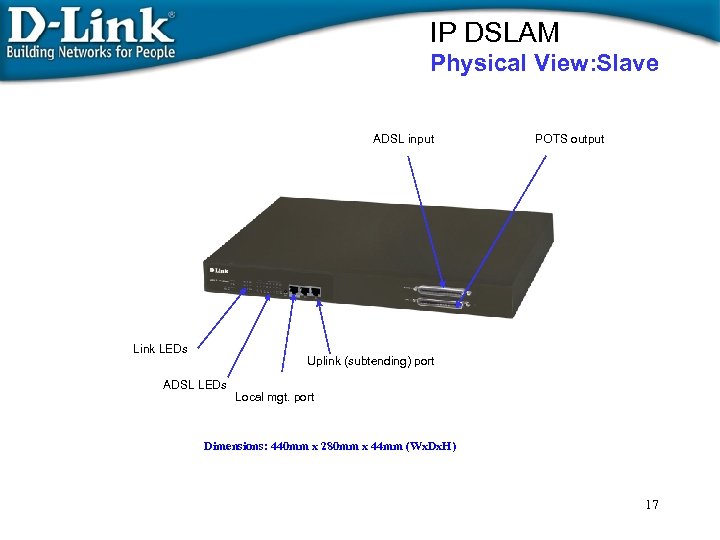 IP DSLAM Physical View: Slave ADSL input Link LEDs POTS output Uplink (subtending) port ADSL LEDs Local mgt. port Dimensions: 440 mm x 280 mm x 44 mm (Wx. Dx. H) 17
IP DSLAM Physical View: Slave ADSL input Link LEDs POTS output Uplink (subtending) port ADSL LEDs Local mgt. port Dimensions: 440 mm x 280 mm x 44 mm (Wx. Dx. H) 17
 IP DSLAM-Master • Features – Built-in Layer 2 Functions – 802. 1 d – Spanning Tree, 802. 1 q - VLAN, 802. 3 ad- Link Aggregation, – 802. 3, 802. 3 u, 802. 3 x - Ethernet – 4094 active VLAN-ID/512 Active VLAN Group – 802. 1 p Class of Service with 4 -level priority queuing – IGMP snooping – Packet filter based on MAC and port – Layer 2 insulation between ADSL ports – Broadcast storm control – Port mirroring 18
IP DSLAM-Master • Features – Built-in Layer 2 Functions – 802. 1 d – Spanning Tree, 802. 1 q - VLAN, 802. 3 ad- Link Aggregation, – 802. 3, 802. 3 u, 802. 3 x - Ethernet – 4094 active VLAN-ID/512 Active VLAN Group – 802. 1 p Class of Service with 4 -level priority queuing – IGMP snooping – Packet filter based on MAC and port – Layer 2 insulation between ADSL ports – Broadcast storm control – Port mirroring 18
 IP DSLAM-Master • • • Target on Outdoor and Small-Size CO 19” Rack Mountable Chassis, 1 U Height 24 G. dmt/G. lite/ ADSL/ADSL 2/+, with splitter Ports WAN Ethernet 10/100 Base-T Interface MPo. A, IPo. A Cos/Tos Remote TFTP/FTP Firmware/Configuration RS-232 & Telnet Command Line Interface SNMP In-Band Management Support EMS and Email Altering • Multicast IP Multicast: IGMP Snooping • Security/Firewall – Access Control List, Packet Filtering – Stateful Packet Inspection – Password Protected System – 4 K VLAN (802. 1 Q) 19
IP DSLAM-Master • • • Target on Outdoor and Small-Size CO 19” Rack Mountable Chassis, 1 U Height 24 G. dmt/G. lite/ ADSL/ADSL 2/+, with splitter Ports WAN Ethernet 10/100 Base-T Interface MPo. A, IPo. A Cos/Tos Remote TFTP/FTP Firmware/Configuration RS-232 & Telnet Command Line Interface SNMP In-Band Management Support EMS and Email Altering • Multicast IP Multicast: IGMP Snooping • Security/Firewall – Access Control List, Packet Filtering – Stateful Packet Inspection – Password Protected System – 4 K VLAN (802. 1 Q) 19
 IP DSLAM-Master 2 Selectable WAN Interface Network Operation and Management - 802. 3, 802. 3 ab Ethernet Standard - User Friendly Web-Based Interface - 1000 Base-SX Module (SC connector) - Telnet Server for Remote Management - 1000 Base-FX Module(SC connector) - TFTP Software Upgrade Utility - 1000 Base-T Module(RJ 45 connector) - Console CLI for Local Management - 100 Base-T RJ 45 Connector - SNMPv 1, v 2 LAN Interface - MIBII, Bridge MIB, Ethernet Like MIB, - 24 -port RJ 45 10/100 Base-T Private MIB, RMON 1, 2, 3, 9 Groups L 2 Switch Function Q. o. S - IEEE 802. 1 d Spanning-Tree Protocol - Packet filter and classification. - IEEE 802. 3 x Flow Control - IEEE 802. 1 q VLAN, GVRP - IEEE 802. 1 p Class of Service (Co. S) Prioritization - 4 -level Prioritization - 802. 3 ad Port Trucking/Link Aggregation 20
