5442a10629b780fefff2ec8ebde8c83f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Customer Relationship Management Customer Actions Taken After Site Unresponsiveness Action Percent n Shopped elsewhere 74% n Sent another e-mail 45 n Called a store representative 32 n Other 8 n Asked elsewhere, bought at store 3 Source: Apr. 2000 Jupiter Media Metrix 1
Customer Relationship Management Customer Actions Taken After Site Unresponsiveness Action Percent n Shopped elsewhere 74% n Sent another e-mail 45 n Called a store representative 32 n Other 8 n Asked elsewhere, bought at store 3 Source: Apr. 2000 Jupiter Media Metrix 1
 Customer Relationship Management Who provides CRM? n Traditional giants such as IBM, Oracle and People. Soft n Siebel Systems, which now has a 21% share of the CRM market n E. piphany n e-mail specialist Kana Communications, Net. Genesis n instant chat provider Live. Person. com, Broadbase, Quintus and Firepond n plus many others. 2
Customer Relationship Management Who provides CRM? n Traditional giants such as IBM, Oracle and People. Soft n Siebel Systems, which now has a 21% share of the CRM market n E. piphany n e-mail specialist Kana Communications, Net. Genesis n instant chat provider Live. Person. com, Broadbase, Quintus and Firepond n plus many others. 2
 Customer Relationship Management Acquisition cost Quarter Average Customer Acquisition Cost n Q 3 1999 $35 n Q 4 1999 $71 n Q 1 2000 $45** n Q 2 2000 $40 Source: Aug. 2000 Boston Consulting Group/shop. org ** Shift from expensive TV advertising to more economical online campaigns 3
Customer Relationship Management Acquisition cost Quarter Average Customer Acquisition Cost n Q 3 1999 $35 n Q 4 1999 $71 n Q 1 2000 $45** n Q 2 2000 $40 Source: Aug. 2000 Boston Consulting Group/shop. org ** Shift from expensive TV advertising to more economical online campaigns 3
 Customer Relationship Management direct customer interaction Jupiter reports that n 76% of respondents say e-mail is an indispensable part of customer service. n a listed phone number (65%) and n a FAQ section (53%). But those e-mails must be answered promptly. 4
Customer Relationship Management direct customer interaction Jupiter reports that n 76% of respondents say e-mail is an indispensable part of customer service. n a listed phone number (65%) and n a FAQ section (53%). But those e-mails must be answered promptly. 4
 Customer Relationship Management n That's why IDC believes the worldwide market for CRM products and services will explode to $125 billion by 2004, from $34 billion last year. n This summer, the Federal Trade Commission fined Toysrus. com, Macys. com and five other online retailers $1. 5 million for making promises they couldn't keep during the 1999 holiday season. 5
Customer Relationship Management n That's why IDC believes the worldwide market for CRM products and services will explode to $125 billion by 2004, from $34 billion last year. n This summer, the Federal Trade Commission fined Toysrus. com, Macys. com and five other online retailers $1. 5 million for making promises they couldn't keep during the 1999 holiday season. 5
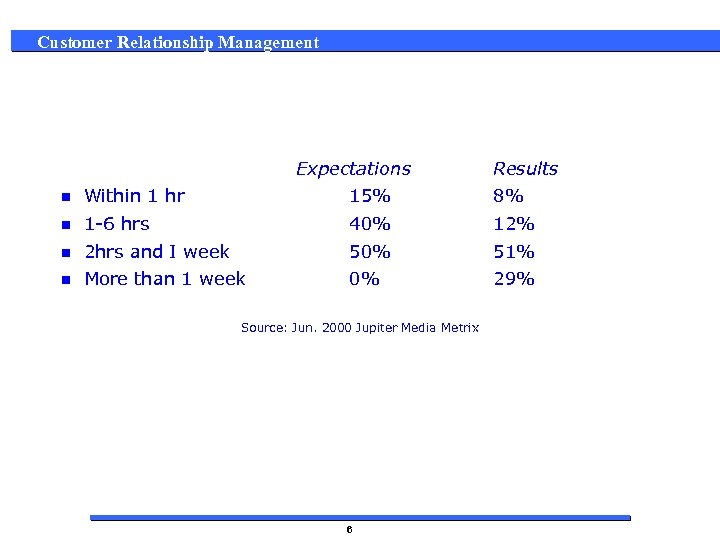 Customer Relationship Management Expectations Results n Within 1 hr 15% 8% n 1 -6 hrs 40% 12% n 2 hrs and I week 50% 51% n More than 1 week 0% 29% Source: Jun. 2000 Jupiter Media Metrix 6
Customer Relationship Management Expectations Results n Within 1 hr 15% 8% n 1 -6 hrs 40% 12% n 2 hrs and I week 50% 51% n More than 1 week 0% 29% Source: Jun. 2000 Jupiter Media Metrix 6
 Customer Relationship Management customer retention n The average online marketer needs three purchases to break even after acquiring a new customer, according to the survey. 7
Customer Relationship Management customer retention n The average online marketer needs three purchases to break even after acquiring a new customer, according to the survey. 7
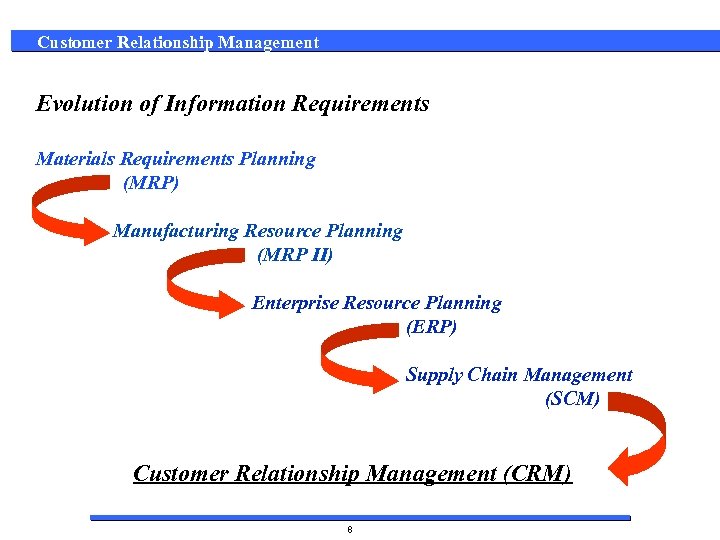 Customer Relationship Management Evolution of Information Requirements Materials Requirements Planning (MRP) Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Supply Chain Management (SCM) Customer Relationship Management (CRM) 8
Customer Relationship Management Evolution of Information Requirements Materials Requirements Planning (MRP) Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Supply Chain Management (SCM) Customer Relationship Management (CRM) 8
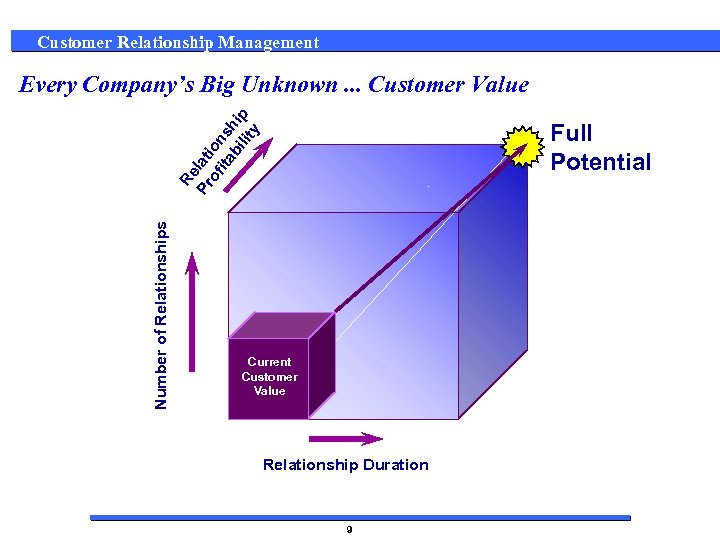 Customer Relationship Management Pr lati of on ita s bi hip lit y Every Company’s Big Unknown. . . Customer Value Number of Relationships Re Full Potential Current Customer Value Current Relationship Duration 9
Customer Relationship Management Pr lati of on ita s bi hip lit y Every Company’s Big Unknown. . . Customer Value Number of Relationships Re Full Potential Current Customer Value Current Relationship Duration 9
