Cyber Crime EMERGING CYBER CRIME TRENDS March 17,


Cyber Crime EMERGING CYBER CRIME TRENDS March 17, 2006 by Kenneth G. McGuire Supv. Special Agent FBI

Topic Overview Current Security Threats & Cases Cyber Crime Incident Handling Working With Law Enforcement

Security Threats & Cases TYPES OF PERPETRATORS INTERNET FRAUD - Identity Theft, Phishing Schemes, Remailer Schemes COMPUTER INTRUSIONS & DISRUPTIONS – RATs (Remote Access Trojans), Extortion by DDoS (distributed denial of service), “Hacker for Hire” Investigation, Wireless Networks Concerns INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS CRIMES – Warez/Movie Servers, P2P

How Severe is the Threat?

Identity Theft Growing sophistication of phishing emails Exploitation of Banking System Keystroke Loggers deployed by worms Exploding International Market for Stolen Credit Card Databases and Identity Data FTC - $50B lost in Identity Theft in 2003 300M manhours devoted to repairing damage caused by this theft
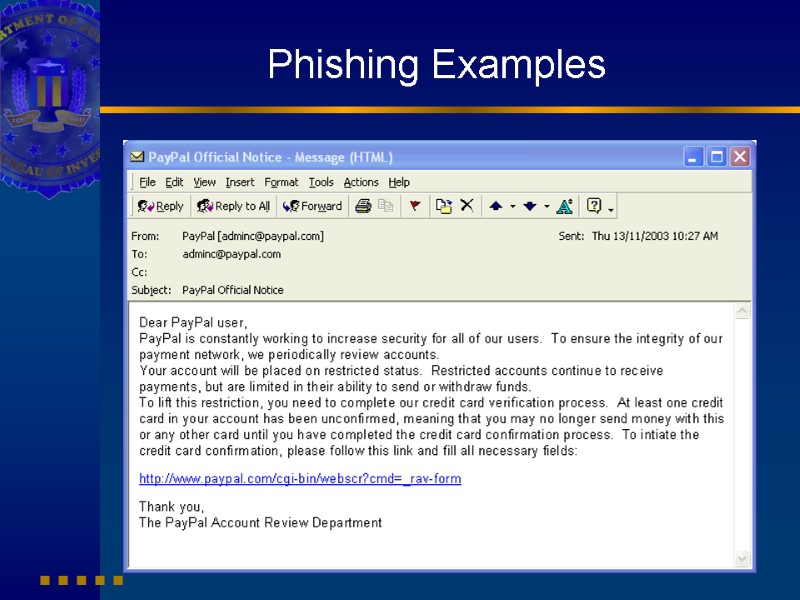
Phishing Examples
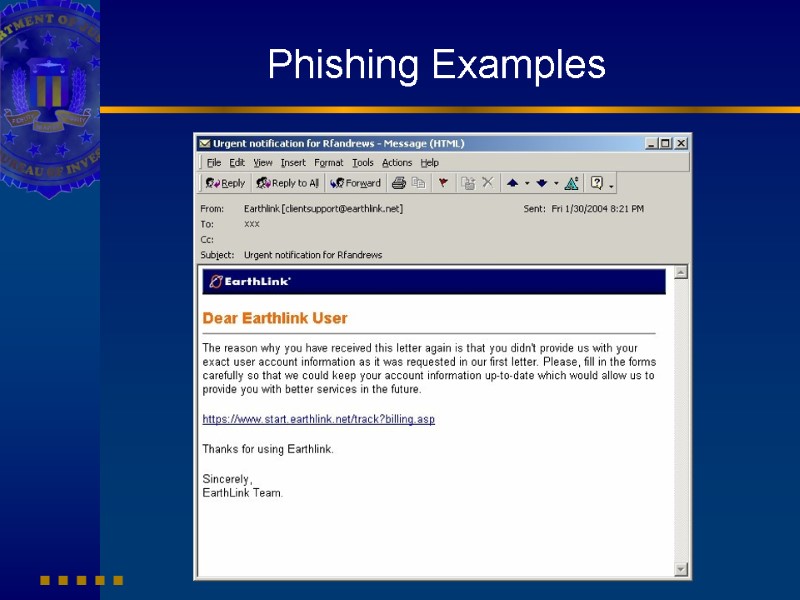
Phishing Examples
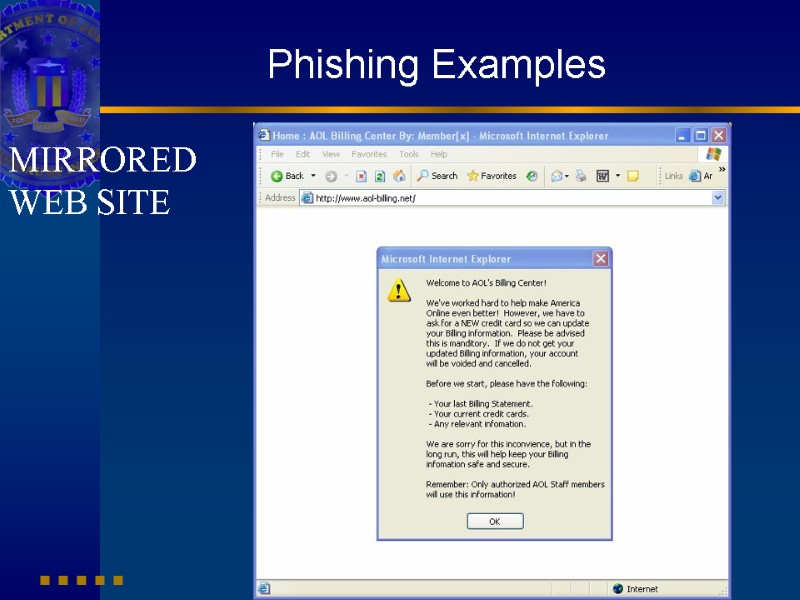
Phishing Examples MIRRORED WEB SITE

