ea7bf10e753a672da2b560a833b6460b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47

CYBER RISK – A NEW FRONTIER David Kimmel Cyber. Risk. Partners

White House Summit on Cyber Security and Consumer Protection February 13, 2015 1

Disclaimer “Nothing exists except atoms and empty space; everything else is opinion. ” – Democritus 2
Agenda Risk in the Digital Universe Cyber Risk Market Trends Risk Transfer Market Dynamics and Opportunities 3
Agenda Risk in the Digital Universe Cyber Risk Market Trends Risk Transfer Market Dynamics and Opportunities 4
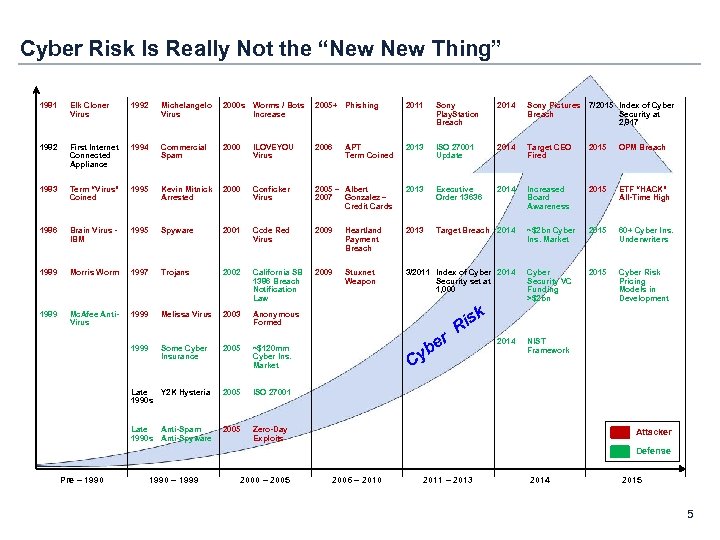
Cyber Risk Is Really Not the “New Thing” 1981 Elk Cloner Virus 1992 Michelangelo Virus 2000 s Worms / Bots Increase 2005+ Phishing 2011 Sony Play. Station Breach 2014 Sony Pictures Breach 7/2015 Index of Cyber Security at 2, 817 1982 First Internet Connected Appliance 1994 Commercial Spam 2000 ILOVEYOU Virus 2006 APT Term Coined 2013 ISO 27001 Update 2014 Target CEO Fired 2015 OPM Breach 1983 Term “Virus” Coined 1995 Kevin Mitnick Arrested 2000 Conficker Virus 2005 – Albert 2007 Gonzalez – Credit Cards 2013 Executive Order 13636 2014 Increased Board Awareness 2015 ETF “HACK” All-Time High 1986 Brain Virus IBM 1995 Spyware 2001 Code Red Virus 2009 Heartland Payment Breach 2013 Target Breach 2014 ~$2 bn Cyber Ins. Market 2015 60+ Cyber Ins. Underwriters 1989 Morris Worm 1997 Trojans 2002 California SB 1386 Breach Notification Law 2009 Stuxnet Weapon 3/2011 Index of Cyber 2014 Security set at 1, 000 Cyber Security VC Funding >$2 bn 2015 Cyber Risk Pricing Models in Development 1989 Mc. Afee Anti. Virus 1999 Melissa Virus 2003 Anonymous Formed 1999 Some Cyber Insurance 2005 ~$120 mm Cyber Ins. Market Late Y 2 K Hysteria 1990 s 2005 ISO 27001 Late Anti-Spam 1990 s Anti-Spyware 2005 Zero-Day Exploits r be Cy isk R 2014 NIST Framework Attacker Defense Pre – 1990 – 1999 2000 – 2005 2006 – 2010 2011 – 2013 2014 2015 5

