90b1c792fba3f0943450b5fece7ca795.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Current Situation Influenza A (H 1 N 1) 17 May 09 1|
Current Situation Influenza A (H 1 N 1) 17 May 09 1|
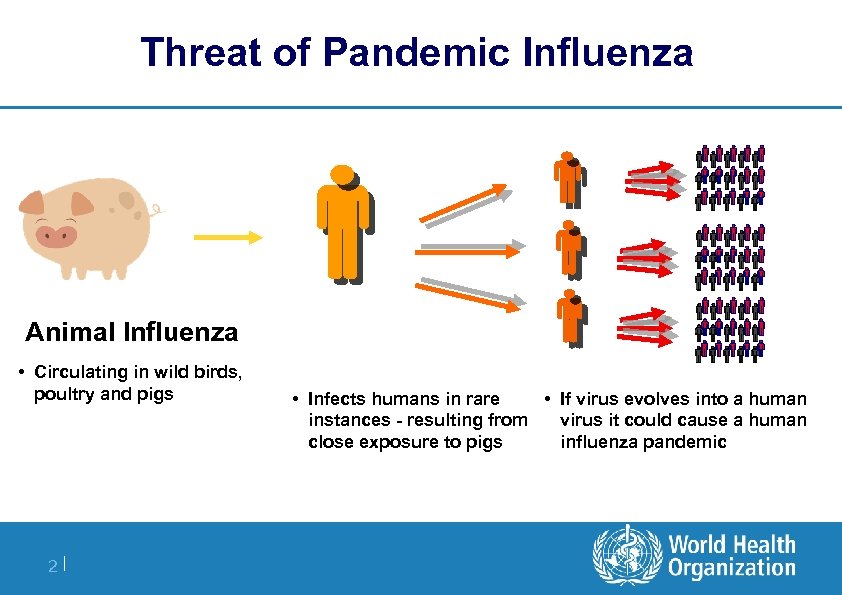 Threat of Pandemic Influenza Animal Influenza • Circulating in wild birds, poultry and pigs 2| • Infects humans in rare • If virus evolves into a human instances - resulting from virus it could cause a human close exposure to pigs influenza pandemic
Threat of Pandemic Influenza Animal Influenza • Circulating in wild birds, poultry and pigs 2| • Infects humans in rare • If virus evolves into a human instances - resulting from virus it could cause a human close exposure to pigs influenza pandemic
 Pandemic requirements Global outbreak of disease l Appearance of flu virus A with pandemic potential l It causes sustained human-to-human transmission l Population has no or limited immunity 3|
Pandemic requirements Global outbreak of disease l Appearance of flu virus A with pandemic potential l It causes sustained human-to-human transmission l Population has no or limited immunity 3|
 Broad Risks of a Pandemic Livelihoods • Food and income loss from poultry deaths/ culling & decreased economic activity Human Health • High illness & potentially higher death rates • Overstretched health facilities • Disproportionate impact on vulnerable Governance & Security Social & Humanitarian Needs Economic Systems 4| • Increased demand for governance & security • Higher public anxiety • Reduced capacity due to illness & death • • • Deterioration of coping & support mechanisms Interruption in public services Quarantine policies Trade & commerce disruptions Degraded labour force Interruption of regular supply systems
Broad Risks of a Pandemic Livelihoods • Food and income loss from poultry deaths/ culling & decreased economic activity Human Health • High illness & potentially higher death rates • Overstretched health facilities • Disproportionate impact on vulnerable Governance & Security Social & Humanitarian Needs Economic Systems 4| • Increased demand for governance & security • Higher public anxiety • Reduced capacity due to illness & death • • • Deterioration of coping & support mechanisms Interruption in public services Quarantine policies Trade & commerce disruptions Degraded labour force Interruption of regular supply systems
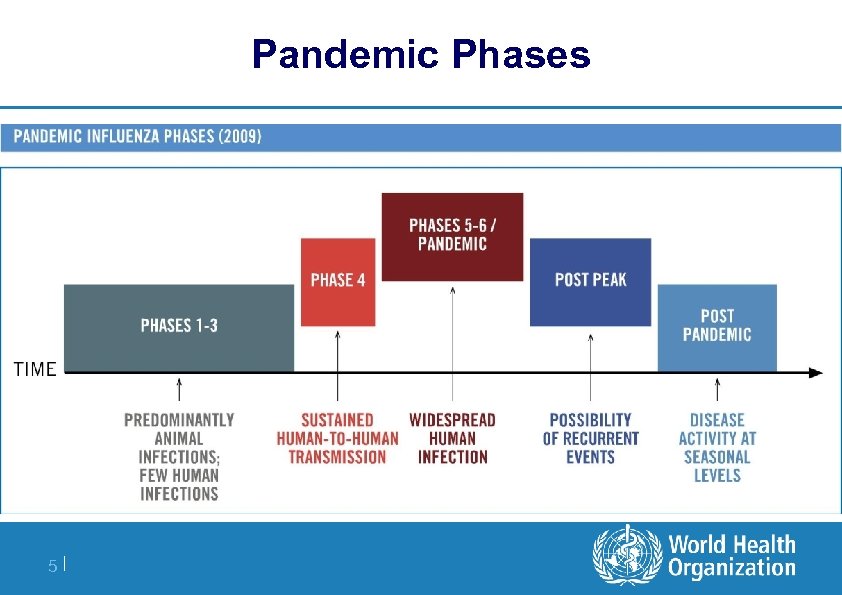 Pandemic Phases 5|
Pandemic Phases 5|
 Phase 5 is characterized by the same identified virus causing sustained community level outbreaks in at least 2 countries in 1 WHO region. l Most countries won't be affected at this stage l Declaration of Phase 5 signals a pandemic could be imminent l Time to finalize organization, communication, implementation of planned mitigation measures is short. 6|
Phase 5 is characterized by the same identified virus causing sustained community level outbreaks in at least 2 countries in 1 WHO region. l Most countries won't be affected at this stage l Declaration of Phase 5 signals a pandemic could be imminent l Time to finalize organization, communication, implementation of planned mitigation measures is short. 6|
