fbea9621d60f4b2216f8ffba40b449dd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68

Current Issues in Maternal. Newborn Nursing: No More Octamom!

What Are Current Issues in Maternal. Newborn Nursing?

Maternal Mortality • 28 countries have lower maternal mortality rates than the US • MM=# of women dying around the time of childbirth • US ranks 41 st in the world (Amnesty International) • 37 th (Lancet) • An American woman is at least twice as likely to die in pregnancy or childbirth as a woman in much of Europe.

The Numbers • Every year at least 1, 000 women die around the time of birthing • That is 3 jumbo jets full of our sisters, daughters and mothers

Maternal Mortality • Lifetime risk of a maternal death during or shortly after pregnancy is 1 in 17, 400 in Sweden • 1 in 8 in Afganistan #2 • 1 in 7 in Niger #1

jhpiego • Hemorrhage #1 cause of maternal death • Community based distribution of misoprostol • “ 3 little pills after you deliver the baby” • http: //www. npr. org/templates/story. php? story. I d=130180983&sc=emaf • Is there a connection between hypocalcemia and preeclampsia, can we distribute calcium to the general public cheaply? Yes $0. 92 for 100 sachets of calcium to sprinkle on food.

“Be the change that you want to be in the world. ” Gandhi • It’s Global • One woman dies every minute from a pregnancy complication • 300, 000 • Most die in developing countries • One woman dies every 2 minutes from cervical cancer, 80% in the developing world • 10, 000 pregnant women die each year from Malaria • 200, 00 newborns die each year from Malaria • 60% of adults with HIV in Sub-Saharan Africa are women

Why? So high in the US • Two to three women die every day due to pregnancy-related complications • The three leading causes of maternal death nationally are: 1. Eclampsia/Pre-eclampsia 2. Embolism 3. Hemorrhage

Need Collaborative Approaches to Early Identification and Treatment • Risk assessment and preparation for possible hemorrhage, EBL, tx of hemorrhage, hypovolemia, development and implementation of Rapid Response OB • Education and simulation drills.

Why study maternal M & M • Evidence suggests that at least one half of pregnancy-related deaths may be preventable through changes in patient, provider, or system factors. • Mortality is disproportionally high among certain racial and ethnic groups. • Deaths are only the tip of the iceberg: morbidity represents a huge burden of disease for women and their families.

The Babies • 41 countries have lower infant mortality rates than the US • Infant mortality = babies dying before their first birthday • US ranks 31 st of developed nations, falling behind South Korea, Cuba, Czech Republic

Infant Mortality • 2 per 1, 000 live births in Iceland • 120 per 1, 000 live births in Mozambique

Power of Nurses • 70 -80% of the health care work force is nurses • 85% of the health care workforce in rural Africa is nurses.

Colorado Statistics • LBW: less than 5. 8 pounds • National average is 8. 3% • Colorado is 9. 6% • Some of the top rated states are as low as 6%
B 4 Babies • B 4 Babies a program in Mesa County has given the county the best ranking in the state 8. 4% • • • Offers every type of care an expectant mother could need: help filling out applications for financial assistance, help with medical appointments, translation, transportation Started 19 years ago Recognized by HHS in 1998 as a “Model that Works”

Costs for LBW babies in CO • $10, 000 per day • March of Dimes has tallied the average cost nationally for the first year of life for LBW babies beyond intensive care at $49, 000 • Prenatal care and education that helps expectant mothers stop risky behaviors is vastly cheaper than paying for the care of babies with problems

Colorado Infant Mortality • The infant mortality disparity seen nationwide among Black infants is observed in Colorado as well, and has been present over time. • In 2006, the infant mortality rate among Black infants in Colorado was 12. 4 per 1, 000 live births to Black mothers while that among White/non-Hispanic infants was 5. 0

