776890eb981d0819836435b0656a385d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Currency Futures Professor Brooks BA 444 02/12/08

The Underlying Asset n FX is the abbreviation foreign currency exchange n Foreign Currency is the underlying asset n n n Just think of the foreign currency as a commodity that you buy or sell Currency relationship around the world Purchasing Power Parity Exchange rates set so that currency of one country should be able to buy the exact same goods of another country Example: Shoes in US vs. Japan

Purchasing Power Parity n Shoe sells for $150 in USA n Same shoe sells for ¥ 18, 750 n Where do you buy your shoes? n n n Note you can have them shipped directly to you and the shipping charge is included in the price The current exchange rate is ¥ 125 for $1 No advantage for where you buy the shoe n What about a year from now? n US inflation rate is 5% and Japanese inflation rate is 8% n US price will be $157. 50 – Japanese will be ¥ 20, 250 Exchange rate in one year will be: ¥ 128. 57 for $1 Forward exchange rates reflect inflation differences n n

Foreign Exchange Rates n Change daily due to expected inflation rates in the various countries n Anticipated or Forward Rates reflect the impact of the expected inflation rate n Future Forward Rate Calculation: Forward Ratet ≈ Spot Rate x (1 + (Inf. For – Inf. US))t n Example Forward Rate ≈ 125 x (1 + (0. 08 – 0. 05)) Forward Rate ≈ 125 x 1. 03 = 128. 75
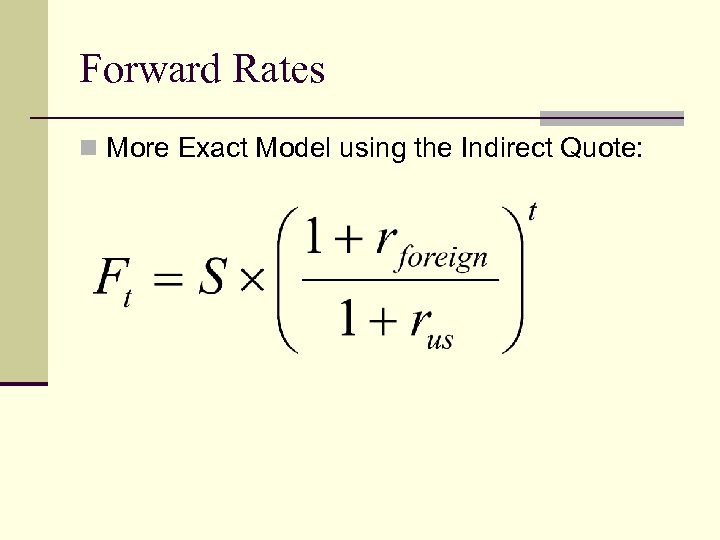
Forward Rates n More Exact Model using the Indirect Quote:

Interest Rate Parity n Components of interest rate n The real rate – compensation for waiting n Inflation rate – the general rise in the prices of goods over time n Risk premium(s) – default, maturity, liquidity, etc. n The real rate is the same the world round n Example…investing in country with the highest nominal interest rate
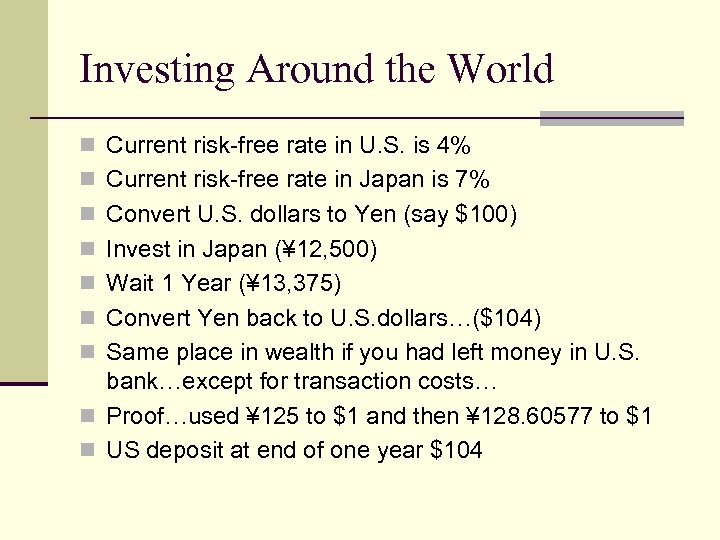
Investing Around the World n Current risk-free rate in U. S. is 4% n Current risk-free rate in Japan is 7% n Convert U. S. dollars to Yen (say $100) n Invest in Japan (¥ 12, 500) n Wait 1 Year (¥ 13, 375) n Convert Yen back to U. S. dollars…($104) n Same place in wealth if you had left money in U. S. bank…except for transaction costs… n Proof…used ¥ 125 to $1 and then ¥ 128. 60577 to $1 n US deposit at end of one year $104

