5ac738c13ac39ae8602141e28d0bafee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Customer Satisfaction Profit Chain Prof. Markus Christen INSEAD Singapore May/June 2007
Customer Satisfaction Profit Chain Prof. Markus Christen INSEAD Singapore May/June 2007
 Customer Satisfaction Is Decreasing American Customer Satisfaction Index (ASCI) Based on annual poll of more than 50. 000 consumes, measuring overall satisfaction with products and services. Source: http: //www. theacsi. org, University of Michigan 2 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Customer Satisfaction Is Decreasing American Customer Satisfaction Index (ASCI) Based on annual poll of more than 50. 000 consumes, measuring overall satisfaction with products and services. Source: http: //www. theacsi. org, University of Michigan 2 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 CRM Investments Approximate Worldwide CRM Investments (applications, hardware and services) 3 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
CRM Investments Approximate Worldwide CRM Investments (applications, hardware and services) 3 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Starbucks: Delivering Customer Service § Why successful • Tight alignment between target market (sophisticated, affluent coffee lover, coffee drinking life style) and highly differentiated value proposition – Drinking coffee as self-indulgent ritual: Best coffee – Tendency to linger, in search of a sanctuary: Physical environment – Friendly people, social interactions: Service Philosophy § Impact of growth strategy • Retail expansion: Ubiquity of stores makes Starbucks less “special” • Customer acquisition: New customers with different service needs – Routine – Pass through – Convenience • Product innovation: Increased production complexity leads to longer lines 4 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Starbucks: Delivering Customer Service § Why successful • Tight alignment between target market (sophisticated, affluent coffee lover, coffee drinking life style) and highly differentiated value proposition – Drinking coffee as self-indulgent ritual: Best coffee – Tendency to linger, in search of a sanctuary: Physical environment – Friendly people, social interactions: Service Philosophy § Impact of growth strategy • Retail expansion: Ubiquity of stores makes Starbucks less “special” • Customer acquisition: New customers with different service needs – Routine – Pass through – Convenience • Product innovation: Increased production complexity leads to longer lines 4 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Starbucks: Delivering Customer Service § Consequence • Conflicts between customer segments affects service quality – Longer lines, more mistakes, less time to interact and socialize – Grumpy customers, grumpy employees • Difficult to keep customer satisfaction very high with a larger and more diverse customer base §What are the appropriate metrics to manage different customers or customer segments? Customer acquisition and retention? 5 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Starbucks: Delivering Customer Service § Consequence • Conflicts between customer segments affects service quality – Longer lines, more mistakes, less time to interact and socialize – Grumpy customers, grumpy employees • Difficult to keep customer satisfaction very high with a larger and more diverse customer base §What are the appropriate metrics to manage different customers or customer segments? Customer acquisition and retention? 5 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
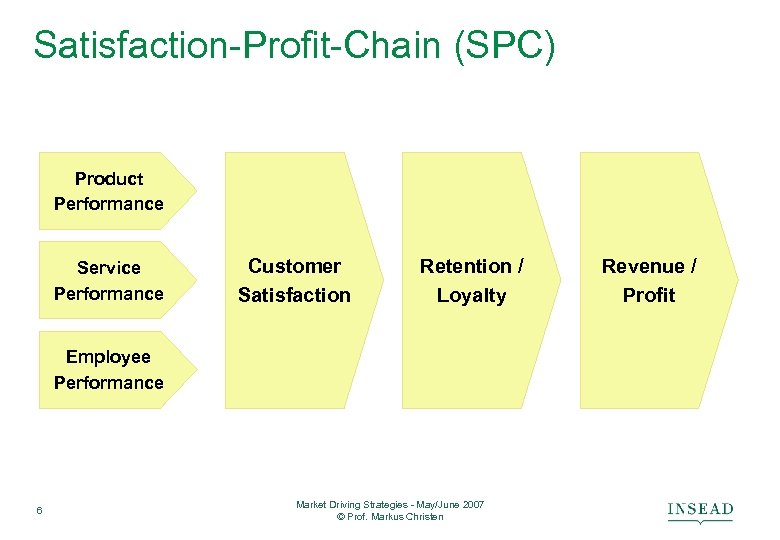 Satisfaction-Profit-Chain (SPC) Product Performance Service Performance Customer Satisfaction Retention / Loyalty Employee Performance 6 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen Revenue / Profit
Satisfaction-Profit-Chain (SPC) Product Performance Service Performance Customer Satisfaction Retention / Loyalty Employee Performance 6 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen Revenue / Profit
 Satisfaction and Customer Behavior Correlations for 418 customers of European paper wholesaler Source: Söderlund, Vilgon & Gunnarsson 2001, European Journal of Marketing 7 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Satisfaction and Customer Behavior Correlations for 418 customers of European paper wholesaler Source: Söderlund, Vilgon & Gunnarsson 2001, European Journal of Marketing 7 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Zone of indifference Source: Jones & Sasser, HBR, Nov/Dec. 1995 8 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Zone of indifference Source: Jones & Sasser, HBR, Nov/Dec. 1995 8 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Satisfaction and Performance Estimated impact of a one-unit change in customer satisfaction (ACSI) on the market value of equity (millions of dollars) Source: Ittner and Larcker, Journal of Accounting Research 9 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Satisfaction and Performance Estimated impact of a one-unit change in customer satisfaction (ACSI) on the market value of equity (millions of dollars) Source: Ittner and Larcker, Journal of Accounting Research 9 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
