4130d0af6718ae15173fa5233fa1c2e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 101
 CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK REPORT MAY 2002 Curriculum Framework Report
CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK REPORT MAY 2002 Curriculum Framework Report
 Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 2
Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 2
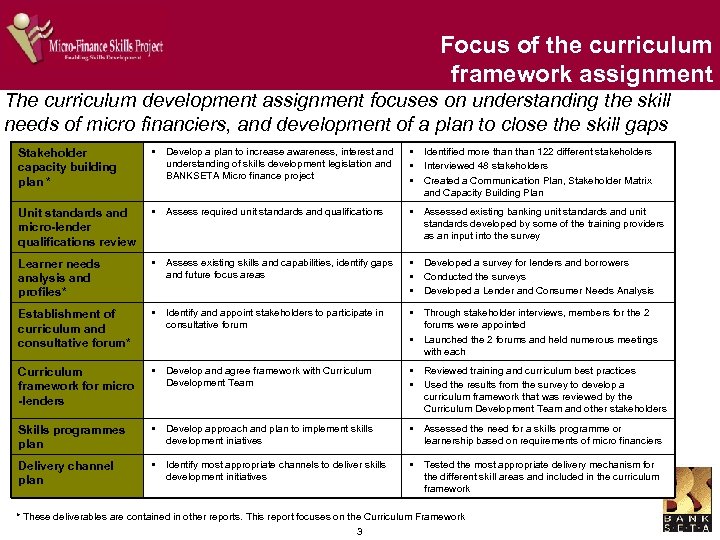 Focus of the curriculum framework assignment The curriculum development assignment focuses on understanding the skill needs of micro financiers, and development of a plan to close the skill gaps Stakeholder capacity building plan * § Develop a plan to increase awareness, interest and understanding of skills development legislation and BANKSETA Micro finance project § Identified more than 122 different stakeholders § Interviewed 48 stakeholders § Created a Communication Plan, Stakeholder Matrix and Capacity Building Plan Unit standards and micro-lender qualifications review § Assess required unit standards and qualifications § Assessed existing banking unit standards and unit standards developed by some of the training providers as an input into the survey Learner needs analysis and profiles* § Assess existing skills and capabilities, identify gaps and future focus areas § Developed a survey for lenders and borrowers § Conducted the surveys § Developed a Lender and Consumer Needs Analysis Establishment of curriculum and consultative forum* § Identify and appoint stakeholders to participate in consultative forum § Through stakeholder interviews, members for the 2 forums were appointed § Launched the 2 forums and held numerous meetings with each Curriculum framework for micro -lenders § Develop and agree framework with Curriculum Development Team § Reviewed training and curriculum best practices § Used the results from the survey to develop a curriculum framework that was reviewed by the Curriculum Development Team and other stakeholders Skills programmes plan § Develop approach and plan to implement skills development iniatives § Assessed the need for a skills programme or learnership based on requirements of micro financiers Delivery channel plan § Identify most appropriate channels to deliver skills development initiatives § Tested the most appropriate delivery mechanism for the different skill areas and included in the curriculum framework * These deliverables are contained in other reports. This report focuses on the Curriculum Framework 3
Focus of the curriculum framework assignment The curriculum development assignment focuses on understanding the skill needs of micro financiers, and development of a plan to close the skill gaps Stakeholder capacity building plan * § Develop a plan to increase awareness, interest and understanding of skills development legislation and BANKSETA Micro finance project § Identified more than 122 different stakeholders § Interviewed 48 stakeholders § Created a Communication Plan, Stakeholder Matrix and Capacity Building Plan Unit standards and micro-lender qualifications review § Assess required unit standards and qualifications § Assessed existing banking unit standards and unit standards developed by some of the training providers as an input into the survey Learner needs analysis and profiles* § Assess existing skills and capabilities, identify gaps and future focus areas § Developed a survey for lenders and borrowers § Conducted the surveys § Developed a Lender and Consumer Needs Analysis Establishment of curriculum and consultative forum* § Identify and appoint stakeholders to participate in consultative forum § Through stakeholder interviews, members for the 2 forums were appointed § Launched the 2 forums and held numerous meetings with each Curriculum framework for micro -lenders § Develop and agree framework with Curriculum Development Team § Reviewed training and curriculum best practices § Used the results from the survey to develop a curriculum framework that was reviewed by the Curriculum Development Team and other stakeholders Skills programmes plan § Develop approach and plan to implement skills development iniatives § Assessed the need for a skills programme or learnership based on requirements of micro financiers Delivery channel plan § Identify most appropriate channels to deliver skills development initiatives § Tested the most appropriate delivery mechanism for the different skill areas and included in the curriculum framework * These deliverables are contained in other reports. This report focuses on the Curriculum Framework 3
 Definitions Within the context of this project, the following definitions were used: § Micro Financier An organisation (private, public or Section 21) which provides loans SMMEs or individuals under the exemption notice to the Usury Act Ø The determination of the amount of knowledge or skill a person has in a particular content area Ø § Skill Ø § Delivery Channel Ø § The medium via which training is delivered in the market place e. g. face-to-face, Distance learning Delivery Method Ø § The ability to repeatedly act on, or apply, basic knowledge The medium through which learning activities are conducted such as videos, CBT’s, internet, manuals, case studies Curriculum Framework Ø A set of principles through which a learning plan can be effectively implemented at various sites of learning 4
Definitions Within the context of this project, the following definitions were used: § Micro Financier An organisation (private, public or Section 21) which provides loans SMMEs or individuals under the exemption notice to the Usury Act Ø The determination of the amount of knowledge or skill a person has in a particular content area Ø § Skill Ø § Delivery Channel Ø § The medium via which training is delivered in the market place e. g. face-to-face, Distance learning Delivery Method Ø § The ability to repeatedly act on, or apply, basic knowledge The medium through which learning activities are conducted such as videos, CBT’s, internet, manuals, case studies Curriculum Framework Ø A set of principles through which a learning plan can be effectively implemented at various sites of learning 4
 SA context The Department of Labour has launched a strategy to partner with a number of institutions to address skills development in South Africa Sector Education and Training Authority (SETA) National Skills Development Strategy (NSDS) § § § Develop a culture of high quality life-long learning Foster skills development in the formal economy for productivity and employment growth Stimulate and support skills development in small business Promote skills development for employability and sustainable livelihoods through social development initiatives Assist new entrants into employment § § Established by the Dept. of Labour to help implement the NSDS and to increase the skills of people in their sector Ø Help firms understand the benefits of training Ø Encourage firms to train by offering a grant Offer services to every sector of the economy Comprised of employer and worker representatives BANKSETA identified a need to support micro finance organisations through skills development and other business development support mechanisms 5
SA context The Department of Labour has launched a strategy to partner with a number of institutions to address skills development in South Africa Sector Education and Training Authority (SETA) National Skills Development Strategy (NSDS) § § § Develop a culture of high quality life-long learning Foster skills development in the formal economy for productivity and employment growth Stimulate and support skills development in small business Promote skills development for employability and sustainable livelihoods through social development initiatives Assist new entrants into employment § § Established by the Dept. of Labour to help implement the NSDS and to increase the skills of people in their sector Ø Help firms understand the benefits of training Ø Encourage firms to train by offering a grant Offer services to every sector of the economy Comprised of employer and worker representatives BANKSETA identified a need to support micro finance organisations through skills development and other business development support mechanisms 5
 Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 6
Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 6
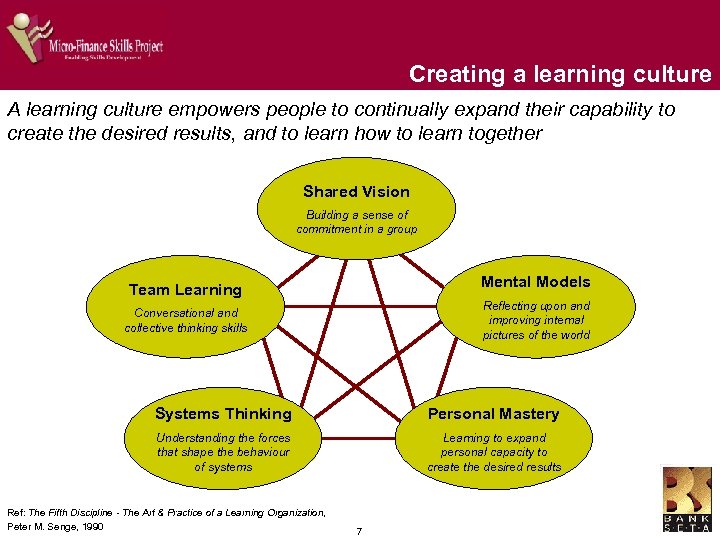 Creating a learning culture A learning culture empowers people to continually expand their capability to create the desired results, and to learn how to learn together Shared Vision Building a sense of commitment in a group Mental Models Team Learning Reflecting upon and improving internal pictures of the world Conversational and collective thinking skills Systems Thinking Personal Mastery Understanding the forces that shape the behaviour of systems Learning to expand personal capacity to create the desired results Ref: The Fifth Discipline - The Art & Practice of a Learning Organization, Peter M. Senge, 1990 7
Creating a learning culture A learning culture empowers people to continually expand their capability to create the desired results, and to learn how to learn together Shared Vision Building a sense of commitment in a group Mental Models Team Learning Reflecting upon and improving internal pictures of the world Conversational and collective thinking skills Systems Thinking Personal Mastery Understanding the forces that shape the behaviour of systems Learning to expand personal capacity to create the desired results Ref: The Fifth Discipline - The Art & Practice of a Learning Organization, Peter M. Senge, 1990 7
 Learning guiding principles Best practice research shows that the fostering of a learning environment should be a key strategic objective, and not merely a training tactic • The learning strategy must be linked to all the organisation’s plans and initiatives Ø Learning and human performance should be viewed as strategic in nature Ø Skills programs must be treated as business initiatives and must be integrated with all projects • Learning strategies must have CEO-level ownership and sponsorship Ø Culture change begins with the leader of the organisation Ø Frequent communication regarding learning objectives, plans, value and results is essential Ø Support for learning must be continually demonstrated Ø Leaders must set up processes to actively solicit and gather feedback • Learning strategies must be implemented on a solid infrastructure Ø The infrastructure must support innovative, effective education driving bottom line results Ø The infrastructure must support employees in sharing knowledge and developing expectations • Learning business partners must be carefully selected Ø The organisation and its partners must work together seamlessly Ø Business relationships must be transparent 8
Learning guiding principles Best practice research shows that the fostering of a learning environment should be a key strategic objective, and not merely a training tactic • The learning strategy must be linked to all the organisation’s plans and initiatives Ø Learning and human performance should be viewed as strategic in nature Ø Skills programs must be treated as business initiatives and must be integrated with all projects • Learning strategies must have CEO-level ownership and sponsorship Ø Culture change begins with the leader of the organisation Ø Frequent communication regarding learning objectives, plans, value and results is essential Ø Support for learning must be continually demonstrated Ø Leaders must set up processes to actively solicit and gather feedback • Learning strategies must be implemented on a solid infrastructure Ø The infrastructure must support innovative, effective education driving bottom line results Ø The infrastructure must support employees in sharing knowledge and developing expectations • Learning business partners must be carefully selected Ø The organisation and its partners must work together seamlessly Ø Business relationships must be transparent 8
 Barriers to learning success Establishing a learning culture is a lengthy process, requiring strong leadership, clear responsibilities and a holistic plan • Implementing piecemeal solutions Ø Implementing a small portion of a comprehensive learning solution frequently ignores the interdependencies between the different components of learning processes and the economies these processes bring to each other • Not defining organisation roles clearly Ø Unclear roles and responsibilities lead to duplication of development and management efforts, resulting in unnecessary cost Ø Clearly defined roles for central and departmental or business unit learning organisations can help mitigate this risk and maximise the learning organisation’s impact on the bottom line • The focus should not just be on “Training” Ø While training is a very visible part of learning programmes, it is important to focus on the holistic picture of what learning is and the strategic capabilities it brings to an organisation Ø Examples of strategic capabilities include knowledge management, information portals, and direct access to vendor resources, job aids, and ongoing performance support 9
Barriers to learning success Establishing a learning culture is a lengthy process, requiring strong leadership, clear responsibilities and a holistic plan • Implementing piecemeal solutions Ø Implementing a small portion of a comprehensive learning solution frequently ignores the interdependencies between the different components of learning processes and the economies these processes bring to each other • Not defining organisation roles clearly Ø Unclear roles and responsibilities lead to duplication of development and management efforts, resulting in unnecessary cost Ø Clearly defined roles for central and departmental or business unit learning organisations can help mitigate this risk and maximise the learning organisation’s impact on the bottom line • The focus should not just be on “Training” Ø While training is a very visible part of learning programmes, it is important to focus on the holistic picture of what learning is and the strategic capabilities it brings to an organisation Ø Examples of strategic capabilities include knowledge management, information portals, and direct access to vendor resources, job aids, and ongoing performance support 9
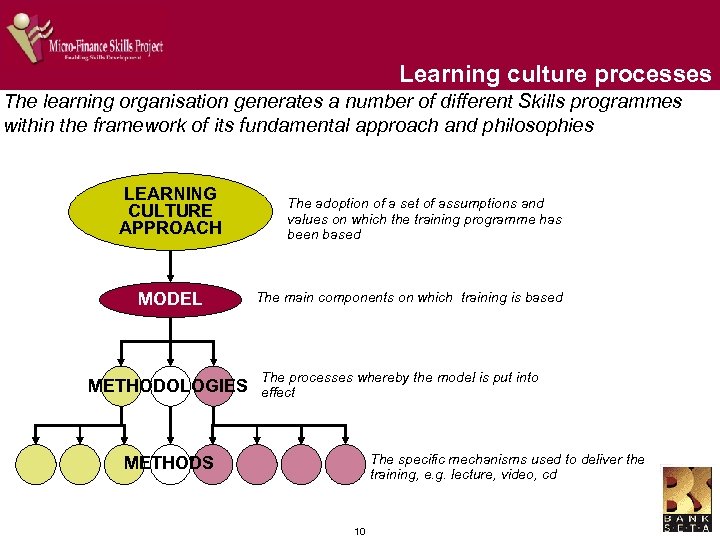 Learning culture processes The learning organisation generates a number of different Skills programmes within the framework of its fundamental approach and philosophies LEARNING CULTURE APPROACH MODEL METHODOLOGIES The adoption of a set of assumptions and values on which the training programme has been based The main components on which training is based The processes whereby the model is put into effect The specific mechanisms used to deliver the training, e. g. lecture, video, cd METHODS 10
Learning culture processes The learning organisation generates a number of different Skills programmes within the framework of its fundamental approach and philosophies LEARNING CULTURE APPROACH MODEL METHODOLOGIES The adoption of a set of assumptions and values on which the training programme has been based The main components on which training is based The processes whereby the model is put into effect The specific mechanisms used to deliver the training, e. g. lecture, video, cd METHODS 10
 Learning culture processes Best practice shows that several areas of integration need to be set up in order to properly manage the delivery of training § The various organisations, training providers and vendors need to be managed in terms of the quality of materials and services as well as in their ability to deliver and fulfill on promised services § An effective learning management system would need to be set up which would cater for the planning requirements, ongoing course development, curriculum requirements, delivery processes, compliance, support and external liaison § A learning process would need to be clearly defined in terms of what programme a learner would follow in order to achieve specified learning outcomes § An integrated system which will cater for performance support, knowledge sharing and the various learning tools would need to be established An integrated model for the management of the above systems has been formulated from best practice examples 11
Learning culture processes Best practice shows that several areas of integration need to be set up in order to properly manage the delivery of training § The various organisations, training providers and vendors need to be managed in terms of the quality of materials and services as well as in their ability to deliver and fulfill on promised services § An effective learning management system would need to be set up which would cater for the planning requirements, ongoing course development, curriculum requirements, delivery processes, compliance, support and external liaison § A learning process would need to be clearly defined in terms of what programme a learner would follow in order to achieve specified learning outcomes § An integrated system which will cater for performance support, knowledge sharing and the various learning tools would need to be established An integrated model for the management of the above systems has been formulated from best practice examples 11
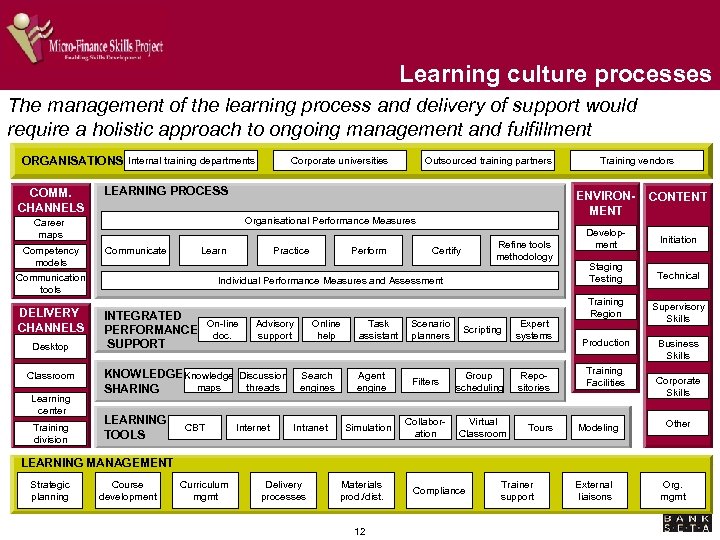 Learning culture processes The management of the learning process and delivery of support would require a holistic approach to ongoing management and fulfillment ORGANISATIONS Internal training departments COMM. CHANNELS Communicate Learn Desktop Classroom Learning center Training division Practice Perform Refine tools methodology Certify Individual Performance Measures and Assessment INTEGRATED On-line PERFORMANCE doc. SUPPORT Advisory support KNOWLEDGE Knowledge Discussion maps threads SHARING LEARNING TOOLS CBT Internet Online help Search engines Intranet Task assistant Scenario planners Agent engine Filters Group scheduling Collaboration Virtual Classroom Simulation Training vendors ENVIRONMENT Organisational Performance Measures Communication tools DELIVERY CHANNELS Outsourced training partners LEARNING PROCESS Career maps Competency models Corporate universities Scripting Expert systems Repositories Tours CONTENT Development Initiation Staging Testing Technical Training Region Production Training Facilities Modeling Supervisory Skills Business Skills Corporate Skills Other LEARNING MANAGEMENT Strategic planning Course development Curriculum mgmt Delivery processes Materials prod. /dist. 12 Compliance Trainer support External liaisons Org. mgmt
Learning culture processes The management of the learning process and delivery of support would require a holistic approach to ongoing management and fulfillment ORGANISATIONS Internal training departments COMM. CHANNELS Communicate Learn Desktop Classroom Learning center Training division Practice Perform Refine tools methodology Certify Individual Performance Measures and Assessment INTEGRATED On-line PERFORMANCE doc. SUPPORT Advisory support KNOWLEDGE Knowledge Discussion maps threads SHARING LEARNING TOOLS CBT Internet Online help Search engines Intranet Task assistant Scenario planners Agent engine Filters Group scheduling Collaboration Virtual Classroom Simulation Training vendors ENVIRONMENT Organisational Performance Measures Communication tools DELIVERY CHANNELS Outsourced training partners LEARNING PROCESS Career maps Competency models Corporate universities Scripting Expert systems Repositories Tours CONTENT Development Initiation Staging Testing Technical Training Region Production Training Facilities Modeling Supervisory Skills Business Skills Corporate Skills Other LEARNING MANAGEMENT Strategic planning Course development Curriculum mgmt Delivery processes Materials prod. /dist. 12 Compliance Trainer support External liaisons Org. mgmt
 Learning approach A fundamental approach of combining experiential and situation learning methodologies generally delivers the most benefits Experiential learning Situation learning • The learner participates completely, and has control over the nature and direction of the learning intervention • Addresses the needs of the learner • Includes personal involvement and selfinitiated training • Learning is primarily based on direct confrontation with practical, social, personal or research problems • Self-evaluation is used to assess success • “Learning to learn” and openness to change are key in experiential learning • Learning occurs via social interaction and collaboration, and as a function of the activity, context, and culture in which it occurs • Social interaction is a critical component because learners become members of a 'community of practice' • Usually unintentional rather than deliberate • Knowledge is presented in authentic context (i. e. , the appropriate settings and applications) Based on this fundamental approach, a number of curricula and training programmes can be designed 13
Learning approach A fundamental approach of combining experiential and situation learning methodologies generally delivers the most benefits Experiential learning Situation learning • The learner participates completely, and has control over the nature and direction of the learning intervention • Addresses the needs of the learner • Includes personal involvement and selfinitiated training • Learning is primarily based on direct confrontation with practical, social, personal or research problems • Self-evaluation is used to assess success • “Learning to learn” and openness to change are key in experiential learning • Learning occurs via social interaction and collaboration, and as a function of the activity, context, and culture in which it occurs • Social interaction is a critical component because learners become members of a 'community of practice' • Usually unintentional rather than deliberate • Knowledge is presented in authentic context (i. e. , the appropriate settings and applications) Based on this fundamental approach, a number of curricula and training programmes can be designed 13
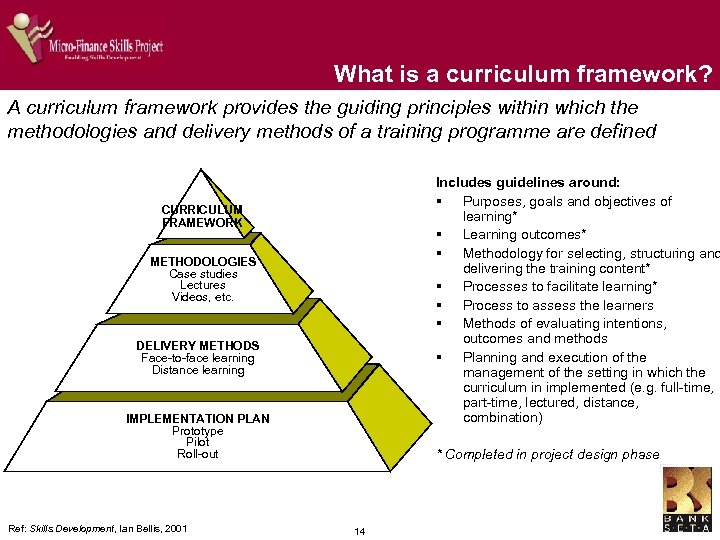 What is a curriculum framework? A curriculum framework provides the guiding principles within which the methodologies and delivery methods of a training programme are defined Includes guidelines around: § Purposes, goals and objectives of learning* § Learning outcomes* § Methodology for selecting, structuring and delivering the training content* § Processes to facilitate learning* § Process to assess the learners § Methods of evaluating intentions, outcomes and methods § Planning and execution of the management of the setting in which the curriculum in implemented (e. g. full-time, part-time, lectured, distance, combination) CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK METHODOLOGIES Case studies Lectures Videos, etc. DELIVERY METHODS Face-to-face learning Distance learning IMPLEMENTATION PLAN Prototype Pilot Roll-out Ref: Skills Development, Ian Bellis, 2001 * Completed in project design phase 14
What is a curriculum framework? A curriculum framework provides the guiding principles within which the methodologies and delivery methods of a training programme are defined Includes guidelines around: § Purposes, goals and objectives of learning* § Learning outcomes* § Methodology for selecting, structuring and delivering the training content* § Processes to facilitate learning* § Process to assess the learners § Methods of evaluating intentions, outcomes and methods § Planning and execution of the management of the setting in which the curriculum in implemented (e. g. full-time, part-time, lectured, distance, combination) CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK METHODOLOGIES Case studies Lectures Videos, etc. DELIVERY METHODS Face-to-face learning Distance learning IMPLEMENTATION PLAN Prototype Pilot Roll-out Ref: Skills Development, Ian Bellis, 2001 * Completed in project design phase 14
 Curriculum framework success factors Best practice suggests that the fostering of a “learning culture” will aid in the successful delivery of training initiatives • Curricula must have a clearly defined vision, mission and goals • Training should be modular and outcomes based • Training content must be relevant to the trainee, and be based on trainee needs • Training standards, systems and models must be clearly defined • Curricula should offer a choice of training content and delivery mechanisms • Training must be prioritised, addressing the most pressing needs first • Training should be delivered at a convenient time, and in a convenient manner • Registering for training should be easy for the trainee • Feedback must be obtained from trainees to continuously improve programs • Skills-based learning and people interfacing skills should ideally be facilitated through a face-to-face delivery channel to cater for questions and problem-solving A curriculum framework should be flexible enough to incorporate a number of different means for developing and delivering training Ref: Training from Scratch, Nancy Kuhn, 15
Curriculum framework success factors Best practice suggests that the fostering of a “learning culture” will aid in the successful delivery of training initiatives • Curricula must have a clearly defined vision, mission and goals • Training should be modular and outcomes based • Training content must be relevant to the trainee, and be based on trainee needs • Training standards, systems and models must be clearly defined • Curricula should offer a choice of training content and delivery mechanisms • Training must be prioritised, addressing the most pressing needs first • Training should be delivered at a convenient time, and in a convenient manner • Registering for training should be easy for the trainee • Feedback must be obtained from trainees to continuously improve programs • Skills-based learning and people interfacing skills should ideally be facilitated through a face-to-face delivery channel to cater for questions and problem-solving A curriculum framework should be flexible enough to incorporate a number of different means for developing and delivering training Ref: Training from Scratch, Nancy Kuhn, 15
 Curriculum framework barriers to success Significant barriers to curriculum success exist, which may significantly undermine the successful adoption of the curriculum by the micro finance industry • Lack of a cohesive approach to the deployment and delivery of training and development initiatives • Lack of ownership and buy-in for training and development • Lack of incentives to take advantage of the learning initiatives and to generate demand for training • Often supply-driven and delivered in a top-down fashion, rather than from the target audience needs • Training should be business-oriented, and not viewed as an extension of the basic general educational system • Training services are not always accessible to the target audience • Must be delivered via a suitable, convenient medium • Geographic dispersion must be taken into account when planning the delivery of curriculum content 16
Curriculum framework barriers to success Significant barriers to curriculum success exist, which may significantly undermine the successful adoption of the curriculum by the micro finance industry • Lack of a cohesive approach to the deployment and delivery of training and development initiatives • Lack of ownership and buy-in for training and development • Lack of incentives to take advantage of the learning initiatives and to generate demand for training • Often supply-driven and delivered in a top-down fashion, rather than from the target audience needs • Training should be business-oriented, and not viewed as an extension of the basic general educational system • Training services are not always accessible to the target audience • Must be delivered via a suitable, convenient medium • Geographic dispersion must be taken into account when planning the delivery of curriculum content 16
 Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 17
Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 17
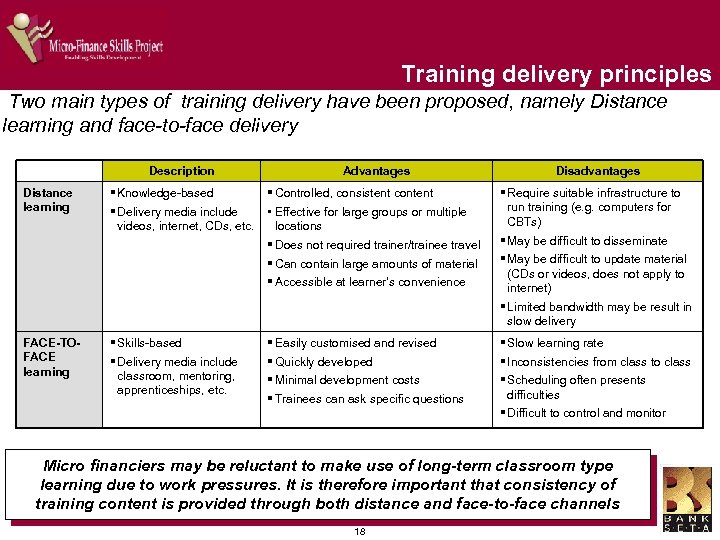 Training delivery principles Two main types of training delivery have been proposed, namely Distance learning and face-to-face delivery Description Advantages Disadvantages Distance learning § Knowledge-based § Delivery media include videos, internet, CDs, etc. § Controlled, consistent content • Effective for large groups or multiple locations § Does not required trainer/trainee travel § Can contain large amounts of material § Accessible at learner’s convenience § Require suitable infrastructure to run training (e. g. computers for CBTs) § May be difficult to disseminate § May be difficult to update material (CDs or videos, does not apply to internet) § Limited bandwidth may be result in slow delivery FACE-TOFACE learning § Skills-based § Delivery media include classroom, mentoring, apprenticeships, etc. § Easily customised and revised § Quickly developed § Minimal development costs § Trainees can ask specific questions § Slow learning rate § Inconsistencies from class to class § Scheduling often presents difficulties § Difficult to control and monitor Micro financiers may be reluctant to make use of long-term classroom type learning due to work pressures. It is therefore important that consistency of training content is provided through both distance and face-to-face channels 18
Training delivery principles Two main types of training delivery have been proposed, namely Distance learning and face-to-face delivery Description Advantages Disadvantages Distance learning § Knowledge-based § Delivery media include videos, internet, CDs, etc. § Controlled, consistent content • Effective for large groups or multiple locations § Does not required trainer/trainee travel § Can contain large amounts of material § Accessible at learner’s convenience § Require suitable infrastructure to run training (e. g. computers for CBTs) § May be difficult to disseminate § May be difficult to update material (CDs or videos, does not apply to internet) § Limited bandwidth may be result in slow delivery FACE-TOFACE learning § Skills-based § Delivery media include classroom, mentoring, apprenticeships, etc. § Easily customised and revised § Quickly developed § Minimal development costs § Trainees can ask specific questions § Slow learning rate § Inconsistencies from class to class § Scheduling often presents difficulties § Difficult to control and monitor Micro financiers may be reluctant to make use of long-term classroom type learning due to work pressures. It is therefore important that consistency of training content is provided through both distance and face-to-face channels 18