Missing on the Timeline: War Games The 1983 movie that turned geeks into stars and introduced the world to “hacking” 6
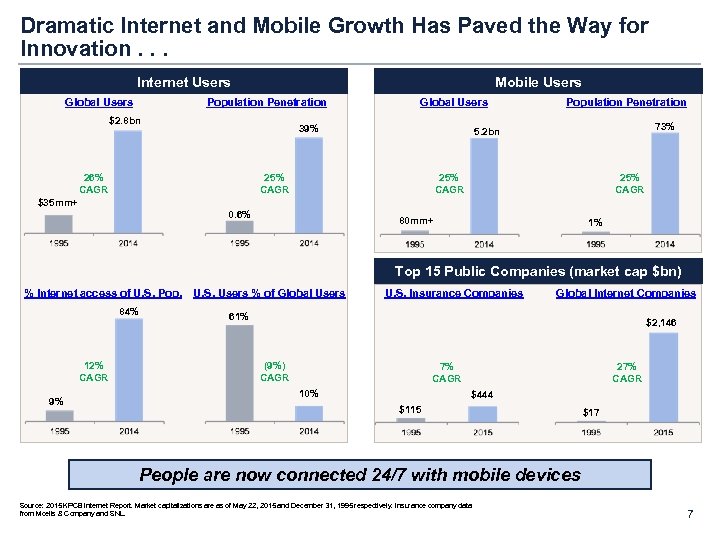
Dramatic Internet and Mobile Growth Has Paved the Way for Innovation. . . Internet Users Global Users Mobile Users Population Penetration $2. 8 bn Global Users 39% $35 mm+ 73% 5. 2 bn 25% CAGR 26% CAGR Population Penetration 25% CAGR 0. 6% 25% CAGR 80 mm+ 1% Top 15 Public Companies (market cap $bn) % Internet access of U. S. Pop. 84% 12% CAGR 9% U. S. Users % of Global Users U. S. Insurance Companies Global Internet Companies 61% $2, 146 (9%) CAGR 7% CAGR 10% 27% CAGR $444 $115 $17 People are now connected 24/7 with mobile devices Source: 2015 KPCB Internet Report. Market capitalizations are as of May 22, 2015 and December 31, 1995 respectively. Insurance company data from Moelis & Company and SNL. 7
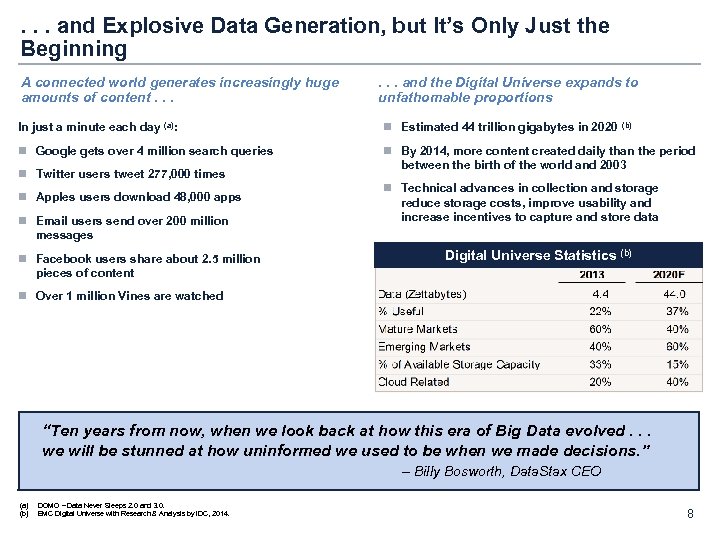
. . . and Explosive Data Generation, but It’s Only Just the Beginning A connected world generates increasingly huge amounts of content. . . In just a minute each day (a): n Google gets over 4 million search queries n Twitter users tweet 277, 000 times n Apples users download 48, 000 apps n Email users send over 200 million messages n Facebook users share about 2. 5 million pieces of content . . . and the Digital Universe expands to unfathomable proportions n Estimated 44 trillion gigabytes in 2020 (b) n By 2014, more content created daily than the period between the birth of the world and 2003 n Technical advances in collection and storage reduce storage costs, improve usability and increase incentives to capture and store data Digital Universe Statistics (b) n Over 1 million Vines are watched “Ten years from now, when we look back at how this era of Big Data evolved. . . we will be stunned at how uninformed we used to be when we made decisions. ” – Billy Bosworth, Data. Stax CEO (a) (b) DOMO – Data Never Sleeps 2. 0 and 3. 0. EMC Digital Universe with Research & Analysis by IDC, 2014. 8
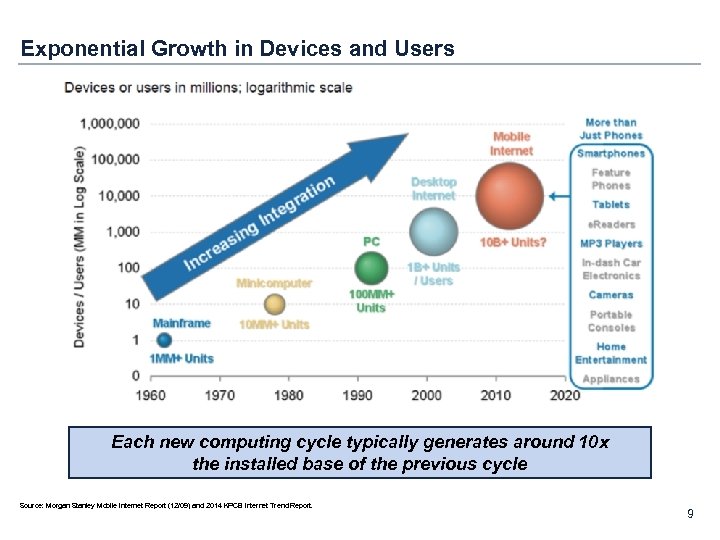
Exponential Growth in Devices and Users Each new computing cycle typically generates around 10 x the installed base of the previous cycle Source: Morgan Stanley Mobile Internet Report (12/09) and 2014 KPCB Internet Trend Report. 9

The Digital Revolution Is All Downhill From Here n Mobile is the device of choice n An always connected and inter-connected world, full of transactions, interactions and observations n Digital transformation and massive networks are driving a new era of data and analytics 10

Privacy and Liability Implications Are Staggering Smoke Detector / Nest Cartoon 11
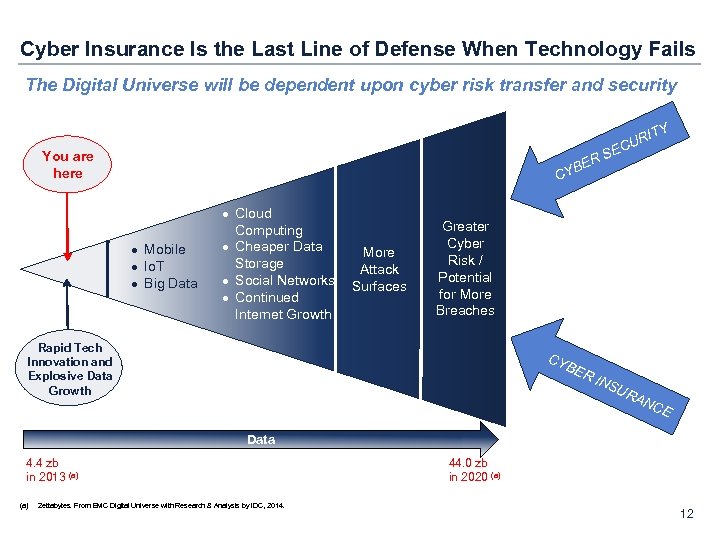
Cyber Insurance Is the Last Line of Defense When Technology Fails The Digital Universe will be dependent upon cyber risk transfer and security ITY R CU E S ER You are here B CY · Mobile · Io. T · Big Data · Cloud Computing · Cheaper Data Storage · Social Networks · Continued Internet Growth More Attack Surfaces Greater Cyber Risk / Potential for More Breaches Rapid Tech Innovation and Explosive Data Growth CY BE RI NS U RA NC E Data 4. 4 zb in 2013 (a) Zettabytes. From EMC Digital Universe with Research & Analysis by IDC, 2014. 44. 0 zb in 2020 (a) 12
Agenda Risk in the Digital Universe Cyber Risk Market Trends Risk Transfer Market Dynamics and Opportunities 13
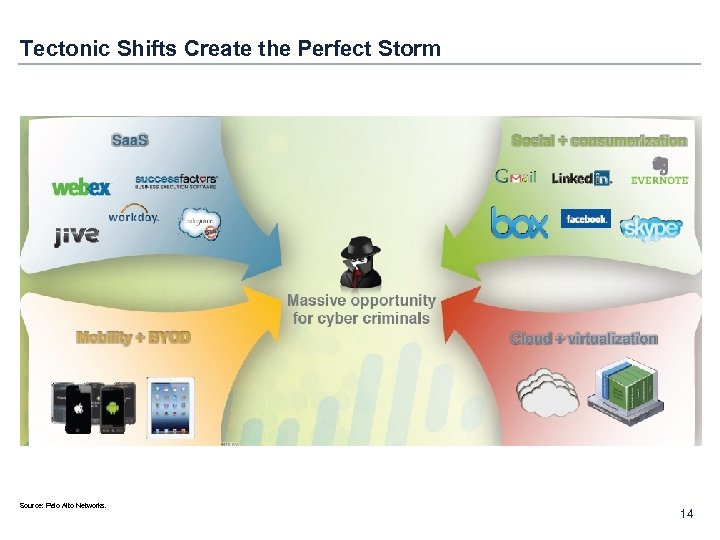
Tectonic Shifts Create the Perfect Storm Source: Palo Alto Networks. 14

