febf0b592e956a48915c114caf9515eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
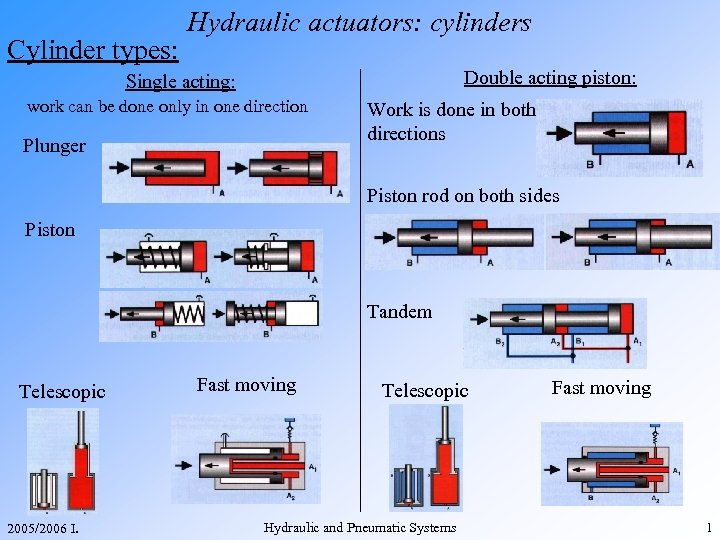
Cylinder types: Hydraulic actuators: cylinders Double acting piston: Single acting: work can be done only in one direction Plunger Work is done in both directions Piston rod on both sides Piston Tandem Telescopic 2005/2006 I. Fast moving Telescopic Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Fast moving 1
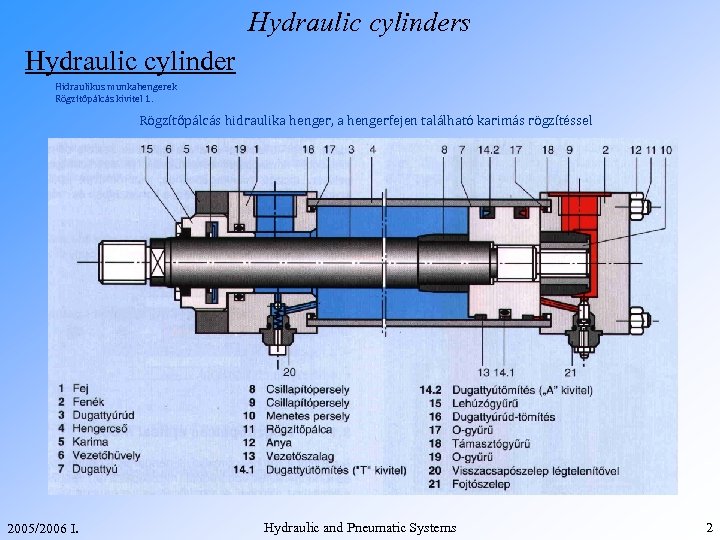
Hydraulic cylinders Hydraulic cylinder Hidraulikus munkahengerek Rögzítőpálcás kivitel 1. Rögzítőpálcás hidraulika henger, a hengerfejen található karimás rögzítéssel 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 2
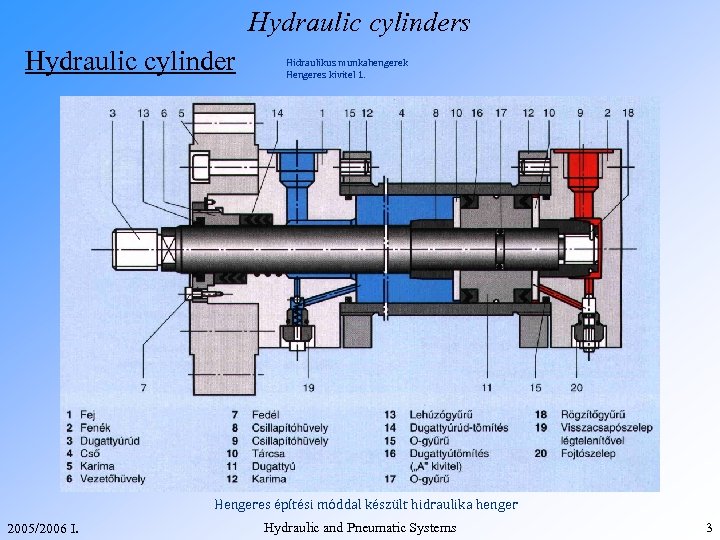
Hydraulic cylinders Hydraulic cylinder Hidraulikus munkahengerek Hengeres kivitel 1. Hengeres építési móddal készült hidraulika henger 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 3