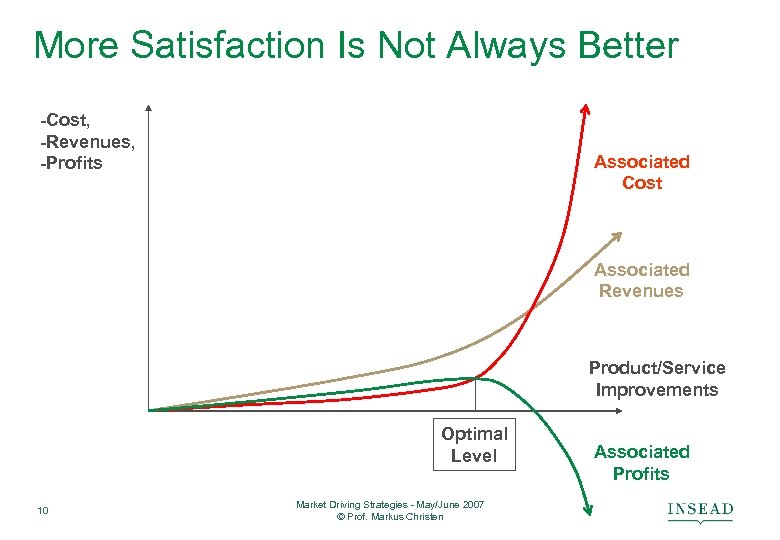 More Satisfaction Is Not Always Better -Cost, -Revenues, -Profits Associated Cost Associated Revenues Product/Service Improvements Optimal Level 10 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen Associated Profits
More Satisfaction Is Not Always Better -Cost, -Revenues, -Profits Associated Cost Associated Revenues Product/Service Improvements Optimal Level 10 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen Associated Profits
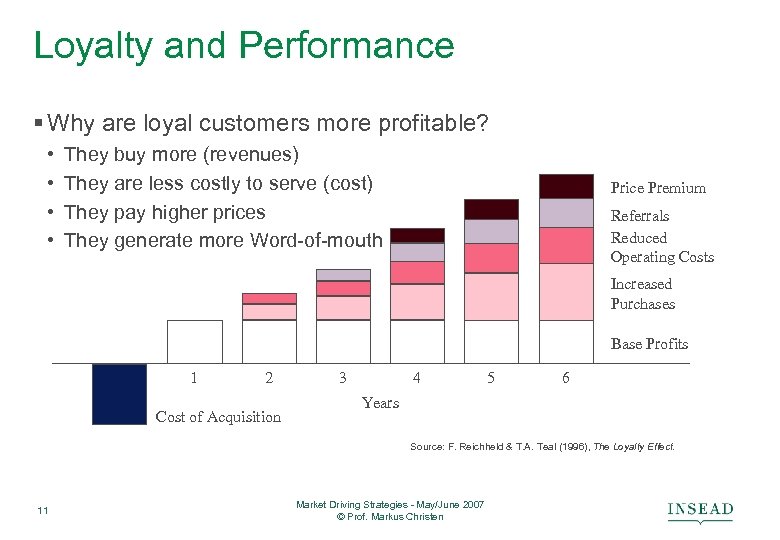 Loyalty and Performance § Why are loyal customers more profitable? • • They buy more (revenues) They are less costly to serve (cost) They pay higher prices They generate more Word-of-mouth Price Premium Referrals Reduced Operating Costs Increased Purchases Base Profits 1 2 Cost of Acquisition 3 4 5 6 Years Source: F. Reichheld & T. A. Teal (1996), The Loyalty Effect. 11 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Loyalty and Performance § Why are loyal customers more profitable? • • They buy more (revenues) They are less costly to serve (cost) They pay higher prices They generate more Word-of-mouth Price Premium Referrals Reduced Operating Costs Increased Purchases Base Profits 1 2 Cost of Acquisition 3 4 5 6 Years Source: F. Reichheld & T. A. Teal (1996), The Loyalty Effect. 11 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
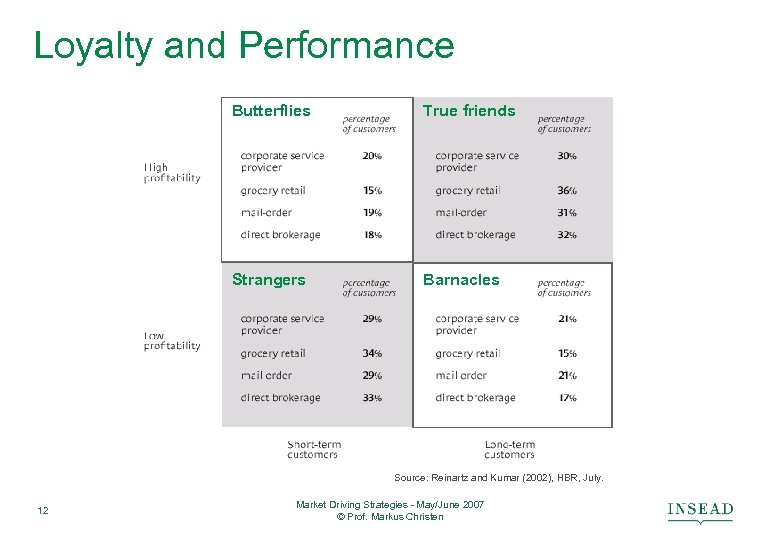 Loyalty and Performance Butterflies True friends Strangers Barnacles Source: Reinartz and Kumar (2002), HBR, July. 12 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Loyalty and Performance Butterflies True friends Strangers Barnacles Source: Reinartz and Kumar (2002), HBR, July. 12 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Loyalty and Performance Do Profits Increase over Time? 13 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Loyalty and Performance Do Profits Increase over Time? 13 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
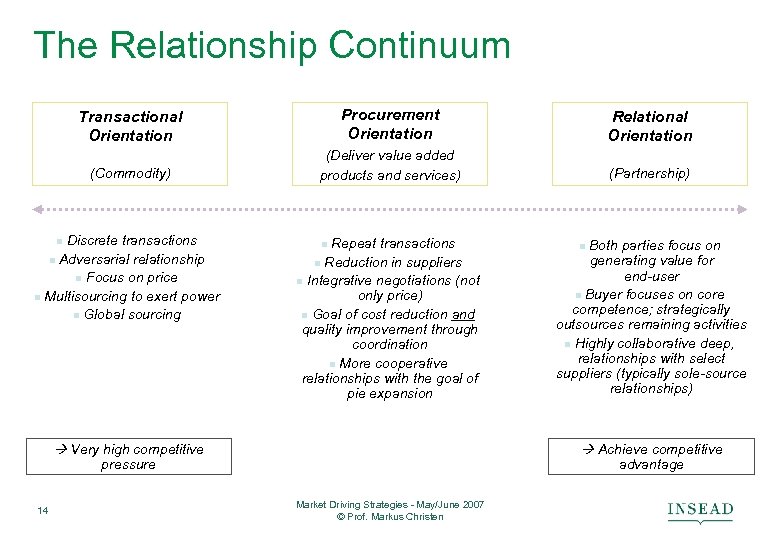 The Relationship Continuum Transactional Orientation Procurement Orientation Relational Orientation (Commodity) (Deliver value added products and services) (Partnership) Repeat transactions n Reduction in suppliers n Integrative negotiations (not only price) n Goal of cost reduction and quality improvement through coordination n More cooperative relationships with the goal of pie expansion Both parties focus on generating value for end-user n Buyer focuses on core competence; strategically outsources remaining activities n Highly collaborative deep, relationships with select suppliers (typically sole-source relationships) Discrete transactions n Adversarial relationship n Focus on price n Multisourcing to exert power n Global sourcing n n Very high competitive Achieve competitive pressure 14 n advantage Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