A Ubiquitous Threat “I am convinced that there are only two types of companies: those that have been hacked and those that will be. And even they are converging into one category: companies that have been hacked and will be hacked again. ” – Robert Mueller, Former FBI Director 15
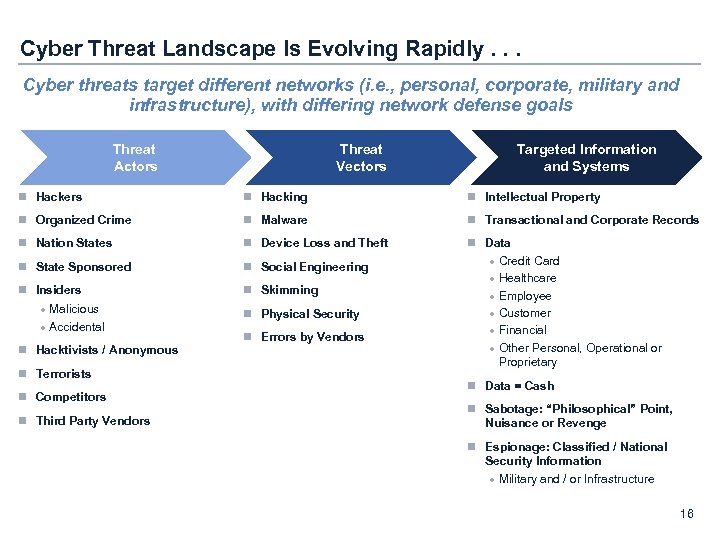
Cyber Threat Landscape Is Evolving Rapidly. . . Cyber threats target different networks (i. e. , personal, corporate, military and infrastructure), with differing network defense goals Threat Actors Threat Vectors Targeted Information and Systems n Hackers n Hacking n Intellectual Property n Organized Crime n Malware n Transactional and Corporate Records n Nation States n Device Loss and Theft n State Sponsored n Social Engineering n Insiders · Malicious · Accidental n Skimming n Data · Credit Card · Healthcare · Employee · Customer · Financial · Other Personal, Operational or Proprietary n Hacktivists / Anonymous n Terrorists n Competitors n Third Party Vendors n Physical Security n Errors by Vendors n Data = Cash n Sabotage: “Philosophical” Point, Nuisance or Revenge n Espionage: Classified / National Security Information · Military and / or Infrastructure 16
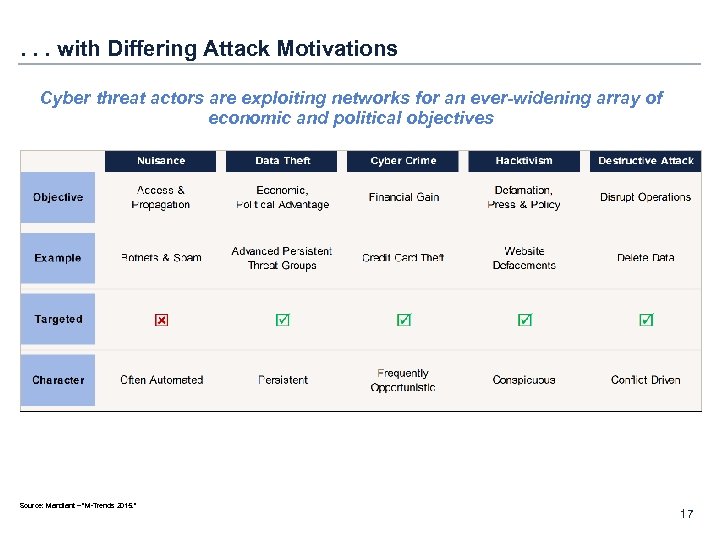
. . . with Differing Attack Motivations Cyber threat actors are exploiting networks for an ever-widening array of economic and political objectives Source: Mandiant – “M-Trends 2015. ” 17
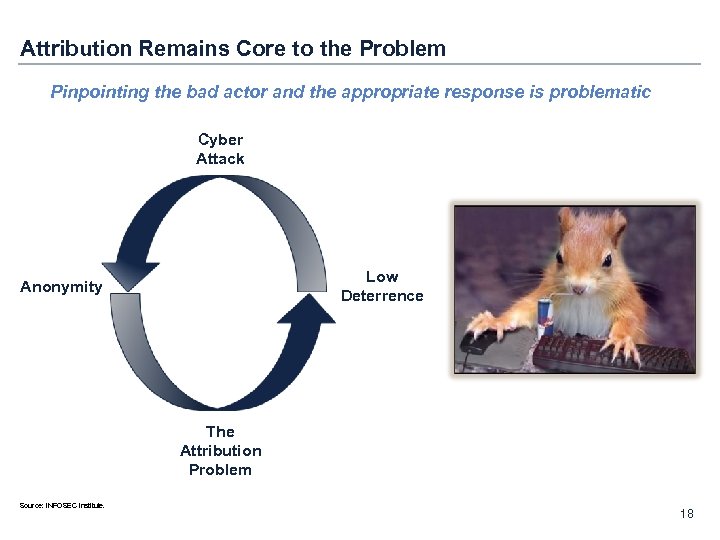
Attribution Remains Core to the Problem Pinpointing the bad actor and the appropriate response is problematic Cyber Attack Low Deterrence Anonymity The Attribution Problem Source: INFOSEC Institute. 18