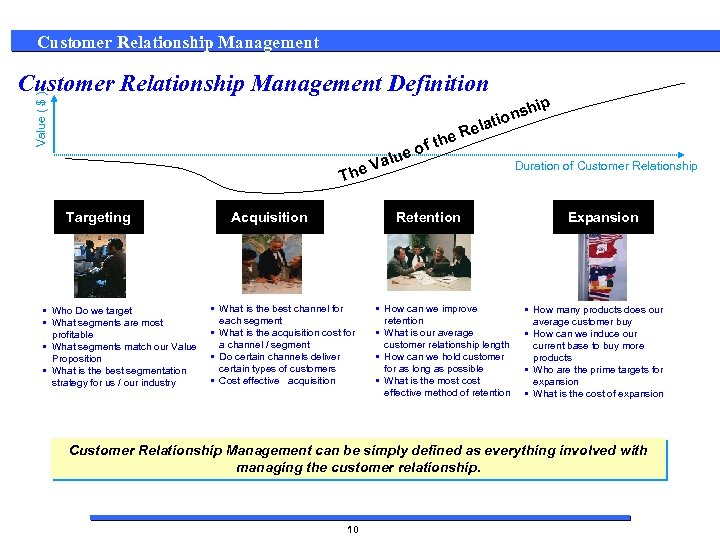 Customer Relationship Management Value ( $ ) Customer Relationship Management Definition he ft ue o al V The Targeting • Who Do we target • What segments are most profitable • What segments match our Value Proposition • What is the best segmentation strategy for us / our industry Acquisition Retention • What is the best channel for each segment • What is the acquisition cost for a channel / segment • Do certain channels deliver certain types of customers • Cost effective acquisition hip ns latio Re • How can we improve retention • What is our average customer relationship length • How can we hold customer for as long as possible • What is the most cost effective method of retention Duration of Customer Relationship Expansion • How many products does our average customer buy • How can we induce our current base to buy more products • Who are the prime targets for expansion • What is the cost of expansion Customer Relationship Management can be simply defined as everything involved with managing the customer relationship. 10
Customer Relationship Management Value ( $ ) Customer Relationship Management Definition he ft ue o al V The Targeting • Who Do we target • What segments are most profitable • What segments match our Value Proposition • What is the best segmentation strategy for us / our industry Acquisition Retention • What is the best channel for each segment • What is the acquisition cost for a channel / segment • Do certain channels deliver certain types of customers • Cost effective acquisition hip ns latio Re • How can we improve retention • What is our average customer relationship length • How can we hold customer for as long as possible • What is the most cost effective method of retention Duration of Customer Relationship Expansion • How many products does our average customer buy • How can we induce our current base to buy more products • Who are the prime targets for expansion • What is the cost of expansion Customer Relationship Management can be simply defined as everything involved with managing the customer relationship. 10
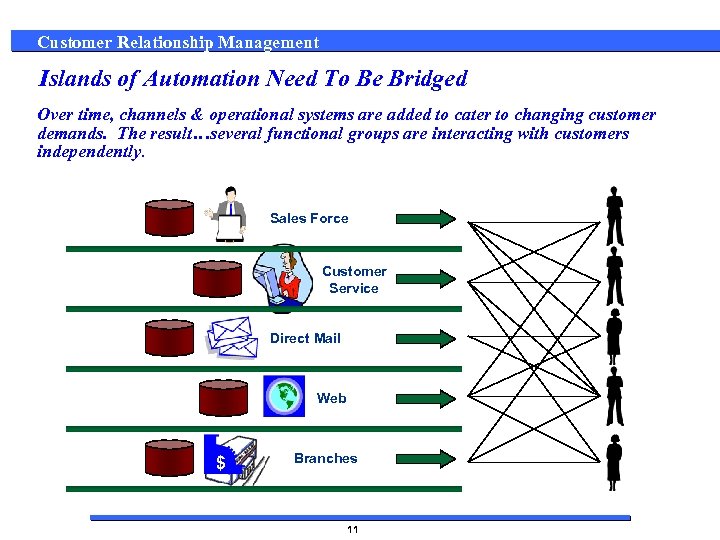 Customer Relationship Management Islands of Automation Need To Be Bridged Over time, channels & operational systems are added to cater to changing customer demands. The result…several functional groups are interacting with customers independently. Sales Force Customer Service Direct Mail Web $ Branches 11
Customer Relationship Management Islands of Automation Need To Be Bridged Over time, channels & operational systems are added to cater to changing customer demands. The result…several functional groups are interacting with customers independently. Sales Force Customer Service Direct Mail Web $ Branches 11
 Customer Relationship Management Why CRM? n n n It costs six times more to sell to new customer than to sell to an existing one. A typical dissatisfied customer will tell 8 -10 people By increasing the customer retention rate by 5%, profits could increase by by 85% Odds of selling to new customers = 15%, as compared to those for existing customers (50%) 70% of the complaining customers will remain loyal if problem is solved 90% of companies do not have the sales and service integration to support e-commerce 12
Customer Relationship Management Why CRM? n n n It costs six times more to sell to new customer than to sell to an existing one. A typical dissatisfied customer will tell 8 -10 people By increasing the customer retention rate by 5%, profits could increase by by 85% Odds of selling to new customers = 15%, as compared to those for existing customers (50%) 70% of the complaining customers will remain loyal if problem is solved 90% of companies do not have the sales and service integration to support e-commerce 12
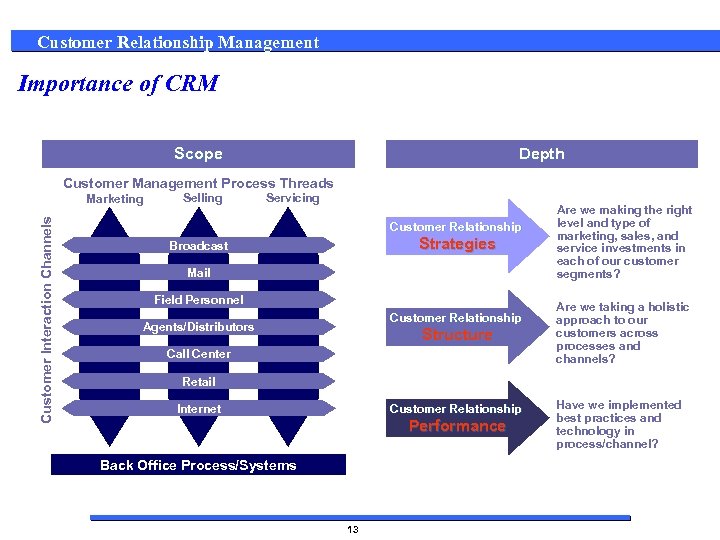 Customer Relationship Management Importance of CRM Scope Depth Customer Management Process Threads Customer Interaction Channels Marketing Selling Servicing Customer Relationship Strategies Broadcast Mail Field Personnel Customer Relationship Agents/Distributors Structure Call Center Are we making the right level and type of marketing, sales, and service investments in each of our customer segments? Are we taking a holistic approach to our customers across processes and channels? Retail Customer Relationship Internet Performance Back Office Process/Systems 13 Have we implemented best practices and technology in process/channel?
Customer Relationship Management Importance of CRM Scope Depth Customer Management Process Threads Customer Interaction Channels Marketing Selling Servicing Customer Relationship Strategies Broadcast Mail Field Personnel Customer Relationship Agents/Distributors Structure Call Center Are we making the right level and type of marketing, sales, and service investments in each of our customer segments? Are we taking a holistic approach to our customers across processes and channels? Retail Customer Relationship Internet Performance Back Office Process/Systems 13 Have we implemented best practices and technology in process/channel?