Phishing Examples MIRRORED WEB SITE

Growing Trends Virus/Worm Payloads Used to Facilitate Intrusion/Fraud Schemes Mercenary Distributed Denial Of Service Attacks Extortion Schemes Fueled by DDOS and Intrusion Spamming used to spread malicious payloads, phish, and pay using adware/malware, spyware Identity Theft Underpins Most Computer Crime Overall increase in sophistication by a geographically diverse criminal element
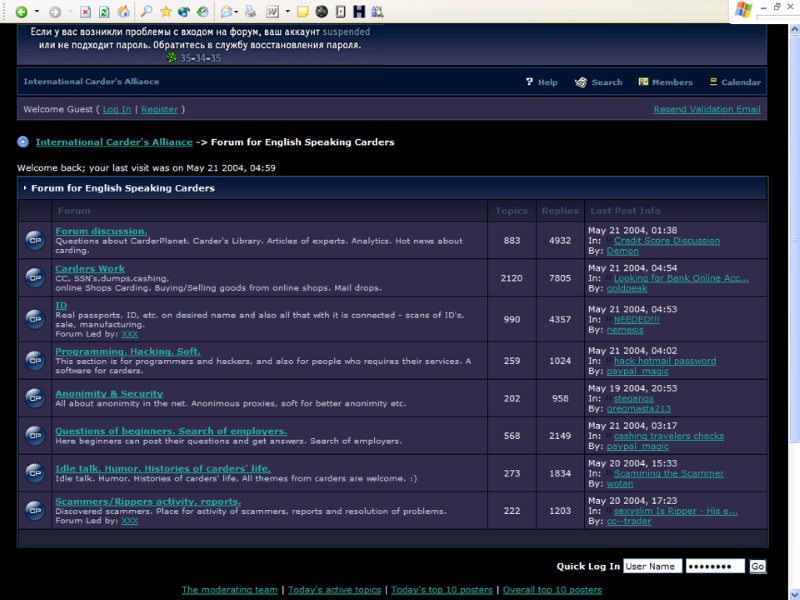
Example of a Carder Site

Banking and Brokerage Account Compromise Internet Worms propagate keystroke logger in payload to steal account usernames & passwords U.S. citizens recruited to wire proceeds cashed counterfeit checks for 30% fee Internet purchase funds first transmitted to other U.S. accounts, then to the Eastern bloc.