Hackers Take Control of Moving Jeep Ethical hackers expose wireless networks as the weakest link in high-tech vehicles 19
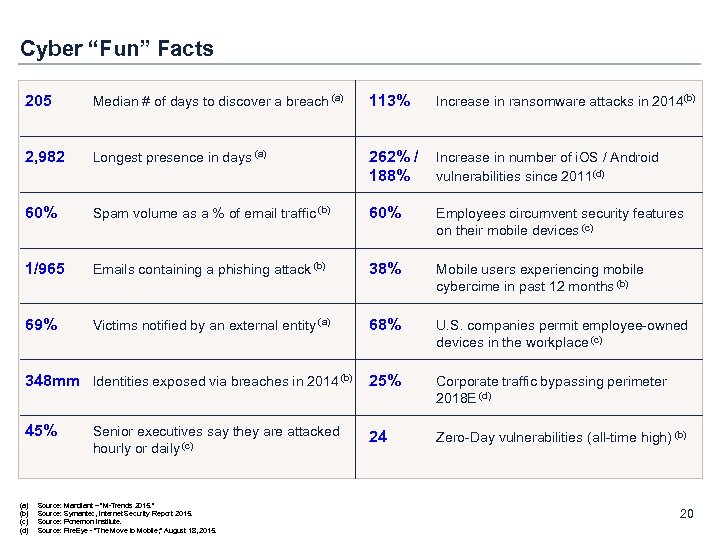
Cyber “Fun” Facts 205 Median # of days to discover a breach (a) 113% Increase in ransomware attacks in 2014(b) 2, 982 Longest presence in days (a) 262% / 188% Increase in number of i. OS / Android vulnerabilities since 2011(d) 60% Spam volume as a % of email traffic (b) 60% Employees circumvent security features on their mobile devices (c) 1/965 Emails containing a phishing attack (b) 38% Mobile users experiencing mobile cybercime in past 12 months (b) 69% Victims notified by an external entity (a) 68% U. S. companies permit employee-owned devices in the workplace (c) 348 mm Identities exposed via breaches in 2014 (b) 25% Corporate traffic bypassing perimeter 2018 E (d) 45% 24 Zero-Day vulnerabilities (all-time high) (b) (a) (b) (c) (d) Senior executives say they are attacked hourly or daily (c) Source: Mandiant – “M-Trends 2015. ” Source: Symantec, Internet Security Report 2015. Source: Ponemon Institute. Source: Fire. Eye - “The Move to Mobile; ” August 18, 2015. 20
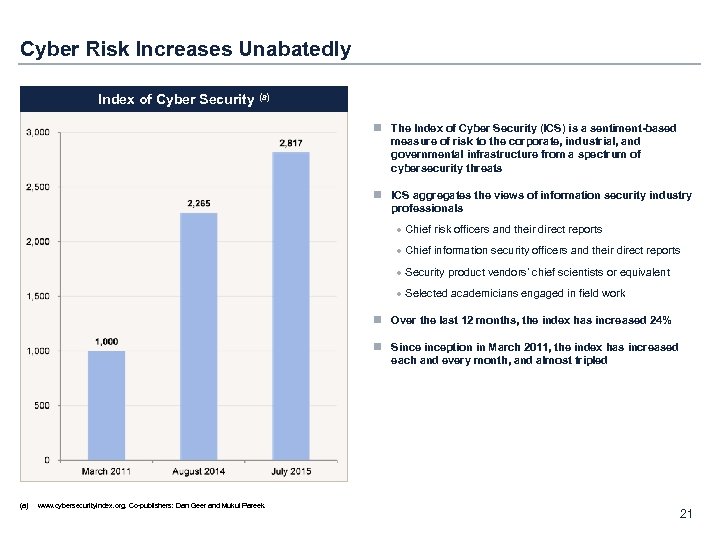
Cyber Risk Increases Unabatedly Index of Cyber Security (a) n The Index of Cyber Security (ICS) is a sentiment-based measure of risk to the corporate, industrial, and governmental infrastructure from a spectrum of cybersecurity threats n ICS aggregates the views of information security industry professionals · Chief risk officers and their direct reports · Chief information security officers and their direct reports · Security product vendors’ chief scientists or equivalent · Selected academicians engaged in field work n Over the last 12 months, the index has increased 24% n Sinception in March 2011, the index has increased each and every month, and almost tripled (a) www. cybersecurityindex. org. Co-publishers: Dan Geer and Mukul Pareek. 21
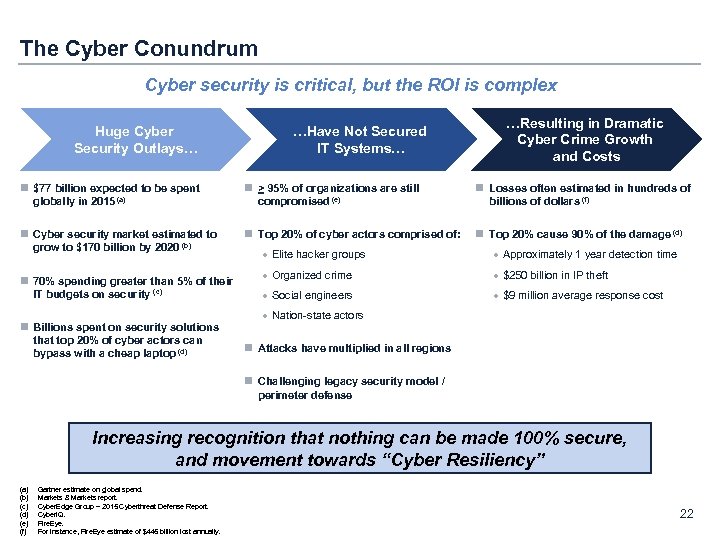
The Cyber Conundrum Cyber security is critical, but the ROI is complex Huge Cyber Security Outlays… …Have Not Secured IT Systems… …Resulting in Dramatic Cyber Crime Growth and Costs n $77 billion expected to be spent globally in 2015 (a) n > 95% of organizations are still compromised (e) n Losses often estimated in hundreds of billions of dollars (f) n Cyber security market estimated to grow to $170 billion by 2020 (b) n Top 20% of cyber actors comprised of: n Top 20% cause 90% of the damage (d) n 70% spending greater than 5% of their IT budgets on security (c) n Billions spent on security solutions that top 20% of cyber actors can bypass with a cheap laptop (d) · Elite hacker groups · Approximately 1 year detection time · Organized crime · $250 billion in IP theft · Social engineers · $9 million average response cost · Nation-state actors n Attacks have multiplied in all regions n Challenging legacy security model / perimeter defense Increasing recognition that nothing can be made 100% secure, and movement towards “Cyber Resiliency” (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Gartner estimate on global spend. Markets & Markets report. Cyber. Edge Group – 2015 Cyberthreat Defense Report. Cyber. IQ. Fire. Eye. For Instance, Fire. Eye estimate of $445 billion lost annually. 22