Women of Color in Colorado • After controlling for maternal age, education, prenatal care, short gestation and low birth weight, multiple births, medical risk factors, and labor and delivery complications, Black mothers still had 50 percent greater odds of infant death compared to White/non. Hispanic mothers (Odds Ratio: 1. 5, 95% Confidence Interval: 1. 3 -1. 8).
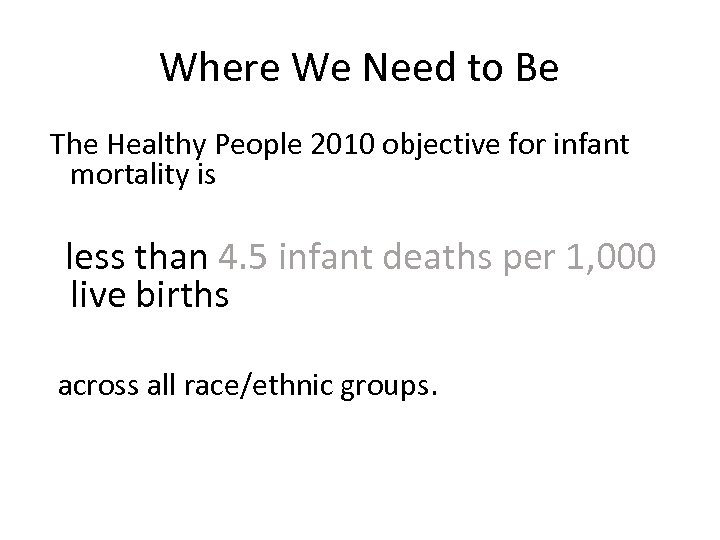
Where We Need to Be The Healthy People 2010 objective for infant mortality is less than 4. 5 infant deaths per 1, 000 live births across all race/ethnic groups.

WHY? • Among the myriad possible explanations for the increase in low-weight births are the use of fertility treatments and the increasing rates of multiple births (twins, triplets, etc. ) • Research has shown that both multiple births and singleton births from assisted reproductive technologies (ART) have higher risks of low birth weight and prematurity compared to infants born without ART. • Colorado’s birth certificate included information about ART for the first time in 2007, which will allow for further study of this issue both in Colorado and nationwide. • More about ART later

Millennium Development Goals • In 2000, world leaders set far-reaching goals to free a major portion of the world’s population from poverty, hunger, illiteracy, and disease. • Targeted achievement by 2015 • Halve extreme poverty • Halt spread of HIV/AIDS • Universal primary education

Poverty’s Affect on Women’s Health • 44 Million Americans • 1 out of 7 adults, 1 out of 5 children • Lack of health insurance: 51 Million Americans in 2009

Poverty in CO • 12. 3% in 2009, the 31 st highest in the US • 16. 3% Colorado poverty rate for children in 2009 • People living without health insurance in Colorado 16%

It is Global • Poverty, economic development, and the poor health of women are a lethal combination of elements, left untouched will result in continued poor health of families, continued high rates of maternal and child mortality and morbidity and limited national development in most resource-poor countries of the world.

MDGs • Aim of the United Nations Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) is to reduce the number of people throughout the world who live on less than $1 a day by 50%, by finding solutions to poverty, hunger, disease, illiteracy, environmental pollution, and discrimination against women.

Social Issues Affecting Women in Poverty • • Divorce Lower wages compared with men Public assistance Homelessness

Two thirds of Americans living in poverty are women and children

Our Children • One half of all children in the US and 90% of Black children will be on food stamps at some point during childhood • Children on food stamps are at risk for malnutrition and other ills linked to poverty

Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) • Provides assistance for childcare • Promotes job preparation, work, and marriage • Reduces the incidence of unplanned pregnancies • Encourages two‑parent families

Wage Gap • 40% of U. S. workforce consists of women (2004) • Expanded career options for women • Male-to-female earnings ratio is 76. 5% (2004) • Widest gap is between well-educated women and men • Lily Ledbetter Act: 1 st bill signed by Obama

Lily Ledbetter Act

Causes of Wage Gap • Deliberate wage discrimination against women • Undervaluing of women’s work • Women’s socialization

Some women rely on the father to provide full-time child care at home while they pursue their career. Stay-at-home fathers provide only 1. 5% of care to children under the age of 5 in the United States

Some mothers are able to combine professional careers with motherhood by telecommuting from a home office.