Remailer Schemes

World’s Largest Computer Equipment Supplier A union of computer intrusion and wire fraud Subjects have placed at least $10M in fraudulent orders Subjects use work-from-home web sites to recruit unwitting U.S. participants 11 convictions to date in the U.S., at least a dozen to follow

REMOTE ACCESS TROJANS (RATs) HACKER versions – Subseven, Backorifice, Netbus Sometimes contained in email or programs downloads, i.e. P2P programs like Kazaa COMMERCIAL PROGRAMS – GotomyPC, PC Anywhere, Laplink OPERATING SYSTEMS PROGRAMS – Telnet, ftp, Secure Shell (SSH), rlogin
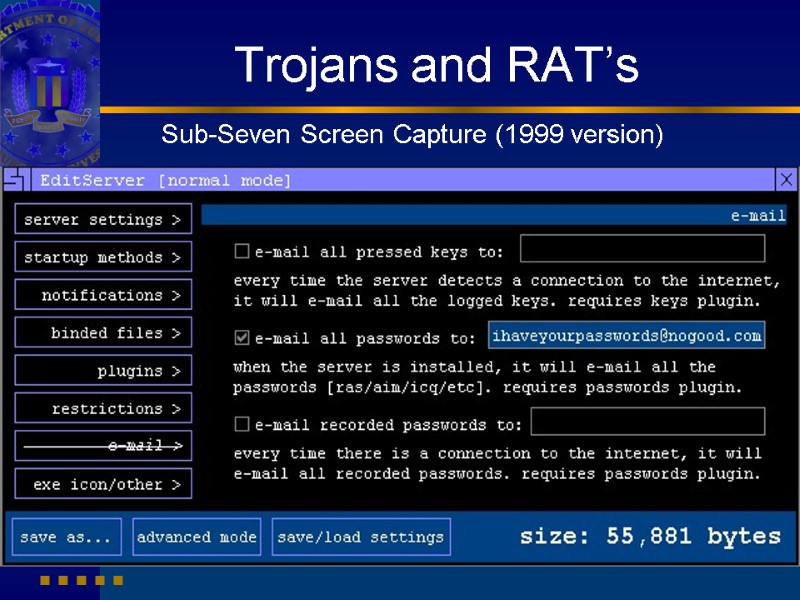
Trojans and RAT’s Sub-Seven Screen Capture (1999 version)
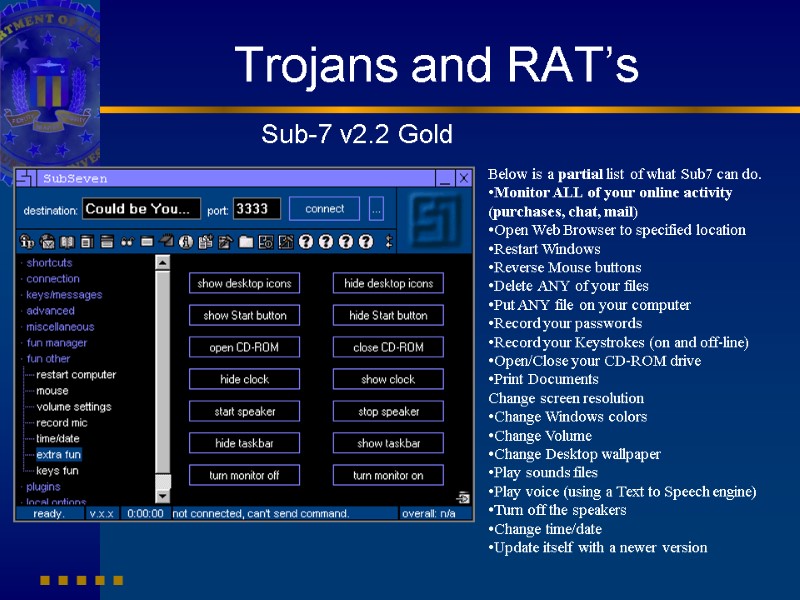
Trojans and RAT’s Sub-7 v2.2 Gold Below is a partial list of what Sub7 can do. Monitor ALL of your online activity (purchases, chat, mail) Open Web Browser to specified location Restart Windows Reverse Mouse buttons Delete ANY of your files Put ANY file on your computer Record your passwords Record your Keystrokes (on and off-line) Open/Close your CD-ROM drive Print Documents Change screen resolution Change Windows colors Change Volume Change Desktop wallpaper Play sounds files Play voice (using a Text to Speech engine) Turn off the speakers Change time/date Update itself with a newer version

Trojans and RAT’s Sub-Seven Screen Capture When run, the backdoor copies itself to the Windows directory with the original name of the file it was run from or as SERVER.EXE, KERNEL16.DL, RUNDLL16.COM, SYSTEMTRAYICON!.EXE or WINDOW.EXE (names are different in different versions of SubSeven). Then it unpacks a single DLL file to the Windows System directory - WATCHING.DLL (some versions don't do this).