The Problem Is Pervasive n Since 2005, 10, 570 studied cyber events / data security breaches (a) n 2014 was a record year (a) · Over 579 million records exposed (41% increase over 2013) · Vast majority of breaches attacked personal information · Hacking most common source · Retail sector hit hardest with dramatic increase in number of compromises and records exposed · The 2014 Sony destructive attack exposed “inner workings, ” a departure from historical attack modes on corporates n Lasting financial consequences based on Cyber. Factors tail analysis n Forecast of 14% CAGR through 2019 (b) n Most breaches are never publicly reported and many simply go undetected (a) (b) Source: Cyber. Factors. Source: Gartner Research 2013. 23
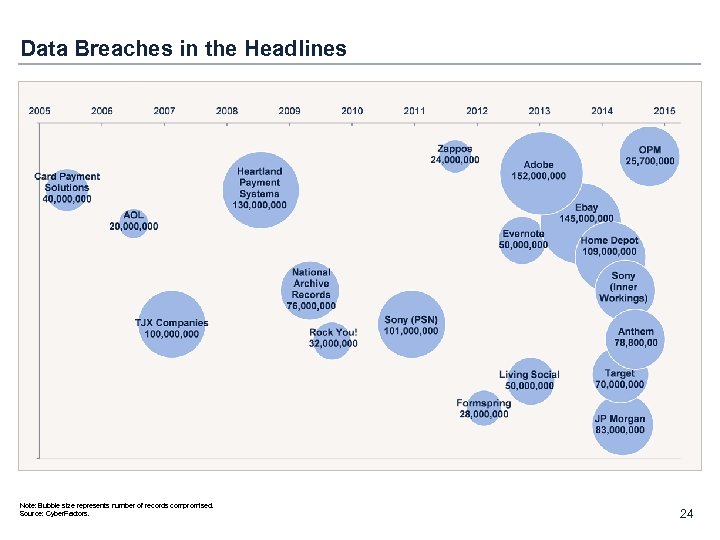
Data Breaches in the Headlines Note: Bubble size represents number of records compromised. Source: Cyber. Factors. 24
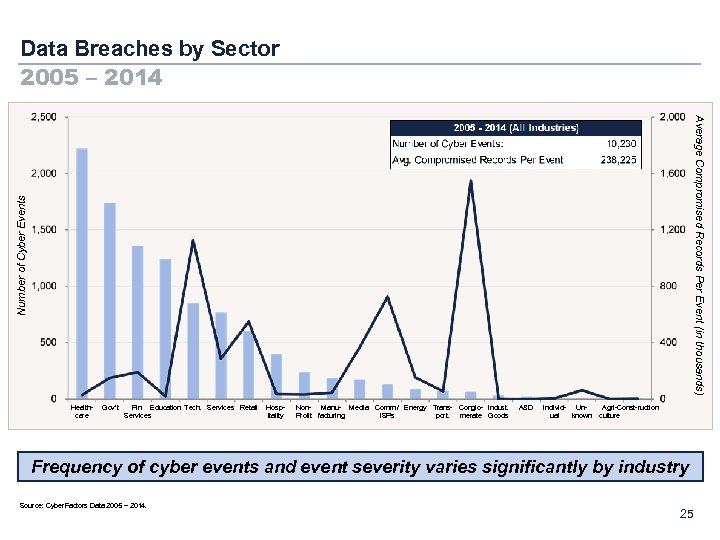
Data Breaches by Sector 2005 – 2014 Number of Cyber Events Average Compromised Records Per Event (in thousands) Healthcare Gov’t Fin. Education Tech. Services Retail Services Hospitality Non- Manu- Media Comm. / Energy Trans- Conglo- Indust. Profit facturing ISPs port. merate Goods A&D Individ- Unual known Agri-Const-ruction culture Frequency of cyber events and event severity varies significantly by industry Source: Cyber. Factors Data 2005 – 2014. 25

Don’t Underestimate Human Error 26
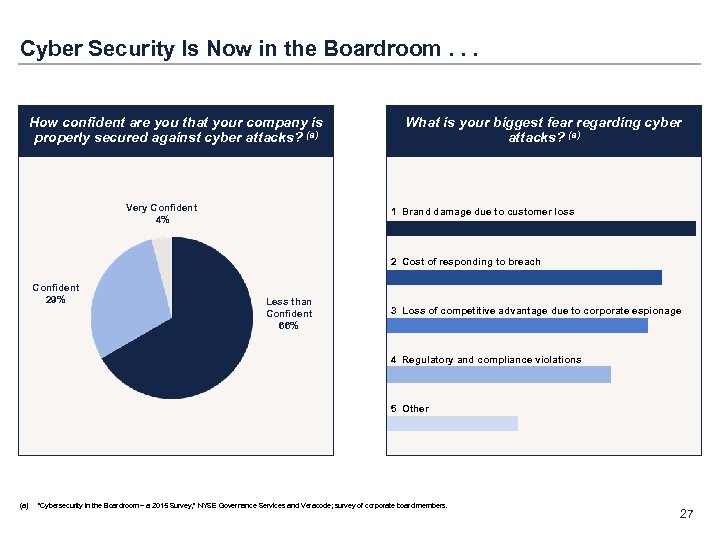
Cyber Security Is Now in the Boardroom. . . How confident are you that your company is properly secured against cyber attacks? (a) Very Confident 4% What is your biggest fear regarding cyber attacks? (a) 1 Brand damage due to customer loss 2 Cost of responding to breach Confident 29% Less than Confident 66% 3 Loss of competitive advantage due to corporate espionage 4 Regulatory and compliance violations 5 Other (a) “Cybersecurity in the Boardroom – a 2015 Survey, ” NYSE Governance Services and Veracode; survey of corporate board members. 27