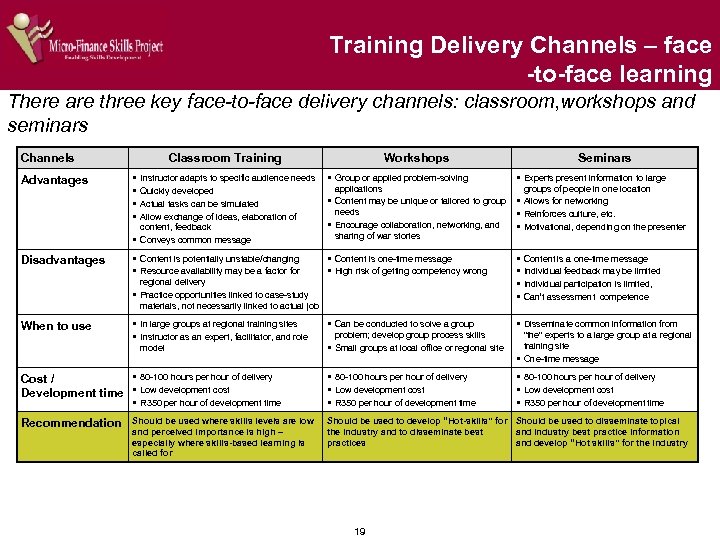 Training Delivery Channels – face -to-face learning There are three key face-to-face delivery channels: classroom, workshops and seminars Channels Classroom Training Workshops Seminars Advantages § § Instructor adapts to specific audience needs § Group or applied problem-solving applications Quickly developed § Content may be unique or tailored to group Actual tasks can be simulated needs Allow exchange of ideas, elaboration of § Encourage collaboration, networking, and content, feedback sharing of war stories § Conveys common message § Experts present information to large Disadvantages § Content is potentially unstable/changing § Resource availability may be a factor for § Content is one-time message § High risk of getting competency wrong § § § Can be conducted to solve a group § Disseminate common information from problem; develop group process skills § Small groups at local office or regional site "the" experts to a large group at a regional training site § One-time message § 80 -100 hours per hour of delivery § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time regional delivery § Practice opportunities linked to case-study materials, not necessarily linked to actual job When to use § In large groups at regional training sites § Instructor as an expert, facilitator, and role model groups of people in one location § Allows for networking § Reinforces culture, etc. § Motivational, depending on the presenter Content is a one-time message Individual feedback may be limited Individual participation is limited, Can’t assessment competence Cost / Development time § 80 -100 hours per hour of delivery § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time Recommendation Should be used where skills levels are low and perceived importance is high – especially where skills-based learning is called for Should be used to develop “Hot-skills” for Should be used to disseminate topical the industry and to disseminate best and industry best practice information practices and develop “Hot skills” for the industry 19
Training Delivery Channels – face -to-face learning There are three key face-to-face delivery channels: classroom, workshops and seminars Channels Classroom Training Workshops Seminars Advantages § § Instructor adapts to specific audience needs § Group or applied problem-solving applications Quickly developed § Content may be unique or tailored to group Actual tasks can be simulated needs Allow exchange of ideas, elaboration of § Encourage collaboration, networking, and content, feedback sharing of war stories § Conveys common message § Experts present information to large Disadvantages § Content is potentially unstable/changing § Resource availability may be a factor for § Content is one-time message § High risk of getting competency wrong § § § Can be conducted to solve a group § Disseminate common information from problem; develop group process skills § Small groups at local office or regional site "the" experts to a large group at a regional training site § One-time message § 80 -100 hours per hour of delivery § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time regional delivery § Practice opportunities linked to case-study materials, not necessarily linked to actual job When to use § In large groups at regional training sites § Instructor as an expert, facilitator, and role model groups of people in one location § Allows for networking § Reinforces culture, etc. § Motivational, depending on the presenter Content is a one-time message Individual feedback may be limited Individual participation is limited, Can’t assessment competence Cost / Development time § 80 -100 hours per hour of delivery § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time Recommendation Should be used where skills levels are low and perceived importance is high – especially where skills-based learning is called for Should be used to develop “Hot-skills” for Should be used to disseminate topical the industry and to disseminate best and industry best practice information practices and develop “Hot skills” for the industry 19
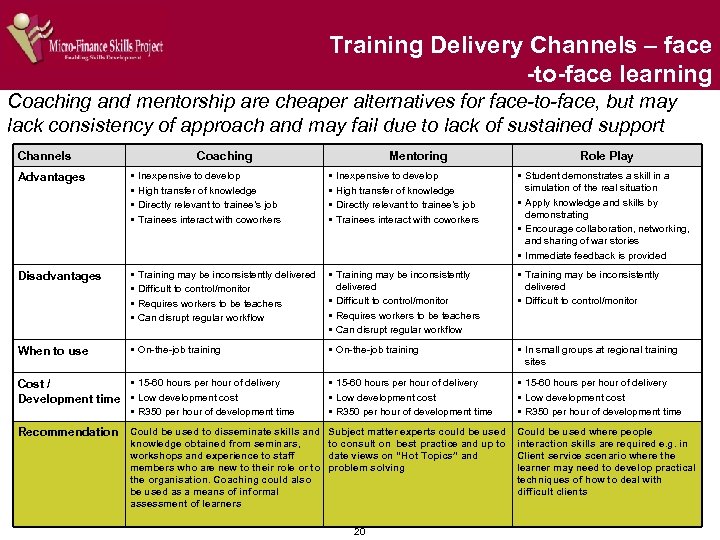 Training Delivery Channels – face -to-face learning Coaching and mentorship are cheaper alternatives for face-to-face, but may lack consistency of approach and may fail due to lack of sustained support Channels Coaching Mentoring Role Play Advantages § § Inexpensive to develop High transfer of knowledge Directly relevant to trainee’s job Trainees interact with coworkers § § Disadvantages § § Training may be inconsistently delivered Difficult to control/monitor Requires workers to be teachers Can disrupt regular workflow § Training may be inconsistently delivered § Difficult to control/monitor § Requires workers to be teachers § Can disrupt regular workflow § Training may be inconsistently delivered § Difficult to control/monitor When to use § On-the-job training § In small groups at regional training sites § 15 -60 hours per hour of delivery § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time § 15 -60 hours per hour of delivery Cost / Development time § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time Inexpensive to develop High transfer of knowledge Directly relevant to trainee’s job Trainees interact with coworkers § Student demonstrates a skill in a simulation of the real situation § Apply knowledge and skills by demonstrating § Encourage collaboration, networking, and sharing of war stories § Immediate feedback is provided Recommendation Could be used to disseminate skills and Subject matter experts could be used Could be used where people knowledge obtained from seminars, to consult on best practice and up to workshops and experience to staff date views on “Hot Topics” and members who are new to their role or to problem solving the organisation. Coaching could also be used as a means of informal assessment of learners 20 interaction skills are required e. g. in Client service scenario where the learner may need to develop practical techniques of how to deal with difficult clients
Training Delivery Channels – face -to-face learning Coaching and mentorship are cheaper alternatives for face-to-face, but may lack consistency of approach and may fail due to lack of sustained support Channels Coaching Mentoring Role Play Advantages § § Inexpensive to develop High transfer of knowledge Directly relevant to trainee’s job Trainees interact with coworkers § § Disadvantages § § Training may be inconsistently delivered Difficult to control/monitor Requires workers to be teachers Can disrupt regular workflow § Training may be inconsistently delivered § Difficult to control/monitor § Requires workers to be teachers § Can disrupt regular workflow § Training may be inconsistently delivered § Difficult to control/monitor When to use § On-the-job training § In small groups at regional training sites § 15 -60 hours per hour of delivery § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time § 15 -60 hours per hour of delivery Cost / Development time § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time Inexpensive to develop High transfer of knowledge Directly relevant to trainee’s job Trainees interact with coworkers § Student demonstrates a skill in a simulation of the real situation § Apply knowledge and skills by demonstrating § Encourage collaboration, networking, and sharing of war stories § Immediate feedback is provided Recommendation Could be used to disseminate skills and Subject matter experts could be used Could be used where people knowledge obtained from seminars, to consult on best practice and up to workshops and experience to staff date views on “Hot Topics” and members who are new to their role or to problem solving the organisation. Coaching could also be used as a means of informal assessment of learners 20 interaction skills are required e. g. in Client service scenario where the learner may need to develop practical techniques of how to deal with difficult clients
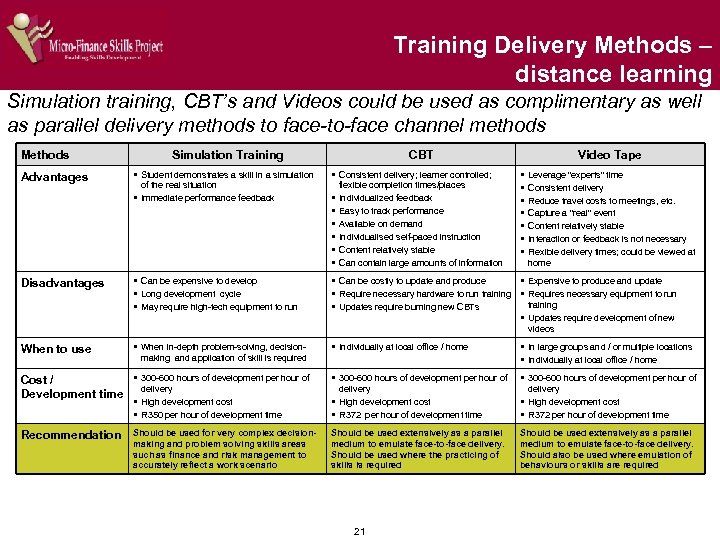 Training Delivery Methods – distance learning Simulation training, CBT’s and Videos could be used as complimentary as well as parallel delivery methods to face-to-face channel methods Methods Advantages Disadvantages Simulation Training § Student demonstrates a skill in a simulation of the real situation § Immediate performance feedback § Can be expensive to develop § Long development cycle § May require high-tech equipment to run CBT § Consistent delivery; learner controlled; § § § flexible completion times/places Individualized feedback Easy to track performance Available on demand Individualised self-paced instruction Content relatively stable Can contain large amounts of information Video Tape § § § § Leverage "experts" time Consistent delivery Reduce travel costs to meetings, etc. Capture a "real" event Content relatively stable Interaction or feedback is not necessary Flexible delivery times; could be viewed at home § Can be costly to update and produce § Expensive to produce and update § Require necessary hardware to run training § Requires necessary equipment to run training § Updates require burning new CBTs § Updates require development of new videos When to use § When in-depth problem-solving, decision- § Individually at local office / home § In large groups and / or multiple locations § Individually at local office / home Cost / Development time § 300 -600 hours of development per hour of delivery § High development cost § R 350 per hour of development time delivery § High development cost § R 372 per hour of development time Recommendation Should be used for very complex decisionmaking and problem solving skills areas such as finance and risk management to accurately reflect a work scenario Should be used extensively as a parallel medium to emulate face-to-face delivery. Should be used where the practicing of skills is required Should be used extensively as a parallel medium to emulate face-to-face delivery. Should also be used where emulation of behaviours or skills are required making and application of skill is required 21
Training Delivery Methods – distance learning Simulation training, CBT’s and Videos could be used as complimentary as well as parallel delivery methods to face-to-face channel methods Methods Advantages Disadvantages Simulation Training § Student demonstrates a skill in a simulation of the real situation § Immediate performance feedback § Can be expensive to develop § Long development cycle § May require high-tech equipment to run CBT § Consistent delivery; learner controlled; § § § flexible completion times/places Individualized feedback Easy to track performance Available on demand Individualised self-paced instruction Content relatively stable Can contain large amounts of information Video Tape § § § § Leverage "experts" time Consistent delivery Reduce travel costs to meetings, etc. Capture a "real" event Content relatively stable Interaction or feedback is not necessary Flexible delivery times; could be viewed at home § Can be costly to update and produce § Expensive to produce and update § Require necessary hardware to run training § Requires necessary equipment to run training § Updates require burning new CBTs § Updates require development of new videos When to use § When in-depth problem-solving, decision- § Individually at local office / home § In large groups and / or multiple locations § Individually at local office / home Cost / Development time § 300 -600 hours of development per hour of delivery § High development cost § R 350 per hour of development time delivery § High development cost § R 372 per hour of development time Recommendation Should be used for very complex decisionmaking and problem solving skills areas such as finance and risk management to accurately reflect a work scenario Should be used extensively as a parallel medium to emulate face-to-face delivery. Should be used where the practicing of skills is required Should be used extensively as a parallel medium to emulate face-to-face delivery. Should also be used where emulation of behaviours or skills are required making and application of skill is required 21
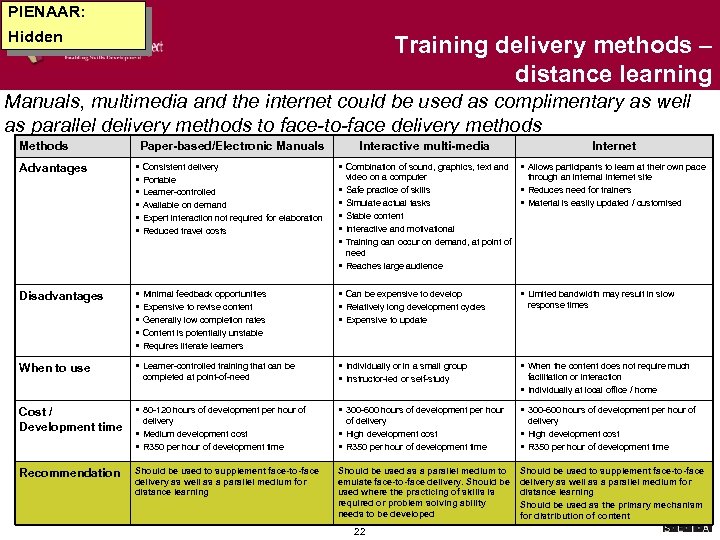 PIENAAR: Hidden Training delivery methods – distance learning Manuals, multimedia and the internet could be used as complimentary as well as parallel delivery methods to face-to-face delivery methods Methods Paper-based/Electronic Manuals Interactive multi-media Internet § § § Consistent delivery Portable Learner-controlled Available on demand Expert interaction not required for elaboration Reduced travel costs § Combination of sound, graphics, text and § Allows participants to learn at their own pace Disadvantages § § § Minimal feedback opportunities Expensive to revise content Generally low completion rates Content is potentially unstable Requires literate learners § Can be expensive to develop § Relatively long development cycles § Expensive to update § Limited bandwidth may result in slow When to use § Learner-controlled training that can be § Individually or in a small group § Instructor-led or self-study § When the content does not require much Cost / Development time § 80 -120 hours of development per hour of § 300 -600 hours of development per hour of delivery § Medium development cost § R 350 per hour of development time of delivery § High development cost § R 350 per hour of development time Recommendation Should be used to supplement face-to-face delivery as well as a parallel medium for distance learning Should be used as a parallel medium to emulate face-to-face delivery. Should be used where the practicing of skills is required or problem solving ability needs to be developed Should be used to supplement face-to-face delivery as well as a parallel medium for distance learning Should be used as the primary mechanism for distribution of content Advantages completed at point-of-need video on a computer through an internal Internet site Safe practice of skills § Reduces need for trainers Simulate actual tasks § Material is easily updated / customised Stable content Interactive and motivational Training can occur on demand, at point of need § Reaches large audience § § § 22 response times facilitation or interaction § Individually at local office / home
PIENAAR: Hidden Training delivery methods – distance learning Manuals, multimedia and the internet could be used as complimentary as well as parallel delivery methods to face-to-face delivery methods Methods Paper-based/Electronic Manuals Interactive multi-media Internet § § § Consistent delivery Portable Learner-controlled Available on demand Expert interaction not required for elaboration Reduced travel costs § Combination of sound, graphics, text and § Allows participants to learn at their own pace Disadvantages § § § Minimal feedback opportunities Expensive to revise content Generally low completion rates Content is potentially unstable Requires literate learners § Can be expensive to develop § Relatively long development cycles § Expensive to update § Limited bandwidth may result in slow When to use § Learner-controlled training that can be § Individually or in a small group § Instructor-led or self-study § When the content does not require much Cost / Development time § 80 -120 hours of development per hour of § 300 -600 hours of development per hour of delivery § Medium development cost § R 350 per hour of development time of delivery § High development cost § R 350 per hour of development time Recommendation Should be used to supplement face-to-face delivery as well as a parallel medium for distance learning Should be used as a parallel medium to emulate face-to-face delivery. Should be used where the practicing of skills is required or problem solving ability needs to be developed Should be used to supplement face-to-face delivery as well as a parallel medium for distance learning Should be used as the primary mechanism for distribution of content Advantages completed at point-of-need video on a computer through an internal Internet site Safe practice of skills § Reduces need for trainers Simulate actual tasks § Material is easily updated / customised Stable content Interactive and motivational Training can occur on demand, at point of need § Reaches large audience § § § 22 response times facilitation or interaction § Individually at local office / home
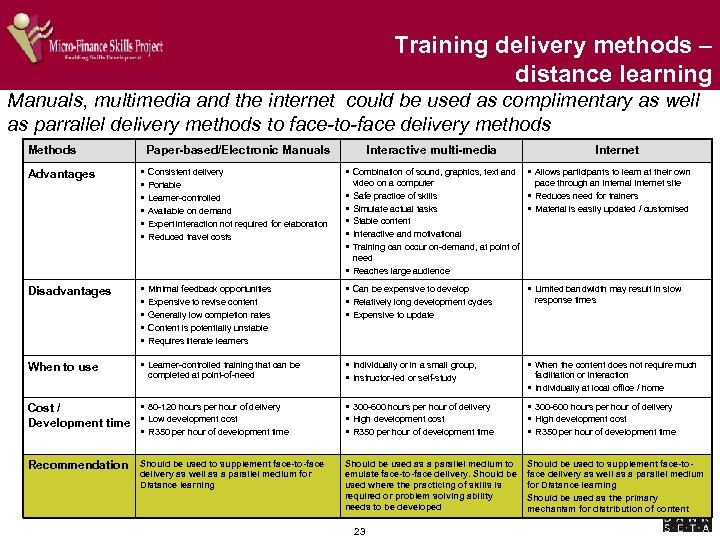 Training delivery methods – distance learning Manuals, multimedia and the internet could be used as complimentary as well as parrallel delivery methods to face-to-face delivery methods Methods Paper-based/Electronic Manuals Interactive multi-media Internet § § § Consistent delivery Portable Learner-controlled Available on demand Expert interaction not required for elaboration Reduced travel costs § Combination of sound, graphics, text and § Allows participants to learn at their own Disadvantages § § § Minimal feedback opportunities Expensive to revise content Generally low completion rates Content is potentially unstable Requires literate learners § Can be expensive to develop § Relatively long development cycles § Expensive to update § Limited bandwidth may result in slow When to use § Learner-controlled training that can be § Individually or in a small group, § Instructor-led or self-study § When the content does not require much Advantages completed at point-of-need video on a computer pace through an internal Internet site Safe practice of skills § Reduces need for trainers Simulate actual tasks § Material is easily updated / customised Stable content Interactive and motivational Training can occur on-demand, at point of need § Reaches large audience § § § response times facilitation or interaction § Individually at local office / home Cost / Development time § 80 -120 hours per hour of delivery § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time § 300 -600 hours per hour of delivery § High development cost § R 350 per hour of development time Recommendation Should be used to supplement face-to-face delivery as well as a parallel medium for Distance learning Should be used as a parallel medium to emulate face-to-face delivery. Should be used where the practicing of skills is required or problem solving ability needs to be developed Should be used to supplement face-toface delivery as well as a parallel medium for Distance learning Should be used as the primary mechanism for distribution of content 23
Training delivery methods – distance learning Manuals, multimedia and the internet could be used as complimentary as well as parrallel delivery methods to face-to-face delivery methods Methods Paper-based/Electronic Manuals Interactive multi-media Internet § § § Consistent delivery Portable Learner-controlled Available on demand Expert interaction not required for elaboration Reduced travel costs § Combination of sound, graphics, text and § Allows participants to learn at their own Disadvantages § § § Minimal feedback opportunities Expensive to revise content Generally low completion rates Content is potentially unstable Requires literate learners § Can be expensive to develop § Relatively long development cycles § Expensive to update § Limited bandwidth may result in slow When to use § Learner-controlled training that can be § Individually or in a small group, § Instructor-led or self-study § When the content does not require much Advantages completed at point-of-need video on a computer pace through an internal Internet site Safe practice of skills § Reduces need for trainers Simulate actual tasks § Material is easily updated / customised Stable content Interactive and motivational Training can occur on-demand, at point of need § Reaches large audience § § § response times facilitation or interaction § Individually at local office / home Cost / Development time § 80 -120 hours per hour of delivery § Low development cost § R 350 per hour of development time § 300 -600 hours per hour of delivery § High development cost § R 350 per hour of development time Recommendation Should be used to supplement face-to-face delivery as well as a parallel medium for Distance learning Should be used as a parallel medium to emulate face-to-face delivery. Should be used where the practicing of skills is required or problem solving ability needs to be developed Should be used to supplement face-toface delivery as well as a parallel medium for Distance learning Should be used as the primary mechanism for distribution of content 23
 Strategy for delivering training Principles guiding the delivery of training to micro financiers were developed, taking into account global best practice § Training design and delivery should be modular § Training must be relevant to the learner, and impact their performace at work § Training development must be prioritised based on micro financier needs § Training development must be flexible, and be easy to update when required § A combination of experiential and situational methodologies should be used § A combination of face-to-face and Distance learning channels should be used § Content should be available over multiple delivery channels Within these guiding principles, an approach to the development, delivery and management of training has been defined 24
Strategy for delivering training Principles guiding the delivery of training to micro financiers were developed, taking into account global best practice § Training design and delivery should be modular § Training must be relevant to the learner, and impact their performace at work § Training development must be prioritised based on micro financier needs § Training development must be flexible, and be easy to update when required § A combination of experiential and situational methodologies should be used § A combination of face-to-face and Distance learning channels should be used § Content should be available over multiple delivery channels Within these guiding principles, an approach to the development, delivery and management of training has been defined 24
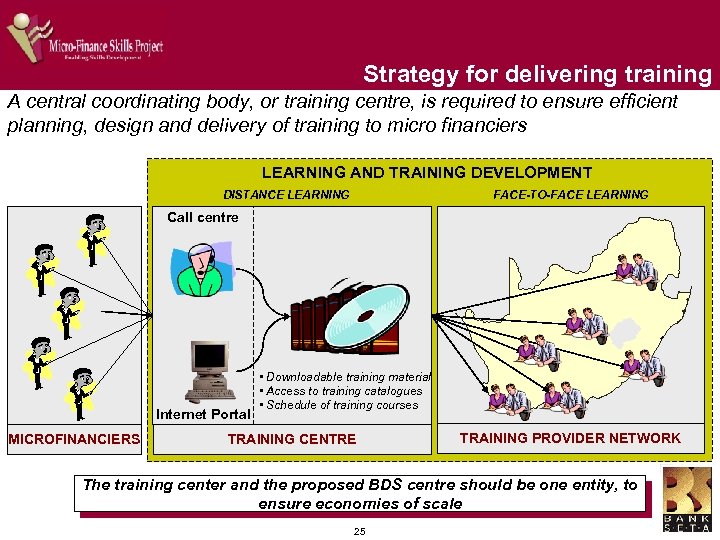 Strategy for delivering training A central coordinating body, or training centre, is required to ensure efficient planning, design and delivery of training to micro financiers LEARNING AND TRAINING DEVELOPMENT DISTANCE LEARNING FACE-TO-FACE LEARNING Call centre Internet Portal MICROFINANCIERS • Downloadable training material • Access to training catalogues • Schedule of training courses TRAINING CENTRE TRAINING PROVIDER NETWORK The training center and the proposed BDS centre should be one entity, to ensure economies of scale 25
Strategy for delivering training A central coordinating body, or training centre, is required to ensure efficient planning, design and delivery of training to micro financiers LEARNING AND TRAINING DEVELOPMENT DISTANCE LEARNING FACE-TO-FACE LEARNING Call centre Internet Portal MICROFINANCIERS • Downloadable training material • Access to training catalogues • Schedule of training courses TRAINING CENTRE TRAINING PROVIDER NETWORK The training center and the proposed BDS centre should be one entity, to ensure economies of scale 25
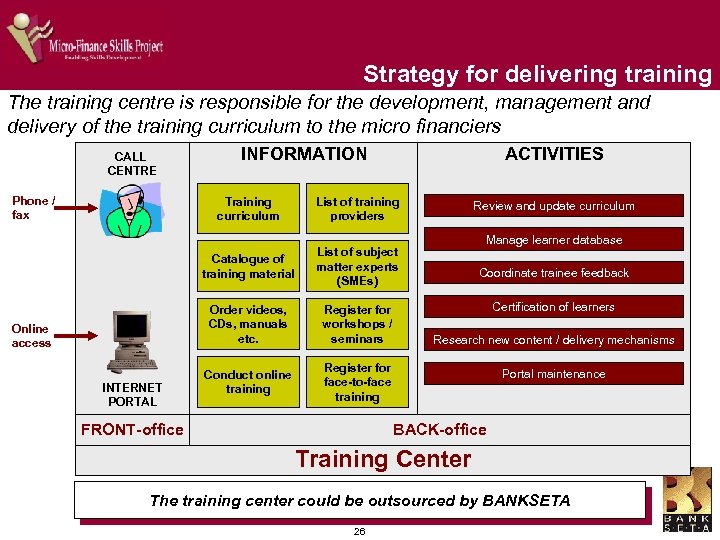 Strategy for delivering training The training centre is responsible for the development, management and delivery of the training curriculum to the micro financiers CALL CENTRE Phone / fax INFORMATION Training curriculum ACTIVITIES List of training providers Catalogue of training material Online access INTERNET PORTAL Register for workshops / seminars Conduct online training Manage learner database List of subject matter experts (SMEs) Order videos, CDs, manuals etc. Review and update curriculum Register for face-to-face training FRONT-office Coordinate trainee feedback Certification of learners Research new content / delivery mechanisms Portal maintenance BACK-office Training Center The training center could be outsourced by BANKSETA 26
Strategy for delivering training The training centre is responsible for the development, management and delivery of the training curriculum to the micro financiers CALL CENTRE Phone / fax INFORMATION Training curriculum ACTIVITIES List of training providers Catalogue of training material Online access INTERNET PORTAL Register for workshops / seminars Conduct online training Manage learner database List of subject matter experts (SMEs) Order videos, CDs, manuals etc. Review and update curriculum Register for face-to-face training FRONT-office Coordinate trainee feedback Certification of learners Research new content / delivery mechanisms Portal maintenance BACK-office Training Center The training center could be outsourced by BANKSETA 26
 Incentives A significant risk to the successful delivery of training to the micro finance industry is the perceived lack of real business benefits § Involvement of micro finance practitioners in the development of the content of the training materials will the create a sense of ownership of the programme Ø Ø § Buy-in for the benefits of the training initiatives will be generated through a needs-driven strategy The creation of micro finance best practices will be generated through practitioner involvement in the project and in so doing generate demand for the training Monetary incentives in the form of skills development grants will afford micro financiers the opportunity to claim back on their skills levies paid. Qualifying employers can access up to 60% of their annual contributions for skills development under the sector grant scheme Ø Planning grants may be obtained through the registration of a skills development facilitator as well as the submission of a workplace skills plan Ø Implementation grants may be obtained through the submission of a skills development implementation report Incentives in the form of skills development grants would be the main monetary incentives for micro finance businesses 27
Incentives A significant risk to the successful delivery of training to the micro finance industry is the perceived lack of real business benefits § Involvement of micro finance practitioners in the development of the content of the training materials will the create a sense of ownership of the programme Ø Ø § Buy-in for the benefits of the training initiatives will be generated through a needs-driven strategy The creation of micro finance best practices will be generated through practitioner involvement in the project and in so doing generate demand for the training Monetary incentives in the form of skills development grants will afford micro financiers the opportunity to claim back on their skills levies paid. Qualifying employers can access up to 60% of their annual contributions for skills development under the sector grant scheme Ø Planning grants may be obtained through the registration of a skills development facilitator as well as the submission of a workplace skills plan Ø Implementation grants may be obtained through the submission of a skills development implementation report Incentives in the form of skills development grants would be the main monetary incentives for micro finance businesses 27
 Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 28
Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 28
 Curriculum content overview The curriculum content has been developed through the application of best practice models, consultation with industry experts, stakeholders as well as a learner needs analysis § The majority of South African micro-finance businesses are small to medium sized businesses and it is with this in mind that the overall modular approach to the training needs of micro-financiers was taken Ø Ø Ø The contextual learning needs of a micro finance business were looked at from a small to medium sized business perspective, where every aspect of the business was seen as a training module International business school models were applied to source the various training modules that would be appropriate to a small to medium-sized financial services business Several Industry practitioners and stakeholders were approached for their input on the training requirements for a micro finance business. Responses from these interviews were used to add micro finance industry-specific topics to the curriculum Existing unit standards for the banking industry were used to include loan granting aspects from a financial services sector perspective An external subject matter expert was consulted on the overall approach and content of the curriculum framework Workshops with the Curriculum Development team and the Consultative Forum were held to validate the approach and high level content 29
Curriculum content overview The curriculum content has been developed through the application of best practice models, consultation with industry experts, stakeholders as well as a learner needs analysis § The majority of South African micro-finance businesses are small to medium sized businesses and it is with this in mind that the overall modular approach to the training needs of micro-financiers was taken Ø Ø Ø The contextual learning needs of a micro finance business were looked at from a small to medium sized business perspective, where every aspect of the business was seen as a training module International business school models were applied to source the various training modules that would be appropriate to a small to medium-sized financial services business Several Industry practitioners and stakeholders were approached for their input on the training requirements for a micro finance business. Responses from these interviews were used to add micro finance industry-specific topics to the curriculum Existing unit standards for the banking industry were used to include loan granting aspects from a financial services sector perspective An external subject matter expert was consulted on the overall approach and content of the curriculum framework Workshops with the Curriculum Development team and the Consultative Forum were held to validate the approach and high level content 29
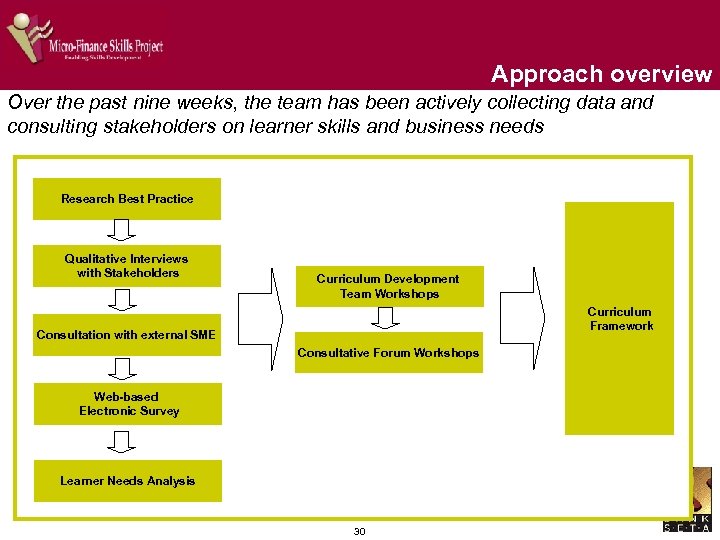 Approach overview Over the past nine weeks, the team has been actively collecting data and consulting stakeholders on learner skills and business needs Research Best Practice Qualitative Interviews with Stakeholders Curriculum Development Team Workshops Curriculum Framework Consultation with external SME Consultative Forum Workshops Web-based Electronic Survey Learner Needs Analysis 30
Approach overview Over the past nine weeks, the team has been actively collecting data and consulting stakeholders on learner skills and business needs Research Best Practice Qualitative Interviews with Stakeholders Curriculum Development Team Workshops Curriculum Framework Consultation with external SME Consultative Forum Workshops Web-based Electronic Survey Learner Needs Analysis 30