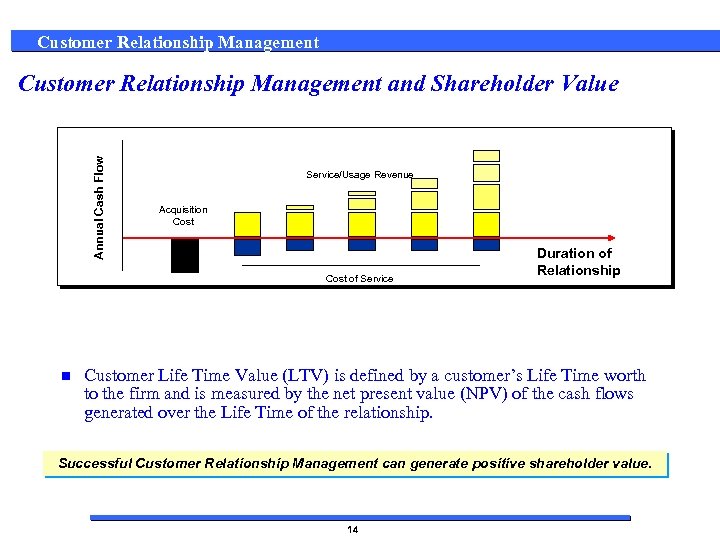 Customer Relationship Management Annual Cash Flow Customer Relationship Management and Shareholder Value Service/Usage Revenue Acquisition Cost of Service n Duration of Relationship Customer Life Time Value (LTV) is defined by a customer’s Life Time worth to the firm and is measured by the net present value (NPV) of the cash flows generated over the Life Time of the relationship. Successful Customer Relationship Management can generate positive shareholder value. 14
Customer Relationship Management Annual Cash Flow Customer Relationship Management and Shareholder Value Service/Usage Revenue Acquisition Cost of Service n Duration of Relationship Customer Life Time Value (LTV) is defined by a customer’s Life Time worth to the firm and is measured by the net present value (NPV) of the cash flows generated over the Life Time of the relationship. Successful Customer Relationship Management can generate positive shareholder value. 14
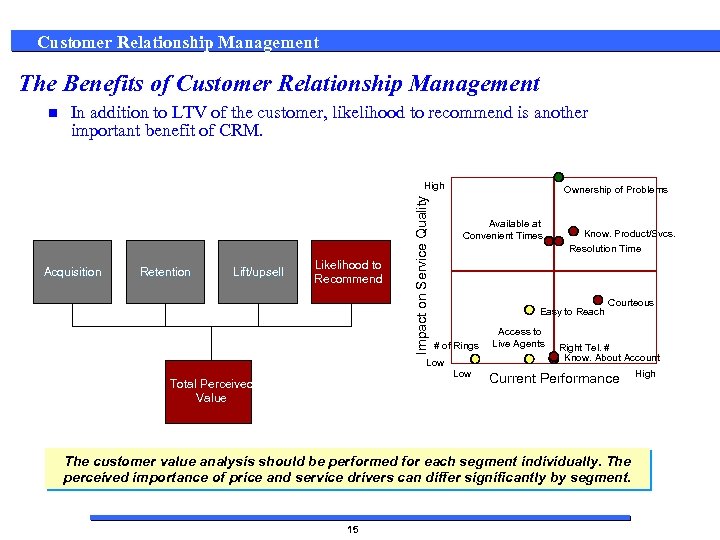 Customer Relationship Management The Benefits of Customer Relationship Management n In addition to LTV of the customer, likelihood to recommend is another important benefit of CRM. Acquisition Retention Lift/upsell Likelihood to Recommend Impact on Service Quality High Ownership of Problems Available at Convenient Times Easy to Reach # of Rings Low Total Perceived Value Know. Product/Svcs. Resolution Time Access to Live Agents Courteous Right Tel. # Know. About Account Current Performance The customer value analysis should be performed for each segment individually. The perceived importance of price and service drivers can differ significantly by segment. 15 High
Customer Relationship Management The Benefits of Customer Relationship Management n In addition to LTV of the customer, likelihood to recommend is another important benefit of CRM. Acquisition Retention Lift/upsell Likelihood to Recommend Impact on Service Quality High Ownership of Problems Available at Convenient Times Easy to Reach # of Rings Low Total Perceived Value Know. Product/Svcs. Resolution Time Access to Live Agents Courteous Right Tel. # Know. About Account Current Performance The customer value analysis should be performed for each segment individually. The perceived importance of price and service drivers can differ significantly by segment. 15 High
 Customer Relationship Management The Five Key Drivers of the Lifetime Value of a Customer n Cost of Targeting; n Cost of Acquisition; n Service and Usage Revenue; n Cost of service; and n Duration of relationship. Customer Relationship Management is about making every customer as valuable as possible over the lifetime of the relationship 16
Customer Relationship Management The Five Key Drivers of the Lifetime Value of a Customer n Cost of Targeting; n Cost of Acquisition; n Service and Usage Revenue; n Cost of service; and n Duration of relationship. Customer Relationship Management is about making every customer as valuable as possible over the lifetime of the relationship 16
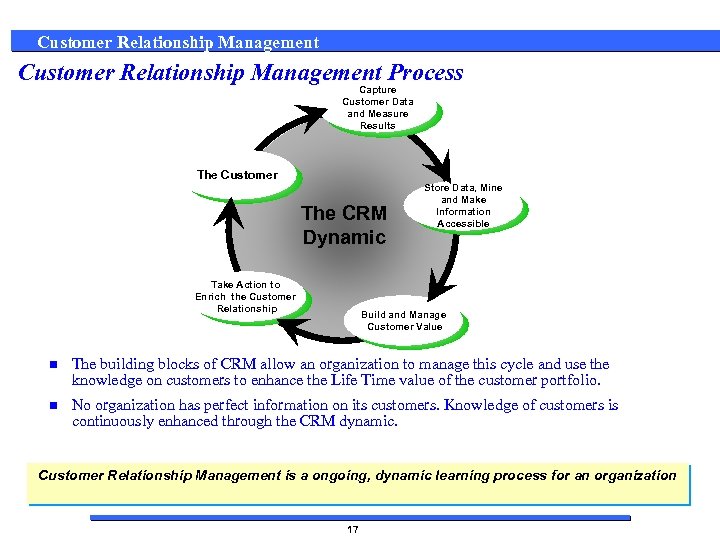 Customer Relationship Management Process Capture Customer Data and Measure Results Capture Customer The Customer Data and Measure Results The CRM Dynamic Take Action to Capture Customer Enrich the Customer Data and Measure Relationship Results Store Data, Mine Capture Customer and Make Data and Measure Information Results Accessible Capture Manage Build and Customer Data and Value Customer. Measure Results n The building blocks of CRM allow an organization to manage this cycle and use the knowledge on customers to enhance the Life Time value of the customer portfolio. n No organization has perfect information on its customers. Knowledge of customers is continuously enhanced through the CRM dynamic. Customer Relationship Management is a ongoing, dynamic learning process for an organization 17
Customer Relationship Management Process Capture Customer Data and Measure Results Capture Customer The Customer Data and Measure Results The CRM Dynamic Take Action to Capture Customer Enrich the Customer Data and Measure Relationship Results Store Data, Mine Capture Customer and Make Data and Measure Information Results Accessible Capture Manage Build and Customer Data and Value Customer. Measure Results n The building blocks of CRM allow an organization to manage this cycle and use the knowledge on customers to enhance the Life Time value of the customer portfolio. n No organization has perfect information on its customers. Knowledge of customers is continuously enhanced through the CRM dynamic. Customer Relationship Management is a ongoing, dynamic learning process for an organization 17