. . . as a Critical Risk Management Priority Cyber risk is an enterprise risk management concern n Cyber security is a major governance issue with reputational, operational and financial implications n The overall cyber risk environment, the Target breach and C-suite shake-up, and lawsuits (e. g. , Wyndham, Target) have heightened board awareness n With cyber in the spotlight, board members must: · Optimize cyber security governance principles and communication with senior management, IT and cyber security professionals · Establish clear plans, both for cyber security and data breach response n As cyber risk moves to measurement in balance sheet terms, boards will become even more focused Boards are increasingly important in the cyber security discussion, including the consideration of cyber insurance 28
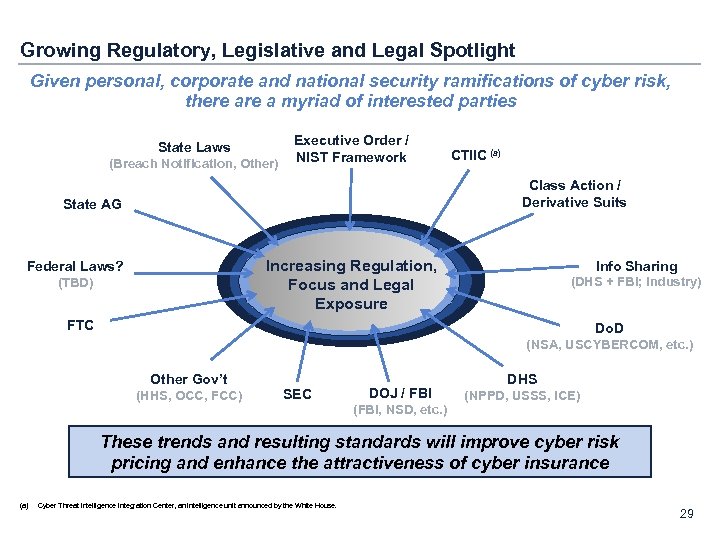
Growing Regulatory, Legislative and Legal Spotlight Given personal, corporate and national security ramifications of cyber risk, there a myriad of interested parties State Laws (Breach Notification, Other) Executive Order / NIST Framework CTIIC (a) Class Action / Derivative Suits State AG Increasing Regulation, Focus and Legal Exposure Federal Laws? (TBD) Info Sharing (DHS + FBI; Industry) FTC Do. D (NSA, USCYBERCOM, etc. ) Other Gov’t (HHS, OCC, FCC) SEC DOJ / FBI (FBI, NSD, etc. ) DHS (NPPD, USSS, ICE) These trends and resulting standards will improve cyber risk pricing and enhance the attractiveness of cyber insurance (a) Cyber Threat Intelligence Integration Center, an intelligence unit announced by the White House. 29
Agenda Risk in the Digital Universe Cyber Risk Market Trends Risk Transfer Market Dynamics and Opportunities 30
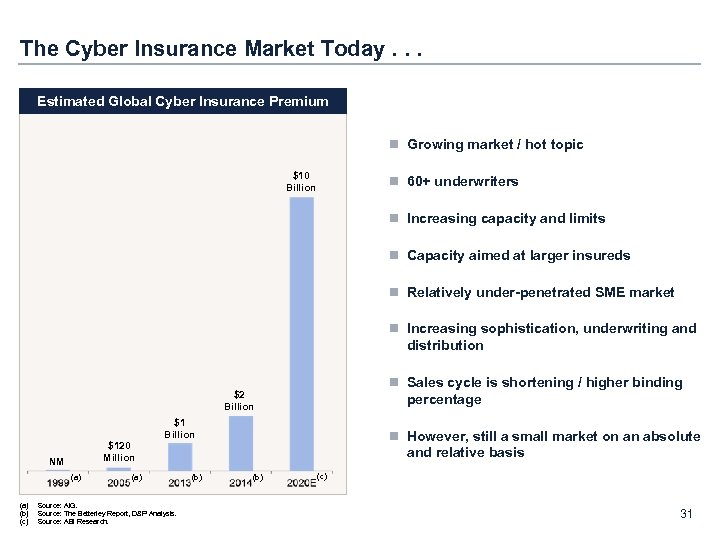
The Cyber Insurance Market Today. . . Estimated Global Cyber Insurance Premium n Growing market / hot topic $10 Billion n 60+ underwriters n Increasing capacity and limits n Capacity aimed at larger insureds n Relatively under-penetrated SME market n Increasing sophistication, underwriting and distribution n Sales cycle is shortening / higher binding percentage $2 Billion $120 Million NM (a) (b) (c) $1 Billion (a) Source: AIG. Source: The Betterley Report, D&P Analysis. Source: ABI Research. (b) n However, still a small market on an absolute and relative basis (b) (c) 31

. . . Reflects Several Historical Challenges n Lack of standardized coverages and insurance product information n Cumbersome application process n Denial: many have not been willing to recognize risk or believe already covered in standard policies n Senior management / boards historically lacked understanding of exposures n Limited provision in corporate budgets for cyber insurance n Cyber risk pricing models not well-developed · Limited historical data · Evolving, iterative nature of necessary data n Risk aggregation concerns (“cyber hurricane”) n Varying levels of sophistication in the underwriting and distribution communities 32