Hydraulic cylinders Properties: The cylinders have to be good quality steel with close tolerances. There have to be good sealing both at the piston rod and at the cylinder. With time dirt may come in and damage the surfaces. This has to be possibly reduced. In this case, the leakage will increase all the time. 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 4
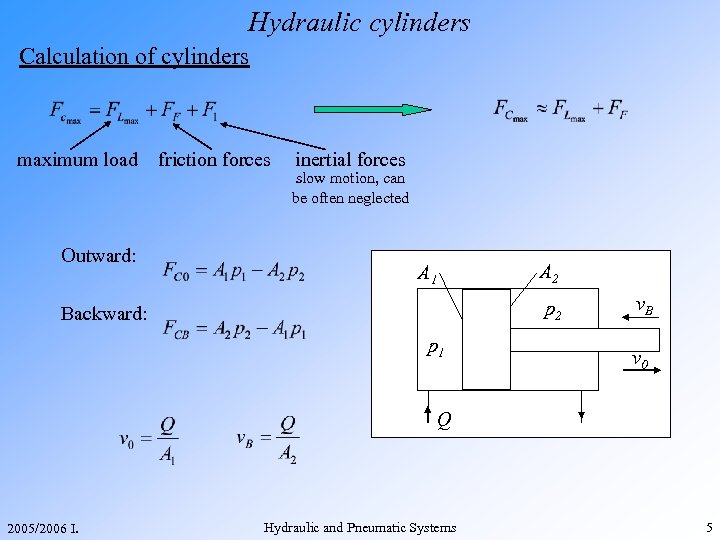
Hydraulic cylinders Calculation of cylinders maximum load Outward: friction forces inertial forces slow motion, can be often neglected A 2 A 1 p 2 Backward: p 1 v. B v 0 Q 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 5
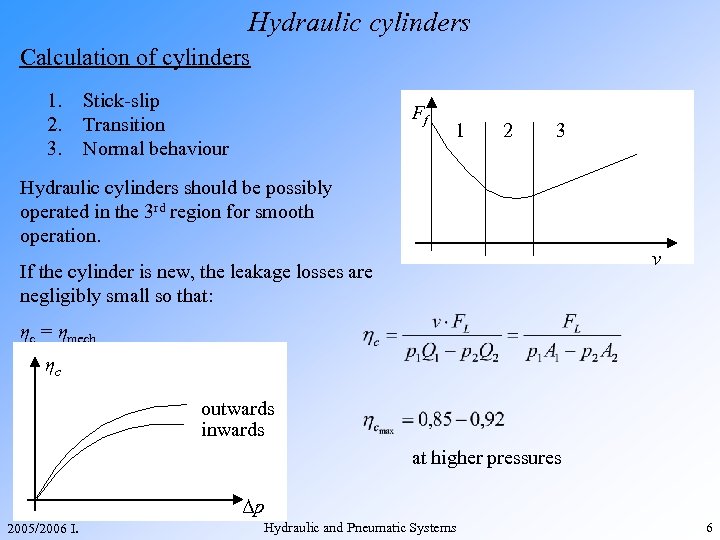
Hydraulic cylinders Calculation of cylinders 1. 2. 3. Stick-slip Transition Normal behaviour Ff 1 2 3 Hydraulic cylinders should be possibly operated in the 3 rd region for smooth operation. v If the cylinder is new, the leakage losses are negligibly small so that: ηc = ηmech ηc outwards inwards at higher pressures Δp 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 6