 Curriculum content summary Based upon the learner needs analysis, a high level view of the curriculum content has been established § Skills areas included in the content of the curriculum : Ø Risk management Ø Staff management Ø Loan book management Ø Complaint procedures Ø Client service Ø Service provider management Ø Legal and regulatory compliance Ø Marketing Ø Cash management Ø SMME Ø Finance Ø Leadership development Ø Funding strategies Ø Management development Ø Business strategies Ø Communications Ø Client administration Ø Personal development 31
Curriculum content summary Based upon the learner needs analysis, a high level view of the curriculum content has been established § Skills areas included in the content of the curriculum : Ø Risk management Ø Staff management Ø Loan book management Ø Complaint procedures Ø Client service Ø Service provider management Ø Legal and regulatory compliance Ø Marketing Ø Cash management Ø SMME Ø Finance Ø Leadership development Ø Funding strategies Ø Management development Ø Business strategies Ø Communications Ø Client administration Ø Personal development 31
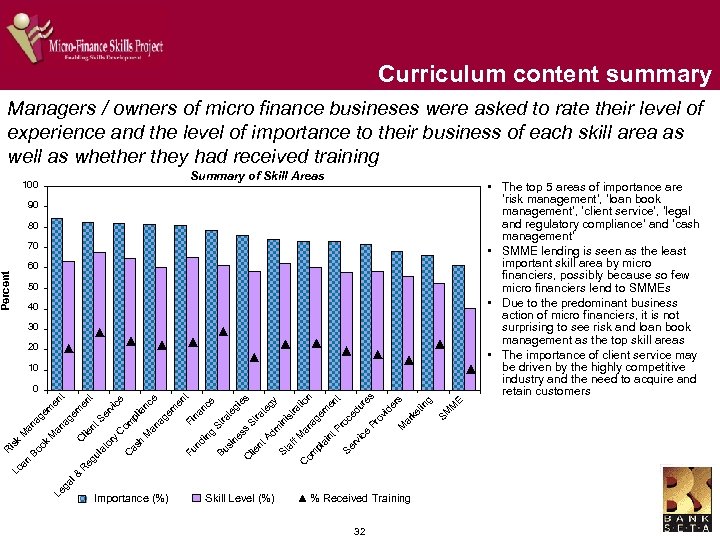 Curriculum content summary Managers / owners of micro finance busineses were asked to rate their level of experience and the level of importance to their business of each skill area as well as whether they had received training Summary of Skill Areas 100 90 80 70 Percent 60 50 40 30 20 10 nt A C lie si Bu te gy dm in St is af tra f M tio C an n om ag pl em ai nt en P t ro Se ce rv du ic re e s Pr ov id er s M ar ke tin g SM M E tra ne ss S ra te gi e e St g in nd Fu h as s t na nc en Fi e ge m ia M an a om pl C at o eg ul Le ga l & R C C ry lie nt S er vi nc ce t m en ag e an M oo k an B Lo R is k M an ag em en t 0 Importance (%) Skill Level (%) % Received Training 32 • The top 5 areas of importance are ‘risk management’, ‘loan book management’, ‘client service’, ‘legal and regulatory compliance’ and ‘cash management’ • SMME lending is seen as the least important skill area by micro financiers, possibly because so few micro financiers lend to SMMEs • Due to the predominant business action of micro financiers, it is not surprising to see risk and loan book management as the top skill areas • The importance of client service may be driven by the highly competitive industry and the need to acquire and retain customers
Curriculum content summary Managers / owners of micro finance busineses were asked to rate their level of experience and the level of importance to their business of each skill area as well as whether they had received training Summary of Skill Areas 100 90 80 70 Percent 60 50 40 30 20 10 nt A C lie si Bu te gy dm in St is af tra f M tio C an n om ag pl em ai nt en P t ro Se ce rv du ic re e s Pr ov id er s M ar ke tin g SM M E tra ne ss S ra te gi e e St g in nd Fu h as s t na nc en Fi e ge m ia M an a om pl C at o eg ul Le ga l & R C C ry lie nt S er vi nc ce t m en ag e an M oo k an B Lo R is k M an ag em en t 0 Importance (%) Skill Level (%) % Received Training 32 • The top 5 areas of importance are ‘risk management’, ‘loan book management’, ‘client service’, ‘legal and regulatory compliance’ and ‘cash management’ • SMME lending is seen as the least important skill area by micro financiers, possibly because so few micro financiers lend to SMMEs • Due to the predominant business action of micro financiers, it is not surprising to see risk and loan book management as the top skill areas • The importance of client service may be driven by the highly competitive industry and the need to acquire and retain customers
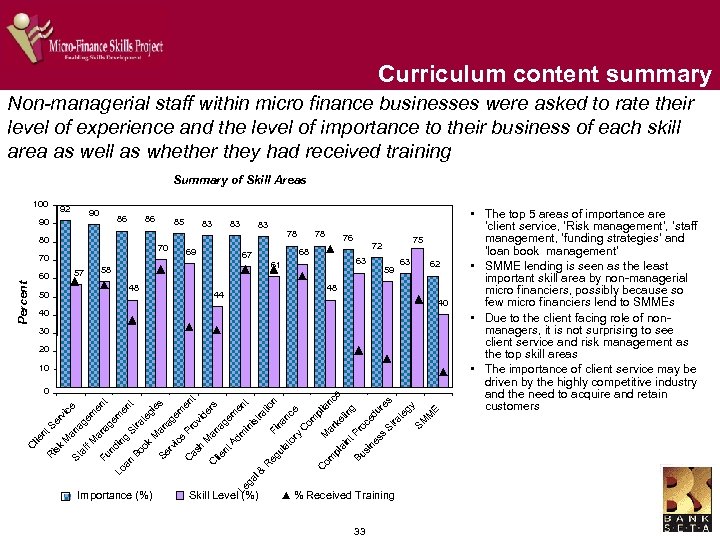 Curriculum content summary Non-managerial staff within micro finance businesses were asked to rate their level of experience and the level of importance to their business of each skill area as well as whether they had received training Summary of Skill Areas 100 92 90 90 86 86 80 70 70 57 60 Percent 85 83 69 83 78 78 76 68 67 44 75 72 63 61 58 48 50 83 59 63 62 48 40 40 30 20 M k is R C lie nt S er 0 vi ce an St ag af em f M en an Fu t ag nd em Lo in en g an St t B ra oo te k gi M es an Se ag rv em ic e en Pr C as t ov h id M er an C s lie ag nt em A dm en Le t in ga is l & tra R tio eg Fi n na ul at nc or e y C om pl C ia M om nc ar pl e ke ai tin nt g P Bu ro si ce ne du ss re S tra s te gy SM M E 10 Importance (%) Skill Level (%) % Received Training 33 • The top 5 areas of importance are ‘client service, ‘Risk management’, ‘staff management, ‘funding strategies’ and ‘loan book management’ • SMME lending is seen as the least important skill area by non-managerial micro financiers, possibly because so few micro financiers lend to SMMEs • Due to the client facing role of nonmanagers, it is not surprising to see client service and risk management as the top skill areas • The importance of client service may be driven by the highly competitive industry and the need to acquire and retain customers
Curriculum content summary Non-managerial staff within micro finance businesses were asked to rate their level of experience and the level of importance to their business of each skill area as well as whether they had received training Summary of Skill Areas 100 92 90 90 86 86 80 70 70 57 60 Percent 85 83 69 83 78 78 76 68 67 44 75 72 63 61 58 48 50 83 59 63 62 48 40 40 30 20 M k is R C lie nt S er 0 vi ce an St ag af em f M en an Fu t ag nd em Lo in en g an St t B ra oo te k gi M es an Se ag rv em ic e en Pr C as t ov h id M er an C s lie ag nt em A dm en Le t in ga is l & tra R tio eg Fi n na ul at nc or e y C om pl C ia M om nc ar pl e ke ai tin nt g P Bu ro si ce ne du ss re S tra s te gy SM M E 10 Importance (%) Skill Level (%) % Received Training 33 • The top 5 areas of importance are ‘client service, ‘Risk management’, ‘staff management, ‘funding strategies’ and ‘loan book management’ • SMME lending is seen as the least important skill area by non-managerial micro financiers, possibly because so few micro financiers lend to SMMEs • Due to the client facing role of nonmanagers, it is not surprising to see client service and risk management as the top skill areas • The importance of client service may be driven by the highly competitive industry and the need to acquire and retain customers
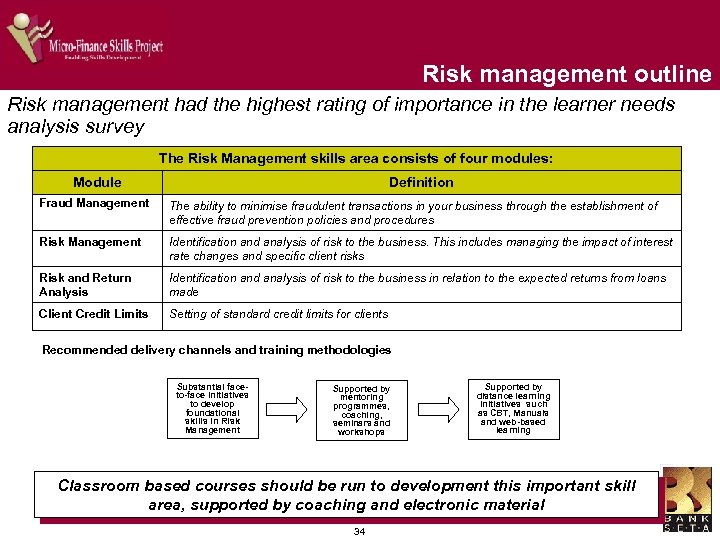 Risk management outline Risk management had the highest rating of importance in the learner needs analysis survey The Risk Management skills area consists of four modules: Module Definition Fraud Management The ability to minimise fraudulent transactions in your business through the establishment of effective fraud prevention policies and procedures Risk Management Identification and analysis of risk to the business. This includes managing the impact of interest rate changes and specific client risks Risk and Return Analysis Identification and analysis of risk to the business in relation to the expected returns from loans made Client Credit Limits Setting of standard credit limits for clients Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Substantial faceto-face initiatives to develop foundational skills in Risk Management Supported by mentoring programmes, coaching, seminars and workshops Supported by distance learning initiatives such as CBT, Manuals and web-based learning Classroom based courses should be run to development this important skill area, supported by coaching and electronic material 34
Risk management outline Risk management had the highest rating of importance in the learner needs analysis survey The Risk Management skills area consists of four modules: Module Definition Fraud Management The ability to minimise fraudulent transactions in your business through the establishment of effective fraud prevention policies and procedures Risk Management Identification and analysis of risk to the business. This includes managing the impact of interest rate changes and specific client risks Risk and Return Analysis Identification and analysis of risk to the business in relation to the expected returns from loans made Client Credit Limits Setting of standard credit limits for clients Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Substantial faceto-face initiatives to develop foundational skills in Risk Management Supported by mentoring programmes, coaching, seminars and workshops Supported by distance learning initiatives such as CBT, Manuals and web-based learning Classroom based courses should be run to development this important skill area, supported by coaching and electronic material 34
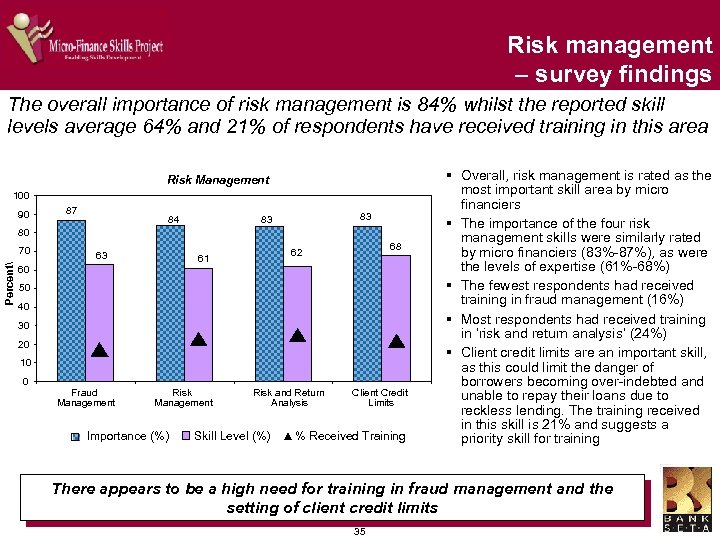 Risk management – survey findings The overall importance of risk management is 84% whilst the reported skill levels average 64% and 21% of respondents have received training in this area Risk Management 100 90 87 84 83 83 80 Percent 70 63 68 62 61 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Fraud Management Risk Management Importance (%) Risk and Return Analysis Skill Level (%) Client Credit Limits % Received Training § Overall, risk management is rated as the most important skill area by micro financiers § The importance of the four risk management skills were similarly rated by micro financiers (83%-87%), as were the levels of expertise (61%-68%) § The fewest respondents had received training in fraud management (16%) § Most respondents had received training in ‘risk and return analysis’ (24%) § Client credit limits are an important skill, as this could limit the danger of borrowers becoming over-indebted and unable to repay their loans due to reckless lending. The training received in this skill is 21% and suggests a priority skill for training There appears to be a high need for training in fraud management and the setting of client credit limits 35
Risk management – survey findings The overall importance of risk management is 84% whilst the reported skill levels average 64% and 21% of respondents have received training in this area Risk Management 100 90 87 84 83 83 80 Percent 70 63 68 62 61 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Fraud Management Risk Management Importance (%) Risk and Return Analysis Skill Level (%) Client Credit Limits % Received Training § Overall, risk management is rated as the most important skill area by micro financiers § The importance of the four risk management skills were similarly rated by micro financiers (83%-87%), as were the levels of expertise (61%-68%) § The fewest respondents had received training in fraud management (16%) § Most respondents had received training in ‘risk and return analysis’ (24%) § Client credit limits are an important skill, as this could limit the danger of borrowers becoming over-indebted and unable to repay their loans due to reckless lending. The training received in this skill is 21% and suggests a priority skill for training There appears to be a high need for training in fraud management and the setting of client credit limits 35
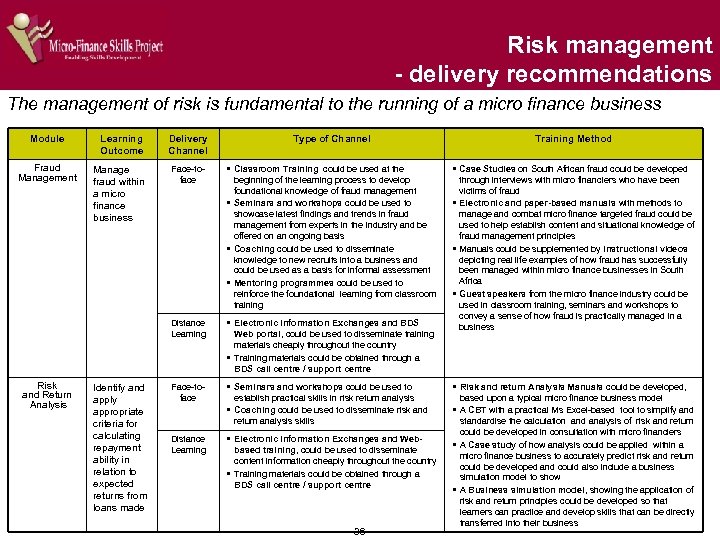 Risk management - delivery recommendations The management of risk is fundamental to the running of a micro finance business Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Fraud Management Manage fraud within a micro finance business Face-toface § Classroom Training could be used at the § Case Studies on South African fraud could be developed beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of fraud management § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in fraud management from experts in the industry and be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and could be used as a basis for informal assessment § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS through interviews with micro financiers who have been victims of fraud § Electronic and paper-based manuals with methods to manage and combat micro finance targeted fraud could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of fraud management principles § Manuals could be supplemented by Instructional videos depicting real life examples of how fraud has successfully been managed within micro finance businesses in South Africa § Guest speakers from the micro finance industry could be used in classroom training, seminars and workshops to convey a sense of how fraud is practically managed in a business Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Risk and return Analysis Manuals could be developed, establish practical skills in risk return analysis § Coaching could be used to disseminate risk and return analysis skills § A CBT with a practical Ms Excel-based tool to simplify and Risk and Return Analysis Identify and apply appropriate criteria for calculating repayment ability in relation to expected returns from loans made Distance Learning Type of Channel Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre § Electronic Information Exchanges and Webbased training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 36 Training Method based upon a typical micro finance business model standardise the calculation and analysis of risk and return could be developed in consultation with micro financiers § A Case study of how analysis could be applied within a micro finance business to accurately predict risk and return could be developed and could also include a business simulation model to show § A Business simulation model, showing the application of risk and return principles could be developed so that learners can practice and develop skills that can be directly transferred into their business
Risk management - delivery recommendations The management of risk is fundamental to the running of a micro finance business Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Fraud Management Manage fraud within a micro finance business Face-toface § Classroom Training could be used at the § Case Studies on South African fraud could be developed beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of fraud management § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in fraud management from experts in the industry and be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and could be used as a basis for informal assessment § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS through interviews with micro financiers who have been victims of fraud § Electronic and paper-based manuals with methods to manage and combat micro finance targeted fraud could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of fraud management principles § Manuals could be supplemented by Instructional videos depicting real life examples of how fraud has successfully been managed within micro finance businesses in South Africa § Guest speakers from the micro finance industry could be used in classroom training, seminars and workshops to convey a sense of how fraud is practically managed in a business Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Risk and return Analysis Manuals could be developed, establish practical skills in risk return analysis § Coaching could be used to disseminate risk and return analysis skills § A CBT with a practical Ms Excel-based tool to simplify and Risk and Return Analysis Identify and apply appropriate criteria for calculating repayment ability in relation to expected returns from loans made Distance Learning Type of Channel Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre § Electronic Information Exchanges and Webbased training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 36 Training Method based upon a typical micro finance business model standardise the calculation and analysis of risk and return could be developed in consultation with micro financiers § A Case study of how analysis could be applied within a micro finance business to accurately predict risk and return could be developed and could also include a business simulation model to show § A Business simulation model, showing the application of risk and return principles could be developed so that learners can practice and develop skills that can be directly transferred into their business
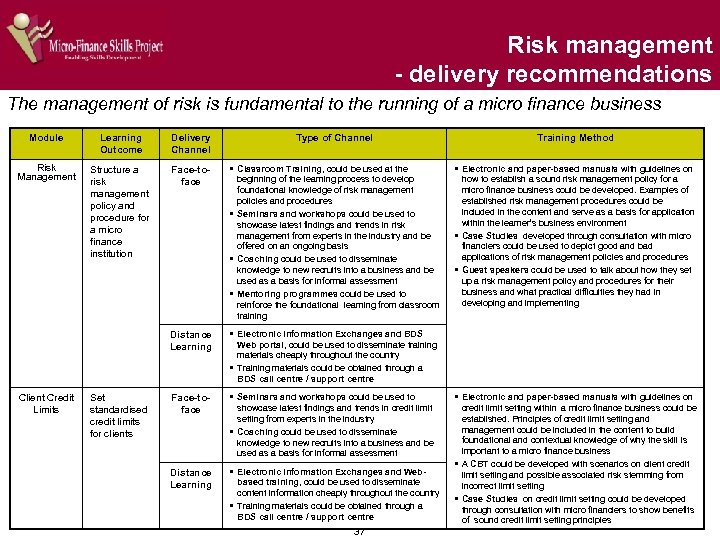 Risk management - delivery recommendations The management of risk is fundamental to the running of a micro finance business Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Risk Management Structure a risk management policy and procedure for a micro finance institution Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the § Electronic and paper-based manuals with guidelines on beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of risk management policies and procedures § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in risk management from experts in the industry and be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training how to establish a sound risk management policy for a micro finance business could be developed. Examples of established risk management procedures could be included in the content and serve as a basis for application within the learner’s business environment § Case Studies developed through consultation with micro financiers could be used to depict good and bad applications of risk management policies and procedures § Guest speakers could be used to talk about how they set up a risk management policy and procedures for their business and what practical difficulties they had in developing and implementing Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals with guidelines on showcase latest findings and trends in credit limit setting from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web- credit limit setting within a micro finance business could be established. Principles of credit limit setting and management could be included in the content to build foundational and contextual knowledge of why the skill is important to a micro finance business § A CBT could be developed with scenarios on client credit limit setting and possible associated risk stemming from incorrect limit setting § Case Studies on credit limit setting could be developed through consultation with micro financiers to show benefits of sound credit limit setting principles Client Credit Limits Set standardised credit limits for clients Type of Channel Training Method Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 37
Risk management - delivery recommendations The management of risk is fundamental to the running of a micro finance business Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Risk Management Structure a risk management policy and procedure for a micro finance institution Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the § Electronic and paper-based manuals with guidelines on beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of risk management policies and procedures § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in risk management from experts in the industry and be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training how to establish a sound risk management policy for a micro finance business could be developed. Examples of established risk management procedures could be included in the content and serve as a basis for application within the learner’s business environment § Case Studies developed through consultation with micro financiers could be used to depict good and bad applications of risk management policies and procedures § Guest speakers could be used to talk about how they set up a risk management policy and procedures for their business and what practical difficulties they had in developing and implementing Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals with guidelines on showcase latest findings and trends in credit limit setting from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web- credit limit setting within a micro finance business could be established. Principles of credit limit setting and management could be included in the content to build foundational and contextual knowledge of why the skill is important to a micro finance business § A CBT could be developed with scenarios on client credit limit setting and possible associated risk stemming from incorrect limit setting § Case Studies on credit limit setting could be developed through consultation with micro financiers to show benefits of sound credit limit setting principles Client Credit Limits Set standardised credit limits for clients Type of Channel Training Method Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 37
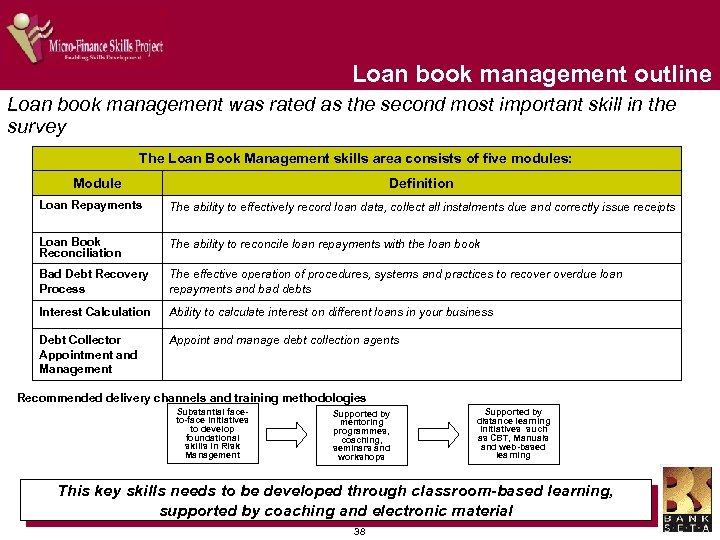 Loan book management outline Loan book management was rated as the second most important skill in the survey The Loan Book Management skills area consists of five modules: Module Definition Loan Repayments The ability to effectively record loan data, collect all instalments due and correctly issue receipts Loan Book Reconciliation The ability to reconcile loan repayments with the loan book Bad Debt Recovery Process The effective operation of procedures, systems and practices to recoverdue loan repayments and bad debts Interest Calculation Ability to calculate interest on different loans in your business Debt Collector Appointment and Management Appoint and manage debt collection agents Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Substantial faceto-face initiatives to develop foundational skills in Risk Management Supported by mentoring programmes, coaching, seminars and workshops Supported by distance learning initiatives such as CBT, Manuals and web-based learning This key skills needs to be developed through classroom-based learning, supported by coaching and electronic material 38
Loan book management outline Loan book management was rated as the second most important skill in the survey The Loan Book Management skills area consists of five modules: Module Definition Loan Repayments The ability to effectively record loan data, collect all instalments due and correctly issue receipts Loan Book Reconciliation The ability to reconcile loan repayments with the loan book Bad Debt Recovery Process The effective operation of procedures, systems and practices to recoverdue loan repayments and bad debts Interest Calculation Ability to calculate interest on different loans in your business Debt Collector Appointment and Management Appoint and manage debt collection agents Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Substantial faceto-face initiatives to develop foundational skills in Risk Management Supported by mentoring programmes, coaching, seminars and workshops Supported by distance learning initiatives such as CBT, Manuals and web-based learning This key skills needs to be developed through classroom-based learning, supported by coaching and electronic material 38
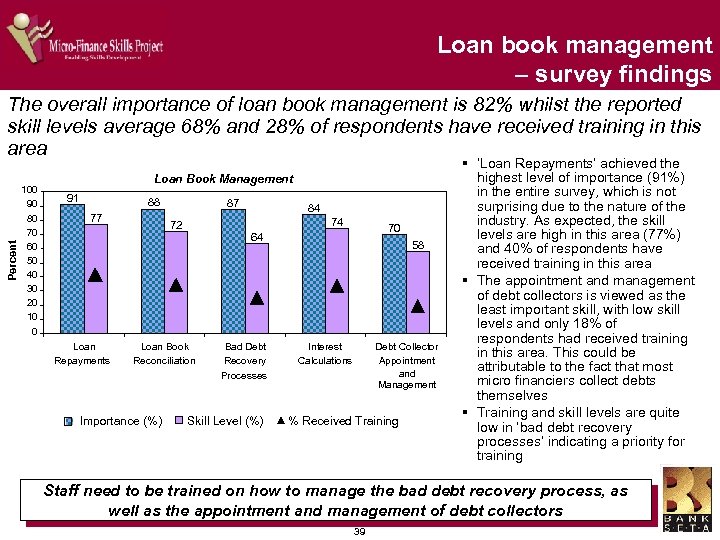 Loan book management – survey findings Percent The overall importance of loan book management is 82% whilst the reported skill levels average 68% and 28% of respondents have received training in this area 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Loan Book Management 91 88 77 Loan Repayments 87 74 72 70 64 Loan Book Reconciliation Importance (%) 84 Bad Debt Recovery Processes Skill Level (%) 58 Interest Calculations Debt Collector Appointment and Management % Received Training § ‘Loan Repayments’ achieved the highest level of importance (91%) in the entire survey, which is not surprising due to the nature of the industry. As expected, the skill levels are high in this area (77%) and 40% of respondents have received training in this area § The appointment and management of debt collectors is viewed as the least important skill, with low skill levels and only 18% of respondents had received training in this area. This could be attributable to the fact that most micro financiers collect debts themselves § Training and skill levels are quite low in ‘bad debt recovery processes’ indicating a priority for training Staff need to be trained on how to manage the bad debt recovery process, as well as the appointment and management of debt collectors 39
Loan book management – survey findings Percent The overall importance of loan book management is 82% whilst the reported skill levels average 68% and 28% of respondents have received training in this area 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Loan Book Management 91 88 77 Loan Repayments 87 74 72 70 64 Loan Book Reconciliation Importance (%) 84 Bad Debt Recovery Processes Skill Level (%) 58 Interest Calculations Debt Collector Appointment and Management % Received Training § ‘Loan Repayments’ achieved the highest level of importance (91%) in the entire survey, which is not surprising due to the nature of the industry. As expected, the skill levels are high in this area (77%) and 40% of respondents have received training in this area § The appointment and management of debt collectors is viewed as the least important skill, with low skill levels and only 18% of respondents had received training in this area. This could be attributable to the fact that most micro financiers collect debts themselves § Training and skill levels are quite low in ‘bad debt recovery processes’ indicating a priority for training Staff need to be trained on how to manage the bad debt recovery process, as well as the appointment and management of debt collectors 39
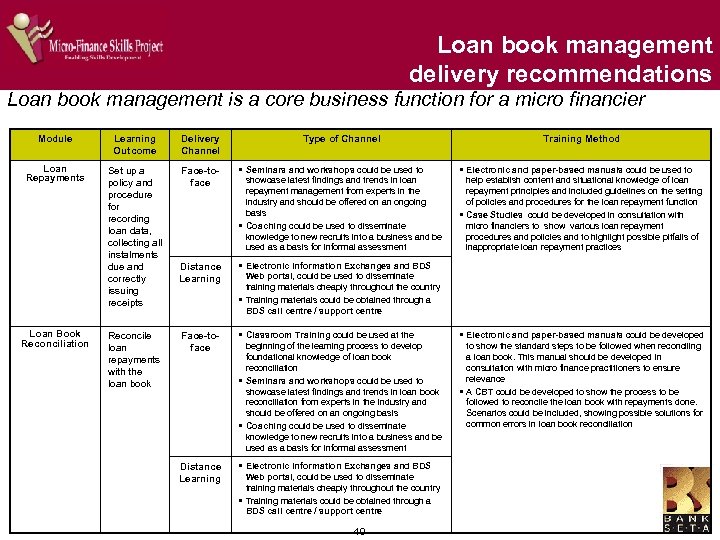 Loan book management delivery recommendations Loan book management is a core business function for a micro financier Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Loan Repayments Set up a policy and procedure for recording loan data, collecting all instalments due and correctly issuing receipts Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in loan repayment management from experts in the industry and should be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment help establish content and situational knowledge of loan repayment principles and included guidelines on the setting of policies and procedures for the loan repayment function § Case Studies could be developed in consultation with micro financiers to show various loan repayment procedures and policies and to highlight possible pitfalls of inappropriate loan repayment practices Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Face-toface § Classroom Training could be used at the § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of loan book reconciliation § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in loan book reconciliation from experts in the industry and should be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment to show the standard steps to be followed when reconciling a loan book. This manual should be developed in consultation with micro finance practitioners to ensure relevance § A CBT could be developed to show the process to be followed to reconcile the loan book with repayments done. Scenarios could be included, showing possible solutions for common errors in loan book reconciliation Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Loan Book Reconciliation Reconcile loan repayments with the loan book Type of Channel Training Method Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 40
Loan book management delivery recommendations Loan book management is a core business function for a micro financier Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Loan Repayments Set up a policy and procedure for recording loan data, collecting all instalments due and correctly issuing receipts Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in loan repayment management from experts in the industry and should be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment help establish content and situational knowledge of loan repayment principles and included guidelines on the setting of policies and procedures for the loan repayment function § Case Studies could be developed in consultation with micro financiers to show various loan repayment procedures and policies and to highlight possible pitfalls of inappropriate loan repayment practices Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Face-toface § Classroom Training could be used at the § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of loan book reconciliation § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in loan book reconciliation from experts in the industry and should be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment to show the standard steps to be followed when reconciling a loan book. This manual should be developed in consultation with micro finance practitioners to ensure relevance § A CBT could be developed to show the process to be followed to reconcile the loan book with repayments done. Scenarios could be included, showing possible solutions for common errors in loan book reconciliation Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Loan Book Reconciliation Reconcile loan repayments with the loan book Type of Channel Training Method Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 40
 Loan book management delivery recommendations Loan book management is a core business function for micro financiers Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Bad Debt Recovery Process Set up procedures, systems and practices to recoverdue loan repayments and bad debts Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of loan book reconciliation § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in bad debt recovery process management from experts in the industry and should be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment help establish content and situational knowledge of loan repayment principles and be supplemented by Instructional videos § Case Studies could be developed in conjunction with micro finance practitioners Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 41 Training Method
Loan book management delivery recommendations Loan book management is a core business function for micro financiers Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Bad Debt Recovery Process Set up procedures, systems and practices to recoverdue loan repayments and bad debts Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of loan book reconciliation § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in bad debt recovery process management from experts in the industry and should be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment help establish content and situational knowledge of loan repayment principles and be supplemented by Instructional videos § Case Studies could be developed in conjunction with micro finance practitioners Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 41 Training Method