The Cyber Risk Transfer Market Continues to Evolve n A variety of risk modeling initiatives in cyber Risk Modelers n Increasing amounts of diverse, accurate and relevant historical breach data n Expanding sample size of claims data (both public and proprietary) n Refinements in IT security rating engines / online risk assessment tools n Improving standards (e. g. , NIST) n Additional information / data sources · Threat analytics · Information sharing – public / private collaboration n Advancements in cyber security technology, tactics, and awareness n New knowledge/strategies to mitigate aggregation risk exposures n Movement towards standardization in rates and forms n Market depth with maturation: reinsurance, cat bonds, cyber captives, SPVs and sidecars 33

Cyber Insurance – a Fast-Growing Specialty Line n Explosion of data, increase in attack surfaces and attackers, and ongoing attribution challenges n Senior management and board pressure n Focus and publicity / increased awareness and education n Substantial SME market opportunity n Regulatory and legal trends n Market need for a holistic solution n Insurance industry capabilities – in unique position to help shape the dialogue n Enhanced actuarial data and approaches n Government initiatives around information sharing and threat collaboration Cyber insurance will be an expected business expense and purchased concurrently with other standard coverages 34

Further Questions / Topics for Discussion n Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning n Internet Governance n Attribution n Net Neutrality n Big Data n New Internet / New Design? n Breach Reporting – Mandatory? n Open Source Trends n Cloud n Privacy / Right to be Forgotten n Code as Regulator n Public / Private Collaboration n Cost of a Networked World n Quantum Computing n Data Integrity n Reputational Risk (See Intangibles) n Federal Backstop (e. g. , TRIA) n Shadow / Parallel Networks n Federal Data Breach Law n Software Security – Like Milk or Wine? n Intangibles – Valuation / Accounting n Who “Owns” the Data? 35

Thank You for Your Time “Risk and time are opposite sides of the same coin, for if there were no tomorrow there would be no risk. Time transforms risk, and the nature of risk is shaped by the time horizon: the future is the playing field. ” – Peter Bernstein, “Against the Gods” 36

Contact Us For further information, please contact: David Kimmel Chief Executive Officer Cyber. Risk. Partners (917) 664 -8798 david@cyberriskpartners. com 37