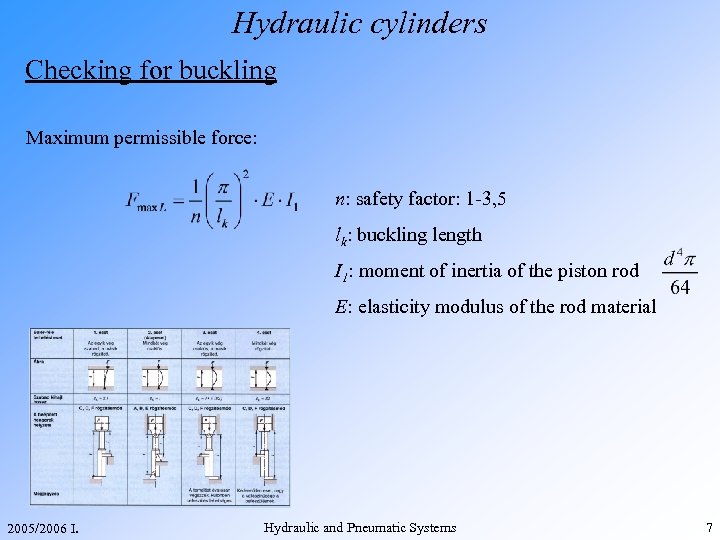
Hydraulic cylinders Checking for buckling Maximum permissible force: n: safety factor: 1 -3, 5 lk: buckling length I 1: moment of inertia of the piston rod E: elasticity modulus of the rod material 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 7
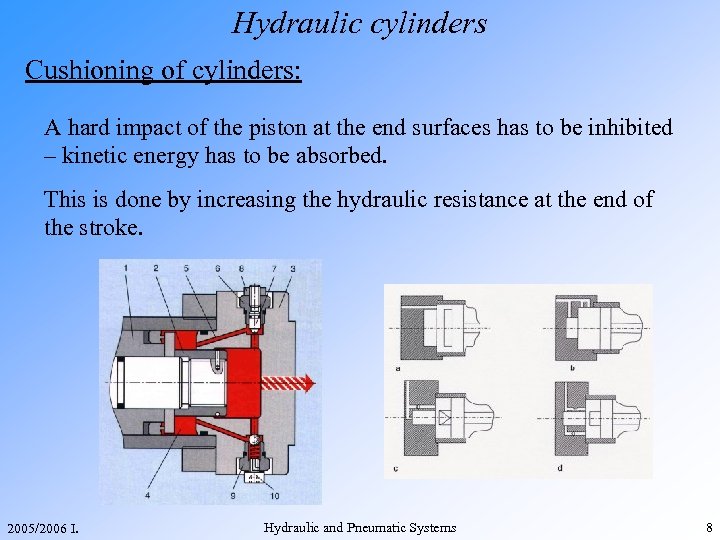
Hydraulic cylinders Cushioning of cylinders: A hard impact of the piston at the end surfaces has to be inhibited – kinetic energy has to be absorbed. This is done by increasing the hydraulic resistance at the end of the stroke. 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 8
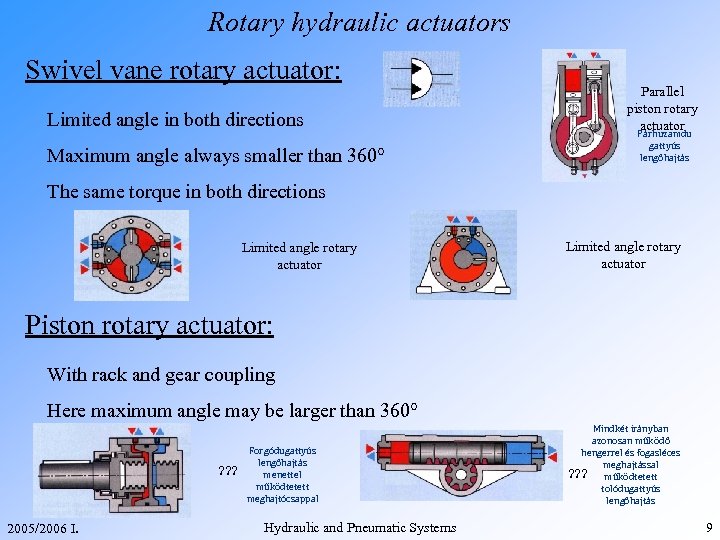
Rotary hydraulic actuators Swivel vane rotary actuator: Limited angle in both directions Maximum angle always smaller than 360° Parallel piston rotary actuator