Family and Medical Leave Act (1993) • 12 weeks of unpaid leave following: – Birth or adoption of a child – Placement of a foster child • Also applies to: – Serious illness – Illness of a spouse, child, or parent

Childhood education centers provide preschoolers with advanced skills for early education and provide care while parents work outside of the home

Ethical Thinking About ART • Autonomy: right to independently chose health care options. • Informed Consent: risks, consequences, benefits, alternatives must be written and spoken in language the pt understands. Witness>18 (what they hear is based on dreams and desires for miracles, does not serve us in way we want) • Justice: equal distribution of life’s good. Canada “every person gets equal share of health care” donor eggs illegal , no free market exchange US according to your effort, free market exchange, can buy ART

What Happened at Kaiser Bellflower: A just thing? ? ? • Walkin : no clue where she came from • Anticipated 7 got 8 • Had staff of 46 present for scheduled c/s (volunteer) • Had to divert admissions and other high risk pts to Hollywood • 2 nurses, one MD for each baby • NICU stay 805, 500 to 3 Million • 50 (150) employees terminated for looking at the chart HIPPA

Justice? • Is this available to every citizen in the U. S. • Is everyone due the same? • The cochrane library metaanalysis of all data on mutiple gestation: • Findings: significant risk of morbidity and mortality to both gestation and life of mother • Conclusion: Regulation was needed • Should be based upon pt’s age and quality of embyos.

Regulation in Response to Cochrane • • Canada England Sweden “One Embryo, One Birth” (Karlstrom and Bergh, 2007)

American Society of Reproductive Medicine 2008 • Recommend (rather than regulate): • Women under the age of 25 should have no more than two embryos implanted. • Women ages 35 -37 should have no more than three embryos implanted. • Women ages 38 -40 should have no more than four embryos implanted. • Women age 40 and over should have no more than five embryos implanted. Yet in U. S. only 0. 5 -3% of all transfers are singletons Nadia Suleman, a woman under 35 received six embryos transferred.

Reduction • Few Families aware of exactly what the procedure was and what the consequences were • Traumatic, chaotic, depressed disturbing, turmoil, guilt • Grieving for the lost fetuses simultaneously compounded due to constant reminder of the non-reduced infants • Even when positive outcomes occurred, negative feelings emerge • Families made the right decision but insufficient respect for their loss

Disenfranchised Grief (Doka, 1989) “Grief Which is Not Openly Acknowledged or Publicly Mourned” Normal Bereavement • Ritual • Religion/Spirituality • Family • Friends • Time Given • Cards, Flowers, Food • Remembrance Reduction Decisions • Made in Isolation • Not discussed with even closest family • Judgment from others • No time allotted • Secrecy of remembrance

IN Conclusion • Bereavement support groups are lacking • Much work to be done on ethics related to multifetal gestation • Committee at ACOG • Increase in multiple gestation and prematurity • Preimplanation genetic diagnosis • What is a nurse to do?
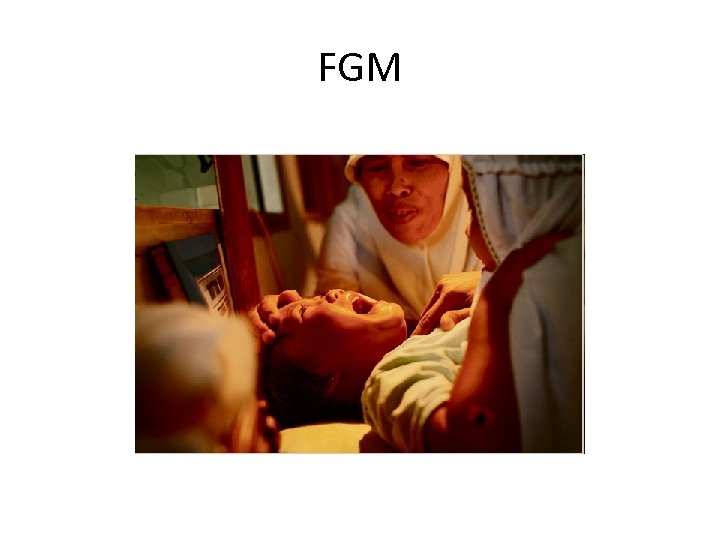