Where is the Risk? n Weak Dollar n The term weak dollar usually means that the U. S. dollar is losing buying power in a foreign currency n Example, today the U. S. dollar can buy 125 yen…but if the dollar weakens next month it can only buy 115 yen n Strong Dollar is just the opposite n What does this mean for imports and exports?
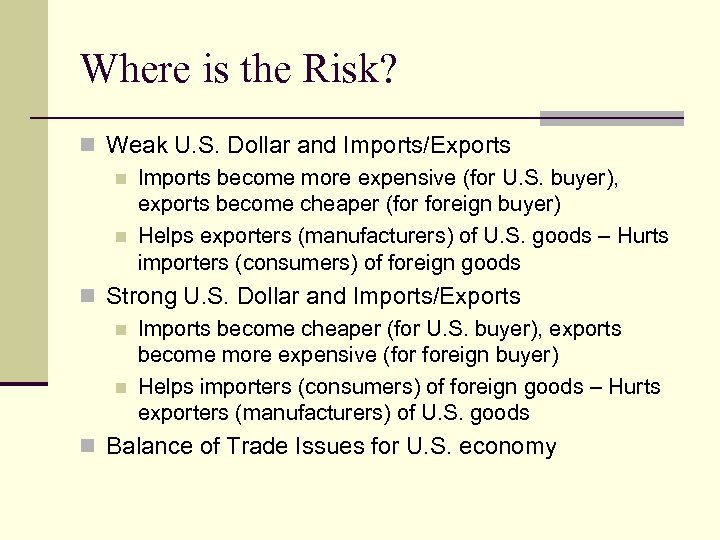
Where is the Risk? n Weak U. S. Dollar and Imports/Exports n Imports become more expensive (for U. S. buyer), exports become cheaper (for foreign buyer) n Helps exporters (manufacturers) of U. S. goods – Hurts importers (consumers) of foreign goods n Strong U. S. Dollar and Imports/Exports n Imports become cheaper (for U. S. buyer), exports become more expensive (for foreign buyer) n Helps importers (consumers) of foreign goods – Hurts exporters (manufacturers) of U. S. goods n Balance of Trade Issues for U. S. economy

Where is the Risk? n Accounting Risks – Multinational Company based in U. S. n n Transaction Risk n Company buys a good (on credit) in a foreign currency n Price of the good may go up or down due to changes in the exchange rate Translation Risk n Company owns property in a foreign country n Must consolidate assets for U. S. reporting n Foreign asset value must be translated into U. S. dollars n Value may go up or down due to changes in the exchange rate

Where is the Risk? n Economic Exposure n Own foreign stock or foreign asset n Value will fluctuate with change in exchange rate n Example – Purchase Nestle stock five years ago at € 45 when the exchange rate was € 1 = $1 n n n In five years the stock has gone up 60% In five years exchange rate has changed to € 1=$0. 75 Gain on stock should be 60% (in Euros) Translated gain is only 20% € 45 x (1. 60) x 0. 75 = $54 and $54 / $45 – 1 = 20%

Dealing with the Risk n Ignore the exposure n Expectation is that FX will have small or very moderate changes n Eliminate the potential risk n Don’t hold foreign assets or securities n Hedge the risk n With forward market, enter into a forward exchange agreement (lock in the future exchange rate) n Hedge with futures contract – contracts large

Hedge Example n Wine Importer – Buys French Wines n Purchases wines at harvest but will not have shipment of wines until following year n Futures on FX for Euros – contract is for € 125, 000 n One year rate is 1. 45 n It would take $181, 250 to purchase € 125, 000 in one year n Assume Wine Importer has ordered $10, 000 of wine (order is in Euros) n n n Current obligation (at € 1. 25 to $1) is for € 8, 000 Needs 64 Futures Contracts to Buy Euros (long in Euros futures contract, short Euros) Locks in exchange rate at 1. 45 for one year from now and anticipates paying $11, 600, 000

Hedge Example Continued n Exchange Rate is higher at 1. 60 n Needs $12, 800, 000 to buy the wine n With Futures…makes $1, 200, 000 on futures contract, n Net outflow is $11, 600, 000 n Exchange Rate is at anticipated 1. 45 n Pays $11, 600, 000 for wine n No gain or loss on futures n Exchange Rate stays at 1. 25 n Needs only $10, 000 to pay for wine n Losses $1, 600, 000 on futures n Net outflow $11, 600, 000 n Locked in cost of wine…$11, 600, 000

What about French Winemaker? n Opposite Risk? n Wine will be purchased with Euros…no currency exposure n Price is € 8, 000 today…tomorrow… n Winemaker has a forward contract for sale of wine in one year…he has hedged wine with a forward contract
776890eb981d0819836435b0656a385d.ppt