aed824c51568f2e578e5acbd88abefe7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Customer Relationship Management CRM: Part of Chapter 4
Customer Relationship Management CRM: Part of Chapter 4
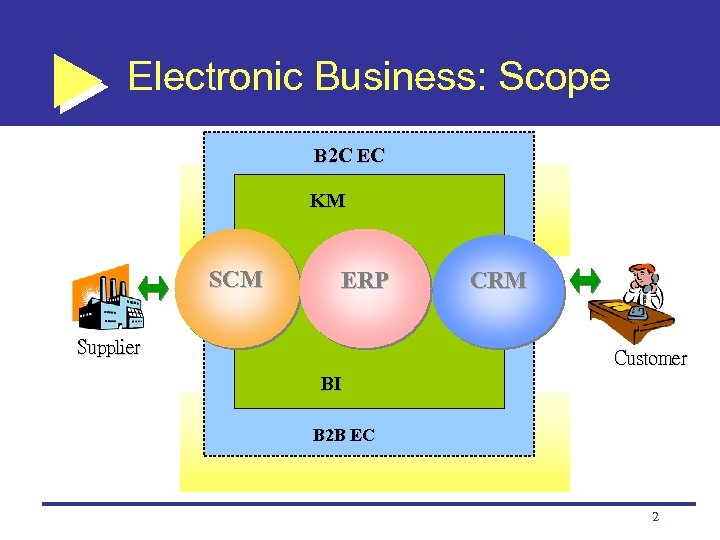 Electronic Business: Scope 企業價值 B 2 C EC 企業策略 KM SCM ERP Supplier CRM Customer BI B 2 B EC 2
Electronic Business: Scope 企業價值 B 2 C EC 企業策略 KM SCM ERP Supplier CRM Customer BI B 2 B EC 2
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC Customer relationship management (CRM): A customer service approach that focuses on building long-term and sustainable customer relationships that add value both for the customer and the company 3
CRM and Its Relationship with EC Customer relationship management (CRM): A customer service approach that focuses on building long-term and sustainable customer relationships that add value both for the customer and the company 3
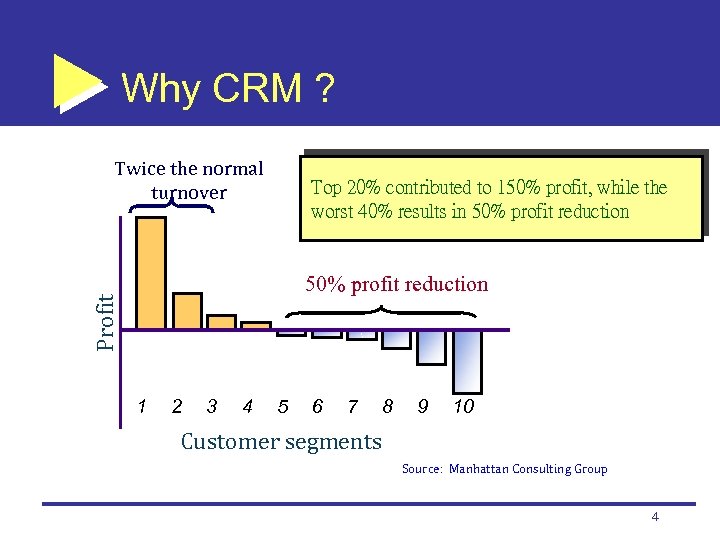 Why CRM ? Twice the normal turnover Top 20% contributed to 150% profit, while the worst 40% results in 50% profit reduction Profit 50% profit reduction 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Customer segments Source: Manhattan Consulting Group 4
Why CRM ? Twice the normal turnover Top 20% contributed to 150% profit, while the worst 40% results in 50% profit reduction Profit 50% profit reduction 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Customer segments Source: Manhattan Consulting Group 4
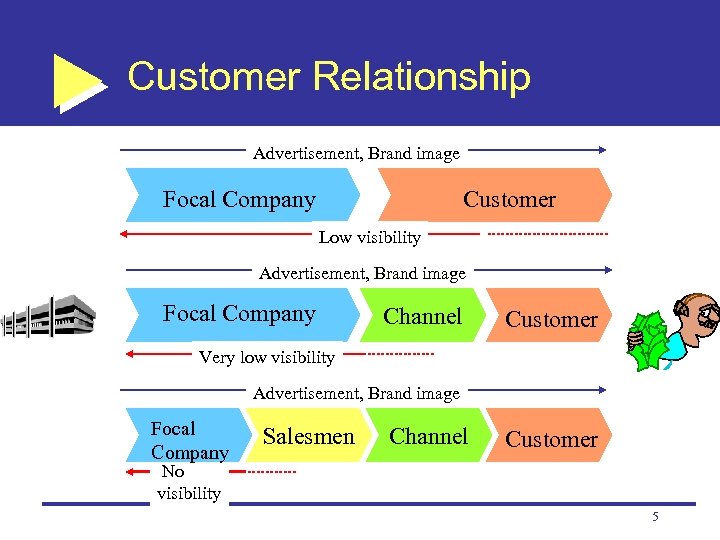 Customer Relationship Advertisement, Brand image Focal Company Customer Low visibility Advertisement, Brand image Focal Company Channel Customer Very low visibility Advertisement, Brand image Focal Company Salesmen Channel Customer No visibility 5
Customer Relationship Advertisement, Brand image Focal Company Customer Low visibility Advertisement, Brand image Focal Company Channel Customer Very low visibility Advertisement, Brand image Focal Company Salesmen Channel Customer No visibility 5
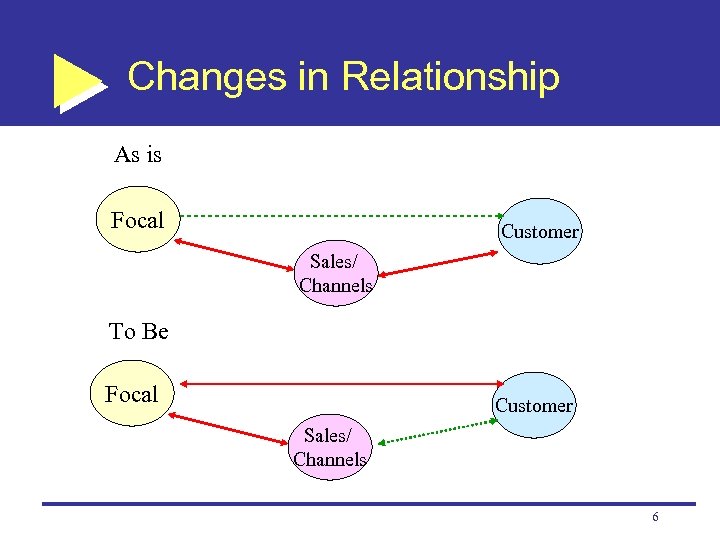 Changes in Relationship As is Focal Customer Sales/ Channels To Be Focal Customer Sales/ Channels 6
Changes in Relationship As is Focal Customer Sales/ Channels To Be Focal Customer Sales/ Channels 6
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Classification of CRM programs Loyalty program Prospecting Save or win back Cross-sell/up-sell e. CRM: Customer relationship management conducted electronically 7
CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Classification of CRM programs Loyalty program Prospecting Save or win back Cross-sell/up-sell e. CRM: Customer relationship management conducted electronically 7