Párhuzamdu gattyús lengőhajtás The same torque in both directions Limited angle rotary actuator Piston rotary actuator: With rack and gear coupling Here maximum angle may be larger than 360° ? ? ? 2005/2006 I. Forgódugattyús lengőhajtás menettel működtetett meghajtócsappal Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Mindkét irányban azonosan működő hengerrel és fogasléces meghajtással ? ? ? működtetett tolódugattyús lengőhajtás 9

Big pictures End of normal presentation Beginning of big pictures 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 10
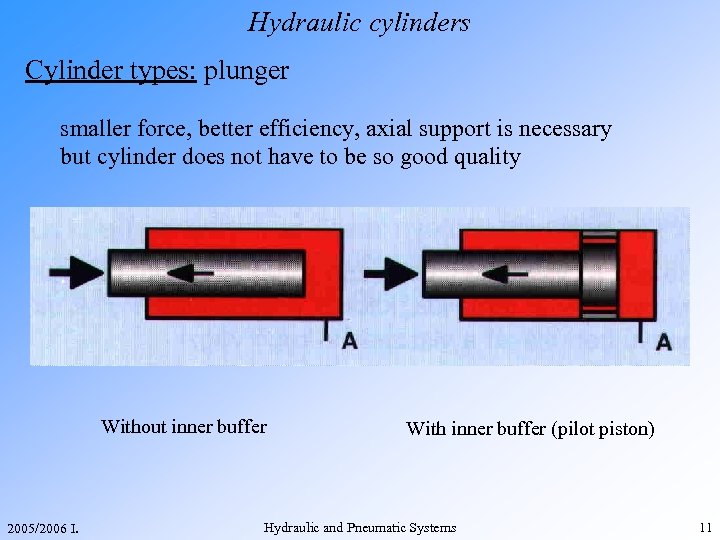
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: plunger smaller force, better efficiency, axial support is necessary but cylinder does not have to be so good quality Without inner buffer 2005/2006 I. With inner buffer (pilot piston) Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 11
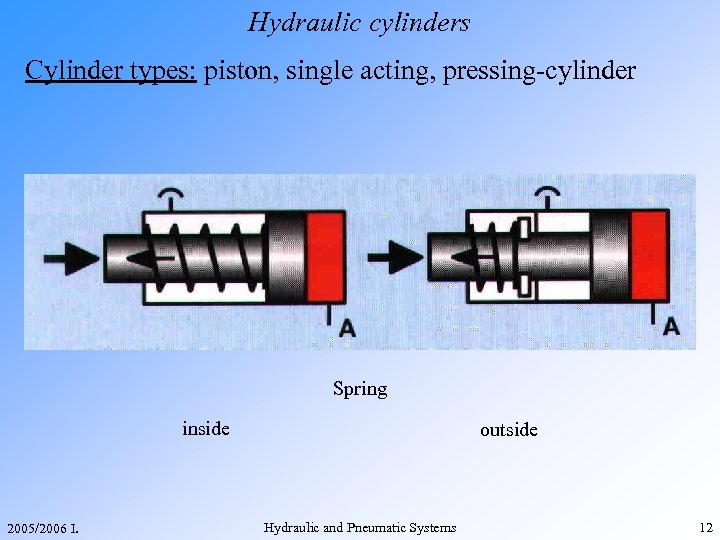