 Phase 6 is characterized by community level outbreaks of the same virus in at least 1 other country in a different WHO region. l Designation of this phase would indicate that a global pandemic is under way. 7|
Phase 6 is characterized by community level outbreaks of the same virus in at least 1 other country in a different WHO region. l Designation of this phase would indicate that a global pandemic is under way. 7|
 Time line current situation (1) l Friday 24 April – Reports of previously undetected Influenza A (H 1 N 1) virus in USA and Mexico – HQ SHOC activated l Sunday 26 April – IHR Emergency Committee convened – WHO Director-General declares a Public Health Emergency of International Concern 8|
Time line current situation (1) l Friday 24 April – Reports of previously undetected Influenza A (H 1 N 1) virus in USA and Mexico – HQ SHOC activated l Sunday 26 April – IHR Emergency Committee convened – WHO Director-General declares a Public Health Emergency of International Concern 8|
 Time line current situation (2) l Monday 27 April - WHO increases pandemic alert phase from 3 to 4 - Geographic Containment not feasible l Wednesday 29 April - WHO raises pandemic alert phase from 4 to 5 l Tuesday 5 May - WHO starts sending antiviral stocks to 72 countries and Regional Offices 9|
Time line current situation (2) l Monday 27 April - WHO increases pandemic alert phase from 3 to 4 - Geographic Containment not feasible l Wednesday 29 April - WHO raises pandemic alert phase from 4 to 5 l Tuesday 5 May - WHO starts sending antiviral stocks to 72 countries and Regional Offices 9|
 Current Epidemiology as of 08: 00 GMT 17/05/09 Laboratory confirmed cases Total global cases 8480 cases/72 deaths Mexico: 2895 cases 66 deaths US: 4714 cases, 4 deaths Argentina: 1 case Australia: 1 case Austria: 1 case Brazil: 8 cases Canada: 496 cases, I death China: 5 cases Colombia: 11 cases Costa Rica: 9 cases, 1 death Cuba: 3 case 10 | Denmark: 1 case El Salvador: 4 cases Finland: 2 cases France: 14 cases Germany: 14 cases Guatemala: 3 cases Ireland: 1 case Israel: 7 cases Italy: 9 cases Japan: 7 cases Netherlands: 3 cases NZ: 9 cases Norway: 2 cases Panama: 54 cases Poland: 1 case Portugal: 1 case Republic of Korea: 3 cases Spain: 103 cases Sweden: 3 cases Switzerland: 1 case Thailand: 2 cases UK: 82 cases
Current Epidemiology as of 08: 00 GMT 17/05/09 Laboratory confirmed cases Total global cases 8480 cases/72 deaths Mexico: 2895 cases 66 deaths US: 4714 cases, 4 deaths Argentina: 1 case Australia: 1 case Austria: 1 case Brazil: 8 cases Canada: 496 cases, I death China: 5 cases Colombia: 11 cases Costa Rica: 9 cases, 1 death Cuba: 3 case 10 | Denmark: 1 case El Salvador: 4 cases Finland: 2 cases France: 14 cases Germany: 14 cases Guatemala: 3 cases Ireland: 1 case Israel: 7 cases Italy: 9 cases Japan: 7 cases Netherlands: 3 cases NZ: 9 cases Norway: 2 cases Panama: 54 cases Poland: 1 case Portugal: 1 case Republic of Korea: 3 cases Spain: 103 cases Sweden: 3 cases Switzerland: 1 case Thailand: 2 cases UK: 82 cases
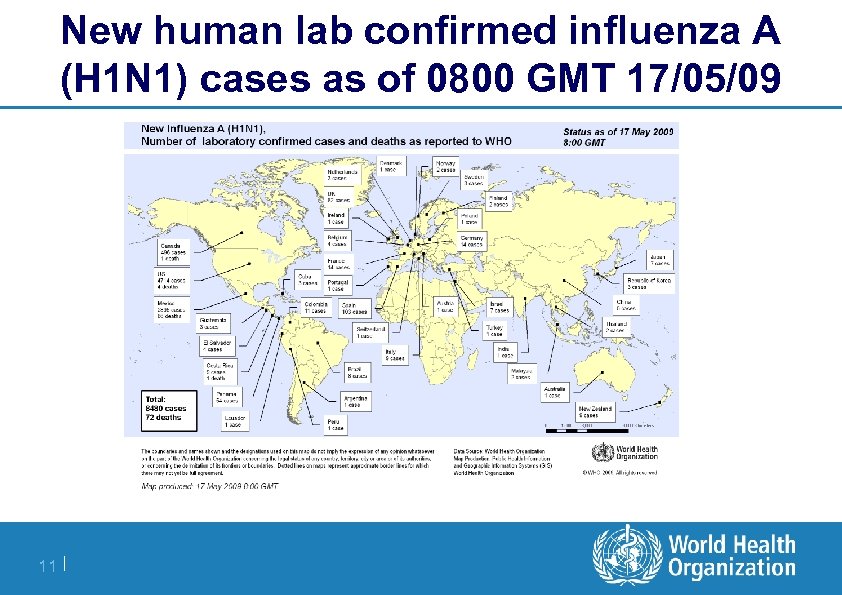 New human lab confirmed influenza A (H 1 N 1) cases as of 0800 GMT 17/05/09 11 |