APPENDIX 38

Source: DOMO – Data Never Sleeps 3. 0. 39
![[ ] Source: DOMO – Data Never Source: Harvard Business School. Sleeps 2. 0. [ ] Source: DOMO – Data Never Source: Harvard Business School. Sleeps 2. 0.](https://present5.com/presentation/ea7bf10e753a672da2b560a833b6460b/image-41.jpg)
[ ] Source: DOMO – Data Never Source: Harvard Business School. Sleeps 2. 0.
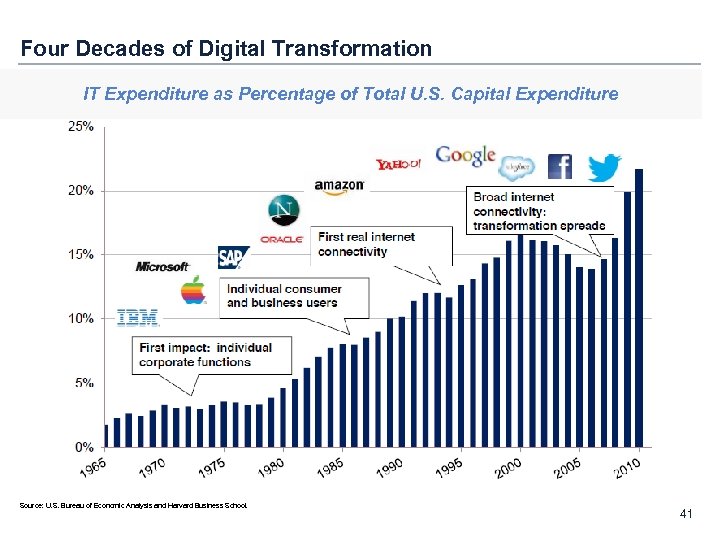
Four Decades of Digital Transformation IT Expenditure as Percentage of Total U. S. Capital Expenditure Source: U. S. Bureau of Economic Analysis and Harvard Business School. 41
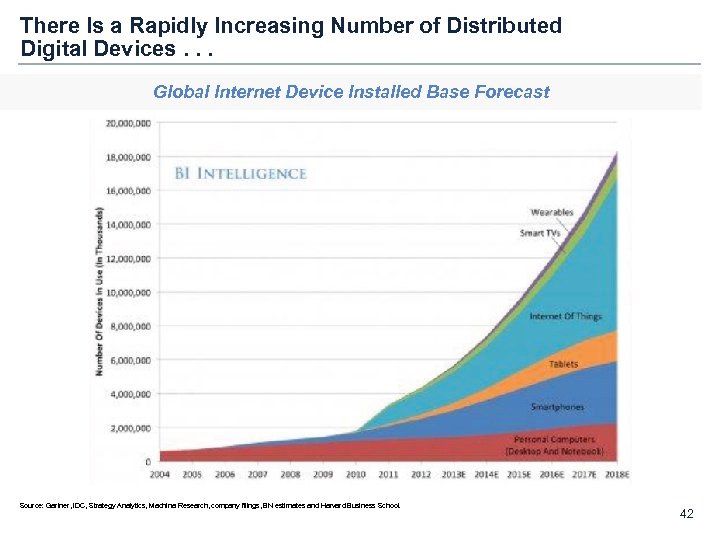
There Is a Rapidly Increasing Number of Distributed Digital Devices. . . Global Internet Device Installed Base Forecast Source: Gartner, IDC, Strategy Analytics, Machina Research, company filings, BN estimates and Harvard Business School. 42
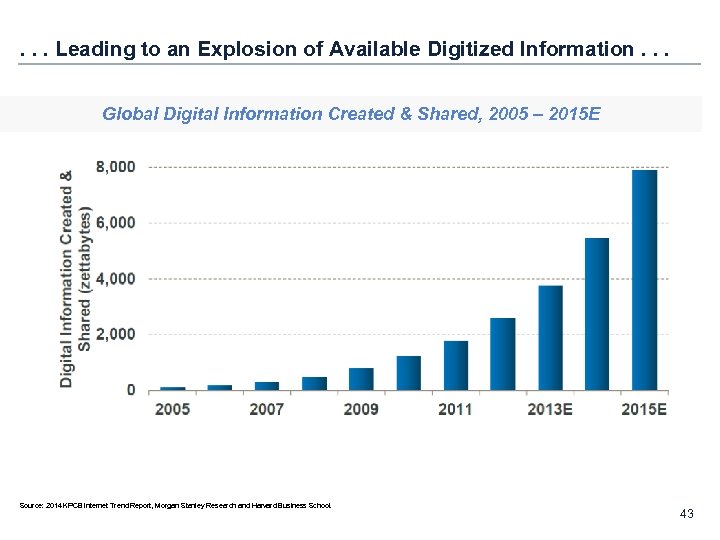
. . . Leading to an Explosion of Available Digitized Information. . . Global Digital Information Created & Shared, 2005 – 2015 E Source: 2014 KPCB Internet Trend Report, Morgan Stanley Research and Harvard Business School. 43
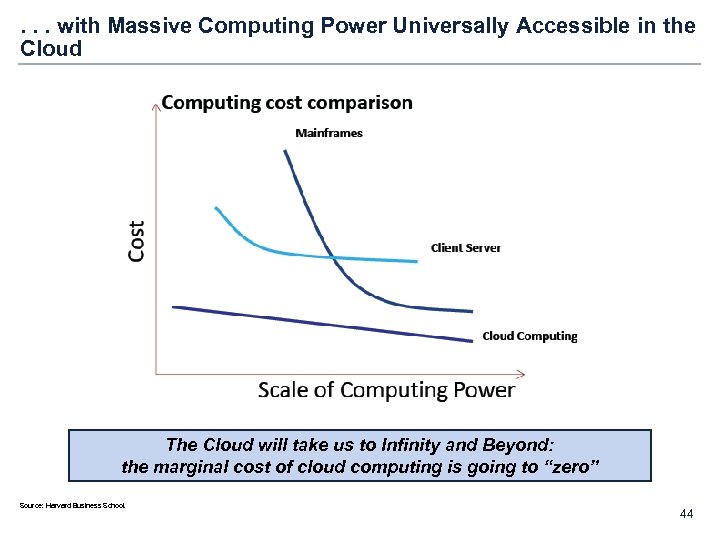
. . . with Massive Computing Power Universally Accessible in the Cloud The Cloud will take us to Infinity and Beyond: the marginal cost of cloud computing is going to “zero” Source: Harvard Business School. 44
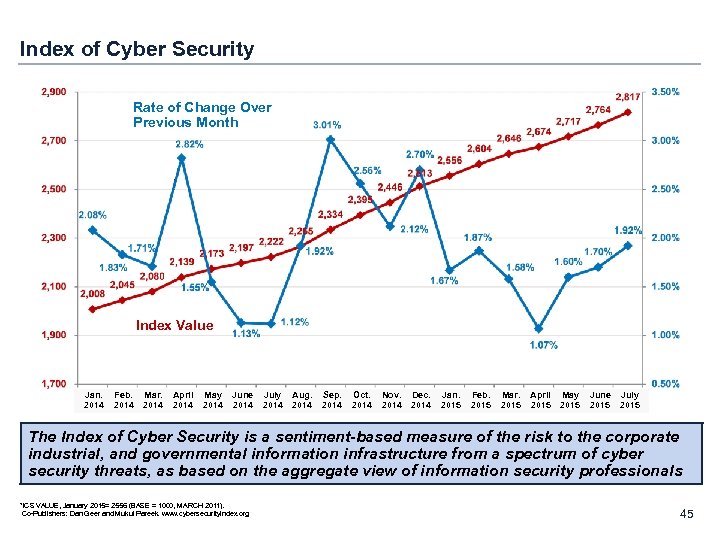
Index of Cyber Security Rate of Change Over Previous Month Index Value Jan. 2014 Feb. 2014 Mar. 2014 April 2014 May 2014 June 2014 July 2014 Aug. 2014 Sep. 2014 Oct. 2014 Nov. 2014 Dec. 2014 Jan. 2015 Feb. 2015 Mar. 2015 April 2015 May 2015 June 2015 July 2015 The Index of Cyber Security is a sentiment-based measure of the risk to the corporate industrial, and governmental information infrastructure from a spectrum of cyber security threats, as based on the aggregate view of information security professionals *ICS VALUE, January 2015= 2556 (BASE = 1000, MARCH 2011). Co-Publishers: Dan Geer and Mukul Pareek. www. cybersecurityindex. org 45
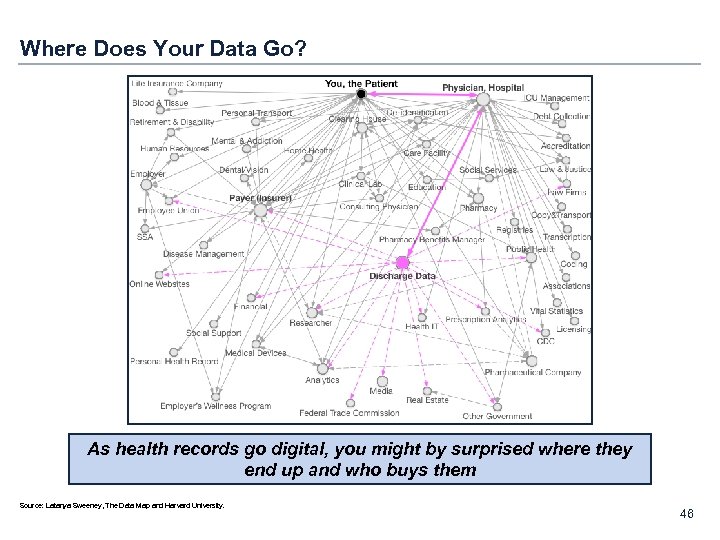
Where Does Your Data Go? As health records go digital, you might by surprised where they end up and who buys them Source: Latanya Sweeney, The Data Map and Harvard University. 46
ea7bf10e753a672da2b560a833b6460b.ppt