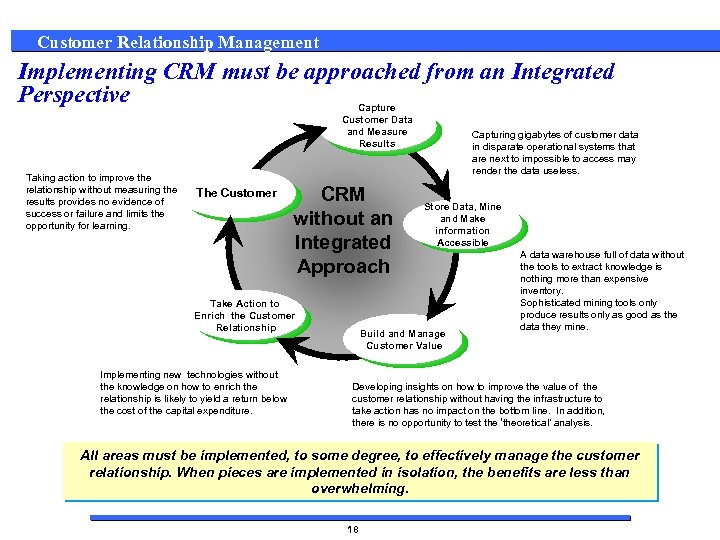 Customer Relationship Management Implementing CRM must be approached from an Integrated Perspective Capture Customer Data and Measure Results Taking action to improve the relationship without measuring the results provides no evidence of success or failure and limits the opportunity for learning. Capture Customer The Customer Data and Measure Results CRM without an Integrated Approach Take Action to Capture Customer Enrich the Customer Data and Measure Relationship Results Implementing new technologies without the knowledge on how to enrich the relationship is likely to yield a return below the cost of the capital expenditure. Capturing gigabytes of customer data in disparate operational systems that are next to impossible to access may render the data useless. Store Data, Mine Capture Customer and Make Data and Measure information Results Accessible Capture Manage Build and Customer Data and Measure Customer Value Results A data warehouse full of data without the tools to extract knowledge is nothing more than expensive inventory. Sophisticated mining tools only produce results only as good as the data they mine. Developing insights on how to improve the value of the customer relationship without having the infrastructure to take action has no impact on the bottom line. In addition, there is no opportunity to test the ‘theoretical’ analysis. All areas must be implemented, to some degree, to effectively manage the customer relationship. When pieces are implemented in isolation, the benefits are less than overwhelming. 18
Customer Relationship Management Implementing CRM must be approached from an Integrated Perspective Capture Customer Data and Measure Results Taking action to improve the relationship without measuring the results provides no evidence of success or failure and limits the opportunity for learning. Capture Customer The Customer Data and Measure Results CRM without an Integrated Approach Take Action to Capture Customer Enrich the Customer Data and Measure Relationship Results Implementing new technologies without the knowledge on how to enrich the relationship is likely to yield a return below the cost of the capital expenditure. Capturing gigabytes of customer data in disparate operational systems that are next to impossible to access may render the data useless. Store Data, Mine Capture Customer and Make Data and Measure information Results Accessible Capture Manage Build and Customer Data and Measure Customer Value Results A data warehouse full of data without the tools to extract knowledge is nothing more than expensive inventory. Sophisticated mining tools only produce results only as good as the data they mine. Developing insights on how to improve the value of the customer relationship without having the infrastructure to take action has no impact on the bottom line. In addition, there is no opportunity to test the ‘theoretical’ analysis. All areas must be implemented, to some degree, to effectively manage the customer relationship. When pieces are implemented in isolation, the benefits are less than overwhelming. 18
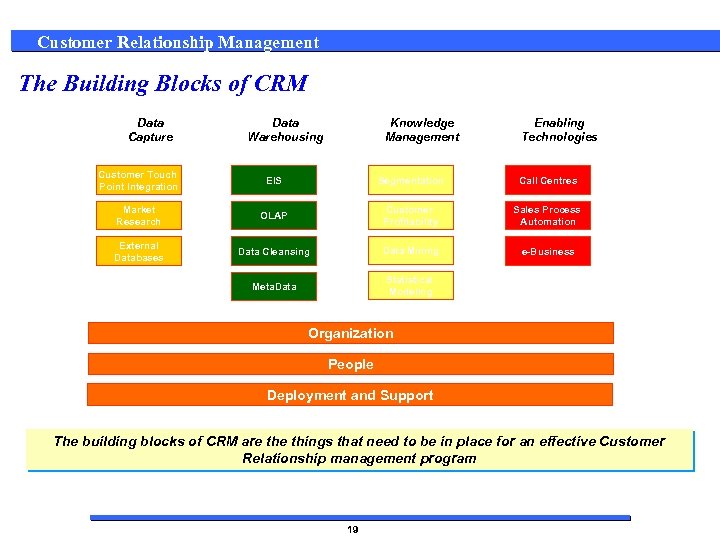 Customer Relationship Management The Building Blocks of CRM Data Capture Data Warehousing Knowledge Management Enabling Technologies Customer Touch Point Integration EIS Segmentation Call Centres Market Research OLAP Customer Profitability Sales Process Automation External Databases Data Cleansing Data Mining e-Business Meta. Data Statistical Modeling Organization People Deployment and Support The building blocks of CRM are things that need to be in place for an effective Customer Relationship management program 19
Customer Relationship Management The Building Blocks of CRM Data Capture Data Warehousing Knowledge Management Enabling Technologies Customer Touch Point Integration EIS Segmentation Call Centres Market Research OLAP Customer Profitability Sales Process Automation External Databases Data Cleansing Data Mining e-Business Meta. Data Statistical Modeling Organization People Deployment and Support The building blocks of CRM are things that need to be in place for an effective Customer Relationship management program 19
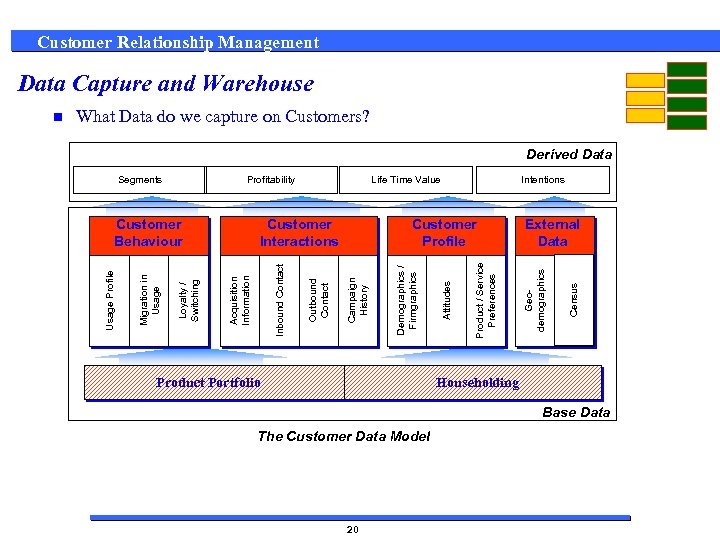 Customer Relationship Management Data Capture and Warehouse What Data do we capture on Customers? Derived Data Intentions Product Portfolio External Data Census Product / Service Preferences Attitudes Demographics / Firmgraphics Customer Profile Campaign History Outbound Contact Customer Interactions Acquisition Information Loyalty / Switching Migration in Usage Customer Behaviour Life Time Value Geodemographics Profitability Inbound Contact Segments Usage Profile n Householding Base Data The Customer Data Model 20
Customer Relationship Management Data Capture and Warehouse What Data do we capture on Customers? Derived Data Intentions Product Portfolio External Data Census Product / Service Preferences Attitudes Demographics / Firmgraphics Customer Profile Campaign History Outbound Contact Customer Interactions Acquisition Information Loyalty / Switching Migration in Usage Customer Behaviour Life Time Value Geodemographics Profitability Inbound Contact Segments Usage Profile n Householding Base Data The Customer Data Model 20
 Customer Relationship Management Enabling Technologies 21
Customer Relationship Management Enabling Technologies 21