New human lab confirmed influenza A (H 1 N 1) cases as of 0800 GMT 17/05/09 11 |
 WHO Response (1) l Emergency response rooms – mobilised – 24/7 l Operations – Field team of 31 experts to Mexico (from WHO and CDC/GOARN) – GOARN network activated – Initiated distribution of oseltamivir stockpile l Global monitoring and assessment – – Triage of information and follow up of alerts Coordination with Regions and National Focal Points (NFP) Case report form EIS web updates l Antivirals Taskforce – Oseltamivir stockpile distribution to regions and 72 priority countries (including Mexico) – Quantities proportional to population – Consultation with manufacturer 12 |
WHO Response (1) l Emergency response rooms – mobilised – 24/7 l Operations – Field team of 31 experts to Mexico (from WHO and CDC/GOARN) – GOARN network activated – Initiated distribution of oseltamivir stockpile l Global monitoring and assessment – – Triage of information and follow up of alerts Coordination with Regions and National Focal Points (NFP) Case report form EIS web updates l Antivirals Taskforce – Oseltamivir stockpile distribution to regions and 72 priority countries (including Mexico) – Quantities proportional to population – Consultation with manufacturer 12 |
 WHO Response (2) l Trigger International Health Regulations on notification, risk assessment and response l Article 48: emergency committee: - DG establishes EC to provide views on PHEIC, temporary recommendations, phases l Article 42, 43 Travel and trade – Monitoring travel and trade measures – Maintaining a dialogue with member states to make sure objective of IHR are mett (least interference with travel and trade) l Ports of Entry and conveyance: – Providing guidance Po. E authority – Guidelines for cases on board of planes, ships, trains etc. 13 |
WHO Response (2) l Trigger International Health Regulations on notification, risk assessment and response l Article 48: emergency committee: - DG establishes EC to provide views on PHEIC, temporary recommendations, phases l Article 42, 43 Travel and trade – Monitoring travel and trade measures – Maintaining a dialogue with member states to make sure objective of IHR are mett (least interference with travel and trade) l Ports of Entry and conveyance: – Providing guidance Po. E authority – Guidelines for cases on board of planes, ships, trains etc. 13 |
 WHO Response (3) l Technical guidance – Analysis of available data (modelling) – Guidelines on surveillance, lab and diagnostic, infection control, health care management, pandemic response plan, vaccines made available to the public l Vaccine Taskforce – Consultation with manufacturers – Consultation with scientific experts l Communication – – 14 | daily press conference interviews will hundreds of media Disease Outbreak News web updates media monitoring
WHO Response (3) l Technical guidance – Analysis of available data (modelling) – Guidelines on surveillance, lab and diagnostic, infection control, health care management, pandemic response plan, vaccines made available to the public l Vaccine Taskforce – Consultation with manufacturers – Consultation with scientific experts l Communication – – 14 | daily press conference interviews will hundreds of media Disease Outbreak News web updates media monitoring