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Scope of CRM 1. Foundation of service 2. Customer-centered services 3. Value-added services 8
CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Scope of CRM 1. Foundation of service 2. Customer-centered services 3. Value-added services 8
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Extent of service 1. Customer acquisition (prepurchase support) 2. Customer support during purchase 3. Customer fulfillment (purchase dispatch) 4. Customer continuance support (postpurchase) 9
CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Extent of service 1. Customer acquisition (prepurchase support) 2. Customer support during purchase 3. Customer fulfillment (purchase dispatch) 4. Customer continuance support (postpurchase) 9
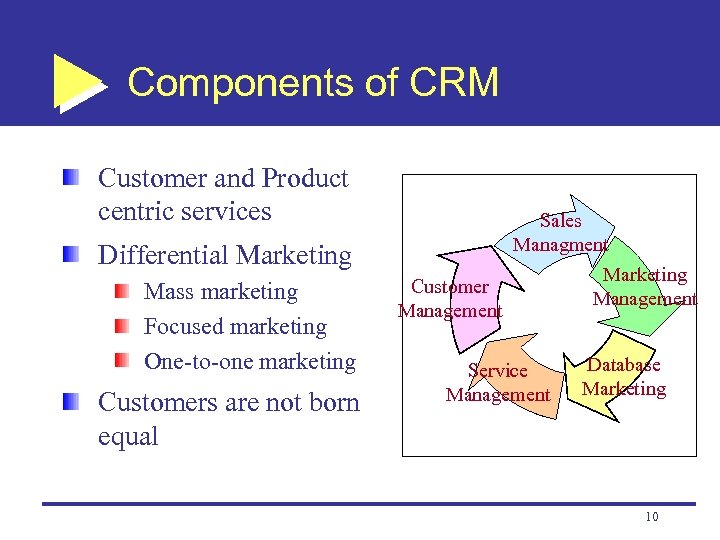 Components of CRM Customer and Product centric services Sales Managment Differential Marketing Mass marketing Focused marketing One-to-one marketing Customers are not born equal Customer Management Service Management Marketing Management Database Marketing 10
Components of CRM Customer and Product centric services Sales Managment Differential Marketing Mass marketing Focused marketing One-to-one marketing Customers are not born equal Customer Management Service Management Marketing Management Database Marketing 10
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Benefits of CRM Provides: choices of products and services fast problem resolution and response easy and quick access to information Limitations of CRM Requires integration with a company’s other information systems which is costly Difficult to support mobile employees 11
CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Benefits of CRM Provides: choices of products and services fast problem resolution and response easy and quick access to information Limitations of CRM Requires integration with a company’s other information systems which is costly Difficult to support mobile employees 11
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) CRM implementation issues Steps in building EC strategy focused on customer: 1. focus on the end customer 2. systems and business processes that are designed for ease of use and from the end customer’s point of view 3. efforts to foster customer loyalty 12
CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) CRM implementation issues Steps in building EC strategy focused on customer: 1. focus on the end customer 2. systems and business processes that are designed for ease of use and from the end customer’s point of view 3. efforts to foster customer loyalty 12