The Relationship Continuum Transactional Orientation Procurement Orientation Relational Orientation (Commodity) (Deliver value added products and services) (Partnership) Repeat transactions n Reduction in suppliers n Integrative negotiations (not only price) n Goal of cost reduction and quality improvement through coordination n More cooperative relationships with the goal of pie expansion Both parties focus on generating value for end-user n Buyer focuses on core competence; strategically outsources remaining activities n Highly collaborative deep, relationships with select suppliers (typically sole-source relationships) Discrete transactions n Adversarial relationship n Focus on price n Multisourcing to exert power n Global sourcing n n Very high competitive Achieve competitive pressure 14 n advantage Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
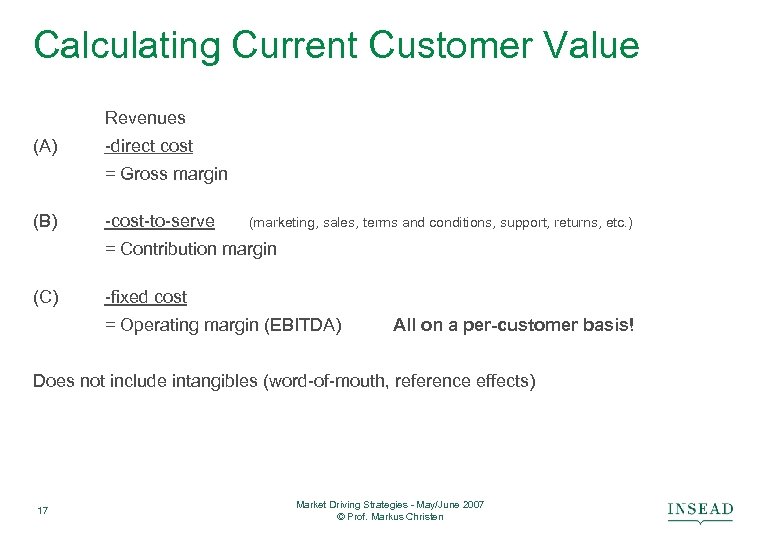 Calculating Current Customer Value Revenues (A) -direct cost = Gross margin (B) -cost-to-serve (marketing, sales, terms and conditions, support, returns, etc. ) = Contribution margin (C) -fixed cost = Operating margin (EBITDA) All on a per-customer basis! Does not include intangibles (word-of-mouth, reference effects) 17 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Calculating Current Customer Value Revenues (A) -direct cost = Gross margin (B) -cost-to-serve (marketing, sales, terms and conditions, support, returns, etc. ) = Contribution margin (C) -fixed cost = Operating margin (EBITDA) All on a per-customer basis! Does not include intangibles (word-of-mouth, reference effects) 17 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
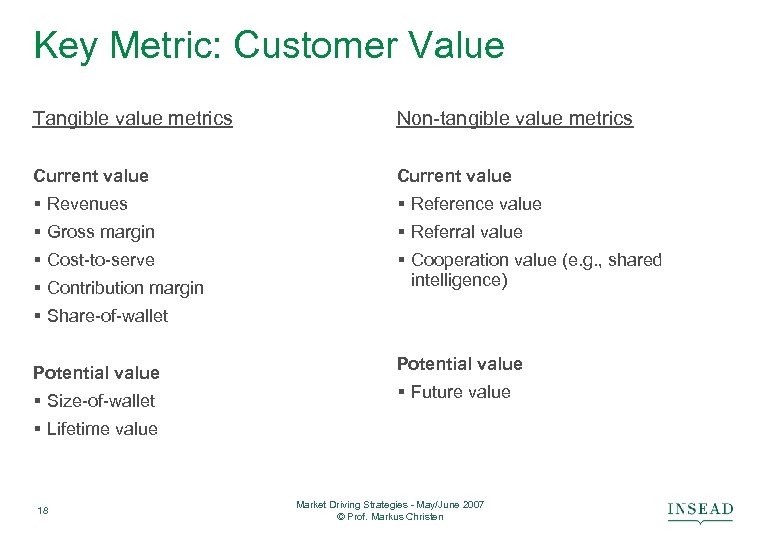 Key Metric: Customer Value Tangible value metrics Non-tangible value metrics Current value § Revenues § Reference value § Gross margin § Referral value § Cost-to-serve § Cooperation value (e. g. , shared intelligence) § Contribution margin § Share-of-wallet Potential value § Size-of-wallet Potential value § Future value § Lifetime value 18 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Key Metric: Customer Value Tangible value metrics Non-tangible value metrics Current value § Revenues § Reference value § Gross margin § Referral value § Cost-to-serve § Cooperation value (e. g. , shared