 Customer Relationship Management The Enabling Technologies n Call Centre n Sales Force Automation n e-Business Techniques: Relationship marketing, automated packaging and pricing, knowledge-based selling • Increase revenue from your customer base • Customer satisfaction measure • Consultative selling • Responsiveness to market conditions Sales Force Automation Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) Incoming Call Queuing Performance Statistics Integrated Voice Response (IVR) Automated Inquiry & Transactions Automated screen “pop” on agent’s screen • Integration with company legacy platforms • Billing & Meter Reading • Direct Access to Customer Data CRM Call Centre • • • Technologies 22 Electronic Business Techniques: ACD, IVR, CTI Techniques: WEB based application, e-mail processing • Automated product and service information • WEB based sales and support through standard menus and automated help screens. • WEB based training • Reaching the global market
Customer Relationship Management The Enabling Technologies n Call Centre n Sales Force Automation n e-Business Techniques: Relationship marketing, automated packaging and pricing, knowledge-based selling • Increase revenue from your customer base • Customer satisfaction measure • Consultative selling • Responsiveness to market conditions Sales Force Automation Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) Incoming Call Queuing Performance Statistics Integrated Voice Response (IVR) Automated Inquiry & Transactions Automated screen “pop” on agent’s screen • Integration with company legacy platforms • Billing & Meter Reading • Direct Access to Customer Data CRM Call Centre • • • Technologies 22 Electronic Business Techniques: ACD, IVR, CTI Techniques: WEB based application, e-mail processing • Automated product and service information • WEB based sales and support through standard menus and automated help screens. • WEB based training • Reaching the global market
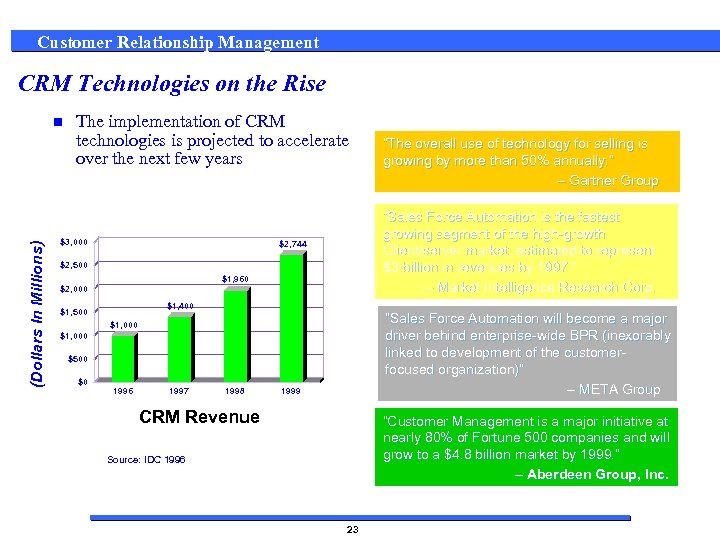 Customer Relationship Management CRM Technologies on the Rise (Dollars In Millions) n The implementation of CRM technologies is projected to accelerate over the next few years $3, 000 “Sales Force Automation is the fastest growing segment of the high-growth Client/server market, estimated to represent $3 billion in revenues by 1997. ” – Market Intelligence Research Corp. $2, 744 $2, 500 $1, 960 $2, 000 $1, 400 $1, 500 “Sales Force Automation will become a major driver behind enterprise-wide BPR (inexorably linked to development of the customerfocused organization)” – META Group $1, 000 $500 $0 1996 1997 1998 “The overall use of technology for selling is growing by more than 50% annually. ” – Gartner Group 1999 CRM Revenue “Customer Management is a major initiative at nearly 80% of Fortune 500 companies and will grow to a $4. 8 billion market by 1999. ” – Aberdeen Group, Inc. Source: IDC 1996 23
Customer Relationship Management CRM Technologies on the Rise (Dollars In Millions) n The implementation of CRM technologies is projected to accelerate over the next few years $3, 000 “Sales Force Automation is the fastest growing segment of the high-growth Client/server market, estimated to represent $3 billion in revenues by 1997. ” – Market Intelligence Research Corp. $2, 744 $2, 500 $1, 960 $2, 000 $1, 400 $1, 500 “Sales Force Automation will become a major driver behind enterprise-wide BPR (inexorably linked to development of the customerfocused organization)” – META Group $1, 000 $500 $0 1996 1997 1998 “The overall use of technology for selling is growing by more than 50% annually. ” – Gartner Group 1999 CRM Revenue “Customer Management is a major initiative at nearly 80% of Fortune 500 companies and will grow to a $4. 8 billion market by 1999. ” – Aberdeen Group, Inc. Source: IDC 1996 23
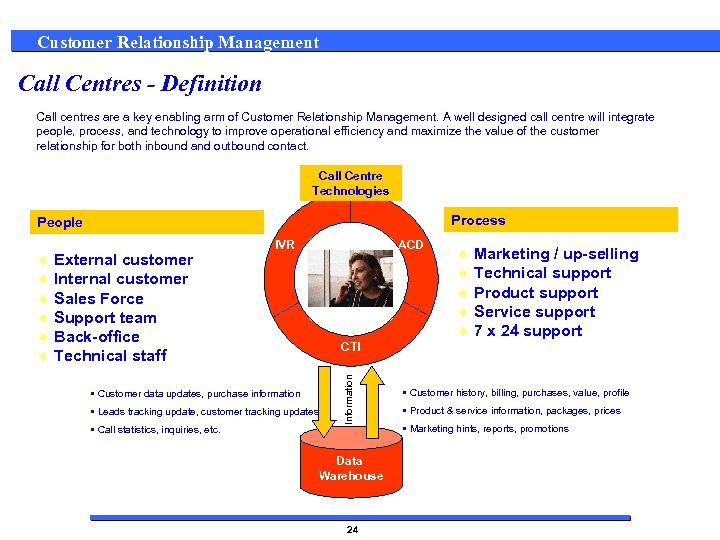 Customer Relationship Management Call Centres - Definition Call centres are a key enabling arm of Customer Relationship Management. A well designed call centre will integrate people, process, and technology to improve operational efficiency and maximize the value of the customer relationship for both inbound and outbound contact. Call Centre Technologies Process People ACD • Customer data updates, purchase information • Leads tracking update, customer tracking updates • Call statistics, inquiries, etc. ¨ Marketing / up-selling ¨ Technical support ¨ Product support ¨ Service support ¨ 7 x 24 support CTI Information ¨ External customer ¨ Internal customer ¨ Sales Force ¨ Support team ¨ Back-office ¨ Technical staff IVR Data Warehouse 24 • Customer history, billing, purchases, value, profile • Product & service information, packages, prices • Marketing hints, reports, promotions
Customer Relationship Management Call Centres - Definition Call centres are a key enabling arm of Customer Relationship Management. A well designed call centre will integrate people, process, and technology to improve operational efficiency and maximize the value of the customer relationship for both inbound and outbound contact. Call Centre Technologies Process People ACD • Customer data updates, purchase information • Leads tracking update, customer tracking updates • Call statistics, inquiries, etc. ¨ Marketing / up-selling ¨ Technical support ¨ Product support ¨ Service support ¨ 7 x 24 support CTI Information ¨ External customer ¨ Internal customer ¨ Sales Force ¨ Support team ¨ Back-office ¨ Technical staff IVR Data Warehouse 24 • Customer history, billing, purchases, value, profile • Product & service information, packages, prices • Marketing hints, reports, promotions