FGM

Cultural Implications of Female Genital Mutilation • Practiced in male-dominated societies: – Patriarchal authority – Control of women’s bodies – Control of fertility • Done between 5 and 12 years of age • 200, 000 women in the US • 130 Million women worldwide
FGM
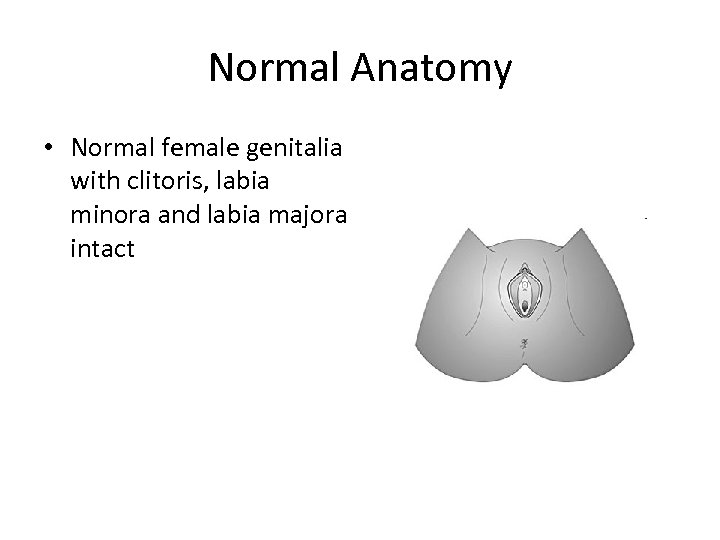
Normal Anatomy • Normal female genitalia with clitoris, labia minora and labia majora intact
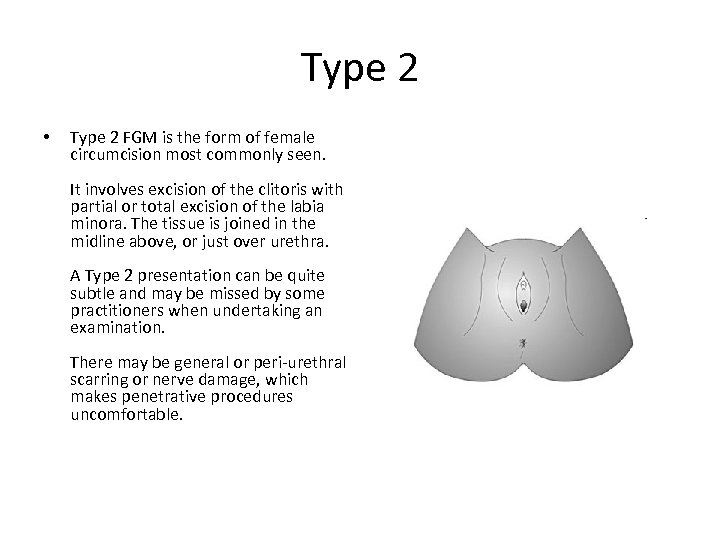
Type 2 • Type 2 FGM is the form of female circumcision most commonly seen. It involves excision of the clitoris with partial or total excision of the labia minora. The tissue is joined in the midline above, or just over urethra. A Type 2 presentation can be quite subtle and may be missed by some practitioners when undertaking an examination. There may be general or peri-urethral scarring or nerve damage, which makes penetrative procedures uncomfortable.