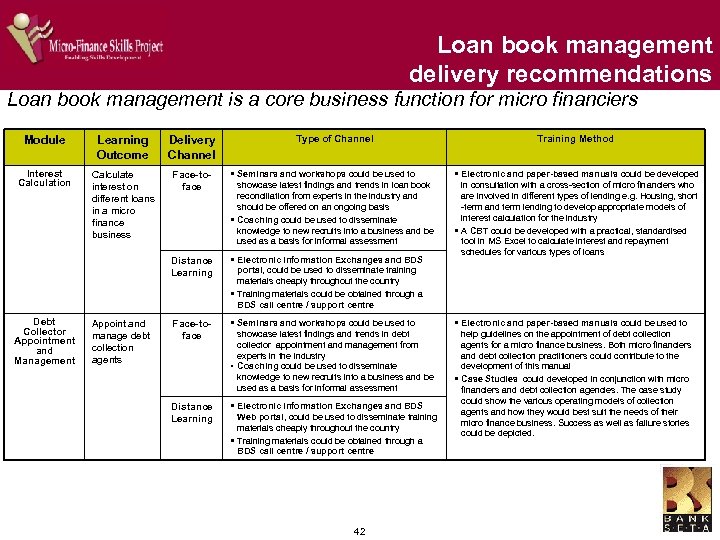 Loan book management delivery recommendations Loan book management is a core business function for micro financiers Type of Channel Training Method Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Interest Calculation Calculate interest on different loans in a micro finance business Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed showcase latest findings and trends in loan book reconciliation from experts in the industry and should be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS in consultation with a cross-section of micro financiers who are involved in different types of lending e. g. Housing, short -term and term lending to develop appropriate models of interest calculation for the industry § A CBT could be developed with a practical, standardised tool in MS Excel to calculate interest and repayment schedules for various types of loans Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in debt collector appointment and management from experts in the industry • Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS help guidelines on the appointment of debt collection agents for a micro finance business. Both micro financiers and debt collection practitioners could contribute to the development of this manual § Case Studies could developed in conjunction with micro financiers and debt collection agencies. The case study could show the various operating models of collection agents and how they would best suit the needs of their micro finance business. Success as well as failure stories could be depicted. Debt Collector Appointment and Management Appoint and manage debt collection agents portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 42
Loan book management delivery recommendations Loan book management is a core business function for micro financiers Type of Channel Training Method Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Interest Calculation Calculate interest on different loans in a micro finance business Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed showcase latest findings and trends in loan book reconciliation from experts in the industry and should be offered on an ongoing basis § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS in consultation with a cross-section of micro financiers who are involved in different types of lending e. g. Housing, short -term and term lending to develop appropriate models of interest calculation for the industry § A CBT could be developed with a practical, standardised tool in MS Excel to calculate interest and repayment schedules for various types of loans Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in debt collector appointment and management from experts in the industry • Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and be used as a basis for informal assessment Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS help guidelines on the appointment of debt collection agents for a micro finance business. Both micro financiers and debt collection practitioners could contribute to the development of this manual § Case Studies could developed in conjunction with micro financiers and debt collection agencies. The case study could show the various operating models of collection agents and how they would best suit the needs of their micro finance business. Success as well as failure stories could be depicted. Debt Collector Appointment and Management Appoint and manage debt collection agents portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 42
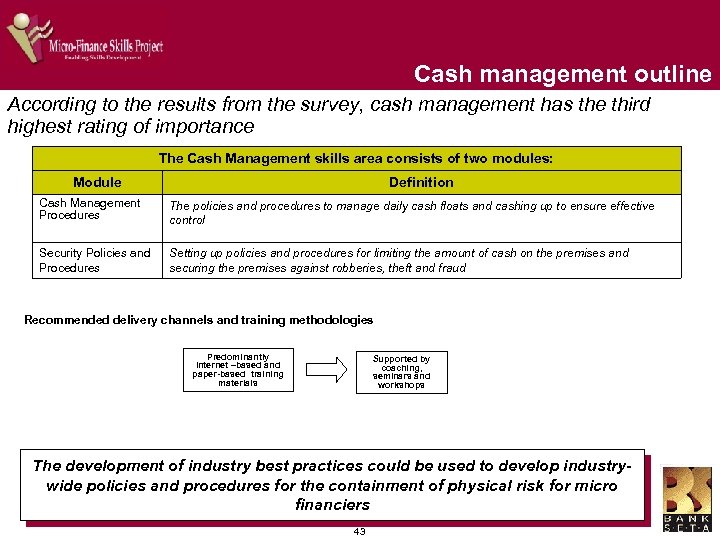 Cash management outline According to the results from the survey, cash management has the third highest rating of importance The Cash Management skills area consists of two modules: Module Definition Cash Management Procedures The policies and procedures to manage daily cash floats and cashing up to ensure effective control Security Policies and Procedures Setting up policies and procedures for limiting the amount of cash on the premises and securing the premises against robberies, theft and fraud Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Predominantly Internet –based and paper-based training materials Supported by coaching, seminars and workshops The development of industry best practices could be used to develop industrywide policies and procedures for the containment of physical risk for micro financiers 43
Cash management outline According to the results from the survey, cash management has the third highest rating of importance The Cash Management skills area consists of two modules: Module Definition Cash Management Procedures The policies and procedures to manage daily cash floats and cashing up to ensure effective control Security Policies and Procedures Setting up policies and procedures for limiting the amount of cash on the premises and securing the premises against robberies, theft and fraud Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Predominantly Internet –based and paper-based training materials Supported by coaching, seminars and workshops The development of industry best practices could be used to develop industrywide policies and procedures for the containment of physical risk for micro financiers 43
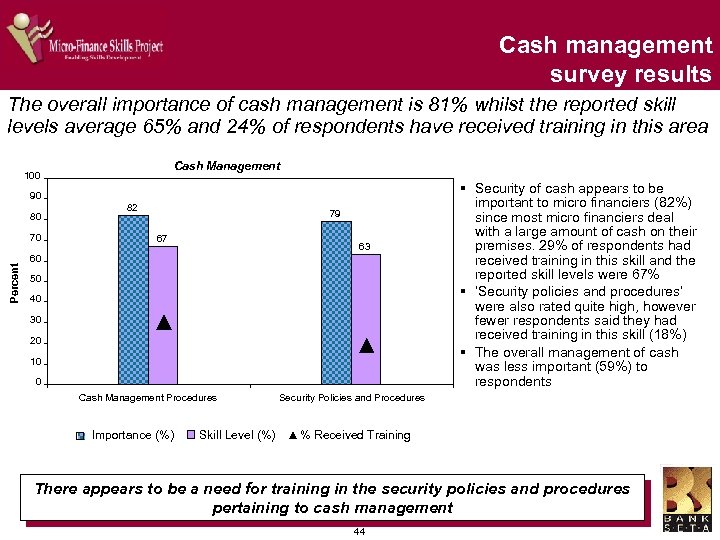 Cash management survey results The overall importance of cash management is 81% whilst the reported skill levels average 65% and 24% of respondents have received training in this area Cash Management 100 90 80 Percent 70 82 79 67 63 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Cash Management Procedures Importance (%) Skill Level (%) § Security of cash appears to be important to micro financiers (82%) since most micro financiers deal with a large amount of cash on their premises. 29% of respondents had received training in this skill and the reported skill levels were 67% § ‘Security policies and procedures’ were also rated quite high, however fewer respondents said they had received training in this skill (18%) § The overall management of cash was less important (59%) to respondents Security Policies and Procedures % Received Training There appears to be a need for training in the security policies and procedures pertaining to cash management 44
Cash management survey results The overall importance of cash management is 81% whilst the reported skill levels average 65% and 24% of respondents have received training in this area Cash Management 100 90 80 Percent 70 82 79 67 63 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Cash Management Procedures Importance (%) Skill Level (%) § Security of cash appears to be important to micro financiers (82%) since most micro financiers deal with a large amount of cash on their premises. 29% of respondents had received training in this skill and the reported skill levels were 67% § ‘Security policies and procedures’ were also rated quite high, however fewer respondents said they had received training in this skill (18%) § The overall management of cash was less important (59%) to respondents Security Policies and Procedures % Received Training There appears to be a need for training in the security policies and procedures pertaining to cash management 44
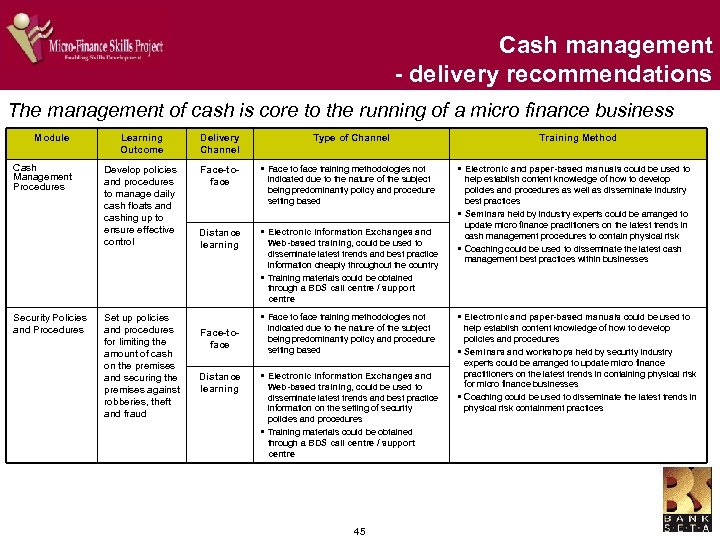 Cash management - delivery recommendations The management of cash is core to the running of a micro finance business Module Cash Management Procedures Security Policies and Procedures Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Develop policies and procedures to manage daily cash floats and cashing up to ensure effective control Face-toface § Face to face training methodologies not Distance learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Set up policies and procedures for limiting the amount of cash on the premises and securing the premises against robberies, theft and fraud Type of Channel indicated due to the nature of the subject being predominantly policy and procedure setting based Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre § Face to face training methodologies not Face-toface Distance learning indicated due to the nature of the subject being predominantly policy and procedure setting based § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information on the setting of security policies and procedures § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 45 Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures as well as disseminate industry best practices § Seminars held by industry experts could be arranged to update micro finance practitioners on the latest trends in cash management procedures to contain physical risk § Coaching could be used to disseminate the latest cash management best practices within businesses § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures § Seminars and workshops held by security industry experts could be arranged to update micro finance practitioners on the latest trends in containing physical risk for micro finance businesses § Coaching could be used to disseminate the latest trends in physical risk containment practices
Cash management - delivery recommendations The management of cash is core to the running of a micro finance business Module Cash Management Procedures Security Policies and Procedures Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Develop policies and procedures to manage daily cash floats and cashing up to ensure effective control Face-toface § Face to face training methodologies not Distance learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Set up policies and procedures for limiting the amount of cash on the premises and securing the premises against robberies, theft and fraud Type of Channel indicated due to the nature of the subject being predominantly policy and procedure setting based Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre § Face to face training methodologies not Face-toface Distance learning indicated due to the nature of the subject being predominantly policy and procedure setting based § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information on the setting of security policies and procedures § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 45 Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures as well as disseminate industry best practices § Seminars held by industry experts could be arranged to update micro finance practitioners on the latest trends in cash management procedures to contain physical risk § Coaching could be used to disseminate the latest cash management best practices within businesses § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures § Seminars and workshops held by security industry experts could be arranged to update micro finance practitioners on the latest trends in containing physical risk for micro finance businesses § Coaching could be used to disseminate the latest trends in physical risk containment practices
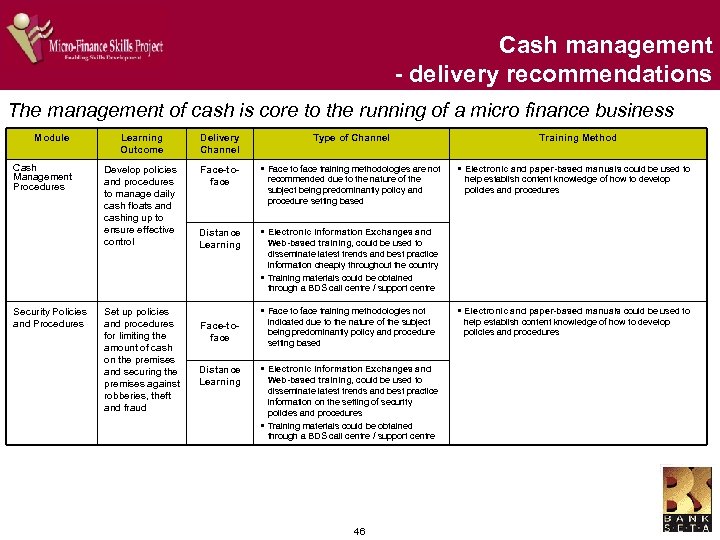 Cash management - delivery recommendations The management of cash is core to the running of a micro finance business Module Cash Management Procedures Security Policies and Procedures Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Develop policies and procedures to manage daily cash floats and cashing up to ensure effective control Face-toface § Face to face training methodologies are not Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Set up policies and procedures for limiting the amount of cash on the premises and securing the premises against robberies, theft and fraud recommended due to the nature of the subject being predominantly policy and procedure setting based Distance Learning § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre § Face to face training methodologies not Face-toface Training Method indicated due to the nature of the subject being predominantly policy and procedure setting based § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information on the setting of security policies and procedures § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 46 § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures
Cash management - delivery recommendations The management of cash is core to the running of a micro finance business Module Cash Management Procedures Security Policies and Procedures Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Develop policies and procedures to manage daily cash floats and cashing up to ensure effective control Face-toface § Face to face training methodologies are not Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Set up policies and procedures for limiting the amount of cash on the premises and securing the premises against robberies, theft and fraud recommended due to the nature of the subject being predominantly policy and procedure setting based Distance Learning § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre § Face to face training methodologies not Face-toface Training Method indicated due to the nature of the subject being predominantly policy and procedure setting based § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information on the setting of security policies and procedures § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 46 § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures
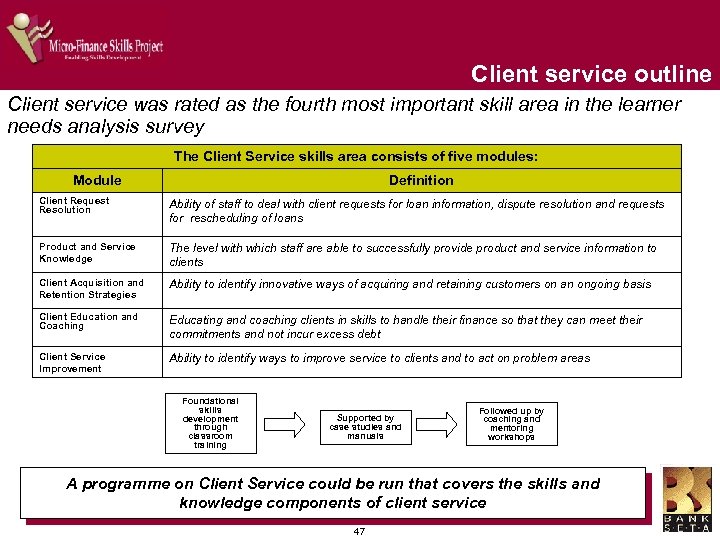 Client service outline Client service was rated as the fourth most important skill area in the learner needs analysis survey The Client Service skills area consists of five modules: Module Definition Client Request Resolution Ability of staff to deal with client requests for loan information, dispute resolution and requests for rescheduling of loans Product and Service Knowledge The level with which staff are able to successfully provide product and service information to clients Client Acquisition and Retention Strategies Ability to identify innovative ways of acquiring and retaining customers on an ongoing basis Client Education and Coaching Educating and coaching clients in skills to handle their finance so that they can meet their commitments and not incur excess debt Client Service Improvement Ability to identify ways to improve service to clients and to act on problem areas Foundational skills development through classroom training Supported by case studies and manuals Followed up by coaching and mentoring workshops A programme on Client Service could be run that covers the skills and knowledge components of client service 47
Client service outline Client service was rated as the fourth most important skill area in the learner needs analysis survey The Client Service skills area consists of five modules: Module Definition Client Request Resolution Ability of staff to deal with client requests for loan information, dispute resolution and requests for rescheduling of loans Product and Service Knowledge The level with which staff are able to successfully provide product and service information to clients Client Acquisition and Retention Strategies Ability to identify innovative ways of acquiring and retaining customers on an ongoing basis Client Education and Coaching Educating and coaching clients in skills to handle their finance so that they can meet their commitments and not incur excess debt Client Service Improvement Ability to identify ways to improve service to clients and to act on problem areas Foundational skills development through classroom training Supported by case studies and manuals Followed up by coaching and mentoring workshops A programme on Client Service could be run that covers the skills and knowledge components of client service 47
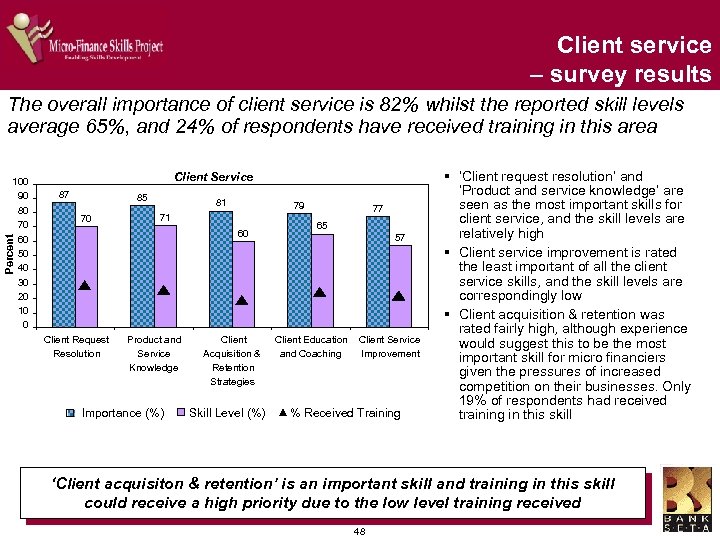 Client service – survey results The overall importance of client service is 82% whilst the reported skill levels average 65%, and 24% of respondents have received training in this area Client Service 87 85 70 81 79 71 60 Percent 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Client Request Resolution Product and Service Knowledge Importance (%) Client Acquisition & Retention Strategies Skill Level (%) 77 65 Client Education and Coaching 57 Client Service Improvement % Received Training § ‘Client request resolution’ and ‘Product and service knowledge’ are seen as the most important skills for client service, and the skill levels are relatively high § Client service improvement is rated the least important of all the client service skills, and the skill levels are correspondingly low § Client acquisition & retention was rated fairly high, although experience would suggest this to be the most important skill for micro financiers given the pressures of increased competition on their businesses. Only 19% of respondents had received training in this skill ‘Client acquisiton & retention’ is an important skill and training in this skill could receive a high priority due to the low level training received 48
Client service – survey results The overall importance of client service is 82% whilst the reported skill levels average 65%, and 24% of respondents have received training in this area Client Service 87 85 70 81 79 71 60 Percent 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Client Request Resolution Product and Service Knowledge Importance (%) Client Acquisition & Retention Strategies Skill Level (%) 77 65 Client Education and Coaching 57 Client Service Improvement % Received Training § ‘Client request resolution’ and ‘Product and service knowledge’ are seen as the most important skills for client service, and the skill levels are relatively high § Client service improvement is rated the least important of all the client service skills, and the skill levels are correspondingly low § Client acquisition & retention was rated fairly high, although experience would suggest this to be the most important skill for micro financiers given the pressures of increased competition on their businesses. Only 19% of respondents had received training in this skill ‘Client acquisiton & retention’ is an important skill and training in this skill could receive a high priority due to the low level training received 48
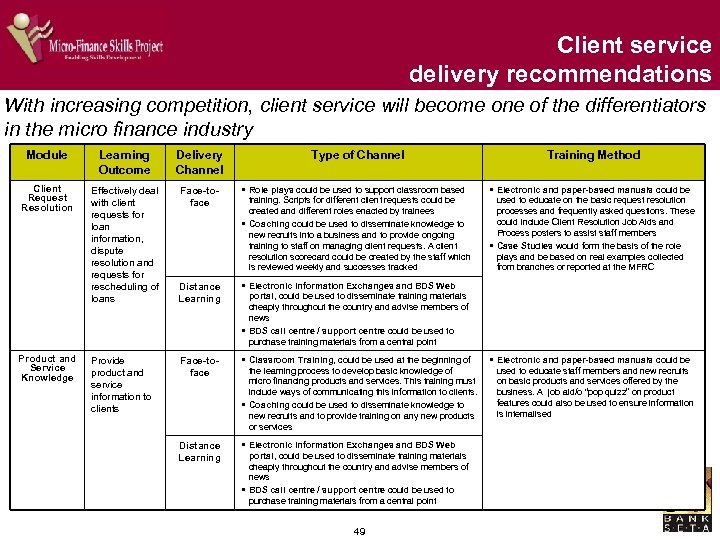 Client service delivery recommendations With increasing competition, client service will become one of the differentiators in the micro finance industry Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Client Request Resolution Effectively deal with client requests for loan information, dispute resolution and requests for rescheduling of loans Face-toface § Role plays could be used to support classroom based § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be training. Scripts for different client requests could be created and different roles enacted by trainees § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and to provide ongoing training to staff on managing client requests. A client resolution scorecard could be created by the staff which is reviewed weekly and successes tracked used to educate on the basic request resolution processes and frequently asked questions. These could include Client Resolution Job Aids and Process posters to assist staff members § Case Studies would form the basis of the role plays and be based on real examples collected from branches or reported at the MFRC Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning of Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web Product and Service Knowledge Provide product and service information to clients Type of Channel Training Method portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point the learning process to develop basic knowledge of micro financing products and services. This training must include ways of communicating this information to clients. § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits and to provide training on any new products or services portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 49 § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to educate staff members and new recruits on basic products and services offered by the business. A job aid/o “pop quizz” on product features could also be used to ensure information is internalised
Client service delivery recommendations With increasing competition, client service will become one of the differentiators in the micro finance industry Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Client Request Resolution Effectively deal with client requests for loan information, dispute resolution and requests for rescheduling of loans Face-toface § Role plays could be used to support classroom based § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be training. Scripts for different client requests could be created and different roles enacted by trainees § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and to provide ongoing training to staff on managing client requests. A client resolution scorecard could be created by the staff which is reviewed weekly and successes tracked used to educate on the basic request resolution processes and frequently asked questions. These could include Client Resolution Job Aids and Process posters to assist staff members § Case Studies would form the basis of the role plays and be based on real examples collected from branches or reported at the MFRC Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning of Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web Product and Service Knowledge Provide product and service information to clients Type of Channel Training Method portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point the learning process to develop basic knowledge of micro financing products and services. This training must include ways of communicating this information to clients. § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits and to provide training on any new products or services portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 49 § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to educate staff members and new recruits on basic products and services offered by the business. A job aid/o “pop quizz” on product features could also be used to ensure information is internalised
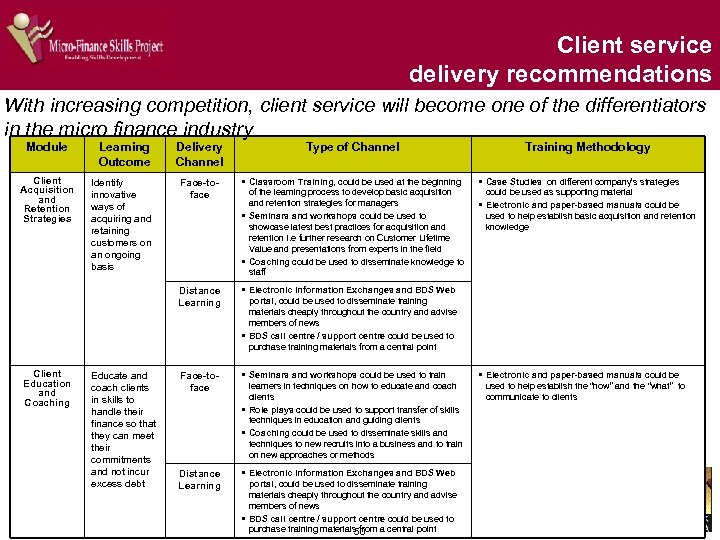 Client service delivery recommendations With increasing competition, client service will become one of the differentiators in the micro finance industry Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Client Acquisition and Retention Strategies Identify innovative ways of acquiring and retaining customers on an ongoing basis Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning § Case Studies on different company’s strategies of the learning process to develop basic acquisition and retention strategies for managers § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest best practices for acquisition and retention I. e further research on Customer Lifetime Value and presentations from experts in the field § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to staff could be used as supporting material § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish basic acquisition and retention knowledge Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to train Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web Client Education and Coaching Educate and coach clients in skills to handle their finance so that they can meet their commitments and not incur excess debt Training Methodology portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point learners in techniques on how to educate and coach clients § Role plays could be used to support transfer of skills techniques in education and guiding clients § Coaching could be used to disseminate skills and techniques to new recruits into a business and to train on new approaches or methods portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 50 § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish the “how” and the “what” to communicate to clients
Client service delivery recommendations With increasing competition, client service will become one of the differentiators in the micro finance industry Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Client Acquisition and Retention Strategies Identify innovative ways of acquiring and retaining customers on an ongoing basis Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning § Case Studies on different company’s strategies of the learning process to develop basic acquisition and retention strategies for managers § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest best practices for acquisition and retention I. e further research on Customer Lifetime Value and presentations from experts in the field § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to staff could be used as supporting material § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish basic acquisition and retention knowledge Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to train Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web Client Education and Coaching Educate and coach clients in skills to handle their finance so that they can meet their commitments and not incur excess debt Training Methodology portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point learners in techniques on how to educate and coach clients § Role plays could be used to support transfer of skills techniques in education and guiding clients § Coaching could be used to disseminate skills and techniques to new recruits into a business and to train on new approaches or methods portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 50 § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish the “how” and the “what” to communicate to clients
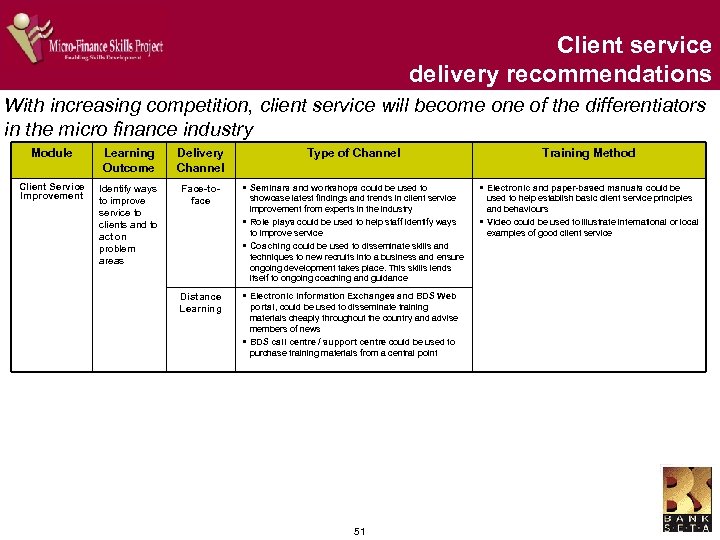 Client service delivery recommendations With increasing competition, client service will become one of the differentiators in the micro finance industry Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Client Service Improvement Identify ways to improve service to clients and to act on problem areas Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be showcase latest findings and trends in client service improvement from experts in the industry § Role plays could be used to help staff identify ways to improve service § Coaching could be used to disseminate skills and techniques to new recruits into a business and ensure ongoing development takes place. This skills lends itself to ongoing coaching and guidance used to help establish basic client service principles and behaviours § Video could be used to illustrate international or local examples of good client service Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 51 Training Method
Client service delivery recommendations With increasing competition, client service will become one of the differentiators in the micro finance industry Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Client Service Improvement Identify ways to improve service to clients and to act on problem areas Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be showcase latest findings and trends in client service improvement from experts in the industry § Role plays could be used to help staff identify ways to improve service § Coaching could be used to disseminate skills and techniques to new recruits into a business and ensure ongoing development takes place. This skills lends itself to ongoing coaching and guidance used to help establish basic client service principles and behaviours § Video could be used to illustrate international or local examples of good client service Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and BDS Web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 51 Training Method
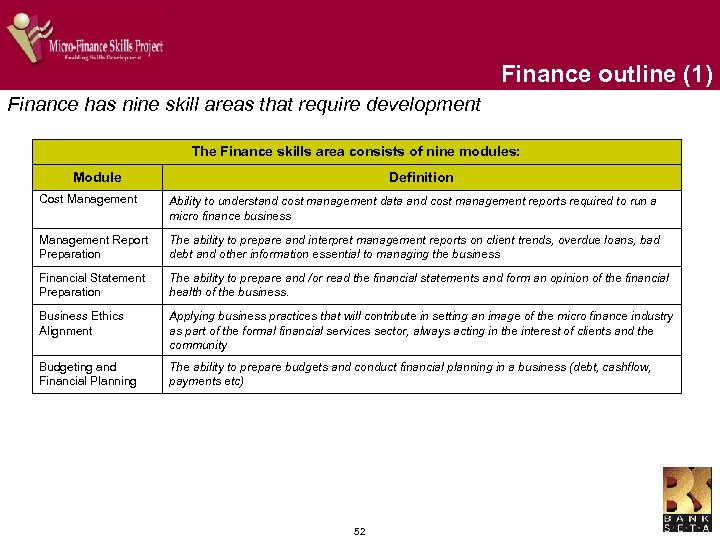 Finance outline (1) Finance has nine skill areas that require development The Finance skills area consists of nine modules: Module Definition Cost Management Ability to understand cost management data and cost management reports required to run a micro finance business Management Report Preparation The ability to prepare and interpret management reports on client trends, overdue loans, bad debt and other information essential to managing the business Financial Statement Preparation The ability to prepare and /or read the financial statements and form an opinion of the financial health of the business. Business Ethics Alignment Applying business practices that will contribute in setting an image of the micro finance industry as part of the formal financial services sector, always acting in the interest of clients and the community Budgeting and Financial Planning The ability to prepare budgets and conduct financial planning in a business (debt, cashflow, payments etc) 52
Finance outline (1) Finance has nine skill areas that require development The Finance skills area consists of nine modules: Module Definition Cost Management Ability to understand cost management data and cost management reports required to run a micro finance business Management Report Preparation The ability to prepare and interpret management reports on client trends, overdue loans, bad debt and other information essential to managing the business Financial Statement Preparation The ability to prepare and /or read the financial statements and form an opinion of the financial health of the business. Business Ethics Alignment Applying business practices that will contribute in setting an image of the micro finance industry as part of the formal financial services sector, always acting in the interest of clients and the community Budgeting and Financial Planning The ability to prepare budgets and conduct financial planning in a business (debt, cashflow, payments etc) 52
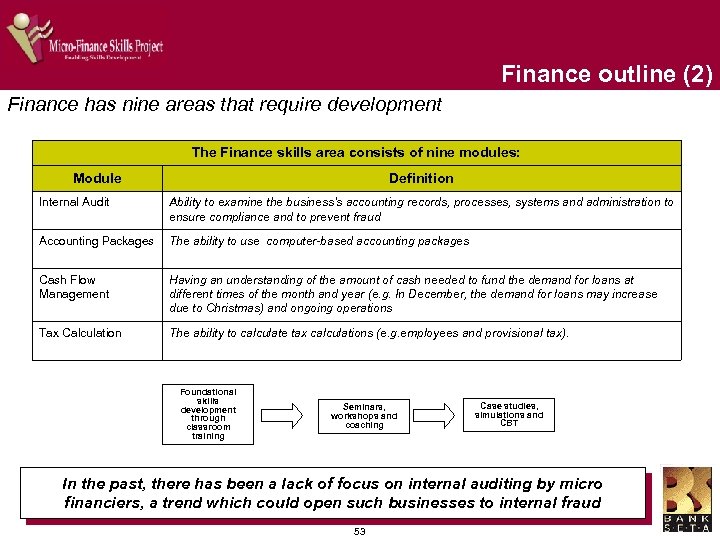 Finance outline (2) Finance has nine areas that require development The Finance skills area consists of nine modules: Module Definition Internal Audit Ability to examine the business’s accounting records, processes, systems and administration to ensure compliance and to prevent fraud Accounting Packages The ability to use computer-based accounting packages Cash Flow Management Having an understanding of the amount of cash needed to fund the demand for loans at different times of the month and year (e. g. In December, the demand for loans may increase due to Christmas) and ongoing operations Tax Calculation The ability to calculate tax calculations (e. g. employees and provisional tax). Foundational skills development through classroom training Seminars, workshops and coaching Case studies, simulations and CBT In the past, there has been a lack of focus on internal auditing by micro financiers, a trend which could open such businesses to internal fraud 53
Finance outline (2) Finance has nine areas that require development The Finance skills area consists of nine modules: Module Definition Internal Audit Ability to examine the business’s accounting records, processes, systems and administration to ensure compliance and to prevent fraud Accounting Packages The ability to use computer-based accounting packages Cash Flow Management Having an understanding of the amount of cash needed to fund the demand for loans at different times of the month and year (e. g. In December, the demand for loans may increase due to Christmas) and ongoing operations Tax Calculation The ability to calculate tax calculations (e. g. employees and provisional tax). Foundational skills development through classroom training Seminars, workshops and coaching Case studies, simulations and CBT In the past, there has been a lack of focus on internal auditing by micro financiers, a trend which could open such businesses to internal fraud 53