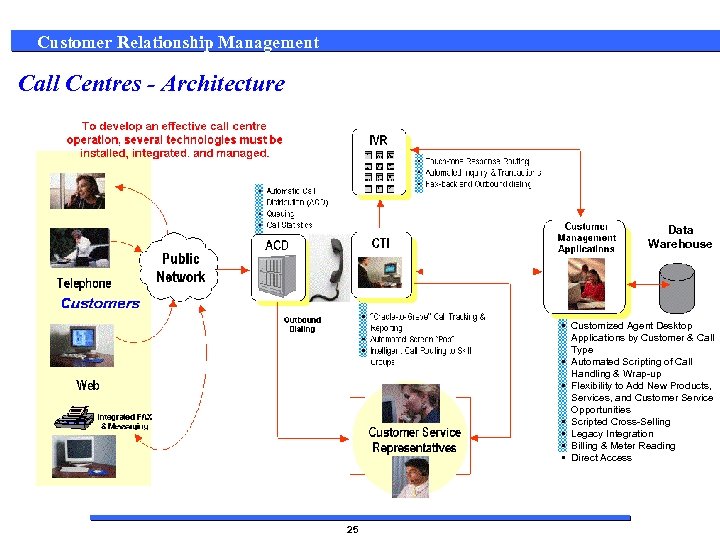 Customer Relationship Management Call Centres - Architecture Data Warehouse • Customized Agent Desktop Applications by Customer & Call Type • Automated Scripting of Call Handling & Wrap-up • Flexibility to Add New Products, Services, and Customer Service Opportunities • Scripted Cross-Selling • Legacy Integration • Billing & Meter Reading • Direct Access 25
Customer Relationship Management Call Centres - Architecture Data Warehouse • Customized Agent Desktop Applications by Customer & Call Type • Automated Scripting of Call Handling & Wrap-up • Flexibility to Add New Products, Services, and Customer Service Opportunities • Scripted Cross-Selling • Legacy Integration • Billing & Meter Reading • Direct Access 25
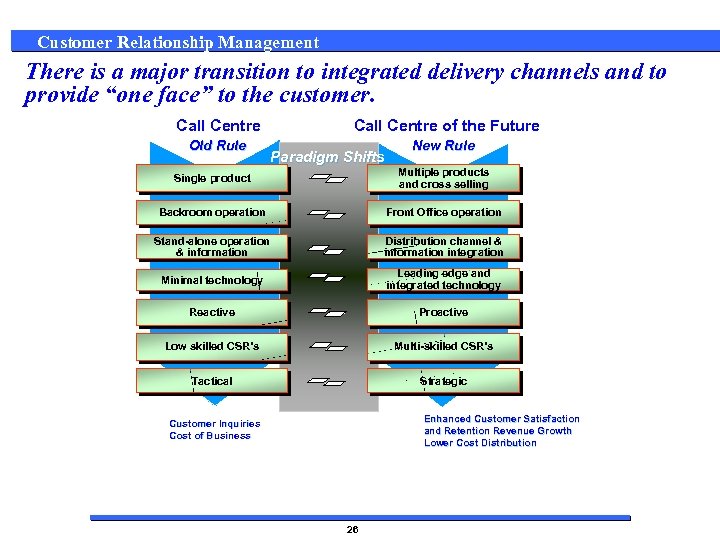 Customer Relationship Management There is a major transition to integrated delivery channels and to provide “one face” to the customer. Call Centre Old Rule Call Centre of the Future Paradigm Shifts New Rule Single product Multiple products and cross selling Backroom operation Front Office operation Stand-alone operation & information Distribution channel & information integration Minimal technology Leading edge and integrated technology Reactive Proactive Low skilled CSR’s Multi-skilled CSR’s Tactical Strategic Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Retention Revenue Growth Lower Cost Distribution Customer Inquiries Cost of Business 26
Customer Relationship Management There is a major transition to integrated delivery channels and to provide “one face” to the customer. Call Centre Old Rule Call Centre of the Future Paradigm Shifts New Rule Single product Multiple products and cross selling Backroom operation Front Office operation Stand-alone operation & information Distribution channel & information integration Minimal technology Leading edge and integrated technology Reactive Proactive Low skilled CSR’s Multi-skilled CSR’s Tactical Strategic Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Retention Revenue Growth Lower Cost Distribution Customer Inquiries Cost of Business 26
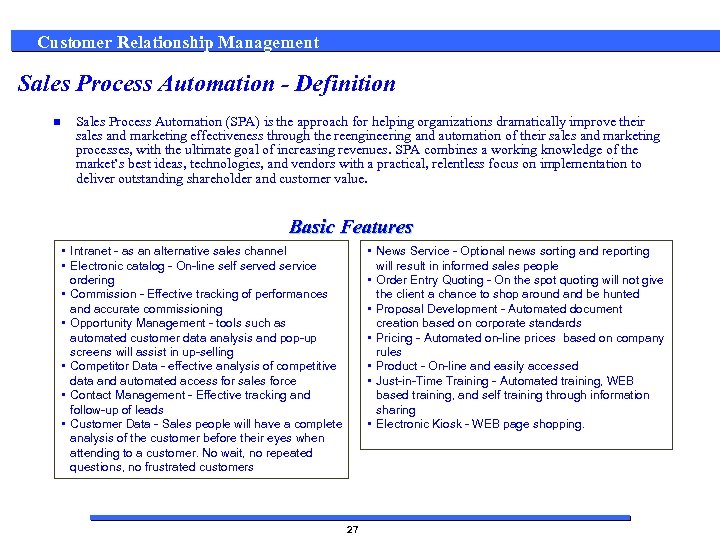 Customer Relationship Management Sales Process Automation - Definition n Sales Process Automation (SPA) is the approach for helping organizations dramatically improve their sales and marketing effectiveness through the reengineering and automation of their sales and marketing processes, with the ultimate goal of increasing revenues. SPA combines a working knowledge of the market’s best ideas, technologies, and vendors with a practical, relentless focus on implementation to deliver outstanding shareholder and customer value. Basic Features • Intranet - as an alternative sales channel • Electronic catalog - On-line self served service ordering • Commission - Effective tracking of performances and accurate commissioning • Opportunity Management - tools such as automated customer data analysis and pop-up screens will assist in up-selling • Competitor Data - effective analysis of competitive data and automated access for sales force • Contact Management - Effective tracking and follow-up of leads • Customer Data - Sales people will have a complete analysis of the customer before their eyes when attending to a customer. No wait, no repeated questions, no frustrated customers • News Service - Optional news sorting and reporting will result in informed sales people • Order Entry Quoting - On the spot quoting will not give the client a chance to shop around and be hunted • Proposal Development - Automated document creation based on corporate standards • Pricing - Automated on-line prices based on company rules • Product - On-line and easily accessed • Just-in-Time Training - Automated training, WEB based training, and self training through information sharing • Electronic Kiosk - WEB page shopping. 27
Customer Relationship Management Sales Process Automation - Definition n Sales Process Automation (SPA) is the approach for helping organizations dramatically improve their sales and marketing effectiveness through the reengineering and automation of their sales and marketing processes, with the ultimate goal of increasing revenues. SPA combines a working knowledge of the market’s best ideas, technologies, and vendors with a practical, relentless focus on implementation to deliver outstanding shareholder and customer value. Basic Features • Intranet - as an alternative sales channel • Electronic catalog - On-line self served service ordering • Commission - Effective tracking of performances and accurate commissioning • Opportunity Management - tools such as automated customer data analysis and pop-up screens will assist in up-selling • Competitor Data - effective analysis of competitive data and automated access for sales force • Contact Management - Effective tracking and follow-up of leads • Customer Data - Sales people will have a complete analysis of the customer before their eyes when attending to a customer. No wait, no repeated questions, no frustrated customers • News Service - Optional news sorting and reporting will result in informed sales people • Order Entry Quoting - On the spot quoting will not give the client a chance to shop around and be hunted • Proposal Development - Automated document creation based on corporate standards • Pricing - Automated on-line prices based on company rules • Product - On-line and easily accessed • Just-in-Time Training - Automated training, WEB based training, and self training through information sharing • Electronic Kiosk - WEB page shopping. 27