Type 3 FGM • Type 3 FGM is the most extreme presentation. It involves excision of part or all of the external genitalia and stitching/ narrowing of the vaginal opening. Infibulation - there will be obvious anterior midline scar tissue. The infibulation may obscure underlying dermatological problems such as abscesses, dermoid and sebaceous cysts, and other scarring. It may predispose to both short and long term health consequences for women. In Type 3 FGM, the extent to which genital tissue has been removed, varies with the individual.
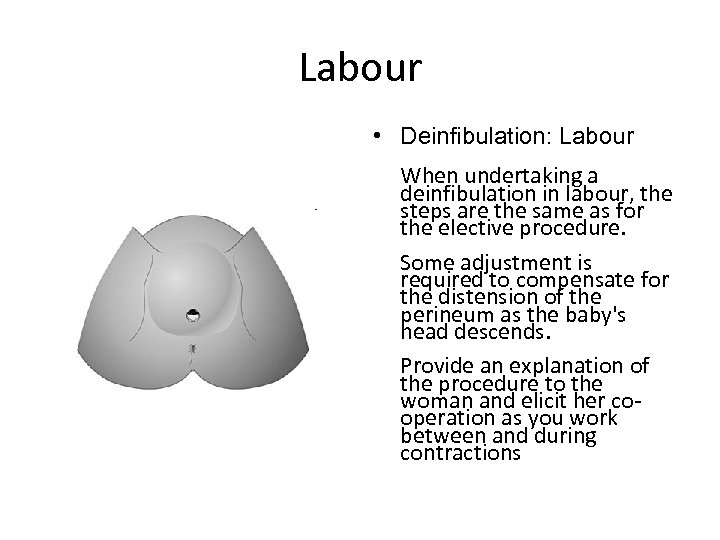
Labour • Deinfibulation: Labour When undertaking a deinfibulation in labour, the steps are the same as for the elective procedure. Some adjustment is required to compensate for the distension of the perineum as the baby's head descends. Provide an explanation of the procedure to the woman and elicit her cooperation as you work between and during contractions
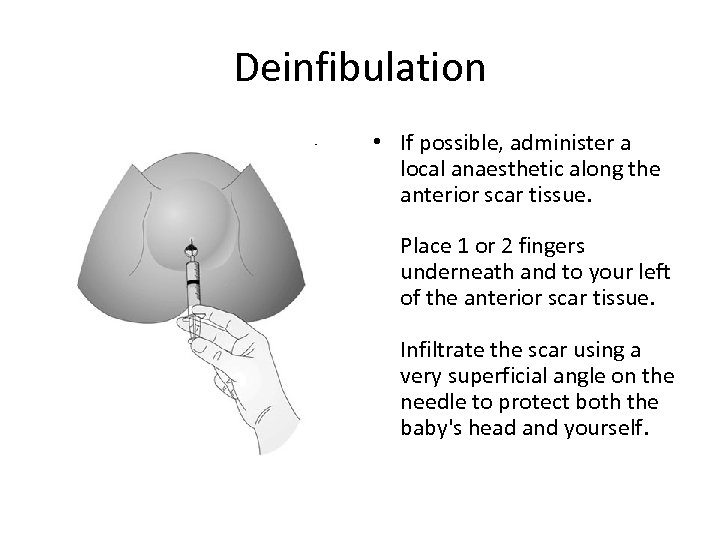
Deinfibulation • If possible, administer a local anaesthetic along the anterior scar tissue. Place 1 or 2 fingers underneath and to your left of the anterior scar tissue. Infiltrate the scar using a very superficial angle on the needle to protect both the baby's head and yourself.