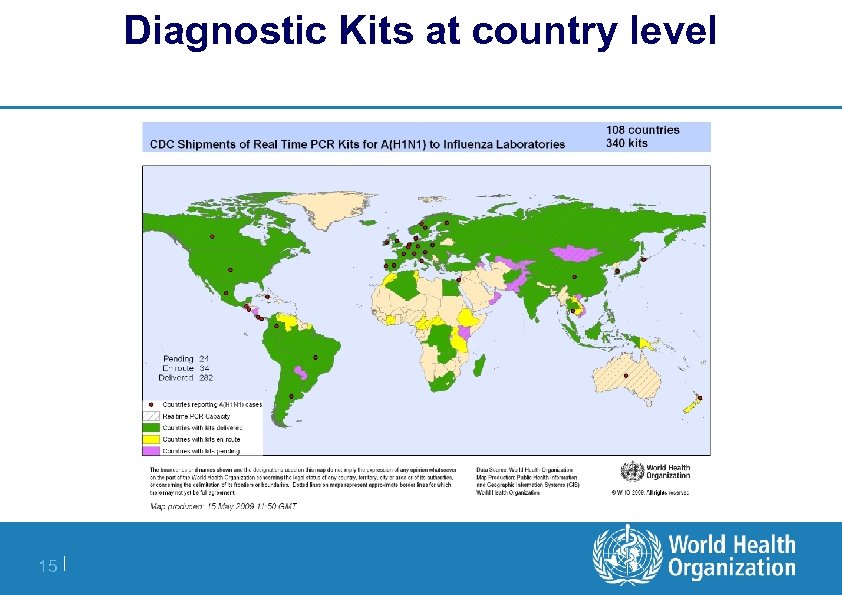 Diagnostic Kits at country level 15 |
Diagnostic Kits at country level 15 |
 WHO Response (4) Technical guidance l Tools and standards adapted for country and community use – – – Checklist on planning and coordination Rapid detection, alert and investigation mechanisms Access to diagnostics Infection control, case management, organization of health care system – Community interventions – Logistics, procurement and supply chain – Risk communication 16 |
WHO Response (4) Technical guidance l Tools and standards adapted for country and community use – – – Checklist on planning and coordination Rapid detection, alert and investigation mechanisms Access to diagnostics Infection control, case management, organization of health care system – Community interventions – Logistics, procurement and supply chain – Risk communication 16 |
 WHO Response (5) Training l Coordinated and targeted training and workshops at regional and sub-regional level l Specific regional, subregional and national context l Web based training and training of trainers l Back up hot line for WR/CO, Qs & As l For COs, MOH, other UN, NGOs 17 |
WHO Response (5) Training l Coordinated and targeted training and workshops at regional and sub-regional level l Specific regional, subregional and national context l Web based training and training of trainers l Back up hot line for WR/CO, Qs & As l For COs, MOH, other UN, NGOs 17 |
 WHO Response (6) Deployment of expert teams l Specific developing countries; sequenced l Experts in epidemiology/PH, IC/case management, risk communication, PH Emergency Management, logistics, lab, etc. – Teams tailored to needs l Materiel to enhance surveillance, facilitate diagnosis, protect personnel, treat and prevent cases l Sample shipment for rapid and reliable diagnostics 18 |
WHO Response (6) Deployment of expert teams l Specific developing countries; sequenced l Experts in epidemiology/PH, IC/case management, risk communication, PH Emergency Management, logistics, lab, etc. – Teams tailored to needs l Materiel to enhance surveillance, facilitate diagnosis, protect personnel, treat and prevent cases l Sample shipment for rapid and reliable diagnostics 18 |
 WHO Response (7) Mechanisms l Coordinated with the RO & CO, in liaison with other UN agencies and NGOs l GOARN l Integrated operational platform in HQ and in the regions l System for prioritization demands l Feedback and adaptation of response 19 |
WHO Response (7) Mechanisms l Coordinated with the RO & CO, in liaison with other UN agencies and NGOs l GOARN l Integrated operational platform in HQ and in the regions l System for prioritization demands l Feedback and adaptation of response 19 |
 IHR in WHA 62 • WHA decision on annual reporting on implementation IHR • Yearly questionnaire, Feb 2009. 82 States parties reported • Evidence of more cross sectoral coordination • • • 20 | On line training, surveillance capacity building Lyon Office Strengthening laboratory quality and bio-safety Strengthening of National Influenza Centres (NIC) Relations with other UN agencies, ports and airports authorities 684 events reviewed (June 2007 -dec 2008). 19% reported through National Focal Points. 7% Risk assessment tool was used. Further research needed