Walter Wiggs Former USMC Scout Sniper Instructor Violent Criminal History Georgia Resident Software Engineer for a Manhattan Beach Telecommunications Company

Walter Wiggs Employment Terminated Disabled telecommunication systems across the country Caused a disruption in the Los Angeles County Child Protective Service Hotline over July 4, 2003 Arrested in August 2003

Extortion By DDOS Hiring hackers to create distributed denial of service (DDOS) attacks Look for use of P2P instead of IRCds
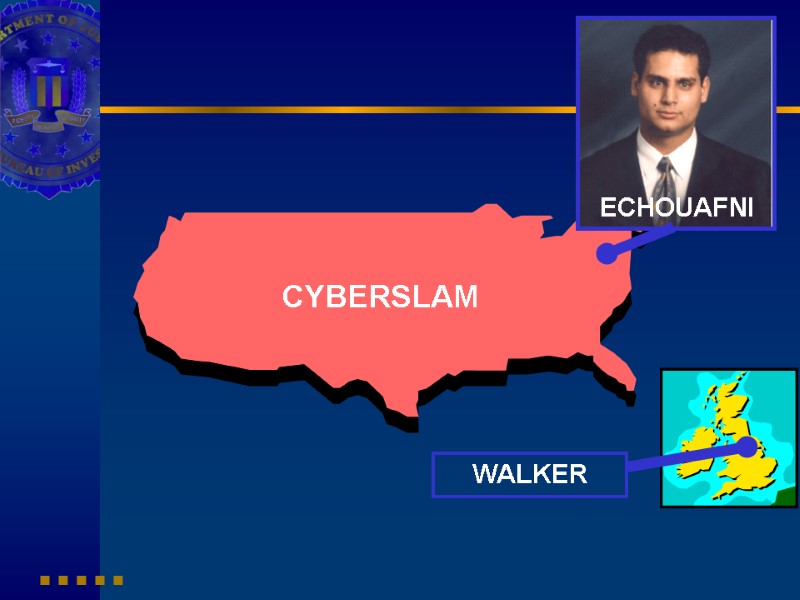

Victims
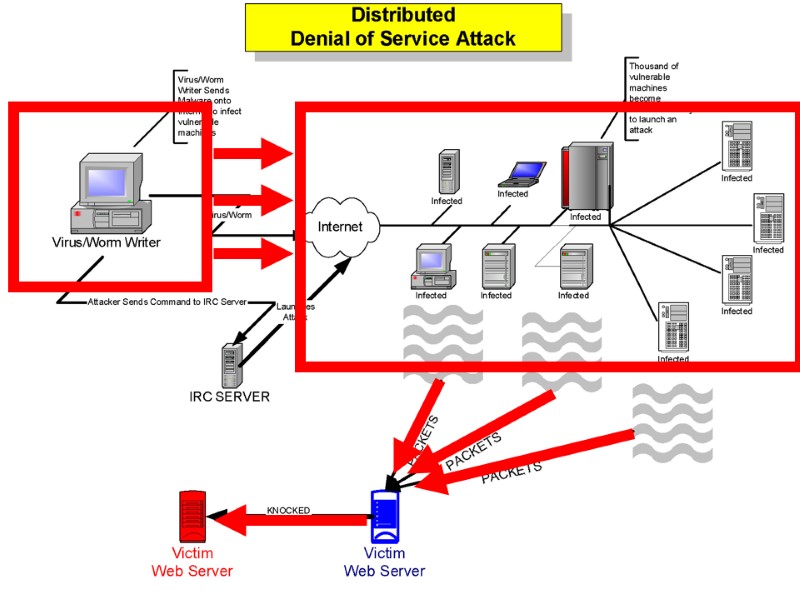

Jeanson James Ancheta, aka ResiLi3nt Hacker pleads guilty to building, renting attack network FBI report estimates viruses, worms & Trojan programs cost U.S. organizations $11.9 billion each year. 20-year-old hacker living w/ mother in Downey Prev. Criminal larceny conviction Using a botnet to send spam. A botnet operator sends out viruses or worms, infecting ordinary users' Windows PCs. The PCs log into an IRC server or other communications medium. A spammer purchases access to the botnet from the operator. The spammer sends instructions via the IRC server to the infected PCs.... ... causing them to send out spam messages to mail servers.