Excision • Use 1 or 2 fingers to create clearance from the emerging head prior to inserting the scissors. Make the anterior incision up the midline scar to just above the urethral meatus
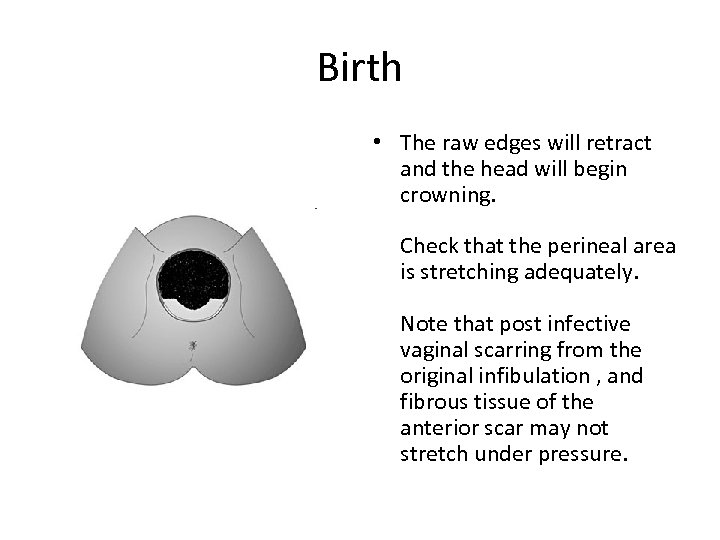
Birth • The raw edges will retract and the head will begin crowning. Check that the perineal area is stretching adequately. Note that post infective vaginal scarring from the original infibulation , and fibrous tissue of the anterior scar may not stretch under pressure.
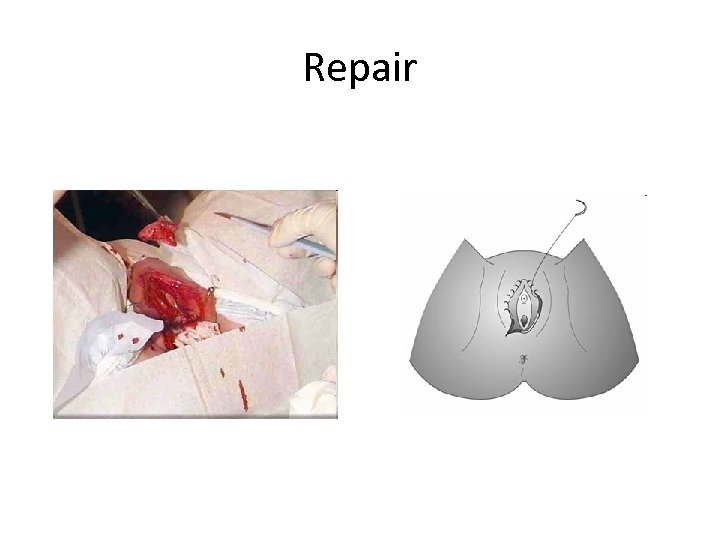
Repair

CXs of FGM • • • Fistulas Leave women incontinent Fixable for about $450 What else? Don’t be shocked, ask her story