IP DSLAM-Master 2 Selectable WAN Interface Network Operation and Management - 802. 3, 802. 3 ab Ethernet Standard - User Friendly Web-Based Interface - 1000 Base-SX Module (SC connector) - Telnet Server for Remote Management - 1000 Base-FX Module(SC connector) - TFTP Software Upgrade Utility - 1000 Base-T Module(RJ 45 connector) - Console CLI for Local Management - 100 Base-T RJ 45 Connector - SNMPv 1, v 2 LAN Interface - MIBII, Bridge MIB, Ethernet Like MIB, - 24 -port RJ 45 10/100 Base-T Private MIB, RMON 1, 2, 3, 9 Groups L 2 Switch Function Q. o. S - IEEE 802. 1 d Spanning-Tree Protocol - Packet filter and classification. - IEEE 802. 3 x Flow Control - IEEE 802. 1 q VLAN, GVRP - IEEE 802. 1 p Class of Service (Co. S) Prioritization - 4 -level Prioritization - 802. 3 ad Port Trucking/Link Aggregation 20
 IP DSLAM-Slave Network Interface - Two 10/100 M Fast Ethernet Interfaces or one Cascade Link is Gigabit Copper Interface Capacity – It Supports 24 ADSL 2/+ Ports. Security – It Supports Packet Filter, and Password Protection. Splitter Build in – It Supports 24 port x. DSL/Splitter. Inventory Savings - Common Equipment across Central Office and Outside Plant Deployments Management – It is managed by IP-DSLAM Master Unit. Q. o. S - Packet Filter and Classification. 21
IP DSLAM-Slave Network Interface - Two 10/100 M Fast Ethernet Interfaces or one Cascade Link is Gigabit Copper Interface Capacity – It Supports 24 ADSL 2/+ Ports. Security – It Supports Packet Filter, and Password Protection. Splitter Build in – It Supports 24 port x. DSL/Splitter. Inventory Savings - Common Equipment across Central Office and Outside Plant Deployments Management – It is managed by IP-DSLAM Master Unit. Q. o. S - Packet Filter and Classification. 21
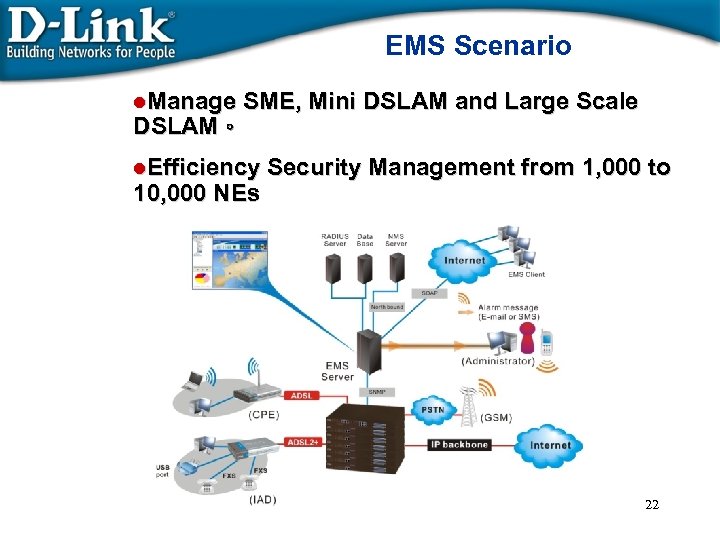 EMS Scenario l. Manage SME, Mini DSLAM and Large Scale DSLAM。 l. Efficiency 10, 000 NEs Security Management from 1, 000 to 22
EMS Scenario l. Manage SME, Mini DSLAM and Large Scale DSLAM。 l. Efficiency 10, 000 NEs Security Management from 1, 000 to 22
 EMS Capability • SNMP In-band through the IP network • Authentication and Security Management • Software Download • Configuration, Alarm, Diagnostics, Status Update • Fault and Performance Management 23