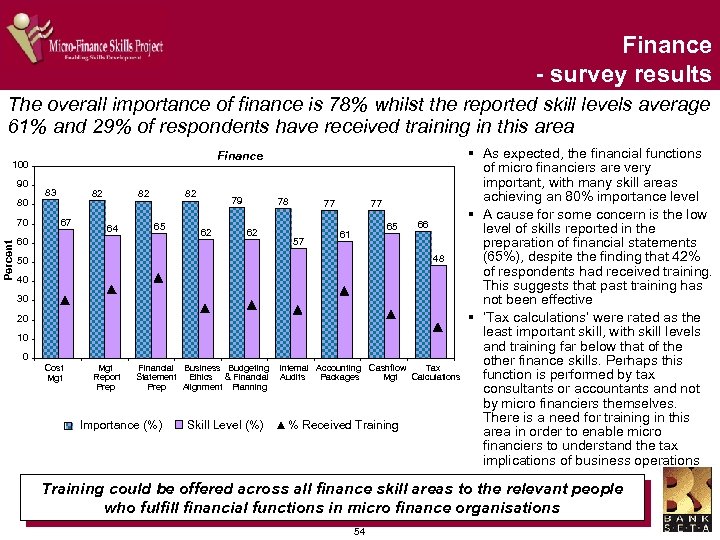 Finance - survey results The overall importance of finance is 78% whilst the reported skill levels average 61% and 29% of respondents have received training in this area Finance 100 90 80 Percent 70 83 82 67 82 64 82 65 60 79 62 78 62 77 57 77 65 61 66 48 50 40 30 20 10 0 Cost Mgt Report Prep Financial Business Budgeting Statement Ethics & Financial Prep Alignment Planning Importance (%) Skill Level (%) Internal Accounting Cashflow Tax Audits Packages Mgt Calculations % Received Training § As expected, the financial functions of micro financiers are very important, with many skill areas achieving an 80% importance level § A cause for some concern is the low level of skills reported in the preparation of financial statements (65%), despite the finding that 42% of respondents had received training. This suggests that past training has not been effective § ‘Tax calculations’ were rated as the least important skill, with skill levels and training far below that of the other finance skills. Perhaps this function is performed by tax consultants or accountants and not by micro financiers themselves. There is a need for training in this area in order to enable micro financiers to understand the tax implications of business operations Training could be offered across all finance skill areas to the relevant people who fulfill financial functions in micro finance organisations 54
Finance - survey results The overall importance of finance is 78% whilst the reported skill levels average 61% and 29% of respondents have received training in this area Finance 100 90 80 Percent 70 83 82 67 82 64 82 65 60 79 62 78 62 77 57 77 65 61 66 48 50 40 30 20 10 0 Cost Mgt Report Prep Financial Business Budgeting Statement Ethics & Financial Prep Alignment Planning Importance (%) Skill Level (%) Internal Accounting Cashflow Tax Audits Packages Mgt Calculations % Received Training § As expected, the financial functions of micro financiers are very important, with many skill areas achieving an 80% importance level § A cause for some concern is the low level of skills reported in the preparation of financial statements (65%), despite the finding that 42% of respondents had received training. This suggests that past training has not been effective § ‘Tax calculations’ were rated as the least important skill, with skill levels and training far below that of the other finance skills. Perhaps this function is performed by tax consultants or accountants and not by micro financiers themselves. There is a need for training in this area in order to enable micro financiers to understand the tax implications of business operations Training could be offered across all finance skill areas to the relevant people who fulfill financial functions in micro finance organisations 54
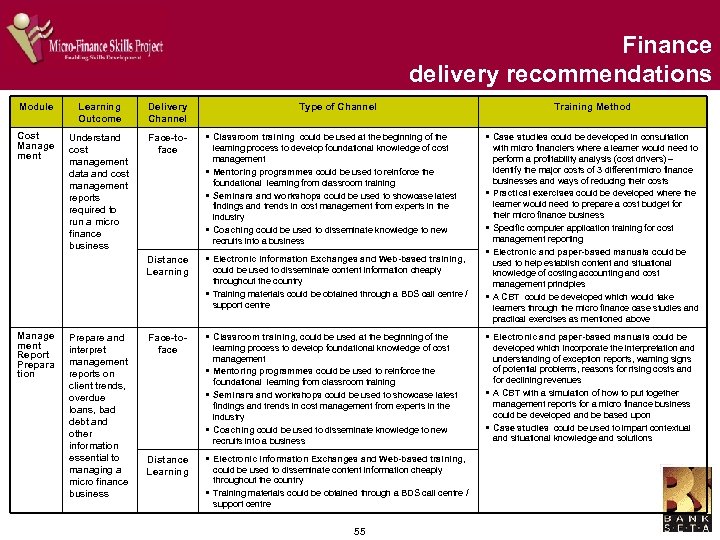 Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Cost Manage ment Understand cost management data and cost management reports required to run a micro finance business Face-toface Distance Learning Manage ment Report Prepara tion Prepare and interpret management reports on client trends, overdue loans, bad debt and other information essential to managing a micro finance business Type of Channel § Classroom training could be used at the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of cost management § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Training Method § Case studies could be developed in consultation § § with micro financiers where a learner would need to perform a profitability analysis (cost drivers) – identify the major costs of 3 different micro finance businesses and ways of reducing their costs Practical exercises could be developed where the learner would need to prepare a cost budget for their micro finance business Specific computer application training for cost management reporting Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of costing accounting and cost management principles A CBT could be developed which would take learners through the micro finance case studies and practical exercises as mentioned above Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of the § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be learning process to develop foundational knowledge of cost management § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business developed which incorporate the interpretation and understanding of exception reports, warning signs of potential problems, reasons for rising costs and for declining revenues § A CBT with a simulation of how to put together management reports for a micro finance business could be developed and be based upon § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 55
Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Cost Manage ment Understand cost management data and cost management reports required to run a micro finance business Face-toface Distance Learning Manage ment Report Prepara tion Prepare and interpret management reports on client trends, overdue loans, bad debt and other information essential to managing a micro finance business Type of Channel § Classroom training could be used at the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of cost management § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Training Method § Case studies could be developed in consultation § § with micro financiers where a learner would need to perform a profitability analysis (cost drivers) – identify the major costs of 3 different micro finance businesses and ways of reducing their costs Practical exercises could be developed where the learner would need to prepare a cost budget for their micro finance business Specific computer application training for cost management reporting Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of costing accounting and cost management principles A CBT could be developed which would take learners through the micro finance case studies and practical exercises as mentioned above Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of the § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be learning process to develop foundational knowledge of cost management § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business developed which incorporate the interpretation and understanding of exception reports, warning signs of potential problems, reasons for rising costs and for declining revenues § A CBT with a simulation of how to put together management reports for a micro finance business could be developed and be based upon § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 55
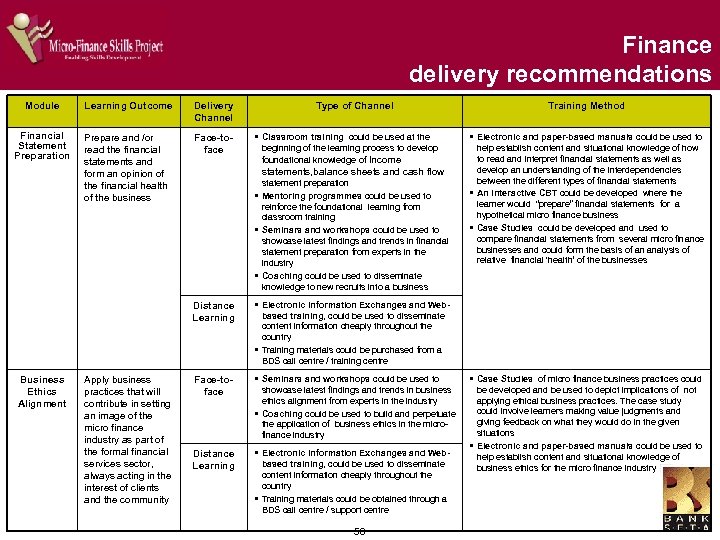 Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Financial Statement Preparation Prepare and /or read the financial statements and form an opinion of the financial health of the business Face-toface Type of Channel § Classroom training could be used at the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of Income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statement preparation § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in financial statement preparation from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of how to read and interpret financial statements as well as develop an understanding of the interdependencies between the different types of financial statements § An interactive CBT could be developed where the learner would “prepare” financial statements for a hypothetical micro finance business § Case Studies could be developed and used to compare financial statements from several micro finance businesses and could form the basis of an analysis of relative financial ‘health’ of the businesses Distance Learning Business Ethics Alignment Apply business practices that will contribute in setting an image of the micro finance industry as part of the formal financial services sector, always acting in the interest of clients and the community § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web- Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Case Studies of micro finance business practices could showcase latest findings and trends in business ethics alignment from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to build and perpetuate the application of business ethics in the microfinance industry Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web- be developed and be used to depict implications of not applying ethical business practices. The case study could involve learners making value judgments and giving feedback on what they would do in the given situations § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of business ethics for the micro finance industry based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be purchased from a BDS call centre / training centre based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 56
Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Financial Statement Preparation Prepare and /or read the financial statements and form an opinion of the financial health of the business Face-toface Type of Channel § Classroom training could be used at the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of Income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statement preparation § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in financial statement preparation from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of how to read and interpret financial statements as well as develop an understanding of the interdependencies between the different types of financial statements § An interactive CBT could be developed where the learner would “prepare” financial statements for a hypothetical micro finance business § Case Studies could be developed and used to compare financial statements from several micro finance businesses and could form the basis of an analysis of relative financial ‘health’ of the businesses Distance Learning Business Ethics Alignment Apply business practices that will contribute in setting an image of the micro finance industry as part of the formal financial services sector, always acting in the interest of clients and the community § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web- Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used to § Case Studies of micro finance business practices could showcase latest findings and trends in business ethics alignment from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to build and perpetuate the application of business ethics in the microfinance industry Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web- be developed and be used to depict implications of not applying ethical business practices. The case study could involve learners making value judgments and giving feedback on what they would do in the given situations § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of business ethics for the micro finance industry based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be purchased from a BDS call centre / training centre based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 56
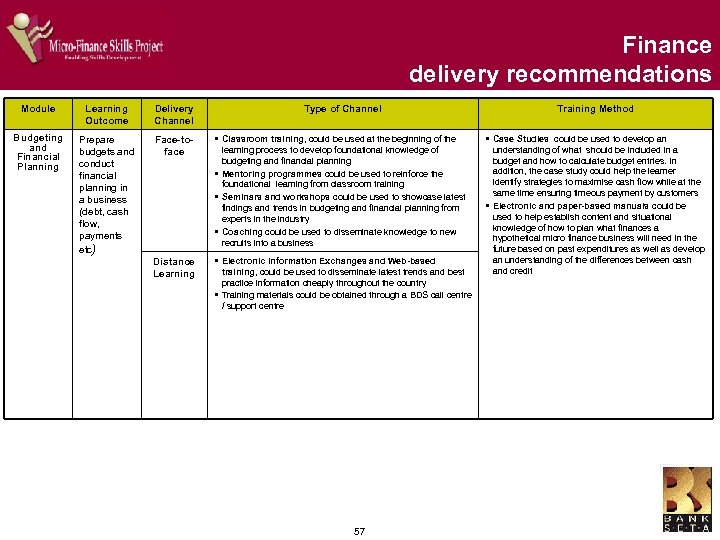 Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Budgeting and Financial Planning Prepare budgets and conduct financial planning in a business (debt, cash flow, payments etc) Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of the § Case Studies could be used to develop an learning process to develop foundational knowledge of budgeting and financial planning § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in budgeting and financial planning from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based understanding of what should be included in a budget and how to calculate budget entries. In addition, the case study could help the learner identify strategies to maximise cash flow while at the same time ensuring timeous payment by customers § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of how to plan what finances a hypothetical micro finance business will need in the future based on past expenditures as well as develop an understanding of the differences between cash and credit training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 57 Training Method
Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Budgeting and Financial Planning Prepare budgets and conduct financial planning in a business (debt, cash flow, payments etc) Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of the § Case Studies could be used to develop an learning process to develop foundational knowledge of budgeting and financial planning § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in budgeting and financial planning from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based understanding of what should be included in a budget and how to calculate budget entries. In addition, the case study could help the learner identify strategies to maximise cash flow while at the same time ensuring timeous payment by customers § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of how to plan what finances a hypothetical micro finance business will need in the future based on past expenditures as well as develop an understanding of the differences between cash and credit training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 57 Training Method
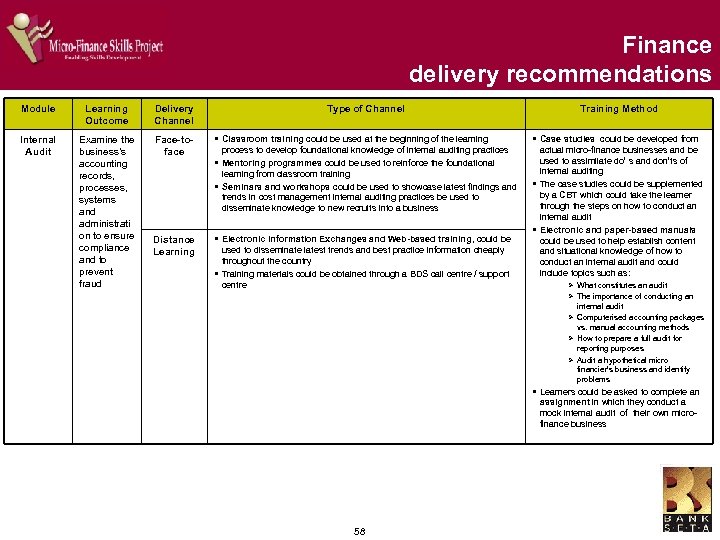 Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Internal Audit Examine the business’s accounting records, processes, systems and administrati on to ensure compliance and to prevent fraud Face-toface § Classroom training could be used at the beginning of the learning § Case studies could be developed from process to develop foundational knowledge of internal auditing practices § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management internal auditing practices be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be actual micro-finance businesses and be used to assimilate do’ s and don’ts of internal auditing § The case studies could be supplemented by a CBT which could take the learner through the steps on how to conduct an internal audit § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of how to conduct an internal audit and could include topics such as: used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Training Method Ø What constitutes an audit Ø The importance of conducting an internal audit Ø Computerised accounting packages vs. manual accounting methods Ø How to prepare a full audit for reporting purposes Ø Audit a hypothetical micro financier’s business and identify problems § Learners could be asked to complete an assignment in which they conduct a mock internal audit of their own microfinance business 58
Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Internal Audit Examine the business’s accounting records, processes, systems and administrati on to ensure compliance and to prevent fraud Face-toface § Classroom training could be used at the beginning of the learning § Case studies could be developed from process to develop foundational knowledge of internal auditing practices § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management internal auditing practices be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be actual micro-finance businesses and be used to assimilate do’ s and don’ts of internal auditing § The case studies could be supplemented by a CBT which could take the learner through the steps on how to conduct an internal audit § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of how to conduct an internal audit and could include topics such as: used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Training Method Ø What constitutes an audit Ø The importance of conducting an internal audit Ø Computerised accounting packages vs. manual accounting methods Ø How to prepare a full audit for reporting purposes Ø Audit a hypothetical micro financier’s business and identify problems § Learners could be asked to complete an assignment in which they conduct a mock internal audit of their own microfinance business 58
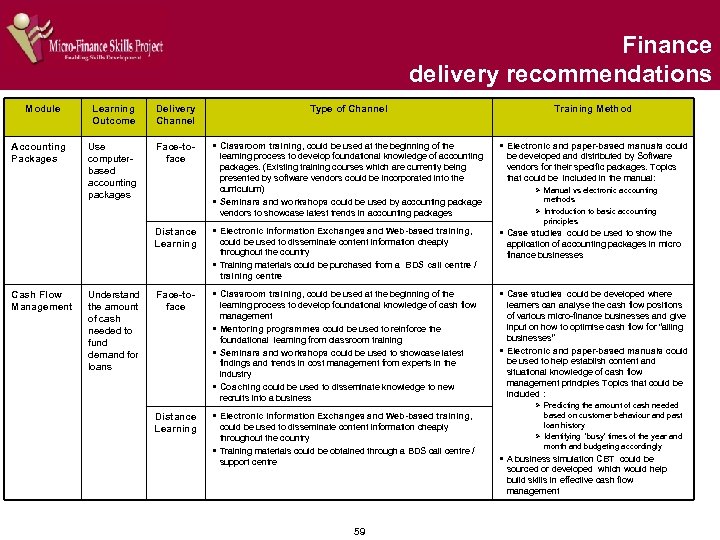 Finance delivery recommendations Module Accounting Packages Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Use computerbased accounting packages Face-toface Type of Channel § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of accounting packages. (Existing training courses which are currently being presented by software vendors could be incorporated into the curriculum) § Seminars and workshops could be used by accounting package vendors to showcase latest trends in accounting packages Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed and distributed by Software vendors for their specific packages. Topics that could be included in the manual: Ø Manual vs electronic accounting methods Ø Introduction to basic accounting principles Distance Learning Cash Flow Management Understand the amount of cash needed to fund demand for loans § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of the § Case studies could be developed where learning process to develop foundational knowledge of cash flow management § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business learners can analyse the cash flow positions of various micro-finance businesses and give input on how to optimise cash flow for “ailing businesses” § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of cash flow management principles Topics that could be included : Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be purchased from a BDS call centre / training centre could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 59 § Case studies could be used to show the application of accounting packages in micro finance businesses Ø Predicting the amount of cash needed based on customer behaviour and past loan history Ø Identifying ‘busy’ times of the year and month and budgeting accordingly § A business simulation CBT could be sourced or developed which would help build skills in effective cash flow management
Finance delivery recommendations Module Accounting Packages Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Use computerbased accounting packages Face-toface Type of Channel § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of accounting packages. (Existing training courses which are currently being presented by software vendors could be incorporated into the curriculum) § Seminars and workshops could be used by accounting package vendors to showcase latest trends in accounting packages Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed and distributed by Software vendors for their specific packages. Topics that could be included in the manual: Ø Manual vs electronic accounting methods Ø Introduction to basic accounting principles Distance Learning Cash Flow Management Understand the amount of cash needed to fund demand for loans § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of the § Case studies could be developed where learning process to develop foundational knowledge of cash flow management § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business learners can analyse the cash flow positions of various micro-finance businesses and give input on how to optimise cash flow for “ailing businesses” § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of cash flow management principles Topics that could be included : Distance Learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be purchased from a BDS call centre / training centre could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 59 § Case studies could be used to show the application of accounting packages in micro finance businesses Ø Predicting the amount of cash needed based on customer behaviour and past loan history Ø Identifying ‘busy’ times of the year and month and budgeting accordingly § A business simulation CBT could be sourced or developed which would help build skills in effective cash flow management
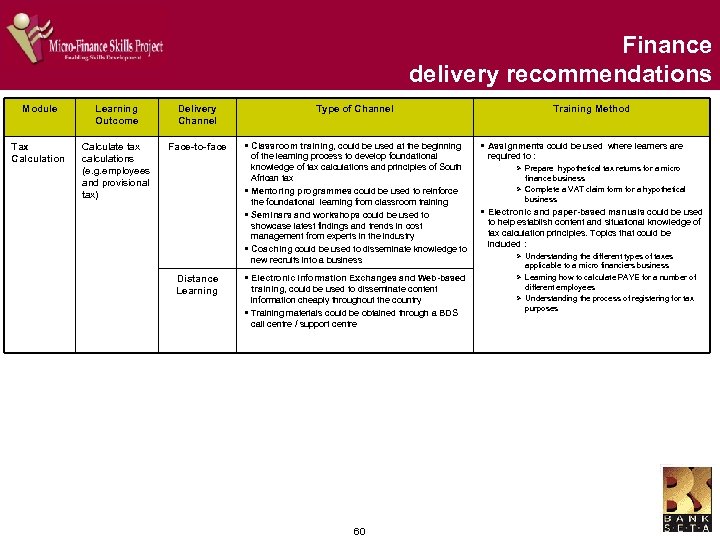 Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Tax Calculation Calculate tax calculations (e. g. employees and provisional tax) Face-to-face § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning Distance Learning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of tax calculations and principles of South African tax § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 60 Training Method § Assignments could be used where learners are required to : Ø Prepare hypothetical tax returns for a micro finance business Ø Complete a VAT claim for a hypothetical business § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of tax calculation principles. Topics that could be included : Ø Understanding the different types of taxes applicable to a micro financiers business Ø Learning how to calculate PAYE for a number of different employees Ø Understanding the process of registering for tax purposes
Finance delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Tax Calculation Calculate tax calculations (e. g. employees and provisional tax) Face-to-face § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning Distance Learning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of tax calculations and principles of South African tax § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 60 Training Method § Assignments could be used where learners are required to : Ø Prepare hypothetical tax returns for a micro finance business Ø Complete a VAT claim for a hypothetical business § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge of tax calculation principles. Topics that could be included : Ø Understanding the different types of taxes applicable to a micro financiers business Ø Learning how to calculate PAYE for a number of different employees Ø Understanding the process of registering for tax purposes
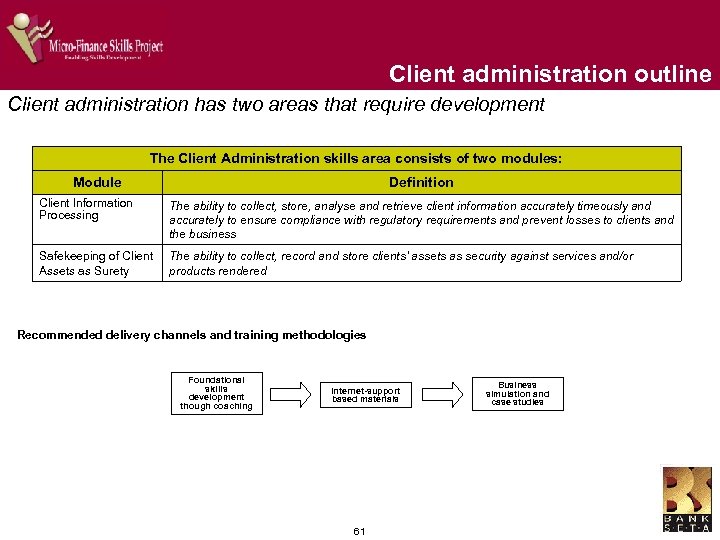 Client administration outline Client administration has two areas that require development The Client Administration skills area consists of two modules: Module Definition Client Information Processing The ability to collect, store, analyse and retrieve client information accurately timeously and accurately to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and prevent losses to clients and the business Safekeeping of Client Assets as Surety The ability to collect, record and store clients' assets as security against services and/or products rendered Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development though coaching Internet-support based materials 61 Business simulation and case studies
Client administration outline Client administration has two areas that require development The Client Administration skills area consists of two modules: Module Definition Client Information Processing The ability to collect, store, analyse and retrieve client information accurately timeously and accurately to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and prevent losses to clients and the business Safekeeping of Client Assets as Surety The ability to collect, record and store clients' assets as security against services and/or products rendered Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development though coaching Internet-support based materials 61 Business simulation and case studies
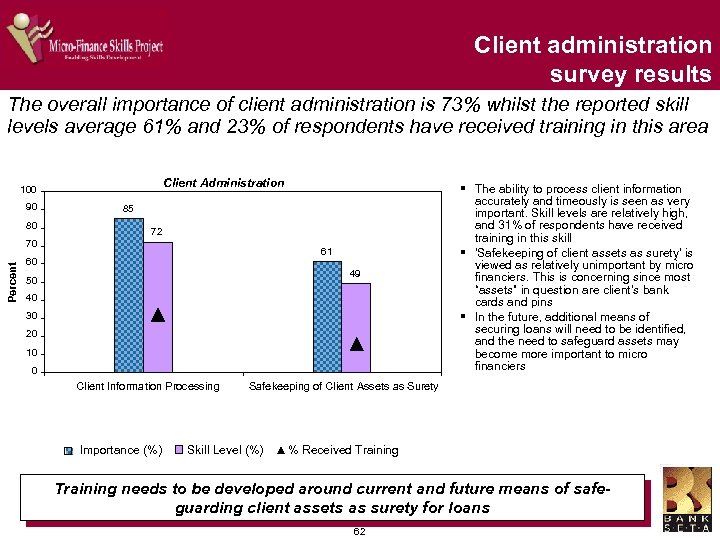 Client administration survey results The overall importance of client administration is 73% whilst the reported skill levels average 61% and 23% of respondents have received training in this area Client Administration 100 90 80 85 72 Percent 70 61 60 49 50 40 30 20 10 0 Client Information Processing Importance (%) § The ability to process client information accurately and timeously is seen as very important. Skill levels are relatively high, and 31% of respondents have received training in this skill § ‘Safekeeping of client assets as surety’ is viewed as relatively unimportant by micro financiers. This is concerning since most “assets” in question are client’s bank cards and pins § In the future, additional means of securing loans will need to be identified, and the need to safeguard assets may become more important to micro financiers Safekeeping of Client Assets as Surety Skill Level (%) % Received Training needs to be developed around current and future means of safeguarding client assets as surety for loans 62
Client administration survey results The overall importance of client administration is 73% whilst the reported skill levels average 61% and 23% of respondents have received training in this area Client Administration 100 90 80 85 72 Percent 70 61 60 49 50 40 30 20 10 0 Client Information Processing Importance (%) § The ability to process client information accurately and timeously is seen as very important. Skill levels are relatively high, and 31% of respondents have received training in this skill § ‘Safekeeping of client assets as surety’ is viewed as relatively unimportant by micro financiers. This is concerning since most “assets” in question are client’s bank cards and pins § In the future, additional means of securing loans will need to be identified, and the need to safeguard assets may become more important to micro financiers Safekeeping of Client Assets as Surety Skill Level (%) % Received Training needs to be developed around current and future means of safeguarding client assets as surety for loans 62
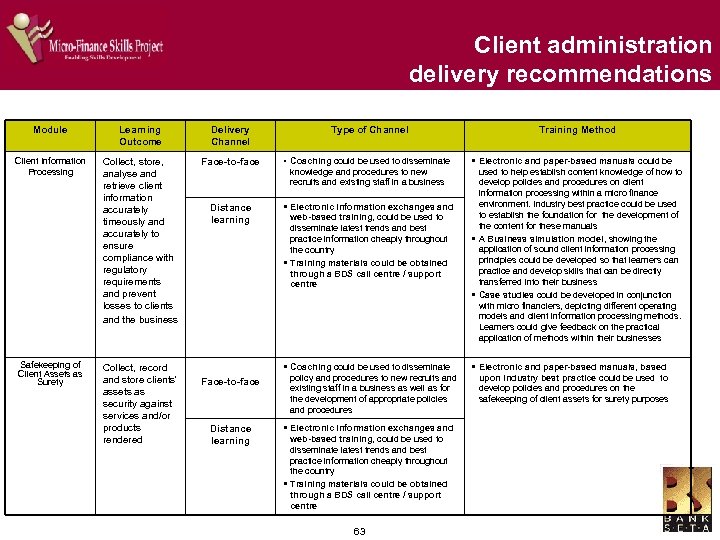 Client administration delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Client Information Processing Collect, store, analyse and retrieve client information accurately timeously and accurately to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and prevent losses to clients and the business Face-to-face • Coaching could be used to disseminate Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and Safekeeping of Client Assets as Surety Collect, record and store clients' assets as security against services and/or products rendered § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be Distance learning web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures on client information processing within a micro finance environment. Industry best practice could be used to establish the foundation for the development of the content for these manuals § A Business simulation model, showing the application of sound client information processing principles could be developed so that learners can practice and develop skills that can be directly transferred into their business § Case studies could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers, depicting different operating models and client information processing methods. Learners could give feedback on the practical application of methods within their businesses § Coaching could be used to disseminate Face-to-face knowledge and procedures to new recruits and existing staff in a business Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals, based policy and procedures to new recruits and existing staff in a business as well as for the development of appropriate policies and procedures § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 63 upon industry best practice could be used to develop policies and procedures on the safekeeping of client assets for surety purposes
Client administration delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Client Information Processing Collect, store, analyse and retrieve client information accurately timeously and accurately to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and prevent losses to clients and the business Face-to-face • Coaching could be used to disseminate Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and Safekeeping of Client Assets as Surety Collect, record and store clients' assets as security against services and/or products rendered § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be Distance learning web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures on client information processing within a micro finance environment. Industry best practice could be used to establish the foundation for the development of the content for these manuals § A Business simulation model, showing the application of sound client information processing principles could be developed so that learners can practice and develop skills that can be directly transferred into their business § Case studies could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers, depicting different operating models and client information processing methods. Learners could give feedback on the practical application of methods within their businesses § Coaching could be used to disseminate Face-to-face knowledge and procedures to new recruits and existing staff in a business Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals, based policy and procedures to new recruits and existing staff in a business as well as for the development of appropriate policies and procedures § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 63 upon industry best practice could be used to develop policies and procedures on the safekeeping of client assets for surety purposes
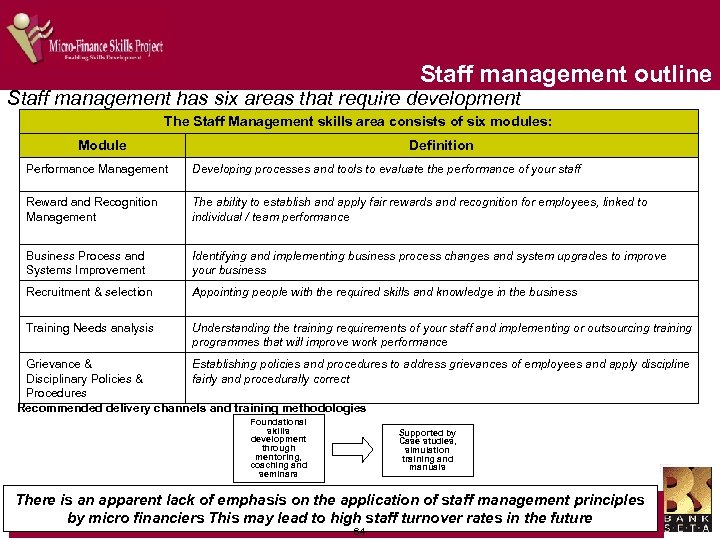 Staff management outline Staff management has six areas that require development The Staff Management skills area consists of six modules: Module Definition Performance Management Developing processes and tools to evaluate the performance of your staff Reward and Recognition Management The ability to establish and apply fair rewards and recognition for employees, linked to individual / team performance Business Process and Systems Improvement Identifying and implementing business process changes and system upgrades to improve your business Recruitment & selection Appointing people with the required skills and knowledge in the business Training Needs analysis Understanding the training requirements of your staff and implementing or outsourcing training programmes that will improve work performance Grievance & Establishing policies and procedures to address grievances of employees and apply discipline Disciplinary Policies & fairly and procedurally correct Procedures Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through mentoring, coaching and seminars Supported by Case studies, simulation training and manuals There is an apparent lack of emphasis on the application of staff management principles by micro financiers This may lead to high staff turnover rates in the future 64