intelligence) § Contribution margin § Share-of-wallet Potential value § Size-of-wallet Potential value § Future value § Lifetime value 18 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Customer Value Concentration Brazilian Grocery Store 19 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Customer Value Concentration Brazilian Grocery Store 19 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Customer Value Concentration US Pharmaceutical Firm 20 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Customer Value Concentration US Pharmaceutical Firm 20 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Customer Value Analysis § Objective: The result of the analysis should allow to evaluate the following: • Value level – Average value over all customers • Value disparity – Difference Highest – Lowest value – Ratio of 90 th percentile /10 th percentile (if > 15 then high disparity) • Value concentration (heterogeneity) – 80/20 rule (80% of contribution come from x% of customers) – Gini Coefficient (> 80% = high concentration) § All analyses to be done • Across all customers • On segment level (geography, business line, etc) 21 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Customer Value Analysis § Objective: The result of the analysis should allow to evaluate the following: • Value level – Average value over all customers • Value disparity – Difference Highest – Lowest value – Ratio of 90 th percentile /10 th percentile (if > 15 then high disparity) • Value concentration (heterogeneity) – 80/20 rule (80% of contribution come from x% of customers) – Gini Coefficient (> 80% = high concentration) § All analyses to be done • Across all customers • On segment level (geography, business line, etc) 21 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
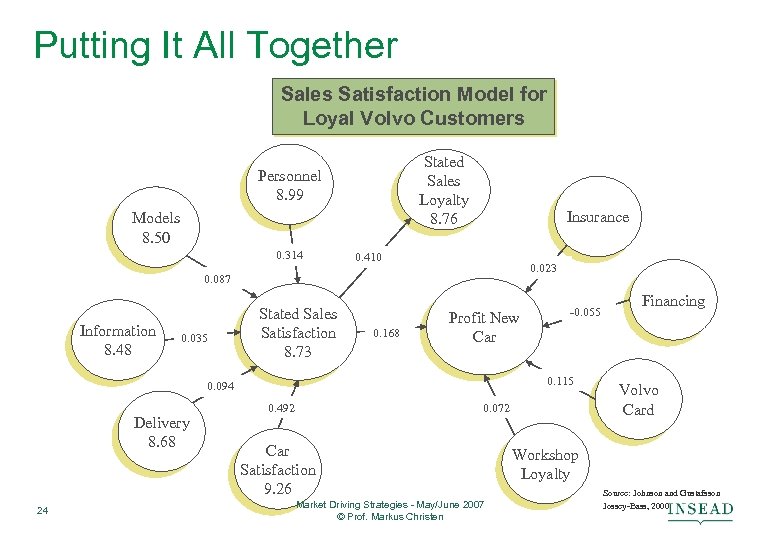 Putting It All Together Sales Satisfaction Model for Loyal Volvo Customers Stated Sales Loyalty 8. 76 Personnel 8. 99 Models 8. 50 0. 314 Insurance 0. 410 0. 023 0. 087 Information 8. 48 0. 035 Stated Sales Satisfaction 8. 73 0. 168 Profit New Car 0. 115 0. 094 Delivery 8. 68 24 -0. 055 0. 492 0. 072 Car Satisfaction 9. 26 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen Financing Volvo Card Workshop Loyalty Source: Johnson and Gustafsson Jossey-Bass, 2000
Putting It All Together Sales Satisfaction Model for Loyal Volvo Customers Stated Sales Loyalty 8. 76 Personnel 8. 99 Models 8. 50 0. 314 Insurance 0. 410 0. 023 0. 087 Information 8. 48 0. 035 Stated Sales Satisfaction 8. 73 0. 168 Profit New Car 0. 115 0. 094 Delivery 8. 68 24 -0. 055 0. 492 0. 072 Car Satisfaction 9. 26 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen Financing Volvo Card Workshop Loyalty Source: Johnson and Gustafsson Jossey-Bass, 2000