EMS Capability • SNMP In-band through the IP network • Authentication and Security Management • Software Download • Configuration, Alarm, Diagnostics, Status Update • Fault and Performance Management 23
 Benefit Management – Configuration Management • Auto Provisioning, Firmware Upgrade – Deployment Management • Deploy Policies for Software Update, etc. – Topology Management • Auto Discovery for Managing Devices. (eg. Add or Delete from Layer Structure Subnets) – Security Management • Authentication, Resource Control – Monitor management • Fault Management, Device Polling – Backend Storage Management • Store Alarms, Events and User Activities. 24 24
Benefit Management – Configuration Management • Auto Provisioning, Firmware Upgrade – Deployment Management • Deploy Policies for Software Update, etc. – Topology Management • Auto Discovery for Managing Devices. (eg. Add or Delete from Layer Structure Subnets) – Security Management • Authentication, Resource Control – Monitor management • Fault Management, Device Polling – Backend Storage Management • Store Alarms, Events and User Activities. 24 24
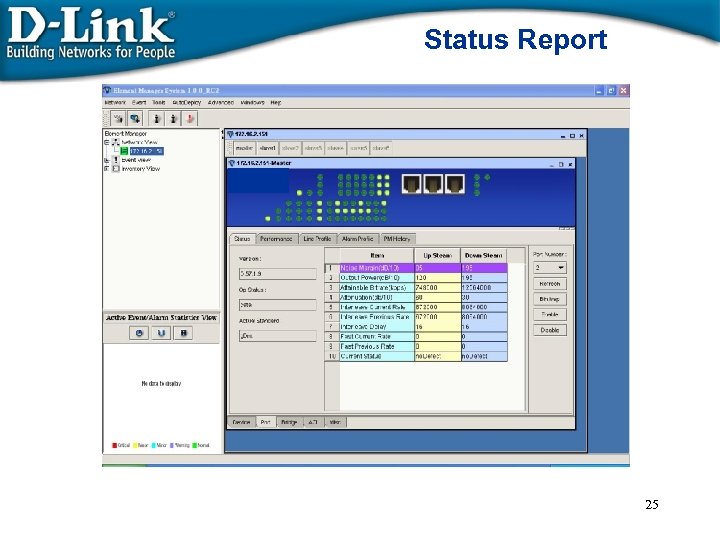 Status Report 25
Status Report 25
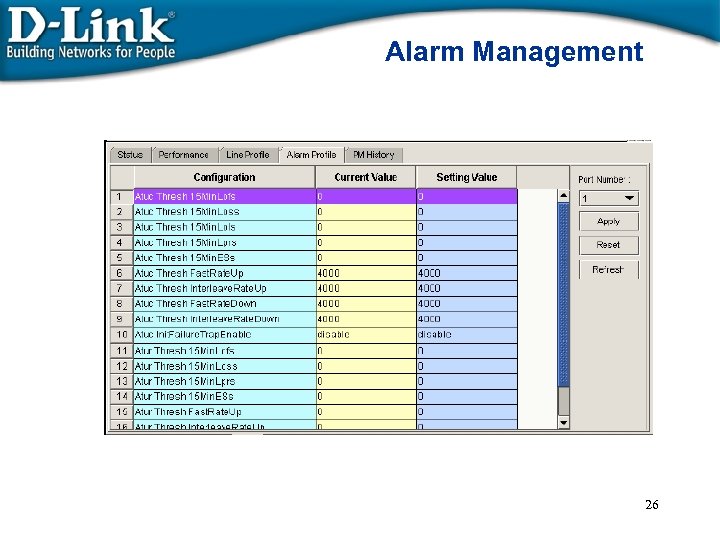 Alarm Management 26
Alarm Management 26
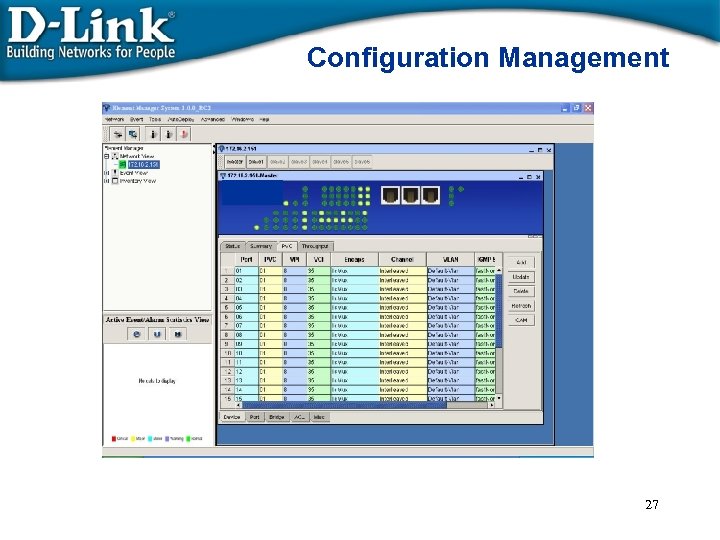 Configuration Management 27
Configuration Management 27
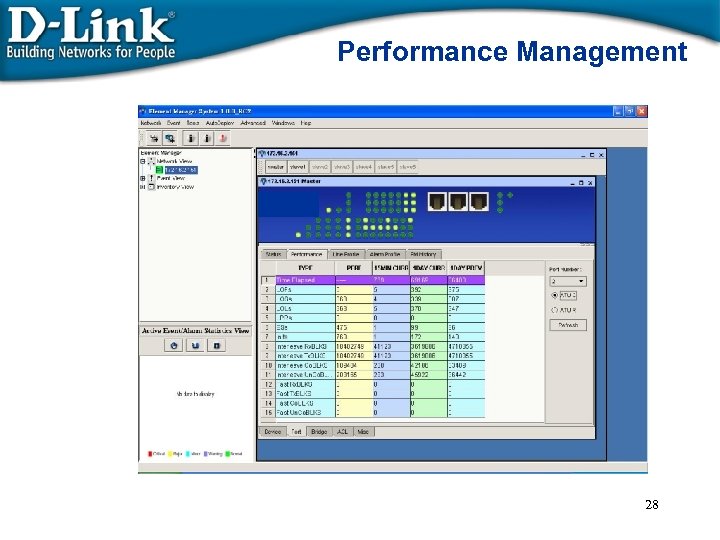 Performance Management 28
Performance Management 28
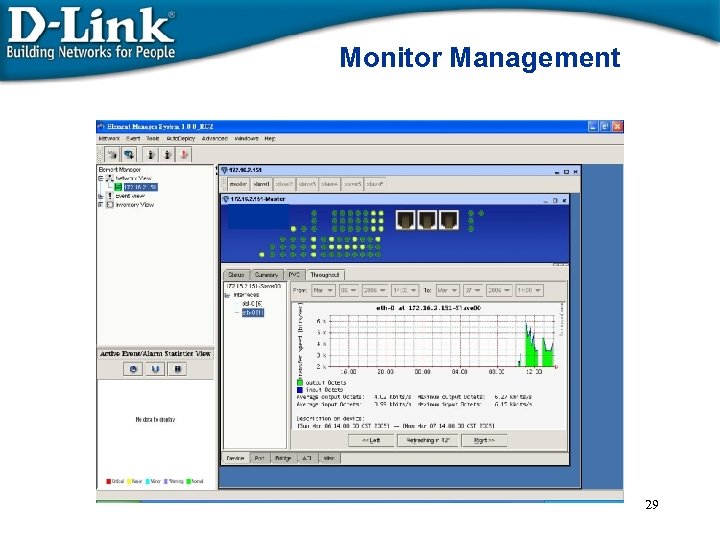 Monitor Management 29
Monitor Management 29
 Roadmap of IP DSLAM Available DAS-3324 24 port ADSL IP DSLAM Annex A Annex B Annex M Q 2/ 2005 Q 3 / 2005 Q 4 / 2005 Q 130 2006 /
Roadmap of IP DSLAM Available DAS-3324 24 port ADSL IP DSLAM Annex A Annex B Annex M Q 2/ 2005 Q 3 / 2005 Q 4 / 2005 Q 130 2006 /
 ADSL 2/+ New Technology 31
ADSL 2/+ New Technology 31
 ADSL 2/2+ • • • Higher Data Rate Longer Reach - READSL 2 Annex M-Uplink 3 M bps Seamless Rate Adaptation Power Management Loop Diagnostics – DELT: Double Ended Line Testing – SELT: Single Ended Line Testing 32
ADSL 2/2+ • • • Higher Data Rate Longer Reach - READSL 2 Annex M-Uplink 3 M bps Seamless Rate Adaptation Power Management Loop Diagnostics – DELT: Double Ended Line Testing – SELT: Single Ended Line Testing 32
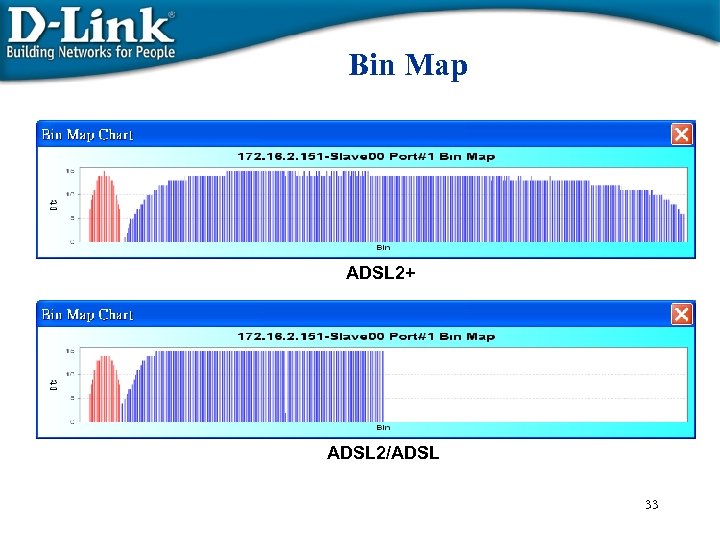 Bin Map ADSL 2+ ADSL 2/ADSL 33
Bin Map ADSL 2+ ADSL 2/ADSL 33
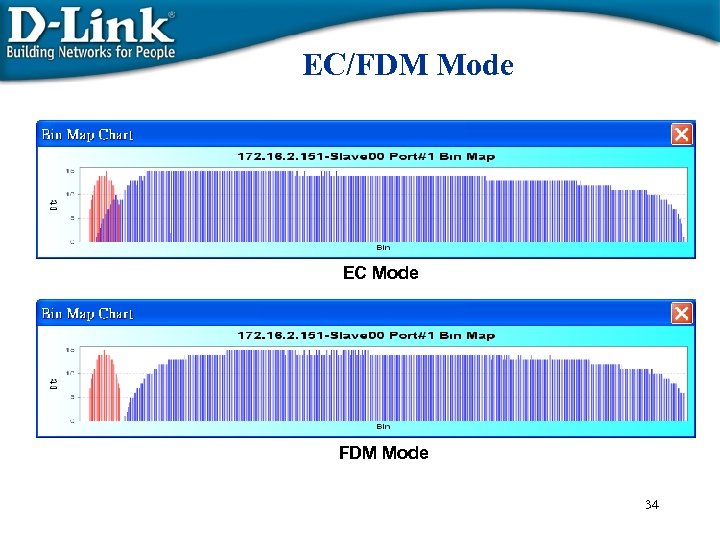 EC/FDM Mode EC Mode FDM Mode 34
EC/FDM Mode EC Mode FDM Mode 34
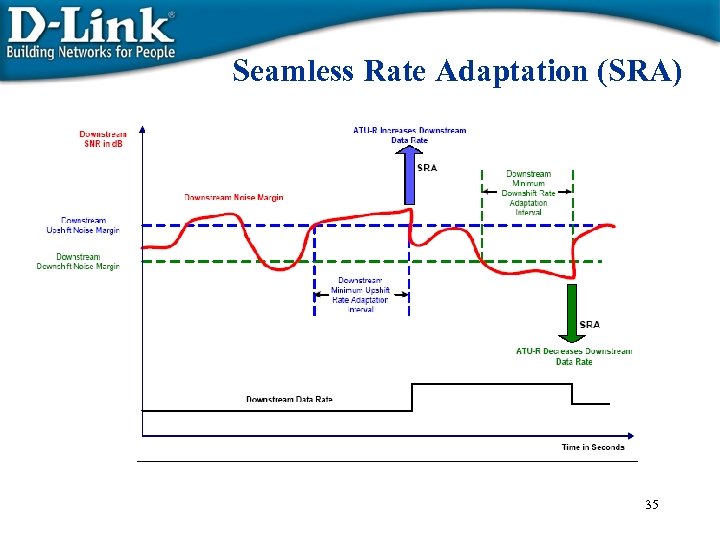 Seamless Rate Adaptation (SRA) 35
Seamless Rate Adaptation (SRA) 35
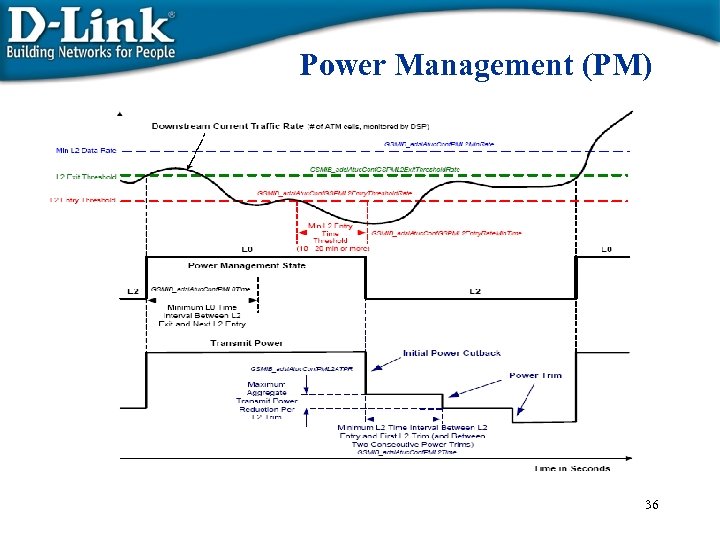 Power Management (PM) 36
Power Management (PM) 36
 Bridging Functions • • 802. 1 d Address Learning and Aging Broadcast Flooding 802. 1 q VLAN Bridging Multicasting - IGMP Snooping 37