Staff management outline Staff management has six areas that require development The Staff Management skills area consists of six modules: Module Definition Performance Management Developing processes and tools to evaluate the performance of your staff Reward and Recognition Management The ability to establish and apply fair rewards and recognition for employees, linked to individual / team performance Business Process and Systems Improvement Identifying and implementing business process changes and system upgrades to improve your business Recruitment & selection Appointing people with the required skills and knowledge in the business Training Needs analysis Understanding the training requirements of your staff and implementing or outsourcing training programmes that will improve work performance Grievance & Establishing policies and procedures to address grievances of employees and apply discipline Disciplinary Policies & fairly and procedurally correct Procedures Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through mentoring, coaching and seminars Supported by Case studies, simulation training and manuals There is an apparent lack of emphasis on the application of staff management principles by micro financiers This may lead to high staff turnover rates in the future 64
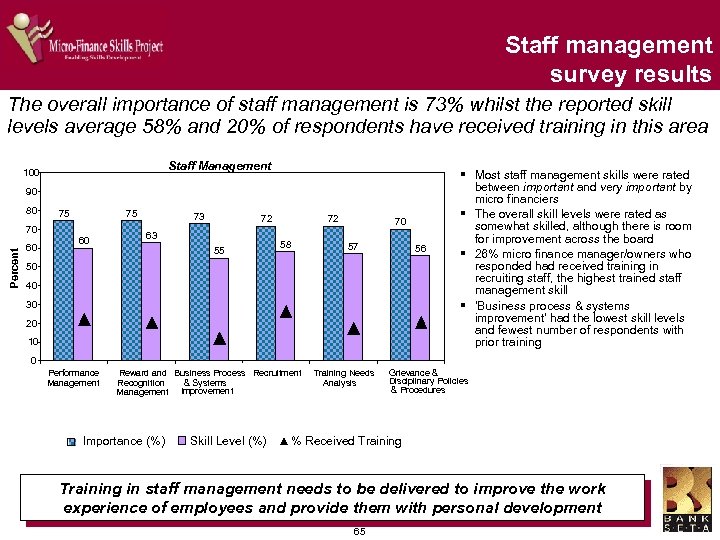 Staff management survey results The overall importance of staff management is 73% whilst the reported skill levels average 58% and 20% of respondents have received training in this area Staff Management 100 90 80 75 75 Percent 70 60 60 73 72 63 55 72 58 70 57 56 50 40 30 20 10 § Most staff management skills were rated between important and very important by micro financiers § The overall skill levels were rated as somewhat skilled, although there is room for improvement across the board § 26% micro finance manager/owners who responded had received training in recruiting staff, the highest trained staff management skill § ‘Business process & systems improvement’ had the lowest skill levels and fewest number of respondents with prior training 0 Performance Management Reward and Business Process Recruitment Recognition & Systems Management Improvement Importance (%) Skill Level (%) Training Needs Analysis Grievance & Disciplinary Policies & Procedures % Received Training in staff management needs to be delivered to improve the work experience of employees and provide them with personal development 65
Staff management survey results The overall importance of staff management is 73% whilst the reported skill levels average 58% and 20% of respondents have received training in this area Staff Management 100 90 80 75 75 Percent 70 60 60 73 72 63 55 72 58 70 57 56 50 40 30 20 10 § Most staff management skills were rated between important and very important by micro financiers § The overall skill levels were rated as somewhat skilled, although there is room for improvement across the board § 26% micro finance manager/owners who responded had received training in recruiting staff, the highest trained staff management skill § ‘Business process & systems improvement’ had the lowest skill levels and fewest number of respondents with prior training 0 Performance Management Reward and Business Process Recruitment Recognition & Systems Management Improvement Importance (%) Skill Level (%) Training Needs Analysis Grievance & Disciplinary Policies & Procedures % Received Training in staff management needs to be delivered to improve the work experience of employees and provide them with personal development 65
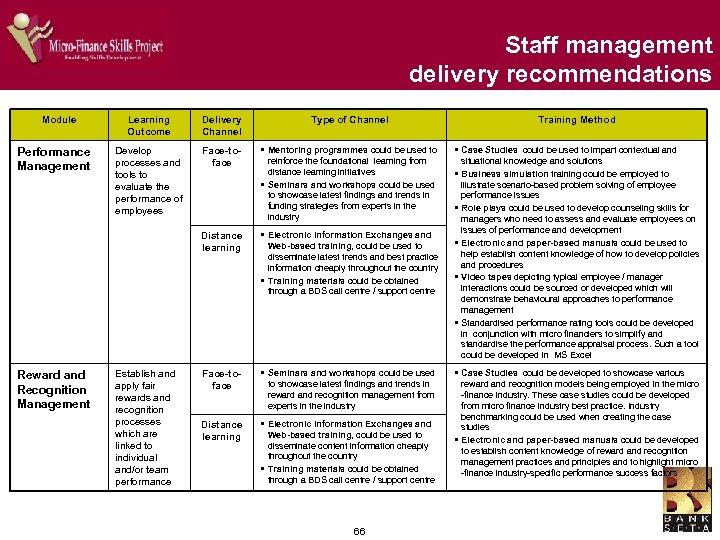 Staff management delivery recommendations Module Performance Management Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Develop processes and tools to evaluate the performance of employees Face-toface § Mentoring programmes could be used to Distance learning reinforce the foundational learning from distance learning initiatives § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in funding strategies from experts in the industry § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Training Method § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and § § § Reward and Recognition Management Establish and apply fair rewards and recognition processes which are linked to individual and/or team performance Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used Distance learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and to showcase latest findings and trends in reward and recognition management from experts in the industry Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 66 situational knowledge and solutions Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario-based problem solving of employee performance issues Role plays could be used to develop counseling skills for managers who need to assess and evaluate employees on issues of performance and development Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures Video tapes depicting typical employee / manager interactions could be sourced or developed which will demonstrate behavioural approaches to performance management Standardised performance rating tools could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers to simplify and standardise the performance appraisal process. Such a tool could be developed in MS Excel § Case Studies could be developed to showcase various reward and recognition models being employed in the micro -finance industry. These case studies could be developed from micro finance industry best practice. Industry benchmarking could be used when creating the case studies § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed to establish content knowledge of reward and recognition management practices and principles and to highlight micro -finance industry-specific performance success factors
Staff management delivery recommendations Module Performance Management Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Develop processes and tools to evaluate the performance of employees Face-toface § Mentoring programmes could be used to Distance learning reinforce the foundational learning from distance learning initiatives § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in funding strategies from experts in the industry § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Training Method § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and § § § Reward and Recognition Management Establish and apply fair rewards and recognition processes which are linked to individual and/or team performance Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used Distance learning § Electronic Information Exchanges and to showcase latest findings and trends in reward and recognition management from experts in the industry Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 66 situational knowledge and solutions Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario-based problem solving of employee performance issues Role plays could be used to develop counseling skills for managers who need to assess and evaluate employees on issues of performance and development Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures Video tapes depicting typical employee / manager interactions could be sourced or developed which will demonstrate behavioural approaches to performance management Standardised performance rating tools could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers to simplify and standardise the performance appraisal process. Such a tool could be developed in MS Excel § Case Studies could be developed to showcase various reward and recognition models being employed in the micro -finance industry. These case studies could be developed from micro finance industry best practice. Industry benchmarking could be used when creating the case studies § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed to establish content knowledge of reward and recognition management practices and principles and to highlight micro -finance industry-specific performance success factors
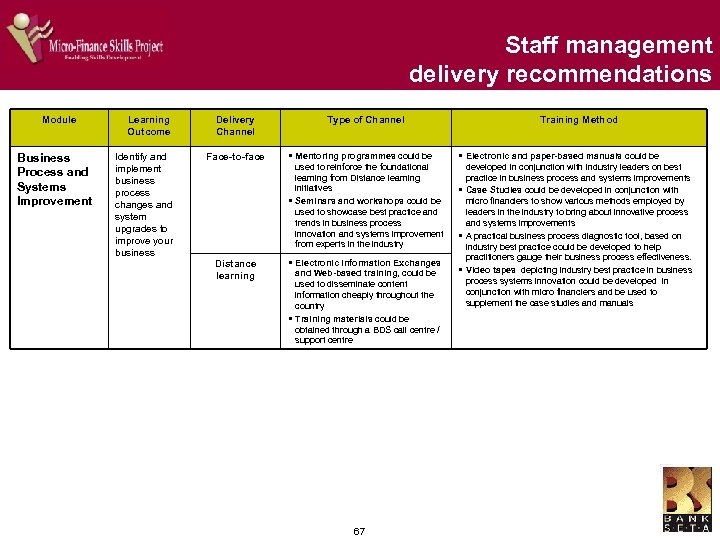 Staff management delivery recommendations Module Business Process and Systems Improvement Learning Outcome Identify and implement business process changes and system upgrades to improve your business Delivery Channel Face-to-face Distance learning Type of Channel Training Method § Mentoring programmes could be § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from Distance learning initiatives § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase best practice and trends in business process innovation and systems improvement from experts in the industry developed in conjunction with industry leaders on best practice in business process and systems improvements § Case Studies could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers to show various methods employed by leaders in the industry to bring about innovative process and systems improvements § A practical business process diagnostic tool, based on industry best practice could be developed to help practitioners gauge their business process effectiveness. § Video tapes depicting industry best practice in business process systems innovation could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers and be used to supplement the case studies and manuals § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 67
Staff management delivery recommendations Module Business Process and Systems Improvement Learning Outcome Identify and implement business process changes and system upgrades to improve your business Delivery Channel Face-to-face Distance learning Type of Channel Training Method § Mentoring programmes could be § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from Distance learning initiatives § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase best practice and trends in business process innovation and systems improvement from experts in the industry developed in conjunction with industry leaders on best practice in business process and systems improvements § Case Studies could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers to show various methods employed by leaders in the industry to bring about innovative process and systems improvements § A practical business process diagnostic tool, based on industry best practice could be developed to help practitioners gauge their business process effectiveness. § Video tapes depicting industry best practice in business process systems innovation could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers and be used to supplement the case studies and manuals § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 67
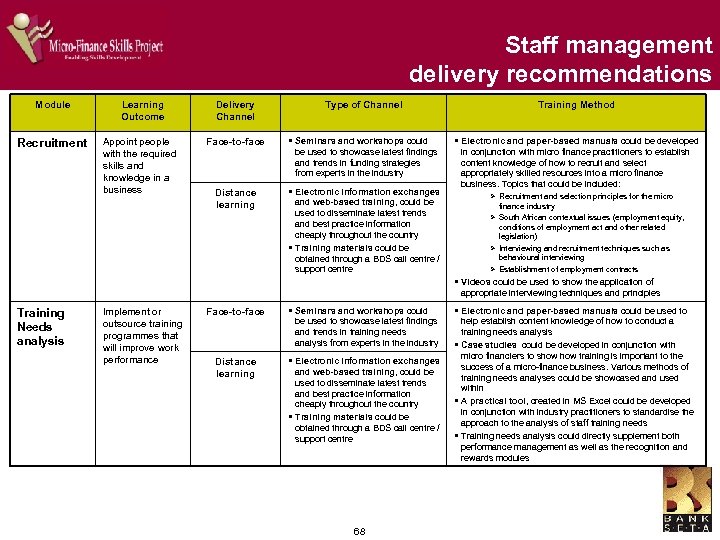 Staff management delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Recruitment Appoint people with the required skills and knowledge in a business Face-to-face Distance learning Type of Channel § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in funding strategies from experts in the industry § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed in conjunction with micro finance practitioners to establish content knowledge of how to recruit and select appropriately skilled resources into a micro finance business. Topics that could be included: Ø Recruitment and selection principles for the micro finance industry Ø South African contextual issues (employment equity, conditions of employment act and other related legislation) Ø Interviewing and recruitment techniques such as behavioural interviewing Ø Establishment of employment contracts § Videos could be used to show the application of appropriate interviewing techniques and principles Training Needs analysis Implement or outsource training programmes that will improve work performance Face-to-face Distance learning § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in training needs analysis from experts in the industry § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 68 § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to conduct a training needs analysis § Case studies could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers to show training is important to the success of a micro-finance business. Various methods of training needs analyses could be showcased and used within § A practical tool, created in MS Excel could be developed in conjunction with industry practitioners to standardise the approach to the analysis of staff training needs § Training needs analysis could directly supplement both performance management as well as the recognition and rewards modules
Staff management delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Recruitment Appoint people with the required skills and knowledge in a business Face-to-face Distance learning Type of Channel § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in funding strategies from experts in the industry § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be developed in conjunction with micro finance practitioners to establish content knowledge of how to recruit and select appropriately skilled resources into a micro finance business. Topics that could be included: Ø Recruitment and selection principles for the micro finance industry Ø South African contextual issues (employment equity, conditions of employment act and other related legislation) Ø Interviewing and recruitment techniques such as behavioural interviewing Ø Establishment of employment contracts § Videos could be used to show the application of appropriate interviewing techniques and principles Training Needs analysis Implement or outsource training programmes that will improve work performance Face-to-face Distance learning § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in training needs analysis from experts in the industry § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 68 § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to conduct a training needs analysis § Case studies could be developed in conjunction with micro financiers to show training is important to the success of a micro-finance business. Various methods of training needs analyses could be showcased and used within § A practical tool, created in MS Excel could be developed in conjunction with industry practitioners to standardise the approach to the analysis of staff training needs § Training needs analysis could directly supplement both performance management as well as the recognition and rewards modules
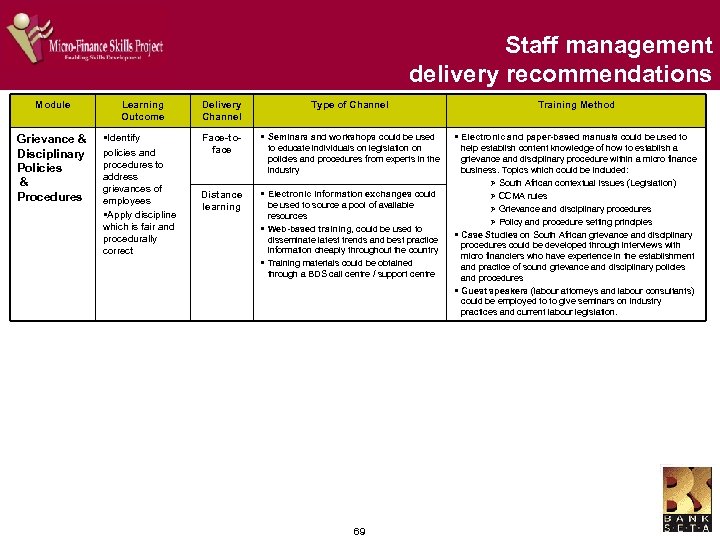 Staff management delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Grievance & Disciplinary Policies & Procedures §Identify policies and procedures to address grievances of employees §Apply discipline which is fair and procedurally correct Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges could to educate individuals on legislation on policies and procedures from experts in the industry be used to source a pool of available resources § Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 69 Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to establish a grievance and disciplinary procedure within a micro finance business. Topics which could be included: Ø South African contextual issues (Legislation) Ø CCMA rules Ø Grievance and disciplinary procedures Ø Policy and procedure setting principles § Case Studies on South African grievance and disciplinary procedures could be developed through interviews with micro financiers who have experience in the establishment and practice of sound grievance and disciplinary policies and procedures § Guest speakers (labour attorneys and labour consultants) could be employed to to give seminars on industry practices and current labour legislation.
Staff management delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Grievance & Disciplinary Policies & Procedures §Identify policies and procedures to address grievances of employees §Apply discipline which is fair and procedurally correct Face-toface § Seminars and workshops could be used Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges could to educate individuals on legislation on policies and procedures from experts in the industry be used to source a pool of available resources § Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 69 Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to establish a grievance and disciplinary procedure within a micro finance business. Topics which could be included: Ø South African contextual issues (Legislation) Ø CCMA rules Ø Grievance and disciplinary procedures Ø Policy and procedure setting principles § Case Studies on South African grievance and disciplinary procedures could be developed through interviews with micro financiers who have experience in the establishment and practice of sound grievance and disciplinary policies and procedures § Guest speakers (labour attorneys and labour consultants) could be employed to to give seminars on industry practices and current labour legislation.
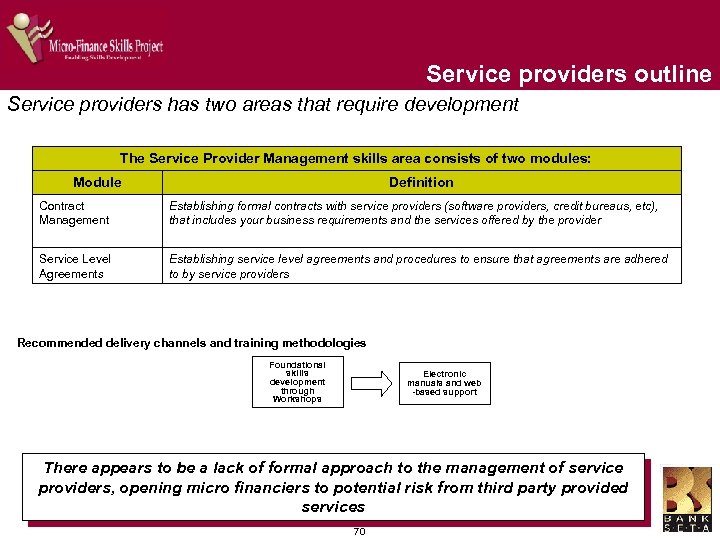 Service providers outline Service providers has two areas that require development The Service Provider Management skills area consists of two modules: Module Definition Contract Management Establishing formal contracts with service providers (software providers, credit bureaus, etc), that includes your business requirements and the services offered by the provider Service Level Agreements Establishing service level agreements and procedures to ensure that agreements are adhered to by service providers Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through Workshops Electronic manuals and web -based support There appears to be a lack of formal approach to the management of service providers, opening micro financiers to potential risk from third party provided services 70
Service providers outline Service providers has two areas that require development The Service Provider Management skills area consists of two modules: Module Definition Contract Management Establishing formal contracts with service providers (software providers, credit bureaus, etc), that includes your business requirements and the services offered by the provider Service Level Agreements Establishing service level agreements and procedures to ensure that agreements are adhered to by service providers Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through Workshops Electronic manuals and web -based support There appears to be a lack of formal approach to the management of service providers, opening micro financiers to potential risk from third party provided services 70
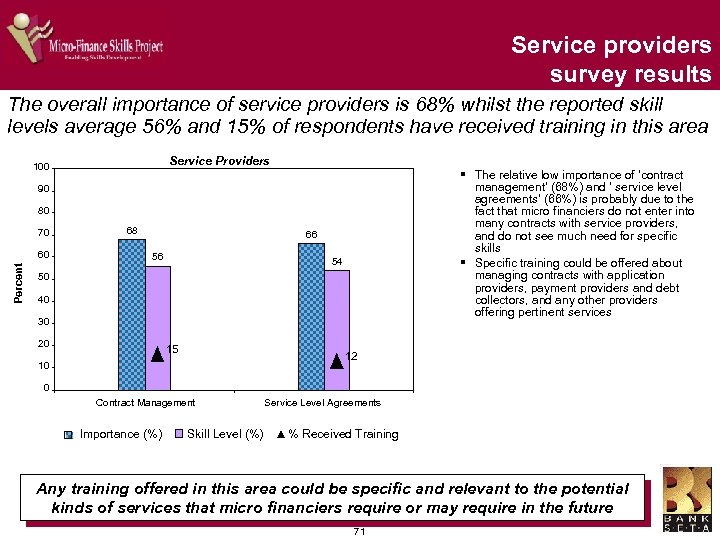 Service providers survey results The overall importance of service providers is 68% whilst the reported skill levels average 56% and 15% of respondents have received training in this area Service Providers 100 § The relative low importance of ‘contract management’ (68%) and ‘ service level agreements’ (66%) is probably due to the fact that micro financiers do not enter into many contracts with service providers, and do not see much need for specific skills § Specific training could be offered about managing contracts with application providers, payment providers and debt collectors, and any other providers offering pertinent services 90 80 70 Percent 60 68 66 56 54 50 40 30 20 15 12 10 0 Contract Management Importance (%) Skill Level (%) Service Level Agreements % Received Training Any training offered in this area could be specific and relevant to the potential kinds of services that micro financiers require or may require in the future 71
Service providers survey results The overall importance of service providers is 68% whilst the reported skill levels average 56% and 15% of respondents have received training in this area Service Providers 100 § The relative low importance of ‘contract management’ (68%) and ‘ service level agreements’ (66%) is probably due to the fact that micro financiers do not enter into many contracts with service providers, and do not see much need for specific skills § Specific training could be offered about managing contracts with application providers, payment providers and debt collectors, and any other providers offering pertinent services 90 80 70 Percent 60 68 66 56 54 50 40 30 20 15 12 10 0 Contract Management Importance (%) Skill Level (%) Service Level Agreements % Received Training Any training offered in this area could be specific and relevant to the potential kinds of services that micro financiers require or may require in the future 71
 Service providers delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Contract Management Establish formal contracts with service providers Face-toface § Workshops presented by industry experts Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and Service Level Agreements Establish service level agreements and procedures to ensure that agreements are adhered to by service providers § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be Distance learning web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre developed in conjunction with micro-financiers, services providers and contract attorneys. These manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to establish and manage contracts with third party service providers § Case studies of how contract management principles have been employed in micro finance businesses could be used to illustrate the content and contextual issues involved in dealing with third party service providers § Guest speakers could be used to consult to micro financiers on industry best practices in contract management principles § Workshops presented by industry experts Face-toface could be used to build contract management capability Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to build a service level agreement capability and build negotiation skills help establish content knowledge of how to develop service level agreements and policies specific to the micro-finance industry needs § Guest speakers who have deep knowledge of how to set up service level agreements could be used to hold workshops with micro-finance practitioners on how to establish SLA’s with third party service providers § Service level agreements could be combined with contract management § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 72
Service providers delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Contract Management Establish formal contracts with service providers Face-toface § Workshops presented by industry experts Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and Service Level Agreements Establish service level agreements and procedures to ensure that agreements are adhered to by service providers § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be Distance learning web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre developed in conjunction with micro-financiers, services providers and contract attorneys. These manuals could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to establish and manage contracts with third party service providers § Case studies of how contract management principles have been employed in micro finance businesses could be used to illustrate the content and contextual issues involved in dealing with third party service providers § Guest speakers could be used to consult to micro financiers on industry best practices in contract management principles § Workshops presented by industry experts Face-toface could be used to build contract management capability Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to build a service level agreement capability and build negotiation skills help establish content knowledge of how to develop service level agreements and policies specific to the micro-finance industry needs § Guest speakers who have deep knowledge of how to set up service level agreements could be used to hold workshops with micro-finance practitioners on how to establish SLA’s with third party service providers § Service level agreements could be combined with contract management § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country § Training materials could be obtained through a BDS call centre / support centre 72
 Funding strategies delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Capital Requirements Provide the correct amount of capital required to grow a business Face-toface § Mentoring programmes could be used to build § Electronic and paper-based manuals with foundational knowledge in capital requirements knowledge § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and web-based guidelines on how to determine capital requirements could be developed. Examples of key forecasting methodologies, formulae and considerations and business case development could be included § Case studies developed through consultation with micro financiers could be used to understand the influencers in growth strategies in micro financing businesses § A CBT simulating business growth and performance on funding methodologies could be developed training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving 73 Training Method
Funding strategies delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Capital Requirements Provide the correct amount of capital required to grow a business Face-toface § Mentoring programmes could be used to build § Electronic and paper-based manuals with foundational knowledge in capital requirements knowledge § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and web-based guidelines on how to determine capital requirements could be developed. Examples of key forecasting methodologies, formulae and considerations and business case development could be included § Case studies developed through consultation with micro financiers could be used to understand the influencers in growth strategies in micro financing businesses § A CBT simulating business growth and performance on funding methodologies could be developed training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving 73 Training Method
 Funding strategies delivery recommendations Module Employment of Capital Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Identify capital employment techniques to grow a business profitably Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning of the § Electronic and paper-based manuals with learning process to develop foundational knowledge of employment of capital § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and web-based guidelines on how to use capital effectively could be developed. Examples of prioritisation techniques could be included § Case Studies developed through consultation with micro financiers could be used to understand the highest return areas in a micro financing businesses § A CBT simulating business growth and performance based on employment of capital could be developed training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving 74 Training Method
Funding strategies delivery recommendations Module Employment of Capital Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Identify capital employment techniques to grow a business profitably Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning of the § Electronic and paper-based manuals with learning process to develop foundational knowledge of employment of capital § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in cost management from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and web-based guidelines on how to use capital effectively could be developed. Examples of prioritisation techniques could be included § Case Studies developed through consultation with micro financiers could be used to understand the highest return areas in a micro financing businesses § A CBT simulating business growth and performance based on employment of capital could be developed training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving 74 Training Method
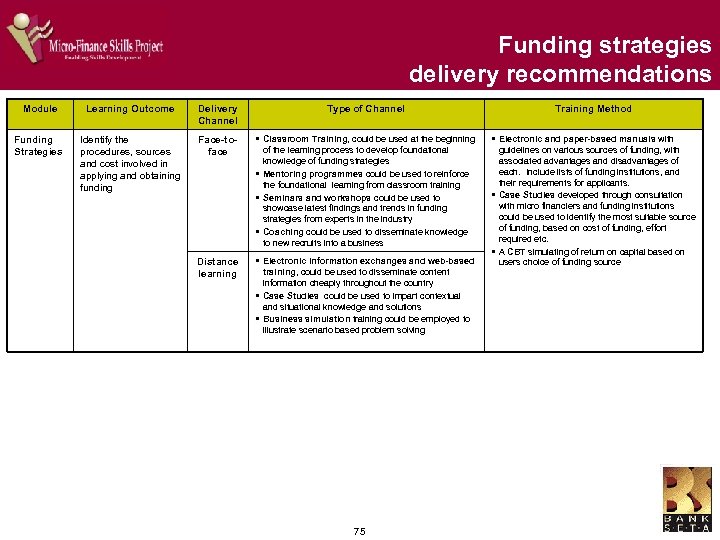 Funding strategies delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Funding Strategies Identify the procedures, sources and cost involved in applying and obtaining funding Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning § Electronic and paper-based manuals with of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of funding strategies § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in funding strategies from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and web-based guidelines on various sources of funding, with associated advantages and disadvantages of each. Include lists of funding institutions, and their requirements for applicants. § Case Studies developed through consultation with micro financiers and funding institutions could be used to identify the most suitable source of funding, based on cost of funding, effort required etc. § A CBT simulating of return on capital based on users choice of funding source training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving 75 Training Method
Funding strategies delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Funding Strategies Identify the procedures, sources and cost involved in applying and obtaining funding Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning § Electronic and paper-based manuals with of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of funding strategies § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in funding strategies from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and web-based guidelines on various sources of funding, with associated advantages and disadvantages of each. Include lists of funding institutions, and their requirements for applicants. § Case Studies developed through consultation with micro financiers and funding institutions could be used to identify the most suitable source of funding, based on cost of funding, effort required etc. § A CBT simulating of return on capital based on users choice of funding source training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving 75 Training Method
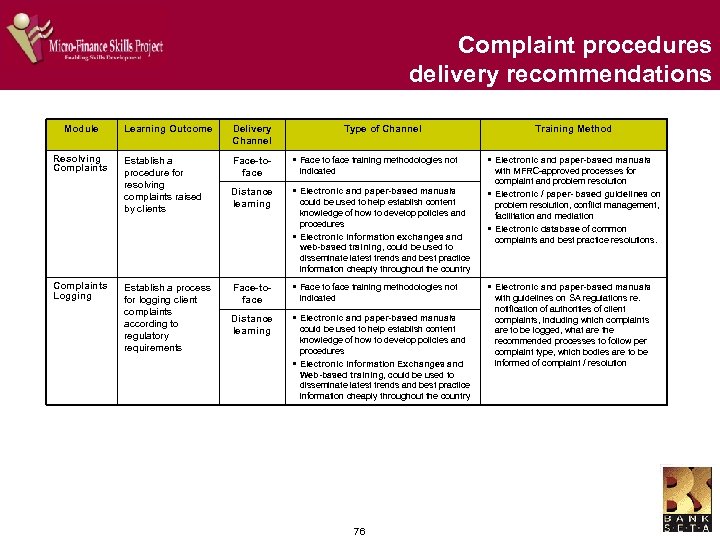 Complaint procedures delivery recommendations Module Resolving Complaints Logging Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Establish a procedure for resolving complaints raised by clients Face-toface § Face to face training methodologies not Distance learning § Electronic and paper-based manuals Establish a process for logging client complaints according to regulatory requirements Type of Channel indicated could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country indicated could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country 76 Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals with MFRC-approved processes for complaint and problem resolution § Electronic / paper- based guidelines on problem resolution, conflict management, facilitation and mediation § Electronic database of common complaints and best practice resolutions. § Electronic and paper-based manuals with guidelines on SA regulations re. notification of authorities of client complaints, including which complaints are to be logged, what are the recommended processes to follow per complaint type, which bodies are to be informed of complaint / resolution