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Five factors required to implement a CRM program effectively: 1. Customer-centric strategy 2. Commitments from people 3. Improved or redesigned processes 4. Software technology 5. Infrastructure 13
CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Five factors required to implement a CRM program effectively: 1. Customer-centric strategy 2. Commitments from people 3. Improved or redesigned processes 4. Software technology 5. Infrastructure 13
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Justifying customer service and CRM programs Metrics: Standards of performance; may be quantitative or qualitative 14
CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Justifying customer service and CRM programs Metrics: Standards of performance; may be quantitative or qualitative 14
 CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Web-related metrics a company uses to determine the appropriate level of customer support: Response time Site availability Download time Timeliness Security and privacy On-time order fulfillment Return policy Navigability 15
CRM and Its Relationship with EC (cont. ) Web-related metrics a company uses to determine the appropriate level of customer support: Response time Site availability Download time Timeliness Security and privacy On-time order fulfillment Return policy Navigability 15
 CRM Applications and Tools: Delivering Customer Service in Cyberspace CRM applications improve upon traditional customer service by means of easier communications and speedier resolution of customer problems Customer service adds value to products and services It is an integral part of a successful business 16
CRM Applications and Tools: Delivering Customer Service in Cyberspace CRM applications improve upon traditional customer service by means of easier communications and speedier resolution of customer problems Customer service adds value to products and services It is an integral part of a successful business 16
 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Classifications of CRM applications Customer-facing applications Customer-touching applications Customer-centric intelligence applications Online networking and other applications 17
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Classifications of CRM applications Customer-facing applications Customer-touching applications Customer-centric intelligence applications Online networking and other applications 17
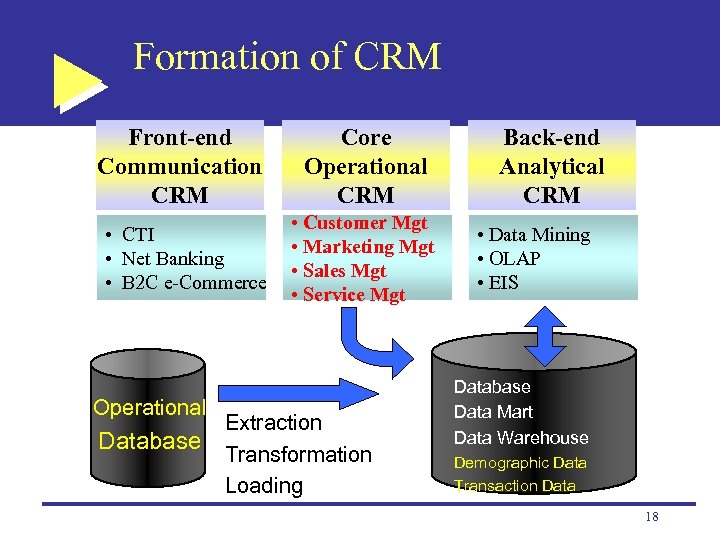 Formation of CRM Front-end Communication CRM Core Operational CRM • CTI • Net Banking • B 2 C e-Commerce • Customer Mgt • Marketing Mgt • Sales Mgt • Service Mgt Operational Database Extraction Transformation Loading Back-end Analytical CRM • Data Mining • OLAP • EIS Database Data Mart Data Warehouse Demographic Data Transaction Data 18