Bridging Functions • • 802. 1 d Address Learning and Aging Broadcast Flooding 802. 1 q VLAN Bridging Multicasting - IGMP Snooping 37
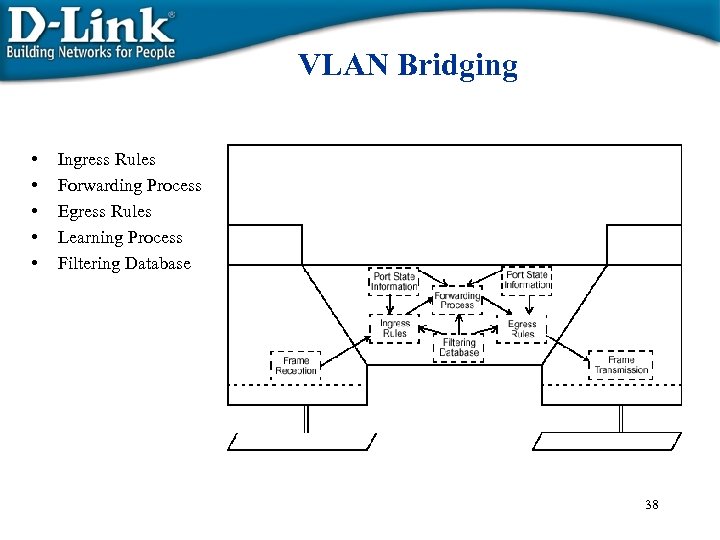 VLAN Bridging • • • Ingress Rules Forwarding Process Egress Rules Learning Process Filtering Database 38
VLAN Bridging • • • Ingress Rules Forwarding Process Egress Rules Learning Process Filtering Database 38
 IGMP Snooping • A layer-2 switch supported IGMP snooping can passively snoop on IGMP Query, Report and Leave packets to learn the IP Multicast group membership. • Multicast traffic of a group is only forwarded to ports that have members of that group. 39
IGMP Snooping • A layer-2 switch supported IGMP snooping can passively snoop on IGMP Query, Report and Leave packets to learn the IP Multicast group membership. • Multicast traffic of a group is only forwarded to ports that have members of that group. 39
 Security • MAC Address Tracking • MAC Address Access Control List – Global Deny – Per Port Accept • IP Address Access Control List 40
Security • MAC Address Tracking • MAC Address Access Control List – Global Deny – Per Port Accept • IP Address Access Control List 40
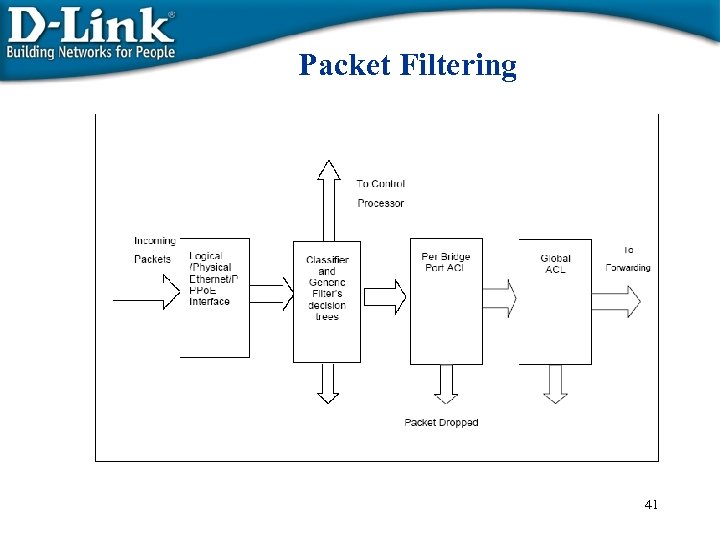 Packet Filtering 41
Packet Filtering 41
 Qo. S • Prioritized Bridging • Input Rate Limiting (IRL) – AAL 5 based • Output Rate Limiting (IRL) – Ethernet/ATM port based • Packet Priority to Traffic Class Mapping • 802. 1 p Re-Tagging 42
Qo. S • Prioritized Bridging • Input Rate Limiting (IRL) – AAL 5 based • Output Rate Limiting (IRL) – Ethernet/ATM port based • Packet Priority to Traffic Class Mapping • 802. 1 p Re-Tagging 42
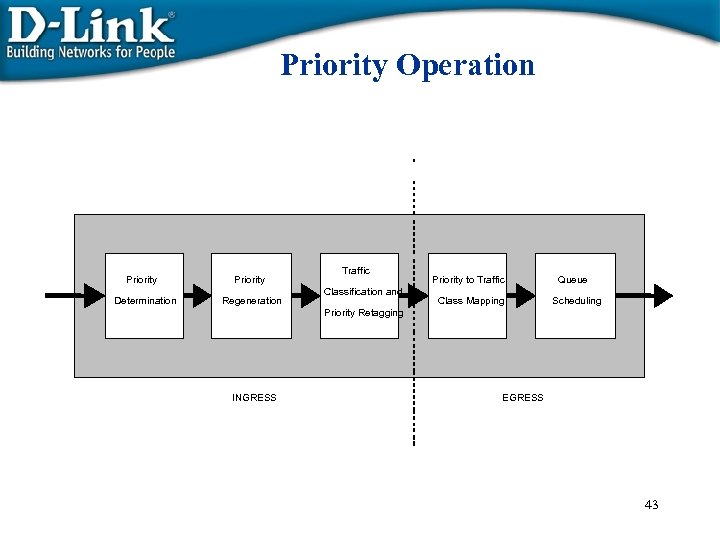 Priority Operation Priority Determination Priority Regeneration Traffic Classification and Priority to Traffic Class Mapping Queue Scheduling Priority Retagging INGRESS EGRESS 43
Priority Operation Priority Determination Priority Regeneration Traffic Classification and Priority to Traffic Class Mapping Queue Scheduling Priority Retagging INGRESS EGRESS 43
 Trouble Shooting and Demo 44
Trouble Shooting and Demo 44
 Introduction • This presentation is to provide a quick guide to configure the IP DSLAM devices and enable them manageable 45
Introduction • This presentation is to provide a quick guide to configure the IP DSLAM devices and enable them manageable 45
 Architecture • Two types of topology – Master-Slave – Slave-Standalone 46
Architecture • Two types of topology – Master-Slave – Slave-Standalone 46
 Management Channels • Serial Port • Telnet • EMS (SNMP-based) 47
Management Channels • Serial Port • Telnet • EMS (SNMP-based) 47