 Customer Focus 25 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Customer Focus 25 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Summary § S-P chain is a powerful concept for guiding customer-level actions • Its all about optimal satisfaction and optimal retention levels • Need for careful application to own environment – Necessitates “correct” measures and operationalizations – Forces to explore causal linkages – Sheds light on correct metrics 26 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Summary § S-P chain is a powerful concept for guiding customer-level actions • Its all about optimal satisfaction and optimal retention levels • Need for careful application to own environment – Necessitates “correct” measures and operationalizations – Forces to explore causal linkages – Sheds light on correct metrics 26 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Summary § Looking at value to and from customers • Provides focus: target only potentially profitable customers • Think about what drives customer value (to the firm) • Enables resource allocation that is fair from a customer perspective and makes business sense economically § CRM is the strategic process of selecting the customers a firm can most profitably serve and shaping the interactions between a company and these customers. § Ultimate goal: Improve marketing decision-making and resource allocation 27 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Summary § Looking at value to and from customers • Provides focus: target only potentially profitable customers • Think about what drives customer value (to the firm) • Enables resource allocation that is fair from a customer perspective and makes business sense economically § CRM is the strategic process of selecting the customers a firm can most profitably serve and shaping the interactions between a company and these customers. § Ultimate goal: Improve marketing decision-making and resource allocation 27 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
 Rule 10: Customer Value Not all happy customers are loyal customers and not all loyal customers are worth keeping: Measure & manage customer profitability 28 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen
Rule 10: Customer Value Not all happy customers are loyal customers and not all loyal customers are worth keeping: Measure & manage customer profitability 28 Market Driving Strategies - May/June 2007 © Prof. Markus Christen