Jeanson James Ancheta, aka ResiLi3nt Sold botnets of 100 to 500 computers for $150 to $500 Infected >400,000 computers installing toolbars for click fees , made $61,000 as affiliates of Loudcash and Gammacash Hacked China Lake Naval Weapons Center computer – Not Classified 1/23/06 Pled Guilty to 4 of 17 counts in 11/05 indictment Sentencing May 1, 2006

Brian Tinney Professional Burglar Created fictitious computer company in Las Vegas Created fictitious escrow company in San Francisco Order $600,000 in high end computer equipment from suppliers around the U.S.

Steven-William:Sutcliffe Global Crossing Employee Sovereign Citizen Adherent www.killercop.com Web Terror Campaign Posted all employee SSN’s Home addresses, telephone numbers, residence maps Death Threats Arrested in New Hampshire “UCC-207” “All Rights Reserved”

Countermeasures Practice good computer security Invest in a personal shredder Examine your credit report annually Scrutinize credit card statements 1-888-5-OPTOUT (1-888-567-8688) Use caution supplying wire transfer info Be alert to anomalous personal info requests http://www.consumer.gov/idtheft/

1) Availability of free WAP detection and logging tools like Netstumbler and Kismet 2) War Driving-where individuals drive (or walk) Around to find unprotected and accessible WAPs 3) Consumer and even system administrators fail to configure their systems adequately Wireless Security Concerns
1. Uses 128-bit encryption 2. WEP’s poor implementation of the algorithm caused it to be broken which is available to hackers. 3. Replacement for WEP called WiFi Protected Access (WPA) not widely implemented. 4. WEP is not configured out of the box and therefore, not protecting the system. 5. When WEP is configured by owner the default password is used -ADMIN Wireless Encryption Protocol or Wireless Equivalency Protection (WEP) Wireless Security Measures

Preventing Disgruntled Employee Problems Terminating System Access BEFORE TERMINATED EMPLOYEES ARE WALKING OUT THE DOOR Well Documented and Proliferated Non-Disclosure and Authorized Activity Agreements/Notifications Review Adequate Logging/Tracking Enforce Your Rules PRACTICE EXCERCISE – “RED TEAMING” BANNER during Log-in of company computers

CYBER CRIME INCIDENT HANDLING Continuing Operations v. Preservation of Evidence Identify the Incident Manager and Team – usually department heads or officers Assess Systems Impaired and Damages Review Adequate Logging/Tracking Note Unusual Activities By Employees or on Computer Network

WORKING WITH LAW ENFORCEMENT Identify your LOSS, HARM, or DAMAGE – lost asset, revenues, expenses, repair cost Identify Capture or Quarantine Electronic or Computerized Equipment, Logs and Files Maintain a “Chain of Custody” for Evidence Begin a written chronology of events Who may have to testify Identify one or two individuals to be your main point of contact with LEOs Alert Your General Counsel or Attorney

WORKING WITH LAW ENFORCEMENT CRIMINAL LAWS THAT APPLY: ECPA (Electronic Communications and Privacy Act) 4th Amendment – Search & Seizure Interception of Communications (Wiretapping) Court Orders – FGJ Subpoenas, Search Warrants, Pen Registers, Trap & Trace Orders, 2703(d) Orders, Title 3 Orders

Prepare for Incident Response Have A Disaster Plan for Human-made and Natural Disasters Need some ideas, try Risk Management Organizations - NIST.GOV,SANS.ORG Practice The Plan! Review The Plan Annually! Include contacts with law enforcement or disaster officials

SANS Top 7 Management Errors #7 Pretend the problem will go away if they ignore it. #6 Authorize reactive, short-term fixes so problems re-emerge rapidly #5 Fail to realize how much money their information and organizational reputations are worth. #4 Rely primarily on a firewall. #3 Fail to deal with the operational aspects of security: make a few fixes and then not allow the follow through necessary to ensure the problems stay fixed #2 Fail to understand the relationship of information security to the business problem -- they understand physical security but do not see the consequences of poor information security. #1 Assign untrained people to maintain security and provide neither the training nor the time to make it possible to do the job.

INFRAGARD PROGRAM

Contact Cyber Crime Supervisor Nakonechniy Maksim E-mail: [email protected]
9082-zrazok!!!!cyber_crime_supervisor.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