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: piston, single acting, pressing-cylinder Spring inside 2005/2006 I. outside Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 12
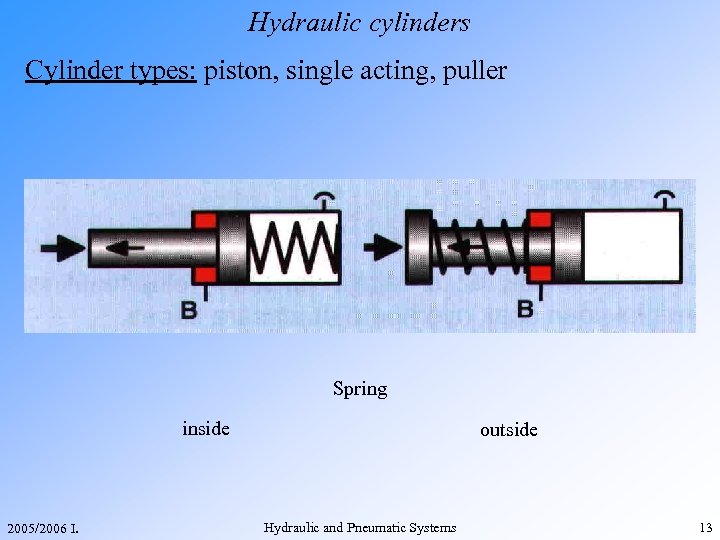
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: piston, single acting, puller Spring inside 2005/2006 I. outside Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 13
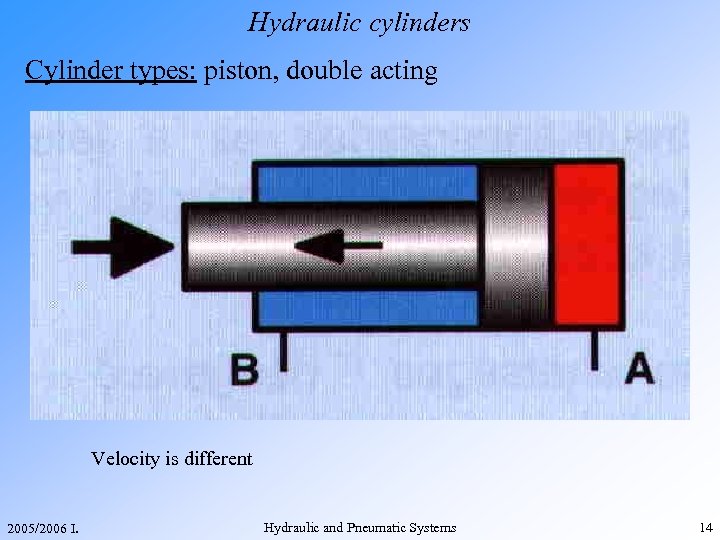
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: piston, double acting Velocity is different 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 14
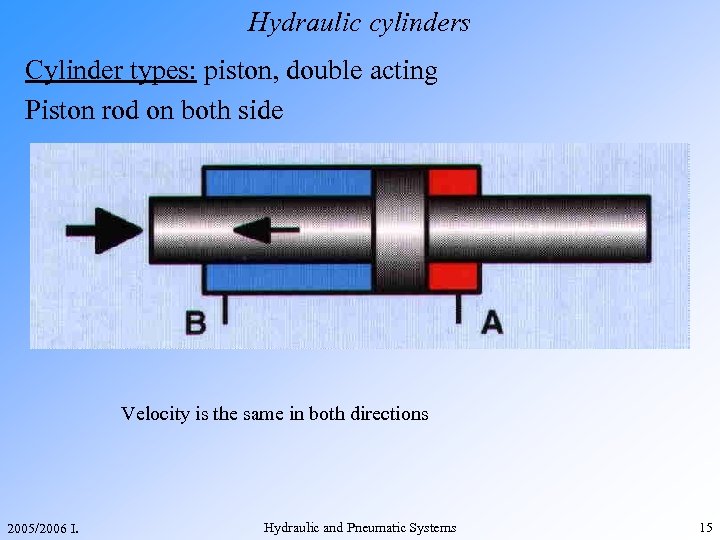
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: piston, double acting Piston rod on both side Velocity is the same in both directions 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 15
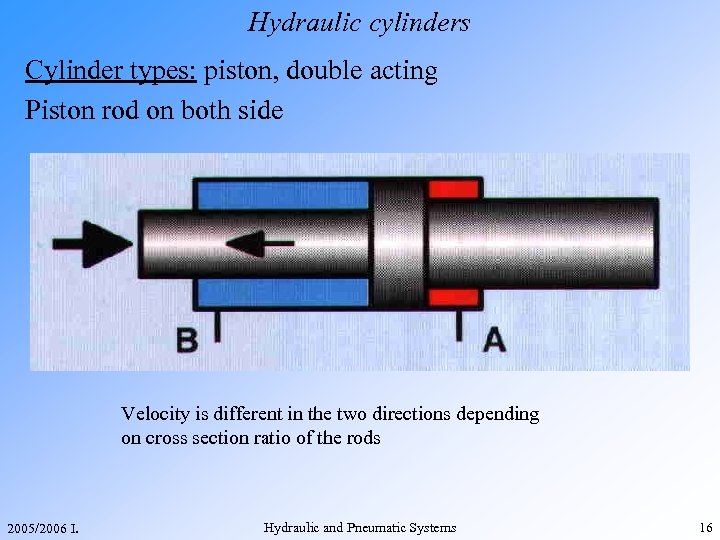