 Serial Port Management • Console Setting – 9600/8/N/1, no flow control • Master-Slave – Connect to [CONSOLE] port – username/password: admin/1234 • Slave-Standalone – Connect to [CONSOLE] port – no password required 48
Serial Port Management • Console Setting – 9600/8/N/1, no flow control • Master-Slave – Connect to [CONSOLE] port – username/password: admin/1234 • Slave-Standalone – Connect to [CONSOLE] port – no password required 48
 Master-Slave Connectivity • By default, ports G 1, G 2, . . . , G 6 are disable – Turn the interfaces ON – Admin>system link -m gn on (where n is 0 to 6) – Admin>system link (check the status) 49
Master-Slave Connectivity • By default, ports G 1, G 2, . . . , G 6 are disable – Turn the interfaces ON – Admin>system link -m gn on (where n is 0 to 6) – Admin>system link (check the status) 49
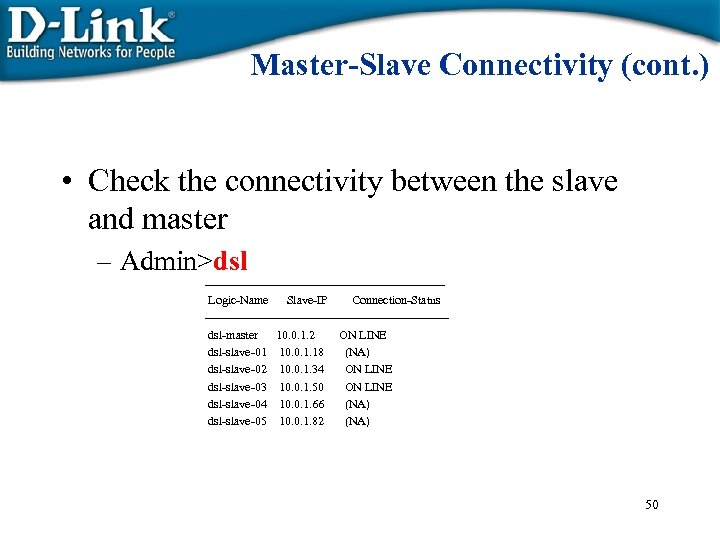 Master-Slave Connectivity (cont. ) • Check the connectivity between the slave and master – Admin>dsl ---------------------------------------- Logic-Name Slave-IP Connection-Status ------------------------------dsl-master 10. 0. 1. 2 ON LINE dsl-slave-01 10. 0. 1. 18 (NA) dsl-slave-02 10. 0. 1. 34 ON LINE dsl-slave-03 10. 0. 1. 50 ON LINE dsl-slave-04 10. 0. 1. 66 (NA) dsl-slave-05 10. 0. 1. 82 (NA) 50
Master-Slave Connectivity (cont. ) • Check the connectivity between the slave and master – Admin>dsl ---------------------------------------- Logic-Name Slave-IP Connection-Status ------------------------------dsl-master 10. 0. 1. 2 ON LINE dsl-slave-01 10. 0. 1. 18 (NA) dsl-slave-02 10. 0. 1. 34 ON LINE dsl-slave-03 10. 0. 1. 50 ON LINE dsl-slave-04 10. 0. 1. 66 (NA) dsl-slave-05 10. 0. 1. 82 (NA) 50
 Login to DSL Module • DSL inside master via serial channel – Admin>dsl -c (type
Login to DSL Module • DSL inside master via serial channel – Admin>dsl -c (type
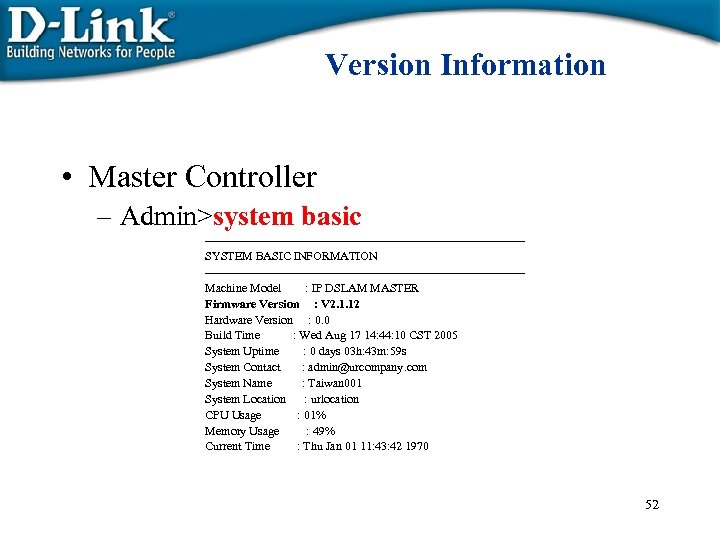 Version Information • Master Controller – Admin>system basic ----------------------------------------SYSTEM BASIC INFORMATION ----------------------------------------Machine Model : IP DSLAM MASTER Firmware Version : V 2. 1. 12 Hardware Version : 0. 0 Build Time : Wed Aug 17 14: 44: 10 CST 2005 System Uptime : 0 days 03 h: 43 m: 59 s System Contact : admin@urcompany. com System Name : Taiwan 001 System Location : urlocation CPU Usage : 01% Memory Usage : 49% Current Time : Thu Jan 01 11: 43: 42 1970 52
Version Information • Master Controller – Admin>system basic ----------------------------------------SYSTEM BASIC INFORMATION ----------------------------------------Machine Model : IP DSLAM MASTER Firmware Version : V 2. 1. 12 Hardware Version : 0. 0 Build Time : Wed Aug 17 14: 44: 10 CST 2005 System Uptime : 0 days 03 h: 43 m: 59 s System Contact : admin@urcompany. com System Name : Taiwan 001 System Location : urlocation CPU Usage : 01% Memory Usage : 49% Current Time : Thu Jan 01 11: 43: 42 1970 52