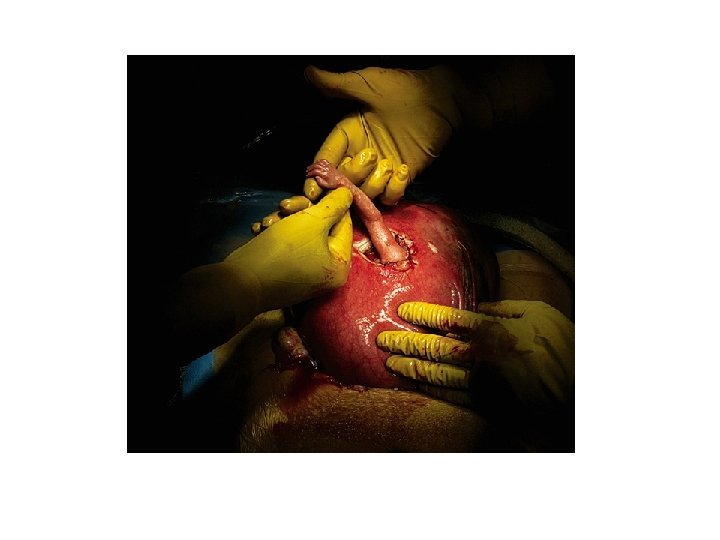
In Utero Surgery • The picture is that of a 21 -week-old unborn baby named Samuel Alexander Armas, who is being operated on by surgeon named Joseph Bruner. The baby was diagnosed with spina bifida and would not survive if removed from his mother's womb. Little Samuel's mother, Julie Armas, is an obstetrics nurse in Atlanta. She knew of Bruner's remarkable Surgical procedure. Practicing at Vanderbilt Univ Med Ctr in Nashville, he performs these special operations while the baby is still in the womb. During the procedure, the doctor removes the uterus via C-section and makes a small incision to operate on the baby. As Dr Bruner completed the surgery on Samuel, the little guy reached his tiny, but fully developed hand through the incision and firmly grasped the surgeon's finger. Dr Bruner was reported as saying that when his finger was grasped, it was the most emotional moment of his life, and that for an instant during the procedure he was just frozen, totally immobile. The photograph captures this amazing event with perfect clarity The editors titled the picture, 'Hand of Hope. ' The text explaining the picture begins, 'The tiny hand of 21 -week-old fetus Samuel Alexander Armas emerges from the mother's uterus to grasp the finger of Dr Joseph Bruner as if thanking the doctor for the gift of life. ' Little Samuel's mother said they 'wept for days' when they saw the picture. She said, 'The photo reminds us pregnancy isn't about disability or an illness, it's about a little person. 'Samuel was born in perfect health, the operation 100 percent successful.
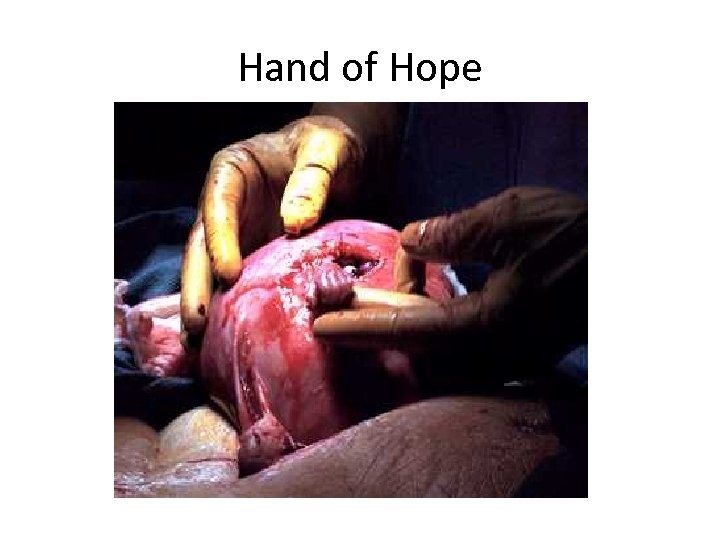
Hand of Hope

Violence

Violence • 31% of women report physical or sexual assault by an intimate partner during their lifetime (Family violence Prevention Fund, 2008) • Health related costs of domestic abuse to society, estimated at $4. 1 billion (Brackley, 2008)

Domestic Abuse Affects Health Care System in Multiple Ways 1. Increased use by victims and witnesses 2. Children exposed to violence in the home are more likely to develop physical and behavior health problems 3. Women who are domestic abuse victims are more likely to engage in negative health behaviors.

Importance of Screening • Nurse concerns: time to perform screen, as important as other nursing assessments, fear of offending client, being able to respond to a victim, help with referrals.

Other Issues • ART • Abortion • Maternal-Fetal Conflict: until fairly recently, the fetus was viewed legally as a nonperson. • Mother and fetus were viewed as one complex client-the pregnant woman. • Fetus increasingly viewed as a client separate from the mother.

Focus intensified • 2002, when George Bush announced that “unborn children” would qualify for government healthcare benefits. More designed to promote prenatal care, but represented the first time U. S. federal policy had defined childhood as starting at conception.

AI, ART and Surrogate Childbearing • Legal problems with AI (TI) using donor sperm Donor must sign a form waiving all parental rights. Husbands sign a form agreeing to insemination and to assume parental responsibility for the child. • ART/IVF: guidelines to limit # of embryos transferred, ethical dilemma of what to do with unused embryos? surplus fertilized oocytes? To whom do the frozen embryos belong? Parents together or separately? The hospital or infertility clinic? Who is liable if a woman or her offspring contracts HIV disease from a donated sperm? Should children be told the method of their conception?

Denver Stem Cell Bank • 3 hospitals participate

Maternal Newborn Nurses APNs: CNMs, NNPs CNS AWHONN Standards for Professional Nursing Practice in the Care of Women and Newborns • HIPPA • Infection Protection • •
fbea9621d60f4b2216f8ffba40b449dd.ppt