Formation of CRM Front-end Communication CRM Core Operational CRM • CTI • Net Banking • B 2 C e-Commerce • Customer Mgt • Marketing Mgt • Sales Mgt • Service Mgt Operational Database Extraction Transformation Loading Back-end Analytical CRM • Data Mining • OLAP • EIS Database Data Mart Data Warehouse Demographic Data Transaction Data 18
 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Customer-facing applications Customer interaction center (CIC): A comprehensive service entity in which EC vendors address customer service issues communicated through various contact channels Intelligent agents in customer service and call centers 19
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Customer-facing applications Customer interaction center (CIC): A comprehensive service entity in which EC vendors address customer service issues communicated through various contact channels Intelligent agents in customer service and call centers 19
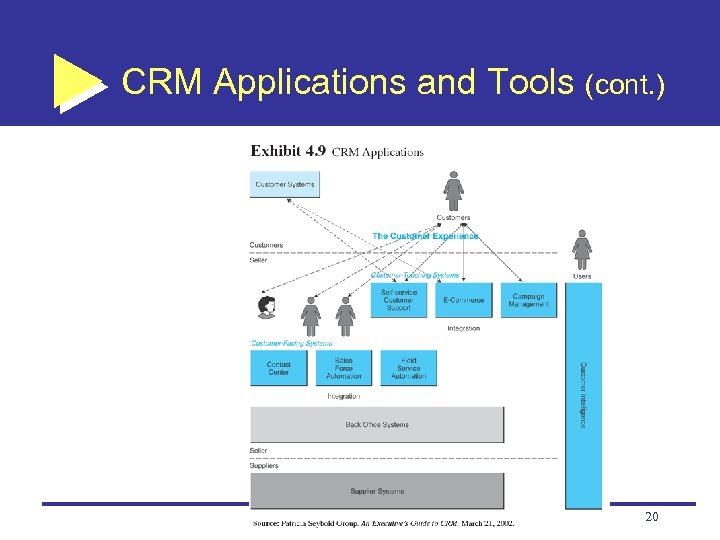 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) 20
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) 20
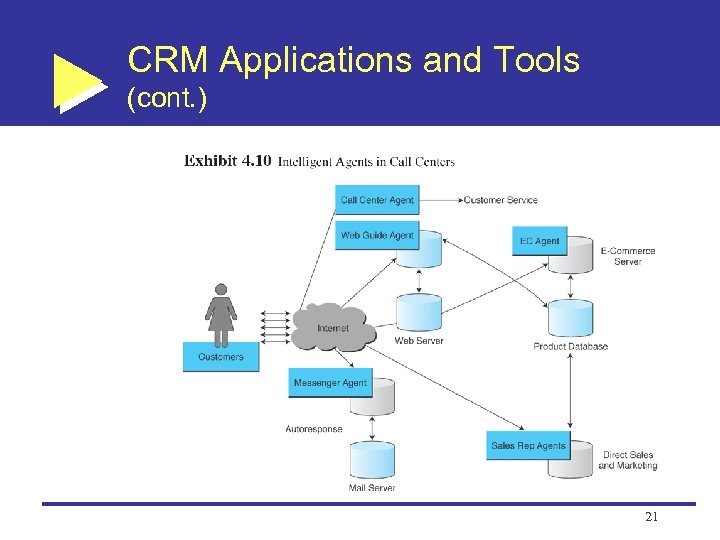 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) 21
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) 21
 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Autoresponders: Automated e-mail reply systems (text files returned via e-mail), which provide answers to commonly asked questions Sales force automation (SFA): Software that automates the tasks performed by sales people in the field, such as data collection and its transmission 22
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Autoresponders: Automated e-mail reply systems (text files returned via e-mail), which provide answers to commonly asked questions Sales force automation (SFA): Software that automates the tasks performed by sales people in the field, such as data collection and its transmission 22
 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Customer-touching applications Personalized Web Pages E-Commerce Applications Campaign Management 23
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Customer-touching applications Personalized Web Pages E-Commerce Applications Campaign Management 23
 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Web Self-Service Activities conducted by users on the Web to provide answers to their questions (e. g. , tracking) or for product configuration Self-tracking Self-configuration and customization 24
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Web Self-Service Activities conducted by users on the Web to provide answers to their questions (e. g. , tracking) or for product configuration Self-tracking Self-configuration and customization 24