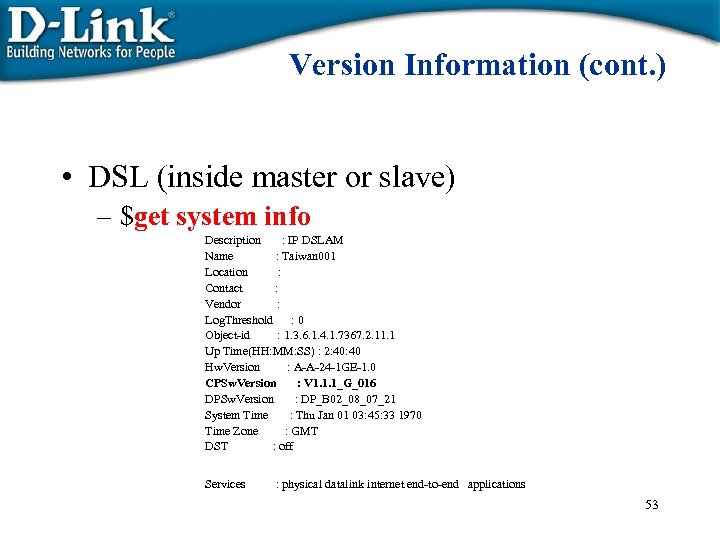 Version Information (cont. ) • DSL (inside master or slave) – $get system info Description : IP DSLAM Name : Taiwan 001 Location : Contact : Vendor : Log. Threshold : 0 Object-id : 1. 3. 6. 1. 4. 1. 7367. 2. 11. 1 Up Time(HH: MM: SS) : 2: 40 Hw. Version : A-A-24 -1 GE-1. 0 CPSw. Version : V 1. 1. 1_G_016 DPSw. Version : DP_B 02_08_07_21 System Time : Thu Jan 01 03: 45: 33 1970 Time Zone : GMT DST : off Services : physical datalink internet end-to-end applications 53
Version Information (cont. ) • DSL (inside master or slave) – $get system info Description : IP DSLAM Name : Taiwan 001 Location : Contact : Vendor : Log. Threshold : 0 Object-id : 1. 3. 6. 1. 4. 1. 7367. 2. 11. 1 Up Time(HH: MM: SS) : 2: 40 Hw. Version : A-A-24 -1 GE-1. 0 CPSw. Version : V 1. 1. 1_G_016 DPSw. Version : DP_B 02_08_07_21 System Time : Thu Jan 01 03: 45: 33 1970 Time Zone : GMT DST : off Services : physical datalink internet end-to-end applications 53
 Save the Configuration • Master Controller – Admin>commit • DSL module (in master or slave) – $commit 54
Save the Configuration • Master Controller – Admin>commit • DSL module (in master or slave) – $commit 54
 IP Address Setting • Mandatory if Telnet or EMS management is required • Default setting – Master • Outband (MGM port): 172. 16. 1. 1/255. 0 • Inband (Uplink port): 0. 0 (disable) – Slave (DSL module) • Propritery DHCP (support only for master-slave architecture) 55
IP Address Setting • Mandatory if Telnet or EMS management is required • Default setting – Master • Outband (MGM port): 172. 16. 1. 1/255. 0 • Inband (Uplink port): 0. 0 (disable) – Slave (DSL module) • Propritery DHCP (support only for master-slave architecture) 55
![Master IP Setting • Outband – Admin>network out <new-ip> <mask> [vlanid] • Inband – Master IP Setting • Outband – Admin>network out <new-ip> <mask> [vlanid] • Inband –](https://present5.com/presentation/7dd9f7f5c95d047aa56379d3331a8856/image-56.jpg) Master IP Setting • Outband – Admin>network out
Master IP Setting • Outband – Admin>network out
 Slave-Standalone IP Setting • For 2 fast-ethernet version – $aggr intf ifname aggr-0 ip
Slave-Standalone IP Setting • For 2 fast-ethernet version – $aggr intf ifname aggr-0 ip
 Telent Management • Device IP configured well • Connect to. . . – Master: MGM port for outband, uplink port for inband – Slave: Any uplink port • Username/Password – admin/1234 (type ‘exit’ to return) 58