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: piston, double acting Piston rod on both side Velocity is different in the two directions depending on cross section ratio of the rods 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 16
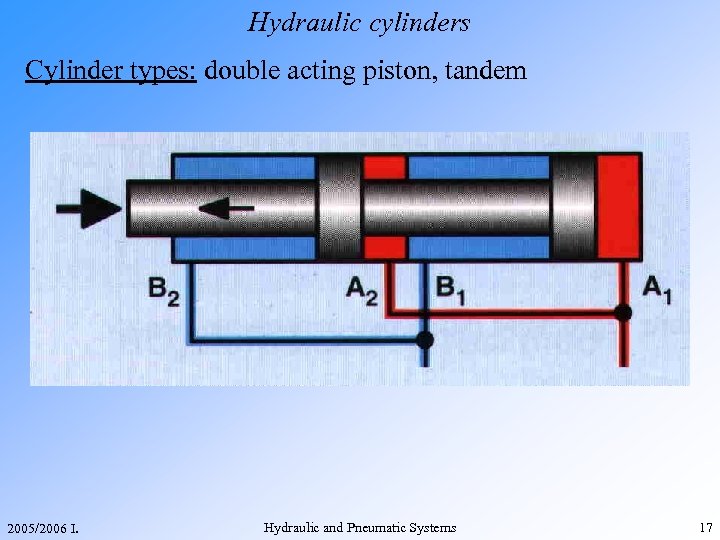
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: double acting piston, tandem 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 17
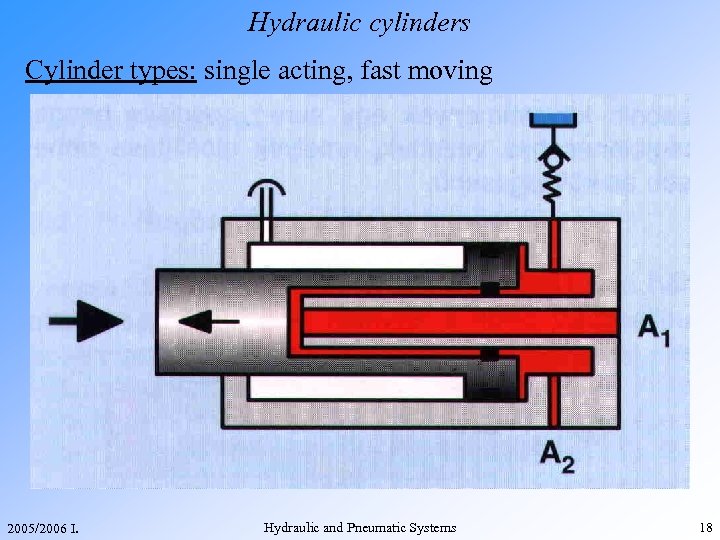
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: single acting, fast moving 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 18
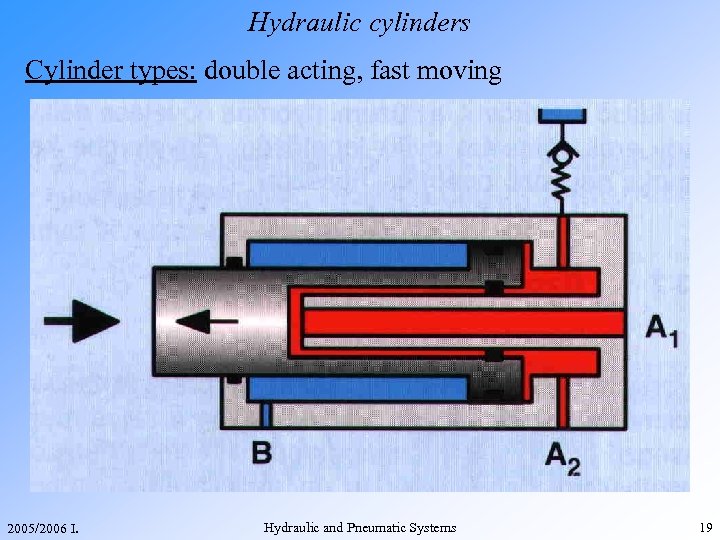
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: double acting, fast moving 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 19
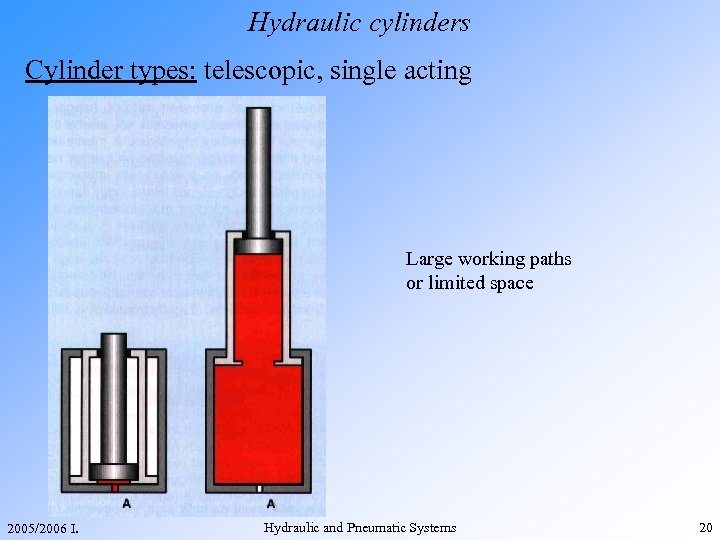
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: telescopic, single acting Large working paths or limited space 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 20