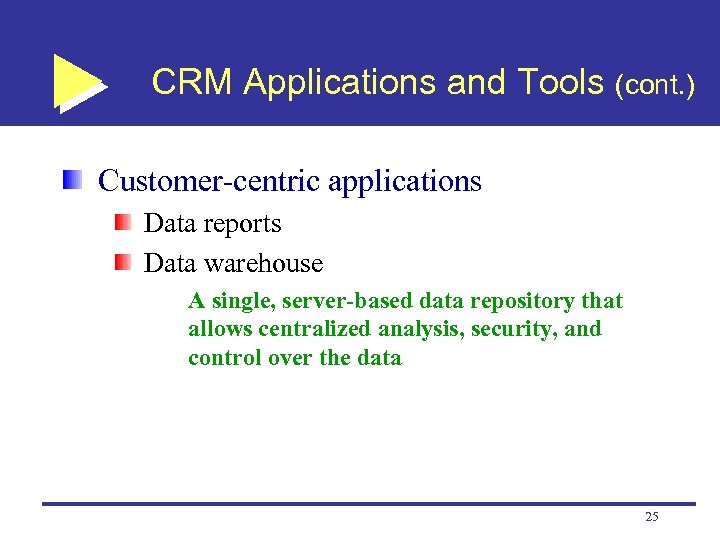 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Customer-centric applications Data reports Data warehouse A single, server-based data repository that allows centralized analysis, security, and control over the data 25
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Customer-centric applications Data reports Data warehouse A single, server-based data repository that allows centralized analysis, security, and control over the data 25
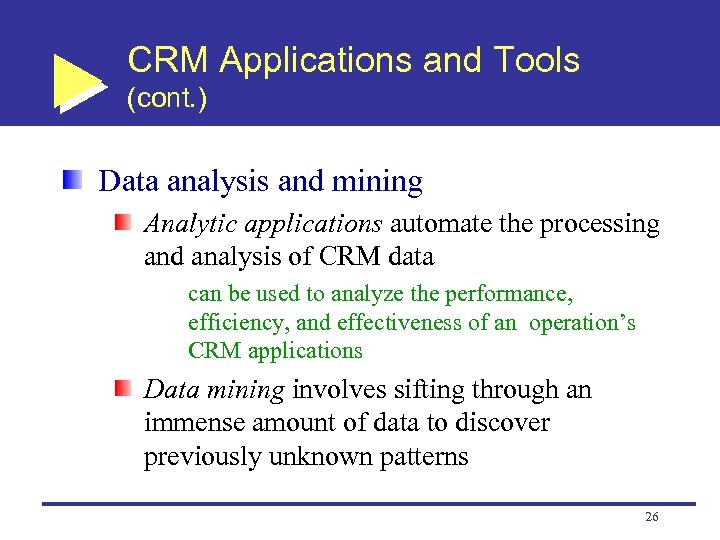 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Data analysis and mining Analytic applications automate the processing and analysis of CRM data can be used to analyze the performance, efficiency, and effectiveness of an operation’s CRM applications Data mining involves sifting through an immense amount of data to discover previously unknown patterns 26
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Data analysis and mining Analytic applications automate the processing and analysis of CRM data can be used to analyze the performance, efficiency, and effectiveness of an operation’s CRM applications Data mining involves sifting through an immense amount of data to discover previously unknown patterns 26
 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Online networking and other applications Forums Chat rooms Usenet groups E-mail newsletters Discussion lists 27
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Online networking and other applications Forums Chat rooms Usenet groups E-mail newsletters Discussion lists 27
 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Mobile CRM the delivery of CRM applications to any user, whenever and wherever needed Voice communication people are more comfortable talking with a person, even a virtual one, than they are interacting with machines. The smile and the clear pronunciation of the agent’s voice increases shoppers’ confidence and trust 28
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Mobile CRM the delivery of CRM applications to any user, whenever and wherever needed Voice communication people are more comfortable talking with a person, even a virtual one, than they are interacting with machines. The smile and the clear pronunciation of the agent’s voice increases shoppers’ confidence and trust 28
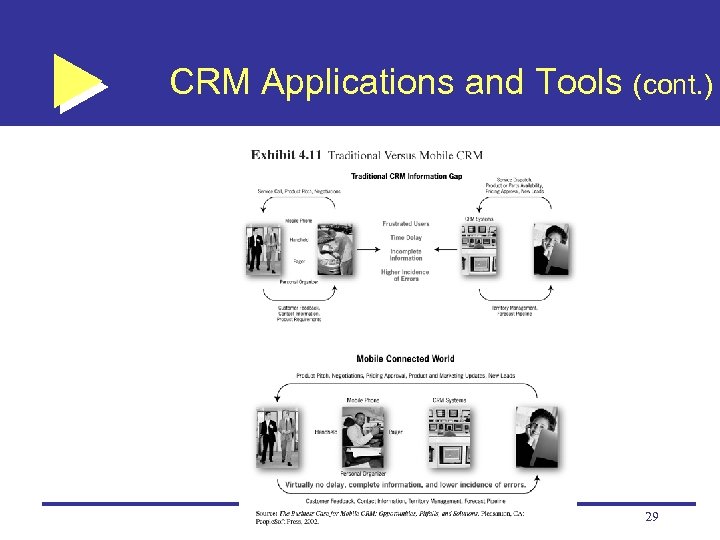 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) 29
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) 29
 CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Role of knowledge management and intelligent agents in CRM Automating inquiry routing and answering queries requires knowledge Generated from historical data and from human expertise and stored in knowledge bases for use whenever needed Intelligent agents support the mechanics of inquiry routing, autoresponders, and so on 30
CRM Applications and Tools (cont. ) Role of knowledge management and intelligent agents in CRM Automating inquiry routing and answering queries requires knowledge Generated from historical data and from human expertise and stored in knowledge bases for use whenever needed Intelligent agents support the mechanics of inquiry routing, autoresponders, and so on 30
 Internet Marketing in B 2 B Organizational buyer behavior number of organizational buyers is much smaller than the number of individual buyers transaction volumes are far larger terms of negotiations and purchasing are more complex 31
Internet Marketing in B 2 B Organizational buyer behavior number of organizational buyers is much smaller than the number of individual buyers transaction volumes are far larger terms of negotiations and purchasing are more complex 31
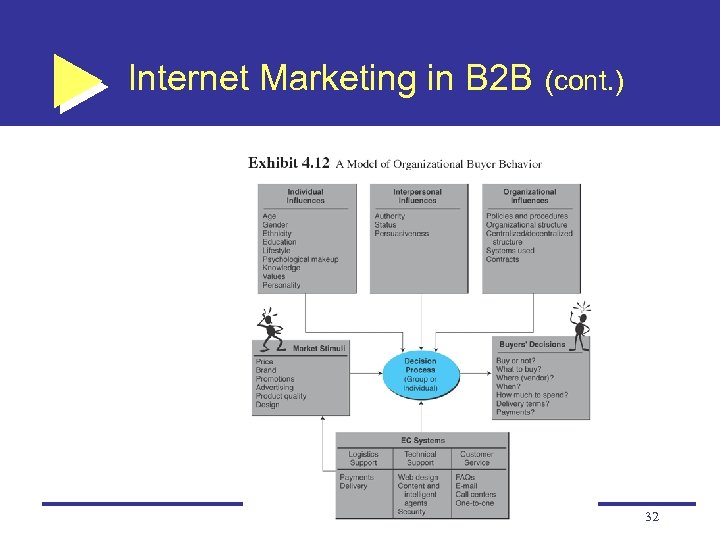 Internet Marketing in B 2 B (cont. ) 32
Internet Marketing in B 2 B (cont. ) 32
 Internet Marketing in B 2 B (cont. ) Methods for B 2 B online marketing Targeting customers contact all of its targeted customers individually when they are part of a welldefined group affiliation service advertising Electronic wholesalers intermediary sells directly to businesses, but does so exclusively online 33
Internet Marketing in B 2 B (cont. ) Methods for B 2 B online marketing Targeting customers contact all of its targeted customers individually when they are part of a welldefined group affiliation service advertising Electronic wholesalers intermediary sells directly to businesses, but does so exclusively online 33
 Internet Marketing in B 2 B (cont. ) Affiliate programs Placing banners on another vendor’s Web site Content alliance program in which content is exchanged so that all can obtain some free content Infomediaries Online data mining services 34
Internet Marketing in B 2 B (cont. ) Affiliate programs Placing banners on another vendor’s Web site Content alliance program in which content is exchanged so that all can obtain some free content Infomediaries Online data mining services 34
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC One-to-one marketing: Marketing that treats each customer in a unique way Personalization: The matching of services, products, and advertising content to individual consumers User profile: The requirements, preferences, behaviors, and demographic traits of a particular customer 35