Telent Management • Device IP configured well • Connect to. . . – Master: MGM port for outband, uplink port for inband – Slave: Any uplink port • Username/Password – admin/1234 (type ‘exit’ to return) 58
 EMS Management • Device IP configured well • SNMP related parameters – Communities – Trap Host 59
EMS Management • Device IP configured well • SNMP related parameters – Communities – Trap Host 59
 Master SNMP Enabled • Communties – Default: public/private/trap – Admin>service snmp -c
Master SNMP Enabled • Communties – Default: public/private/trap – Admin>service snmp -c
 Slave-Standalone SNMP Enabled • CLI commands. . . $create snmp community
Slave-Standalone SNMP Enabled • CLI commands. . . $create snmp community
 EMS Architecture • Element Management System • Client-Server Model • Pure Java Cross-Platform Architecture 62
EMS Architecture • Element Management System • Client-Server Model • Pure Java Cross-Platform Architecture 62
 EMS Installation • Retrieve the EMS Software • Following the installation guide. . . – Server • Install JDK • Install My. SQL Database • Install EMSServer – Client • Install EMSClient 63
EMS Installation • Retrieve the EMS Software • Following the installation guide. . . – Server • Install JDK • Install My. SQL Database • Install EMSServer – Client • Install EMSClient 63
![EMS Startup • EMS Server – Edit [Bind IP of EMSServer] – Start EMSServer EMS Startup • EMS Server – Edit [Bind IP of EMSServer] – Start EMSServer](https://present5.com/presentation/7dd9f7f5c95d047aa56379d3331a8856/image-64.jpg) EMS Startup • EMS Server – Edit [Bind IP of EMSServer] – Start EMSServer (My. SQL will be launched automatically) • EMS Client – Start EMSClient – Username/Password • root/admin 123 64
EMS Startup • EMS Server – Edit [Bind IP of EMSServer] – Start EMSServer (My. SQL will be launched automatically) • EMS Client – Start EMSClient – Username/Password • root/admin 123 64
![Add Device into EMS • Choose [Add a Device] – Fill the name of Add Device into EMS • Choose [Add a Device] – Fill the name of](https://present5.com/presentation/7dd9f7f5c95d047aa56379d3331a8856/image-65.jpg) Add Device into EMS • Choose [Add a Device] – Fill the name of the device – Fill the IP address of the device – Choose the correct Type of the device • Master-Slave • Slave-Standalone • Double-Click the device icon for further management 65
Add Device into EMS • Choose [Add a Device] – Fill the name of the device – Fill the IP address of the device – Choose the correct Type of the device • Master-Slave • Slave-Standalone • Double-Click the device icon for further management 65
 Advanced • How to set G 6 port as uplink • How to set the default gateway • How to upgrade firmware via EMS 66