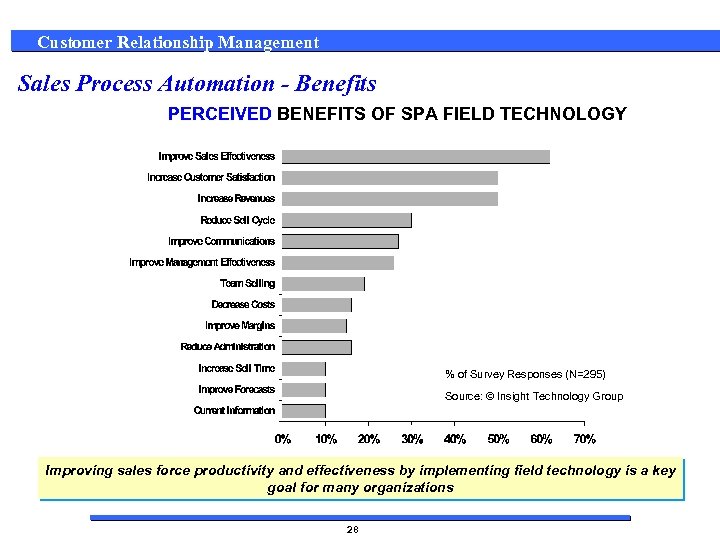 Customer Relationship Management Sales Process Automation - Benefits PERCEIVED BENEFITS OF SPA FIELD TECHNOLOGY % of Survey Responses (N=295) Source: © Insight Technology Group Improving sales force productivity and effectiveness by implementing field technology is a key goal for many organizations 28
Customer Relationship Management Sales Process Automation - Benefits PERCEIVED BENEFITS OF SPA FIELD TECHNOLOGY % of Survey Responses (N=295) Source: © Insight Technology Group Improving sales force productivity and effectiveness by implementing field technology is a key goal for many organizations 28
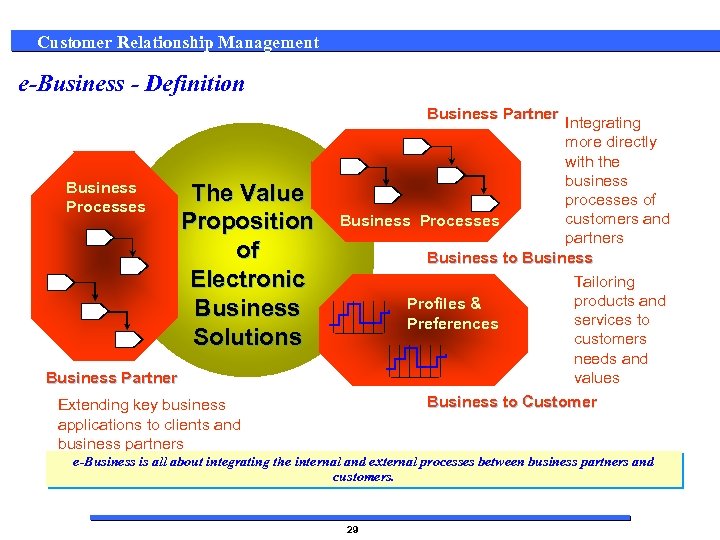 Customer Relationship Management e-Business - Definition Business Partner Business Processes The Value Proposition of Electronic Business Solutions Business Partner Integrating more directly with the business processes of customers and Business Processes partners Business to Business Tailoring products and Profiles & services to Preferences customers needs and values Business to Customer Extending key business applications to clients and business partners e-Business is all about integrating the internal and external processes between business partners and customers. 29
Customer Relationship Management e-Business - Definition Business Partner Business Processes The Value Proposition of Electronic Business Solutions Business Partner Integrating more directly with the business processes of customers and Business Processes partners Business to Business Tailoring products and Profiles & services to Preferences customers needs and values Business to Customer Extending key business applications to clients and business partners e-Business is all about integrating the internal and external processes between business partners and customers. 29
 Customer Relationship Management e-Business - Benefits n On average, it costs about $5 - $50 per query to support via phone n On average, it costs about $1 - $3 per query to support via E-mail n On average, it cost less than $1 per query to support via WWW Internet technology can improve the level of customer care, while reducing the cost of maintaining the customer base. 30
Customer Relationship Management e-Business - Benefits n On average, it costs about $5 - $50 per query to support via phone n On average, it costs about $1 - $3 per query to support via E-mail n On average, it cost less than $1 per query to support via WWW Internet technology can improve the level of customer care, while reducing the cost of maintaining the customer base. 30
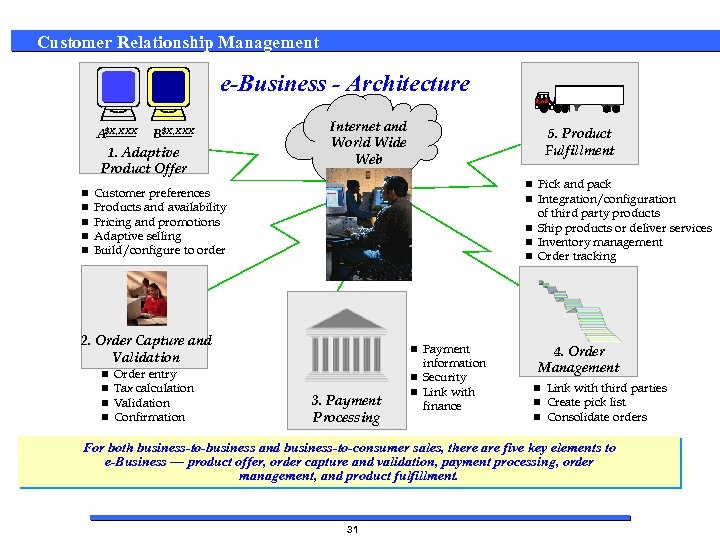 Customer Relationship Management e-Business - Architecture A$X, XXX B$X, XXX 1. Adaptive Product Offer n n n Internet and World Wide Web 5. Product Fulfillment n Pick and pack n Integration/configuration Customer preferences Products and availability Pricing and promotions Adaptive selling Build/configure to order of third party products n Ship products or deliver services n Inventory management n Order tracking 2. Order Capture and Validation n n Order entry Tax calculation Validation Confirmation n Payment 3. Payment Processing information n Security n Link with finance 4. Order Management n Link with third parties n Create pick list n Consolidate orders For both business-to-business and business-to-consumer sales, there are five key elements to e-Business — product offer, order capture and validation, payment processing, order management, and product fulfillment. 31
Customer Relationship Management e-Business - Architecture A$X, XXX B$X, XXX 1. Adaptive Product Offer n n n Internet and World Wide Web 5. Product Fulfillment n Pick and pack n Integration/configuration Customer preferences Products and availability Pricing and promotions Adaptive selling Build/configure to order of third party products n Ship products or deliver services n Inventory management n Order tracking 2. Order Capture and Validation n n Order entry Tax calculation Validation Confirmation n Payment 3. Payment Processing information n Security n Link with finance 4. Order Management n Link with third parties n Create pick list n Consolidate orders For both business-to-business and business-to-consumer sales, there are five key elements to e-Business — product offer, order capture and validation, payment processing, order management, and product fulfillment. 31
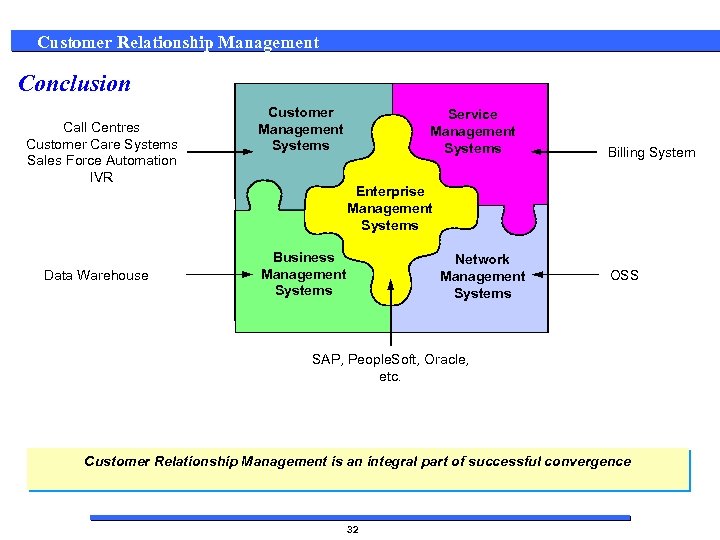 Customer Relationship Management Conclusion Call Centres Customer Care Systems Sales Force Automation IVR Data Warehouse Customer Management Systems Service Management Systems Billing System Enterprise Management Systems Business Management Systems Network Management Systems OSS SAP, People. Soft, Oracle, etc. Customer Relationship Management is an integral part of successful convergence 32
Customer Relationship Management Conclusion Call Centres Customer Care Systems Sales Force Automation IVR Data Warehouse Customer Management Systems Service Management Systems Billing System Enterprise Management Systems Business Management Systems Network Management Systems OSS SAP, People. Soft, Oracle, etc. Customer Relationship Management is an integral part of successful convergence 32