Complaint procedures delivery recommendations Module Resolving Complaints Logging Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Establish a procedure for resolving complaints raised by clients Face-toface § Face to face training methodologies not Distance learning § Electronic and paper-based manuals Establish a process for logging client complaints according to regulatory requirements Type of Channel indicated could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures § Electronic information exchanges and web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country indicated could be used to help establish content knowledge of how to develop policies and procedures § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training, could be used to disseminate latest trends and best practice information cheaply throughout the country 76 Training Method § Electronic and paper-based manuals with MFRC-approved processes for complaint and problem resolution § Electronic / paper- based guidelines on problem resolution, conflict management, facilitation and mediation § Electronic database of common complaints and best practice resolutions. § Electronic and paper-based manuals with guidelines on SA regulations re. notification of authorities of client complaints, including which complaints are to be logged, what are the recommended processes to follow per complaint type, which bodies are to be informed of complaint / resolution
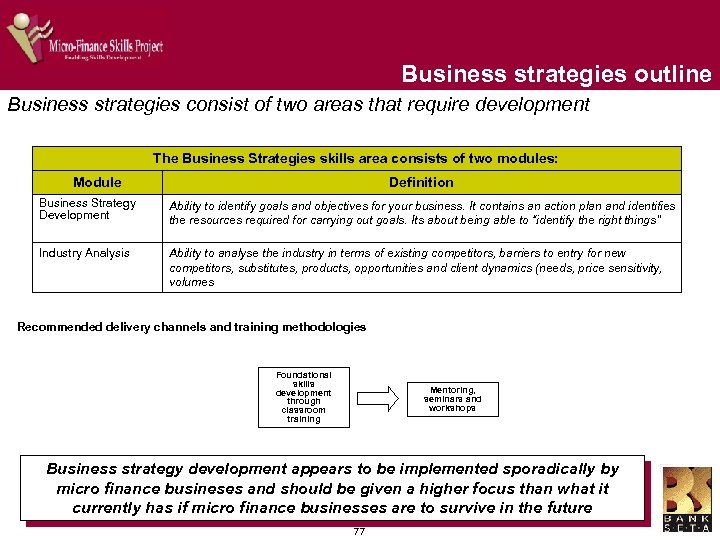 Business strategies outline Business strategies consist of two areas that require development The Business Strategies skills area consists of two modules: Module Definition Business Strategy Development Ability to identify goals and objectives for your business. It contains an action plan and identifies the resources required for carrying out goals. Its about being able to “identify the right things” Industry Analysis Ability to analyse the industry in terms of existing competitors, barriers to entry for new competitors, substitutes, products, opportunities and client dynamics (needs, price sensitivity, volumes Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through classroom training Mentoring, seminars and workshops Business strategy development appears to be implemented sporadically by micro finance busineses and should be given a higher focus than what it currently has if micro finance businesses are to survive in the future 77
Business strategies outline Business strategies consist of two areas that require development The Business Strategies skills area consists of two modules: Module Definition Business Strategy Development Ability to identify goals and objectives for your business. It contains an action plan and identifies the resources required for carrying out goals. Its about being able to “identify the right things” Industry Analysis Ability to analyse the industry in terms of existing competitors, barriers to entry for new competitors, substitutes, products, opportunities and client dynamics (needs, price sensitivity, volumes Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through classroom training Mentoring, seminars and workshops Business strategy development appears to be implemented sporadically by micro finance busineses and should be given a higher focus than what it currently has if micro finance businesses are to survive in the future 77
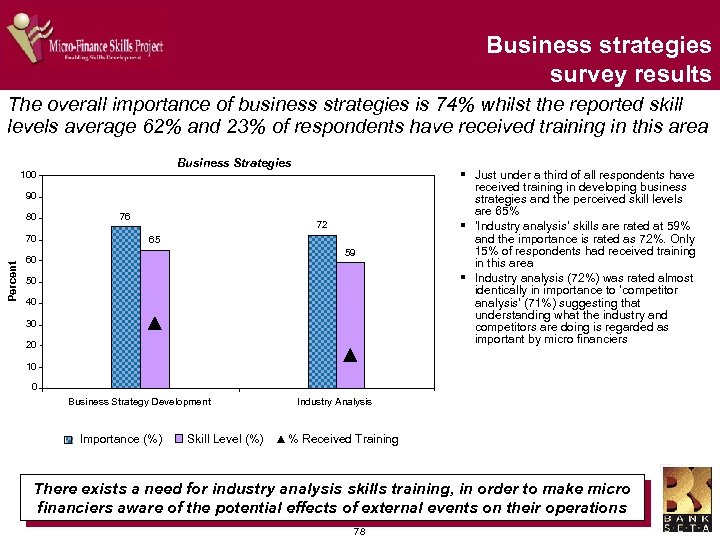 Business strategies survey results The overall importance of business strategies is 74% whilst the reported skill levels average 62% and 23% of respondents have received training in this area Business Strategies 100 90 80 Percent 70 76 72 65 59 60 50 40 30 20 § Just under a third of all respondents have received training in developing business strategies and the perceived skill levels are 65% § ‘Industry analysis’ skills are rated at 59% and the importance is rated as 72%. Only 15% of respondents had received training in this area § Industry analysis (72%) was rated almost identically in importance to ‘competitor analysis’ (71%) suggesting that understanding what the industry and competitors are doing is regarded as important by micro financiers 10 0 Business Strategy Development Importance (%) Skill Level (%) Industry Analysis % Received Training There exists a need for industry analysis skills training, in order to make micro financiers aware of the potential effects of external events on their operations 78
Business strategies survey results The overall importance of business strategies is 74% whilst the reported skill levels average 62% and 23% of respondents have received training in this area Business Strategies 100 90 80 Percent 70 76 72 65 59 60 50 40 30 20 § Just under a third of all respondents have received training in developing business strategies and the perceived skill levels are 65% § ‘Industry analysis’ skills are rated at 59% and the importance is rated as 72%. Only 15% of respondents had received training in this area § Industry analysis (72%) was rated almost identically in importance to ‘competitor analysis’ (71%) suggesting that understanding what the industry and competitors are doing is regarded as important by micro financiers 10 0 Business Strategy Development Importance (%) Skill Level (%) Industry Analysis % Received Training There exists a need for industry analysis skills training, in order to make micro financiers aware of the potential effects of external events on their operations 78
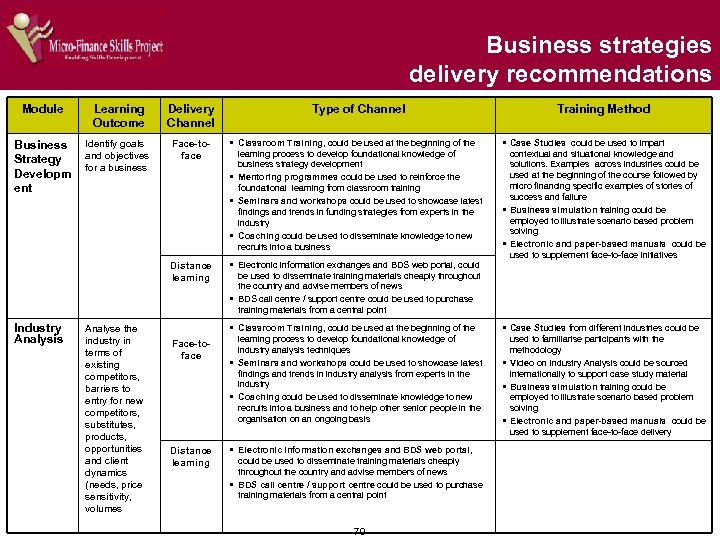 Business strategies delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Business Strategy Developm ent Identify goals and objectives for a business Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning of the § Case Studies could be used to impart learning process to develop foundational knowledge of business strategy development § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in funding strategies from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web portal, could contextual and situational knowledge and solutions. Examples across industries could be used at the beginning of the course followed by micro financing specific examples of stories of success and failure § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to supplement face-to-face initiatives Industry Analysis Analyse the industry in terms of existing competitors, barriers to entry for new competitors, substitutes, products, opportunities and client dynamics (needs, price sensitivity, volumes Type of Channel Training Method be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning of the § Case Studies from different industries could be Face-toface learning process to develop foundational knowledge of industry analysis techniques § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in industry analysis from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and to help other senior people in the organisation on an ongoing basis used to familiarise participants with the methodology § Video on Industry Analysis could be sourced internationally to support case study material § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to supplement face-to-face delivery Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 79
Business strategies delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Business Strategy Developm ent Identify goals and objectives for a business Face-toface § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning of the § Case Studies could be used to impart learning process to develop foundational knowledge of business strategy development § Mentoring programmes could be used to reinforce the foundational learning from classroom training § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in funding strategies from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web portal, could contextual and situational knowledge and solutions. Examples across industries could be used at the beginning of the course followed by micro financing specific examples of stories of success and failure § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to supplement face-to-face initiatives Industry Analysis Analyse the industry in terms of existing competitors, barriers to entry for new competitors, substitutes, products, opportunities and client dynamics (needs, price sensitivity, volumes Type of Channel Training Method be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point § Classroom Training, could be used at the beginning of the § Case Studies from different industries could be Face-toface learning process to develop foundational knowledge of industry analysis techniques § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in industry analysis from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and to help other senior people in the organisation on an ongoing basis used to familiarise participants with the methodology § Video on Industry Analysis could be sourced internationally to support case study material § Business simulation training could be employed to illustrate scenario based problem solving § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be used to supplement face-to-face delivery Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 79
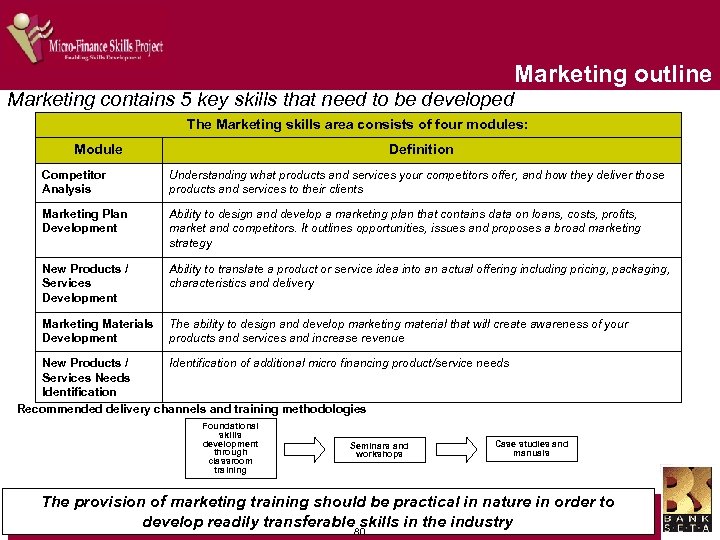 Marketing outline Marketing contains 5 key skills that need to be developed The Marketing skills area consists of four modules: Module Definition Competitor Analysis Understanding what products and services your competitors offer, and how they deliver those products and services to their clients Marketing Plan Development Ability to design and develop a marketing plan that contains data on loans, costs, profits, market and competitors. It outlines opportunities, issues and proposes a broad marketing strategy New Products / Services Development Ability to translate a product or service idea into an actual offering including pricing, packaging, characteristics and delivery Marketing Materials Development The ability to design and develop marketing material that will create awareness of your products and services and increase revenue New Products / Identification of additional micro financing product/service needs Services Needs Identification Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through classroom training Seminars and workshops Case studies and manuals The provision of marketing training should be practical in nature in order to develop readily transferable skills in the industry 80
Marketing outline Marketing contains 5 key skills that need to be developed The Marketing skills area consists of four modules: Module Definition Competitor Analysis Understanding what products and services your competitors offer, and how they deliver those products and services to their clients Marketing Plan Development Ability to design and develop a marketing plan that contains data on loans, costs, profits, market and competitors. It outlines opportunities, issues and proposes a broad marketing strategy New Products / Services Development Ability to translate a product or service idea into an actual offering including pricing, packaging, characteristics and delivery Marketing Materials Development The ability to design and develop marketing material that will create awareness of your products and services and increase revenue New Products / Identification of additional micro financing product/service needs Services Needs Identification Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through classroom training Seminars and workshops Case studies and manuals The provision of marketing training should be practical in nature in order to develop readily transferable skills in the industry 80
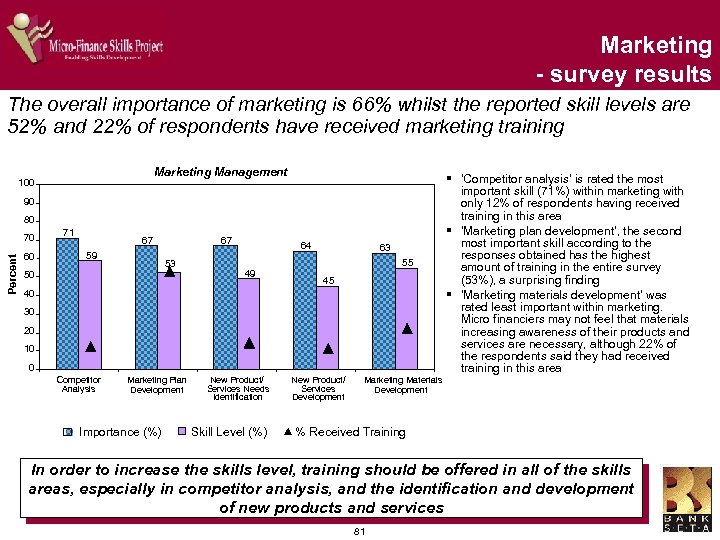 Marketing - survey results The overall importance of marketing is 66% whilst the reported skill levels are 52% and 22% of respondents have received marketing training Marketing Management 100 90 80 Percent 70 60 71 67 59 67 53 50 64 49 63 55 45 40 30 20 10 0 Competitor Analysis Marketing Plan Development Importance (%) New Product/ Services Needs Identification Skill Level (%) New Product/ Services Development § ‘Competitor analysis’ is rated the most important skill (71%) within marketing with only 12% of respondents having received training in this area § ‘Marketing plan development’, the second most important skill according to the responses obtained has the highest amount of training in the entire survey (53%), a surprising finding § ‘Marketing materials development’ was rated least important within marketing. Micro financiers may not feel that materials increasing awareness of their products and services are necessary, although 22% of the respondents said they had received training in this area Marketing Materials Development % Received Training In order to increase the skills level, training should be offered in all of the skills areas, especially in competitor analysis, and the identification and development of new products and services 81
Marketing - survey results The overall importance of marketing is 66% whilst the reported skill levels are 52% and 22% of respondents have received marketing training Marketing Management 100 90 80 Percent 70 60 71 67 59 67 53 50 64 49 63 55 45 40 30 20 10 0 Competitor Analysis Marketing Plan Development Importance (%) New Product/ Services Needs Identification Skill Level (%) New Product/ Services Development § ‘Competitor analysis’ is rated the most important skill (71%) within marketing with only 12% of respondents having received training in this area § ‘Marketing plan development’, the second most important skill according to the responses obtained has the highest amount of training in the entire survey (53%), a surprising finding § ‘Marketing materials development’ was rated least important within marketing. Micro financiers may not feel that materials increasing awareness of their products and services are necessary, although 22% of the respondents said they had received training in this area Marketing Materials Development % Received Training In order to increase the skills level, training should be offered in all of the skills areas, especially in competitor analysis, and the identification and development of new products and services 81
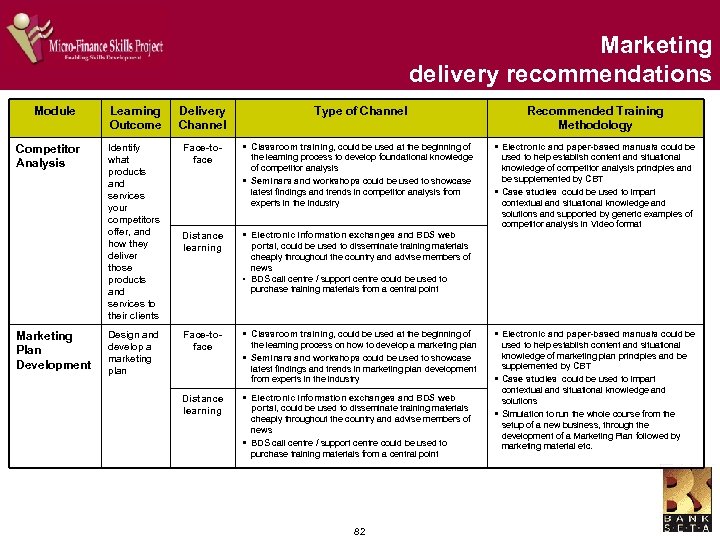 Marketing delivery recommendations Module Competitor Analysis Marketing Plan Development Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Identify what products and services your competitors offer, and how they deliver those products and services to their clients Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of competitor analysis § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in competitor analysis from experts in the industry used to help establish content and situational knowledge of competitor analysis principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions and supported by generic examples of competitor analysis in Video format Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be the learning process on how to develop a marketing plan § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in marketing plan development from experts in the industry Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web used to help establish content and situational knowledge of marketing plan principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Simulation to run the whole course from the setup of a new business, through the development of a Marketing Plan followed by marketing material etc. Design and develop a marketing plan Type of Channel Recommended Training Methodology portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news • BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 82
Marketing delivery recommendations Module Competitor Analysis Marketing Plan Development Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Identify what products and services your competitors offer, and how they deliver those products and services to their clients Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of competitor analysis § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in competitor analysis from experts in the industry used to help establish content and situational knowledge of competitor analysis principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions and supported by generic examples of competitor analysis in Video format Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be the learning process on how to develop a marketing plan § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in marketing plan development from experts in the industry Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web used to help establish content and situational knowledge of marketing plan principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Simulation to run the whole course from the setup of a new business, through the development of a Marketing Plan followed by marketing material etc. Design and develop a marketing plan Type of Channel Recommended Training Methodology portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news • BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 82
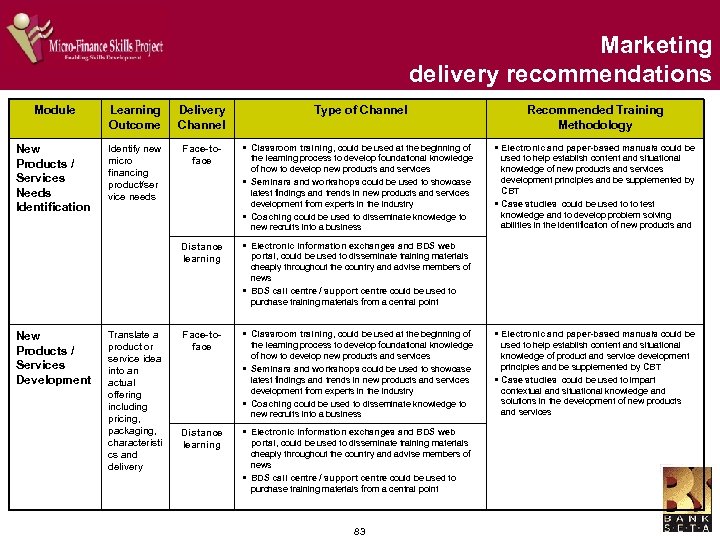 Marketing delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel New Products / Services Needs Identification Identify new micro financing product/ser vice needs Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to develop new products and services § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in new products and services development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business used to help establish content and situational knowledge of new products and services development principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to to test knowledge and to develop problem solving abilities in the identification of new products and Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to develop new products and services § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in new products and services development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business used to help establish content and situational knowledge of product and service development principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions in the development of new products and services Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web New Products / Services Development Translate a product or service idea into an actual offering including pricing, packaging, characteristi cs and delivery Type of Channel Recommended Training Methodology portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 83
Marketing delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel New Products / Services Needs Identification Identify new micro financing product/ser vice needs Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to develop new products and services § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in new products and services development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business used to help establish content and situational knowledge of new products and services development principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to to test knowledge and to develop problem solving abilities in the identification of new products and Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning of § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to develop new products and services § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in new products and services development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business used to help establish content and situational knowledge of product and service development principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions in the development of new products and services Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web New Products / Services Development Translate a product or service idea into an actual offering including pricing, packaging, characteristi cs and delivery Type of Channel Recommended Training Methodology portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 83
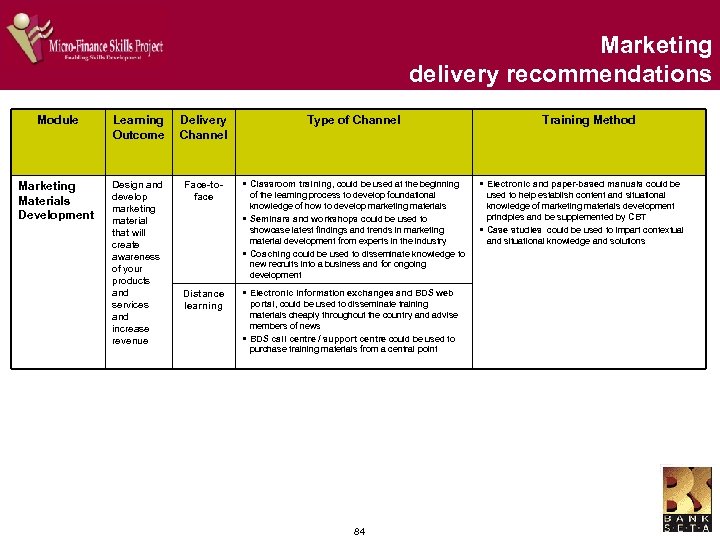 Marketing delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Marketing Materials Development Design and develop marketing material that will create awareness of your products and services and increase revenue Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to develop marketing materials § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in marketing material development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and for ongoing development used to help establish content and situational knowledge of marketing materials development principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 84 Training Method
Marketing delivery recommendations Module Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Type of Channel Marketing Materials Development Design and develop marketing material that will create awareness of your products and services and increase revenue Face-toface § Classroom training, could be used at the beginning § Electronic and paper-based manuals could be of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to develop marketing materials § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in marketing material development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business and for ongoing development used to help establish content and situational knowledge of marketing materials development principles and be supplemented by CBT § Case studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions Distance learning § Electronic information exchanges and BDS web portal, could be used to disseminate training materials cheaply throughout the country and advise members of news § BDS call centre / support centre could be used to purchase training materials from a central point 84 Training Method
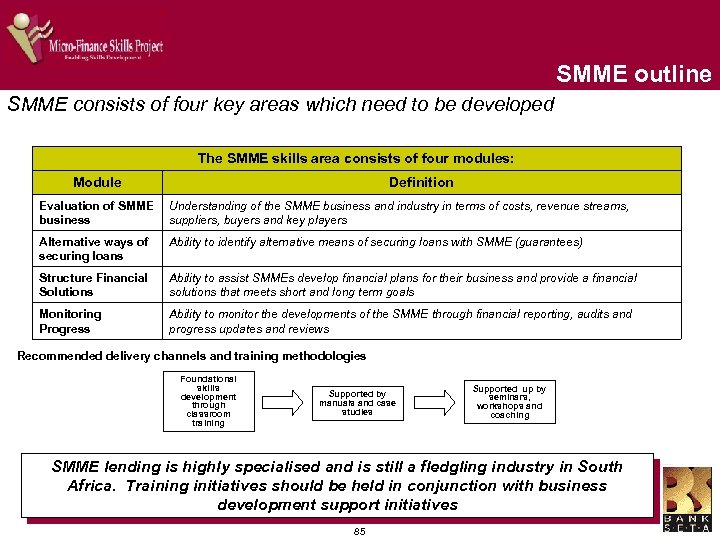 SMME outline SMME consists of four key areas which need to be developed The SMME skills area consists of four modules: Module Definition Evaluation of SMME business Understanding of the SMME business and industry in terms of costs, revenue streams, suppliers, buyers and key players Alternative ways of securing loans Ability to identify alternative means of securing loans with SMME (guarantees) Structure Financial Solutions Ability to assist SMMEs develop financial plans for their business and provide a financial solutions that meets short and long term goals Monitoring Progress Ability to monitor the developments of the SMME through financial reporting, audits and progress updates and reviews Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through classroom training Supported by manuals and case studies Supported up by seminars, workshops and coaching SMME lending is highly specialised and is still a fledgling industry in South Africa. Training initiatives should be held in conjunction with business development support initiatives 85
SMME outline SMME consists of four key areas which need to be developed The SMME skills area consists of four modules: Module Definition Evaluation of SMME business Understanding of the SMME business and industry in terms of costs, revenue streams, suppliers, buyers and key players Alternative ways of securing loans Ability to identify alternative means of securing loans with SMME (guarantees) Structure Financial Solutions Ability to assist SMMEs develop financial plans for their business and provide a financial solutions that meets short and long term goals Monitoring Progress Ability to monitor the developments of the SMME through financial reporting, audits and progress updates and reviews Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through classroom training Supported by manuals and case studies Supported up by seminars, workshops and coaching SMME lending is highly specialised and is still a fledgling industry in South Africa. Training initiatives should be held in conjunction with business development support initiatives 85
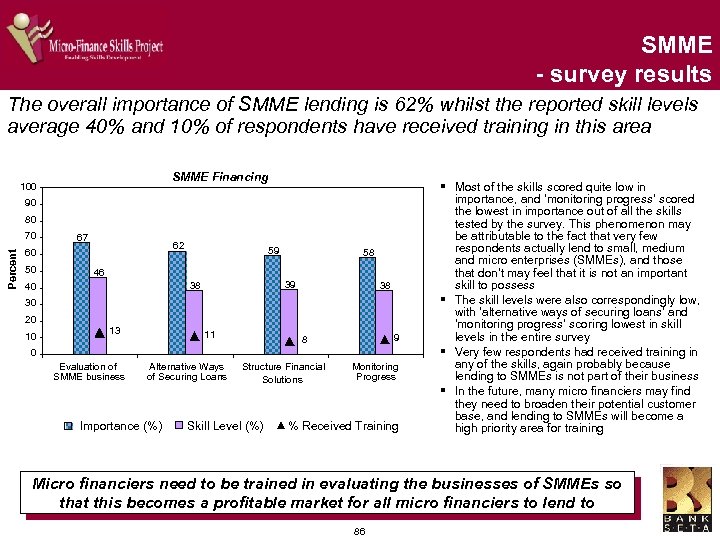 SMME - survey results The overall importance of SMME lending is 62% whilst the reported skill levels average 40% and 10% of respondents have received training in this area SMME Financing 100 90 80 Percent 70 67 62 60 50 59 58 46 39 38 40 38 30 20 10 13 11 9 8 0 Evaluation of SMME business Alternative Ways of Securing Loans Importance (%) Structure Financial Solutions Skill Level (%) Monitoring Progress % Received Training § Most of the skills scored quite low in importance, and ‘monitoring progress’ scored the lowest in importance out of all the skills tested by the survey. This phenomenon may be attributable to the fact that very few respondents actually lend to small, medium and micro enterprises (SMMEs), and those that don’t may feel that it is not an important skill to possess § The skill levels were also correspondingly low, with ‘alternative ways of securing loans’ and ‘monitoring progress’ scoring lowest in skill levels in the entire survey § Very few respondents had received training in any of the skills, again probably because lending to SMMEs is not part of their business § In the future, many micro financiers may find they need to broaden their potential customer base, and lending to SMMEs will become a high priority area for training Micro financiers need to be trained in evaluating the businesses of SMMEs so that this becomes a profitable market for all micro financiers to lend to 86
SMME - survey results The overall importance of SMME lending is 62% whilst the reported skill levels average 40% and 10% of respondents have received training in this area SMME Financing 100 90 80 Percent 70 67 62 60 50 59 58 46 39 38 40 38 30 20 10 13 11 9 8 0 Evaluation of SMME business Alternative Ways of Securing Loans Importance (%) Structure Financial Solutions Skill Level (%) Monitoring Progress % Received Training § Most of the skills scored quite low in importance, and ‘monitoring progress’ scored the lowest in importance out of all the skills tested by the survey. This phenomenon may be attributable to the fact that very few respondents actually lend to small, medium and micro enterprises (SMMEs), and those that don’t may feel that it is not an important skill to possess § The skill levels were also correspondingly low, with ‘alternative ways of securing loans’ and ‘monitoring progress’ scoring lowest in skill levels in the entire survey § Very few respondents had received training in any of the skills, again probably because lending to SMMEs is not part of their business § In the future, many micro financiers may find they need to broaden their potential customer base, and lending to SMMEs will become a high priority area for training Micro financiers need to be trained in evaluating the businesses of SMMEs so that this becomes a profitable market for all micro financiers to lend to 86
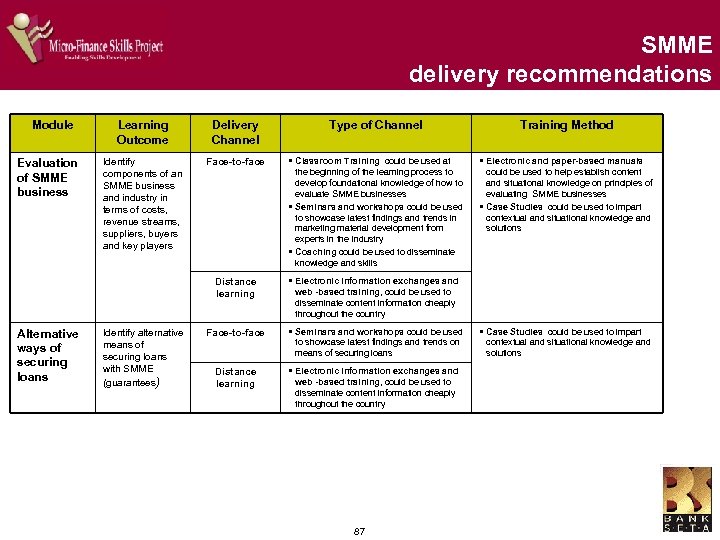 SMME delivery recommendations Module Alternative ways of securing loans Delivery Channel Identify components of an SMME business and industry in terms of costs, revenue streams, suppliers, buyers and key players Face-to-face § Classroom Training could be used at § Electronic and paper-based manuals the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to evaluate SMME businesses § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in marketing material development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge and skills could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge on principles of evaluating SMME businesses § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions Distance learning Evaluation of SMME business Learning Outcome § Electronic information exchanges and Identify alternative means of securing loans with SMME (guarantees) Face-to-face Distance learning Type of Channel Training Method web -based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends on means of securing loans § Electronic information exchanges and web -based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country 87 § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions
SMME delivery recommendations Module Alternative ways of securing loans Delivery Channel Identify components of an SMME business and industry in terms of costs, revenue streams, suppliers, buyers and key players Face-to-face § Classroom Training could be used at § Electronic and paper-based manuals the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to evaluate SMME businesses § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in marketing material development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge and skills could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge on principles of evaluating SMME businesses § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions Distance learning Evaluation of SMME business Learning Outcome § Electronic information exchanges and Identify alternative means of securing loans with SMME (guarantees) Face-to-face Distance learning Type of Channel Training Method web -based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends on means of securing loans § Electronic information exchanges and web -based training, could be used to disseminate content information cheaply throughout the country 87 § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions
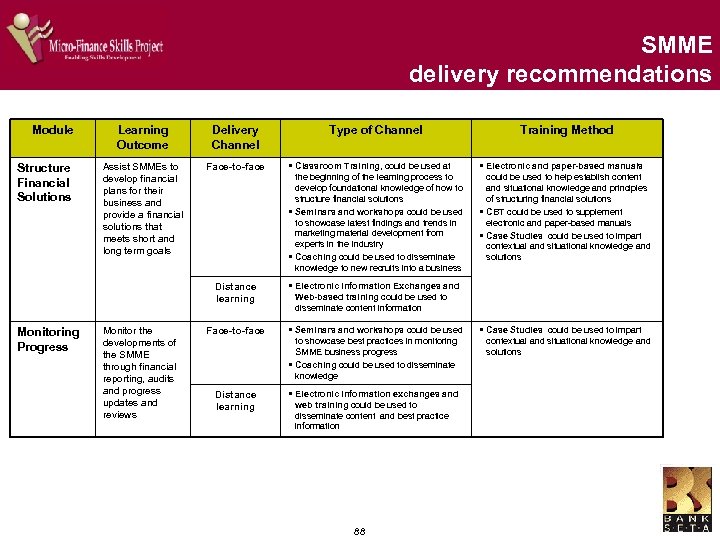 SMME delivery recommendations Module Structure Financial Solutions Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Assist SMMEs to develop financial plans for their business and provide a financial solutions that meets short and long term goals Face-to-face Distance learning Monitoring Progress Monitor the developments of the SMME through financial reporting, audits and progress updates and reviews Face-to-face Distance learning Type of Channel Training Method § Classroom Training, could be used at § Electronic and paper-based manuals the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to structure financial solutions § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in marketing material development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge and principles of structuring financial solutions § CBT could be used to supplement electronic and paper-based manuals § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training could be used to disseminate content information § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase best practices in monitoring SMME business progress § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge § Electronic information exchanges and web training could be used to disseminate content and best practice information 88 § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions