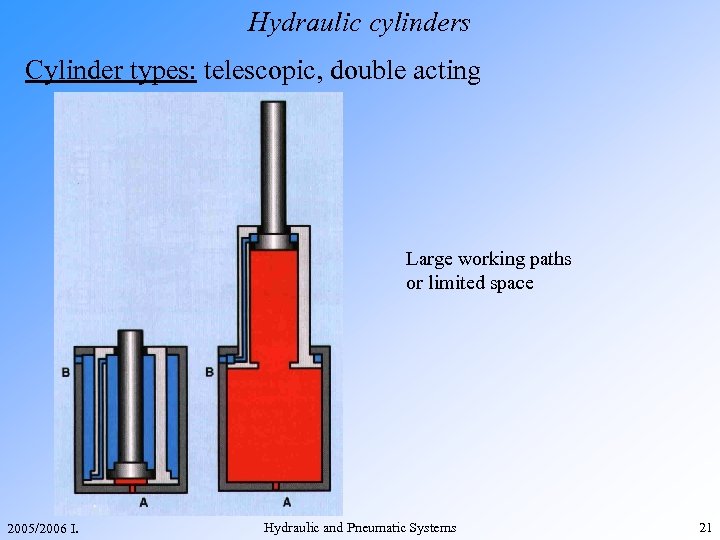
Hydraulic cylinders Cylinder types: telescopic, double acting Large working paths or limited space 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 21
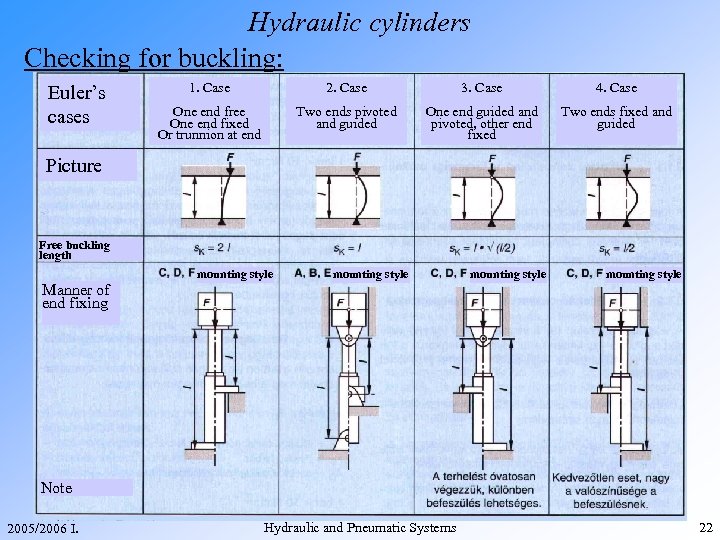
Hydraulic cylinders Checking for buckling: Euler’s cases 1. Case 2. Case 3. Case 4. Case One end free One end fixed Or trunnion at end Two ends pivoted and guided One end guided and pivoted, other end fixed Two ends fixed and guided Picture Free buckling length Manner of end fixing mounting style Note 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 22
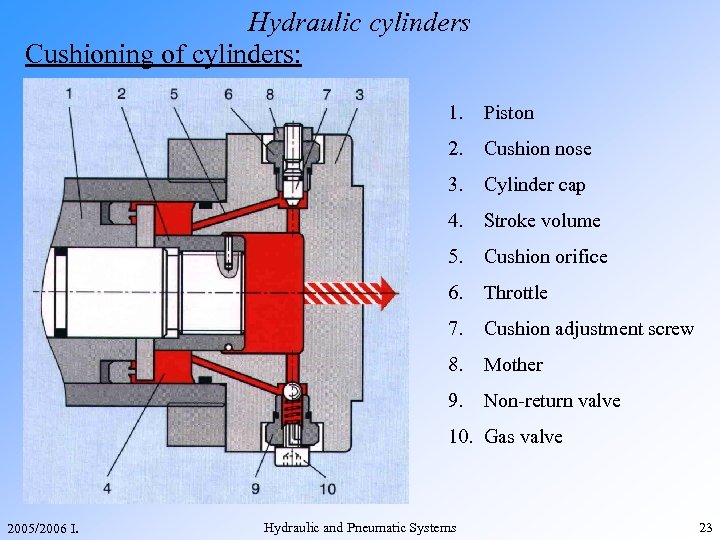
Hydraulic cylinders Cushioning of cylinders: 1. Piston 2. Cushion nose 3. Cylinder cap 4. Stroke volume 5. Cushion orifice 6. Throttle 7. Cushion adjustment screw 8. Mother 9. Non-return valve 10. Gas valve 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 23
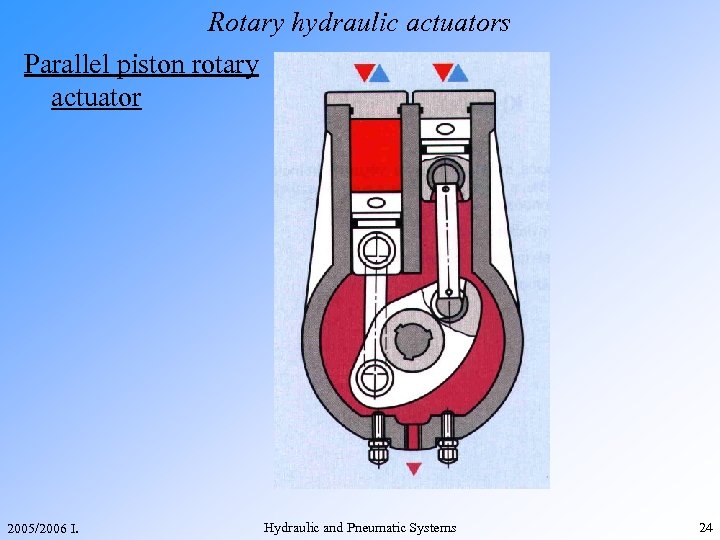