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC One-to-one marketing: Marketing that treats each customer in a unique way Personalization: The matching of services, products, and advertising content to individual consumers User profile: The requirements, preferences, behaviors, and demographic traits of a particular customer 35
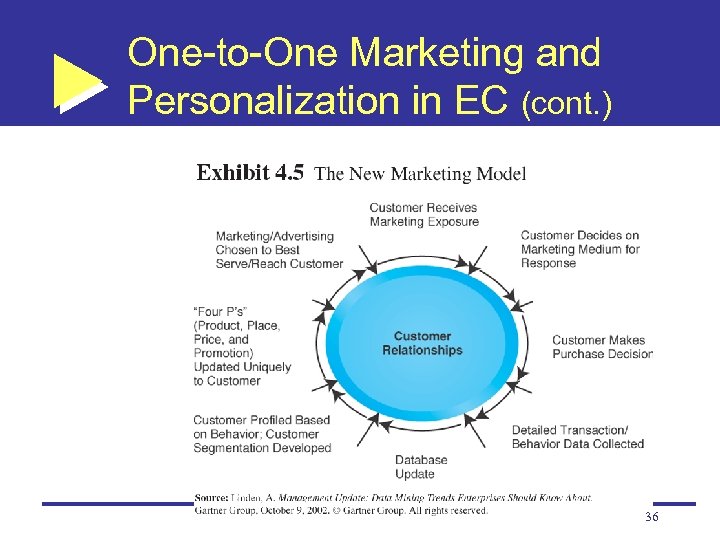 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) 36
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) 36
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Major strategies used to compile user profiles Solicit information directly from the user Observe what people are doing online Build from previous purchase patterns Perform marketing research 37
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Major strategies used to compile user profiles Solicit information directly from the user Observe what people are doing online Build from previous purchase patterns Perform marketing research 37
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Cookie: A data file that is placed on a user’s hard drive by a Web server, frequently without disclosure or the user’s consent, that collects information about the user’s activities at a site 38
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Cookie: A data file that is placed on a user’s hard drive by a Web server, frequently without disclosure or the user’s consent, that collects information about the user’s activities at a site 38
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Collaborative filtering: A personalization method that uses customer data to predict, based on formulas derived from behavioral sciences, what other products or services a customer may enjoy; predictions can be extended to other customers with similar profiles 39
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Collaborative filtering: A personalization method that uses customer data to predict, based on formulas derived from behavioral sciences, what other products or services a customer may enjoy; predictions can be extended to other customers with similar profiles 39
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Variations of collaborative filtering: Rule-based filtering Content-based filtering Activity-based filtering Legal and ethical issues in collaborative filtering Invasion-of-privacy issues Permission-based personalization tools to request customer permission 40
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Variations of collaborative filtering: Rule-based filtering Content-based filtering Activity-based filtering Legal and ethical issues in collaborative filtering Invasion-of-privacy issues Permission-based personalization tools to request customer permission 40