SMME delivery recommendations Module Structure Financial Solutions Learning Outcome Delivery Channel Assist SMMEs to develop financial plans for their business and provide a financial solutions that meets short and long term goals Face-to-face Distance learning Monitoring Progress Monitor the developments of the SMME through financial reporting, audits and progress updates and reviews Face-to-face Distance learning Type of Channel Training Method § Classroom Training, could be used at § Electronic and paper-based manuals the beginning of the learning process to develop foundational knowledge of how to structure financial solutions § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase latest findings and trends in marketing material development from experts in the industry § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge to new recruits into a business could be used to help establish content and situational knowledge and principles of structuring financial solutions § CBT could be used to supplement electronic and paper-based manuals § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions § Electronic Information Exchanges and Web-based training could be used to disseminate content information § Seminars and workshops could be used to showcase best practices in monitoring SMME business progress § Coaching could be used to disseminate knowledge § Electronic information exchanges and web training could be used to disseminate content and best practice information 88 § Case Studies could be used to impart contextual and situational knowledge and solutions
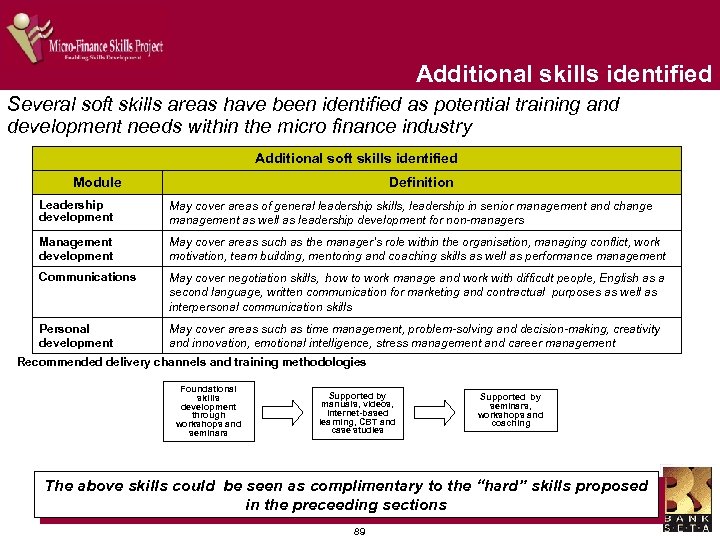 Additional skills identified Several soft skills areas have been identified as potential training and development needs within the micro finance industry Additional soft skills identified Module Definition Leadership development May cover areas of general leadership skills, leadership in senior management and change management as well as leadership development for non-managers Management development May cover areas such as the manager’s role within the organisation, managing conflict, work motivation, team building, mentoring and coaching skills as well as performance management Communications May cover negotiation skills, how to work manage and work with difficult people, English as a second language, written communication for marketing and contractual purposes as well as interpersonal communication skills Personal development May cover areas such as time management, problem-solving and decision-making, creativity and innovation, emotional intelligence, stress management and career management Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through workshops and seminars Supported by manuals, videos, internet-based learning, CBT and case studies Supported by seminars, workshops and coaching The above skills could be seen as complimentary to the “hard” skills proposed in the preceeding sections 89
Additional skills identified Several soft skills areas have been identified as potential training and development needs within the micro finance industry Additional soft skills identified Module Definition Leadership development May cover areas of general leadership skills, leadership in senior management and change management as well as leadership development for non-managers Management development May cover areas such as the manager’s role within the organisation, managing conflict, work motivation, team building, mentoring and coaching skills as well as performance management Communications May cover negotiation skills, how to work manage and work with difficult people, English as a second language, written communication for marketing and contractual purposes as well as interpersonal communication skills Personal development May cover areas such as time management, problem-solving and decision-making, creativity and innovation, emotional intelligence, stress management and career management Recommended delivery channels and training methodologies Foundational skills development through workshops and seminars Supported by manuals, videos, internet-based learning, CBT and case studies Supported by seminars, workshops and coaching The above skills could be seen as complimentary to the “hard” skills proposed in the preceeding sections 89
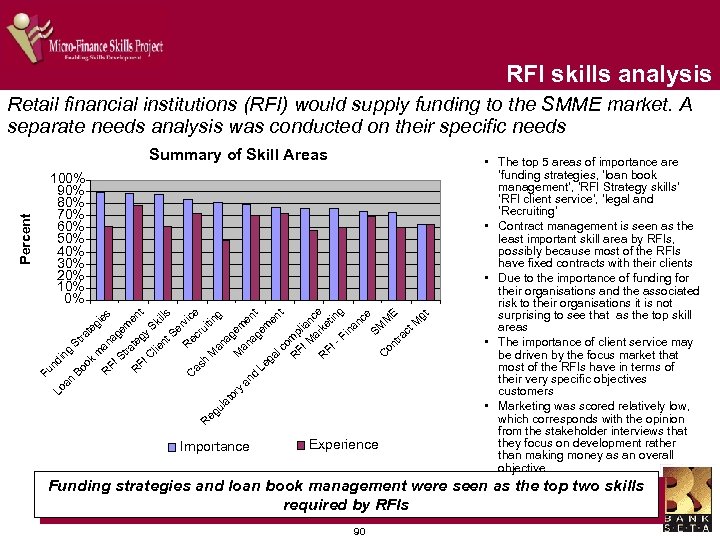 RFI skills analysis Retail financial institutions (RFI) would supply funding to the SMME market. A separate needs analysis was conducted on their specific needs Percent Summary of Skill Areas 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% t g t t g e gt ce ME nc tin an ia rke M t M t n c ru S pl a g g Fi gy nt S ec ra tra na ate om I M na ana - nt S R a a o lie FI g l c F m Str C M R M in k ga R I C d I o e sh F n F a L R R Bo Fu C nd n a a y Lo or t la gu e R s ie eg m ge en lls i Sk ce vi er n iti en em Importance en em Experience • The top 5 areas of importance are ‘funding strategies, ‘loan book management’, ‘RFI Strategy skills’ ‘RFI client service’, ‘legal and ‘Recruiting’ • Contract management is seen as the least important skill area by RFIs, possibly because most of the RFIs have fixed contracts with their clients • Due to the importance of funding for their organisations and the associated risk to their organisations it is not surprising to see that as the top skill areas • The importance of client service may be driven by the focus market that most of the RFIs have in terms of their very specific objectives customers • Marketing was scored relatively low, which corresponds with the opinion from the stakeholder interviews that they focus on development rather than making money as an overall objective Funding strategies and loan book management were seen as the top two skills required by RFIs 90
RFI skills analysis Retail financial institutions (RFI) would supply funding to the SMME market. A separate needs analysis was conducted on their specific needs Percent Summary of Skill Areas 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% t g t t g e gt ce ME nc tin an ia rke M t M t n c ru S pl a g g Fi gy nt S ec ra tra na ate om I M na ana - nt S R a a o lie FI g l c F m Str C M R M in k ga R I C d I o e sh F n F a L R R Bo Fu C nd n a a y Lo or t la gu e R s ie eg m ge en lls i Sk ce vi er n iti en em Importance en em Experience • The top 5 areas of importance are ‘funding strategies, ‘loan book management’, ‘RFI Strategy skills’ ‘RFI client service’, ‘legal and ‘Recruiting’ • Contract management is seen as the least important skill area by RFIs, possibly because most of the RFIs have fixed contracts with their clients • Due to the importance of funding for their organisations and the associated risk to their organisations it is not surprising to see that as the top skill areas • The importance of client service may be driven by the focus market that most of the RFIs have in terms of their very specific objectives customers • Marketing was scored relatively low, which corresponds with the opinion from the stakeholder interviews that they focus on development rather than making money as an overall objective Funding strategies and loan book management were seen as the top two skills required by RFIs 90
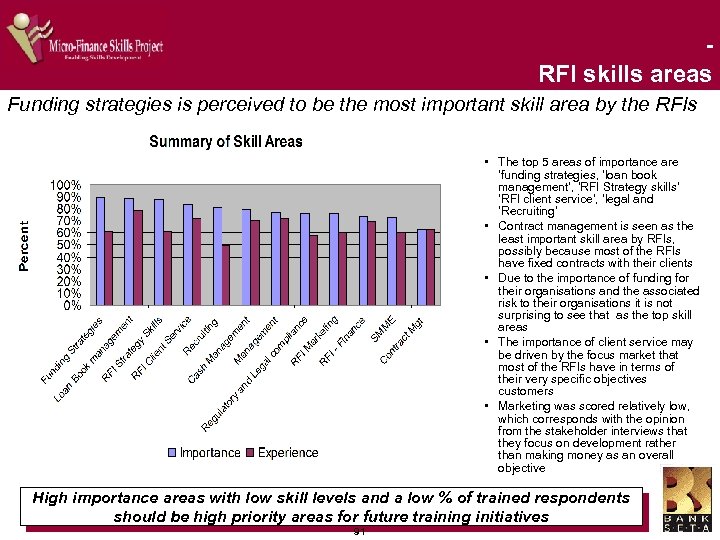 RFI skills areas Funding strategies is perceived to be the most important skill area by the RFIs • The top 5 areas of importance are ‘funding strategies, ‘loan book management’, ‘RFI Strategy skills’ ‘RFI client service’, ‘legal and ‘Recruiting’ • Contract management is seen as the least important skill area by RFIs, possibly because most of the RFIs have fixed contracts with their clients • Due to the importance of funding for their organisations and the associated risk to their organisations it is not surprising to see that as the top skill areas • The importance of client service may be driven by the focus market that most of the RFIs have in terms of their very specific objectives customers • Marketing was scored relatively low, which corresponds with the opinion from the stakeholder interviews that they focus on development rather than making money as an overall objective High importance areas with low skill levels and a low % of trained respondents should be high priority areas for future training initiatives 91
RFI skills areas Funding strategies is perceived to be the most important skill area by the RFIs • The top 5 areas of importance are ‘funding strategies, ‘loan book management’, ‘RFI Strategy skills’ ‘RFI client service’, ‘legal and ‘Recruiting’ • Contract management is seen as the least important skill area by RFIs, possibly because most of the RFIs have fixed contracts with their clients • Due to the importance of funding for their organisations and the associated risk to their organisations it is not surprising to see that as the top skill areas • The importance of client service may be driven by the focus market that most of the RFIs have in terms of their very specific objectives customers • Marketing was scored relatively low, which corresponds with the opinion from the stakeholder interviews that they focus on development rather than making money as an overall objective High importance areas with low skill levels and a low % of trained respondents should be high priority areas for future training initiatives 91
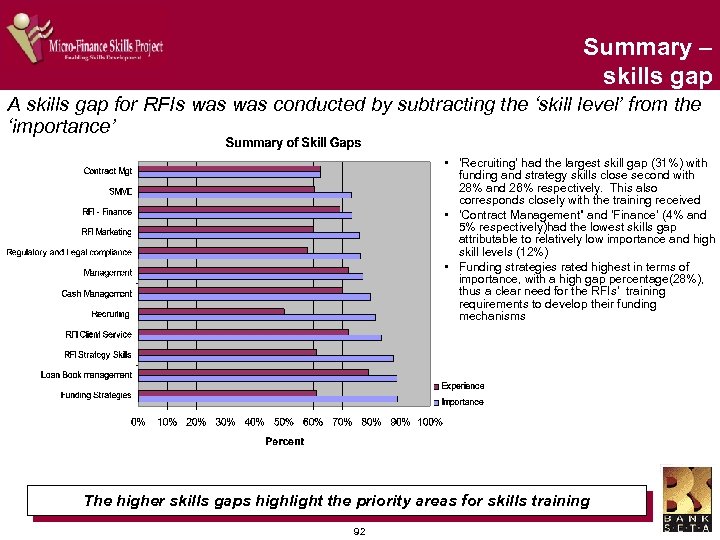 Summary – skills gap A skills gap for RFIs was conducted by subtracting the ‘skill level’ from the ‘importance’ • ‘Recruiting’ had the largest skill gap (31%) with funding and strategy skills close second with 28% and 26% respectively. This also corresponds closely with the training received • ‘Contract Management” and ‘Finance’ (4% and 5% respectively)had the lowest skills gap attributable to relatively low importance and high skill levels (12%) • Funding strategies rated highest in terms of importance, with a high gap percentage(28%), thus a clear need for the RFIs’ training requirements to develop their funding mechanisms The higher skills gaps highlight the priority areas for skills training 92
Summary – skills gap A skills gap for RFIs was conducted by subtracting the ‘skill level’ from the ‘importance’ • ‘Recruiting’ had the largest skill gap (31%) with funding and strategy skills close second with 28% and 26% respectively. This also corresponds closely with the training received • ‘Contract Management” and ‘Finance’ (4% and 5% respectively)had the lowest skills gap attributable to relatively low importance and high skill levels (12%) • Funding strategies rated highest in terms of importance, with a high gap percentage(28%), thus a clear need for the RFIs’ training requirements to develop their funding mechanisms The higher skills gaps highlight the priority areas for skills training 92
 RFI recommendations Recommendations § § § Further investigation into the gaps identified from this survey needs to be done from a more representative sample. Although the analysis identified some issues for the RFIs, a focused analysis on RFIs must be done to ensure identification of their needs on a specific basis All the RFIs noted the need for application processing training that ensures quality loan book. This, together with the focus on clear cut collection processes will ensure good management of their loan book Recruiting was identified as the area where there was the biggest gap between importance and current skill level. Provisionally, the recommendation is that skills development interventions should focus on this area for development Funding Strategy was also identified as a key area of development for the RFIs. They are dependent on sourcing cost effective funding at a cheaper rate than the normal institutions, with the added complexity of above average risk exposure. This adds to the difficulty of sourcing funds for expanding their operations. Strategy Skills rated high in terms of importance for both the RFIs and the RFI clients (SMME). The reason for this is that they need to make sure that their clients have a solid understanding of their business and a viable business strategy and plan, that will help them with repayment of their loans. The strategy skills for the RFIs themsevles will help them identify better ways in which to approach a highly complex and difficult market and reach their specific developmental objectives 93
RFI recommendations Recommendations § § § Further investigation into the gaps identified from this survey needs to be done from a more representative sample. Although the analysis identified some issues for the RFIs, a focused analysis on RFIs must be done to ensure identification of their needs on a specific basis All the RFIs noted the need for application processing training that ensures quality loan book. This, together with the focus on clear cut collection processes will ensure good management of their loan book Recruiting was identified as the area where there was the biggest gap between importance and current skill level. Provisionally, the recommendation is that skills development interventions should focus on this area for development Funding Strategy was also identified as a key area of development for the RFIs. They are dependent on sourcing cost effective funding at a cheaper rate than the normal institutions, with the added complexity of above average risk exposure. This adds to the difficulty of sourcing funds for expanding their operations. Strategy Skills rated high in terms of importance for both the RFIs and the RFI clients (SMME). The reason for this is that they need to make sure that their clients have a solid understanding of their business and a viable business strategy and plan, that will help them with repayment of their loans. The strategy skills for the RFIs themsevles will help them identify better ways in which to approach a highly complex and difficult market and reach their specific developmental objectives 93
 Next steps for RFIs 1. More detailed analysis is required on the RFIs over a broader spectrum of representatives, specifically identifying micro financiers that provide similar services to the SMME market and identifying similarities and differences in terms of skill development requirements 2. Implement skills and training initiatives that can address funding, contract management and recruiting skill needs based on initial assessment of the situation 3. Analysis of the overlaps between different market SETA objectives to identify synergies and opportunities for collaboration 4. Identify opportunities where BDS support currently available to the RFIs and the SMME clientele can be developed and enhanced to fit to specific requirements of the RFI business objectives 94
Next steps for RFIs 1. More detailed analysis is required on the RFIs over a broader spectrum of representatives, specifically identifying micro financiers that provide similar services to the SMME market and identifying similarities and differences in terms of skill development requirements 2. Implement skills and training initiatives that can address funding, contract management and recruiting skill needs based on initial assessment of the situation 3. Analysis of the overlaps between different market SETA objectives to identify synergies and opportunities for collaboration 4. Identify opportunities where BDS support currently available to the RFIs and the SMME clientele can be developed and enhanced to fit to specific requirements of the RFI business objectives 94
 Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 95
Contents § § § § § Introduction International best practice Training delivery mechanisms Curriculum content Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Overall conclusions Implementation plan Pre-project decisions Next steps 95
 Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Skills programmes should be instituted initially, with scope to develop a learnership in the future as soon as a formal qualification in micro finance is developed and capacity has been built for training providers § The reasons for our recommendation are listed below No qualification in micro finance exists at present, leaving the learner without a specific goal / qualification to work towards Ø The approach to the training of micro finance-related topics has been very fragmented, with little agreement between providers on content, methodologies and guiding principles Ø • Ø There is a lack of existing micro finance-specific accredited education and training institutions to offer the formal training components of the learnership • • § Capacity needs to be developed within the training industry to cater for the specific training needs of micro-financiers Capacity building may take a number of years before training providers are proficient in the delivery of micro-finance specific training content Learning should be prioritised by industry demand for learning initiatives Ø § In the past, training has either been very generic in nature or very specific to a particular business Extensive use of the 80/20 principle should be used in this regard where the key skills areas for microfinanciers are prioritised Modules within identified skills areas could form the basis of skills programmes, which could form the basis for credits towards a future qualification in micro finance Skills programmes could be made up of modules within skills areas which micro financiers can pick and choose from, depending upon their training needs 96
Recommendations on skills programmes / learnerships Skills programmes should be instituted initially, with scope to develop a learnership in the future as soon as a formal qualification in micro finance is developed and capacity has been built for training providers § The reasons for our recommendation are listed below No qualification in micro finance exists at present, leaving the learner without a specific goal / qualification to work towards Ø The approach to the training of micro finance-related topics has been very fragmented, with little agreement between providers on content, methodologies and guiding principles Ø • Ø There is a lack of existing micro finance-specific accredited education and training institutions to offer the formal training components of the learnership • • § Capacity needs to be developed within the training industry to cater for the specific training needs of micro-financiers Capacity building may take a number of years before training providers are proficient in the delivery of micro-finance specific training content Learning should be prioritised by industry demand for learning initiatives Ø § In the past, training has either been very generic in nature or very specific to a particular business Extensive use of the 80/20 principle should be used in this regard where the key skills areas for microfinanciers are prioritised Modules within identified skills areas could form the basis of skills programmes, which could form the basis for credits towards a future qualification in micro finance Skills programmes could be made up of modules within skills areas which micro financiers can pick and choose from, depending upon their training needs 96
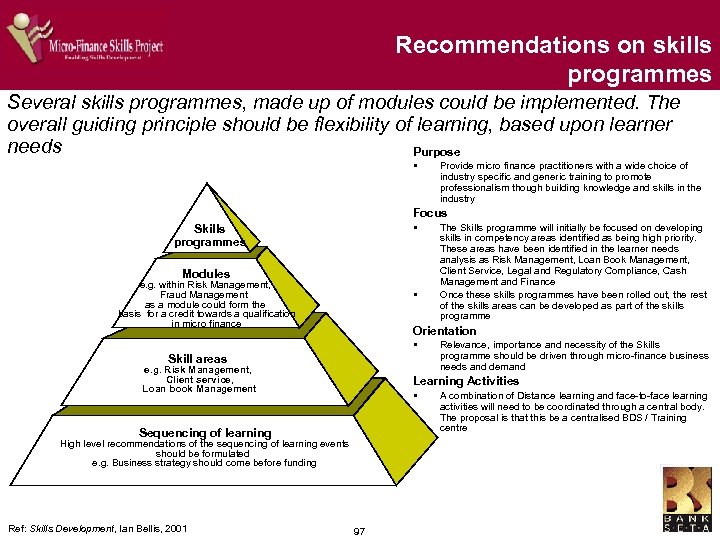 Recommendations on skills programmes Several skills programmes, made up of modules could be implemented. The overall guiding principle should be flexibility of learning, based upon learner needs Purpose § Provide micro finance practitioners with a wide choice of industry specific and generic training to promote professionalism though building knowledge and skills in the industry Focus § Skills programmes Modules e. g. within Risk Management, Fraud Management as a module could form the basis for a credit towards a qualification in micro finance § Orientation § Skill areas e. g. Risk Management, Client service, Loan book Management Relevance, importance and necessity of the Skills programme should be driven through micro-finance business needs and demand Learning Activities § Sequencing of learning High level recommendations of the sequencing of learning events should be formulated e. g. Business strategy should come before funding Ref: Skills Development, Ian Bellis, 2001 The Skills programme will initially be focused on developing skills in competency areas identified as being high priority. These areas have been identified in the learner needs analysis as Risk Management, Loan Book Management, Client Service, Legal and Regulatory Compliance, Cash Management and Finance Once these skills programmes have been rolled out, the rest of the skills areas can be developed as part of the skills programme 97 A combination of Distance learning and face-to-face learning activities will need to be coordinated through a central body. The proposal is that this be a centralised BDS / Training centre
Recommendations on skills programmes Several skills programmes, made up of modules could be implemented. The overall guiding principle should be flexibility of learning, based upon learner needs Purpose § Provide micro finance practitioners with a wide choice of industry specific and generic training to promote professionalism though building knowledge and skills in the industry Focus § Skills programmes Modules e. g. within Risk Management, Fraud Management as a module could form the basis for a credit towards a qualification in micro finance § Orientation § Skill areas e. g. Risk Management, Client service, Loan book Management Relevance, importance and necessity of the Skills programme should be driven through micro-finance business needs and demand Learning Activities § Sequencing of learning High level recommendations of the sequencing of learning events should be formulated e. g. Business strategy should come before funding Ref: Skills Development, Ian Bellis, 2001 The Skills programme will initially be focused on developing skills in competency areas identified as being high priority. These areas have been identified in the learner needs analysis as Risk Management, Loan Book Management, Client Service, Legal and Regulatory Compliance, Cash Management and Finance Once these skills programmes have been rolled out, the rest of the skills areas can be developed as part of the skills programme 97 A combination of Distance learning and face-to-face learning activities will need to be coordinated through a central body. The proposal is that this be a centralised BDS / Training centre
 Recommendations on skills programmes In order for the skills programme to work, a clustering of skills areas into core, fundamental and elective learning needs to be performed Fundamental Learning Core Learning Elective Learning Definition: Learning which forms the grounding or basis needed to undertake further learning required in obtaining a qualification Compulsory learning required in situations contextually relevant to a particular qualification A selection of additional credits at the level of the NQF specified, from a choice of may be made to ensure that the purposes of the qualification is achieved Suggested fundamental skill areas: Suggested core skill areas: • • • Client Service Client Administration Complaint Procedures Communications Personal development Risk Management Cash Management Legal and Regulatory Compliance Loan Book Management Staff Management Leadership Development Management development 98 Suggested elective areas: • • Finance Marketing Funding strategies Business Strategies
Recommendations on skills programmes In order for the skills programme to work, a clustering of skills areas into core, fundamental and elective learning needs to be performed Fundamental Learning Core Learning Elective Learning Definition: Learning which forms the grounding or basis needed to undertake further learning required in obtaining a qualification Compulsory learning required in situations contextually relevant to a particular qualification A selection of additional credits at the level of the NQF specified, from a choice of may be made to ensure that the purposes of the qualification is achieved Suggested fundamental skill areas: Suggested core skill areas: • • • Client Service Client Administration Complaint Procedures Communications Personal development Risk Management Cash Management Legal and Regulatory Compliance Loan Book Management Staff Management Leadership Development Management development 98 Suggested elective areas: • • Finance Marketing Funding strategies Business Strategies
 Overall conclusions Skills programmes, made up of prioritised modules could be implemented as flexible learning offerings to the micro-finance industry § § The implementation of the training should be pushed through in the form of modularbased skills programmes, offering the learner flexibility of learning, based upon training and development needs The overall guiding principle should be that of a learning organisation approach The delivery of training materials should be through a combination of different delivery channels and should be offered in parallel through both distance and face-to-face methods Use should be made of the 80 / 20 principle when implementing the Skills programme Ø § § The 20 percent of learning that will deliver 80% of the value to micro financiers should be prioritised in the roll-out Extensive use should be made of South African, micro-finance industry specific content for case studies and other training materials Extensive marketing of the Skills programme should be done to increase awareness Learning initiatives should be prioritised by industry skills needs 99
Overall conclusions Skills programmes, made up of prioritised modules could be implemented as flexible learning offerings to the micro-finance industry § § The implementation of the training should be pushed through in the form of modularbased skills programmes, offering the learner flexibility of learning, based upon training and development needs The overall guiding principle should be that of a learning organisation approach The delivery of training materials should be through a combination of different delivery channels and should be offered in parallel through both distance and face-to-face methods Use should be made of the 80 / 20 principle when implementing the Skills programme Ø § § The 20 percent of learning that will deliver 80% of the value to micro financiers should be prioritised in the roll-out Extensive use should be made of South African, micro-finance industry specific content for case studies and other training materials Extensive marketing of the Skills programme should be done to increase awareness Learning initiatives should be prioritised by industry skills needs 99
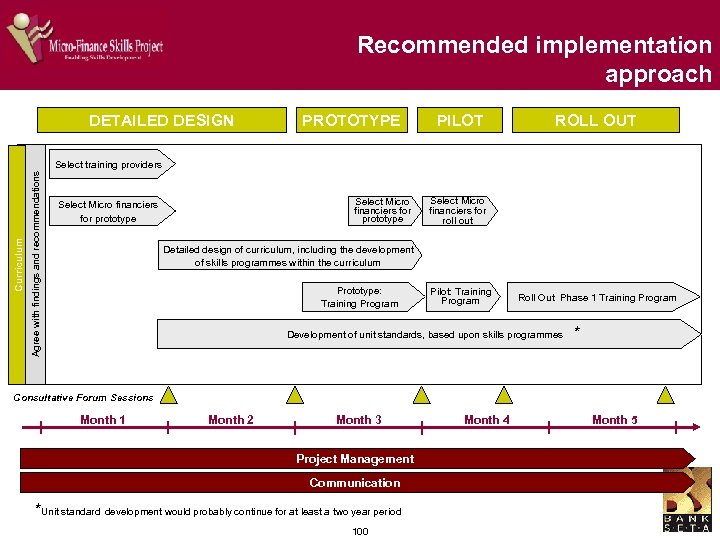 Recommended implementation approach Agree with findings and recommendations Curriculum DETAILED DESIGN PROTOTYPE PILOT ROLL OUT Select training providers Select Micro financiers for prototype Select Micro financiers for roll out Detailed design of curriculum, including the development of skills programmes within the curriculum Prototype: Training Program Pilot: Training Program Roll Out Phase 1 Training Program Development of unit standards, based upon skills programmes * Consultative Forum Sessions Month 1 Month 2 Month 3 Project Management Communication *Unit standard development would probably continue for at least a two year period 100 Month 4 Month 5
Recommended implementation approach Agree with findings and recommendations Curriculum DETAILED DESIGN PROTOTYPE PILOT ROLL OUT Select training providers Select Micro financiers for prototype Select Micro financiers for roll out Detailed design of curriculum, including the development of skills programmes within the curriculum Prototype: Training Program Pilot: Training Program Roll Out Phase 1 Training Program Development of unit standards, based upon skills programmes * Consultative Forum Sessions Month 1 Month 2 Month 3 Project Management Communication *Unit standard development would probably continue for at least a two year period 100 Month 4 Month 5
 Next steps Prioritised skills areas should be agreed upon and developed first § § Final agreement on the prioritisation of skills areas should be reached by the project steering committee More in-depth content knowledge for each skills area should be identified through consultation with a wide range of industry experts Expression of interest communications need to be developed should be expressly geared towards service providers who are able to deliver on the development of agreed prioritised skills training materials Training providers who were identified by the project team as well as those who responded to the expression of interest should be attend a detailed briefing session on the express requirements for the development of training materials for the prioritised skills areas Development timelines, level of detail, materials content quality assurance standards, guidelines for delivery methods of training materials such as CBT, videos and manuals should be outlined in the briefing sessions Ø Feedback from attendees should be obtained and recorded for RFP purposes Ø § § An RFP (Request for proposal) should be sent out to all interested training provider parties Unit standards should be developed from the skills programmes once the detailed design of the curriculum has been established Learning initiatives should be prioritised by industry skills needs 101
Next steps Prioritised skills areas should be agreed upon and developed first § § Final agreement on the prioritisation of skills areas should be reached by the project steering committee More in-depth content knowledge for each skills area should be identified through consultation with a wide range of industry experts Expression of interest communications need to be developed should be expressly geared towards service providers who are able to deliver on the development of agreed prioritised skills training materials Training providers who were identified by the project team as well as those who responded to the expression of interest should be attend a detailed briefing session on the express requirements for the development of training materials for the prioritised skills areas Development timelines, level of detail, materials content quality assurance standards, guidelines for delivery methods of training materials such as CBT, videos and manuals should be outlined in the briefing sessions Ø Feedback from attendees should be obtained and recorded for RFP purposes Ø § § An RFP (Request for proposal) should be sent out to all interested training provider parties Unit standards should be developed from the skills programmes once the detailed design of the curriculum has been established Learning initiatives should be prioritised by industry skills needs 101