Rotary hydraulic actuators Parallel piston rotary actuator 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 24
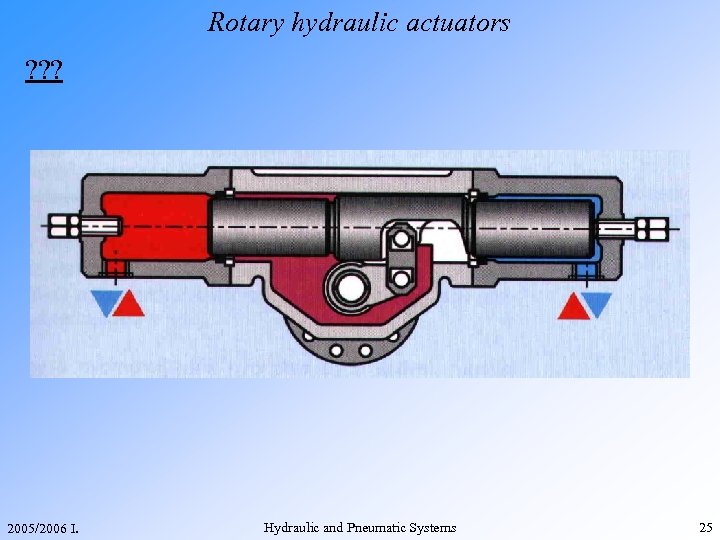
Rotary hydraulic actuators ? ? ? 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 25
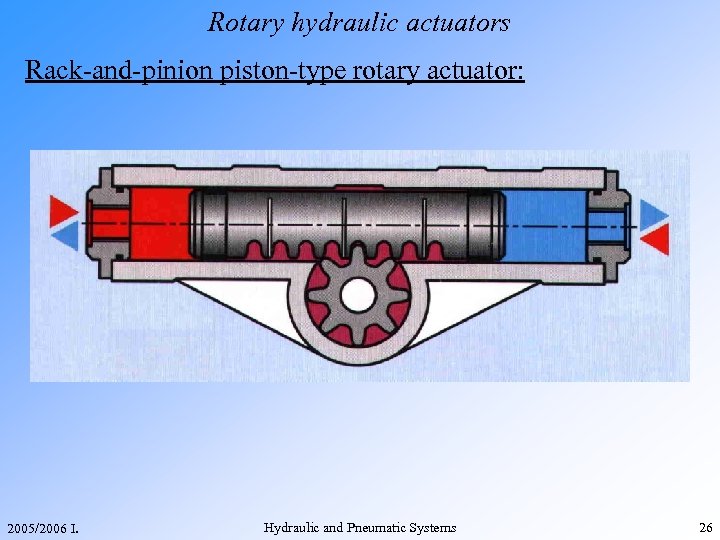
Rotary hydraulic actuators Rack-and-pinion piston-type rotary actuator: 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 26
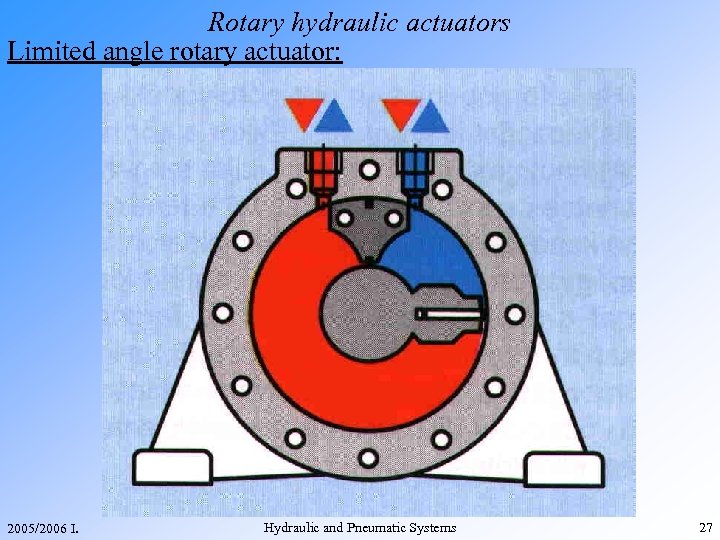
Rotary hydraulic actuators Limited angle rotary actuator: 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 27
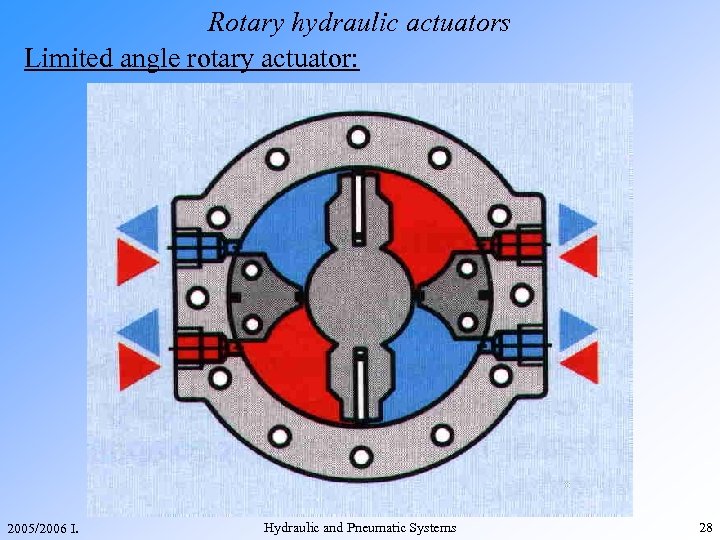
Rotary hydraulic actuators Limited angle rotary actuator: 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 28
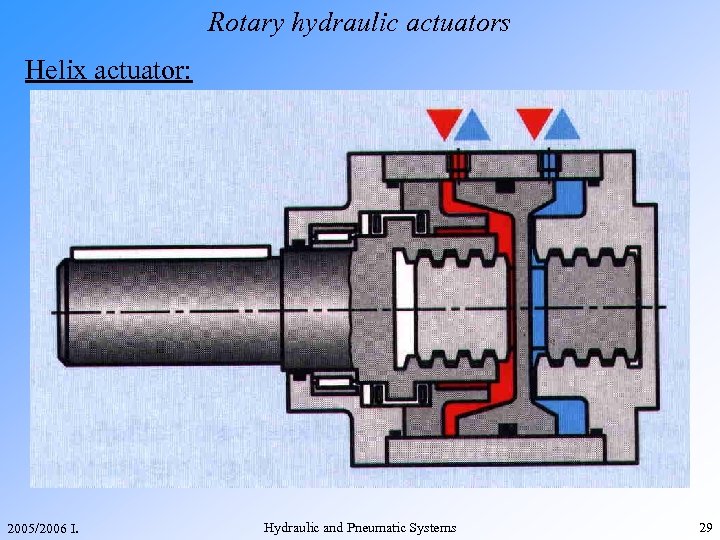
Rotary hydraulic actuators Helix actuator: 2005/2006 I. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems 29
febf0b592e956a48915c114caf9515eb.ppt