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Customer loyalty: Degree to which a customer will stay with a specific vendor or brand Increased customer loyalty produces cost savings through: lower marketing costs lower transaction costs lower customer turnover expenses lower failure costs E-loyalty: Customer loyalty to an e-tailer 41
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Customer loyalty: Degree to which a customer will stay with a specific vendor or brand Increased customer loyalty produces cost savings through: lower marketing costs lower transaction costs lower customer turnover expenses lower failure costs E-loyalty: Customer loyalty to an e-tailer 41
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Trust in EC Trust: The psychological status of involved parties who are willing to pursue further interaction to achieve a planned goal Trust is influenced by many variables 42
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Trust in EC Trust: The psychological status of involved parties who are willing to pursue further interaction to achieve a planned goal Trust is influenced by many variables 42
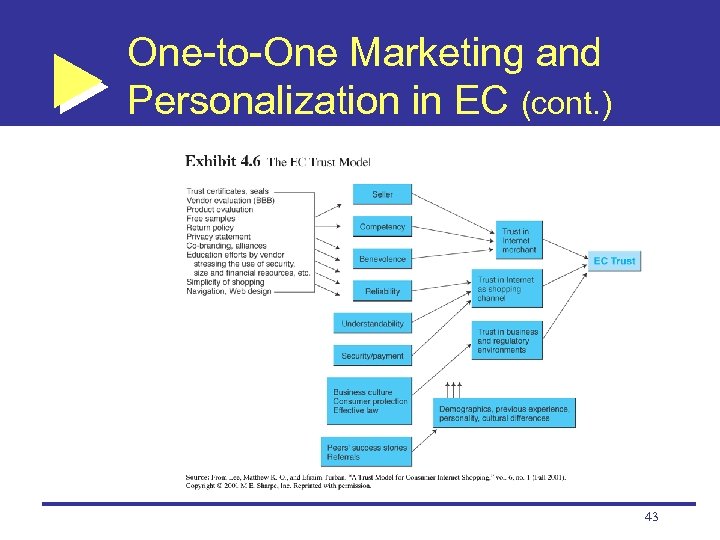 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) 43
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) 43
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) How to increase EC trust between buyers and sellers trust is determined by: degree of initial success that each party experienced with EC and with each other well-defined roles and procedures for all parties involved realistic expectations as to outcomes from EC 44
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) How to increase EC trust between buyers and sellers trust is determined by: degree of initial success that each party experienced with EC and with each other well-defined roles and procedures for all parties involved realistic expectations as to outcomes from EC 44
 One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Issues in personalization brand recognition security mechanisms help solidify trust disclose and update latest business status and practices to potential customers and to build transaction integrity into the system guarantee information and protection privacy through various communication channels 45
One-to-One Marketing and Personalization in EC (cont. ) Issues in personalization brand recognition security mechanisms help solidify trust disclose and update latest business status and practices to potential customers and to build transaction integrity into the system guarantee information and protection privacy through various communication channels 45