Advanced • How to set G 6 port as uplink • How to set the default gateway • How to upgrade firmware via EMS 66
 How to Set G 6 Port as Uplink • For Master Controller – Admin>system G 6 up or Admin>system uplink G 6 up (the latest version) – Admin>system link -m g 6 on – Admin>commit (on demand) 67
How to Set G 6 Port as Uplink • For Master Controller – Admin>system G 6 up or Admin>system uplink G 6 up (the latest version) – Admin>system link -m g 6 on – Admin>commit (on demand) 67
 How to Set the Default Gateway • Master Controller – Admin>network route default
How to Set the Default Gateway • Master Controller – Admin>network route default
 How to Upgrade Firmware via EMS • Firmware Type – Master Controller • V 1. 1. 7 all for example – DSL Module • 2 fast-ethernet version, ex, V 1. 1. 1_M_016 • 1 giga-ethernet version, ex, V 1. 1. 1_G_016 the one inside master box 69
How to Upgrade Firmware via EMS • Firmware Type – Master Controller • V 1. 1. 7 all for example – DSL Module • 2 fast-ethernet version, ex, V 1. 1. 1_M_016 • 1 giga-ethernet version, ex, V 1. 1. 1_G_016 the one inside master box 69
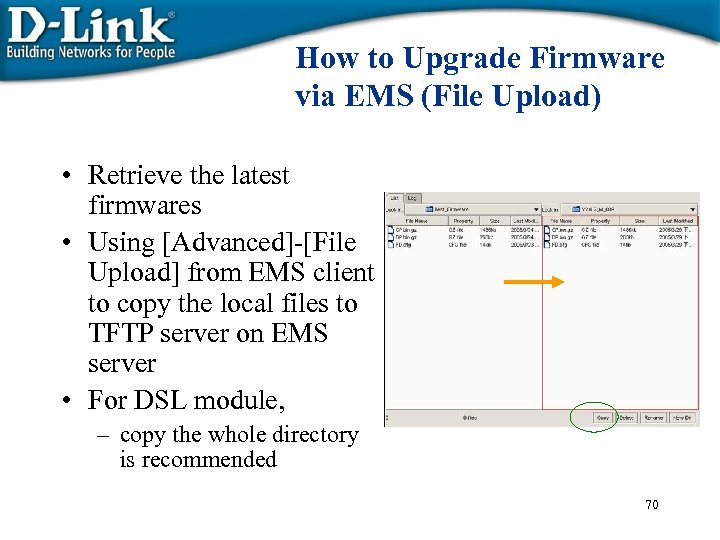 How to Upgrade Firmware via EMS (File Upload) • Retrieve the latest firmwares • Using [Advanced]-[File Upload] from EMS client to copy the local files to TFTP server on EMS server • For DSL module, – copy the whole directory is recommended 70
How to Upgrade Firmware via EMS (File Upload) • Retrieve the latest firmwares • Using [Advanced]-[File Upload] from EMS client to copy the local files to TFTP server on EMS server • For DSL module, – copy the whole directory is recommended 70
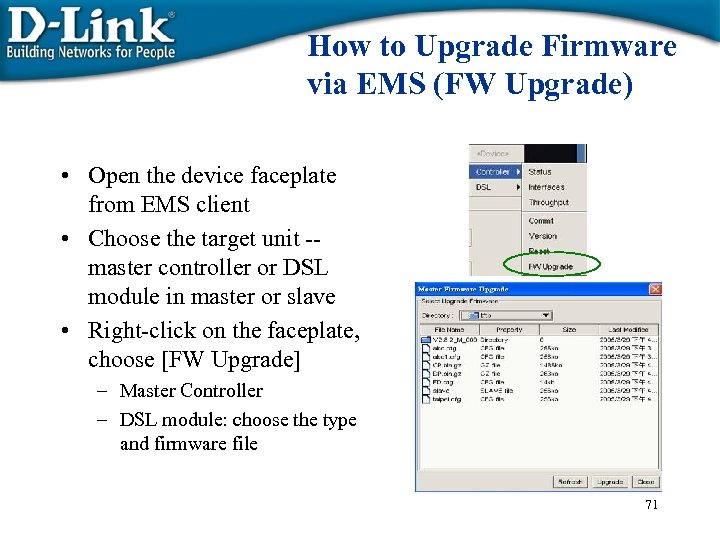 How to Upgrade Firmware via EMS (FW Upgrade) • Open the device faceplate from EMS client • Choose the target unit -master controller or DSL module in master or slave • Right-click on the faceplate, choose [FW Upgrade] – Master Controller – DSL module: choose the type and firmware file 71
How to Upgrade Firmware via EMS (FW Upgrade) • Open the device faceplate from EMS client • Choose the target unit -master controller or DSL module in master or slave • Right-click on the faceplate, choose [FW Upgrade] – Master Controller – DSL module: choose the type and firmware file 71
 How to Upgrade Firmware via EMS (DSL Component) • Upgradable DSL Firmware Components – CP (Control Plane) – DP (Data Plane) – DSL DSP code – Factory Default Setting CP. bin. gz DP. bin. gz gsv_dsl_AD_DM_3 C 00000 C. bin. gz FD. cfg 72
How to Upgrade Firmware via EMS (DSL Component) • Upgradable DSL Firmware Components – CP (Control Plane) – DP (Data Plane) – DSL DSP code – Factory Default Setting CP. bin. gz DP. bin. gz gsv_dsl_AD_DM_3 C 00000 C. bin. gz FD. cfg 72