IHR in WHA 62 • WHA decision on annual reporting on implementation IHR • Yearly questionnaire, Feb 2009. 82 States parties reported • Evidence of more cross sectoral coordination • • • 20 | On line training, surveillance capacity building Lyon Office Strengthening laboratory quality and bio-safety Strengthening of National Influenza Centres (NIC) Relations with other UN agencies, ports and airports authorities 684 events reviewed (June 2007 -dec 2008). 19% reported through National Focal Points. 7% Risk assessment tool was used. Further research needed
 IHR in WHA A 62/6 Public Events • • • Lead intoxication Resistance to oseltamivir seasonal influenza Networks on chemical and radio-nuclear thretas up-dated on IHR Nuclear emergency exercise with IAEA in 2008 Work on Yellow fever transmitted by conveyances Legal issues and monitoring of access of NFP to IHR Event Site (IES) • Increased awareness of IHR at regional offices and country level 21 |
IHR in WHA A 62/6 Public Events • • • Lead intoxication Resistance to oseltamivir seasonal influenza Networks on chemical and radio-nuclear thretas up-dated on IHR Nuclear emergency exercise with IAEA in 2008 Work on Yellow fever transmitted by conveyances Legal issues and monitoring of access of NFP to IHR Event Site (IES) • Increased awareness of IHR at regional offices and country level 21 |
 Pandemic Influenza Preparedness WHA A 62/5 • Report by the DG " PIP, Sharing of Influenza Viruses and access to vaccines and other benefits" • Intergovernmental Meeting (IGM) with report from 15 -16 May 2009 meeting • Advisory board to DG-WHO • Development for the Terms of reference for current and potential future (WHO Network) laboratories for H 5 N 1 and other human pandemic influenza viruses • Fro use in vaccines, diagnostic test materials and pharmaceuticals • Good progress but still some points to solve on International Property Rights, transfer of materials 22 |
Pandemic Influenza Preparedness WHA A 62/5 • Report by the DG " PIP, Sharing of Influenza Viruses and access to vaccines and other benefits" • Intergovernmental Meeting (IGM) with report from 15 -16 May 2009 meeting • Advisory board to DG-WHO • Development for the Terms of reference for current and potential future (WHO Network) laboratories for H 5 N 1 and other human pandemic influenza viruses • Fro use in vaccines, diagnostic test materials and pharmaceuticals • Good progress but still some points to solve on International Property Rights, transfer of materials 22 |
 Current WHO Pandemic Alert phase Phase 5 INFLUENZA A(H 1 N 1): SPECIAL HIGHLIGHTS available at http: //www. who. int/en/ Phase 5 23 |
Current WHO Pandemic Alert phase Phase 5 INFLUENZA A(H 1 N 1): SPECIAL HIGHLIGHTS available at http: //www. who. int/en/ Phase 5 23 |
 IHR in WHA 62 24 |
IHR in WHA 62 24 |
 IHR in WHA 62 25 |
IHR in WHA 62 25 |
 IHR in WHA 62 26 |
IHR in WHA 62 26 |