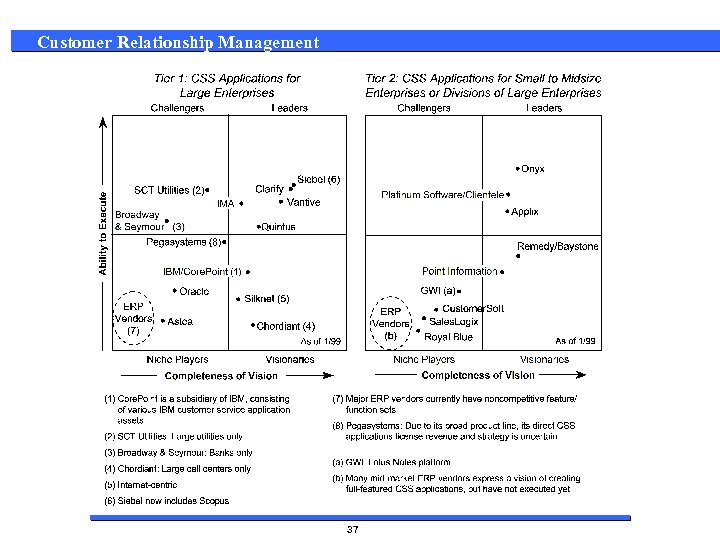
 Customer Relationship Management The CRM Market 33
Customer Relationship Management The CRM Market 33
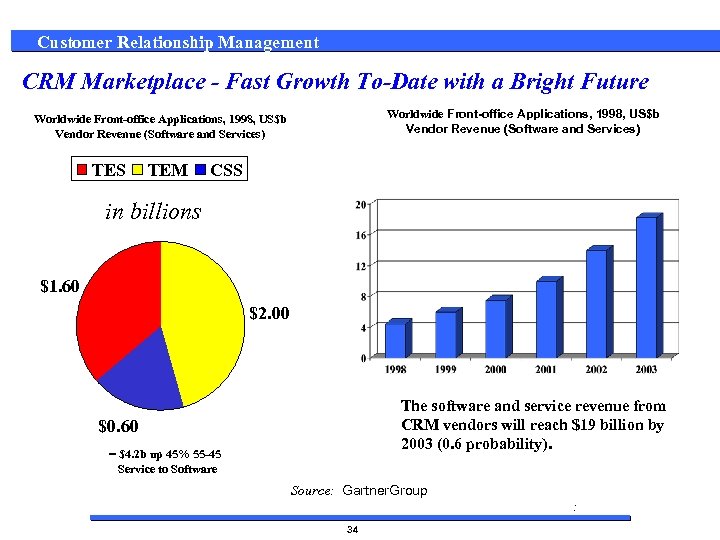 Customer Relationship Management CRM Marketplace - Fast Growth To-Date with a Bright Future Worldwide Front-office Applications, 1998, US$b Vendor Revenue (Software and Services) TES TEM CSS in billions $1. 60 $2. 00 The software and service revenue from CRM vendors will reach $19 billion by 2003 (0. 6 probability). $0. 60 = $4. 2 b up 45% 55 -45 Service to Software Source: Gartner. Group : 34
Customer Relationship Management CRM Marketplace - Fast Growth To-Date with a Bright Future Worldwide Front-office Applications, 1998, US$b Vendor Revenue (Software and Services) TES TEM CSS in billions $1. 60 $2. 00 The software and service revenue from CRM vendors will reach $19 billion by 2003 (0. 6 probability). $0. 60 = $4. 2 b up 45% 55 -45 Service to Software Source: Gartner. Group : 34
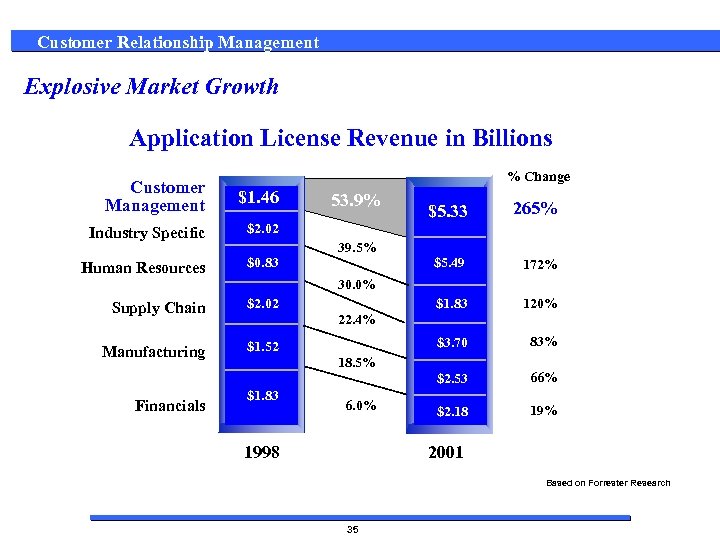 Customer Relationship Management Explosive Market Growth Application License Revenue in Billions % Change Customer Management $1. 46 Industry Specific $2. 02 Human Resources $0. 83 53. 9% 265% $5. 49 172% $1. 83 120% $3. 70 83% $2. 53 39. 5% $5. 33 66% $2. 18 19% 30. 0% Supply Chain $2. 02 Manufacturing $1. 52 Financials 22. 4% 18. 5% $1. 83 6. 0% 1998 2001 Based on Forrester Research 35
Customer Relationship Management Explosive Market Growth Application License Revenue in Billions % Change Customer Management $1. 46 Industry Specific $2. 02 Human Resources $0. 83 53. 9% 265% $5. 49 172% $1. 83 120% $3. 70 83% $2. 53 39. 5% $5. 33 66% $2. 18 19% 30. 0% Supply Chain $2. 02 Manufacturing $1. 52 Financials 22. 4% 18. 5% $1. 83 6. 0% 1998 2001 Based on Forrester Research 35
 Customer Relationship Management The CRM Market - No Clear Market Leader n 60% of the $2. 0 B CRM software license market is controlled by 3 vendors §Siebel §Trilogy §Baan/Aurum n 60% of the Top 3 share is controlled by Siebel n No vendor will have complete CRM functionality until 2003 (Gartner) n The 1998 consulting market for CRM is estimated to be $4. 0 B (2: 1) n The consulting market for CRM is a large and growing high margin / high revenue opportunity in contrast to the shrinking ERP market 36
Customer Relationship Management The CRM Market - No Clear Market Leader n 60% of the $2. 0 B CRM software license market is controlled by 3 vendors §Siebel §Trilogy §Baan/Aurum n 60% of the Top 3 share is controlled by Siebel n No vendor will have complete CRM functionality until 2003 (Gartner) n The 1998 consulting market for CRM is estimated to be $4. 0 B (2: 1) n The consulting market for CRM is a large and growing high margin / high revenue opportunity in contrast to the shrinking ERP market 36
 Customer Relationship Management 37
Customer Relationship Management 37
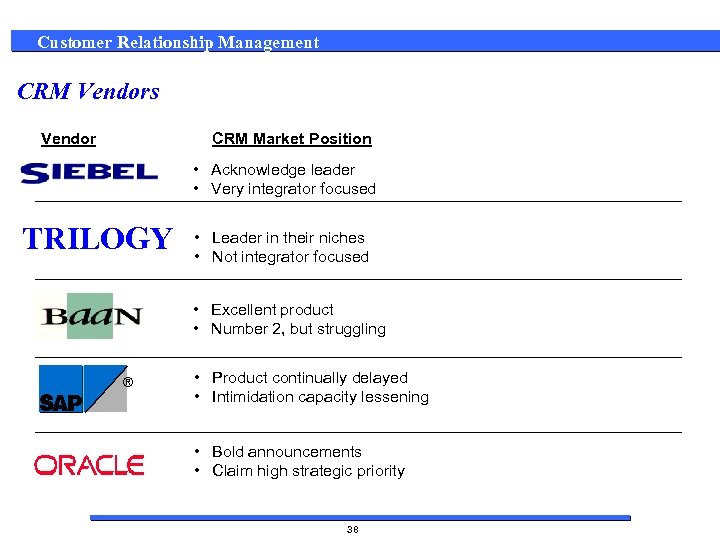 Customer Relationship Management CRM Vendors Vendor CRM Market Position • Acknowledge leader • Very integrator focused TRILOGY • Leader in their niches • Not integrator focused • Excellent product • Number 2, but struggling ® • Product continually delayed • Intimidation capacity lessening • Bold announcements • Claim high strategic priority 38
Customer Relationship Management CRM Vendors Vendor CRM Market Position • Acknowledge leader • Very integrator focused TRILOGY • Leader in their niches • Not integrator focused • Excellent product • Number 2, but struggling ® • Product continually delayed • Intimidation capacity lessening • Bold announcements • Claim high strategic priority 38
 Customer Relationship Management Siebel 99 n Siebel Sales Enterprise™ n Siebel Marketing Enterprise™ n Siebel Service Enterprise™ n Siebel Call Center™ n Siebel Field Service™ n Siebel Handheld™ n Siebel Inter. Active ™ n Siebel Product Configurator ™ n Siebel Sales ™ The Most Complete ERM Solution 39
Customer Relationship Management Siebel 99 n Siebel Sales Enterprise™ n Siebel Marketing Enterprise™ n Siebel Service Enterprise™ n Siebel Call Center™ n Siebel Field Service™ n Siebel Handheld™ n Siebel Inter. Active ™ n Siebel Product Configurator ™ n Siebel Sales ™ The Most Complete ERM Solution 39
 Customer Relationship Management Siebel Industry Solutions n Siebel Finance™ n Siebel Insurance™ n Siebel Communications™ n Siebel Consumer Goods™ n Siebel Pharma™ n Siebel Utilities™ n Siebel Public Sector™ n Siebel High Technology™ 40
Customer Relationship Management Siebel Industry Solutions n Siebel Finance™ n Siebel Insurance™ n Siebel Communications™ n Siebel Consumer Goods™ n Siebel Pharma™ n Siebel Utilities™ n Siebel Public Sector™ n Siebel High Technology™ 40
 Customer Relationship Management Siebel 99 Product n More than 600 Person Years of Engineering n 1100 Screens n 1300 Business Objects/Components n 110 Reports n 900 Database Tables n 144 Interface Tables 41
Customer Relationship Management Siebel 99 Product n More than 600 Person Years of Engineering n 1100 Screens n 1300 Business Objects/Components n 110 Reports n 900 Database Tables n 144 Interface Tables 41


